Genetic Characterization of Primordial Germ Cells in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Sample Collection
2.2. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
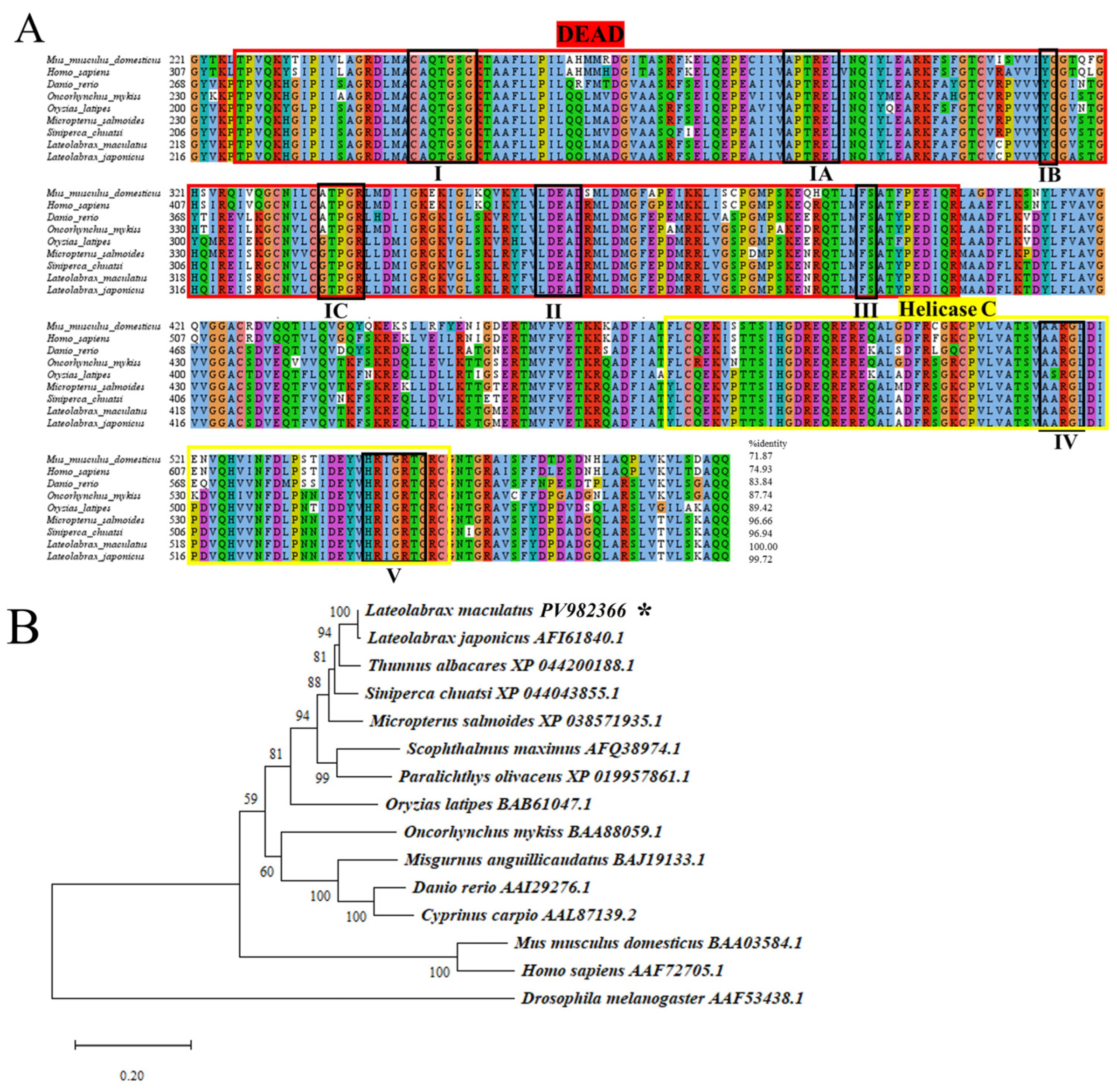
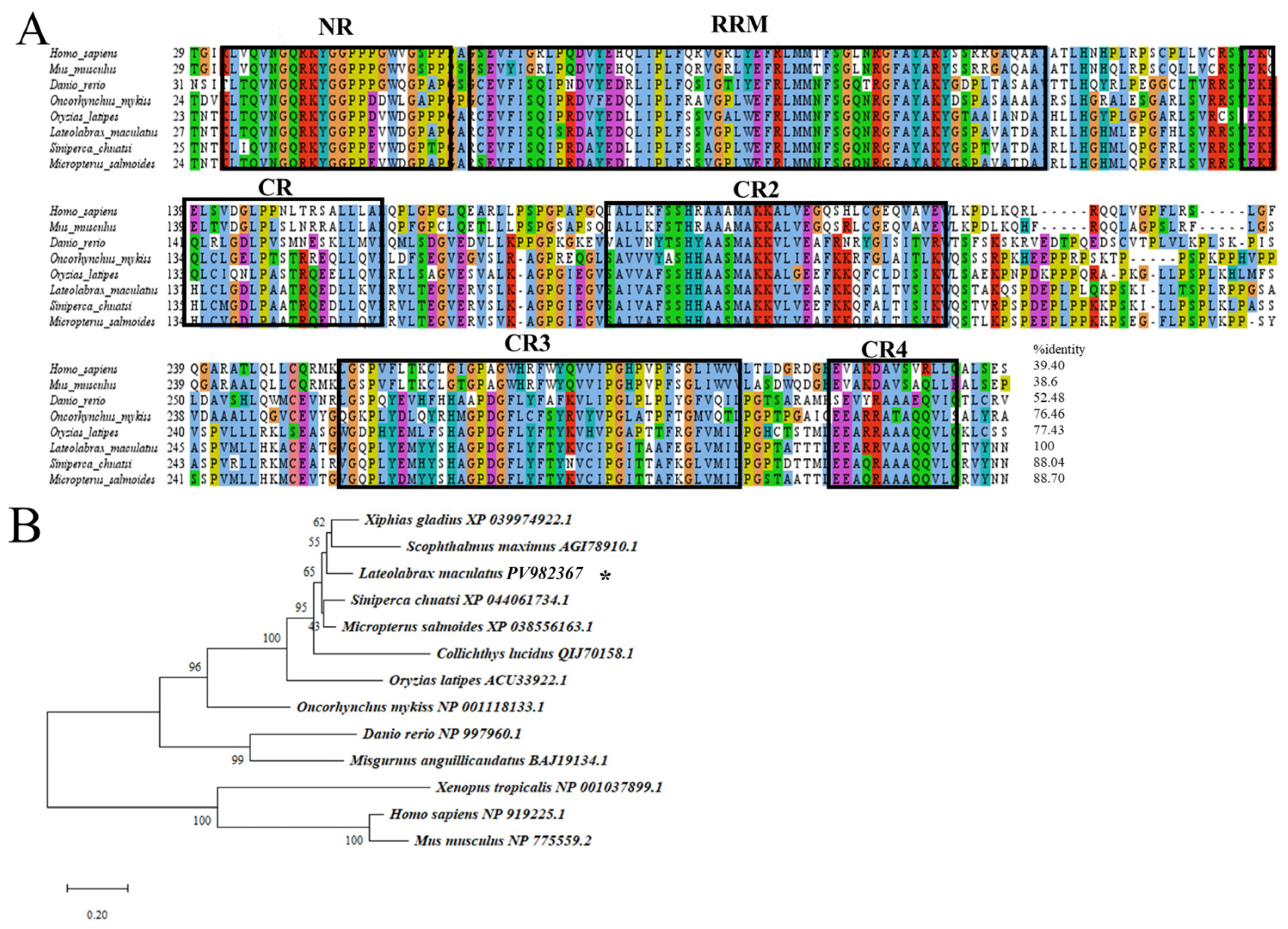
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. RT-qPCR and RT-PCR
2.5. WISH and Histology
2.6. Expression of Recombinant Lmvasa Protein and Preparation of Its Antibody
2.7. Western Blotting Analysis
2.8. Preparation of Chimeric mRNAs and Microinjection
2.9. Microscopy
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Characterization of Lmvasa and Lmdnd
3.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Lmvasa Protein
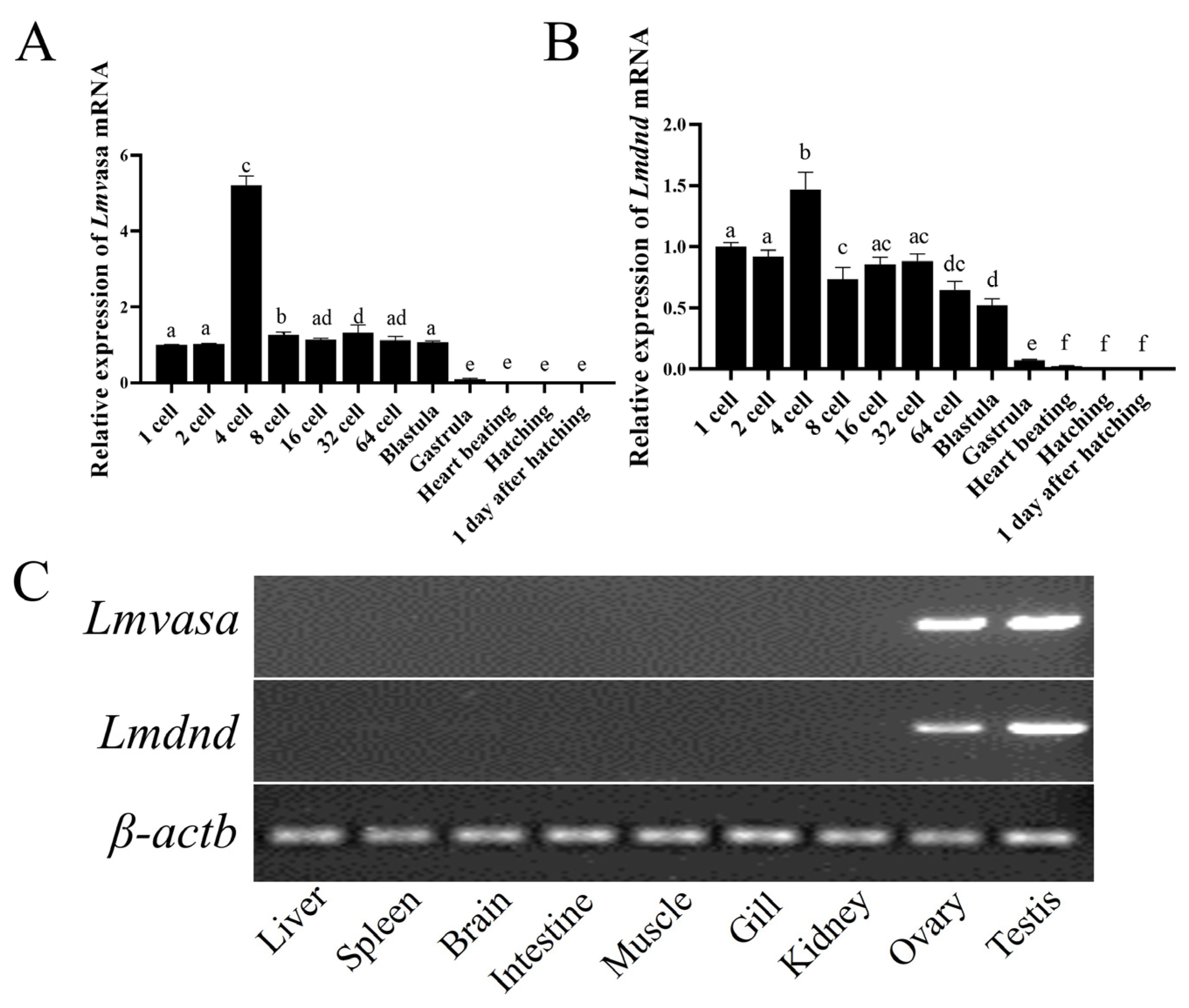
3.3. Lmvasa and Lmdnd Are Specifically Expressed in Germ Cells and During Embryonic Development
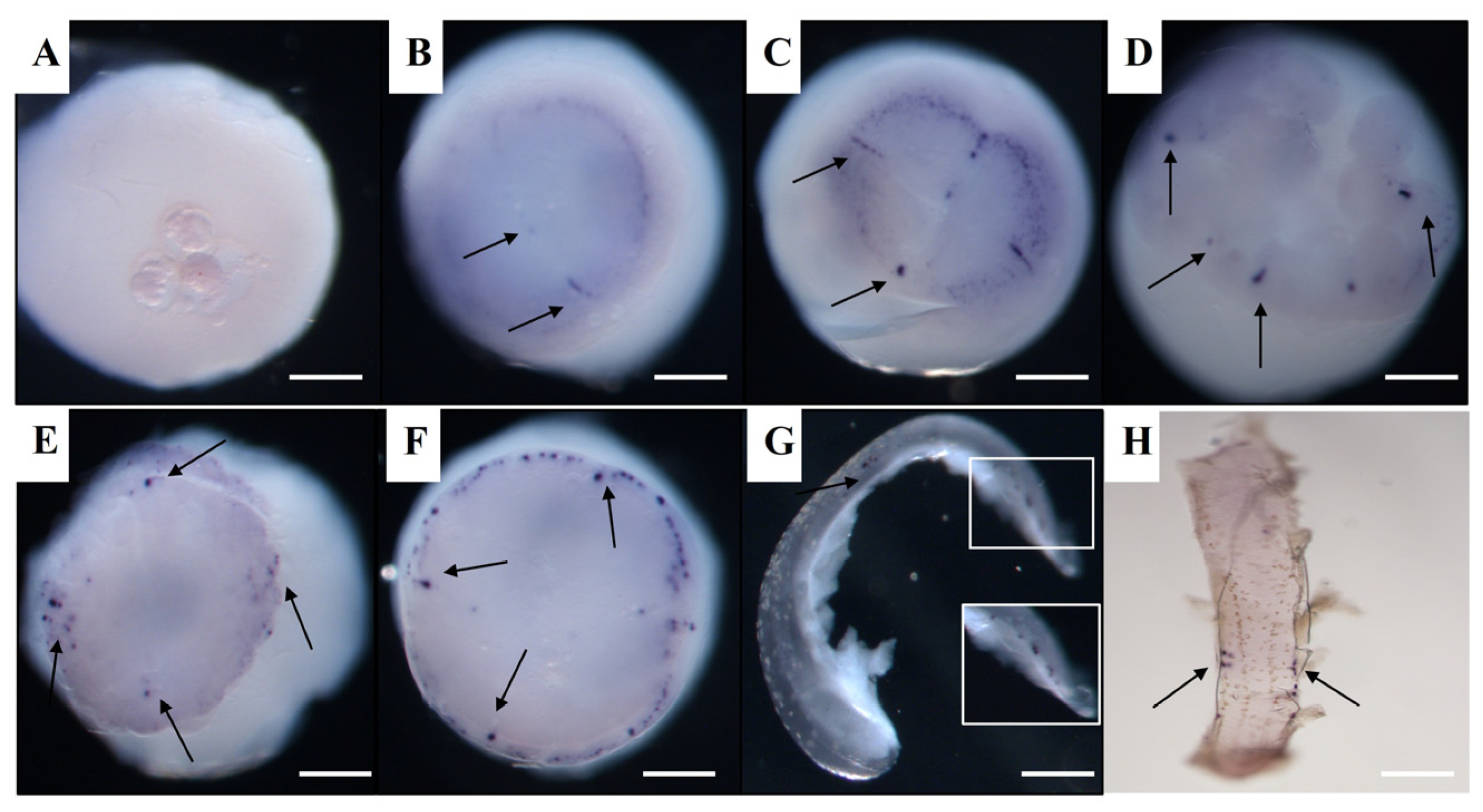
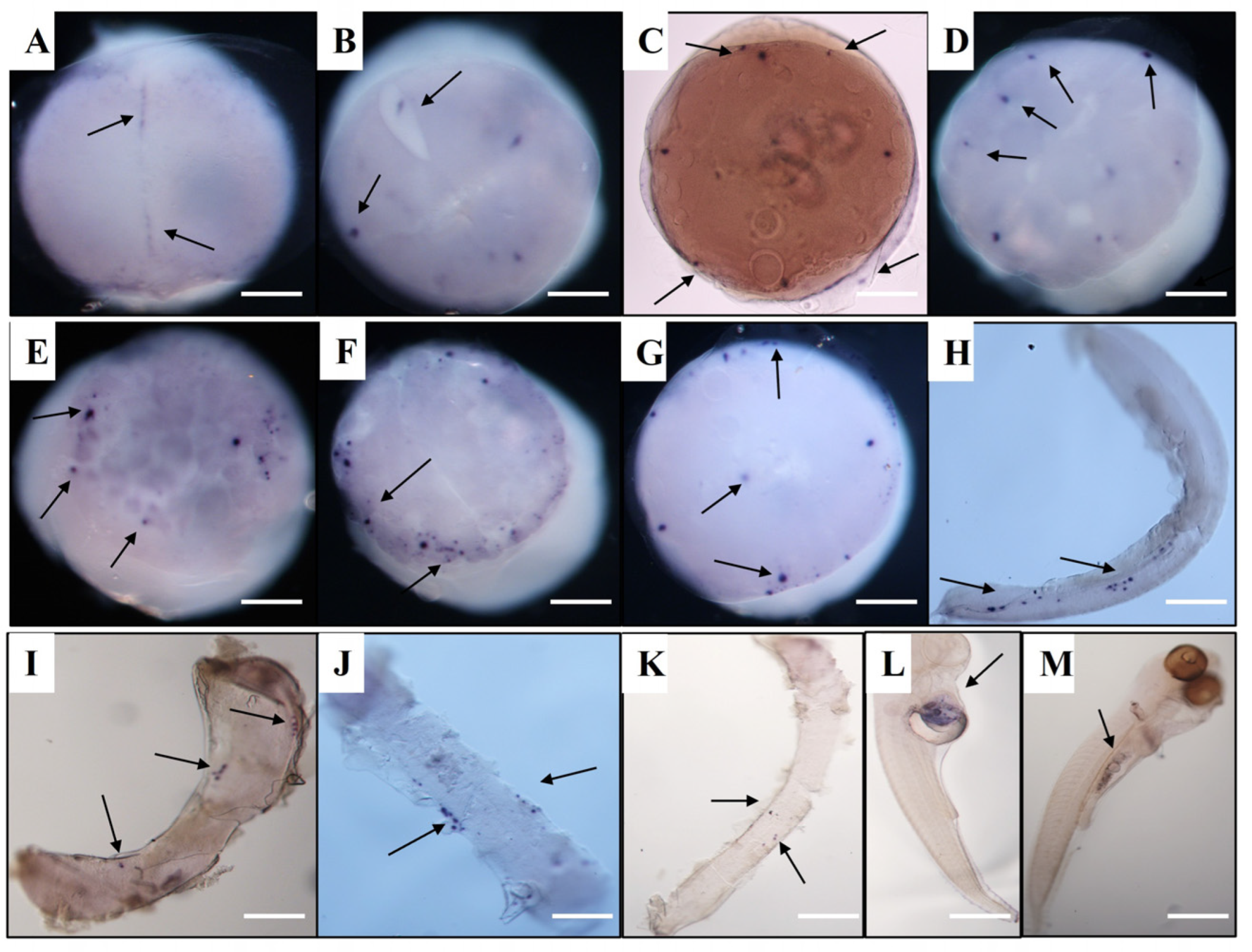
3.4. Vasa and Dnd RNA Localization in Spotted Sea Bass Visualized by WISH
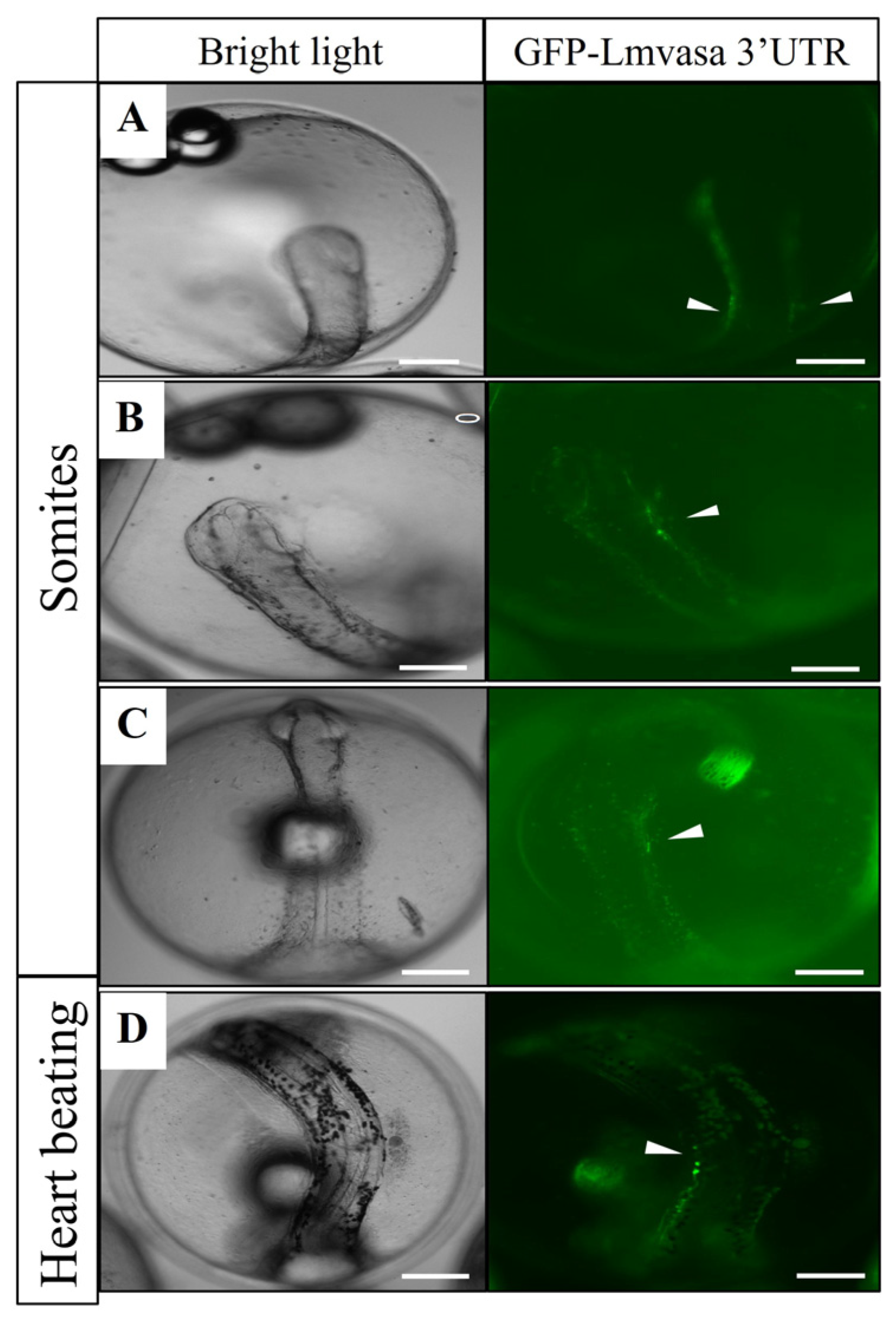
3.5. Visualization of Three Fish PGCs by GFP-Lmvasa 3′-UTR mRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PGCs | Primordial germ cells |
| dnd | Dead end |
| WISH | Whole mount in situ hybridization |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| 3′-UTR | 3′ untranslated region |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| H&E | Hematoxylin-eosin |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| RRM | RNA recognition motif |
| dah | days after hatching |
References
- Raz, E. Primordial germ cell development in zebrafish. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, C. Germ Cells. Cell 2000, 10, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, I.; Aoki, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kinjo, M. Analysis of the molecular dynamics of medaka nuage proteins by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenishi, K.; Nakazato, S.; Okuda, T. Direct Evidence for the Presence of Germ Cell Determinant in Vegetal Pole Cytoplasm of Xenopus laevis and in a Subcellular Fraction of It: (Xenopus laevis/germ cell determinant/germ plasm/PGC induction). Dev. Growth Differ. 