Abstract
Xanthomonas albilineans is the bacterium responsible for leaf scald, a lethal disease of sugarcane. Within the Xanthomonas genus, X. albilineans exhibits distinctive genomic characteristics including the presence of significant genome erosion, a non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) locus involved in albicidin biosynthesis, and a type 3 secretion system (T3SS) of the Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 (SPI-1) family. We sequenced two X. albilineans-like strains isolated from unusual environments, i.e., from dew droplets on sugarcane leaves and from the wild grass Paspalum dilatatum, and compared these genomes sequences with those of two strains of X. albilineans and three of Xanthomonas sacchari. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) and multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA) showed that both X. albilineans-like strains belong to a new species close to X. albilineans that we have named “Xanthomonas pseudalbilineans”. X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” share many genomic features including (i) the lack of genes encoding a hypersensitive response and pathogenicity type 3 secretion system (Hrp-T3SS), and (ii) genome erosion that probably occurred in a common progenitor of both species. Our comparative analyses also revealed specific genomic features that may help X. albilineans interact with sugarcane, e.g., a PglA endoglucanase, three TonB-dependent transporters and a glycogen metabolism gene cluster. Other specific genomic features found in the “X. pseudalbilineans” genome may contribute to its fitness and specific ecological niche.
1. Introduction
Leaf scald disease of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) is caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson—a xylem-invading pathogen. This bacterial disease was first recorded in 1911 in Australia [1]. Today, leaf scald disease occurs in numerous locations worldwide where sugarcane is grown and where it can cause large yield losses in susceptible cultivars (Saccharum interspecific hybrids) [2,3]. Disease symptoms vary from a single, narrow, sharply defined white stripe to complete bleaching and necrosis of infected leaves resulting in desiccation, scalding and plant death [3]. First isolated in 1920 by Wilbrink, X. albilineans is a vascular systemic pathogen that can colonize the roots, stalks and leaves of sugarcane [4]. X. albilineans is a representative of the genus Xanthomonas, members of which are exclusively Gram-negative plant-associated bacteria that collectively cause dramatic damage to hundreds of plant species of ornamental or agronomical interest. A recent highly resolved phylogenetic tree of the Xanthomonadales, based on 25 concatenated conserved proteins, confirmed anterior studies showing that X. albilineans belongs to the same clade as Xanthomonas translucens, Xanthomonas sacchari and Xanthomonas hyacinthi [5].
Previous studies showed that X. albilineans has experienced a genome reduction and exhibits distinctive genomic features compared to other species of Xanthomonas [6,7,8,9]. For example, the genome of X. albilineans lacks two loci required for pathogenicity in other plant pathogenic species of Xanthomonas: the xanthan gum biosynthesis, and the hypersensitive response and pathogenicity type 3 secretion system (Hrp-T3SS) gene clusters. In contrast, although reduced in size, the genome of X. albilineans encodes specific genomic features including a T3SS of the Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 (SPI-1) family and six non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) loci including one directing albicidin biosynthesis [8,9]. Albicidin is a DNA gyrase inhibitor acting as both the phytotoxin responsible for leaf scald symptoms and an antibiotic contributing to the competitiveness of X. albilineans with other bacteria spreading in sugarcane [10]. Albicidin has some unique structural features [11] and its mode of action differs from that of other DNA gyrase inhibitors [12].
X. albilineans exhibits large intra-species genetic variability, with the existence of numerous haplotypes having been described previously using different methodologies including pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA) [7,13]. Additionally, three serotypes associated with antigenic variations within X. albilineans were detected using three antisera (polyclonal antibodies) prepared against strains from three different geographical locations. Serotyping of 215 strains from 28 worldwide locations affected by sugarcane leaf scald disease distributed strains into three groups according to serotype: (i) serotype 1 represents the largest group, with strains from various geographic locations; (ii) serotype 2 consists of strains from tropical African countries; and (iii) serotype 3 contains strains from Caribbean islands (Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint-Kitts) as well as from Asia (Sri Lanka) and Oceania (Fiji) [14,15]. This serological characterization of X. albilineans strains has been corroborated using a combination of monoclonal antibodies on 38 strains from different locations worldwide [16].
Although X. albilineans is transmitted mainly via symptomless infected setts and infested cutting implements [17], aerial transmissions were recorded in the 1990s in Guadeloupe and in Mauritius [4,18,19]. Thereafter, aerial transmission and an epiphytic phase were proposed as important steps in the epidemiological cycle of leaf scald disease [20]. To better understand aerial transmission and the epiphytic survival of this sugarcane pathogen, a study was conducted in Guadeloupe in 1997 in experimental plots set up with disease-free tissue cultured sugarcane in a banana-growing location, distant from any other sugarcane field [19]. Thirteen weeks after planting, and during a two-day weather tropical disturbance, a strain belonging to X. albilineans serotype 3 (XaS3) was isolated from dew droplets on sugarcane leaf surfaces [19] (this isolate was stored and recorded in CIRAD’s collection as strain GPE 39). Five weeks later, at least half of the experimental sugarcane field canopy was found to be invaded by strains XaS3. During the same time frame, the population density of strains XaS3 on the surfaces of leaves gradually increased. A subsequent decrease in the population density of strains XaS3 on the leaf surface was correlated with the appearance—once again shortly after a tropical storm—and expansion of a second aerially transmitted strain belonging to X. albilineans serotype 1 (XaS1) [19] (this isolate was stored and recorded in CIRAD’s collection as strain GPE 40). Unlike GPE 40, GPE 39 was unable to penetrate sugarcane leaves or to colonize sugarcane stalks. GPE 39 also failed to induce any leaf scald symptoms on leaves after artificial inoculation performed in greenhouse experiments, leading the authors to consider it as a non-aggressive epiphyte strain.
In 1940, during the hot and rainy season in an experimental station in Mauritius, a strain resembling X. albilineans was isolated from the wild grass Paspalum dilatatum Poir. [21]. The infected plants showed leaf symptoms similar to those of leaf scald disease of sugarcane. When inoculated on sugarcane, the Paspalum pathogen was able to cause leaf scald symptoms but was unable to spread systemically in the plant. According to its pathogenicity traits and its cultural and biochemical characteristics, the Paspalum pathogen was considered as a variety of X. albilineans, and was named X. albilineans var. paspali [21]. This strain isolated on Paspalum in Mauritius in 1940 is stored in CIRAD’s collection under the reference MUS 060.
