The Genome of the Northern Sea Otter (Enhydra lutris kenyoni)
Abstract
1. Introduction
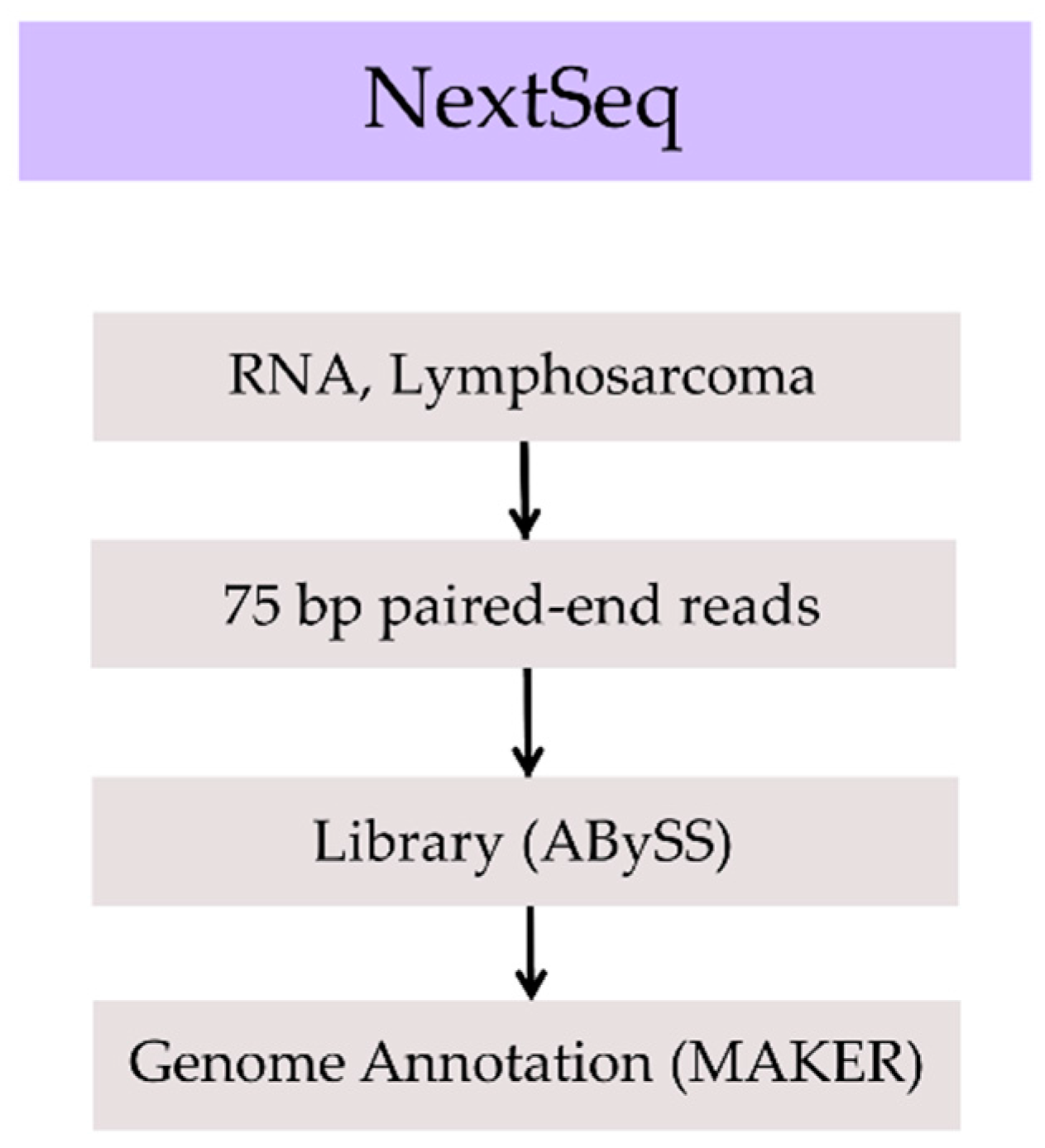
2. Methods, Results, and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeates, L.C.; Williams, T.M.; Fink, T.L. Diving and foraging energetics of the smallest marine mammal, the sea otter (Enhydra lutris). J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, J.A.; Palmisano, J.F. Sea otters: Their role in structuring nearshore communities. Science 1974, 185, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, J.A.; Duggins, D.O. Sea otters and kelp forests in Alaska: Generality and variation in a community ecological paradigm. Ecol. Monogr. 1995, 65, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, L.; Miles, A.K.; Murray, M.; Haulena, M.; Tuttle, J.; Van Bonn, W.; Adams, L.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.; Estes, J.; et al. Gene transcription in sea otters (Enhydra lutris); development of a diagnostic tool for sea otter and ecosystem health. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuder, C.; Miller, M.A.; Jessup, D.A.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Harris, M.D.; Ames, J.A.; Carpenter, T.E.; Conrad, P.A.; Mazet, J.A. Patterns of mortality in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) from 1998–2001. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; Thomas, N.J.; Dubielzig, R.R.; Drees, R. Osteosarcoma of the maxilla with concurrent osteoma in a southern sea otter (Enhydra lutris nereis). J. Comp. Pathol. 2012, 147, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Conrad, P.A.; Harris, M.; Hatfield, B.; Langlois, G.; Jessup, D.A.; Magargal, S.L.; Packham, A.E.; Toy-Choutka, S.; Melli, A.C.; et al. A protozoal-associated epizootic impacting marine wildlife: Mass-mortality of southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) due to sarcocystis neurona infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, M.S.; Milonas, L.; Bowlby, C.E.; Jameson, R.; Davis, J.W. Chemical Contaminants, Pathogen Exposure and General Health Status of Live and Beach-Cast Washington Sea Otters (Enhydra lutris kenyoni); NOAA/National Ocean Service/Office of National Marine Sanctuaries: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009.
