Evolution of Karyotypes in Chameleons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Material
2.2. DNA Barcoding
2.3. Chromosome Preparation and Staining
2.4. Comparative Genomic Hybridization
2.5. Fluorescence In Situ hybridization with Telomeric Probe and rRNA Gene
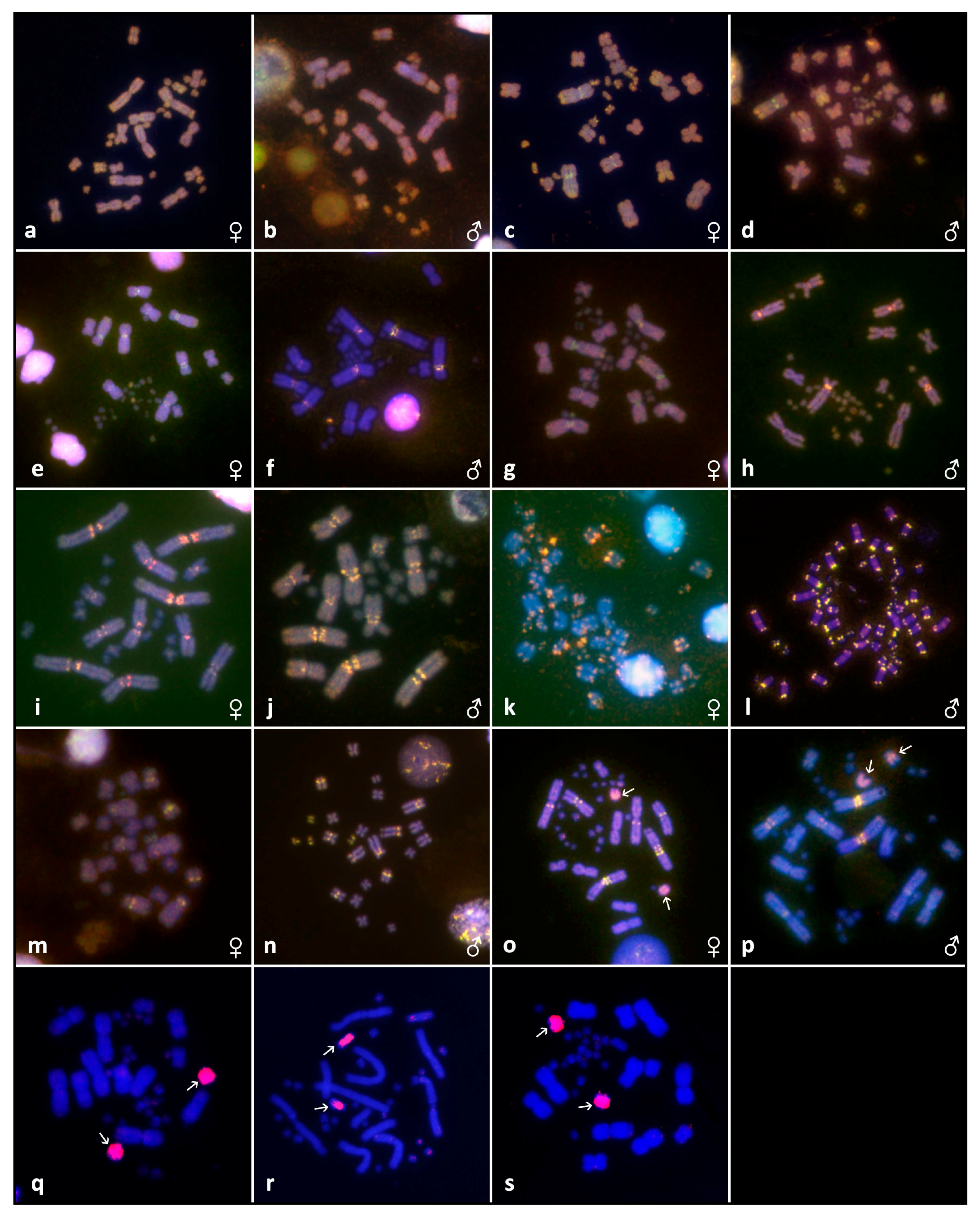
2.6. Microdissection and Chromosome Painting
2.7. Microscopy and Image Analyses
2.8. Phylogenetic Analyses
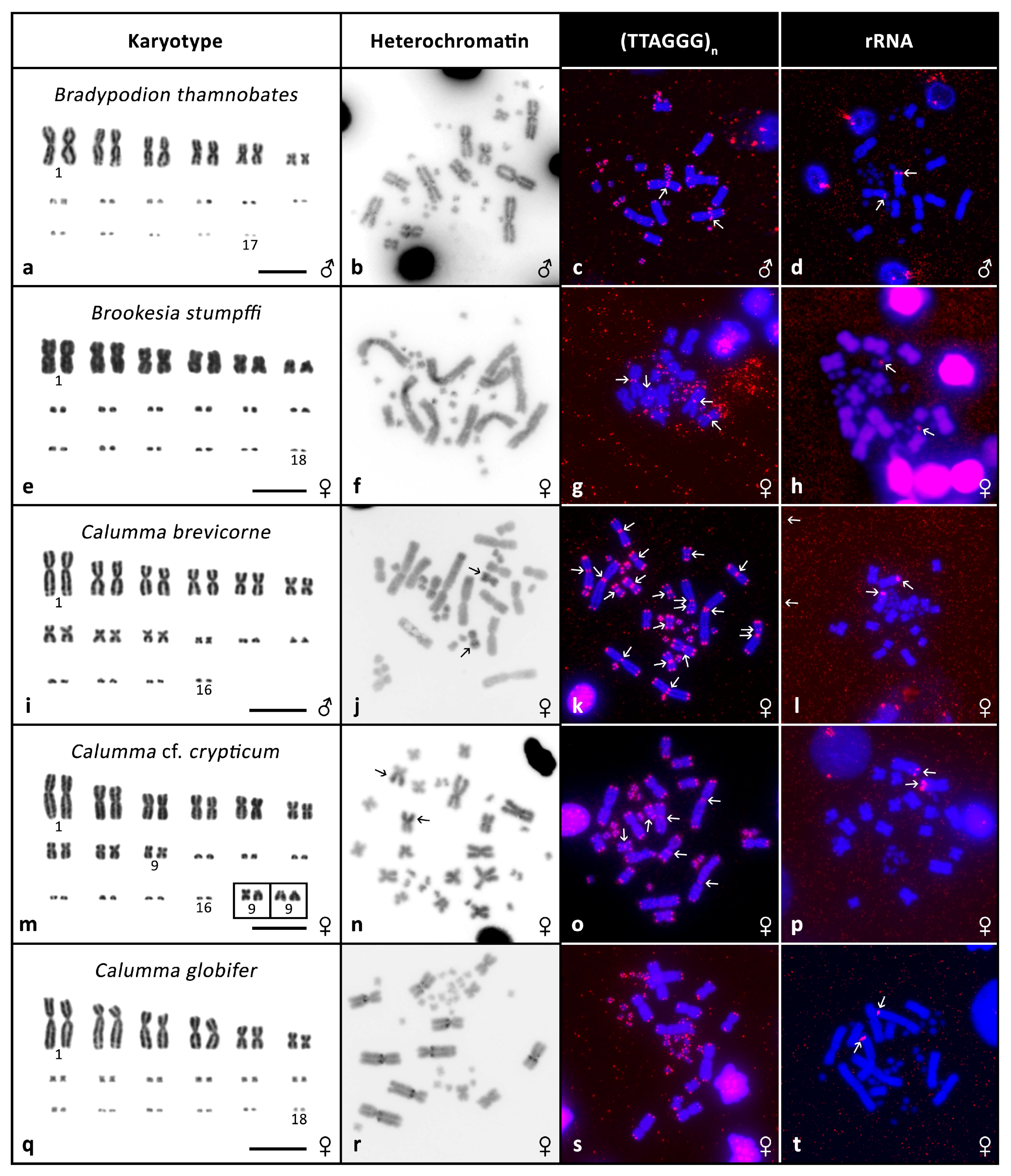
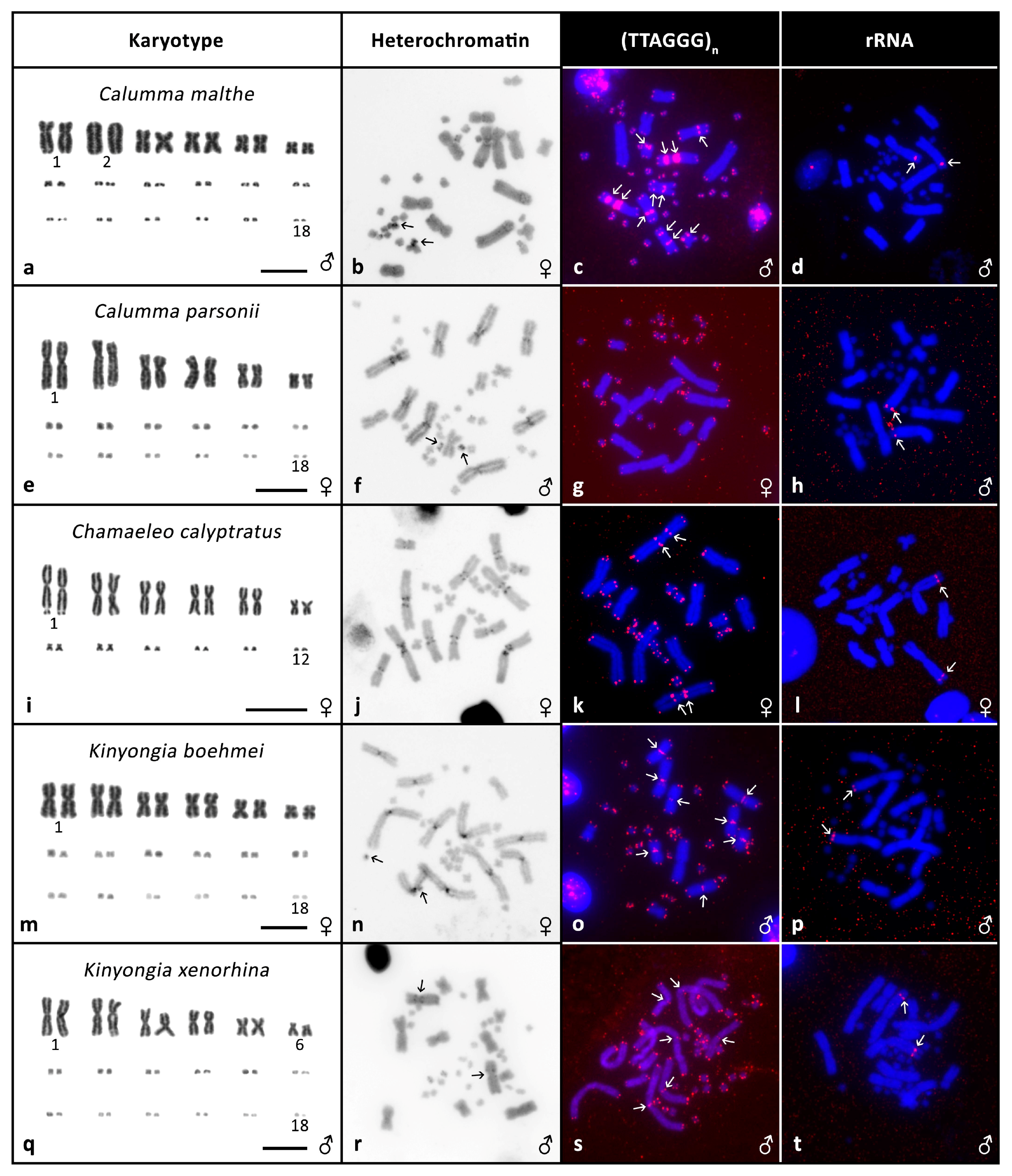
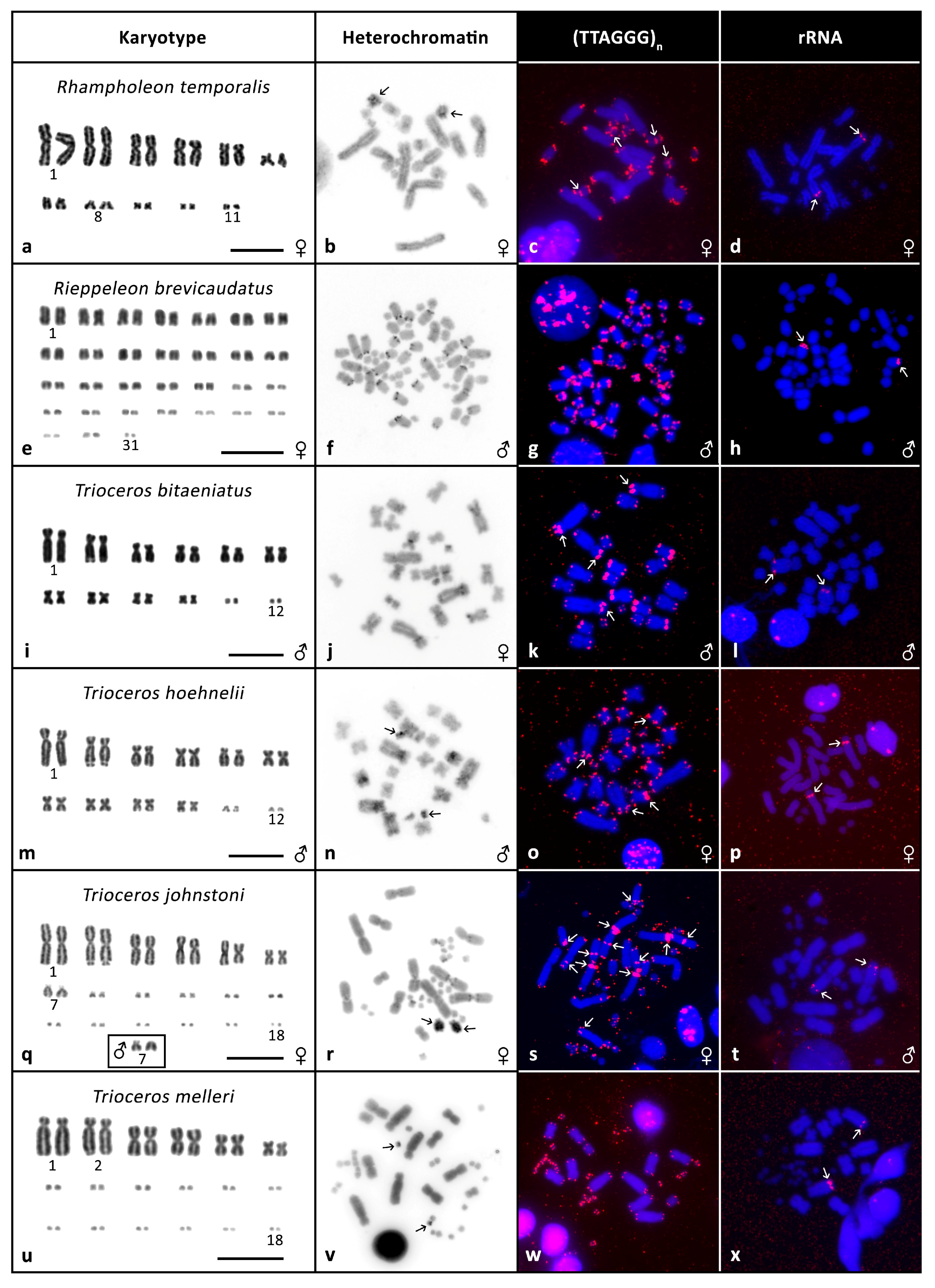
3. Results
3.1. DNA Barcoding
3.2. Cytogenetic Analyses
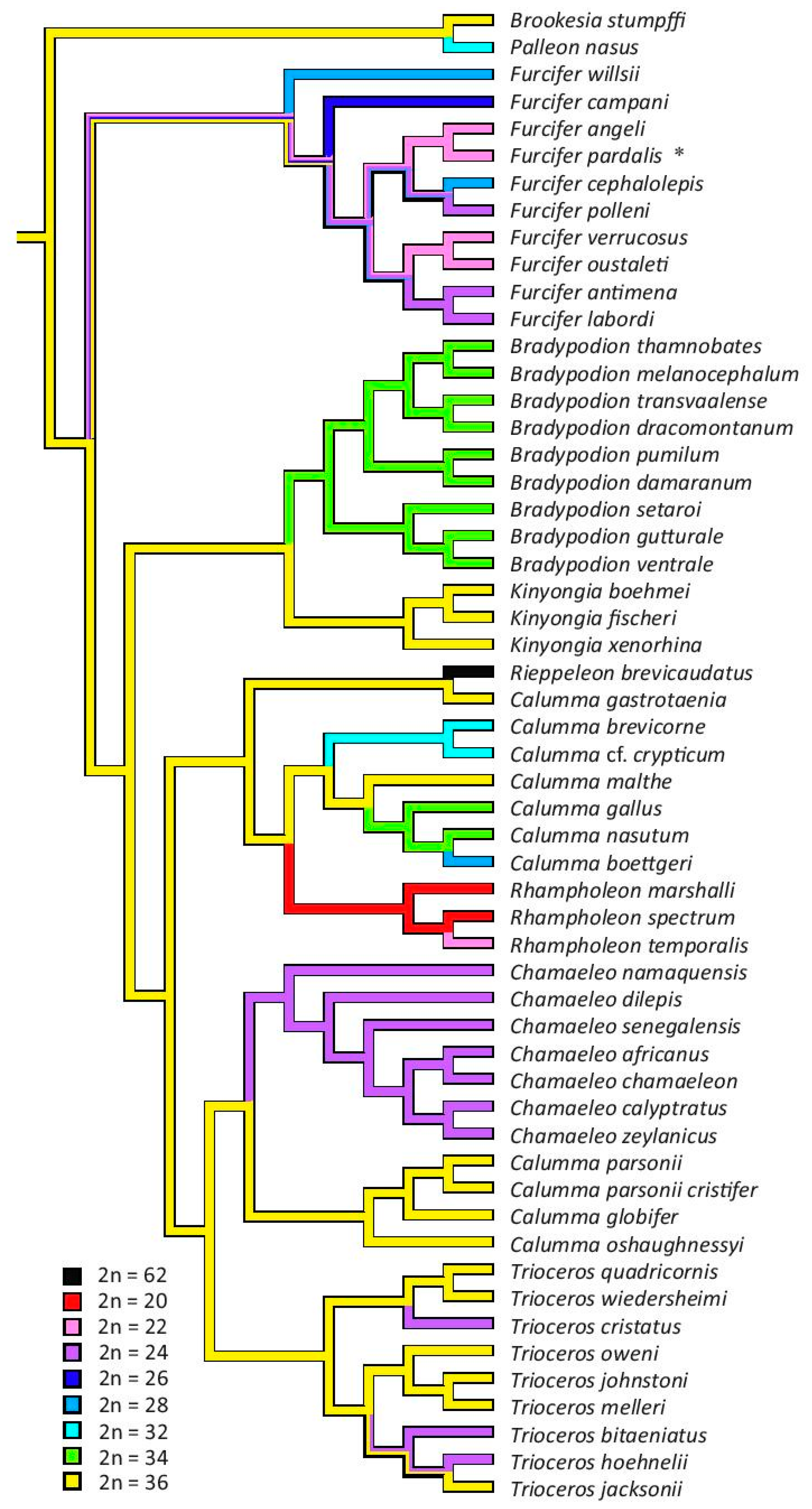
3.3. The Reconstruction of Ancestral Chromosome Number
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tolley, K.A.; Townsend, T.M.; Vences, M. Large-scale phylogeny of chameleons suggests African origins and Eocene diversification. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20130184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetz, P.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. 2017. Available online: http://www.reptile-database.org (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Olmo, E.; Signorino, G.G. Chromorep: A Reptile Chromosomes Database. 