Current and Future Prospects for Epigenetic Biomarkers of Substance Use Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
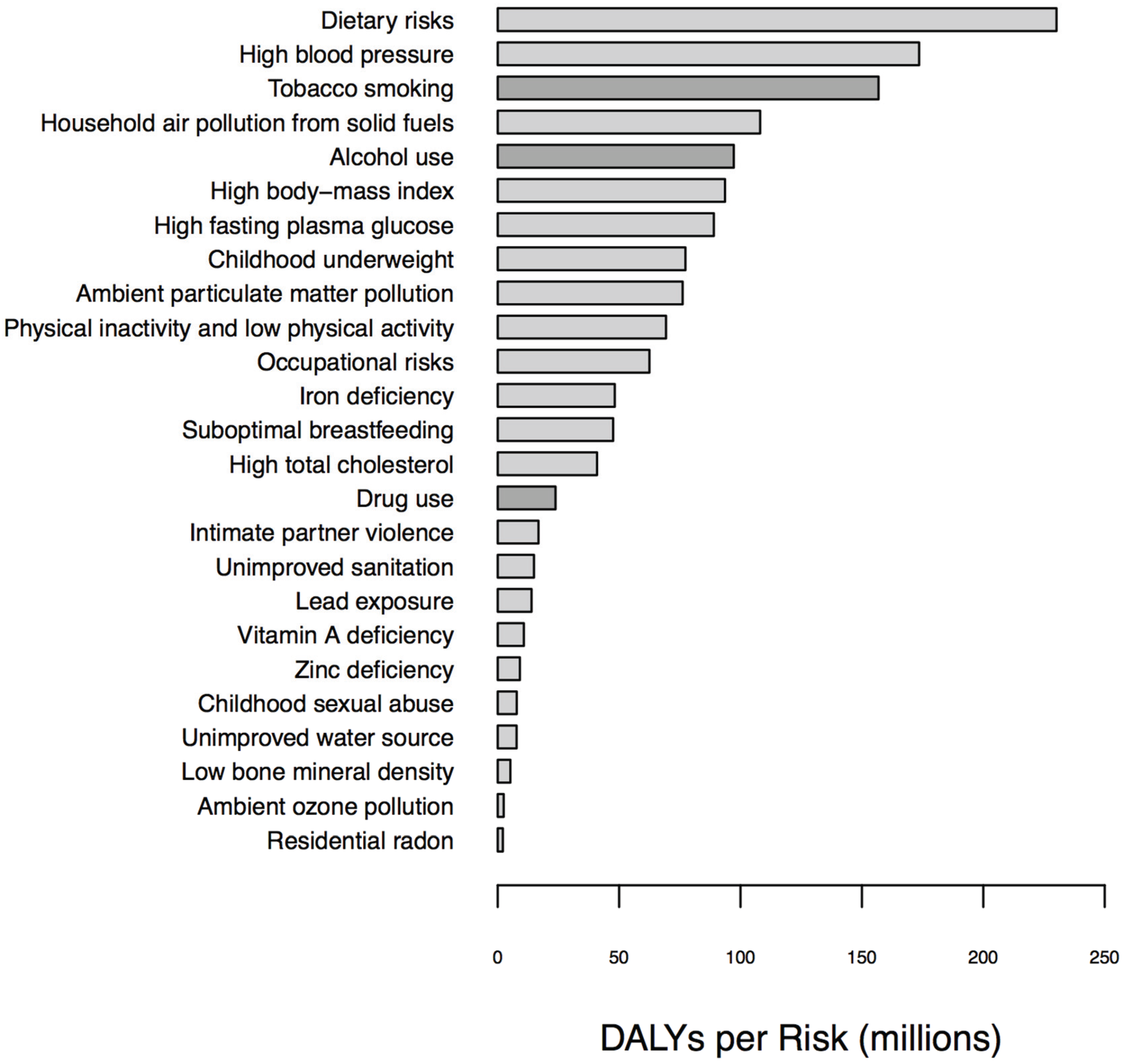
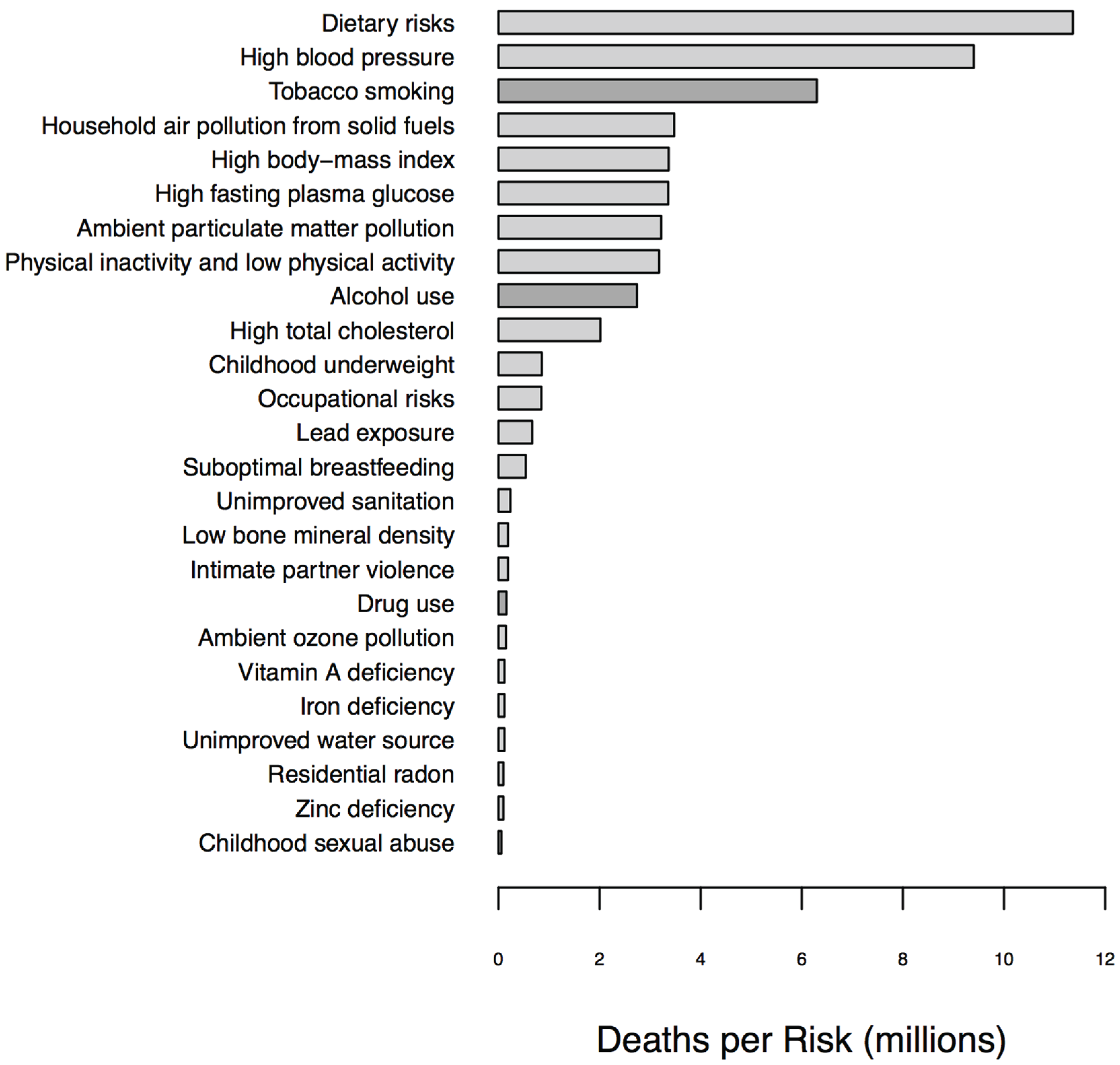
1.1. Biomarkers
| Drug | Detection Time (Urine) | False Positives |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | ||
| - Ethanol | Less than 12 h | No |
| - Ethyl glucuronide (metabolite) | 5 days | No |
| Amphetamine/Methamphetamine | 2–3 days | Amantadine, bupropion, chlorpromazine, desipramine, fluoxetine, labetalol, methylphenidate, phentermine, phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, promethazine, pseudoephedrine, ranitidine, thioridazine, trazodone |
| Cocaine | Topical anesthetics containing cocaine | |
| - Occasional use | 2–3 days | |
| - Heavy use | Up to 8 days | |
| Cannabis | Dronabinol, ibuprofen, naproxen, sulindac, proton pump inhibitors | |
| - Single use | 3 days | |
| - Less than daily | Up to 1 week | |
| - Daily | 1 to 2 weeks | |
| - Daily, heavy use | >30 days | |
| Opioids | Dextromethorphan, diphenhydramine, fluoroquinolones, poppy seeds, quinine, rifampin, verapamil (methadone assays only) | |
| - Codeine | 2 days | |
| - Heroin (morphine) | 2 days | |
| - Hydromorphone | 2–4 days | |
| - Methadone | 3 days | |
| - Morphine | 2–3 days | |
| - Oxycodone | 2–4 days | |
| Tobacco | Up to 1 week | Nicotine replacement therapy, nicotine vaporizers |
1.2. Epigenetic Biomarkers
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Smoking
3.2. F2RL3/cg03636183
3.3. AHRR/cg05575921
3.4. Other Regions
| AHRR/cg05575921 | 15 studies |
| F2RL3/cg03636183 | 13 studies |
| 2q37.1 | 10 studies |
| CNTNAP2 | 10 studies |
| GFI1 | 10 studies |
| MYO1G | 9 studies |
| GPR15 | 9 studies |
| 6p21.33 | 8 studies |
| GNG12 | 7 studies |
3.5. Alcohol
3.6. Cannabis
3.7. Opioids
3.8. Psychostimulants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). GBD Compare. Available online: http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare (accessed on 17 June 2015).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vital signs: Current cigarette smoking among adults aged 18 ≥ years—United States, 2005–2010. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Rep. 2011, 60, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchery, E.E.; Harwood, H.J.; Sacks, J.J.; Simon, C.J.; Brewer, R.D. Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the US, 2006. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Results from the 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Staines, G.L.; Magura, S.; Foote, J.; Deluca, A.; Kosanke, N. Polysubstance use among alcoholics. J. Addict. Dis. 2001, 20, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, A.; Ferrence, R.; Einarson, T.; Selby, P.; Soldin, O.; Koren, G. Methods for quantification of exposure to cigarette smoking and environmental tobacco smoke: Focus on developmental toxicology. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatlow, P.; Toll, B.A.; Leary, V.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; O’Malley, S.S. Comparison of expired carbon monoxide and plasma cotinine as markers of cigarette abstinence. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2008, 98, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, A.; Skold, C.M.; Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A.; Wheelock, A.M. Assessing recent smoking status by measuring exhaled carbon monoxide levels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, H.R.; Hull, M.; Okasinski, L.M. Review of current clinical biomarkers for the detection of alcohol dependence. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Standridge, J.B.; Adams, S.M.; Zotos, A.P. Urine drug screening: A valuable office procedure. Am. Fam. Phys. 2010, 81, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Moeller, K.E.; Lee, K.C.; Kissack, J.C. Urine drug screening: Practical guide for clinicians. