Identification of Differentially Expressed IGFBP5-Related Genes in Breast Cancer Tumor Tissues Using cDNA Microarray Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Clinicopathological Parameters of Breast Cancer Patients
| Characteristics | Tumoral Expression of IGFBP5 Compared to Adjacent Normal Tissue | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 21) | Low (n = 17) | ||
| Age (years) | 55.66 | 55.52 | 0.9684 |
| Menarche age (years) | 12.95 | 14.18 | 0.0149 |
| Pregnancy (number) | 3.66 | 3.11 | 0.5876 |
| Menopausal state | |||
| Pre | 7 | 3 | ns |
| Peri | 2 | 1 | |
| Post | 12 | 13 | |
| Tumor size (mm) | 26.71 | 23 | 0.3578 |
| Tumor localization | |||
| Left | 10 | 13 | ns |
| Right | 10 | 4 | |
| Bilateral | 1 | 0 | |
| Estrogen receptor status | |||
| Positive | 16 | 13 | ns |
| Negative | 5 | 4 | |
| Progesterone receptor status | |||
| Positive | 14 | 13 | 0.7210 |
| Negative | 7 | 4 | |
| Her2 status | |||
| Positive | 5 | 2 | 0.4267 |
| Negative | 16 | 15 | |
| Ki67 status | |||
| Positive | 11 | 12 | 0.3264 |
| Negative | 10 | 5 | |
| Tumor grade | |||
| 1 | 0 | 5 | 0.0123 |
| 2&3 | 21 | 12 | |
| Tumor histology | |||
| IDC | 15 | 11 | ns |
| ILC | 1 | 0 | |
| IMC | 3 | 3 | |
| Others | 2 | 3 | |
| Molecular subtypes | |||
| Luminal A | 6 | 5 | ns |
| Luminal B Her2(−) | 4 | 7 | |
| Luminal B Her2(+) | 6 | 1 | |
| Erb-B2 overexpression | 1 | 2 | |
| Basal-like | 4 | 2 | |
2.2. RNA Isolation and Quantification of IGFBP5 Expression in Breast Cancer Using qPCR
2.3. Selection of Samples and Coding for Microarray
| Patients Code | Age | ER | PR | Her2 | Histology | Molecular Subtypes | Stage | Size (mm) | Fold Changes of IGFBP5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 47 | 60% | 60% | (neg.) | ILC | lumA | T1N1 | 15 | 2.276 |
| T2 | 73 | 50% | 10% | (neg.) | IDC | lumA | T2N3 | 23 | 16.528 |
| T3 | 40 | 90% | 90% | (neg.) | IMC | lumB | T2N2 | 30 | 3.233 |
| T4 | 42 | 90% | 60% | (neg.) | IDC | lumA | T2N0 | 22 | 2.022 |
| T5 | 67 | 70% | 70% | (neg.) | IDC | lumA | T2N2 | 30 | 4.892 |
2.4. Gene Expression Profiling by Microarray and Validation with qPCR
2.5. Pathways Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. IGFBP5 mRNA Expression Levels in Breast Cancer Patients
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes and Hierarchical Clustering of Microarray Data
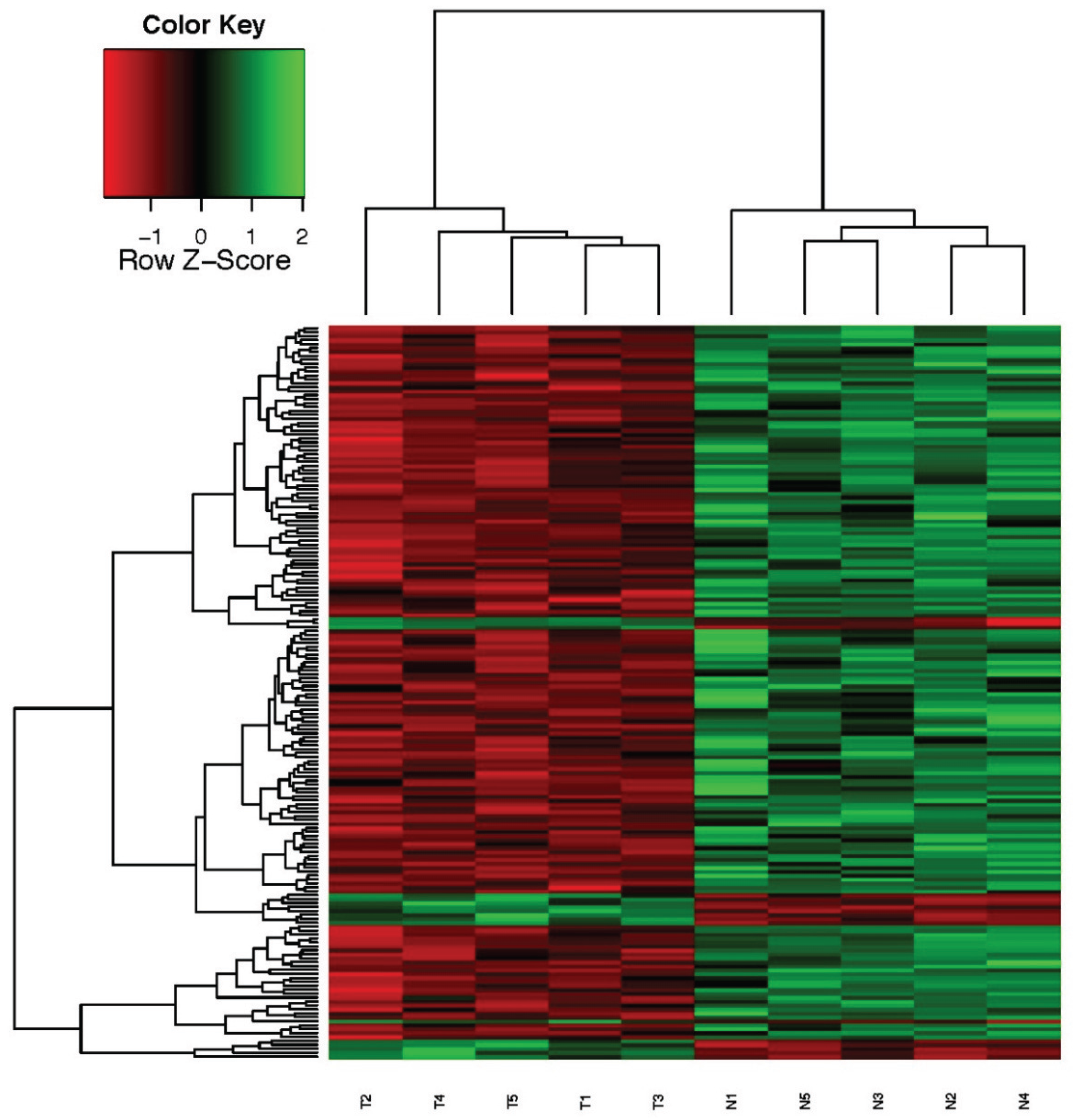
| Gene Symbol | RefSeq | Fold Change | Q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CST1 | NM_001898.2 | 58.11773612 | 5.88 × 10−6 |
| MMP11 | NM_005940.3 | 41.38923113 | 1.08 × 10−5 |