2005. Available online: http://chromorep.univpm.it (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Viets, B.E.; Ewert, M.A.; Talent, L.G.; Nelson, C.E. Sex-determining mechanisms in squamate reptiles. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 1994, 270, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, P.S. Temperature-dependent sex determination in lizards. In Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination in Vertebrates; Valenzuela, N., Lance, V., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Scholarly Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.M. Incubation temperature and sex ratio of the veiled chameleon (Chamaeleo calyptratus). J. Herpetol. 2005, 39, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M.; Altmanová, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Female heterogamety in Madagascar chameleons (Squamata: Chamaeleonidae: Furcifer): Differentiation of sex and neo-sex chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorná, M.; Altmanová, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Multiple sex chromosomes in the light of female meiotic drive in amniote vertebrates. Chromosome Res. 2014, 22, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennell, M.W.; Kirkpatrick, M.; Otto, S.P.; Vamosi, J.C.; Peichel, C.L.; Valenzuela, N.; Kitano, J. Y fuse? Sex chromosome fusions in fishes and reptiles. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmanová, M. Evoluce pohlavních chromozomů a karyotypů u leguánů (Squamata: Pleurodonta) [Evolution of Sex Chromosomes and Karyotypes in Iguanas (Squamata: Pleurodonta)]. Ph.D. Thesis, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pokorná, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Phylogeny of sex-determining mechanisms in squamate reptiles: Are sex chromosomes an evolutionary trap? Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 156, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson Pokorná, M.; Kratochvíl, L. What was the ancestral sex-determining mechanism in amniote vertebrates? Biol. Rev. 2016, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovatsos, M.; Altmanová, M.; Pokorná, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Conserved sex chromosomes across adaptively radiated Anolis lizards. Evolution 2014, 68, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovatsos, M.; Pokorná, M.; Altmanová, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Cretaceous park of sex determination: Sex chromosomes are conserved across iguanas. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20131093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovatsos, M.; Vukić, J.; Altmanová, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M.; Moravec, J.; Kratochvíl, L. Conservation of sex chromosomes in lacertid lizards. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3120–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmanová, M.; Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Johnson Pokorná, M. Minute Y chromosomes and karyotype evolution in Madagascan iguanas (Squamata: Iguania: Opluridae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 118, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Molecular sexing applicable in 4000 species of lizards and snakes? From dream to real possibility. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.T.; Sonet, G.; Glaw, F.; Vences, M. First large-scale DNA barcoding assessment of reptiles in the biodiversity hotspot of Madagascar, based on newly designed COI primers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubová, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M.; Rovatsos, M.; Farkačová, K.; Altmanová, M.; Kratochvíl, L. Sex determination in Madagascar geckos of the genus Paroedura (Squamata: Gekkonidae): Are differentiated sex chromosomes indeed so evolutionary stable? Chromosome Res. 2014, 22, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorná, M.; Rens, W.; Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L. A ZZ/ZW sex chromosome system in the thick-tailed gecko (Underwoodisaurus milii; Squamata: Gekkota: Carphodactylidae), a member of the ancient gecko lineage. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 142, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, A.T. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovatsos, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Altmanová, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M. Interstitial telomeric motifs in squamate reptiles: When the exceptions outnumber the rule. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijdo, J.W.; Wells, R.A.; Baldini, A.; Reeders, S.T. Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telenius, H.; Pelmear, A.H.; Tunnacliffe, A.; Carter, N.P.; Behmel, A.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Pfragner, R.; Ponder, B.A. Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosome Cancer 1992, 4, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, J.A.; Acosta, M.J.; Nietzel, H.; Sperling, K.; Bullejos, M.; Díaz de la Guardia, R.; Sánchez, A. X chromosome painting in Microtus: Origin and evolution of the giant sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2004, 12, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.2. Available online: http://mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Pyron, R.A.; Burbrink, F.T.; Wiens, J.J. A phylogeny and revised classification of Squamata, including 4161 species of lizards and snakes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthey, R.; Van Brink, J. Nouvelle contribution à la cytologie comparée des Chamaeleontidae (Reptilia-Lacertilia). Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1960, 67, 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgat, R.M. Caryotypes des caméléons malgaches et systématique. Synthèse des données acquises. Ann. Univ. Madagascar (Sci.) 1972, 9, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Klaver, C.; Böhme, W. Phylogeny and classification of the Chamaeleonidae (Sauria) with special reference to hemipenis morphology. Bonn. Zool. Monogr. 1986, 22, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D.H. 1989 Unpublished Data Ex. Olmo, E.; Signorino, G. Chromorep: A Reptile Chromosomes Database. 2005. Available online: http://chromorep.univpm.it (accessed on 26 August 2017).