- Conrad, P.A.; Miller, M.A.; Kreuder, C.; James, E.R.; Mazet, J.; Dabritz, H.; Jessup, D.A.; Gulland, F.; Grigg, M.E. Transmission of Toxoplasma: Clues from the study of sea otters as sentinels of Toxoplasma gondii flow into the marine environment. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissy, A.S.; Garzia, L.; Shih, D.J.; Zuyderduyn, S.; Huang, X.; Skowron, P.; Remke, M.; Cavalli, F.M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Lindsay, P.E.; et al. Divergent clonal selection dominates medulloblastoma at recurrence. Nature 2016, 529, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandervalk, B.P.; Yang, C.; Xue, Z.; Raghavan, K.; Chu, J.; Mohamadi, H.; Jackman, S.D.; Chiu, R.; Warren, R.L.; Birol, I. Konnector v2.0: Pseudo-long reads from paired-end sequencing data. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8 (Suppl. 3), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.A.; Warren, R.L.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Kucuk, E.; Khan, H.; Gibb, E.A.; Pandoh, P.; Kirk, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jones, M.; et al. The North American bullfrog draft genome provides insight into hormonal regulation of long noncoding RNA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.L. Rails and cobbler: Scaffolding and automated finishing of draft genomes using long DNA sequences. J. Open Source Softw. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.L.; Chen, Y.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Behsaz, B.; Lagman, A.; Jones, S.J.M.; Birol, I. Links: Scalable, alignment-free scaffolding of draft genomes with long reads. GigaScience 2015, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.; Coombe, L.; Chu, J.; Warren, R.L.; Birol, I. Arcs: Scaffolding genome drafts with linked reads. Bioinformatics 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, D.; Warren, R.L.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Raymond, A.; Jackman, S.D.; Birol, I. Sealer: A scalable gap-closing application for finishing draft genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.; Bradnam, K.; Korf, I. CEGMA: A pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.S.; Holt, C.; Moore, B.; Yandell, M. Genome annotation and curation using MAKER and MAKER-P. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 48, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- RepeatMasker, Open-4.0. Smit, A.F.A., Hubley, R., Green, P., Eds.; Institute for Systems Biolog: Seattle, WA, USA, 2013–2015. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 12 September 2017).
