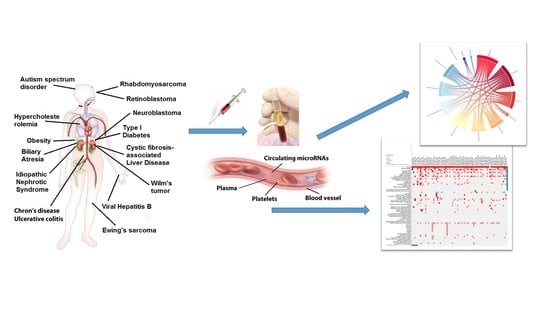
Circulating microRNAs and Bioinformatics Tools to Discover Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Pediatric Diseases
Abstract
1. Biogenesis and Regulatory Functions of microRNAs
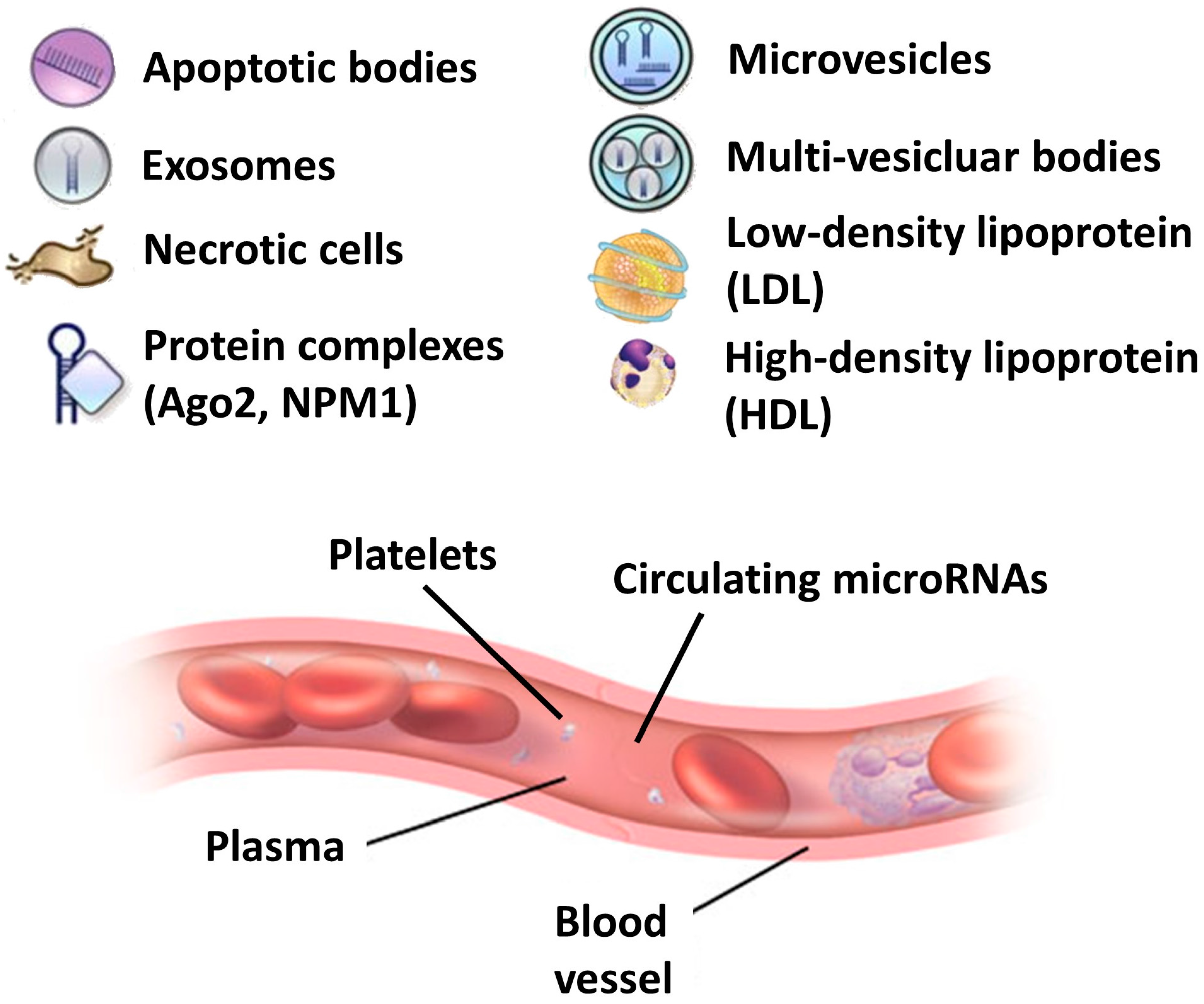
2. Biogenesis, Stability and Cellular Recognition of Circulating microRNAs
3. Circulating miRNAs and Toll-Like Receptors
4. Quantification and Analysis of Circulating microRNAs
5. Circulating microRNAs in Biological Fluids
6. Circulating MicroRNAs in Plasma/Serum
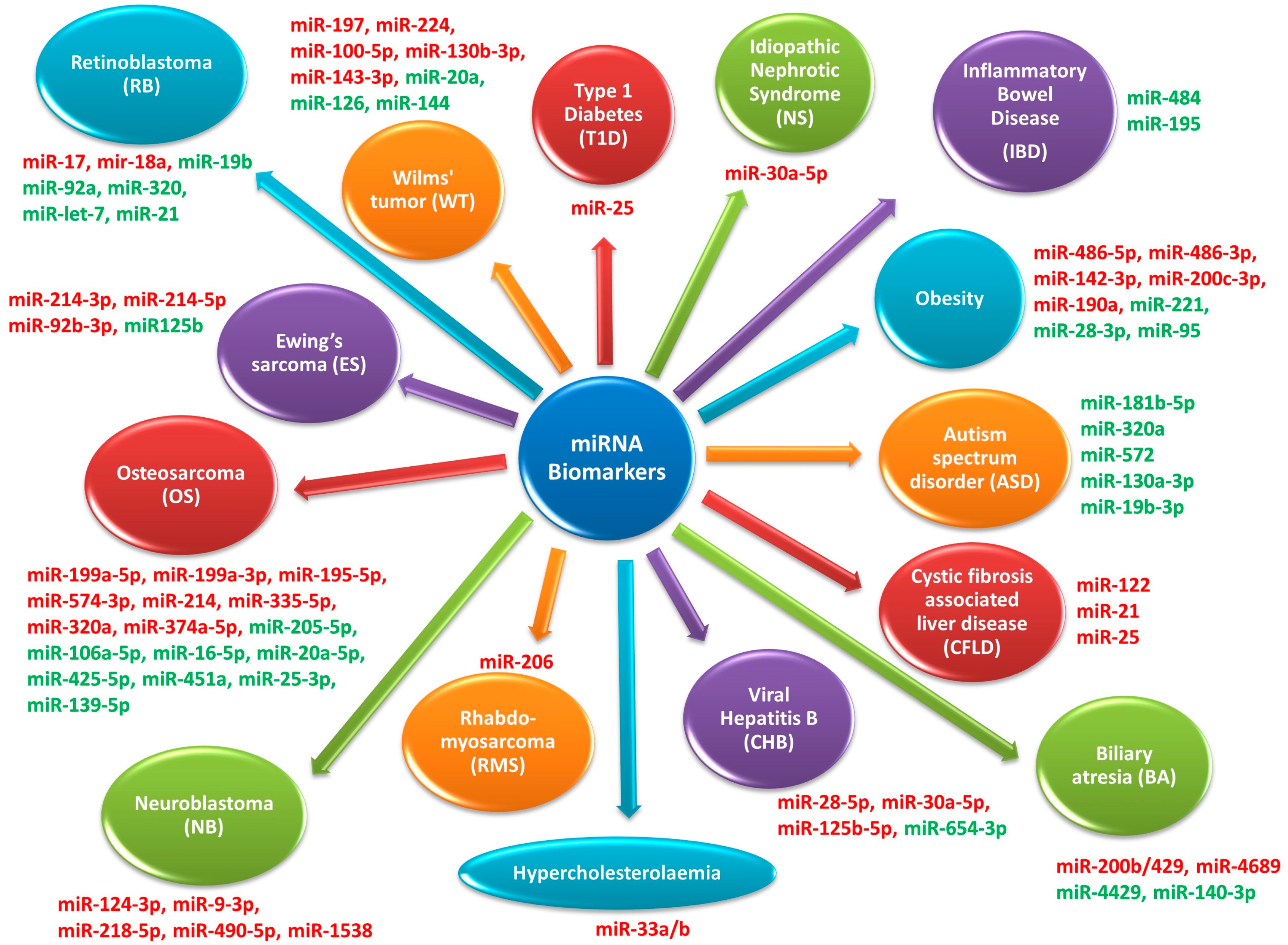
6.1. Type 1 Diabetes
6.2. Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome
6.3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
6.4. Obesity
6.5. Autism Spectrum Disorder
6.6. Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease
6.7. Biliary Atresia
6.8. Viral Hepatitis B
6.9. Hypercholesterolemia
6.10. Solid Tumors
7. Bioinformatics Tools and Databases for Circulating Extracellular microRNAs
8. An Integrated Collection of Small RNA Research Tools
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ASCA | anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BA | Biliary atresia |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| CFLD | Cystic fibrosis-associated Liver Disease |
| CHB | Chronic hepatitis B |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CVD | Cardiovascular diseases |
| FMD | Flow-mediated dilatation |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis Be antigen |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HC | Hypercholesterolemia |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDL-C | High density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IgAN | IgA nephropathy |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| INRG | International Neuroblastoma Risk Group |
| isomiRs | isoforms of miRNAs |
| LDL-C | Low density lipoprotein |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| NGS | Next generation sequencing |
| NMP1 | Nucleolar phosphoprotein |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NS | Nephrotic syndrome |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| ssRNA | single-stranded RNA |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| TAPIR | target prediction for plant microRNAs |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TLRs | Toll-like Recetors |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer. Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chim, S.S.; Shing, T.K.; Hung, E.C.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.; Lo, Y.M. Detection and characterization of placental microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gelfond, J.A.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids—the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Quinton, L.J.; Blahna, M.T.; Neilson, J.R.; Fu, S.; Ivanov, A.R.; Wolf, D.A.; Mizgerd, J.P. Zcchc11-dependent uridylation of microRNA directs cytokine expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Miyauchi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kashiwabara, S.; Baba, T.; Suzuki, T. Selective stabilization of mammalian microRNAs by 3’ adenylation mediated by the cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase GLD-2. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, T.; Jin, G.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.; et al. Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbings, D.J.; Ciaudo, C.; Erhardt, M.; Voinnet, O. Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Mundkur, S.; Catalano, D.; Levin, I.; Ward, J.; Alao, H.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Circulating microRNAs in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C., Jr. Innate immune recognition: Mechanisms and pathways. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 173, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, F.; Hemmi, H.; Hochrein, H.; Ampenberger, F.; Kirschning, C.; Akira, S.; Lipford, G.; Wagner, H.; Bauer, S. Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science 2004, 303, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M. TLRs as miRNA receptors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6333–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, S.M.; Krüger, C.; Park, B.; Derkow, K.; Rosenberger, K.; Baumgart, J.; Trimbuch, T.; Eom, G.; Hinz, M.; Kaul, D.; et al. An unconventional role for miRNA: Let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, A.