1986, 28, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.T.; Zohar, Y. Production of reproductively sterile fish by a non-transgenic gene silencing technology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G.; Takeuchi, T. Biotechnology: Surrogate broodstock produces salmonids. Nature 2004, 430, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.W.; King, M.L. Germ plasm and molecular determinants of germ cell fate. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2000, 50, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshizaki, G.; Sakatani, S.; Tominaga, H.; Takeuchi, T. Cloning and characterization of a vasa-like gene in rainbow trout and its expression in the germ cell lineage. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2000, 55, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüpbach, T.; Wieschaus, E. Maternal-effect mutations altering the anterior-posterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol. 1986, 195, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Diehl-Jones, W.; Lasko, P. Localization of vasa protein to the Drosophila pole plasm is independent of its RNA-binding and helicase activities. Development 1994, 120, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, P.; Lasko, P. Bent out of shape: RNA unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Vasa. Cell 2006, 125, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yajima, M.; Wessel, G.M. The multiple hats of Vasa: Its functions in the germline and in cell cycle progression. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2011, 78, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Kawakami, K.; Hopkins, N. Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 1997, 124, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinomiya, A.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Hamaguchi, S. The vasa-like gene, olvas, identifies the migration path of primordial germ cells during embryonic body formation stage in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Dev. Growth Differ. 2000, 42, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Gui, J.; Hong, Y. Differential expression of vasa RNA and protein during spermatogenesis and oogenesis in the gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio), a bisexually and gynogenetically reproducing vertebrate. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Zhao, C.Y.; Xu, S.H.; Ma, D.Y.; Xiao, Z.Z.; Xiao, Y.S.; Xu, C.A.; Liu, Q.H.; Li, J. Germline-specific and sexually dimorphic expression of a dead end gene homologue in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Theriogenology 2013, 80, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, X.; Tian, X.Q.; Cui, Z.; Feng, H.Y.; Qiu, G.F. Germ plasm and the origin of the primordial germ cells in the oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 386, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaut, H.; Steinbeisser, H.; Schwarz, H.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. An evolutionary conserved region in the vasa 3′UTR targets RNA translation to the germ cells in the zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G.; Takeuchi, T. Generation of live fry from intraperitoneally transplanted primordial germ cells in rainbow trout. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Katayama, N.; Yoshizaki, G. Generation of juvenile rainbow trout derived from cryopreserved whole ovaries by intraperitoneal transplantation of ovarian germ cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; You, F.; Song, Z.; Li, J. Successful Spermatogonial Stem Cells Transplantation within Pleuronectiformes: First Breakthrough at inter-family Level in Marine Fish. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4426–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, A.R.; Franěk, R.; Saito, T.; Pšenička, M. Dead-end (dnd) protein in fish-a review. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidinger, G.; Stebler, J.; Slanchev, K.; Dumstrei, K.; Wise, C.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; Raz, E. dead end, a novel vertebrate germ plasm component, is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvay, K.; Claussen, M.; Katzer, M.; Landgrebe, J.; Pieler, T. Xenopus Dead end mRNA is a localized maternal determinant that serves a conserved function in germ cell development. Dev. Biol. 2006, 291, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngren, K.K.; Coveney, D.; Peng, X.; Bhattacharya, C.; Schmidt, L.S.; Nickerson, M.L.; Lamb, B.T.; Deng, J.M.; Behringer, R.R.; Capel, B.; et