Characterization and Expression Profiling of Camellia sinensis Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase Genes in Phenylpropanoid Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. RNA and cDNAPreperation
2.3. Cloning of CsC4Ha, CsC4Hb, and CsC4Hc
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
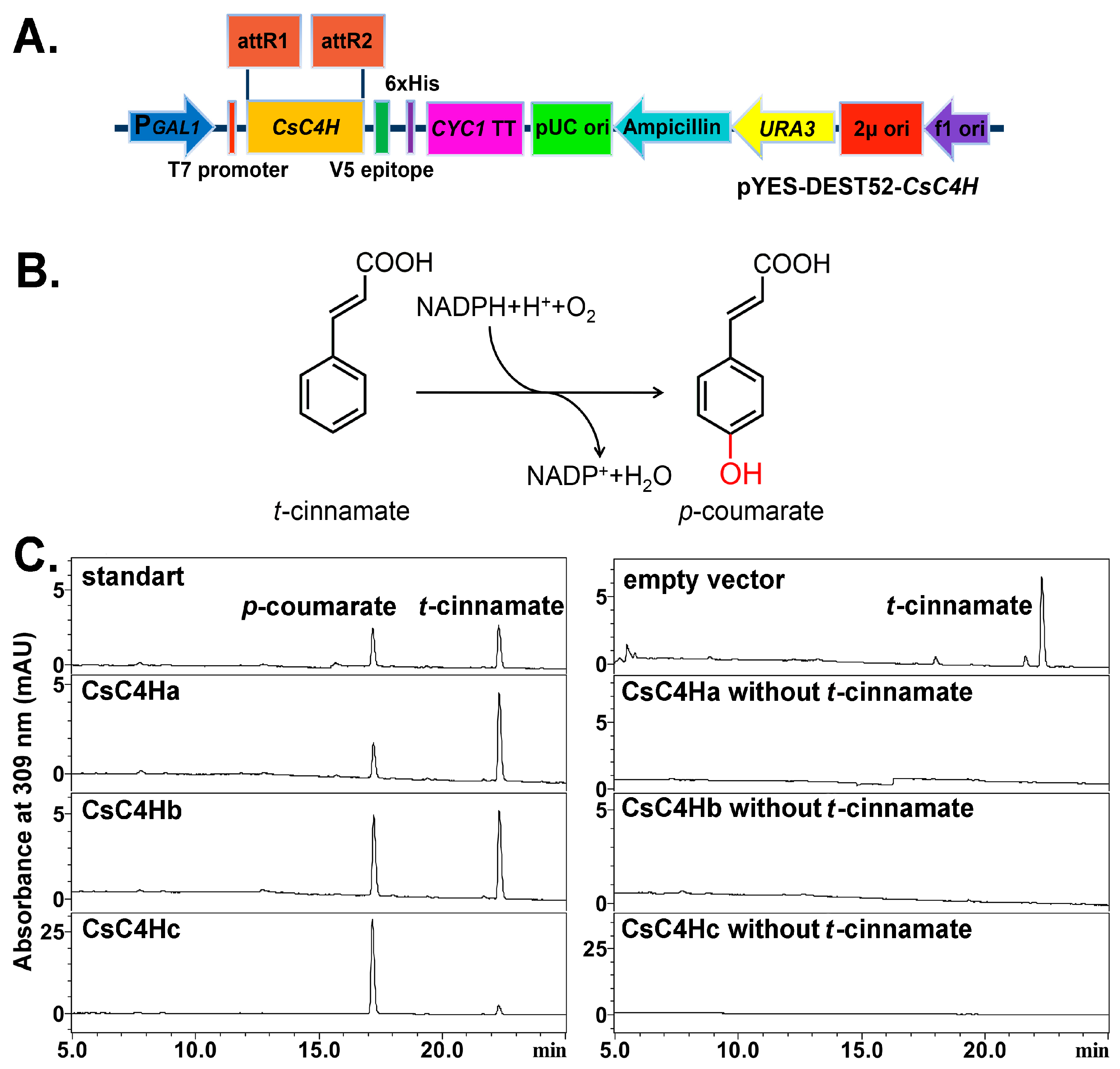
2.5. Heterologous Expression and Enzymatic Activity Analysis of Recombinant CsC4Hs
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
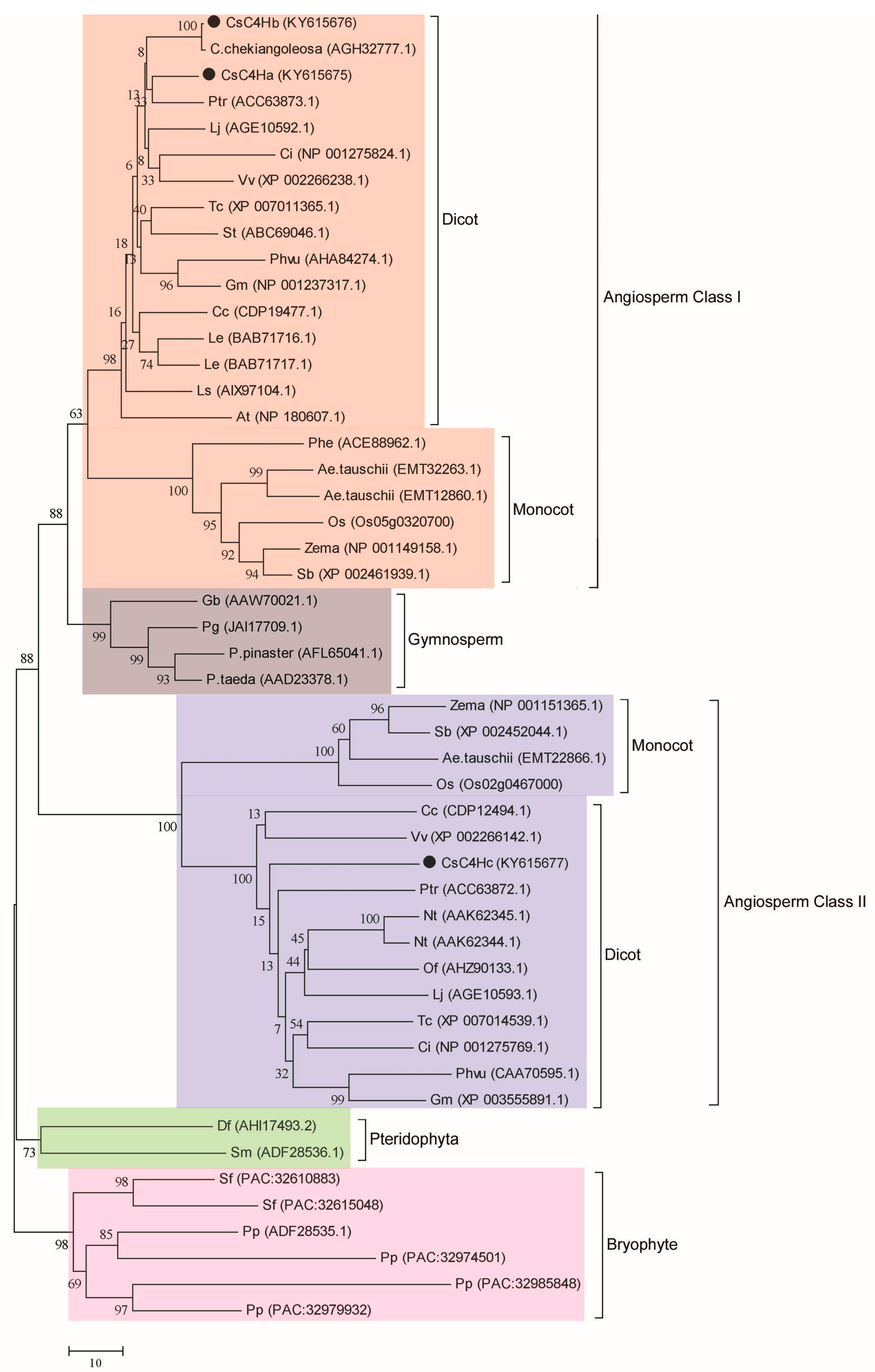
3.1. Screening, Analysis, and Cloning of CsC4H Candidate Genes
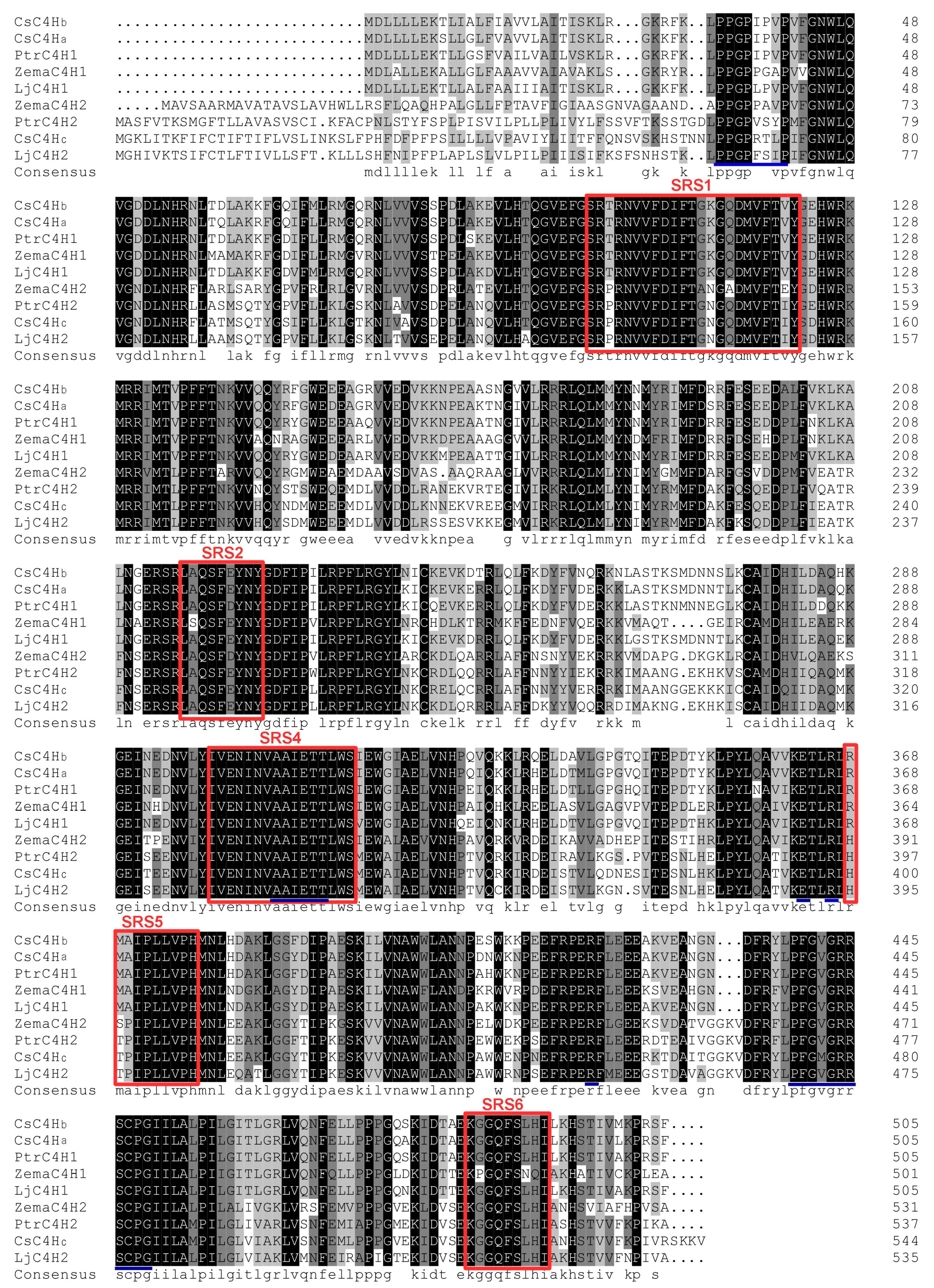
3.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
3.3. Heterologous Expression in Yeast and Enzymatic Analysis of CsC4H Proteins
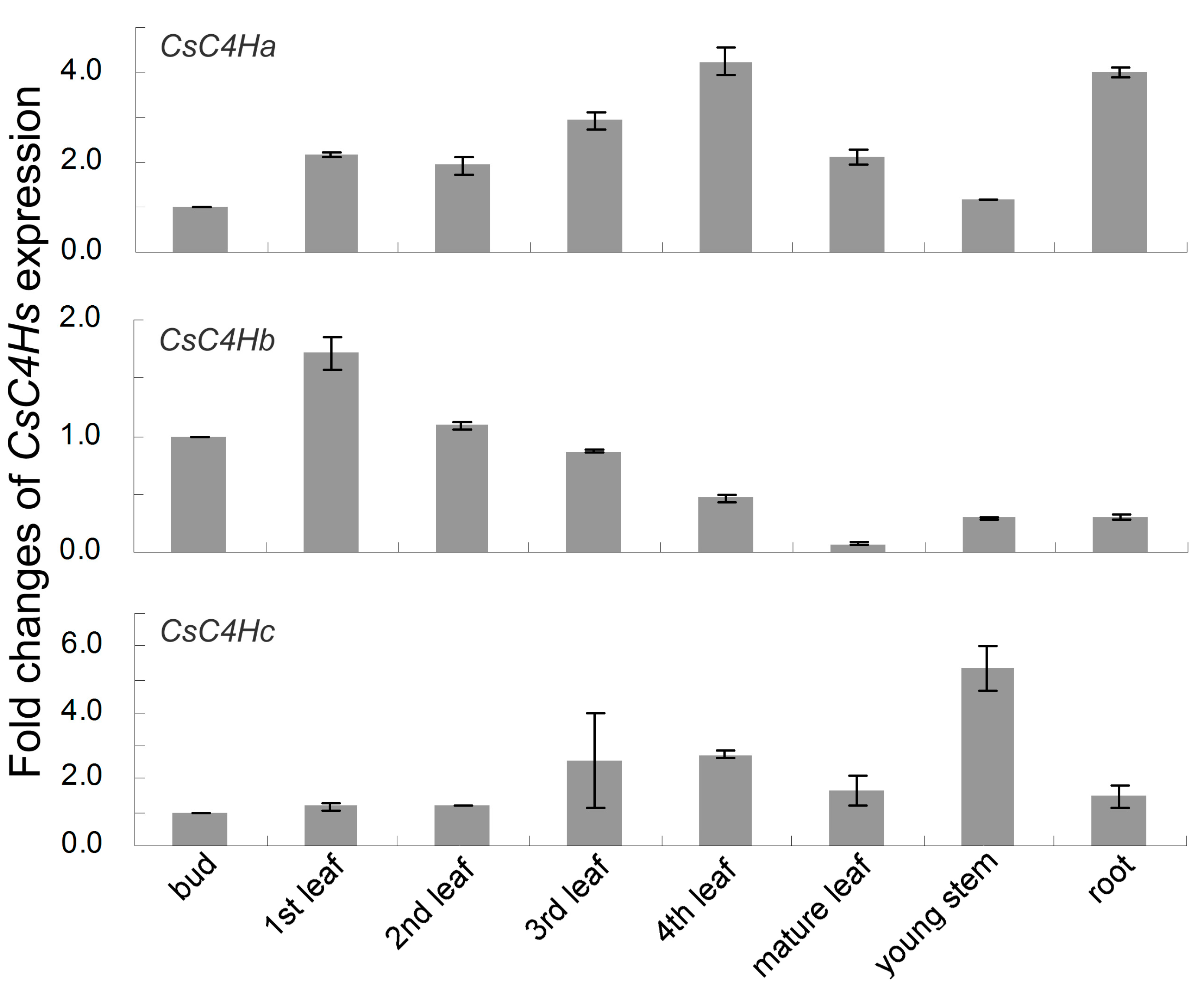
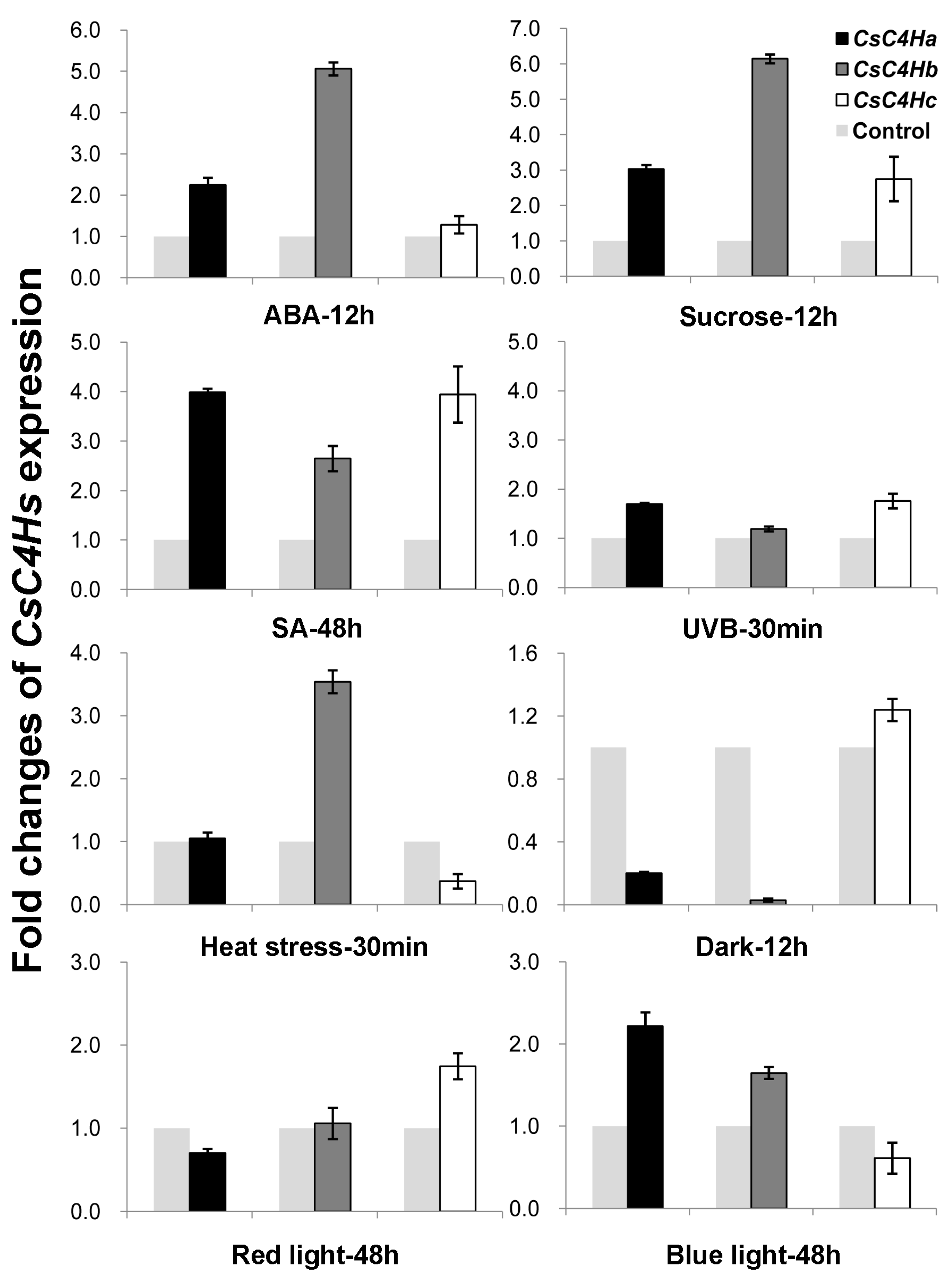
3.4. Real-Time PCR Analysis of C4H Genes Expression in C. sinensis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.F.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, X.C.; Yao, M.Z.; Luo, D.; Li, X.; Chen, L. Global transcriptome and gene regulation network for secondary metabolite biosynthesis of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Yao, S.; Dai, X.; Yin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Gao, L. Identification of UDP-glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of astringent taste compounds in tea (Camellia sinensis). J. Exp. Botany 2016, 67, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. An overview of compounds derived from the shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways and their medicinal importance. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahlbrock, K.; Scheel, D. Physiology and molecular biology of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 40, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Omer, S.; Patel, K.; Khan, B.M. Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) genes from Leucaena leucocephala: A pulp yielding leguminous tree. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlting, J.; Hamberger, B.; Million-Rousseau, R.; Werck-Reichhart, D. Cytochromes P450 in phenolic metabolism. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerjan, W.; Ralph, J.; Baucher, M. Lignin biosynthesis. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 519–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neutelings, G. Lignin variability in plant cell walls: Contribution of new models. Plant Scie. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2011, 181, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havsteen, B.H. The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 67–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochs, G.; Grisebach, H. Phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: Purification and reconstitution of cytochrome P450 3,9-dihydroxypterocarpan 6A-hydroxylase and separation from cytochrome P450 cinnamate 4-hydroxylase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 273, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochs, G.; Werckreichhart, D.; Grisebach, H. Further characterization of cytochrome P450 involved in phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: Cytochrome P450 cinnamate 4-hydroxylase and 3,9-dihydroxypterocarpan 6A-hydroxylase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 293, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achnine, L.; Blancaflor, E.B.; Rasmussen, S.; Dixon, R.A. Colocalization of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase for metabolic channeling in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2004, 16, 3098–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Park, N.I.; Li, X.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.U. Molecular cloning and characterization of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase and genes involved in flavone biosynthesis in Scutellaria baicalensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9715–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcnulty, J.; Nair, J.J.; Singh, M.; Crankshaw, D.J.; Holloway, A.C.; Bastida, J. Selective cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitory activity of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3233–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raes, J.; Rohde, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Van de Peer, Y.; Boerjan, W. Genome-wide characterization of the lignification toolbox in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmann, E.; Logemann, E.; Hahlbrock, K. Regulation and Functional Expression of Cinnamate 4-Hydroxylase from Parsley. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Y. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a cinnamate 4-hydroxylase-encoding gene from Camptotheca acuminata. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.H.; Chai, Y.R.; Li, J.N.; Chen, L. Molecular cloning of two genes encoding cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) from oilseed rape (Brassica napus). J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, C.; Wan, X.; et al. Tissue-Specific, Development-Dependent Phenolic Compounds Accumulation Profile and Gene Expression Pattern in Tea Plant (Camellia Sinensis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Hua, Y.; Wei, C.; Wan, X.; Tao, X. The R2R3-MYB, bHLH, WD40, and related transcription factors in flavonoid biosynthesis. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2013, 13, 75–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; Dicuccio, M.; Edgar, R.; Federhen, S. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 39, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Takaya, A.; Yamamoto, T. Meta-analytic approach to the accurate prediction of secreted virulence effectors in gram-negative bacteria. BMC Bioinf. 2011, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ro, D.K.; Mah, N.; Ellis, B.E.; Douglas, C.J. Functional characterization and subcellular localization of poplar (Populus trichocarpa × Populus deltoides) cinnamate 4-hydroxylase. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Tomiyoshi, R.; Kuroiwa, T.; Mihara, K.; Omura, T. Functions of signal and signal-anchor sequences are determined by the balance between the hydrophobic segment and the N-terminal charge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.A.; Paiva, N.L. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, C.; Artacho, R.; Giménez, R. Beneficial Effects of Green Tea—A Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Tea polyphenols: Prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1698S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Nao-I, N.; Sawada, A.; Hayashida, T. Isolation and analysis of cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase homologous genes from a hybrid aspen, Populus kitakamiensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Song, S.; Cheng, H.; Lin, Z. Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding cinnamate 4-hydroxylase from Parthenocissus henryana. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harakava, R. Genes encoding enzymes of the lignin biosynthesis pathway in Eucalyptus. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 28, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Q.Z.; Heber, S.; Sederoff, R.; Chiang, V.L. Towards a systems approach for lignin biosynthesis in Populus trichocarpa: Transcript abundance and specificity of the monolignol biosynthetic genes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Chiang, V.L. Distinct roles of cinnamate 4-hydroxylase genes in Populus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Cominelli, E.; Bailey, P.; Parr, A.; Mehrtens, F.; Jones, J.; Tonelli, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C. Transcriptional repression by AtMYB4 controls production of UV-protecting sunscreens in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6150–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Hu, B.; Chang, Y. Cloning and expression analysis of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) gene family and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) from Dryopteris fragrans. Biologia 2015, 70, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Duan, Y.; Yi, B.; Sun, L.; Lu, B.; Yu, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Characterization and expression profiling of cinnamate 4-hydroxylase gene from Salvia miltiorrhiza in rosmarinic acid biosynthesis pathway. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 55, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yun, P.Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Lim, Y.P.; Lee, M.C. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of the rice Cinnamate-4-Hydroxylase gene, a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase involved in the general phenylpropanoid pathway. J. Plant Biol. 2005, 48, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, M.; Dehghan, S.; Fischer, R.; Wenzel, U.