At first glance, the cultural, biochemical, serotyping and/or phenotypic characteristics of the MUS 060 and GPE 39 isolates, as determined in previous studies, led researchers to consider both strains as belonging to the species X. albilineans [19,21,22]. In order to deepen and refine the taxonomic characterization of these isolates, we sequenced their genomes and compared the resulting draft sequences to sequence data from the genome of two X. albilineans strains representative of the two main clades (MLSA-1 and MLSA-2) of this species, namely strain Xa23R1, for which a draft genome sequence was obtained in the frame of this study, and strain GPE PC73, for which a finished genome sequence has already been published [6,7]. Our comparative analyses also included genome sequences of Xanthomonas sacchari—a well-characterized species previously identified as phylogenetically closest to X. albilineans [5,23,24]. More precisely, we used the published draft genome sequences of strain LMG 476 isolated from a sugarcane stem [25], of strain NCPPB4393 isolated from an insect collected on a banana [26,27], and of strain R1 isolated from a rice seed [28]. The comparative phylogenetic and genomic analyses described in the present study refines the taxonomic classification of strains MUS 060 and GPE 39 and provides additional data that shed light on the evolutionary history of the sugarcane pathogen X. albilineans.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Taxonomic Characterization of MUS 060 and GPE 39 Isolates
Comparison of complete 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed a nucleotide identity of over 99.7% between X. albilineans strains and MUS 060 or GPE 39 strains, and 98.6% when comparing X. albilineans strains to X. sacchari strains (Supplementary File S1). As previously reported for other xanthomonads [23], comparison of the 16S–23S ITS revealed somewhat more variability than with 16S rRNA, with nucleotide identities of 94.4% and 98.4% when comparing MUS 060 or GPE 39 isolates with X. sacchari and X. albilineans strains, respectively. Nucleotide identities between MUS 060 and GPE 39 reached 99.9% and 100% when considering 16S rDNA and 16S–23S ITS, respectively, suggesting that both strains belong to the same species (Supplementary File S2). Most taxonomists consider that a 16S rRNA gene nucleotide sequence identity below 97% means that the compared sequences belong to different species; however, the meaning of identity greater than 97% remains unclear, partly due to the variable evolutionary histories of bacterial species [29,30]. Nevertheless, assuming an ideal nucleotide identity threshold of 99.5% for species identification [31], the values for 16S rRNA gene sequence identity between MUS 060 or GPE 39 versus X. albilineans strains (~99.7%) suggest that MUS 060 and GPE 39 belong to the species X. albilineans. To further confirm or refute this taxonomic classification, we performed whole-genome-based comparisons using the ANI method [32], which provides a higher taxonomic resolution equivalent to that of DNA-DNA hybridization (DDH) methods [33]. ANI values between MUS 060 or GPE 39 and both X. albilineans strains reached 91% at most, whereas those between MUS 060 or GPE 39 and each of the X. sacchari strains were below 87% (Supplementary File S3), showing unambiguously that strains MUS 060 and GPE 39 do not belong to the X. albilineans species. However, since it is commonly held that an ANI threshold of 95%–96% is equivalent to a DDH threshold of 70% for species identification [32,34], the genomes of MUS 060 and GPE 39 are closer to those of X. albilineans than to X. sacchari. MUS 060 and GPE 39 sequences display a genomic identity of ~96% (ANI), suggesting that both strains belong to the same species, thus together belonging to a new species within the Xanthomonas genus. The ANI results were confirmed by our MLSA phylogenetic analysis and its resulting robust MLSA tree, which groups MUS 060 and GPE 39 in a clade distinct from that containing the X. albilineans strains (Figure 1). As a result, strains MUS 060 and GPE 39, first assigned by their discoverers to X. albilineans, belong in fine to a novel Xanthomonas species not described to date, leading us to reconsider X. albilineans var. paspali strain MUS 060 and X. albilineans strain GPE 39 as representatives of this novel species that we propose to name “X. pseudalbilineans” (not valid name).
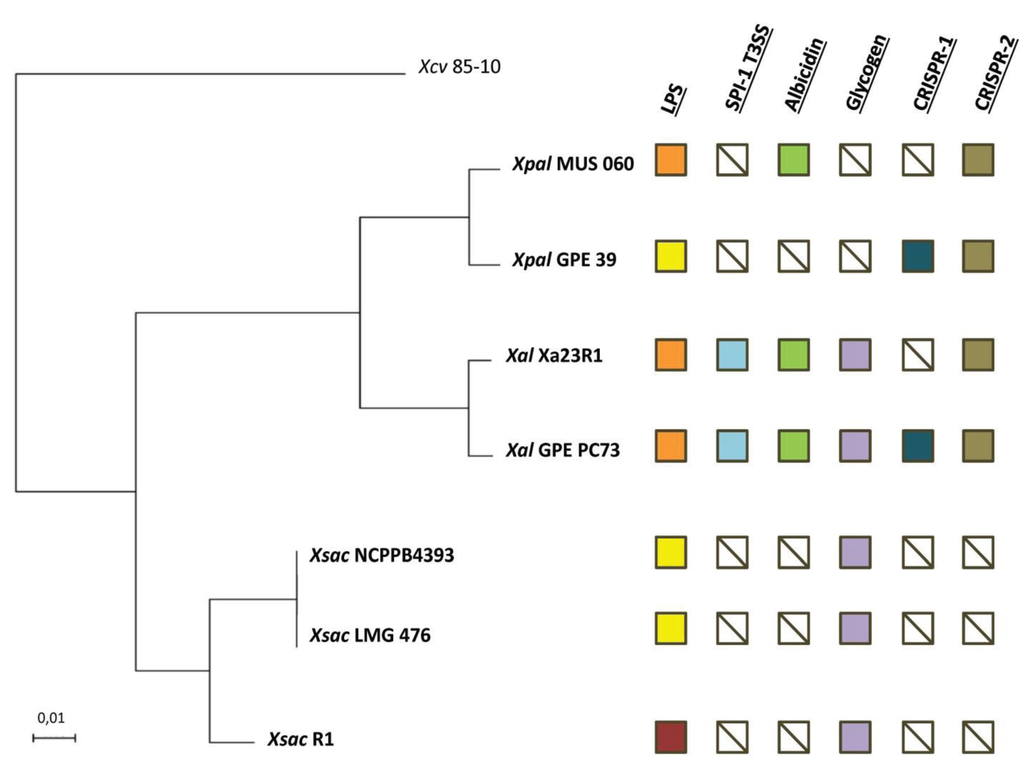
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relationship and overview of some variable genomic regions between strains of Xanthomonas albilineans (Xal), “Xanthomonas pseudalbilineans” (Xpal) and Xanthomonas sacchari (Xsac). Multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA) tree based on seven concatenated housekeeping gene sequences generated using the maximum likelihood method. Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 (Xcv) was used as outgroup. All branches were supported by bootstrap values of 100% after 500 replicates. The scale bar indicates the fraction of substitution per site. Orange and yellow squares indicate the presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) loci LPS1 or LPS3, respectively. The dark red square corresponds to the LPS locus of strain R1 of X. sacchari, which does not share any gene with loci LPS1 or LPS3. Other squares indicate the absence (crossed white) or presence of type 3 secretion system of the Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 family (SPI-1 T3SS; blue), albicidin (green), glycogen (violet) and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPRs) (dark blue or brown) loci.
2.2. Orthology Analysis
OrthoMCL analyses based on pairwise comparisons [35] were performed in order to identify orthologous groups shared between X. albilineans strains Xa23R1 and GPE PC73 and “X. pseudalbilineans” strains MUS 060 and GPE 39. The four strains share 2415 “core” orthologous protein sequences or coding DNA sequences (CDSs; Figure 2) and each strain possesses a similar number of unique CDSs, with the notable exception of strain MUS 060 for which a higher number of specific CDSs was identified. In this analysis, the core genome represents 66%–80% of each of the four genomes. This value is similar to the one estimated from comparison of X. axonopodis pv. citrumelo strain F1, X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85–10 and X. axonopodis pv. citri strain 306, i.e., about three-quarters of each total genome [36]. When performing such a comparative analysis with a larger number of xanthomonads, the core genome size represented on average 30% of any genome of the 13 strains analyzed, and this value increased to 44% when X. albilineans was excluded from the analysis [37].
