Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Alternative Splicing of VEGF-A
2.1. Modes of Alternative Splicing
2.2. Regulation of Alternative Splicing
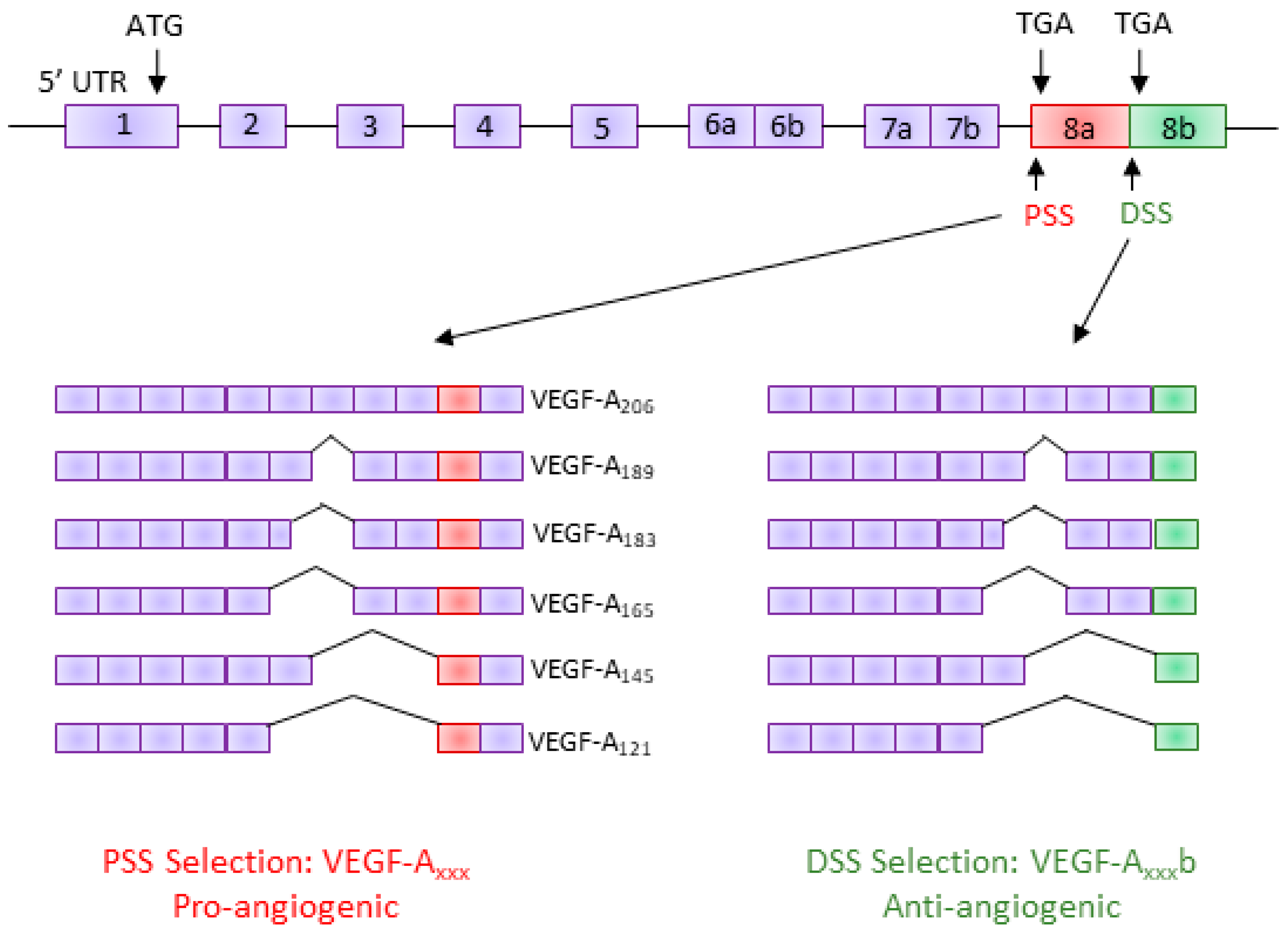
2.3. Alternative Splicing of VEGF-A
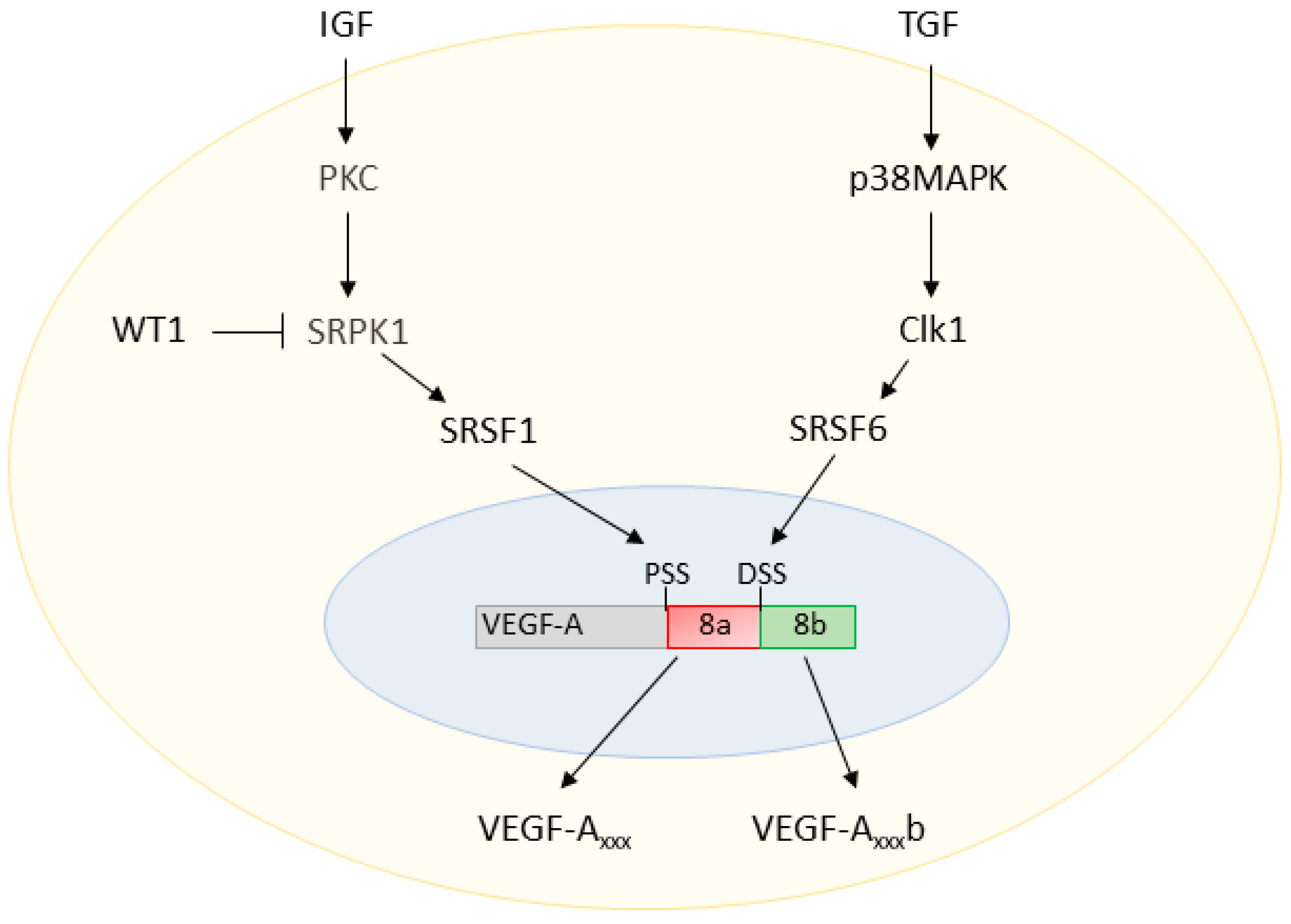
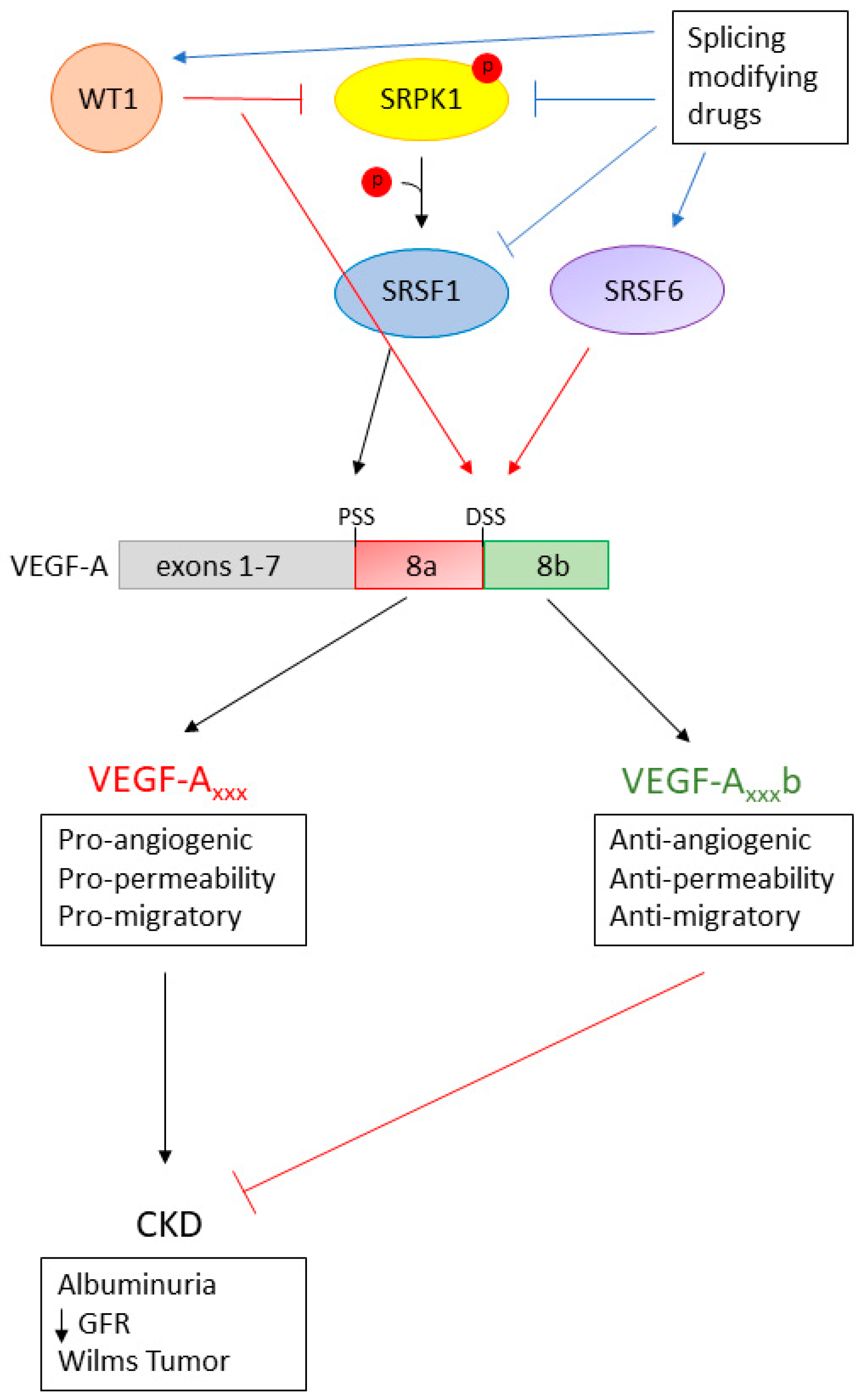
2.4. Regulation of VEGF-A Exon 8 Splicing
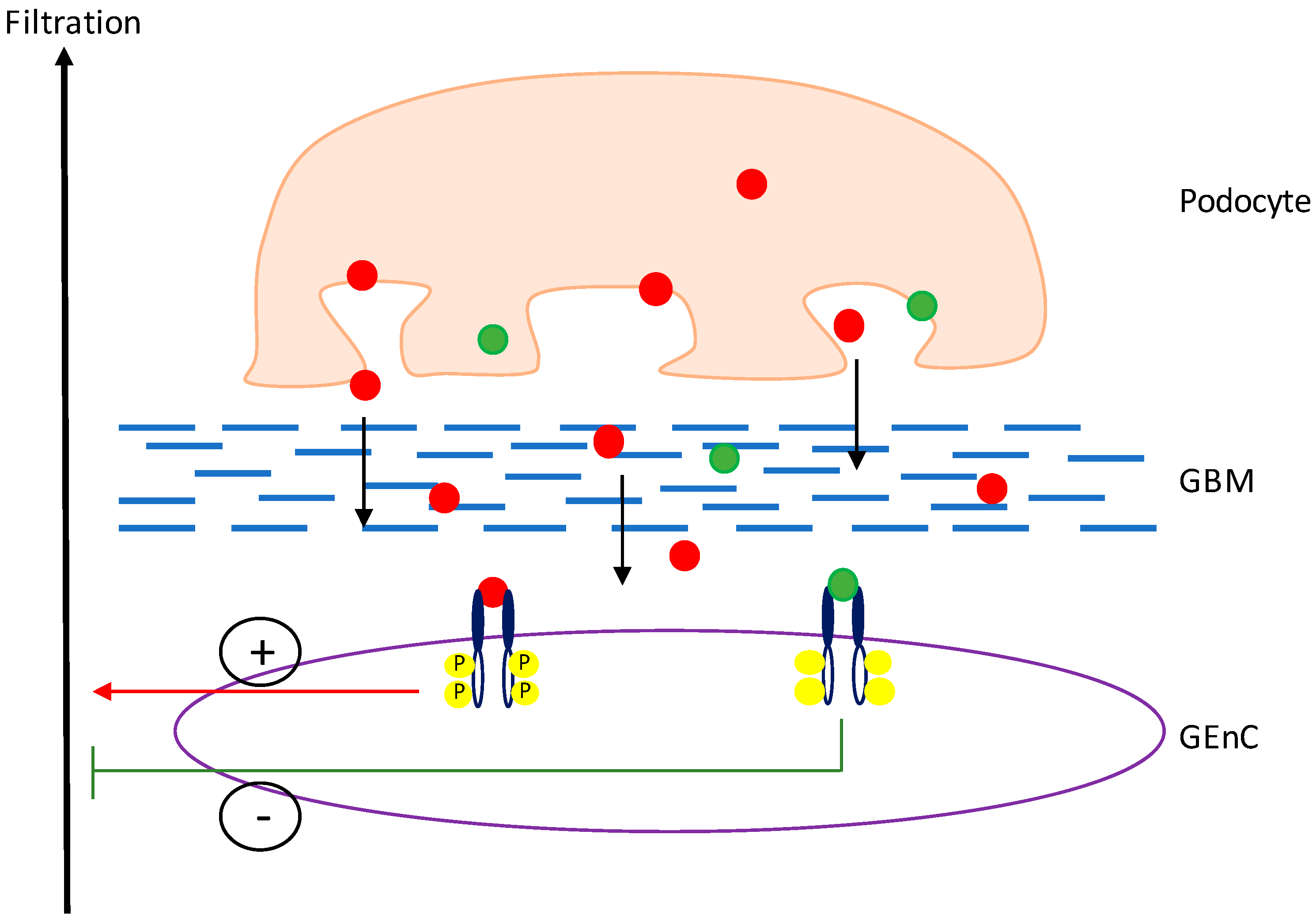
3. VEGF-A Splice Variants in Chronic Kidney Disease
4. Manipulation of VEGF-A Splicing as a Potential Therapeutic Avenue in Kidney Disease
5. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Klerk, E.; t Hoen, P.A. Alternative mRNA transcription, processing, and translation: Insights from RNA sequencing. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlin, A.J.; Clark, F.; Smith, C.W. Understanding alternative splicing: Towards a cellular code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Shai, O.; Lee, L.J.; Frey, B.J.; Blencowe, B.J. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.T.; Sandberg, R.; Luo, S.; Khrebtukova, I.; Zhang, L.; Mayr, C.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Schroth, G.P.; Burge, C.B. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 2008, 456, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Irimia, M.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, H.Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Lee, L.J.; Slobodeniuc, V.; Kutter, C.; Watt, S.; Colak, R.; et al. The evoluntionary landscape of alternative splicing in vertebrate species. Science 2012, 338, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltean, S.; Bates, D.O. Hallmarks of alternative splicing in cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biamonti, G.; Catillo, M.; Pignataro, D.; Montecucco, A.; Ghigna, C. The alternative splicing side of cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 32, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Weiss, W.A. Alternative splicing in cancer: Implications for biology and therapy. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltean, S.; Qiu, Y.; Ferguson, J.K.; Stevens, M.; Neal, C.; Russell, A.; Kaura, A.; Arkill, K.P.; Harris, K.; Symonds, C.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A165b is protective and restores endothelial glycocalyx in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1889–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Neal, C.R.; Salmon, A.H.J.; Bates, D.O.; Harper, S.J.; Oltean, S. VEGF-A165 b protects against proteinuria in a mouse model with progressive depletion of all endogenous VEGF-A splice isoforms from the kidney. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 6281–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Claesson-Welsh, L. VEGF receptor signal transduction. Sci. STKE 2001, 11, re21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, S.; Nair, V.; Keller, B.J.; Eichinger, F.; Hawkins, J.J.; Randolph, A.; Boger, C.A.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Fox, C.S.; Cohen, C.D.; et al. Integrative biology identifies shared transcriptional networks in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.O.; Cui, T.G.; Doughty, J.M.; Winkler, M.; Sugiono, M.; Shields, J.C.; Peat, D.; Gillatt, D.; Harper, S.J. VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4123–4131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, X.D. Regulation of splicing by SR proteins and SR protein-specific