Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Potato bHLH Sequence Retrieval and Analysis
2.2. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Characterization
2.3. Chromosomal Location and Gene Duplication
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification
2.5. GO Annotation and RNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.6. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions and Stress Treatments
2.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification and Characterization of bHLH Proteins in Potato
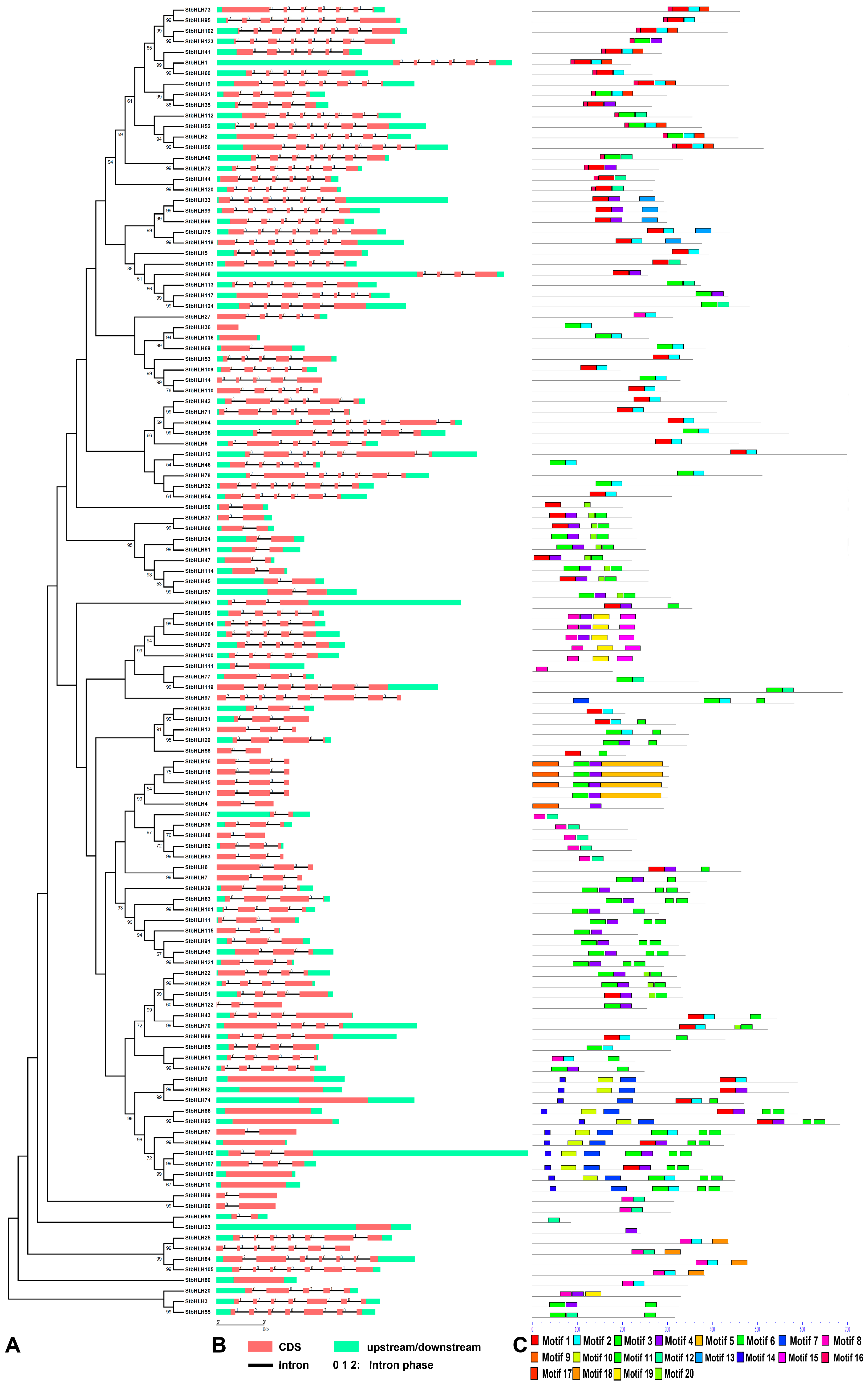
3.2. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of StbHLH
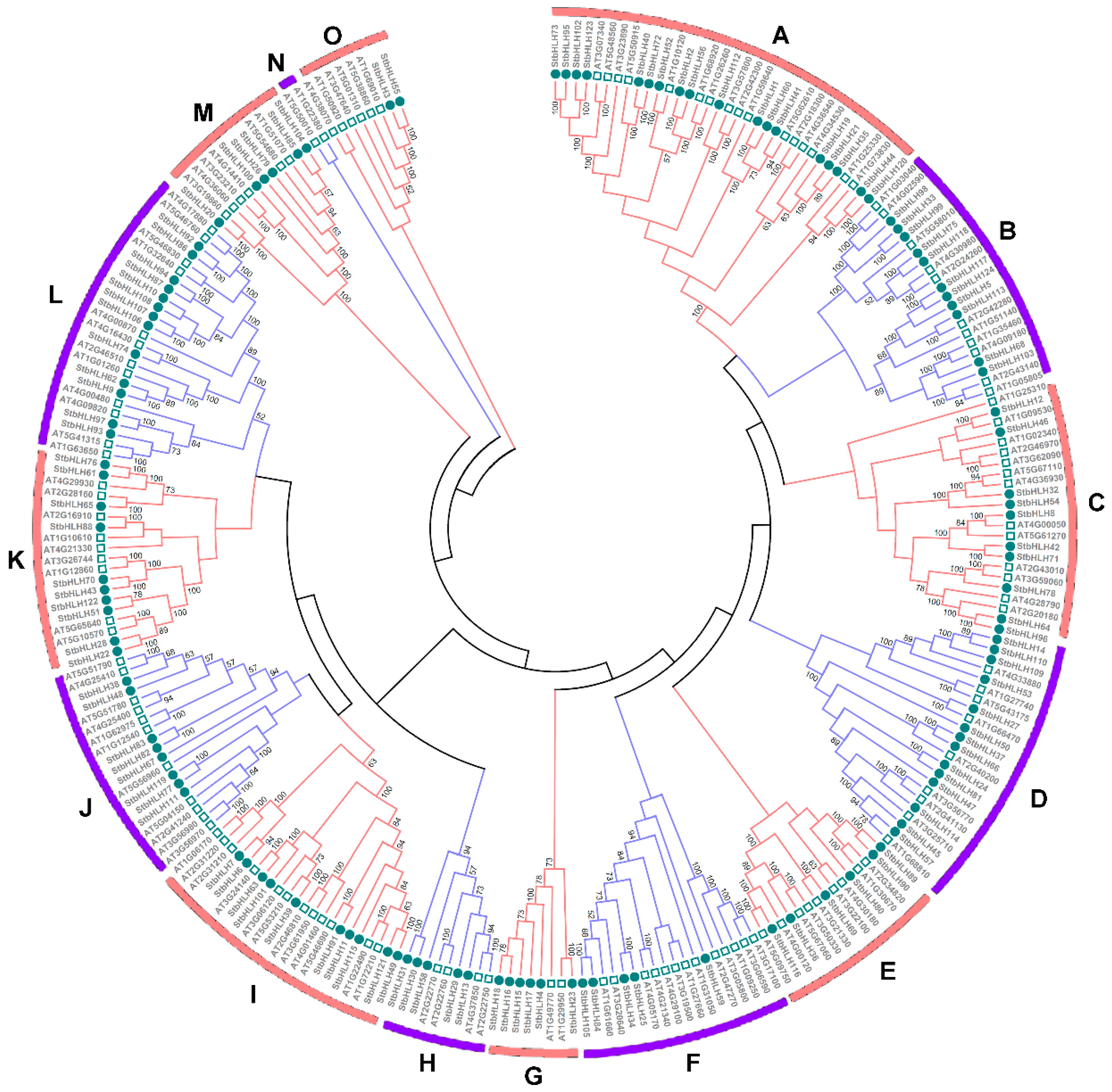
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the StbHLH Protein Family
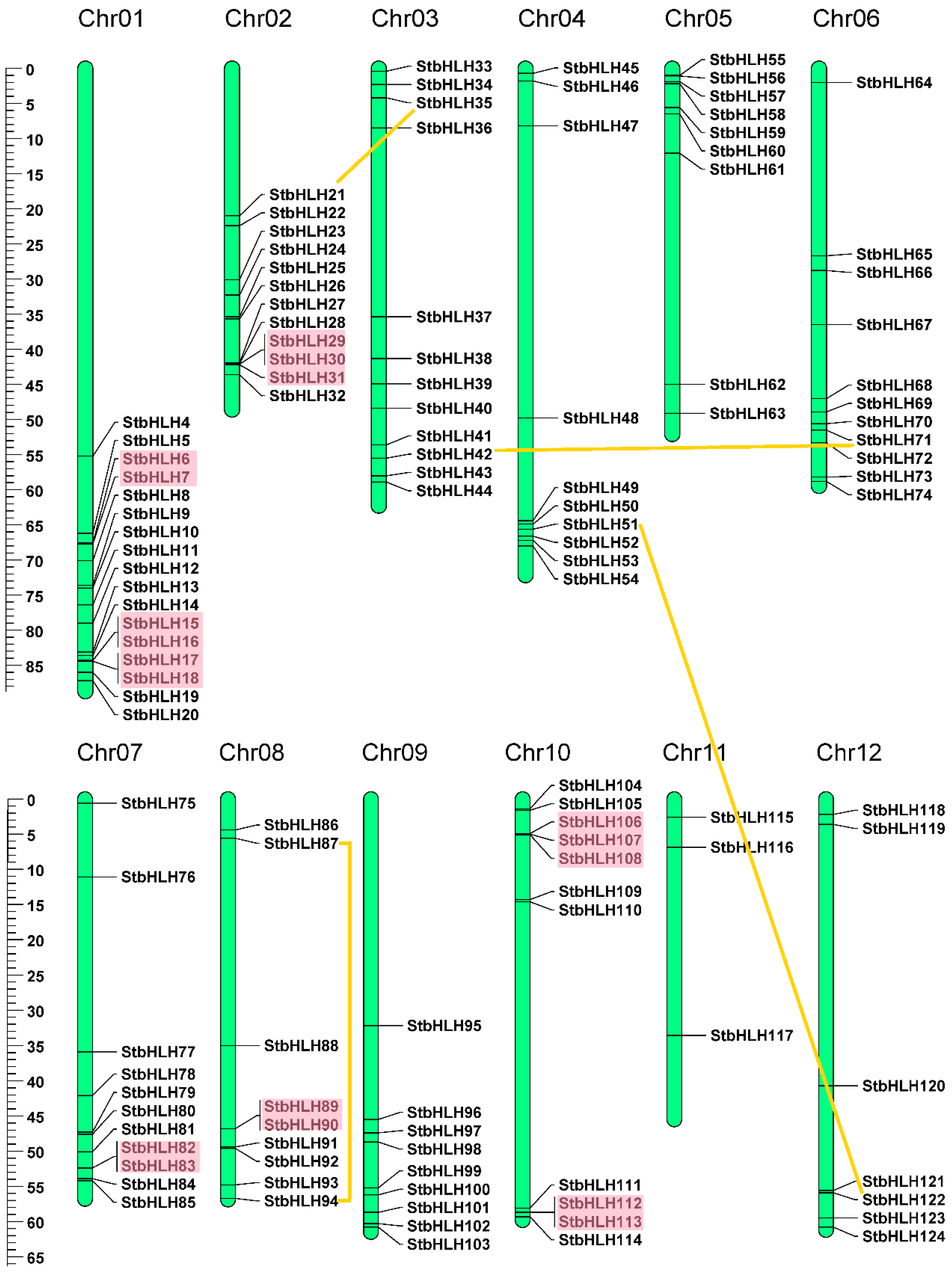
3.4. Chromosomal Location and Gene Duplication
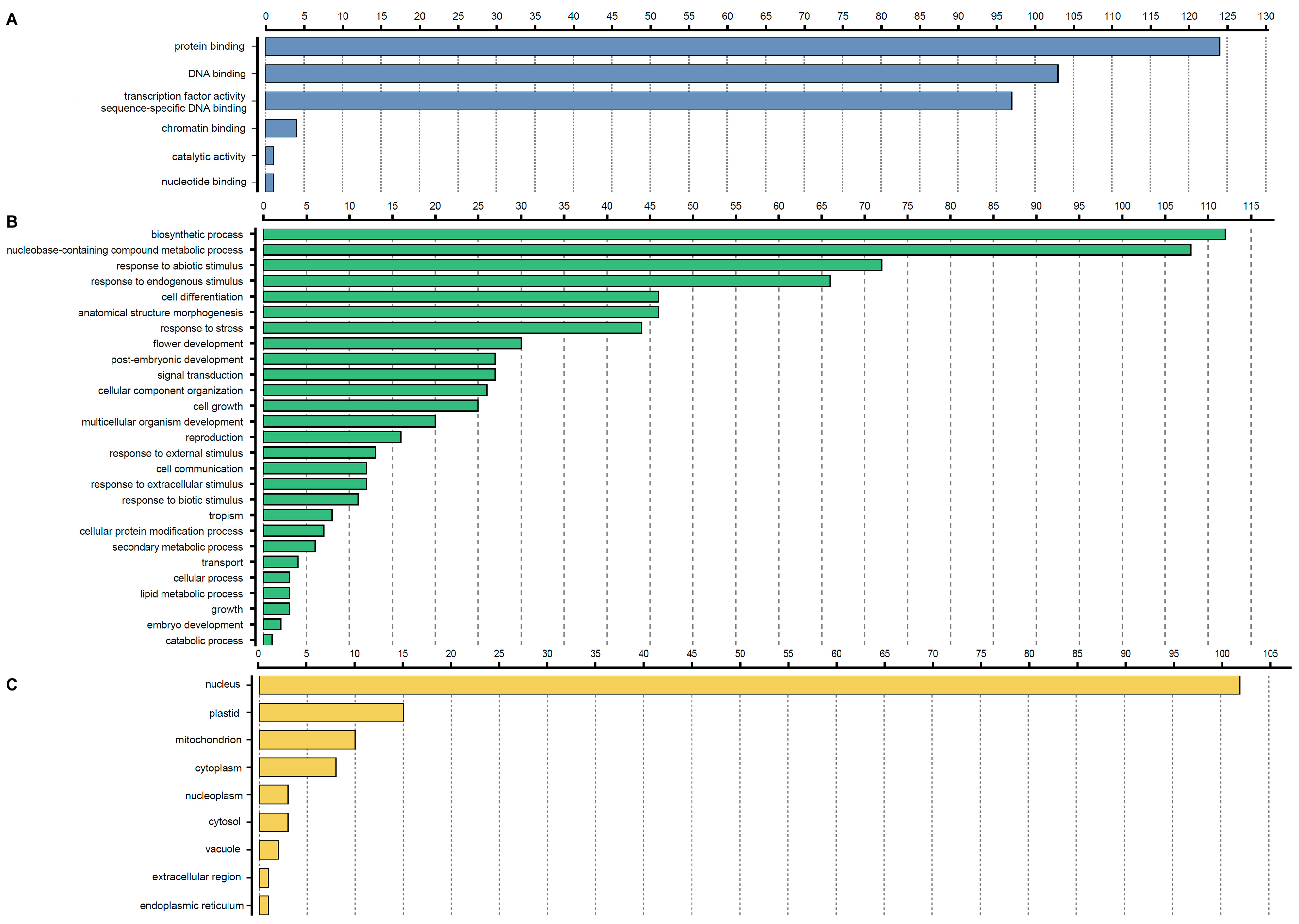
3.5. GO Annotation of StbHLH Proteins
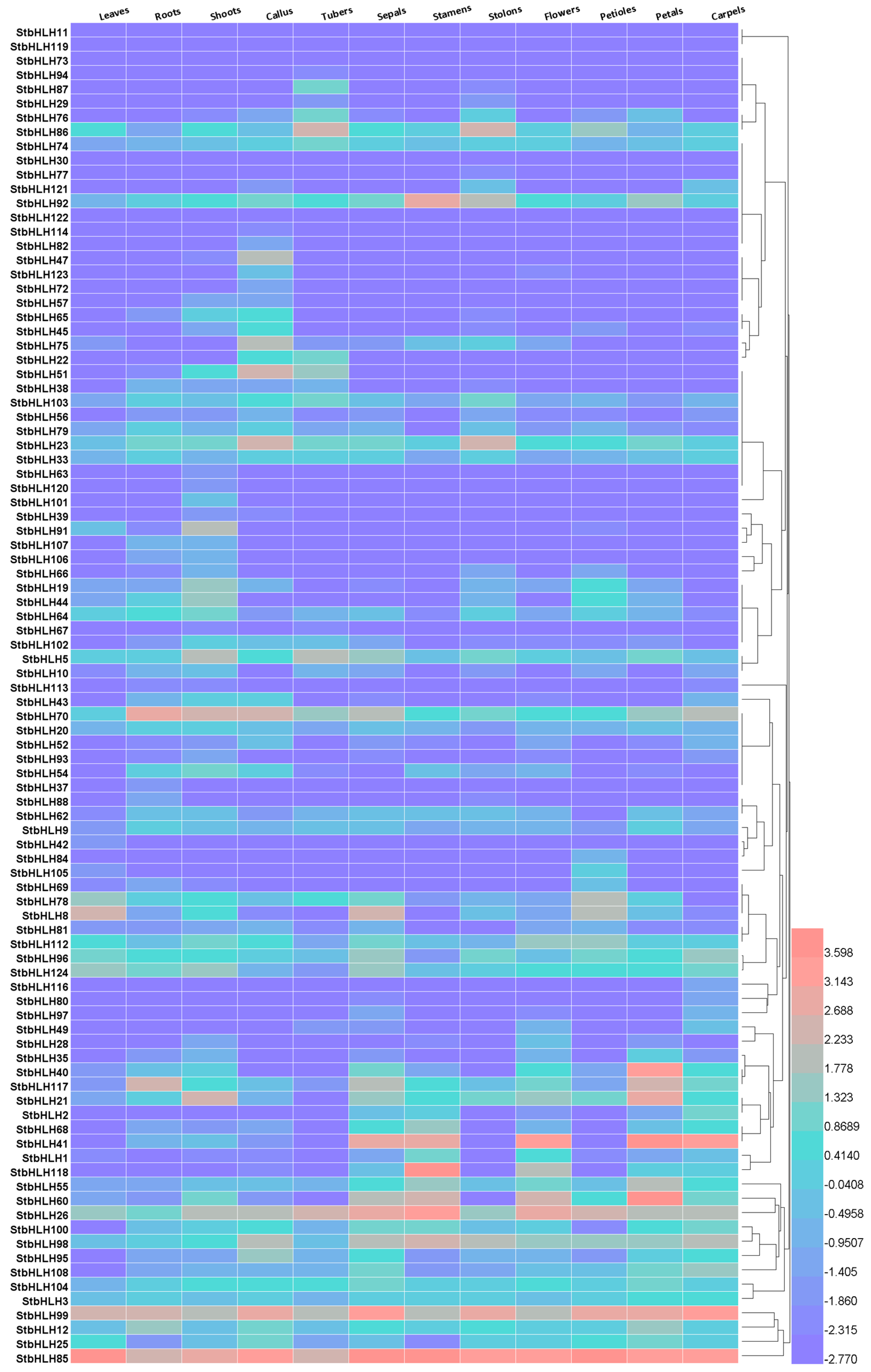
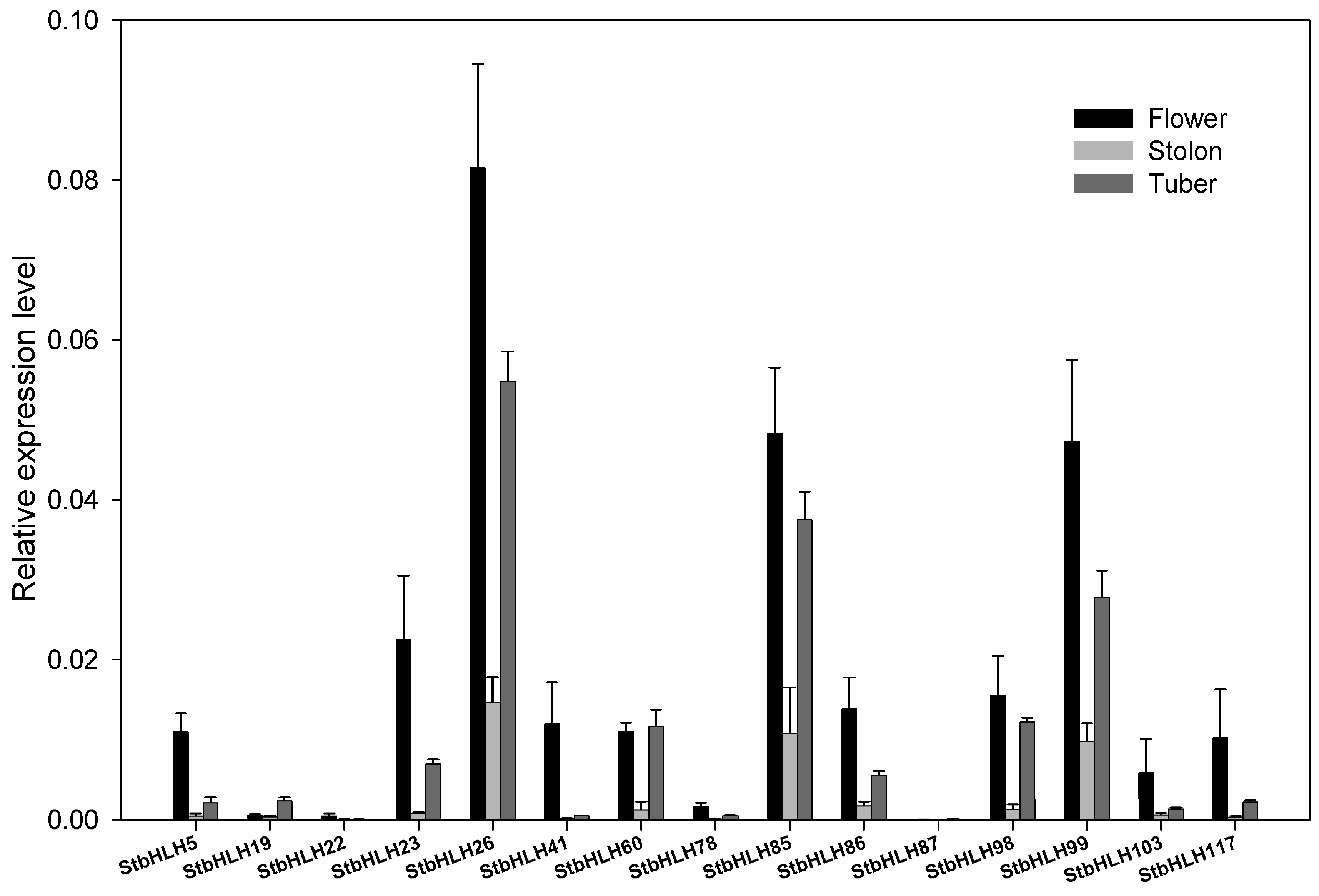
3.6. The StbHLH Expression Pattern in Various Tissues
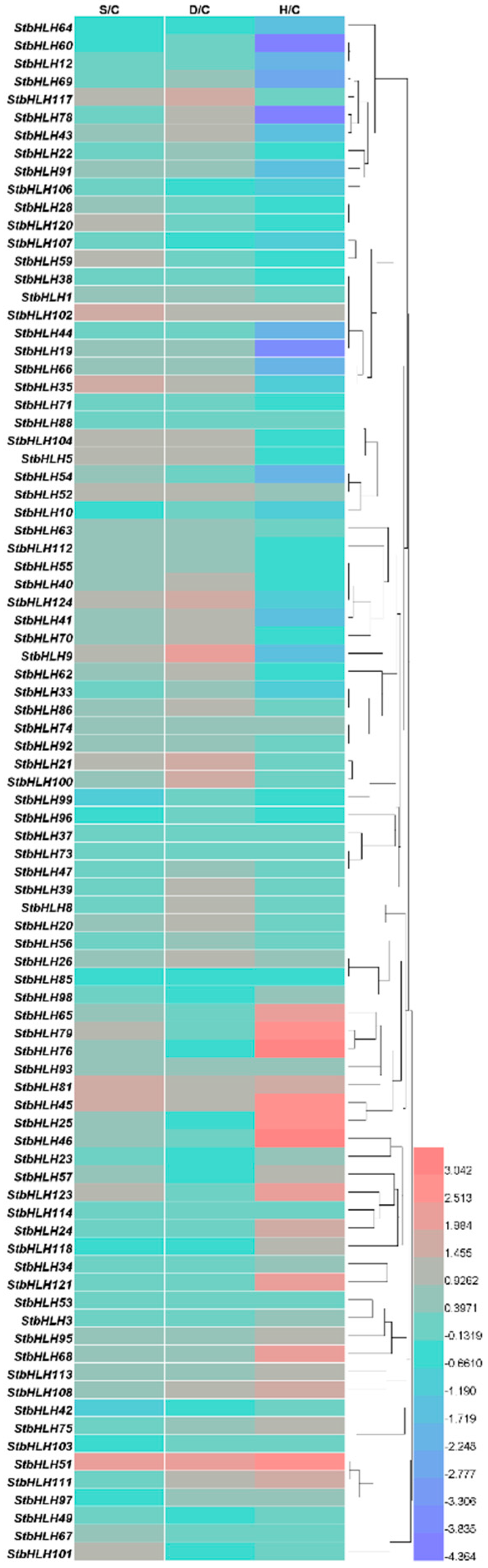
3.7. Expression Analysis of StbHLH under Abiotic Stresses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, S.; Gallagher, K.L. Transcription factors on the move. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Lv, F.F.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, P.W.; Gao, Z.H.; Hu, K.P.; Sui, C.; Jin, Y.; Wei, J.H. Transcription Factor AsMYC2 Controls the Jasmonate-responsive Expression of ASS1 Regulating Sesquiterpene Biosynthesis in Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Chang, X.; Kasuga, T.; Bui, M.; Reid, M.S.; Jiang, C.Z. A basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, PhFBH4, regulates flower senescence by modulating ethylene biosynthesis pathway in petunia. Hortic. Res. 2015, 2, 15059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karchner, S.I.; Powell, W.H.; Hahn, M.E. Identification and functional characterization of two highly divergent aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AHR1 and AHR2) in the teleost Fundulus heteroclitus. Evidence for a novel subfamily of ligand-binding basic helix loop helix-Per-ARNT-Sim (bHLH-PAS) factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33814–33824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Andrejszki, L.; Bjelic, S.; Naud, J.F.; Lavigne, P.; Jelesarov, I. Thermodynamics of b-HLH-LZ protein binding to DNA: The energetic importance of protein-DNA contacts in site-specific E-box recognition by the complete gene product of the Max p21 transcription factor. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12427–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murre, C.; McCaw, P.S.; Vaessin, H.; Caudy, M.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N.; Cabrera, C.V.; Buskin, J.N.; Hauschka, S.D.; Lassar, A.B.; et al. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell 1989, 58, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairman, R.; Beran-Steed, R.K.; Handel, T.M. Heteronuclear (1H, 13C, 15N) NMR assignments and secondary structure of the basic region-helix-loop-helix domain of E47. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.K.; Burley, S.K. Recognizing DNA in the library. Nature 2000, 404, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, B.; Atchley, W.R. Evolution of bHLH transcription factors: Modular evolution by domain shuffling? Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.A.; Lopes, J.M. Survey and summary: Saccharomyces cerevisiae basic helix-loop-helix proteins regulate diverse biological processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchley, W.R.; Fitch, W.M. A natural classification of the basic helix-loop-helix class of transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5172–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervoort, M.; Ledent, V. The evolution of the neural basic Helix-Loop-Helix proteins. ScientificWorldJournal 2001, 1, 396–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoutzias, G.D.; Robertson, D.L.; Bornberg-Bauer, E. The evolution of protein interaction networks in regulatory proteins. Comp. Funct. Genom. 2004, 5, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.D.; Roalson, E.H.; Skinner, M.K. Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family: Genomic approach to cellular differentiation. Differentiation 2008, 76, 1006–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S.R.; Habera, L.F.; Dellaporta, S.L.; Wessler, S.R. Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7092–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. PIF4, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor, functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fursova, O.V.; Pogorelko, G.V.; Tarasov, V.A. Identification of ICE2, a gene involved in cold acclimation which determines freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 2009, 429, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Yang, K.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Soh, M.S. Overexpression of PRE1 and its homologous genes activates Gibberellin-dependent responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Nemhauser, J.; Muramitsu, T.; Maloof, J.N.; Alonso, J.; Ecker, J.R.; Furuya, M.; Chory, J. Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 2002, 162, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.G.; Sun, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; An, J.P.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. Glucose Sensor MdHXK1 Phosphorylates and Stabilizes MdbHLH3 to Promote Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Apple. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, C.; Lee, M.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Zhang, F.; Lloyd, A.; Schiefelbein, J. The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development 2003, 130, 6431–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, B.; Amyot, L.; Johansen, C.; Sato, S.; Tabata, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Szczyglowski, K. Conservation of lotus and Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix proteins reveals new players in root hair development. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, K.A.; Hudson, M.E. A classification of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors of soybean. Int. J. Genom. 2015, 2015, 603182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, H.; Liang, S.; Shao, J.; Qi, Y.; An, L.; Yu, F. The over-expression of two transcription factors, ABS5/bHLH30 and ABS7/MYB101, leads to upwardly curly leaves. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ren, Y.R.; Wang, Q.J.; Yao, Y.X.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. Overexpression of MdbHLH104 gene enhances the tolerance to iron deficiency in apple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.H.