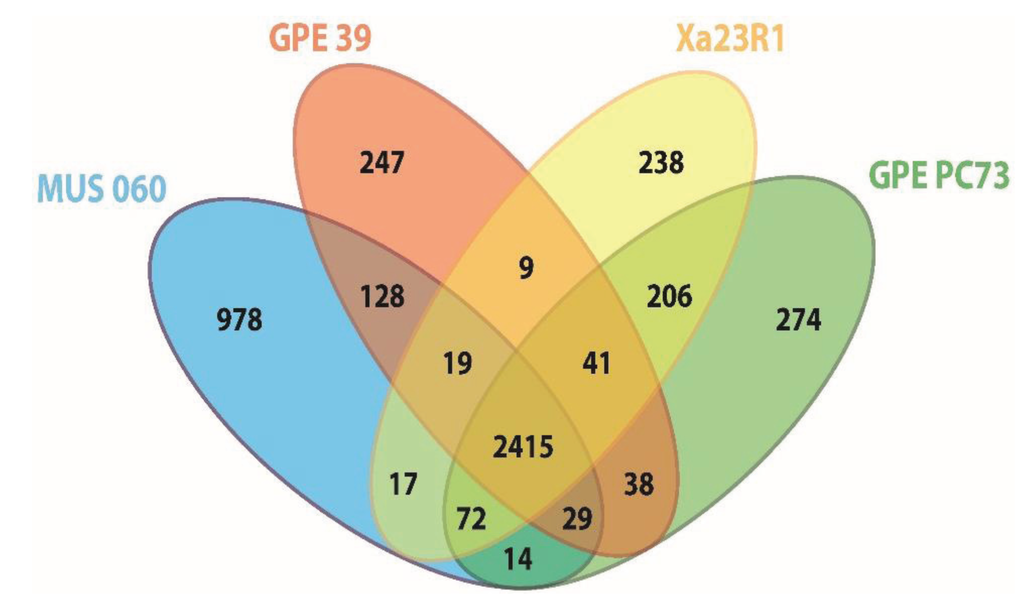
Figure 2.
Venn diagram showing the number of orthologous proteins (OrthoMCL groups) shared by proteomes of strains of X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” species (numbers shown do not include paralogous protein sequences). The number of specific elements of each proteome is the sum of specific inparalog groups and of specific single copy proteins of this proteome. GPE PC73: X. albilineans strain GPE PC73, Xa23R1: X. albilineans strain Xa23R1, GPE 39: “X. pseudalbilineans” strain GPE 39 and MUS 060: “X. pseudalbilineans” strain MUS 060.
Orthology comparisons identified 206 CDSs specific to X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1, and 128 CDSs specific to “X. pseudalbilineans” strains MUS 060 and GPE 39. Upon excluding CDSs from the core genome and those specific to each of the four strains, only a very small number of CDSs remain that are shared by at least one strain of X. albilineans and one strain of “X. pseudalbilineans”, as illustrated for instance by the low number of CDSs shared by both X. albilineans strains with either “X. pseudalbilineans” strain MUS 060 or strain GPE 39 (72 and 41 CDSs, respectively) (Figure 2). Both species are indeed closely related, “X. pseudalbilineans” sharing the main X. albilineans genomic features compared to other xanthomonads, such as the lack of gum, Hrp T3SS and Type 6 secretion system gene clusters.
2.3. Serotypes and Variability of LPS Loci
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are involved in biofilm formation and pathogenicity of numerous Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. LPS components on the cell surface of plant-pathogenic Xanthomonas species can be recognized as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) factors that activate the basal response of the infected plant (see, e.g., [38,39]). Within the LPS locus of most xanthomonads, numerous horizontal gene transfer (HGT) events have resulted in chimeric LPS loci and in a large diversification of this locus between strains (at both inter- and intra-species levels) [40], thus probably affecting recognition of these molecules as PAMPs by the host plant [41]. Analysis of the LPS loci of the two X. albilineans (GPE PC73 and Xa23R1) and the two “X. pseudalbilineans” (MUS 060 and GPE 39) strains revealed two distinct LPS loci (Figure 3). By analogy with descriptions of numerous other bacteria [42], antigenic variations in serotypes 1 and 3 are most probably associated with the existence of these two LPS loci. Strains belonging to serotype 1 (GPE PC73, Xa23R1 and MUS 060) share the same LPS locus: LPS1, whereas the strain belonging to serotype 3 (GPE 39) exhibits another LPS locus: LPS3 (nucleic acid sequence of genes specific to the LPS3 locus of strain GPE 39 is provided in Supplementary File S4). As with all xanthomonads sequenced to date, both LPS clusters are located between the highly conserved etfA and metB genes. The variable portion that differentiates LPS1 from LPS3 may contain genes involved in the mechanism of serotype specificity for these species. Locus LPS3 contains 14 genes, all of which are conserved in the LPS locus of X. sacchari excluding strain R1, which possesses a specific LPS locus (Figure 3). The LPS1 locus contains five specific genes and shares seven genes with LPS3 (Figure 3). Interestingly, these seven genes are also conserved in the LPS locus of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vasculorum—a phylogenetically distant species that is also pathogenic on sugarcane—and five of them are conserved in the LPS locus of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris B100 [7]. Locus LPS1 of MUS 060 contains specific insertion- and phage-related sequences located between orthologous genes XALc_2704 and XALc_2705 from strain GPE PC73. Most probably, these do not interfere with expression of other genes of the locus (Figure 3).
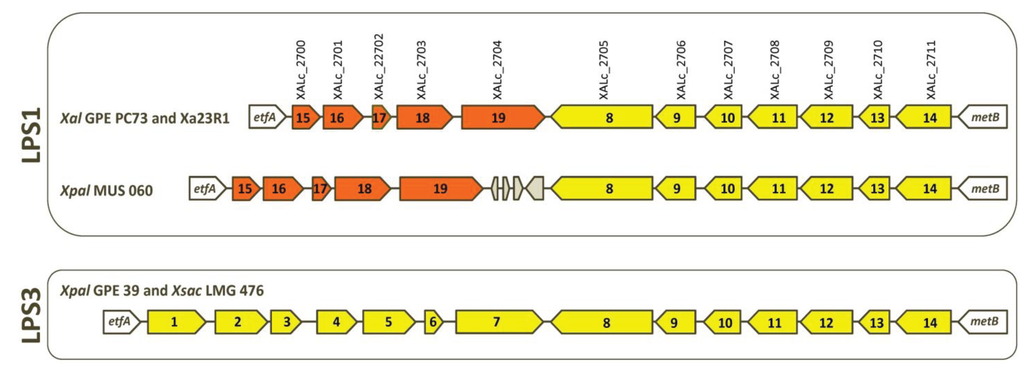
Figure 3.
Schematic comparison of LPS loci of strains of X. albilineans (Xal GPE PC73 and Xal Xa23R1), “X. pseudalbilineans” (Xpal GPE 39 and Xpal MUS 060) and X. sacchari (Xsac LMG 476). An arrow with a same color and a same number represents an identical gene. Grey-colored arrows are transposase sequences.
2.4. The Albicidin Locus and other NRPS Loci
NRPS is a pathway based on multimodular megasynthetases used by bacteria and fungi to produce peptides in a ribosome-independent manner [43]. The NRPS albicidin locus is present in the “X. pseudalbilineans” strain MUS 060 draft genome but not in the genome of the “X. pseudalbilineans” strain GPE 39, confirming the results of albicidin production bioassays (data not shown). The albicidin locus of strain MUS 060 contains all the albicidin biosynthesis genes described in X. albilineans, except alb18 encoding an aminodeoxychorismate lyase, which is most likely complemented by a gene present elsewhere in the genome encoding the same enzyme (ortholog of gene XALc_0280 in strain GPE PC73). Interestingly, alb18 is also partially frameshifted in X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1, supporting the hypothesis of complementation with the ortholog of XALc_0280. HPLC analysis of an albicidin extract from strain MUS 060 showed a chromatographic profile very similar to those usually observed for extracts of X. albilineans strains [11]; peaks containing albicidin antibiotic activity eluted at similar retention times for both species. The absence of the albicidin locus in strain GPE 39 is in accordance with the inability of this isolate to produce albicidin. The gene encoding the phosphopantetheinyl-transferase required for albicidin production and for post-translational activation of NRPS megasynthetases, which is present outside the albicidin locus, is conserved in strains MUS 060, GPE 39, Xa23R1 and GPE PC73 and is located at the same position in these genomes (between orthologs of XALc_1735 and XALc_1737).