al. The Ter mutation in the dead end gene causes germ cell loss and testicular germ cell tumours. Nature 2005, 435, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linger, R.; Dudakia, D.; Huddart, R.; Tucker, K.; Friedlander, M.; Phillips, K.A.; Hogg, D.; Jewett, M.A.; Lohynska, R.; Daugaard, G.; et al. Analysis of the DND1 gene in men with sporadic and familial testicular germ cell tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2008, 47, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, C.; Aggarwal, S.; Zhu, R.; Kumar, M.; Zhao, M.; Meistrich, M.L.; Matin, A. The mouse dead-end gene isoform alpha is necessary for germ cell and embryonic viability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, W.; Jin, Z.; Lai, F.; Schwend, T.; Houston, D.W.; King, M.L.; Yang, J. Maternal Dead-End1 is required for vegetal cortical microtubule assembly during Xenopus axis specification. Development 2013, 140, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiguemoto, G.F.; Coelho, G.C.Z.; López, L.S.; Pessoa, G.P.; Dos Santos, S.C.A.; Senhorini, J.A.; Monzani, P.S.; Yasui, G.S. Primordial germ cell identification and traceability during the initial development of the Siluriformes fish Pseudopimelodus mangurus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, S.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. Both of marine fish species Oryzias melastigma and Pagrus major all failing in early localization at embryo stage by vasa RNA. Gene 2021, 769, 145204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Wen, Z.; Jawad, M.; Gui, L.; Li, M. Spinyhead Croaker Germ Cells Gene dnd Visualizes Primordial Germ Cells in Medaka. Life 2022, 12, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, H.B.; Park, J.Y.; Lim, H.K. Dead-End (dnd) Gene Cloning and Gonad-Specific Expression Pattern in Starry Flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Animals 2021, 11, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Guo, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, P. Population Genomics Reveals Genetic Divergence and Adaptive Differentiation of Chinese Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, L.; Lin, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, L. Asymmetric