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Baltimore, D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 5603–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozatier, M.; Valle, D.; Dubois, L.; Ibnsouda, S.; Vincent, A. Collier, a novel regulator of Drosophila head development, is expressed in a single mitotic domain. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.J.; Atchley, W.R. Phylogenetic analysis of plant basic helix-loop-helix proteins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero-Paulet, L.; Galstyan, A.; Roig-Villanova, I.; Martinez-Garcia, J.F.; Bilbao-Castro, J.R.; Robertson, D.L. Genome-wide classification and evolutionary analysis of the bHLH family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis, poplar, rice, moss, and algae. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.M.; Huang, Z.N.; Duan, W.K.; Ren, J.; Liu, T.K.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.L. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Dong, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, F. Genome Wide Identification and Characterization of Apple bHLH Transcription Factors and Expression Analysis in Response to Drought and Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Fan, H.J.; Ling, H.Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family in tomato. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jung, C.S.; De Jong, W.S. Genetic analysis of pigmented tuber flesh in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelia, V.; Aversano, R.; Batelli, G.; Caruso, I.; Castellano Moreno, M.; Castro-Sanz, A.B.; Chiaiese, P.; Fasano, C.; Palomba, F.; Carputo, D. High AN1 variability and interaction with basic helix-loop-helix co-factors related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in potato leaves. Plant J. 2014, 80, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin-Wang, K.; Espley, R.V.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Dare, A.; Varkonyi-Gasic, E.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Functional diversification of the potato R2R3 MYB anthocyanin activators AN1, MYBA1, and MYB113 and their interaction with basic helix-loop-helix cofactors. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2159–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buell, C.R. Michigan State University PGSC. Available online: http://solanaceae.plantbiology.msu.edu (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acid Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.S.; Eddy, S.R.; Portugaly, E. Hidden Markov model speed heuristic and iterative HMM search procedure. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.B.Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; et al. CDD. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Letunic, I. SMART. Available online: http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/ (accessed on 16 March 2017).
- ExPASy. Available online: http://web.expasy.org/protparam/ (accessed on 30 March 2017).
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Cavalcanti, A.; Chen, F.C.; Bouman, P.; Li, W.H. Extent of gene duplication in the genomes of Drosophila, nematode, and yeast. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yue, J.X.; Tian, D.; Chen, J.Q. Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 280, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, B.; Cui, X.; Peng, L. Expression profiling and integrative analysis of the CESA/CSL superfamily in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Paterson, A.H. PGDD: A database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, D1152–D1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, H.; Xue, Y. HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Cao, X.; Shi, S.; Li, S.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Q. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the amino acid transporter superfamily in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 107, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of the arabinogalactan protein gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2647–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon-intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.Y.; Vorst, O.; Fiers, M.W.; Stiekema, W.J.; Nap, J.P. In plants, highly expressed genes are the least compact. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bahler, J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell 1981, 23, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Stoeckert, C.J., Jr.; Roos, D.S. OrthoMCL: Identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, W.J.; Baertsch, R.; Hinrichs, A.; Miller, W.; Haussler, D. Evolution’s cauldron: Duplication, deletion, and rearrangement in the mouse and human genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11484–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehan, M.R.; Freimer, N.B.; Ophoff, R.A. A genome-wide survey of segmental duplications that mediate common human genetic variation of chromosomal architecture. Hum. Genom. 2004, 1, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vision, T.J.; Brown, D.G.; Tanksley, S.D. The origins of genomic duplications in Arabidopsis. Science 2000, 290, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Landherr, L.L.; Frohlich, M.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Ma, H.; de Pamphilis, C.W. Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: Evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J. 2007, 50, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Du, J.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Ling, H.Q. Requirement and functional redundancy of Ib subgroup bHLH proteins for iron deficiency responses and uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, E.; You, C.; Wang, S.; Cui, J.; Niu, B.; Wang, Y.; Qi, J.; Ma, H.; Chang, F. The DYT1-interacting proteins bHLH010, bHLH089 and bHLH091 are redundantly required for Arabidopsis anther development and transcriptome. Plant J. 2015, 83, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Chini, A.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Chico, J.M.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Geerinck, J.; Eeckhout, D.; Schweizer, F.; Godoy, M.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; et al. The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesi, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Jond, C.; Pelletier, G.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, B.; Deyholos, M.K. Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis bHLH92 transcription factor in abiotic stress. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2009, 282, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Caitar, V.S.; de Carvalho, M.C.; Darben, L.M.; Kuwahara, M.K.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Dias, W.P.; Abdelnoor, R.V.; Marcelino-Guimaraes, F.C. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsp20 gene family in soybean: Comprehensive sequence, genomic organization and expression profile analysis under abiotic and biotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, H.; Iwamoto, K.; Kariya, Y.; Asakawa, T.; Kan, T.; Fukuda, H.; Ohashi-Ito, K. A Negative Feedback Loop Controlling bHLH Complexes Is Involved in Vascular Cell Division and Differentiation in the Root Apical Meristem. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, I.; Kathare, P.K.; Kim, J.I.; Huq, E. Expanding Roles of PIFs in Signal Integration from Multiple Processes. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, L.M.; Greaves, I.K.; Zhu, A.; Dennis, E.S.; Peacock, W.J. PIF4-controlled auxin pathway contributes to hybrid vigor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3555–E3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukurba, K.R.; Montgomery, S.B. RNA Sequencing and Analysis. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2015, 2015, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi-Ito, K.; Saegusa, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Oda, Y.; Katayama, H.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Fukuda, H. A bHLH complex activates vascular cell division via cytokinin action in root apical meristem. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Motif | Width | Motif Sequence | Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36 | [RK]RGQA[TA]D[SP]H[SV][LE]AER[RK]RRE[KR][IL][NS][EQ]R[MLF][KY]AL[QR][DS][LV]VP[NG]C[NS]K | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 2 | 24 | [TM][DG]KASML[DG][ED][AI]I[EN]Y[VIL][KQ][FSQ]LQLQ[VI][KEQ]FL | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 3 | 36 | KR[EG]S[AQ][RT]XXH[SI]LAERRRR[EK][KR][ILM][NS]ER[LFM]XAL[RQ][SE]LVP[NG]STK | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 4 | 26 | [MT]DKAS[IL]L[GD][DE]A[IV][DN][YH][VI]KEL[KQ]X[QK]VQ[EK]L[ES]S | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 5 | 138 | QKL[EK]RL[EK]EYSI[RK]LM[SG]SQK[VI]GNSWEKY[VL]GDQGST[NC]NST[AT]ITP[TI][TN]HGASPLIP[TK][GS]FMTWSS[PL]NVILN[IV]CGEDAHISVCCPKKPGLFT[IM]ICYVLEKH[KN]I[DN]IV[SF]AQISSDQFRSMFMIQAHAKG[GE][SR][GE][VIL][AT]QFS[GV]AF[TK]VE[DE][MR][YL]K | – |