kinases. Chromosoma 2013, 122, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.D.; Ares, M., Jr. Context-dependent control of alternative splicing by RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Tang, Y.H.; Smith, R. Functional diversity of the hnRNPs: Past, present and perspectives. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.W.; Cachianes, G.; Kuang, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V.; Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 1989, 246, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O. VEGF-A splicing: The key to anti-angiogenic therapeutics? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, H.S.; van den Akker, N.M.; Qiu, Y.; Polman, J.A.; Foster, R.R.; Yem, J.; Nishikawa, A.; Satchell, S.C.; Harper, S.J.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C.; et al. The alternatively spliced anti-angiogenic family of VEGF isoforms VEGFxxxb in human kidney development. Nephron Physiol. 2008, 110, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.G.; Foster, R.R.; Saleem, M.; Mathieson, P.W.; Gillatt, D.A.; Bates, D.O.; Harper, S.J. Differentiated human podocytes endogenously express an inhibitory isoform of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165b) mRNA and protein. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2004, 286, F767–F773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, H.; Li, X.; Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A165b is a weak in vitro agonist for VEGF receptor-2 due to lack of coreceptor binding and deficient regulation of kinase activity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4683–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris-Pages, M. The role of VEGF 165b in pathophysiology. Cell Adh. Migr. 2012, 6, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, D.G.; Woolard, J.; Amin, E.M.; Konopatskaya, O.; Saleem, M.A.; Churchill, A.J.; Ladomery, M.R.; Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O. Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic isoforms of VEGF is differentially regulated by splicing and growth factors. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3487–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, E.M.; Oltean, S.; Hua, J.; Gammons, M.V.; Hamdollah-Zadeh, M.; Welsh, G.I.; Cheung, M.K.; Ni, L.; Kase, S.; Rennel, E.S.; et al. WT1 mutants reveal SRPK1 to be a downstream angiogenesis target by altering VEGF splicing. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrou, A.; Brakspear, K.; Hamdollah-Zadeh, M.; Damodaran, G.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Oxley, J.; Gillatt, D.A.; Ladomery, M.R.; Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O.; et al. Serine-arginine protein kinase 1 (SRPK1) inhibition as a potential novel targeted therapeutic strategy in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4311–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammons, M.V.; Dick, A.D.; Harper, S.J.; Bates, D.O. SRPK1 inhibition modulates VEGF splicing to reduce pathological neovascularization in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity. Invest. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5797–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batson, J.; Toop, H.D.; Redondo, C.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Chaikuad, A.; Wearmouth, S.F.; Gibbons, B.; Allen, C.; Tallant, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Development of potent, selective SRPK1 inhibitors as potential topical therapeutics for neovascular eye disease. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Baelde, H.J.; Quaggin, S.E. Role of the VEGF-a signaling pathway in the glomerulus: Evidence for crosstalk between components of the glomerular filtration barrier. Nephron Physiol. 2007, 106, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, V.A.; Jeruschke, S.; Eitner, F.; Becker, J.U.; Pitschke, G.; Ince, Y.; Miner, J.H.; Leuschner, I.; Engers, R.; Everding, A.S.; et al. Impaired glomerular maturation and lack of VEGF165b in Denys-Drash syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, M.; Fang, Y.; Feng, J.; Liu, B. Protective effect of vascular endothelial growth factor against cardiopulmonary bypass-associated acute kidney injury in beagles. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lgue, O.C.; McGowan, J.W.; George, E.M.; Bidwell, G.L., 3rd. Therapeutic angiogenesis by vascular endothelial growth factor supplementation for treatment of renal disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veron, D.; Reidy, K.; Marlier, A.; Bertuccio, C.; Villegas, G.; Jimenez, J.; Kashgarian, M.; Tufro, A. Induction of podocyte VEGF164 overexpression at different stages of development causes congenital nephrosis or steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Sood, M.; Haigh, J.; Nagy, A.; Lajoie, G.; Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; Kikkawa, Y.; Miner, J.H.; Quaggin, S.E. Glomerular-specific alterations of VEGF-A expression lead to distinct congenital and acquired renal diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veron, D.; Reidy, K.J.; Bertuccio, C.; Teichman, J.; Villegas, G.; Jimenez, J.; Shen, W.; Kopp, J.B.; Thomas, D.B.; Tufro, A. Overexpression