Previous genome mining data has led to the identification of a new NRPS locus, named META-B, present in the genome of five strains: X. albilineans strain GPE PC73, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains BAI3 and X11-5A, Xanthomonas translucens strain DAR61454 and “X. pseudalbilineans” strain GPE 39 [9]. In addition to NRPS megasynthetases, META-B encodes a transcription regulator of the AraC family, a cyclic peptide transporter, a MbtH-like protein and enzymes involved in biosynthesis of the non-proteinogenic amino acids 2,4-diaminobutyric acid and 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine. The function of the small molecule encoded by this locus remains unknown. Despite the similar organization of the META-B locus in all five strains, in silico prediction of peptide sequences assembled by NRPS megasynthetases indicates that each strain produces a different lipopeptide. The META-B locus is partially deleted in strain MUS 060; genes encoding the transcription regulator of the AraC family and enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine are missing in this strain.
Two short NRPS loci have also been identified on the chromosome of X. albilineans strain GPE PC73: they both encode only one NRPS module. Interestingly, there is an overlap between both these genes and a gene encoding a glycosyltransferase. It has been hypothesized that these genes encode glycosylated amino acids, but no precise function for these has yet been attributed [9]. Strains MUS 060 and GPE 39 each possess only one of these two short NRPS loci (orthologs of XALc_0364 and XALc_0365, respectively). The two short NRPS loci are absent in the three strains of X. sacchari.
2.5. Genes of X. albilineans Linked to a Xylem-Invading Lifestyle
Five cell-wall-degrading enzymes (CWDEs) of X. albilineans strain GPE PC73 exhibit specific features compared to their respective orthologs in X. sacchari and other sequenced species of Xanthomonas [7]. They harbor a cellulose-binding domain (CBD) and a long linker region both predicted to be adapted to the utilization of cell-wall breakdown products as carbon source and to the ability to spread in sugarcane xylem vessels [7]. These specific features are probably important for the ability of X. albilineans to spread in xylem and for its pathogenicity. The long linker is rich in proline, threonine, serine, and glycine. Similar CBDs and long linkers have been found in the draft genomes of strains Xa23R1, MUS 060 and GPE 39. However, read misalignments in draft genomes due to the repeated sequence within linkers have led to sequences encoding CBDs and CWDEs being found in separate contigs and it has not been possible to clearly identify the corresponding CBD for each CWDE. X. albilineans strains produce an endopolygalacturonase encoded by pglA (XALc_0811), which is missing in both “X. pseudalbilineans” strains. This CWDE, which lacks any CBD and long linker, may represent a component of the offensive arsenal of X. albilineans allowing it to penetrate and colonize sugarcane xylem vessels.
TonB-dependent transporters (TBDTs) are known to be involved in the uptake of a large variety of substrates, such as cobalamin, iron-siderophore complexes, carbohydrates and organic acids (see e.g., [44,45]). TBDTs may be used by X. albilineans to transport cell-wall-degrading products resulting from the activity of CWDEs, and thus facilitate spread of the organism in the nutrient-poor conditions prevailing in sugarcane xylem. In the genome of X. albilineans strain GPE PC73, 35 TBDT genes have been identified, including one specific to this species (XALc_2962) and two others (XALc_0643 and XALc_0723) that were functionally associated with pathogenicity of the bacterium [7,46]. These three TBDT genes are conserved in both MUS 060 and GPE 39 strains; however, the notable absence in both MUS 060 and GPE 39 strains of three TBDT genes present in both GPE PC73 and Xa23R1 strains (XALc_2778, XALc_3025 and XALc_1949) is striking. On the other hand, in strains MUS 060 and GPE 39, we identified a TBDT that is absent in both X. albilineans strains but similar to those found in X. sacchari strain LMG 476 (nucleic acid sequence of this gene is provided in Supplementary File S4).
2.6. Variability of the Locus Encoding the Type IV Pilus
Bacterial pili are filamentous flexible cell-surface appendages involved in numerous bacterial virulence processes, including attachment and invasion, biofilm formation, twitching motility, cellular invasion, and transport of protein and DNA across membranes [47,48]. Biogenesis of a type IV pilus involves a large number of proteins, with PilA representing the major pilin subunit and thus the main structural protein of the type IV pilus. The sequence variability in the pilA gene observed among sequenced Xanthomonas could be correlated with host specificity [49]. In Xanthomonas fuscans subsp. fuscans, PilA is involved in adhesion and transmission to seeds, and mutation of pilA results in reduced pathogenicity on bean [50]. It has also been reported that this variability could be due to the selective pressure exerted by phages, leading to optimization of plant interactions and bacterial infection by phages [51,52,53]. All genes within the locus pilDCABRS exhibit higher amino acid similarity between X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1 than with both MUS 060 and GPE 39 isolates, except for gene pilA, for which an even stronger polymorphism is observed between X. albilineans strains. PilA protein of strains GPE PC73 and GPE 39 share 77% similarity, whereas PilA from Xa23R1 is highly divergent from that of strains GPE PC73, GPE 39 and MUS 060 at both nucleic acid and amino acid sequence levels. Furthermore, PilA identified in the MUS 060 genome exhibits no significant similarity with PilA encoded by GPE PC73, Xa23R1 and GPE 39. The complete pilVWXYE gene cluster exhibits higher amino acid similarity between X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1 than with either of the MUS 060 and GPE 39 isolates, whereas this locus in MUS 060 exhibits higher amino acid similarity with the two X. albilineans strains than with GPE 39.
2.7. CRISPR and Restriction-Modification System Loci
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPRs) are repetitive structures in bacteria and Archaea composed of exact 24- to 48-bp repeated sequences (“repeats”) separated by unique sequences of similar length (“spacers”). Additionally, CRISPRs are characterized by CRISPR-associated (cas) genes and a leader sequence located near the repeats (see e.g., [54,55]). CRISPRs systems are involved in phage and plasmid defense, thus limiting HGT. Sequencing of the genome of X. albilineans strain GPE PC73 revealed the presence of two different CRISPR/cas systems named CRISPR-1 and CRISPR-2, respectively [7]. The CRISPR-2 locus is associated with six cas genes (cas1, cas3, csy1, csy2, csy3 and csy4) and contains 28-bp repeats. CRISPR-2 is shared by the four strains of this study (X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1 and “X. pseudalbilineans” strains GPE 39 and MUS 060), as well as by Xanthomonas campestris pv. raphani [7,56]. Interestingly, regarding CRISPR-2, the nucleic acid sequences of the repeats are 100% identical among the four strains, thus confirming the common origin of this locus. In contrast, no common CRISPR-2 spacers are shared by the four strains, underlying distinct phage exposure and strain adaptation according to their respective environment. Furthermore, spacers of MUS 060 and GPE 39 isolates show no identity to phages described in GenBank to date. None of the CRISPR-2 spacers of strain MUS 060 exhibit identity with other nucleic acid sequences of its own genome or with genomes of strains GPE PC73, Xa23R1 and GPE 39. Also, none of the CRISPR-2 spacers of strain GPE 39 share identity with other nucleic acid sequences of its own genome, but spacer-2 is 96% identical to spacer-13 of the CRISPR-1 system of GPE PC73, and spacer-54 is 100% identical to a gene sequence located in one of the three plasmids of strain GPE PC73 (XALr_3262). The CRISPR-1 locus, present only in strains GPE PC73 and GPE 39, is associated with seven cas genes (cas3, cas5d, csd1, csd2, cas4, cas1 and cas2) and contains 31-bp repeats. The nucleic acid sequences of CRISPR-1 repeats are 100% identical in both strains and all CRISPR-1 spacers from strains GPE PC73 and GPE 39 are specific to each strain. The CRISPR-1 locus is also conserved in other strains belonging to X. oryzae pv. oryzae, X. axonopodis pv. citri, X. campestris pv. vasculorum or X. campestris pv. musacearum [7].