- Stanke, M.; Tzvetkova, A.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS at EGASP: Using EST, protein and genomic alignments for improved gene prediction in the human genome. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukashin, A.V.; Borodovsky, M. Genemark.Hmm: New solutions for gene finding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Alfoldi, J.; Gori, K.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Tyler, S.R.; Tisoncik-Go, J.; Brawand, D.; Law, G.L.; Skunca, N.; Hatta, M.; et al. The draft genome sequence of the ferret (Mustela putorius furo) facilitates study of human respiratory disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.L.; Keeling, C.I.; Yuen, M.M.; Raymond, A.; Taylor, G.A.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Mohamadi, H.; Paulino, D.; Chiu, R.; Jackman, S.D.; et al. Improved white spruce (Picea glauca) genome assemblies and annotation of large gene families of conifer terpenoid and phenolic defense metabolism. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 83, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
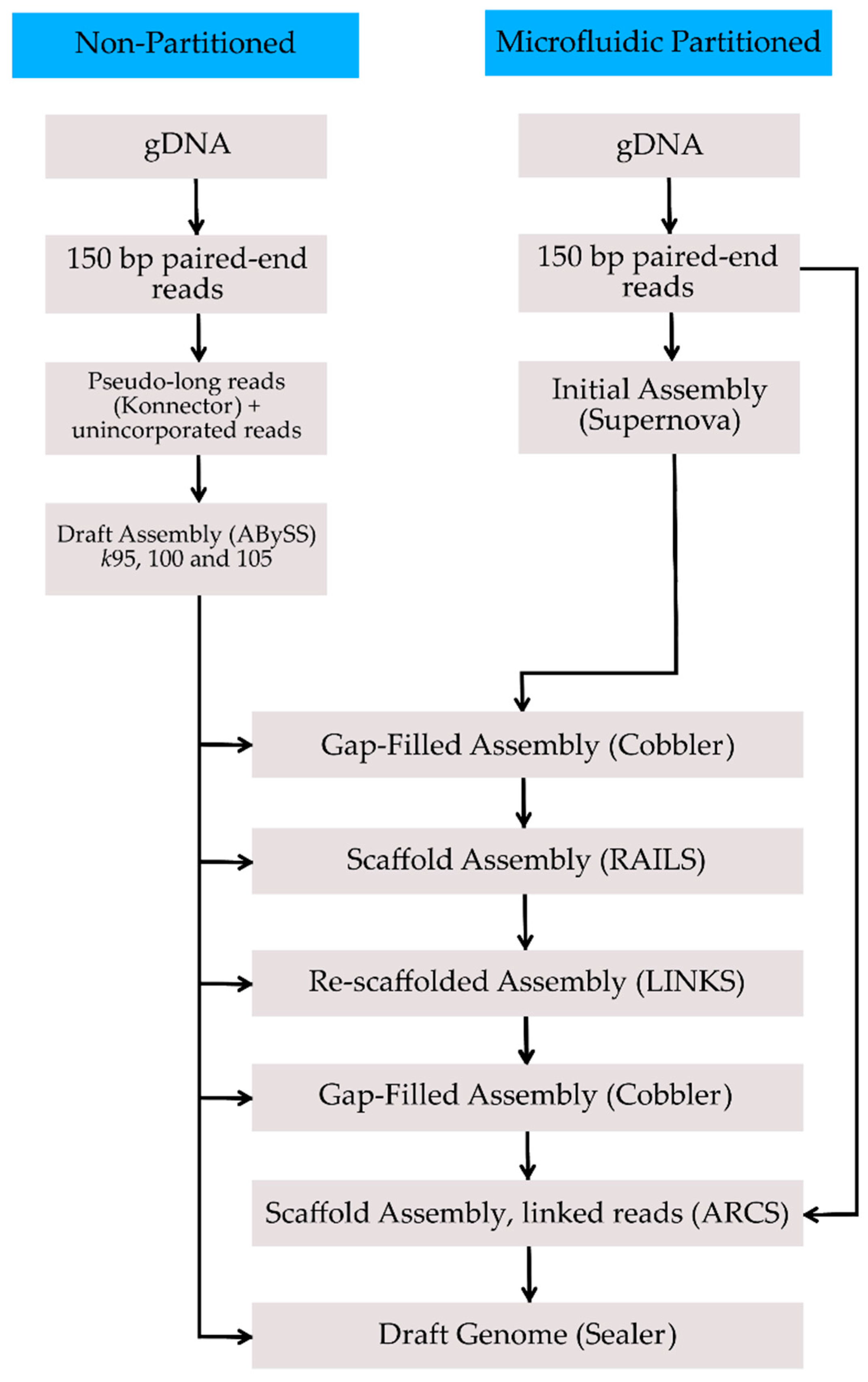
| Assembly | Total Size (Gbp) | No. of Gaps | No. of Scaffolds | Scaffold N50 (Mbp) | Longest Scaffold (Mbp) | BUSCO Complete Genes | BUSCO Complete + Fragmented Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABySS-pe | 2.555 + 0.132% in gaps | 121,917 | 70,247 | 0.115 | 2.301 | 5534 (88.50%) | 5931 (94.85%) |
| Supernova | 2.394 + 1.27% in gaps | 26,442 | 10,285 | 21.34 | 97.14 | 5785 (92.52%) | 6047 (96.71%) |
| Rails/Cobbler | 2.426 + 1.23% in gaps | 23,659 | 6770 | 38.45 | 107.2 | 5806 (92.85%) | 6051 (96.77%) |
| Sealer | 2.426 + 1.22% in gaps | 22,813 | 6770 | 38.45 | 107.2 | 5806 (92.85%) | 6051 (96.77%) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, S.J.; Haulena, M.; Taylor, G.A.; Chan, S.; Bilobram, S.; Warren, R.L.; Hammond, S.A.; Mungall, K.L.; Choo, C.; Kirk, H.; et al. The Genome of the Northern Sea Otter (Enhydra lutris kenyoni). Genes 2017, 8, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120379
Jones SJ, Haulena M, Taylor GA, Chan S, Bilobram S, Warren RL, Hammond SA, Mungall KL, Choo C, Kirk H, et al. The Genome of the Northern Sea Otter (Enhydra lutris kenyoni). Genes. 2017; 8(12):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120379
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Samantha J., Martin Haulena, Gregory A. Taylor, Simon Chan, Steven Bilobram, René L. Warren, S. Austin Hammond, Karen L. Mungall, Caleb Choo, Heather Kirk, and et al. 2017. "The Genome of the Northern Sea Otter (Enhydra lutris kenyoni)" Genes 8, no. 12: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120379
APA StyleJones, S. J., Haulena, M., Taylor, G. A., Chan, S., Bilobram, S., Warren, R. L., Hammond, S. A., Mungall, K. L., Choo, C., Kirk, H., Pandoh, P., Ally, A., Dhalla, N., Tam, A. K. Y., Troussard, A., Paulino, D., Coope, R. J. N., Mungall, A. J., Moore, R., ... Jones, S. J. M. (2017). The Genome of the Northern Sea Otter (Enhydra lutris kenyoni). Genes, 8(12), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8120379