| 6 | 26 | [KRS][LT][MI]X[AT]L[QEK]SLGLD[VI]LHA[NS][IV][ST][TS][VL][GN][GD][LRF][VM]L | signal peptide |
| 7 | 36 | [HA]GIQT[IFL]VCIPTS[NS]GV[VL]ELGS[STV][EQ][LV]I[KP][EQ][DNS]L[EN]L[VI]QQ[VI]KS | bHLH–MYC N–terminal |
| 8 | 26 | D[RA]E[KR][LQ]RREK[LM][NS][DE][RKL][FIY]QEL[RQ]SL[LV]PPGR[KP] | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 9 | 59 | MNG[GS]GENN[HD][GV][LF]PW[EG]TND[FLV]WSYLNLND[IN]Q[IV]GS[GE][EV]TFEGDKLPD[PL]TRSDT[CY]QPLTV[VI]NEV[VI] | – |
| 10 | 34 | E[WM]F[YF]L[MAIV]S[ML][APTY][QF][SC]F[SVP][NRV][GE][DE]G[LVG][PV]GK[AC][FY][SY]S[GDS][SK][HFP][VI]W[LV][TAS][GD][ADTY] | bHLH–MYC N–terminal |
| 11 | 19 | [ED][IV][ED]V[KR]I[IV][GE]X[DE][AV][ML][IVL][RK][IV]Q[SC]E[KRN] | – |
| 12 | 26 | [RTM][SDGN]T[AS][DS][MVH]L[DQ]E[AIT][VI][NE]Y[IV][KQ]SL[QK]N[QN][VI][EK][EF]L[SE][KM] | Helix–loop–helix DNA–binding domain |
| 13 | 36 | E[HQR][QE]VAKLMEE[DN][VM]G[AST]AMQ[YF]LQ[SG]K[GSA]LC[IL]MP[IV]SLA[ATS][AL]I[YS] | – |
| 14 | 14 | AX[ES][SDW]WAYAIFWQSS | – |
| 15 | 35 | K[LM][MVA][PV][FIY][ILMP][SG]Y[PG][GSY][VI][AP]MWQ[FY][MLV][PQ]P[AS][ASV][VIR]DTS[QE]DH[VMS]LRPP[VA]A | – |
| 16 | 10 | [PK][PK]KDY[IV]HVRA | – |
| 17 | 23 | SMKL[AE][TA]VNPR[LM][DN]F[DN]I[DE][ANS][LI][LFP][AS]K[DE][IFM] | – |
| 18 | 36 | [DG]LRS[RK]GLCLVP[IV]SSTFP[VL][AT][HAT]ET[ANST][VMT][DE][FL]WTP[TN][FL]G[GRS]TFR | – |
| 19 | 36 | LQE[KE]IKELK[AV]EKNELR[DE]EKQRLK[AS][ED]KEKLEQQLK[AT][MT] | – |
| 20 | 14 | [ITV]K[AI][SE][IL]CC[ED]D[RK][PS][EGD]LL | – |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Zhao, P.; Kong, N.; Lu, R.; Pei, Y.; Huang, C.; Ma, H.; Chen, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family. Genes 2018, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010054
Wang R, Zhao P, Kong N, Lu R, Pei Y, Huang C, Ma H, Chen Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family. Genes. 2018; 9(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruoqiu, Peng Zhao, Nana Kong, Ruize Lu, Yue Pei, Chenxi Huang, Haoli Ma, and Qin Chen. 2018. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family" Genes 9, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010054
APA StyleWang, R., Zhao, P., Kong, N., Lu, R., Pei, Y., Huang, C., Ma, H., & Chen, Q. (2018). Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato bHLH Transcription Factor Family. Genes, 9(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010054