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat. Res. 2011, 717, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Ni, S.; Peng, Z.; Sheng, W.; Du, X. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.J.; Zhou, H.; Elashoff, D.; Henson, B.S.; Kastratovic, D.A.; Abemayor, E.; Wong, D.T. Salivary microRNA: Discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsten, M.F.; Dennert, R.; Jochems, S.; Kuznetsova, T.; Devaux, Y.; Hofstra, L.; Wagner, D.R.; Staessen, J.A.; Heymans, S.; Schroen, B. Circulating MicroRNA-208b and MicroRNA-499 reflect myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodes, M.J.; Caraballo, M.; Suciu, D.; Munro, S.; Kumar, A.; Anderson, B. Detection of cancer with serum miRNAs on an oligonucleotide microarray. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, K.E.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Richardson, D.L.; Croce, C.M.; Cohn, D.E. The detection of differentially expressed microRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schamberger, A.; Orban, T.I. 3’ IsomiR species and DNA contamination influence reliable quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop quantitative PCR. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.C. Next-generation sequencing transforms today’s biology. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wach, S.; Nolte, E.; Szczyrba, J.; Stohr, R.; Hartmann, A.; Orntoft, T.; Dyrskjot, L.; Eltze, E.; Wieland, W.; Keck, B.; et al. MicroRNA profiles of prostate carcinoma detected by multiplatform microRNA screening. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Chen, J.; et al. MicroRNA expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, Z.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Elias, R.; Mihailovic, A.; Brown, M.; Rosenwaks, Z.; Tuschl, T. Comprehensive profiling of circulating microRNA via small RNA sequencing of cDNA libraries reveals biomarker potential and limitations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4255–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellingham, S.A.; Coleman, B.M.; Hill, A.F. Small RNA deep sequencing reveals a distinct miRNA signature released in exosomes from prion-infected neuronal cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10937–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Somlo, G.; Yu, Y.; Palomares, M.R.; Li, A.X.; Zhou, W.; Chow, A.; Ye, Y.; Rossi, J.J.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; et al. De novo sequencing of circulating miRNAs identifies novel markers predicting clinical outcome of locally advanced breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, P.; Hartmann, N.; Baeriswyl, L.; Andreasen, D.; Bernard, N.; Chen, C.; Cheo, D.; D'Andrade, P.; DeMayo, M.; Dennis, L.; Derveaux, S.; et al. Evaluation of quantitative miRNA expression platforms in the microRNA quality control (miRQC) study. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.H.; Yi, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kroh, E.M.; Chien, J.W.; Eaton, K.D.; Goodman, M.T.; Tait, J.F.; Tewari, M.; Pritchard, C.C. Plasma processing conditions substantially influence circulating microRNA biomarker levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlexander, M.A.; Phillips, M.J.; Witwer, K.W. Comparison of Methods for miRNA Extraction from Plasma and Quantitative Recovery of RNA from Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’haene, B.; Mestdagh, P.; Hellemans, J.; Vandesompele, J. miRNA expression profiling: From reference genes to global mean normalization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 822, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.S.; Ishibashi, O.; Ishikawa, G.; Ishikawa, T.; Katayama, A.; Mishima, T.; Takizawa, T.; Shigihara, T.; Goto, T.; Izumi, A.; et al. Human villous trophoblasts express and secrete placenta-specific microRNAs into maternal circulation via exosomes. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardizabal, M.N.; Nocito, A.L.; Daniele, S.M.; Ornella, L.A.; Palatnik, J.F.; Veggi, L.M. Reference genes for real-time PCR quantification of microRNAs and messenger RNAs in rat models of hepatotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, Y.; Pu, J. Circulating microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.L.