| COL1A1 | NM_000088.3 | 20.28765826 | 3.05 × 10−5 |
| GRIA2 | NM_000826.2 | 19.475709 | 4.92 × 10−5 |
| COL5A2 | NM_000393.3 | 8.154198414 | 4.28 × 10−5 |
| SPOCK1 | NM_004598.3 | 7.717882382 | 5.69 × 10−5 |
| NKAIN1 | NM_024522.1 | 5.686495097 | 3.71 × 10−5 |
| DSCR6 | NM_018962.1 | 4.853586146 | 4.65 × 10−5 |
| CLGN | NM_004362.1 | 4.372809335 | 7.25 × 10−5 |
| KCNF1 | NM_002236.4 | 4.03710734 | 4.96 × 10−6 |
| SLC44A4 | NM_025257.2 | 3.372736146 | 3.20 × 10−5 |
| SLC44A4 | NM_032794.1 | 3.353011207 | 2.99 × 10−5 |
| FAM83D | NM_030919.2 | 3.063515303 | 4.59 × 10−5 |
| ESM1 | NM_007036.3 | 2.393905549 | 3.23 × 10−5 |
| NINJ1 | NM_004148.3 | 2.24489298 | 6.78 × 10−5 |
| LCLAT1 | NM_001002257.1 | 1.733148032 | 6.39 × 10−5 |
| SLC12A8 | NM_024628.4 | 1.699383326 | 6.41 × 10−5 |
| Gene Symbol | RefSeq | Fold Change | Q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DST | NM_001723.4 | −10.5318799 | 3.31 × 10−6 |
| OXTR | NM_000916.3 | −11.0105517 | 2.19 × 10−5 |
| COL17A1 | NM_000494.3 | −11.04207984 | 3.03 × 10−5 |
| HAS3 | NM_005329.2 | −11.24842575 | 7.35 × 10−7 |
| SAA1 | NM_199161.1 | −11.59121389 | 1.25 × 10−5 |
| KRT17 | NM_000422.1 | −12.70489015 | 3.84 × 10−5 |
| ACTG2 | NM_001615.3 | −14.48863197 | 1.91 × 10−5 |
| KRT14 | NM_000526.3 | −15.692027 | 2.20 × 10−6 |
| KRT5 | NM_000424.3 | −15.77641561 | 2.44 × 10−5 |
| KRT15 | NM_002275.2 | −16.38531094 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| SYNM | NM_015286.5 | −17.22861604 | 5.91 × 10−5 |
| PPP1R1B | NM_181505.1 | −17.74088495 | 1.65 × 10−6 |
| KLK7 | NM_005046.2 | −17.88824515 | 6.61 × 10−6 |
| SOX10 | NM_006941.3 | −19.24267129 | 1.84 × 10−7 |
| KLK5 | NM_001077491.1 | −20.72022752 | 3.53 × 10−5 |
| KRT6B | NM_005555.3 | −21.63963922 | 1.82 × 10−5 |
| STAC2 | NM_198993.2 | −21.88100857 | 9.37 × 10−6 |
| KLK5 | NM_012427.4 | −22.06231675 | 4.41 × 10−6 |
| MUCL1 | NM_058173.2 | 46.66120963 | 2.7 × 10−4 |
3.3. Analysis of KEGG Pathways
| Pathway | Reference Genes in Category | Expected Number in the Category | Gene Count | Enrichment Ratio | Raw p-val | Adjusted p-val |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein digestion and absorption | 77 | 0.58 | 5 | 8.62 | 0.0003 | 0.0087 |
| Focal adhesion | 184 | 1.39 | 6 | 4.33 | 0.0027 | 0.0217 |
| Salivary secretion | 79 | 0.6 | 4 | 6.72 | 0.003 | 0.0217 |
| Drug metabolism | 72 | 0.54 | 4 | 7.37 | 0.0021 | 0.0217 |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | 17 | 0.13 | 2 | 15.62 | 0.0071 | 0.0412 |