of VEGF-A in podocytes of adult mice causes glomerular disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltean, S.; Neal, C.R.; Mavrou, A.; Patel, P.; Ahad, T.; Alsop, C.; Lee, T.; Sison, K.; Qiu, Y.; Harper, S.J.; et al. VEGF165b overexpression restores normal glomerular water permeability in VEGF164-overexpressing adult mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F1026–F1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, V.; Jefferson, J.A.; Kowalewska, J.; Hochster, H.; Haas, M.; Weisstuch, J.; Richardson, C.; Kopp, J.B.; Kabir, M.G.; Backx, P.H.; et al. VEGF inhibition and renal thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Ferguson, J.; Oltean, S.; Neal, C.R.; Kaura, A.; Bevan, H.; Wood, E.; Sage, L.M.; Lanati, S.; Nowak, D.G.; et al. Overexpression of VEGF165b in podocytes reduces glomerular permeability. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevens, M.; Oltean, S. Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease. Genes 2018, 9, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020098
Stevens M, Oltean S. Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease. Genes. 2018; 9(2):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020098
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevens, Megan, and Sebastian Oltean. 2018. "Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease" Genes 9, no. 2: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020098
APA StyleStevens, M., & Oltean, S. (2018). Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease. Genes, 9(2), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020098