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.S.; Huang, X.; Cao, H.; Christman-Skieller, C.; Bennewith, K.; Le, Q.T.; Koong, A.C. Circulating miR-210 as a Novel Hypoxia Marker in Pancreatic Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2010, 3, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, W.; Atasoy, U.; Sauter, E.R. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shen, J.; Medico, L.; Wang, D.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Liu, S. A pilot study of circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of early stage breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Afdhal, N.H.; Albitar, M. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, A.; Cox, M.A.; Gaffney, K.A.; Moreland, A.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Technical factors involved in the measurement of circulating microRNA biomarkers for the detection of colorectal neoplasia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, P.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; De Weer, A.; Muth, D.; Westermann, F.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneron, N. Towards a new standardized method for circulating miRNAs profiling in clinical studies: Interest of the exogenous normalization to improve miRNA signature accuracy. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, S.; Meiri, E.; Yogev, Y.; Benjamin, S.; Lebanony, D.; Yerushalmi, N.; Benjamin, H.; Kushnir, M.; Cholakh, H.; Melamed, N.; et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNA identification in plasma and serum: A new tool to diagnose and monitor diseases. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, M.; Hoefig, K.; Merz, H.; Feller, A.C.; Kausch, I.; Jocham, D.; Warnecke, J.M.; Sczakiel, G. A robust methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: MicroRNA-126 and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2010, 28, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Bella, S.D.; Nigita, G.; Macca, V.; Lagana, A.; Giugno, R.; Pulvirenti, A.; Ferro, A. miRandola: Extracellular circulating microRNAs database. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, H.; Gottlieb, P. The honeymoon phase: Intersection of metabolism and immunology. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2009, 16, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.B.; Wang, C.; Sorensen, K.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Hansen, L.; Andersen, M.L.; Hougaard, P.; Juul, A.; Zhang, C.Y.; Pociot, F.; et al. Circulating levels of microRNA from children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes and healthy controls: Evidence that miR-25 associates to residual beta-cell function and glycaemic control during disease progression. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 2012:896362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erener, S.; Marwaha, A.; Tan, R.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Kieffer, T.J. Profiling of circulating microRNAs in children with recent onset of type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e89656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagga, A.; Mantan, M. Nephrotic syndrome in children. Indian J. Med. Res. 2005, 122, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boute, N.; Gribouval, O.; Roselli, S.; Benessy, F.; Lee, H.; Fuchshuber, A.; Dahan, K.; Gubler, M.C.; Niaudet, P.; Antignac, C. NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Q.; Wu, J.; Niu, D.M.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhang, C.N.; Wang, J.J. The level of native and oxidized lipoprotein(a) in children with nephrotic syndrome. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyagunawardena, A.S. Treatment of steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Indian J. Pediatr. 2005, 72, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, A.A.; Symons, J.M. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 2003, 362, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tam, L.S.; Li, E.K.; Kwan, B.C.; Chow, K.M.; Luk, C.C.