The genomes of strains GPE PC73 and GPE 39 both contain distinct restriction-modification systems that also could contribute to resistance against phages. Strain GPE PC73 possesses a restriction enzyme (XALc_2635) associated with a XamI N6-adenine methyltransferase (XALc_2634). Strain GPE 39 possesses two other type II restriction endonucleases: (i) PaeR71 associated with N4/N6 methyltransferase PaeR71, which is 100% identical to those found in a X. axonopodis strain (GenBank Accession No. WP_017173568 and WP_017173569, respectively) and (ii) another type II restriction endonuclease associated with a C-5 cytosine methyltransferase (nucleic acid sequence of these genes is provided in Supplementary File S4). The presence of such restriction-modification systems as well as of CRISPR-1 in both GPE PC73 and GPE 39, but not in Xa23R1 and MUS 060, suggests that strains GPE PC73 and GPE 39 are better adapted to both phage-containing environments and epiphytic survival.
2.8. Other Genes or Loci Specific to X. albilineans
Among the 206 genes that are conserved in the two strains of X. albilineans and absent in “X. pseudalbilineans” strains (i.e., genes specific to the X. albilineans species) are genes encoding the SPI-1 T3SS. This particular secretion system, usually found in mammals and insect bacterial pathogens or symbionts, exhibits high similarity to one described in Burkholderia pseudomallei [8,57]. Although the SPI-1 T3SS is not associated directly with the pathogenicity of X. albilineans based on our knockout mutant analysis [8], it may nevertheless be required for bacterium-plant interaction, in particular to establish plant colonization, as reported for Salmonella typhimurium in Arabidopsis thaliana [58].
The MUS 060 and GPE 39 genomes also lack a locus encoding glycogen biosynthesis. In strain GPE PC73, this locus comprises six genes: glgA (XALc_2591), glgB (XALc_2592), a gene encoding a glucanotransferase (XALc_2593), glgY (XALc_2594), a short gene with unknown function (XALc_2595), and glgX (XALc_2596). Compared to the glycogen metabolism locus usually found in other xanthomonads, glgC and glgP genes are missing in X. albilineans genomes [59]. The glg locus is missing in both “X. pseudalbilineans” strains, as is also the case for Xanthomonadales Xylella fastidiosa strain 9a5c and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain R551-3 [59]. HGT events have been suggested to play an important role in the evolutionary history of glg genes and these latter genes may confer some advantages to the bacteria for better survival under varying environmental conditions [59]. Although glycogen is not an essential component for bacterial growth or survival, the loss of glg genes from the glycogen pathway may reduce the survival time of bacteria when placed in an environment lacking an exogenous carbon source. It has been reported previously that the lack of bacterial glycogen metabolism is a trait associated with parasitic or symbiotic behavior of bacteria [60]. The gene encoding a helicase found in X. albilineans strains (XALc_3107 in GPE PC73) and in other xanthomonads including X. sacchari LMG 476, is missing in both “X. pseudalbilineans” strains. An additional 155 CDSs that encode hypothetical proteins or proteins with diverse functions are also missing in strains MUS 060 and GPE 39.
2.9. Other Genes or Loci Specific to “X. pseudalbilineans”
Strains MUS 060 and GPE 39 share 128 CDSs encoding hypothetical proteins or proteins with diverse functions, among which are three specific methyltransferases not associated with a cognate restriction endonuclease. However, these orphan methyltransferases may play a role in regulatory processes of isolates MUS 060 and GPE 39 in functions such as replication, transcription, DNA repair and population evolution [61].
Among the 977 genes specific to strain MUS 060, the following are of particular interest (nucleic sequence of these genes is provided in Supplementary File S4): (i) seven clustered genes involved in surface polysaccharide biosynthesis. These genes are identical to those identified in X. sacchari LMG 476 genome, exhibiting 80%–89% nucleic acid sequence identity. According to their protein domains, the encoded proteins are predicted to correspond to a glycosyl transferase, a polysaccharide biosynthesis protein, a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent transferase, an acyl-CoA N-acyltransferase, a glycosyl hydrolase, a sugar O-acyltransferase and a dTDP-6-deoxy-3,4-keto-hexulose isomerase. (ii) a large CDS (1450 amino acids) that shows no significant amino acid similarity to other bacteria found in GenBank, but which consists of a C-terminal autotransporter domain associated with an N-terminal passenger domain as well as four autotransporter-associated beta-stranded repeat domains and a left-handed parallel beta-helix (LbH) domain. The presence of such domains, usually found in autotransporter proteins of the type V secretion system of Gram-negative bacteria, suggests a possible adhesion function associated with this CDS; however, the involvement of this protein in bacterial virulence and attachment to leaves remains to be demonstrated.
2.10. Genome Erosion
A previous OrthoMCL study identified 592 ancestral genes present in strain 85-10 of X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria that are absent in strain GPE PC73 and considered as genes lost by X. albilineans during its speciation [6]. BLAST analysis showed that 359 of these 592 genes are present in X. sacchari. A new OrthoMCL analysis, including strain 85-10 of X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria, indicated that 295 of these 359 CDSs are absent in both MUS 060 and GPE 39 strains. Considering the MLSA tree presented in Figure 1, the 295 CDSs present in X. sacchari strain LMG 476 and absent in X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” strains most probably correspond to ancestral genes lost by a common ancestor of these two species. The chromosome size of strain GPE PC73 is 3.8 Mb and the genome sizes of strains Xa23R1, MUS 060 and GPE 39, estimated on the basis of draft genome sequences, are 3.5 Mb, 3.9 Mb and 3.5 Mb, respectively. The G + C content of X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” genomes is 63%, while the G + C content of X. sacchari strain LMG 476 genome is 69% [25]. Genome erosion is associated with elevated frequencies of adenine and thymine (A + T) in obligate host-associated bacteria (see e.g., [62,63]). A lower G + C content for X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” species supports the hypothesis that genome erosion occurred in a common ancestor of these two species. Acquisition of the albicidin locus was postulated to be one of the triggers for genome reduction in the ancestor of X. albilineans; Pieretti et al. [6] proposed that albicidin production in the X. albilineans ancestor induced the SOS response to bypass DNA damage occurring from gyrase inhibition and thus caused genome rearrangements and mutation. Genome erosion eventually stopped when the gene encoding the bacterial DNA gyrase mutated, conferring resistance to the toxin [6]. The presence of the albicidin locus in strain MUS 060 suggests that this locus was present in the common ancestor of X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” and supports the hypothesis of a link between acquisition of the albicidin locus and genome erosion. Further experimental studies will be required to study the susceptibility to albicidin of the DNA gyrase of X. sacchari in order to explore this hypothesis.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strains and DNA Preparation
Characteristics of the bacterial strains used in this study are summarized in Table 1. Pure cultures of bacterial strains GPE 39, MUS 060 (NCPPB 208) and Xa23R1 stored at CIRAD’s collection (Montpellier, France) were grown for 48 h at 28 °C in Wilbrink’s liquid medium [64] for isolation of total genomic DNA using a Qiagen DNeasy Tissue extraction kit (Qiagen SA, Courtaboeuf, France) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.

Table 1.