| Pathway | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein digestion and absorption | COL17A1 | Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1 | −8.19 |
| COL5A2 | Collagen, type V, alpha 2 | 8.15 | |
| COL1A1 | Collagen, type I, alpha 1 | 20.29 | |
| KCNN4 | Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 | −5.43 | |
| MME | Membrane metallo-endopeptidase | −7.67 | |
| Focal adhesion | COL5A2 | Collagen, type V, alpha 2 | 8.15 |
| MET | Met proto-oncogen (hepatocyte growth factor) | −2.43 | |
| LAMC2 | Laminin, gamma 2 | −2.61 | |
| COL1A1 | Collagen, type I, alpha 1 | 20.29 | |
| CAV2 | Caveolin 2 | −3.37 | |
| MYLK | Myosin light chain kinase | −6.93 | |
| Salivary secretion | TRPV6 | Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily | −3.64 |
| CST1 | Cystatin SN | 58.12 | |
| KCNN4 | Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4 | −5.43 | |
| RYR3 | Ryanodine receptor 3 | −4.76 | |
| Drug metabolism cytochrome P450 | FMO2 | Flavin containing monooxygenase 2 (non-functional) | −5.23 |
| GSTP1 | Glutation S-transferase pi 1 | −3.79 | |
| ALDH3A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A1 | −2.86 | |
| ALDH1A3 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3 | −9.46 | |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | ALDH3A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family, member A1 | −2.86 |
| ALDH1A3 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3 | −9.46 |
3.4. Advanced Level Bioinformatics

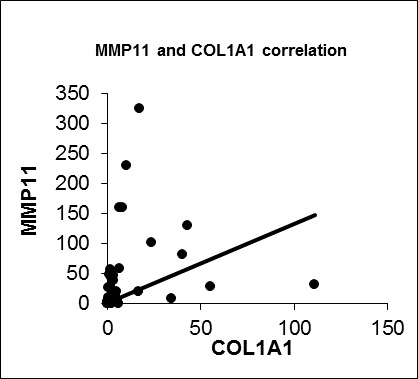
3.5. Validation Experiments of COL1A1 and MMP11 with IGFBP5 by Real Time qPCR
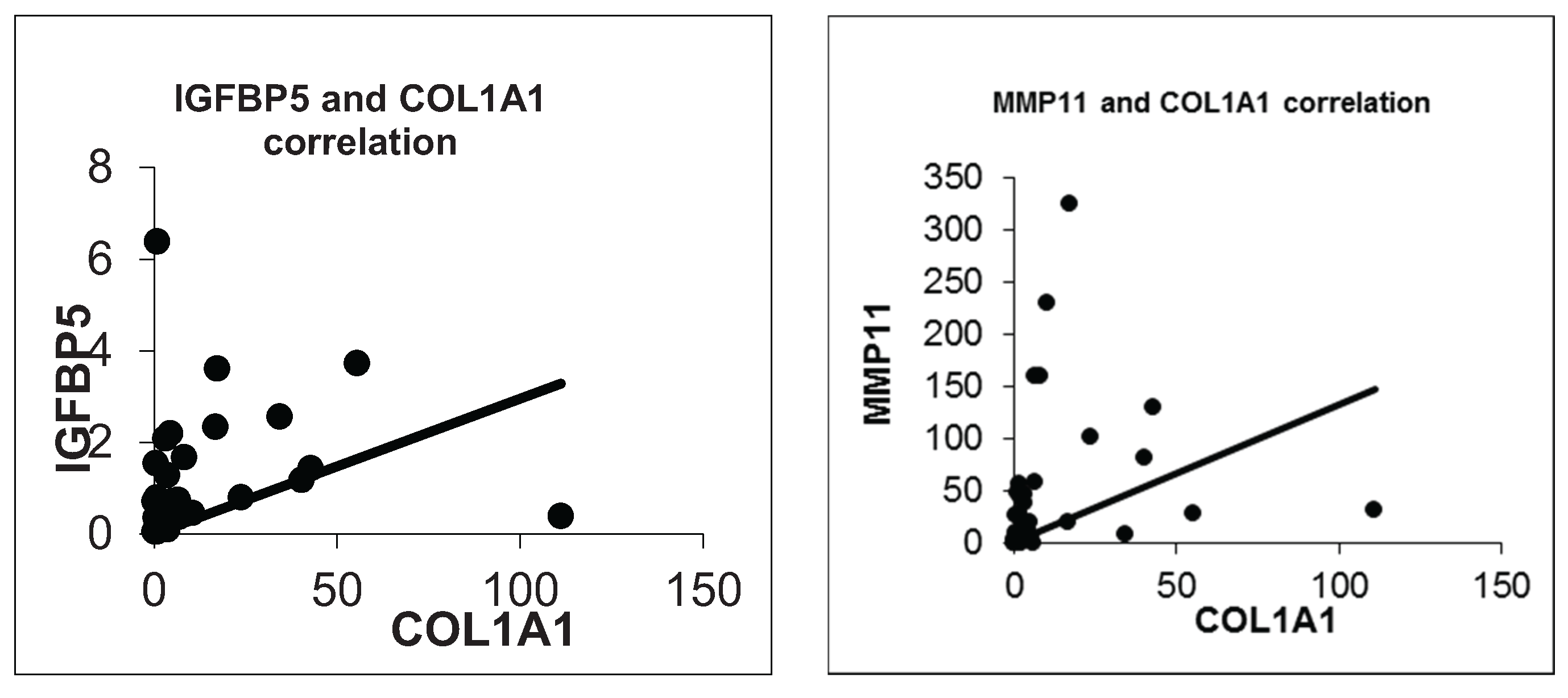
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gullu, G.; Karabulut, S.; Akkiprik, M. Functional roles and clinical values of insulin-like growth factor binding pro- tein-5 in different types of cancers. Chin. J. Cancer 2012, 6, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Baylink, D.J. IGF-binding proteins are multi- functional and act via IGF-dependent and independent mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 175, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ando, Y.; Toyama, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Hayashi, S.I.; Fujii, Y.; Iwase, H.; Yamashita, H. Prognostic significance of insulin like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-4 and IGFBP-5 expression in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 37, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen, F.; Nyman, T.; Ilvesmaki, V.; Partanen, S. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 5204–5207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perks, C.M.; Bowen, S.; Gill, Z.P.; Newcomb, P.V.; Holly, J.M. Differential IGF-independent effects of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (1–6) on apoptosis of breast epithelial cells. J. Cell Biochem. 1999, 75, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.; Mao, M.; Peterse, H.L.; van der Kooy, K.; Marton, M.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002, 415, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkiprik, M.; Hu, L.; Sahin, A.; Hao, X.; Zhang, W. The subcellular localization of IGFBP5 affects its cell growth and migration functions in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Y. Expression level of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 mRNA is a prognostic factor for breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.I.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, T.F.; Wu, W.R.; Liao, A.C.; Shen, K.H.; Hsing, C.H.; Shiue, Y.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsu, H.P.; et al. IGFBP-5 overexpression as a poor prognostic factor in patients with urothelial carcinomas of upper urinary tracts and urinary bladder. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoussaini, M.; Edwards, S.L.; Michailidou, K.; Nord, S.; Cowper-Sal Lari, R.; Desai, K.; Kar, S.; Hillman, K.M.; Kaufmann, S.; Glubb, D.M.; et al. Evidence that breast cancer risk at the 2q35 locus is mediated through IGFBP5 regulation. Nat. Commun. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.Y.; Elwi, A.N.; Lee, B.; Trinh, D.L.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Yau, A.; Chan, J.A.; Magliocco, A.; Kim, S.W. Genetic screen identifies insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 as a modulator of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ruan, X.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) functions as a tumor suppressor in human melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20636–20649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wagner, E.R.; Luo, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; He, B.C.; Zuo, G.W.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhu, G.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human osteosarcoma. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3907–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, S.B.; Dong, S.M.; Kang, S.; Seo, S.S.; Yoo, C.W.; Lee, D.O.; Woo, J.S.; Park, S.Y. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.K.; Haun, R.S. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 influences pancreatic cancer cell growth. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3355–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureshbabu, A.; Okajima, H.; Yamanaka, D.; Tonner, E.; Shastri, S.; Maycock, J.; Szymanowska, M.; Shand, J.; Takahashi, S.I.; Beattie, J.; et al. IGFBP5 induces cell adhesion, increases cell survival and inhibits cell migration in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshman, E.; Green, K.A.; Flint, D.J.; White, A.; Streuli, C.H.; Westwood, M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.J.; Dickson, K.A.; Jambazov, S.; Baxter, R.C. Enhancement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced growth inhibition by insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5), but not IGFBP-3 in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, T.; Pollak, M.; Huynh, H. Castration-induced apoptosis in the rat ventral prostate is associated with increased expression of genes encoding insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2–5. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adashi, E.Y.; Resnick, C.E.; Hernandez, E.R.; Hurwitz, A.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Ovarian granulosa cell-derived insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins: release of low molecular weight, high-affinity IGF-selective species. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1990, 74, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Xu, J.; Le, C.; Huang, E.; Liu, C.; Qiu, P.; Lin, Z.M.; Xie, W.B.; Wang, H.J. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) mediates methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neuron apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Panel members. Strategies for subtypes—Dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Lee, S.J.; Kang, M.A.; Park, J.E.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, D.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Yeom, Y.I.; Choe, Y.K.; et al. Cystatin SN neutralizes the inhibitory effect of cystatin C on cathepsin B activity. Cell Death Dis. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, H.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Tan, S.W.; Wu, B. Identification of cystatin SN as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Becker, K.G.; Bera, T.K.; Pastan, I. CAPC negatively regulates NF-κB activation and suppresses tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Eiró, N.; Marín, L.; González-Reyes, S.; González, L.O.; Lamelas, M.L.; Vizoso, F.J. Expression and prognostic