evolution of ISG15 homologs and the immune adaptation to LBUSV infection in spotted seabass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 148, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Ouyang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of Lateolabrax maculatus from Chinese coastal waters using polymorphic microsatellite markers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Lim, M.; Dwarakanath, M.; Hong, Y. Vasa identifies germ cells and critical stages of oogenesis in the Asian seabass. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ye, H.; Xu, H. Transcriptome Profiling of the Ovarian Cells at the Single-Cell Resolution in Adult Asian Seabass. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 647892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Holterman, M.; Karssen, G.; Mooyman, P.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. A phylogenetic tree of nematodes based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology 2009, 11, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Qiu, L. RNA-Seq-based transcriptome analysis of reproduction- and growth-related genes in Lateolabrax japonicus ovaries at four different ages. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; Oates, A.C. Detection of mRNA by Whole Mount in situ Hybridization and DNA Extraction for Genotyping of Zebrafish Embryos. Bio Protoc. 2019, 9, e3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köprunner, M.; Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; Raz, E. A zebrafish nanos-related gene is essential for the development of primordial germ cells. Genes. Dev. 2001, 15, 2877–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; An, H.; Song, Z.; You, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, J. Germ Cell Migration, Proliferation and Differentiation during Gonadal Morphogenesis in All-Female Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, E.A.; Wessel, G.M. Vasa genes: Emerging roles in the germ line and in multipotent cells. Bioessays 2010, 32, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakharuthai, C.; Sreebun, S.; Kabpha, A.; Phuong, T.V.; Boonanuntanasarn, S. Characterization of ddx4 and dnd Homologs in Snakeskin