Description of Xanthomonas strains analyzed.
| Organism | Geographical Origin | Date of Isolation | Biological Origin | GenBank Accession n° | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X. albilineans GPE PC73 | Caribbean/Guadeloupe | 2006 | Sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) | GCA_000087965.1 | [6] |
| X. albilineans Xa23R1 | USA/Florida | 1993 | Sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) | JZIK00000000 | [65] |
| “X. pseudalbilineans” MUS 060 | Indian ocean/Mauritius | 1940 | Dallis grass (Paspalum dilatatum Poir.) | JZIM00000000 | [21] |
| “X. pseudalbilineans” GPE 39 | Caribbean/Guadeloupe | 1997 | Water droplets collected on leaves of sugarcane | JZHZ00000000 | [19] |
| X. sacchari LMG 476 | Caribbean/Guadeloupe | 1980 | Sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) | JXQE00000000 | [25] |
| X. sacchari NCPPB4393 | Africa/Tanzania | 2007 | Insect collected on a banana plant (Musa spp.) | AGDB00000000 | [26] |
| X. sacchari R1 | China/Heilongjiang | 2011 | Asymptomatic seed of rice (Oriza sativa) | GCA_000815185.1 | [28] |
3.2. DNA Sequencing and Assembly
Shotgun sequencing of strains Xa23R1 and GPE 39 was performed on a Solexa GAIIx (Illumina) sequencer (Genoscope, Évry, France), yielding 35,491,178 and 32,445,653 76-bp paired-end reads, respectively, with an insert size of 200 bp. Whole genome shotgun (WGS) BioProject sequences of strains Xa23R1 and GPE 39 have been deposited with the BioProject/GenBank databases under the references PRJNA270034 and PRJNA270166, respectively.
Shotgun sequencing of strain MUS 060 was performed on a MiSeq 2000 sequencer (Fasteris, Geneva, Switzerland), yielding 3,139,946 125-bp paired-end reads. WGS BioProject of strain MUS 060 has been deposited with the BioProject/GenBank database under the reference PRJNA270312.
The draft assemblies of strains Xa23R1, GPE 39 and MUS 060 are available from the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under accession numbers JZIK00000000, JZHZ00000000 and JZIM00000000, respectively.
We used a combination of Velvet [66], SOAPdenovo and SOAPGapCloser [67] to assemble the three strains Xa23R1, GPE 39 and MUS 060. This protocol yielded 4, 8 and 126 scaffolds, respectively, larger than 500 bp, and a largest scaffold of 3,529,636 bp, 3,511,121 bp, and 670,305 bp (using X. albilineans GPE PC73 as a reference for guided scaffolding final step for Xa23R1 and GPE 39) for a total assembly size of 3,538,317 bp, 3,528,360 bp and 3,857,307 bp (excluding scaffolding gaps).
3.3. Genotyping with 16S–23S rRNA ITS and 16S rRNA Gene Sequence
16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequences and the 16S–23S rRNA internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) of strains MUS 060, GPE 39, X. sacchari LMG 476, X. sacchari NCPPB4393, X. sacchari R1 and X. albilineans Xa23R1 were searched on their respective draft genome sequences (see corresponding accessions in Table 1) using blastn (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastHome [68]) with the query being the 16S ribosomal DNA sequence provided by the reference strain GPE PC73. The seven resulting sequences were compared using the MAFFT alignment program (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/ [69] (see sequences and alignments in Supplementary Files S1 and S2, respectively).
3.4. Phylogenetic Core Genome Analysis: MLSA
MLSA based on seven complete housekeeping genes (atpD, dnaK, efp, glnA, groL, gyrB and recA) was performed on MUS 060 and GPE 39 isolates, on X. sacchari strains (strains NCPPB4393, R1 and LMG 476), on X. albilineans strains (strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1) as well as on Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria strain 85–10 (see Table 1 for references and GenBank accessions of available genome sequences). Alignment of concatenated nucleotide gene sequences performed with MAFFT alignment program using default parameters [69] resulted in a 10,490-bp long sequence (including gaps) (see alignment in Supplementary File S5). The phylogenetic core genome MLSA tree was generated using the maximum likelihood method implemented in the PhyML program version 3 [70] with GTR as substitution model and four gamma-distributed rate categories to account for rate heterogeneity across sites. Five hundred bootstrap replicates were performed and X. axonopodis pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 was used to root the consensus tree.
3.5. Whole-Genome Sequences Analyses: ANI Calculation
Genomic relatedness between strain MUS 060, strain GPE 39, X. albilineans strains GPE PC73 and Xa23R1, and X. sacchari strains NCPPB4393, R1 and LMG 476 was estimated using whole-genome sequencing data of each strain. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) was calculated with ANIb and ANIm software, respectively, based on BLASTN and MUMmer algorithms using the tool JSpecies and default parameters (http://www.imedea.uib.es/jspecies/ [32]) (see ANI scores in Supplementary File S3).
3.6. OrthoMCL Analyses
Identification of orthologous groups between Xa23R1, GPE 39, MUS 060 and GPE PC73 genomes was achieved by orthoMCL analyses [35]. OrthoMCL clustering analyses were performed using the following parameters: p-value Cut-off = 1 × 10−5; Percent Identity Cut-off = 0; Percent Match Cut-off = 80; MCL Inflation = 1.5; Maximum Weight = 316. We modified OrthoMCL analysis by inactivating the filter query sequence during the BLASTP pre-process. From results are defined unique CDSs, corresponding to CDSs present only in one copy in one genome, and groups of orthologs that correspond to CDSs present in one copy in at least two genomes. The main part of comparative analyses of genomes and figures are deduced from their distribution. Groups of homologs refer to groups of orthologs having or not having paralogs.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed draft genome sequences of two previously collected isolates belonging to the Xanthomonas genus: strain GPE 39 isolated from water droplets on S. officinarum leaves in Guadeloupe, and strain MUS 060 collected from P. dilatatum in Mauritius. Our comparative study also included genome sequencing data of two strains of X. albilineans and three strains belonging to X. sacchari. Comparative analyses, including ANI and MLSA analyses, revealed that GPE 39 and MUS 060 belong to a new species. Because GPE 39 and MUS 060 are close to the X. albilineans species, with which they form a phylogenetic sister clade, we hereby propose the name “X. pseudalbilineans” for this novel species. Compared to X. sacchari, X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” species have experienced genome erosion that probably occurred predominantly in the common progenitor of both species. Genes encoding the injectisome and associated effectors of the Hrp-T3SS are missing in the genome of X. sacchari, X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” species. Unlike the sugarcane pathogen X. albilineans, which is able to colonize the xylem vessels of sugarcane, previous experimental studies showed that strains GPE 39 and MUS 060 failed to colonize sugarcane stalks systemically [19,21]. The host range specificity and, more broadly, the ecological niche of strains GPE 39 and MUS 060 remain unclear. X. albilineans and “X. pseudalbilineans” have probably specialized in separate environmental niches. The presence of the same LPS form (LPS1) in sugarcane pathogens (X. albilineans strains) and in the P. dilatatum pathogen (MUS 060 strain) is in accordance with a previous study showing no apparent correlation between LPS variation and host- or tissue-specificity [71]. Among the set of accessory genes of “X. pseudalbilineans” and X. albilineans strains, we listed some candidate genomic determinants that may play a role in the life cycle of these bacteria. In depth functional analyses are now required to explore the role of these genes in the successful invasion of sugarcane xylem vessels by X. albilineans. Further analyses conducted on a larger collection of strains of “X. pseudalbilineans” should help us to better understand the genetic determinants involved in niche-specific adaptation of “X. pseudalbilineans” and to complete species demarcation, for which borders with X. albilineans are narrow.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
We thank Martial Briand for his help in using the ANI calculation software, and François Bonnot for his help in R-analysis of OrthoMCL data. We are indebted to Valérie Barbe at Genoscope for sequencing of strains Xa23R1 and GPE 39. This work was supported by Genoscope, Institut de génomique CEA/DSV, Evry, France (AP10/11-28 projet Xanthomonas numéro 28 ROTT). We are indebted to Fasteris Company for sequencing of strain MUS 060. We thank Helen Rothnie for English editing.