- Matthey, R. Cytologie comparée et taxonomie des Chamaeleontidae (Reptilia-Lacertilia). Rev. Suisse Zool. 1957, 64, 709–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgat, R.M. Cytogénétique des caméléons de Madagascar. Incidences taxonomiques, biogéographiques et phylogénétiques. Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 1973, 98, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pokorná, M.; Giovannotti, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Kasai, F.; Trifonov, V.A.; O’Brien, P.C.M.; Caputo, V.; Olmo, E.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Rens, W. Strong conservation of the bird Z chromosome in reptilian genomes is revealed by comparative painting despite 275 million years divergence. Chromosoma 2011, 120, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthey, R.; Van Brink, J. Note préliminaire sur la cytologie chromosomique comparée des Caméléons. Rev. Suisse Zool. 1956, 60, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, W.H.O. Description of the orcien stained karyotypes of 27 lizard species (Lacertilia: Reptilia) belonging to the families Iguanidae, Agamidae Chameleontidae and Gekkonidae (Ascalabota). Acta Zool. Pathol. Antverp. 1981, 76, 35–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gorman, G. The chromosomes of the Reptilia, a cytotaxonomic interpretation. In Cytotaxonomy and Vertebrate Evolution; Chiarelli, A.B., Capanna, E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Srikulnath, K.; Uno, Y.; Nishida, C.; Matsuda, Y. Karyotype evolution in monitor lizards: cross-species chromosome mapping of cDNA reveals highly conserved synteny and gene order in the Toxicofera clade. Chromosome Res. 2013, 21, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, K.C.M.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Yonenaga-Yassuda, Y. Chromosomal polymorphisms due to supernumerary chromosomes and pericentric inversions in the eyelidless microteiid lizard Nothobachia ablephara (Squamata, Gymnophthalmidae). Chromosome Res. 1999, 7, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorná, M.; Giovannotti, M.; Kratochvíl, L.; Caputo, V.; Olmo, E.; Ferguson-Smith, M.A.; Rens, W. Conservation of chromosomes syntenic with avian autosomes in squamate reptiles revealed by comparative chromosome painting. Chromosoma 2012, 121, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.; Sahara, K.; Yoshido, A.; Marec, F. Evolutionary dynamics of rDNA clusters on chromosomes of moths and butterflies (Lepidoptera). Genetica 2010, 138, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rovatsos, M.; Altmanová, M.; Johnson Pokorná, M.; Velenský, P.; Sánchez Baca, A.; Kratochvíl, L. Evolution of Karyotypes in Chameleons. Genes 2017, 8, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120382
Rovatsos M, Altmanová M, Johnson Pokorná M, Velenský P, Sánchez Baca A, Kratochvíl L. Evolution of Karyotypes in Chameleons. Genes. 2017; 8(12):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120382
Chicago/Turabian StyleRovatsos, Michail, Marie Altmanová, Martina Johnson Pokorná, Petr Velenský, Antonio Sánchez Baca, and Lukáš Kratochvíl. 2017. "Evolution of Karyotypes in Chameleons" Genes 8, no. 12: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120382
APA StyleRovatsos, M., Altmanová, M., Johnson Pokorná, M., Velenský, P., Sánchez Baca, A., & Kratochvíl, L. (2017). Evolution of Karyotypes in Chameleons. Genes, 8(12), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120382