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikeska, T.; Craig, J.M. DNA methylation biomarkers: Cancer and beyond. Genes 2014, 5, 821–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissick, W.L. Medicine’s Dilemmas: Infinite Needs versus Finite Resources; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Committee, I.E. International expert committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guintivano, J.; Brown, T.; Newcomer, A.; Jones, M.; Cox, O.; Maher, B.; Eaton, W.; Payne, J.L.; Wilcox, A.J.; Kaminsky, Z.A. Identification and replication of a combined epigenetic and genetic biomarker predicting suicide and suicidal behaviors. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, D.E.; Amick, H.R.; Feltner, C.; Wines, R.; Shanahan, E.; Rowe, C.J.; Garbutt, J.C. Genetic polymorphisms and response to medications for alcohol use disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 1687–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. The role of biomarkers in the treatment of alcohol use disorders. Subst. Abuse Treat. Advis. 2006, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd-Acosta, C. Epigenetic signatures as biomarkers of exposure. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Utrankar, A.; Reyes, J.A.; Simons, D.D.; Kosten, T.R. Epigenetics of drug abuse: Predisposition or response. Pharmacogenomics 2012, 13, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassoler, F.M.; White, S.L.; Schmidt, H.D.; Sadri-Vakili, G.; Pierce, R.C. Epigenetic inheritance of a cocaine-resistance phenotype. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Landthaler, M.; Schlussman, S.D.; Yuferov, V.; Ho, A.; Tuschl, T.; Kreek, M.J. Mu opioid receptor knockdown in the substantia nigra/ventral tegmental area by synthetic small interfering RNA blocks the rewarding and locomotor effects of heroin. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasek, A.W.; Janak, P.H.; He, L.; Whistler, J.L.; Heberlein, U. Downregulation of mu opioid receptor by RNA interference in the ventral tegmental area reduces ethanol consumption in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuferov, V.; Nielsen, D.A.; Levran, O.; Randesi, M.; Hamon, S.; Ho, A.; Morgello, S.; Kreek, M.J. Tissue-specific DNA methylation of the human prodynorphin gene in post-mortem brain tissues and PBMCs. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.V.; Turner, S.T.; Smith, J.A.; Hammond, P.I.; Lazarus, A.; van de Rostyne, J.L.; Cunningham, J.M.; Kardia, S.L. Comparison of the DNA methylation profiles of human peripheral blood cells and transformed B-lymphocytes. Hum. Genet. 2010, 127, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseman, E.A.; Accomando, W.P.; Koestler, D.C.; Christensen, B.C.; Marsit, C.J.; Nelson, H.H.; Wiencke, J.K.; Kelsey, K.T. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinform. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, M.V.; Shields, B.; Cutrona, C.; Gao, L.; Gibbons, F.X.; Simons, R.; Monick, M.; Brody, G.; Tan, K.; Philibert, R. The effect of smoking on DNA methylation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from African American women. BMC Genom. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, H.; Tillin, T.; McArdle, W.; Ho, K.; Duggirala, A.; Frayling, T.; Davey Smith, G.; Hughes, A.; Chaturvedi, N.; Relton, C. Differences in smoking associated DNA methylation patterns in South Asians and Europeans. Clin. Epigenetics 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allione, A.; Marcon, F.; Fiorito, G.; Guarrera, S.; Siniscalchi, E.; Zijno, A.; Crebelli, R.; Matullo, G. Novel epigenetic changes unveiled by monozygotic twins discordant for smoking habits. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artis, D.; Spits, H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2015, 517, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.F.; Cardarelli, R.; Carroll, J.; Fulda, K.G.; Kaur, M.; Gonzalez, K.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Santella, R.M.; Morabia, A. Significant differences in global genomic DNA methylation by gender and race/ethnicity in peripheral blood. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhout, R.; Schulz, T.; Florek, E.; van Benthem, J.; Wester, P.; Opperhuizen, A. Hazardous compounds in tobacco smoke. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotkin, T.A. Nicotine and the adolescent brain: Insights from an animal model. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2002, 24, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Chaparro, C. Human monoamine oxidase is inhibited by tobacco smoke: Beta-carboline alkaloids act as potent and reversible inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.A.; Beach, S.R.; Gunter, T.D.; Brody, G.H.; Madan, A.; Gerrard, M. The effect of smoking on MAOA promoter methylation in DNA prepared from lymphoblasts and whole blood. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010, 153B, 619–628. [Google Scholar]
- Philibert, R.A.; Gunter, T.D.; Beach, S.R.; Brody, G.H.; Madan, A. MAOA methylation is associated with nicotine and alcohol dependence in women. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147B, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Launay, J.M.; del Pino, M.; Chironi, G.; Callebert, J.; Peoc’h, K.; Megnien, J.L.; Mallet, J.; Simon, A.; Rendu, F. Smoking induces long-lasting effects through a monoamine-oxidase epigenetic regulation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, J.Z.; Payne, T.J.; Li, M.D. Determination of methylated CpG sites in the promoter region of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and their involvement in the etiology of tobacco smoking. Front. Psychiatry 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Rodriguez, M.; Lotfipour, S.; Leonard, G.; Perron, M.; Richer, L.; Veillette, S.; Pausova, Z.; Paus, T. Maternal smoking during pregnancy is associated with epigenetic modifications of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-6 exon in adolescent offspring. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010, 153B, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, M.; Abramovici, A.; Showalter, L.; Hu, M.; Shope, C.D.; Varner, M.; Aagaard-Tillery, K. In utero tobacco exposure epigenetically modifies placental CYP1A1 expression. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.K.; Adigun, A.; Huang, Z.; Overcash, F.; Wang, F.; Jirtle, R.L.; Schildkraut, J.M.; Murtha, A.P.; Iversen, E.S.; Hoyo, C. Gender-specific methylation differences in relation to prenatal exposure to cigarette smoke. Gene 2012, 494, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Wang, T.; Reilly, A.A.; Keller, S.M.; Spivack, S.D. Gene promoter methylation assayed in exhaled breath, with differences in smokers and lung cancer patients. Respir. Res. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, B.C.; Houseman, E.A.; Marsit, C.J.; Zheng, S.; Wrensch, M.R.; Wiemels, J.L.; Nelson, H.H.; Karagas, M.R.; Padbury, J.F.; Bueno, R.; et al. Aging and environmental exposures alter tissue-specific DNA methylation dependent upon CpG island context. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, C.V.; Byun, H.M.; Wenten, M.; Pan, F.; Yang, A.; Gilliland, F.D. Prenatal tobacco smoke exposure affects global and gene-specific DNA methylation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitling, L.P.; Salzmann, K.; Rothenbacher, D.; Burwinkel, B.; Brenner, H. Smoking, F2RL3 methylation, and prognosis in stable coronary heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitling, L.P.; Yang, R.; Korn, B.; Burwinkel, B.; Brenner, H. Tobacco-smoking-related differential DNA methylation: 27k Discovery and replication. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, E.S.; Qiu, W.; Baccarelli, A.; Carey, V.J.; Bacherman, H.; Rennard, S.I.; Agusti, A.; Anderson, W.; Lomas, D.A.; Demeo, D.L. Cigarette smoking behaviors and time since quitting are associated with differential DNA methylation across the human genome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3073–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.V.; Smith, A.K.; Conneely, K.N.; Chang, Q.; Li, W.; Lazarus, A.; Smith, J.A.; Almli, L.M.; Binder, E.B.; Klengel, T.; et al. Epigenomic association analysis identifies smoking-related DNA methylation sites in African Americans. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilinger, S.; Kuhnel, B.; Klopp, N.; Baurecht, H.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Gieger, C.; Weidinger, S.; Lattka, E.; Adamski, J.; Peters, A.; et al. Tobacco smoking leads to extensive genome-wide changes in DNA methylation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenker, N.S.; Polidoro, S.; van Veldhoven, K.; Sacerdote, C.; Ricceri, F.; Birrell, M.A.; Belvisi, M.G.; Brown, R.; Vineis, P.; Flanagan, J.M. Epigenome-wide association study in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC-Turin) identifies novel genetic loci associated with smoking. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besingi, W.; Johansson, A. Smoke-related DNA methylation changes in the etiology of human disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlid, S.; Xu, Z.; Panduri, V.; Sandler, D.P.; Taylor, J.A. CpG sites associated with cigarette smoking: Analysis of epigenome-wide data from the sister study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsaprouni, L.G.; Yang, T.P.; Bell, J.; Dick, K.J.; Kanoni, S.; Nisbet, J.; Vinuela, A.; Grundberg, E.; Nelson, C.P.; Meduri, E.; et al. Cigarette smoking reduces DNA methylation levels at multiple genomic loci but the effect is partially reversible upon cessation. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Sandanger, T.M.; Castagne, R.; Campanella, G.; Polidoro, S.; Palli, D.; Krogh, V.; Tumino, R.; Sacerdote, C.; Panico, S.; et al. Dynamics of smoking-induced genome-wide methylation changes with time since smoking cessation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghlool, S.B.; Al-Shafai, M.; Al Muftah, W.A.; Kumar, P.; Falchi, M.; Suhre, K. Association of DNA methylation with age, gender, and smoking in an Arab population. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.-H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Burwinkel, B.; Breitling, L.P.; Holleczek, B.; Schottker, B.; Brenner, H. F2RL3 methylation in blood DNA is a strong predictor of mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Schottker, B.; Ordonez-Mena, J.; Holleczek, B.; Yang, R.; Burwinkel, B.; Butterbach, K.; Brenner, H. F2RL3 methylation, lung cancer incidence and mortality. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Schottker, B.; Florath, I.; Stock, C.; Butterbach, K.; Holleczek, B.; Mons, U.; Brenner, H. Smoking-associated DNA methylation biomarkers and their predictive value for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.P.; Bradfield, C.A. The search for endogenous activators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 21, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monick, M.M.; Beach, S.R.; Plume, J.; Sears, R.; Gerrard, M.; Brody, G.H.; Philibert, R.A. Coordinated changes in AHRR methylation in lymphoblasts and pulmonary macrophages from smokers. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2012, 159B, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, E.S.; Qiu, W.; Carey, V.J.; Morrow, J.; Bacherman, H.; Foreman, M.G.; Hokanson, J.E.; Bowler, R.P.; Crapo, J.D.; DeMeo, D.L. Smoking associated site specific differential methylation in buccal mucosa in the COPDGene study. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, D.; Sharma, S.; Kho, A.T.; Gaedigk, R.; Vyhlidal, C.A.; Leeder, J.S.; Morrow, J.; Carey, V.J.; Weiss, S.T.; Tantisira, K.G.; et al. Fetal lung and placental methylation is associated with in utero nicotine exposure. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivorra, C.; Fraga, M.F.; Bayon, G.F.; Fernandez, A.F.; Garcia-Vicent, C.; Chaves, F.J.; Redon, J.; Lurbe, E. DNA methylation patterns in newborns exposed to tobacco in utero. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, R.; Beach, S.R.; Lei, M.-K.; Brody, G.H. Changes in DNA methylation at the aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor may be a new biomarker for smoking. Clin. Epigenetics 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.A.; Beach, S.R.; Brody, G.H. Demethylation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor as a biomarker for nascent smokers. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, B.R.; Haberg, S.E.; Nilsen, R.M.; Wang, X.; Vollset, S.E.; Murphy, S.K.; Huang, Z.; Hoyo, C.; Midttun, O.; Cupul-Uicab, L.A.; et al. 450k Epigenome-wide scan identifies differential DNA methylation in newborns related to maternal smoking during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markunas, C.A.; Xu, Z.; Harlid, S.; Wade, P.A.; Lie, R.T.; Taylor, J.A.; Wilcox, A.J. Identification of DNA methylation changes in newborns related to maternal smoking during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, B.R.; Haberg, S.E.; Bell, D.A.; Nilsen, R.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Midttun, O.; Ueland, P.M.; Wu, M.C.; Nystad, W.; Peddada, S.D.; et al. Maternal smoking and DNA methylation in newborns: In utero effect or epigenetic inheritance? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakovic, B.; Ryan, J.; Pereira, N.; Boughton, B.; Craig, J.M.; Saffery, R. Postnatal stability, tissue, and time specific effects of AHRR methylation change in response to maternal smoking in pregnancy. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenker, N.S.; Ueland, P.M.; Polidoro, S.; van Veldhoven, K.; Ricceri, F.; Brown, R.; Flanagan, J.M.; Vineis, P. DNA methylation as a long-term biomarker of exposure to tobacco smoke. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.; Hollenbeck, N.; Andersen, E.; Osborn, T.; Gerrard, M.; Gibbons, F.X.; Wang, K. A quantitative epigenetic approach for the assessment of cigarette consumption. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Bagnardi, V.; Donati, M.; Iacoviello, L.; de Gaetano, G. Alcohol dosing and total mortality in men and women: An updated meta-analysis of 34 prospective studies. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschl, G.; Seitz, H. Alcohol and cancer. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marron, M.; Boffetta, P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Zaridze, D.; Wunsch-Filho, V.; Winn, D.M.; Wei, Q.; Talamini, R.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Sturgis, E.M.; et al. Cessation of alcohol drinking, tobacco smoking and the reversal of head and neck cancer risk. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuyns, A.J.; Esteve, J.; Raymond, L.; Berrino, F.; Benhamou, E.; Blanchet, F.; Boffetta, P.; Crosignani, P.; Moral, A.D.; Lehmann, W. Cancer of the larynx/hypopharynx, tobacco and alcohol: Iarc international case-control study in Turin and Varese (Italy), Zaragoza and Navarra (Spain), Geneva (Switzerland) and Calvados (France). Int. J. Cancer 1988, 41, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsch, D.; Bernd, L.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. DNA hypermethylation of the alpha synuclein promoter in patients with alcoholism. Mol. Neurosci. 2005, 16, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Bonsch, D.; Lenz, B.; Fiszer, R.; Frieling, H.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Lowered DNA methyltransferase (DNMT-3b) mRNA expression is associated with genomic DNA hypermethylation in patients with chronic alcoholism. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleich, S.; Lenz, B.; Ziegenbein, M.; Beutler, S.; Frieling, H.; Kornhuber, J.; Bonsch, D. Epigenetic DNA hypermethylation of the HERP gene promoter induces down-regulation of its mRNA expression in patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, T.; Reulbach, U.; Lenz, B.; Frieling, H.; Muschler, M.; Hillemacher, T.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. N-methyl-D-aspartate 2b receptor subtype (NR2B) promoter methylation in patients during alcohol withdrawal. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.A.; Sandhu, H.; Hollenbeck, N.; Gunter, T.; Adams, W.; Madan, A. The relationship of 5HTT (SLC6A4) methylation and genotype on mRNA expression and liability to major depression and alcohol dependence in subjects from the Iowa Adoption Studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147B, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.Y.; Lee, B.C.; Jung, K.H.; Jung, M.H.; Park, B.L.; Chai, Y.G.; Choi, I.G. Epigenetic changes of serotonin transporter in the patients with alcohol dependence: Methylation of an serotonin transporter promoter CpG island. Psychiatry Investig. 