Author Contributions
Isabelle Pieretti, Monique Royer, Philippe Rott and Stéphane Cociancich conceived the study. Stéphanie Bolot and Sébastien Carrère performed the bioinformatic analyses. Isabelle Pieretti, Monique Royer and Alexandre Morisset performed the genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Isabelle Pieretti, Monique Royer and Stéphane Cociancich wrote the manuscript. Isabelle Pieretti prepared the figures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- North, D.S.; Colonial Sugar Refining Company. Leaf-Scald: A Bacterial Disease of Sugar Cane; Colonial Sugar Refining Company: Sydney, Australia, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.; Robinson, P. Leaf scald. In Sugar-Cane Diseases of the World; Martin, J., Abbott, E., Hughes, C., Eds.; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1961; Volume I, pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Rott, P.; Davis, M. Leaf scald. In A Guide to Sugarcane Diseases; Rott, P., Bailey, R., Comstock, J., Croft, B., Saumtally, A., Eds.; CIRAD-ISSCT: Montpellier, France, 2000; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Klett, P.; Rott, P. Inoculum sources for the spread of leaf scald disease of sugarcane caused by Xanthomonas albilineans in Guadeloupe. Phytopathology 1994, 142, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, S.; Adeolu, M.; Wong, S.; Sohail, M.; Schellhorn, H.E.; Gupta, R.S. A phylogenomic and molecular marker based taxonomic framework for the order Xanthomonadales: Proposal to transfer the families Algiphilaceae and Solimonadaceae to the order Nevskiales ord. nov. and to create a new family within the order Xanthomonadales, the family Rhodanobacteraceae fam. nov., containing the genus Rhodanobacter and its closest relatives. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, I.; Royer, M.; Barbe, V.; Carrere, S.; Koebnik, R.; Cociancich, S.; Couloux, A.; Darrasse, A.; Gouzy, J.; Jacques, M.-A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Xanthomonas albilineans provides new insights into the reductive genome evolution of the xylem-limited Xanthomonadaceae. BMC Genomics 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, I.; Royer, M.; Barbe, V.; Carrere, S.; Koebnik, R.; Couloux, A.; Darrasse, A.; Gouzy, J.; Jacques, M.-A.; Lauber, E.; et al. Genomic insights into strategies used by Xanthomonas albilineans with its reduced artillery to spread within sugarcane xylem vessels. BMC Genomics 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marguerettaz, M.; Pieretti, I.; Gayral, P.; Puig, J.; Brin, C.; Cociancich, S.; Poussier, S.; Rott, P.; Royer, M. Genomic and evolutionary features of the SPI-1 type III secretion system that is present in Xanthomonas albilineans but is not essential for xylem colonization and symptom development of sugarcane leaf scald. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, M.; Koebnik, R.; Marguerettaz, M.; Barbe, V.; Robin, G.; Brin, C.; Carrere, S.; Gomez, C.; Hügelland, M.; Völler, G.; et al. Genome mining reveals the genus Xanthomonas to be a promising reservoir for new bioactive non-ribosomally synthesized peptides. BMC Genomics 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, R.G. Xanthomonas albilineans and the antipathogenesis approach to disease control. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cociancich, S.; Pesic, A.; Petras, D.; Uhlmann, S.; Kretz, J.; Schubert, V.; Vieweg, L.; Duplan, S.; Marguerettaz, M.; Noëll, J.; et al. The gyrase inhibitor albicidin consists of p-aminobenzoic acids and cyanoalanine. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimi, S.M.; Wall, M.K.; Smith, A.B.; Maxwell, A.; Birch, R.G. The phytotoxin albicidin is a novel inhibitor of DNA gyrase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.; Rott, P.; Warmuth, C.; Chatenet, M.; Baudin, P. Intraspecific genomic variation within Xanthomonas albilineans, the sugarcane leaf scald pathogen. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, P.; Arnaud, M.; Baudin, P. Serological and lysotypical variability of Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson, Causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. J. Phytopathol. 1986, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.; Davis, M.J.; Baudin, P. Serological variability in Xanthomonas albilineans, causal agent of leaf scald disease of sugarcane. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.M.; Schenck, S.; Benedict, A.A. Differentiation of Xanthomonas albilineans strains with monoclonal antibody reaction pattern and DNA fingerprints. Plant Pathol. 1996, 45, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaud, C.; Ryan, C. Leaf scald. In Diseases of Sugarcane: Major Diseases; Ricaud, C., Egan, B., Gillaspie, A., Hugues, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Saumtally, S.; Medan, H.; Autrey, L. Evolution of Aerial Infection of Leaf Scald Caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson in Sugarcane. In Proceedings of the XXII Congress, Cartagena, Colombia, 11–15 September 1995; Cock, J., Brekelbaum, T., Eds.; International Society of Sugarcane Technologists: Cartagena, Colombia, 1996; pp. 493–497.
- Daugrois, J.H.; Dumont, V.; Champoiseau, P.; Costet, L.; Boisne-Noc, R.; Rott, P. Aerial contamination of sugarcane in Guadeloupe by two strains of Xanthomonas albilineans. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 109, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoiseau, P.; Rott, P.; Daugrois, J.H. Epiphytic populations of Xanthomonas albilineans and subsequent sugarcane stalk infection are linked to rainfall in Guadeloupe. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian, G. A disease of Paspalum dilatatum in Mauritius caused by a species of bacterium closely resembling Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson. Rev. Agric. Sucr. Ile Maurice 1962, 41, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Daugrois, J.H.; Boisne-Noc, R.; Champoiseau, P.; Rott, P. The revisited infection cycle of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of leaf scald of sugarcane. Func. Plant Sci. Biotech. 2012, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, E.R.; Rosato, Y.B. Phylogenetic analysis of Xanthomonas species based upon 16S–23S rDNA intergenic spacer sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, J.M.; Park, D.C.; Shearman, H.M.; Fargier, E. A multilocus sequence analysis of the genus Xanthomonas. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 31, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieretti, I.; Bolot, S.; Carrère, S.; Barbe, V.; Cociancich, S.; Rott, P.; Royer, M. Draft genome sequence of Xanthomonas sacchari Strain LMG 476. Genome Announc. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studholme, D.J.; Wasukira, A.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Aritua, V.; Thwaites, R.; Smith, J.; Grant, M. Draft genome sequences of Xanthomonas sacchari and two banana-associated xanthomonads reveal insights into the Xanthomonas group 1 clade. Genes 2011, 2, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studholme, D.J.; Wasukira, A.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Aritua, V.; Thwaites, R.; Smith, J.; Grant, M. Correction: Studholme et al., Draft Genome Sequences of Xanthomonas sacchari and Two Banana-Associated Xanthomonads Reveal Insights into the Xanthomonas Group 1 clade. Genes 2011, 2, 1050–1065. Genes 2012, 3, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wu, L.; Ren, D.; Ye, W.; Dong, G.; Zhu, L.; Guo, L. Genome sequence of Xanthomonas sacchari R1, a biocontrol bacterium isolated from the rice seed. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 206, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, C.A. Detection and identification of microorganisms by gene amplification and sequencing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drancourt, M.; Bollet, C.; Carlioz, A.; Martelin, R.; Gayral, J.-P.; Raoult, D. 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis of a large collection of environmental and clinical unidentifiable bacterial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3623–3630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. 16S rRNA Gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: Pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Rossello-Mora, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Papke, R.T. Molecular Phylogeny of Microorganisms; Horizon Scientific Press: Norfolk, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goris, J.