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kavousi, H.R.; Rahnamaeian, M. Isolation and characterization of isochorismate synthase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase during salinity stress, wounding, and salicylic acid treatment in Carthamus tinctorius. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, 2420–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, C.; Mccollum, T.G.; Mayer, R.T. Differential expression of two cinnamate 4-hydroxylase genes in ‘Valencia’ orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck). Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 46, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonggeun, K.; Bosung, C.; Natarajan, S.; Hanhong, B. Expression analysis of kenaf cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) ortholog during developmental and stress responses. Plant Omics 2013, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bellés, J.M.; Lopéz-Gresa, M.P.; Fayos, J.; Pallás, V.; Rodrigo, I.; Conejero, V. Induction of cinnamate 4-hydroxylase and phenylpropanoids in virus-infected cucumber and melon plants. Plant Sci. 2008, 174, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimchan, P.; Chanthai, S.; Bosland, P.W.; Techawongstien, S. Enzymatic changes in phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, cinnamic-4-hydroxylase, capsaicin synthase, and peroxidase activities in Capsicum under drought stress. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.; Guo, H.; Wan, F.; Cheng, H. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase genes’ response to HHO in Eupatorium adenophorum. Weed Biol. Manag. 2012, 12, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsC4Ha | CsC4Ha- F | 5′-ATGGATCTTCTCCTCCTAGAGAAG-3′ | Cloning |
| CsC4Ha- R | 5′-TCAGAACGATCTTGGTTTCAGAAC-3′ | Cloning | |
| qPCR-F | 5′-GCTCTCTGGCTATGACATCCCT-3′ | qRT-PCR | |