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Serum and urinary free microRNA level in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2011, 20, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kwan, B.C.; Lai, F.M.; Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Elevated levels of miR-146a and miR-155 in kidney biopsy and urine from patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis. Markers 2011, 30, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kwan, B.C.; Lai, F.M.; Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Expression of microRNAs in the urinary sediment of patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis. Markers 2010, 28, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, J.M.; Kielstein, J.T.; Hafer, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Kumpers, P.; Faulhaber-Walter, R.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D.; Thum, T. Circulating miR-210 predicts survival in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.S.; Michael, M.Z.; Pimlott, L.K.; Yong, T.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Gleadle, J.M. Circulating microRNA expression is reduced in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3794–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhong, T.; Cai, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Hu, J.; Guan, X.; Xia, Z.; et al. Increased serum and urinary microRNAs in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieson, P.W. Update on the podocyte. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yu, L.; Chiu, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Khitrov, G.; Merkenschlager, M.; Holzman, L.B.; Zhang, W.; Mundel, P.; et al. Podocyte-selective deletion of dicer induces proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdanova, O.; Srivastava, S.; Di, L.; Li, Z.; Tchelebi, L.; Dworkin, S.; Johnstone, D.B.; Zavadil, J.; Chong, M.M.; Littman, D.R.; et al. The inducible deletion of Drosha and microRNAs in mature podocytes results in a collapsing glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, S.J.; Jarad, G.; Cunningham, J.; Goldberg, S.; Schermer, B.; Harfe, B.D.; McManus, M.T.; Benzing, T.; Miner, J.H. Podocyte-specific deletion of dicer alters cytoskeletal dynamics and causes glomerular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, L.B.; Schug, J.; Vourekas, A.; McKenna, J.B.; Bramswig, N.C.; Friedman, J.R.; Kaestner, K.H. MicroRNAs control intestinal epithelial differentiation, architecture, and barrier function. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1654–1664, 1664.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masotti, A. Interplays between gut microbiota and gene expression regulation by miRNAs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celluzzi, A.; Masotti, A. How Our Other Genome Controls Our Epi-Genome. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, A.M.; Thayu, M.; Hand, N.J.; Horner, A.; Leonard, M.B.; Friedman, J.R. Circulating microRNA is a biomarker of pediatric Crohn disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duttagupta, R.; DiRienzo, S.; Jiang, R.; Bowers, J.; Gollub, J.; Kao, J.; Kearney, K.; Rudolph, D.; Dawany, N.B.; Showe, M.K.; et al. Genome-wide maps of circulating miRNA biomarkers for ulcerative colitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, A.M.; Hand, N.J.; Tsoucas, D.M.; Guen, C.L.L.; Baldassano, R.N.; Friedman, J.R. Rectal microRNAs are perturbed in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease of the colon. J. Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felli, C.; Baldassarre, A.; Masotti, A. Intestinal and Circulating MicroRNAs in Coeliac Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Kaaks, R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: Epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004, 4, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, E. microRNAs and cancer: Role in tumorigenesis, patient classification and therapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2007, 9, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, U.; Buyukinan, M.; Yerlikaya, F.H. The investigation of circulating microRNAs associated with lipid metabolism in childhood obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prats-Puig, A.; Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Moreno, M.; Bonet, N.; Ricart, W.; Lopez-Bermejo, A.