2011, 8, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Ryu, H.M.; Shin, C.Y.; Ko, K.N.; Han, J.Y.; Koren, G.; Cho, Y.H. Changes in the methylation status of DAT, SERT, and MeCP2 gene promoters in the blood cell in families exposed to alcohol during the periconceptional period. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillemacher, T.; Frieling, H.; Hartl, T.; Wilhelm, J.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Promoter specific methylation of the dopamine transporter gene is altered in alcohol dependence and associated with craving. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieratschker, V.; Grosshans, M.; Frank, J.; Strohmaier, J.; von der Goltz, C.; El-Maarri, O.; Witt, S.H.; Cichon, S.; Nothen, M.M.; Kiefer, F.; et al. Epigenetic alteration of the dopamine transporter gene in alcohol-dependent patients is associated with age. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiewicz, A.; Rubis, B.; Samochowiec, J.; Malecka, I.; Suchanecka, A.; Jablonski, M.; Grzywacz, A. DAT1 methylation changes in alcohol-dependent individuals vs. controls. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 64, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouko, L.A.; Shantikumar, K.; Knezovich, J.; Haycock, P.; Schnugh, D.J.; Ramsay, M. Effect of alcohol consumption on CpG methylation in the differentially methylated regions of H19 and IG-DMR in male gametes—Implications for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillemacher, T.; Frieling, H.; Luber, K.; Yazici, A.; Muschler, M.A.; Lenz, B.; Wilhelm, J.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Epigenetic regulation and gene expression of vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide in alcohol withdrawal. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschler, M.A.; Hillemacher, T.; Kraus, C.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Frieling, H. DNA methylation of the POMC gene promoter is associated with craving in alcohol dependence. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayerlein, K.; Kraus, T.; Leinonen, I.; Pilniok, D.; Rotter, A.; Hofner, B.; Schwitulla, J.; Sperling, W.; Kornhuber, J.; Biermann, T. Orexin A expression and promoter methylation in patients with alcohol dependence comparing acute and protracted withdrawal. Alcohol 2011, 45, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberlein, A.; Muschler, M.; Frieling, H.; Behr, M.; Eberlein, C.; Wilhelm, J.; Groschl, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Hillemacher, T. Epigenetic down regulation of nerve growth factor during alcohol withdrawal. Addict. Biol. 2013, 18, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillemacher, T.; Weinland, C.; Lenz, B.; Kraus, T.; Heberlein, A.; Glahn, A.; Muschler, M.A.; Bleich, S.; Kornhuber, J.; Frieling, H. DNA methylation of the LEP gene is associated with craving during alcohol withdrawal. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Herman, A.I.; Kranzler, H.R.; Anton, R.F.; Simen, A.A.; Gelernter, J. Hypermethylation of OPRM1 promoter region in European Americans with alcohol dependence. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, M.; Covault, J.; Hesselbrock, V.; Bonkovsky, H.L. DNA methylation patterns in alcoholics and family controls. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 4, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Herman, A.I.; Kranzler, H.R.; Anton, R.F.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, W.; Gelernter, J. Array-based profiling of DNA methylation changes associated with alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, E108–E115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Kranzler, H.R.; Zhao, H.; Gelernter, J. Profiling of childhood adversity-associated DNA methylation changes in alcoholic patients and healthy controls. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.T.; Wu, L.S.; Lee, C.S.; Hsu, P.W.; Cheng, A.T. Integrative epigenetic profiling analysis identifies DNA methylation changes associated with chronic alcohol consumption. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 64, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Miao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhao, R.; Li, W.; Haile, C.N.; Hao, W.; Zhang, X.Y. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in alcohol dependence. Addict. Biol. 2013, 18, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.A.; Plume, J.M.; Gibbons, F.X.; Brody, G.H.; Beach, S.R. The impact of recent alcohol use on genome wide DNA methylation signatures. Front. Genet. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Liao, Y.; Tang, J.; Miao, Q.; Hao, W. Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in discordant sib pairs with alcohol dependence. Asia Pac. Psychiatry 2013, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.A.; Penaluna, B.; White, T.; Shires, S.; Gunter, T.; Liesveld, J.; Erwin, C.; Hollenbeck, N.; Osborn, T. A pilot examination of the genome-wide DNA methylation signatures of subjects entering and exiting short-term alcohol dependence treatment programs. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, S.L.; Aberg, K.A.; Nerella, S.; Kumar, G.; McClay, J.L.; Chen, W.; Xie, L.Y.; Harada, A.; Shabalin, A.A.; Gao, G.; et al. Combined whole methylome and genomewide association study implicates CNTN4 in alcohol use. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsch, D.; Lenz, B.; Reulbach, U.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S. Homocysteine associated genomic DNA hypermethylation in patients with chronic alcoholism. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Hou, L.; Bollati, V.; Tarantini, L.; Marinelli, B.; Cantone, L.; Yang, A.S.; Vokonas, P.; Lissowska, J.; Fustinoni, S.; et al. Predictors of global methylation levels in blood DNA of healthy subjects: A combined analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Kuchiba, A.; Kasuga, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Onuma, H.; Nishimura, H.; Kusama, R.; Ohnami, S.; Sakamoto, H.; et al. Association of dietary and genetic factors related to one-carbon metabolism with global methylation level of leukocyte DNA. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarev, I.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene coexpression networks in human brain identify epigenetic modifications in alcohol dependence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzardo, A.M.; Henkhaus, R.S.; Butler, M.G. Global DNA promoter methylation in frontal cortex of alcoholics and controls. Gene 2012, 498, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, A.; Heese, P.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Muschler, M.; Heberlein, A.; Bigler, L.; Prost, J.C.; Frieling, H.; Kornhuber, J.; Banger, M.; et al. Alcohol abuse and cigarette smoking are associated with global DNA hypermethylation: Results from the german investigation on neurobiology in alcoholism (GINA). Alcohol 2015, 49, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, S.R.H.; Dogan, M.V.; Lei, M.-K.; Cutrona, C.; Gerrard, M.; Gibbons, F.X.; Simons, R.; Brody, G.; Philibert, R. Methylomic aging as a window on lifestyle impact: Tobacco and alcohol use alter the rate of biological aging. J. Am. Gerontol. Assoc. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, G.C.; Coffey, C.; Carlin, J.B.; Sawyer, S.M.; Lynskey, M. Reverse gateways? Frequent cannabis use as a predictor of tobacco initiation and nicotine dependence. Addiction 2005, 100, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N. National longitudinal study of the neurodevelopmental consequences of substance use. Available online: http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/news-events/news-noteworthy/national-longitudinal-study-neurodevelopmental-consequences-substance (accessed on 29 September 2014).