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Klappenbach, J.A.; Coenye, T.; Vandamme, P.; Tiedje, J.M. DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Stoeckert, C.J.; Roos, D. OrthoMCL: Identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, N.; Aritua, V.; Kumar, D.; Yu, F.; Jones, J.B.; Graham, J.H.; Setubal, J.C.; Wang, N. Comparative genomic analysis of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citrumelo F1, which causes citrus bacterial spot disease, and related strains provides insights into virulence and host specificity. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6342–6357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darrasse, A.; Carrere, S.; Barbe, V.; Boureau, T.; Arrieta-Ortiz, M.; Bonneau, S.; Briand, M.; Brin, C.; Cociancich, S.; Durand, K.; et al. Genome sequence of Xanthomonas fuscans subsp. fuscans strain 4834-R reveals that flagellar motility is not a general feature of xanthomonads. BMC Genomics 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desaki, Y.; Miya, A.; Venkatesh, B.; Tsuyumu, S.; Yamane, H.; Kaku, H.; Minami, E.; Shibuya, N. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides induce defense responses associated with programmed cell death in rice cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrocelli, S.; Tondo, M.L.; Daurelio, L.D.; Orellano, E.G. Modifications of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri lipopolysaccharide affect the basal response and the virulence process during citrus canker. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.; Bogdanove, A.; Sonti, R. The role of horizontal transfer in the evolution of a highly variable lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis locus in xanthomonads that infect rice, citrus and crucifers. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A.; Sturiale, L.; Dow, J.M.; Erbs, G.; Lanzetta, R.; Newman, M.-A.; Parrilli, M. The elicitation of plant innate immunity by lipooligosaccharide of Xanthomonas campestris. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33660–33668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhölter, F.J.; Niehaus, K.; Pühler, A. Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris: A cluster of 15 genes is involved in the biosynthesis of the LPS O-antigen and the LPS core. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2001, 266, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Strieker, M.; Tanovic, A.; Marahiel, M.A. Nonribosomal peptide synthetases: Structures and dynamics. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010, 20, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postle, K.; Kadner, R.J. Touch and go: Tying TonB to transport. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, F.; Kitajima, S.; Oda, K.; Higasa, T.; Charoenpanich, J.; Hu, X.; Mamoto, R. Polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol form polymer bodies in the periplasm of sphingomonads that are able to assimilate them. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, P.; Fleites, L.; Marlow, G.; Royer, M.; Gabriel, D.W. Identification of new candidate pathogenicity factors in the xylem-invading pathogen Xanthomonas albilineans by transposon mutagenesis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fronzes, R.; Remaut, H.; Waksman, G. Architectures and biogenesis of non-flagellar protein appendages in Gram-negative bacteria. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Rangaraj, N.; Sonti, R.V. Multiple adhesin-like functions of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae are involved in promoting leaf attachment, entry, and virulence on rice. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Sluys, M.A.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Camargo, L.E.A.; Menck, C.F.M.; da Silva, A.C.R.; Ferro, J.A.; Oliveira, M.C.; Setubal, J.C.; Kitajima, J.P.; Simpson, A.J. Comparative genomic analysis of plant-associated bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2002, 40, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darsonval, A.; Darrasse, A.; Durand, K.; Bureau, C.; Cesbron, S.; Jacques, M.-A. Adhesion and fitness in the bean phyllosphere and transmission to seed of Xanthomonas fuscans subsp. fuscans. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.-J.; Chung, I.-Y.; Choi, K.B.; Lau, G.W.; Cho, Y.-H. Genome sequence comparison and superinfection between two related Pseudomonas aeruginosa phages, D3112 and MP22. Microbiology 2007, 153, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhedbi-Hajri, N.; Darrasse, A.; Pigne, S.; Durand, K.; Fouteau, S.; Barbe, V.; Manceau, C.; Lemaire, C.; Jacques, M.-A. Sensing and adhesion are adaptive functions in the plant pathogenic xanthomonads. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasukira, A.; Coulter, M.; al-Sowayeh, N.; Thwaites, R.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Kubiriba, J.; Smith, J.; Grant, M.; Studholme, D. Genome sequencing of Xanthomonas vasicola pathovar vasculorum reveals variation in plasmids and genes encoding lipopolysaccharide synthesis, type-IV pilus and type-III secretion effectors. Pathogens 2014, 3, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrangou, R.; Fremaux, C.; Deveau, H.; Richards, M.; Boyaval, P.; Moineau, S.; Romero, D.A.; Horvath, P. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 2007, 315, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenova, E.; Nagornykh, M.; Pyatnitskiy, M.; Artamonova, I.I.; Severinov, K. Analysis of CRISPR system function in plant pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 296, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanove, A.J.; Koebnik, R.; Lu, H.; Furutani, A.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Patil, P.B.; van Sluys, M.-A.; Ryan, R.P.; Meyer, D.F.; Han, S.-W.; et al. Two new complete genome sequences offer insight into host and tissue specificity of plant pathogenic Xanthomonas spp. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5450–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.P.; Wood, M.W.; Taylor, L.A.; Monaghan, P.; Hawes, P.; Jones, P.W.; Wallis, T.S.; Galyov, E.E. An Inv/Mxi-Spa-like type III protein secretion system in Burkholderia pseudomallei modulates intracellular behaviour of the pathogen. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schikora, A.; Virlogeux-Payant, I.; Bueso, E.; Garcia, A.V.; Nilau, T.; Charrier, A.l.; Pelletier, S.; Menanteau, P.; Baccarini, M.; Velge, P.; et al. Conservation of Salmonella infection mechanisms in plants and animals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro, G.; Viale, A.M.; Montero, M.; Rahimpour, M.; Muñoz, F.J.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Bahaji, A.; Zúñiga, M.; González-Candelas, F.; Pozueta-Romero, J. Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses of Gammaproteobacterial glg genes traced the origin of the Escherichia coli glycogen glgBXCAP operon to the last common ancestor of the sister orders Enterobacteriales and Pasteurellales. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrissat, B.; Deleury, E.; Coutinho, P.M. Glycogen metabolism loss: A common marker of parasitic behaviour in bacteria? Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Mahony, J.; Ainsworth, S.; Nauta, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bacteriophage orphan DNA methyltransferases: Insights from their bacterial origin, function, and occurrence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7547–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A. Microbial minimalism: Genome reduction in bacterial pathogens. Cell 2002, 108, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, A.; Pereto, J.; Gil, R.; Latorre, A. Learning how to live together: Genomic insights into prokaryote-animal symbioses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rott, P.; Abel, M.; Soupa, D.; Feldman, P.; Letourmy, P. Population dynamics of Xanthomonas albilineans in sugarcane plants as determined with an antibiotic-resistant mutant. Plant Dis. 1994, 78, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, P.C.; Costet, L.; Davis, M.J.; Frutos, R.; Gabriel, D.W. At least two separate gene clusters are involved in albicidin production by Xanthomonas albilineans. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4590–4596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Asimenos, G.; Toh, H. Multiple alignment of DNA Sequences with MAFFT. In Bioinformatics for DNA Sequence Analysis; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 537, pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Patil, P.; van Sluys, M.-A.; White, F.F.; Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M.; Rabinowicz, P.; Salzberg, S.L.; Leach, J.E.; Sonti, R.; et al. Acquisition and evolution of plant pathogenesis-associated gene clusters and candidate determinants of tissue-specificity in Xanthomonas. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).