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Changes in circulating microRNAs are associated with childhood obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1655–E1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masotti, A.; Baldassarre, A.; Fabrizi, M.; Olivero, G.; Loreti, M.C.; Giammaria, P.; Veronelli, P.; Graziani, M.P.; Manco, M. Oral glucose tolerance test unravels circulating miRNAs associated with insulin resistance in obese preschoolers. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalyfa, A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Khalyfa, A.A.; Gozal, D. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Obese Children. Chest 2016, 149, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalyfa, A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Circulating exosomes in obstructive sleep apnea as phenotypic biomarkers and mechanistic messengers of end-organ morbidity. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persico, A.M.; Napolioni, V. Autism genetics. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 251, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristino, A.S.; Williams, S.M.; Hawi, Z.; An, J.Y.; Bellgrove, M.A.; Schwartz, C.E.; Lda, F.C.; Claudianos, C. Neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders represent an interconnected molecular system. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, S.E.; Lemery-Chalfant, K.; Jahromi, L.B.; Valiente, C. A review of gene-environment correlations and their implications for autism: A conceptual model. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 120, 497–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, K.; Hirasawa, T.; Koide, T.; Kubota, T. Epigenetics in autism and other neurodevelopmental diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 724, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delcuve, G.P.; Rastegar, M.; Davie, J.R. Epigenetic control. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, M.M.; Anitha, A.; Thanseem, I.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, T.; Wakuda, T.; Iwata, K.; Tsujii, M.; Sugiyama, T.; et al. Serum microRNA profiles in children with autism. Mol. Autism 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeuwen, L.; Fitzgerald, D.A.; Gaskin, K.J. Liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewindon, P.J.; Shepherd, R.W.; Walsh, M.J.; Greer, R.M.; Williamson, R.; Pereira, T.N.; Frawley, K.; Bell, S.C.; Smith, J.L.; Ramm, G.A. Importance of hepatic fibrosis in cystic fibrosis and the predictive value of liver biopsy. Hepatology 2011, 53, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.L.; Pereira, T.N.; Lewindon, P.J.; Shepherd, R.W.; Ramm, G.A. Circulating microRNAs as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers of liver disease in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, J.; Harnden, A.; Kelly, D. Biliary atresia. BMJ 2010, 340, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, A.M.; Hand, N.J.; Boateng, L.A.; Friedman, J.R. Circulating microRNA is a biomarker of biliary atresia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Shen, Z.; Zheng, C.; Chen, G.; Zheng, S. Serum microRNA microarray analysis identifies miR-4429 and miR-4689 are potential diagnostic biomarkers for biliary atresia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Pang, S.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, B.; et al. Identification of Circulating MicroRNAs in Biliary Atresia by Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, B.J. The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 49, S45–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; Heathcote, E.J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Management of hepatitis B: 2000—Summary of a workshop. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1828–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.M.; Hu, Z.B.; Zhou, Z.X.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Shen, H.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Serum microRNA profiles serve as novel biomarkers for HBV infection and diagnosis of HBV-positive hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9798–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Yang, B.; Peng, X.; Ding, H.; You, H.; Tien, P. Circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, e242–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winther, T.N.