- McLaren, J.; Swift, W.; Dillon, P.; Allsop, S. Cannabis potency and contamination: A review of the literature. Addiction 2008, 103, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, A.; Bayerlein, K.; Hansbauer, M.; Weiland, J.; Sperling, W.; Kornhuber, J.; Biermann, T. Orexin A expression and promoter methylation in patients with cannabis dependence in comparison to nicotine-dependent cigarette smokers and nonsmokers. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 66, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, A.; Bayerlein, K.; Hansbauer, M.; Weiland, J.; Sperling, W.; Kornhuber, J.; Biermann, T. CB1 and CB2 receptor expression and promoter methylation in patients with cannabis dependence. Eur. Addict. Res. 2013, 19, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNieri, J.A.; Wang, X.; Szutorisz, H.; Spano, S.M.; Kaur, J.; Casaccia, P.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Hurd, Y.L. Maternal cannabis use alters ventral striatal dopamine D2 gene regulation in the offspring. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppin, J.F.; Passik, S.D.; Couto, J.E.; Fine, P.G.; Christo, P.J.; Argoff, C.; Aronoff, G.M.; Bennett, D.; Cheatle, M.D.; Slevin, K.A. Recommendations for urine drug monitoring as a component of opioid therapy in the treatment of chronic pain. Pain Med. 2012, 13, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C. Opioid receptors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 67. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Yuferov, V.; Hamon, S.; Jackson, C.; Ho, A.; Ott, J.; Kreek, M.J. Increased OPRM1 DNA methylation in lymphocytes of methadone-maintained former heroin addicts. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Hamon, S.; Yuferov, V.; Jackson, C.; Ho, A.; Ott, J.; Kreek, M.J. Ethnic diversity of DNA methylation in the OPRM1 promoter region in lymphocytes of heroin addicts. Hum. Genet. 2010, 127, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCowan, T.; Dhasarathy, A.; Carvelli, L. The epigenetic mechanisms of amphetamine. J. Addict. Prev. 2015, S(1), 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.D.; McGinty, J.F.; West, A.E.; Sadri-Vakili, G. Epigenetics and psychostimulant addiction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Shao, N.; Szulwach, K.E.; Vialou, V.; Huynh, J.; Zhong, C.; Le, T.; Ferguson, D.; Cahill, M.E.; Li, Y.; et al. Role of Tet1 and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in cocaine action. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Nestler, E.J. Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeurwaerder, S.; Defrance, M.; Bizet, M.; Calonne, E.; Bontempi, G.; Fuks, F. A comprehensive overview of Infinium HumanMethylation450 data processing. Briefings Bioinform. 2014, 15, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mu, W.; Zhang, W. On the analysis of the illumina 450k array data: Probes ambiguously mapped to the human genome. Front. Genet. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.E.; Cotton, A.M.; Lam, L.L.; Farre, P.; Emberly, E.; Brown, C.J.; Robinson, W.P.; Kobor, M.S. Additional annotation enhances potential for biologically-relevant analysis of the illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 Beadchip array. Epigenet. Chromatin 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andersen, A.M.; Dogan, M.V.; Beach, S.R.H.; Philibert, R.A. Current and Future Prospects for Epigenetic Biomarkers of Substance Use Disorders. Genes 2015, 6, 991-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6040991
Andersen AM, Dogan MV, Beach SRH, Philibert RA. Current and Future Prospects for Epigenetic Biomarkers of Substance Use Disorders. Genes. 2015; 6(4):991-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6040991
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndersen, Allan M., Meeshanthini V. Dogan, Steven R.H. Beach, and Robert A. Philibert. 2015. "Current and Future Prospects for Epigenetic Biomarkers of Substance Use Disorders" Genes 6, no. 4: 991-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6040991
APA StyleAndersen, A. M., Dogan, M. V., Beach, S. R. H., & Philibert, R. A. (2015). Current and Future Prospects for Epigenetic Biomarkers of Substance Use Disorders. Genes, 6(4), 991-1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6040991