| qPCR-R | 5′-TCCTCCTTCCGACACCAAACG-3′ | qRT-PCR | |
| CsC4Hb | CsC4Hb- F | 5′-ATGGATCTTCTTCTCCTAGAG-3′ | Cloning |
| CsC4Hb- R | 5′-TTAAAATGATCTTGGTTTCATC-3′ | Cloning | |
| qPCR-F | 5′-GCTCGGCAGCTATGACATCC-3′ | qRT-PCR | |
| qPCR-R | 5′-CTCCTCCTACCAACACCGAATG-3′ | qRT-PCR | |
| CsC4Hc | CsC4Hc- F | 5′-ATGGGCAAACTTATTACAAAATTTAT-3′ | Cloning |
| CsC4Hc- R | 5′-TTAAACTTTTTTTGAACGAACAATTG-3′ | Cloning | |
| qPCR-F | 5′-GCGATGAAATCTCAACCGTCC-3′ | qRT-PCR | |
| qPCR-R | 5′-TGACCACAACCTTTGACTCCTTAG-3′ | qRT-PCR |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, M.; Huang, K.; Gao, L.; Xia, T. Characterization and Expression Profiling of Camellia sinensis Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase Genes in Phenylpropanoid Pathways. Genes 2017, 8, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080193
Xia J, Liu Y, Yao S, Li M, Zhu M, Huang K, Gao L, Xia T. Characterization and Expression Profiling of Camellia sinensis Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase Genes in Phenylpropanoid Pathways. Genes. 2017; 8(8):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080193
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Jinxin, Yajun Liu, Shengbo Yao, Ming Li, Mengqing Zhu, Keyi Huang, Liping Gao, and Tao Xia. 2017. "Characterization and Expression Profiling of Camellia sinensis Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase Genes in Phenylpropanoid Pathways" Genes 8, no. 8: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080193
APA StyleXia, J., Liu, Y., Yao, S., Li, M., Zhu, M., Huang, K., Gao, L., & Xia, T. (2017). Characterization and Expression Profiling of Camellia sinensis Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase Genes in Phenylpropanoid Pathways. Genes, 8(8), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080193