Gourami (Trichopodus pectoralis) and Their Expression Levels during Larval Development and in Gonads of Males and Females. Animals 2022, 12, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangkaew, R.; Jangprai, A.; Ichida, K.; Yoshizaki, G.; Boonanuntanasarn, S. Characterization and expression of a vasa homolog in the gonads and primordial germ cells of the striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Theriogenology 2019, 131, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Collodi, P. Zebrafish dead end possesses ATPase activity that is required for primordial germ cell development. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hong, N.; Xu, H.; Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Purwanti, Y.; Yi, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Hong, Y. Medaka dead end encodes a cytoplasmic protein and identifies embryonic and adult germ cells. Gene Expr. Patterns. 2009, 9, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, A.K.; Speksnijder, J.E.; Zivkovic, D. Germ line development in fishes. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1999, 43, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reunov, A.A.; Au, D.W.T.; Alexandrova, Y.N.; Chiang, M.W.L.; Wan, M.T.; Yakovlev, K.V.; Reunova, Y.A.; Komkova, A.V.; Cheung, N.K.; Peterson, D.R.; et al. Germ plasm-related structures in marine medaka gametogenesis; novel sites of Vasa localization and the unique mechanism of germ plasm granule arising. Zygote 2020, 28, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, Q. Characterization of vasa and dnd homologs in summer flounder, Paralichthys dentatus: Expression analysis and colocalization of PGCs during embryogenesis. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Xue, L.; Song, P.; Jawad, M.; Xu, C.; Bu, W.; Li, M. Dazl and dnd Identify Both Embryonic and Gonadal Germ Cells in Chinese Hook Snout Carp (Opsariichthys bidens). Fishes 2024, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, Q.; Xu, H.; Wong, F.M.; Cui, J.; Li, Z.; Hong, N.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Ma, B.; et al. Differential conservation and divergence of fertility genes boule and dazl in the rainbow trout. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Gui, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Dnd is required for primordial germ cell specification in Oryzias celebensis. Gene 2018, 679, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Maegawa, S.; Inoue, K.; Tanaka, M.; Arai, K.; Yamaha, E. Visualization of primordial germ cells in vivo using GFP-nos1 3′UTR mRNA. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2006, 50, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, A.K.; Zandbergen, T.; van de Water, S.; Goos, H.J.; Zivkovic, D. Characterization of zebrafish primordial germ cells: Morphology and early distribution of vasa RNA. Dev. Dyn. 1999, 216, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, S.; Kitauchi, T.; Saito, T.; Sakao, S.; Maegawa, S.; Inoue, K.; Arai, K.; Yamaha, E. The formation of primordial germ cells from germline cells in spherical embryos derived from the blastodisc of 2-cell embryos in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2005, 49, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, S.; Zhao, H.; Han, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Li, J. Visualization of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Primordial Germ Cells in vivo Using Fluorescent Protein Mediated by the 3′ Untranslated Region of nanos3 or vasa Gene. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Shao, C.; Lin, F.; Wang, N.; Hu, Q. Molecular characterization, sexually dimorphic expression, and functional analysis of 3′-untranslated region of vasa gene in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Theriogenology 2014, 82, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Du, T.; Yu, J.; Wu, L.; Song, Z.; Liu, Q.; et al. Germline Specific Expression of a vasa Homologue Gene in the Viviparous Fish Black Rockfish (Sebastes schlegelii) and Functional Analysis of the vasa 3′ Untranslated Region. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 575788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Primer Name | Sequence 5′-3′ | Size (bp) | Temperature, °C | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vasa oF | ATGGACGAATGGGAAGAAGAAGGAAC | 1905 | 56 | ORF |
| vasa oR | CTACTCCCATTCTTCATCATCAGCTG | |||
| dnd oF | ATGGAGATGATGGAGAACAAGCGGAGC | 1158 | 56 | |