significance of fibronectin and matrix metalloproteases in breast cancer metastasis. Histopathology 2014, 64, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Adachi, Y.; Nagayama, T.; Furihata, M. Matrix metalloproteinase-11 overexpressed in lobular carcinoma cells of the breast promotes anoikis resistance. Virchows Arch. 2011, 459, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.W.; Kim, D.H.; Do, S.I.; Pyo, J.S.; Kim, K.; Chae, S.W.; Sohn, J.H.; Oh, Y.H.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of MMP-11 expression in the stromal fibroblast-like cells adjacent to invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 3, S433–S442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipes, J.M.; Guo, N.; Nègre, E.; Vogel, T.; Krutzsch, H.C.; Roberts, D.D. Inhibition of fibronectin binding and fibronectin-mediated cell adhesion to collagen by a peptide from the second type I repeat of thrombospondin. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 121, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yan, B.; Li, S.; Duan, C. Fibronectin binds insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 and abolishes Its ligand-dependent action on cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4269–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akkiprik, M.; Peker, İ.; Özmen, T.; Amuran, G.G.; Güllüoğlu, B.M.; Kaya, H.; Özer, A. Identification of Differentially Expressed IGFBP5-Related Genes in Breast Cancer Tumor Tissues Using cDNA Microarray Experiments. Genes 2015, 6, 1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041201
Akkiprik M, Peker İ, Özmen T, Amuran GG, Güllüoğlu BM, Kaya H, Özer A. Identification of Differentially Expressed IGFBP5-Related Genes in Breast Cancer Tumor Tissues Using cDNA Microarray Experiments. Genes. 2015; 6(4):1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041201
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkkiprik, Mustafa, İrem Peker, Tolga Özmen, Gökçe Güllü Amuran, Bahadır M. Güllüoğlu, Handan Kaya, and Ayşe Özer. 2015. "Identification of Differentially Expressed IGFBP5-Related Genes in Breast Cancer Tumor Tissues Using cDNA Microarray Experiments" Genes 6, no. 4: 1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041201
APA StyleAkkiprik, M., Peker, İ., Özmen, T., Amuran, G. G., Güllüoğlu, B. M., Kaya, H., & Özer, A. (2015). Identification of Differentially Expressed IGFBP5-Related Genes in Breast Cancer Tumor Tissues Using cDNA Microarray Experiments. Genes, 6(4), 1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041201