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Heiberg, I.L.; Pociot, F.; Hogh, B. Differential plasma microRNA profiles in HBeAg positive and HBeAg negative children with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winther, T.N.; Jacobsen, K.S.; Mirza, A.H.; Heiberg, I.L.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Pociot, F.; Hogh, B. Circulating MicroRNAs in Plasma of Hepatitis B e Antigen Positive Children Reveal Liver-Specific Target Genes. Int. J. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 791045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winther, T.N.; Heiberg, I.L.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Pociot, F.; Hogh, B. Hepatitis B surface antigen quantity positively correlates with plasma levels of microRNAs differentially expressed in immunological phases of chronic hepatitis B in children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggoun, Y.; Bonnet, D.; Sidi, D.; Girardet, J.P.; Brucker, E.; Polak, M.; Safar, M.E.; Levy, B.I. Arterial mechanical changes in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcaro, G.; Zenere, B.M.; Travia, D.; Zenti, M.G.; Covi, G.; Lechi, A.; Muggeo, M. Non-invasive detection of early endothelial dysfunction in hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Atherosclerosis 1995, 114, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.; Carlomosti, F.; Avitabile, D.; Persico, L.; Picozza, M.; Barilla, F.; Arca, M.; Montali, A.; Martino, E.; Zanoni, C.; et al. Circulating miR-33a and miR-33b are up-regulated in familial hypercholesterolaemia in paediatric age. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, I.N.; de Freitas, R.M.; Vargas, F.R. Translating microRNAs into biomarkers: What is new for pediatric cancer? Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, N.E.; Sevier, N. Solid tumors in children. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2003, 18, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.J.; Raby, K.L.; Saini, H.K.; Bailey, S.; Wool, S.V.; Tunnacliffe, J.M.; Enright, A.J.; Nicholson, J.C.; Coleman, N. Solid tumors of childhood display specific serum microRNA profiles. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2015, 24, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyachi, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yagyu, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Misawa, A.; Iehara, T.; Hosoi, H. Circulating muscle-specific microRNA, miR-206, as a potential diagnostic marker for rhabdomyosarcoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.; Ye, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. A three-plasma miRNA signature serves as novel biomarkers for osteosarcoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Jia, J.; Ling, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z. A causal role for circulating miR-34b in osteosarcoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, W.; Zhou, X. Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemosensitivity and prognosis in human osteosarcoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, X.; Chai, J.; Chen, P.; Ren, P.; Gong, M. Circulating miR-148a is a significant diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12467–12472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yao, C.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; He, X. Serum levels of microRNA-133b and microRNA-206 expression predict prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4194–4203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.H.; Ouyang, Y.; Guo, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Bu, J.; Xiao, T. MicroRNA screening identifies circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, G.; Lu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, S. Identification of miR-199a-5p in serum as noninvasive biomarkers for detecting and monitoring osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8845–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, F.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, C.; Gao, K.; Wu, L. Identification of a plasma four-microRNA panel as potential noninvasive biomarker for osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen-Rhoades, W.; Kurenbekova, L.; Satterfield, L.; Parikh, N.; Fuja, D.; Shuck, R.L.; Rainusso, N.; Trucco, M.