| dnd oR | TCAGTGGGCAAACTGGTTATTGTACACC | |||
| 5′RACE-vasa | TTCCGATTCTCGTCACCACC | 292 | 70 | RACE |
| 3′RACE-vasa | TATTGGAAGAACTGGCCGCT | 619 | 68 | |
| 5′RACE-dnd | CAGCTCCTGAACACGCTCAAGGT | 300 | 70 | |
| 3′RACE-dnd | GGATAACGGCCGCCTTTGAAGGGC | 414 | 68 | |
| vasa qF | GTGGAACACCAGGGAGACTG | 169 | 60 | RT-qPCR |
| vasa qR | TGACGGTTCTCTTTGGACGG | |||
| dnd qF | GCACGGAGAAGAGACACCTC | 145 | 60 | |
| dnd qR | ATGGCAGACACCCCCTCTAT | |||
| vasa F | CCCACTATGAGACGGGCATC | 394 | 56 | RT-PCR |
| vasa R | CCAAAGGCAAACTTCCTGGC | |||
| dnd F | ACCTTGAGCGTGTTCAGGAG | 377 | 56 | |
| dnd R | GAGGTGTCTCTTCTCCGTGC | |||
| β-actin F | CAACTGGGATGACATGGAGAAG | 114 | 58 | |
| β-actin R | TTGGCTTTGGGGTTCAGG | |||
| vasa-28a F | TGGGTCGCGGATCCGAATTCATGGACGA ATGGGAAGAAGAAG | 1942 | 60 | WISH |
| vasa-28a R | TGGTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCTCCCATTCT TCATCATCAGCT | |||
| WISH-vasa F | GCAGCTGACTTTCTCAAGACGGA | 1013 | 56 | |
| WISH-vasa R | AATTTTTCTTTTTTATTGGTGATC | |||
| WISH-dnd F | ATGGAGATGATGGAGAACAAGCGGAGC | 1158 | 56 | |
| WISH-dnd R | TCAGTGGGCAAACTGGTTATTGTACACC | |||
| 3′UTR-vasa F | ATGAACTATACAAACTCGAGAAGGAATATTAGAGAAGC | 327 | 56 | 3′UTR |
| 3′UTR-vasa R | ATGAACTATACAAATAACTCGAGAAACCCATTAACCAATTTTTCT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, L. Genetic Characterization of Primordial Germ Cells in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Genes 2025, 16, 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091012
Guo J, Yan L, Zhao C, Zhang B, Zhang B, Qiu L. Genetic Characterization of Primordial Germ Cells in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Genes. 2025; 16(9):1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jieyun, Lulu Yan, Chao Zhao, Bo Zhang, Bo Zhang, and Lihua Qiu. 2025. "Genetic Characterization of Primordial Germ Cells in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus)" Genes 16, no. 9: 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091012
APA StyleGuo, J., Yan, L., Zhao, C., Zhang, B., Zhang, B., & Qiu, L. (2025). Genetic Characterization of Primordial Germ Cells in Spotted Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus). Genes, 16(9), 1012. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091012