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Jo, E.; et al. Cross-species identification of a plasma microRNA signature for detection, therapeutic monitoring, and prognosis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vito, C.; Riggi, N.; Suva, M.L.; Janiszewska, M.; Horlbeck, J.; Baumer, K.; Provero, P.; Stamenkovic, I. Let-7a is a direct EWS-FLI-1 target implicated in Ewing’s sarcoma development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.L.; Ren, W.H.; Ma, Y.; Xi, J.S.; Han, B. Circulating miR-125b as a biomarker of Ewing’s sarcoma in Chinese children. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 19049–19056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabchi, K.; Soleimani-Jelodar, R.; Aghadoost, N.; Momeni, F.; Moridikia, A.; Nahand, J.S.; Masoudifar, A.; Razmjoo, H.; Mirzaei, H. MicroRNAs in retinoblastoma: Potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beta, M.; Venkatesan, N.; Vasudevan, M.; Vetrivel, U.; Khetan, V.; Krishnakumar, S. Identification and Insilico Analysis of Retinoblastoma Serum microRNA Profile and Gene Targets Towards Prediction of Novel Serum Biomarkers. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2013, 7, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, Y.F.; Miao, L.X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.S.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, Q.L. Plasma microRNA-320, microRNA-let-7e and microRNA-21 as novel potential biomarkers for the detection of retinoblastoma. Biomed. Rep. 2014, 2, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, J.; Backes, C.; Nourkami-Tutdibi, N.; Leidinger, P.; Deutscher, S.; Beier, M.; Gessler, M.; Graf, N.; Lenhof, H.P.; Keller, A.; et al. Treatment-independent miRNA signature in blood of Wilms tumor patients. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, N.; Nourkami-Tutdibi, N.; Backes, C.; Lenhof, H.P.; Graf, N.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Circulating serum miRNAs as potential biomarkers for nephroblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagana, A.; Forte, S.; Giudice, A.; Arena, M.R.; Puglisi, P.L.; Giugno, R.; Pulvirenti, A.; Shasha, D.; Ferro, A. miRò: A miRNA knowledge base. Database 2009, 2009, bap008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Fahner, C.J.; Reid, G.E.; Simpson, R.J. ExoCarta 2012: Database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1241–D1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.; Simpson, R.J.; Lotvall, J.; Gho, Y.S. EVpedia: A community web resource for prokaryotic and eukaryotic extracellular vesicles research. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito-Martin, A.; Peinado, H. FunRich proteomics software analysis, let the fun begin! Proteomics 2015, 15, 2555–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Bella, S.D.; Bonnici, V.; Lagana, A.; Rainaldi, G.; Pellegrini, M.; Pulvirenti, A.; Giugno, R.; Ferro, A. A knowledge base for the discovery of function, diagnostic potential and drug effects on cellular and extracellular miRNAs. BMC Genom. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 3), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon, S.; Schwach, F.; Dalmay, T.; Maclean, D.; Studholme, D.J.; Moulton, V. A toolkit for analysing large-scale plant small RNA datasets. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2252–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Chen, W.; Adamidi, C.; Maaskola, J.; Einspanier, R.; Knespel, S.; Rajewsky, N. Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, M.; Sturm, M.; Langenberger, D.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Aransay, A.M. miRanalyzer: A microRNA detection and analysis tool for next-generation sequencing experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W68–W76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, M.; Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Aransay, A.M. miRanalyzer: An update on the detection and analysis of microRNAs in high-throughput sequencing experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W132–W138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, L.; Estivill, X.; Marti, E. SeqBuster, a bioinformatic tool for the processing and analysis of small RNAs datasets, reveals ubiquitous miRNA modifications in human embryonic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasold, M.; Langenberger, D.; Binder, H.; Stadler, P.F.; Hoffmann, S. DARIO: A ncRNA detection and analysis tool for next-generation sequencing experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W112–W117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocks, M.B.; Moxon, S.; Mapleson, D.; Woolfenden, H.C.; Mohorianu, I.; Folkes, L.; Schwach, F.; Dalmay, T.; Moulton, V. The UEA sRNA workbench: A suite of tools for analysing and visualizing next generation sequencing microRNA and small RNA datasets. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, M.J. ShortStack: Comprehensive annotation and quantification of small RNA genes. RNA 2013, 19, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.; You, M.; Sun, Z.S.; Shi, Q. mirTools 2.0 for non-coding RNA discovery, profiling, and functional annotation based on high-throughput sequencing. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barturen, G.; Rueda, A.; Hamberg, M.; Alganza, A.; Lebron, R.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Shi, B.-J.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M. sRNAbench: Profiling of small RNAs and its sequence variants in single or multi-species high-throughput experiments. Methods Next Gener. Seq. 2014, 1, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, S.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Dopazo, J.; Ferrer, A.; Conesa, A. Differential expression in RNA-seq: A matter of depth. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, M.; Iovino, N.; Unnerstall, U.; Gaul, U.; Segal, E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, M.; Hackenberg, M.; Langenberger, D.; Frishman, D. TargetSpy: A supervised machine learning approach for microRNA target prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.J. PsRobot: A web-based plant small RNA meta-analysis toolbox. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, E.; He, Y.; Billiau, K.; Peer, Y.V.D. TAPIR, a web server for the prediction of plant microRNA targets, including target mimics. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.E.; Holmes, I.H. Setting up the JBrowse genome browser. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010. Chapter 9, Unit 9.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, A.; Barturen, G.; Lebron, R.; Gomez-Martin, C.; Alganza, A.; Oliver, J.L.; Hackenberg, M. sRNAtoolbox: An integrated collection of small RNA research tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W467–W473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bioinformatics Resources | Year | Web Link | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miRandola | 2012 | http://atlas.dmi.unict.it/mirandola/index.html | [56] |
| miRò | 2009 | http://ferrolab.dmi.unict.it/miro | [133] |
| Evpedia | 2012 | http://evpedia.info | [134] |
| ExoCarta | 2009 | http://www.exocarta.org | [135] |
| FunRich | 2015 | http://www.funrich.org | [136] |
| Vesiclepedia | 2011 | http://www.microvesicles.org | [137] |
| exRNA Research Portal | 2014 | http://exrna.org | [138] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldassarre, A.; Felli, C.; Prantera, G.; Masotti, A. Circulating microRNAs and Bioinformatics Tools to Discover Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Pediatric Diseases. Genes 2017, 8, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090234
Baldassarre A, Felli C, Prantera G, Masotti A. Circulating microRNAs and Bioinformatics Tools to Discover Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Pediatric Diseases. Genes. 2017; 8(9):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090234
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldassarre, Antonella, Cristina Felli, Giorgio Prantera, and Andrea Masotti. 2017. "Circulating microRNAs and Bioinformatics Tools to Discover Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Pediatric Diseases" Genes 8, no. 9: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090234
APA StyleBaldassarre, A., Felli, C., Prantera, G., & Masotti, A. (2017). Circulating microRNAs and Bioinformatics Tools to Discover Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Pediatric Diseases. Genes, 8(9), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090234