Identification of a Pathogenic Mutation for Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease) in Japanese Quails (Coturnix japonica)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Specimens
2.2. Light Microscopy
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Real-Time PCR Assay and Genotyping
3. Results
3.1. Light Microscopic Features
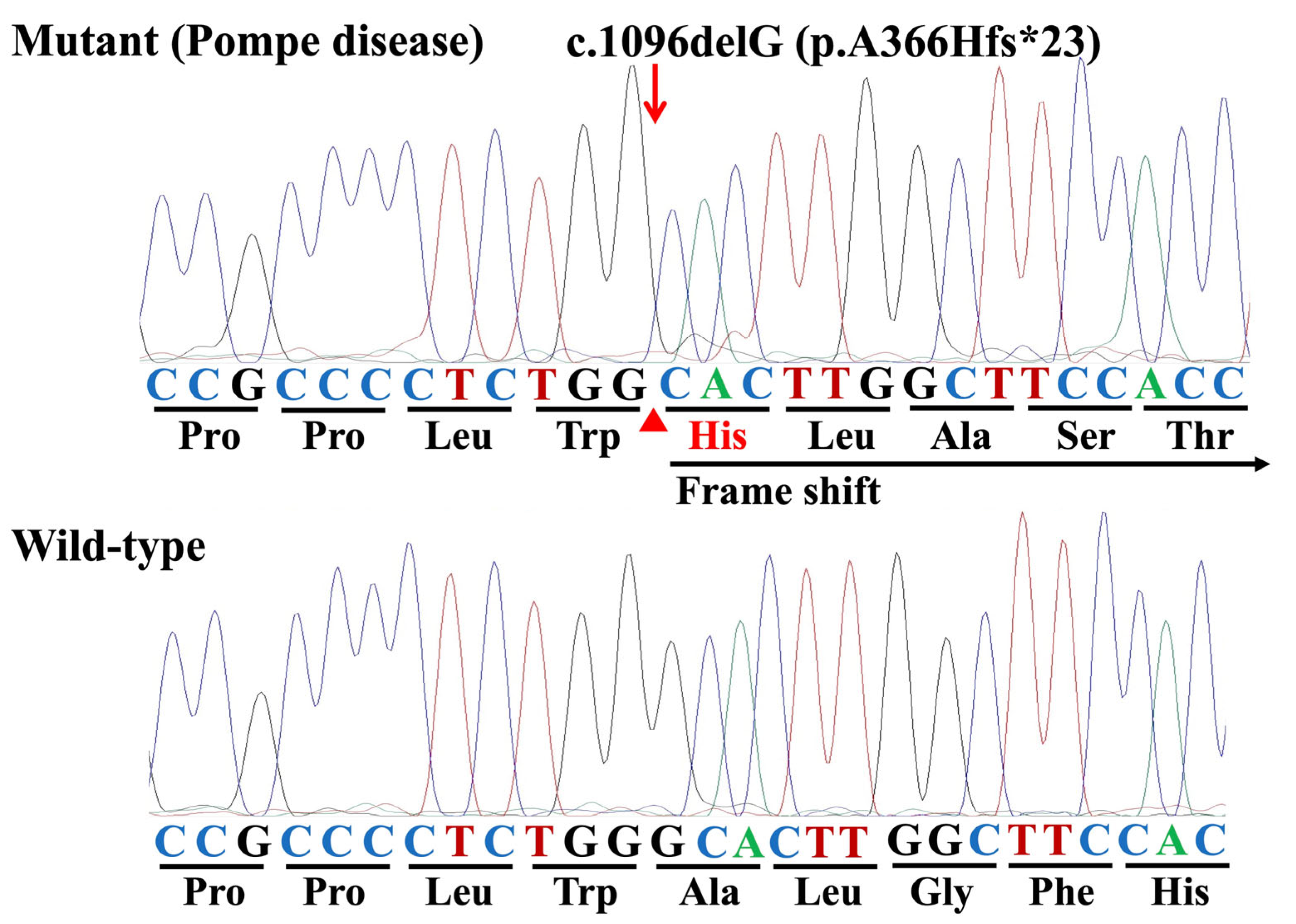
3.2. Identification of Variants and a Mutation
3.3. Genotyping Survey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Pompe disease |
| GAA | acid α-1,4-glucosidase |
| IOPD | infantile-onset Pompe disease |
| LOPD | late-onset Pompe disease |
| OMIA | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals |
| JQ | Japanese quail |
| NIBS | Nippon Institute for Biological Science |
| TMIMS | Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science |
| NIN-NCNP | National Institute of Neuroscience, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| PAS | periodic acid–Schiff |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| NMD | nonsense-mediated mRNA decay |
| ERT | enzyme replacement therapy |
References
- OMIM #232300, Pompe Disease. Available online: https://omim.org/entry/232300 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Raben, N.; Plotz, P.; Byrne, B.J. Acid α-glucosidase deficiency (glycogenosis type II, Pompe disease). Curr. Mol. Med. 2002, 2, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtariye, A.; Hagh-Nazari, L.; Varasteh, A.-R.; Keyfi, F. Diagnostic methods for lysosomal storage disease. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 7, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niño, M.Y.; In’t Groen, S.L.; Bergsma, A.J.; van der Beek, N.A.; Kroos, M.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; van der Ploeg, A.T.; Pijnappel, W.P. Extension of the Pompe mutation database by linking disease-associated variants to clinical severity. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompe Disease GAA Variant Database. Available online: https://www.pompevariantdatabase.clmz.nl/pompe_mutations_list.php?orderby=aMut_ID1 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Fukuhara, Y.; Fuji, N.; Yamazaki, N.; Hirakiyama, A.; Kamioka, T.; Seo, J.-H.; Mashima, R.; Kosuga, M.; Okuyama, T. A molecular analysis of the GAA gene and clinical spectrum in 38 patients with Pompe disease in Japan. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2018, 14, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasouki, M.; Jawdat, O.; Almadhoun, O.; Pasnoor, M.; McVey, A.L.; Abuzinadah, A.; Herbelin, L.; Barohn, R.J.; Dimachkie, M.M. Pompe disease: Literature review and case series. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 751–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.; Conceição, I.; Fineza, I.; Coelho, T.; Silveira, F.; Santos, M.; Valverde, A.; Geraldo, A.; Maré, R.; Aguiar, T.C. Screening for Pompe disease in a Portuguese high-risk population. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2017, 27, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, F.; Buchignani, B.; Unluturk, Z.; Vadi, G.; Loprieno, S.; Battini, R.; Mancuso, M.; Siciliano, G. The involvement of central nervous system across the phenotypic spectrum of Pompe disease: A systematic review. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2025, 51, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals (OMIA). Available online: https://www.omia.org/home/ (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Skelly, B.J.; Franklin, R.J. Recognition and diagnosis of lysosomal storage diseases in the cat and dog. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2002, 16, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodóvar-Payá, A.; Villarreal-Salazar, M.; de Luna, N.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Real-Martínez, A.; Andreu, A.L.; Martín, M.A.; Arenas, J.; Lucia, A.; Vissing, J.; et al. Preclinical research in glycogen storage diseases: A comprehensive review of current animal models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, E.H.; Reuser, A.J.; Lohi, H. A nonsense mutation in the acid α-glucosidase gene causes Pompe disease in Finnish and Swedish Lapphunds. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, B.; Westman, J.; Öckerman, P. Glycogenosis of the central nervous system in the cat. Acta Neuropathol. 1969, 14, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Suzuki, R.; Koyama, H.; Machida, N.; Yabuki, A.; Yamato, O. Glycogen storage disease in a young cat with heart failure. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakib, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Tanaka, S.; Yabuki, A.; Pervin, S.; Maki, S.; Faruq, A.A.; Tacharina, M.R.; Yamato, O. Novel mutation in the feline GAA gene in a cat with glycogen storage disease type II (Pompe disease). Animals 2023, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, J.A.; Moran, C.; Healy, P.J. The bovine α-glucosidase gene: Coding region, genomic structure, and mutations that cause bovine generalized glycogenosis. Mamm. Genome 2000, 11, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manktelow, B.; Hartley, W. Generalized glycogen storage disease in sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 1975, 85, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Takagi, A.; Nonaka, S.; Ishiura, S.; Sugita, H. Glycogenesis II in Japanese quails. Exp. Anim. 1980, 29, 475–485. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, T.; Kuroda, S.; Mizutani, M.; Kiuchi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Ono, T. Generalized glycogen storage disease in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Vet. Pathol. 1983, 20, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunoya, T.; Tajima, M.; Mizutani, M. A new mutant of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) characterized by generalized glycogenosis. Lab. Anim. 1983, 17, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M. Establishment of inbred strains of chicken and Japanese quail and their potential as animal models. Exp. Anim. 2002, 51, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, M. The Japanese quail. In The Relationship between Indigenous Animals and Humans in APEC Region; Chang, H.L., Huang, Y.C., Eds.; The Chinese Society of Animal Science: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 143–163. Available online: https://www.angrin.tlri.gov.tw/apec2003/ (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Higuchi, I.; Nonaka, I.; Usuki, F.; Ishiura, S.; Sugita, H. Acid maltase deficiency in the Japanese quail; early morphological event in skeletal muscle. Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 73, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhara, Y.; Ishiura, S.; Tsukahara, T.; Sugita, H. Mature 98,000-dalton acid α-glucosidase is deficient in Japanese quails with acid maltase deficiency. Muscle Nerve 1989, 12, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunita, R.; Nakabayashi, O.; Wu, J.-Y.; Hagiwara, Y.; Mizutani, M.; Pennybacker, M.; Chen, Y.-T.; Kikuchi, T. Molecular cloning of acid α-glucosidase cDNA of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) and the lack of its mRNA in acid maltase deficient quails. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1362, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, K.; Chang, H.-S.; Yabuki, A.; Kawamichi, T.; Kawahara, N.; Hayashi, D.; Hossain, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.M.; Yamato, O. Novel rapid genotyping assays for neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis in Border Collie dogs and high frequency of the mutant allele in Japan. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.E.; Parker, R. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Terminating erroneous gene expression. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Imam, J.S.; Wilkinson, M.F. The nonsense-mediated decay RNA surveillance pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendran-Braun, S.; Vinatzer, U.; Liebmann-Reindl, S.; Lux, M.; Oliva, P.; Sansen, S.; Mechtler, T.; Kasper, D.C.; Streubel, B. Biochemical and genetic testing of GAA in over 30.000 symptomatic patients suspected to be affected with Pompe disease. Hum. Mutat. 2024, 2024, 6248437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A. Improving the treatment of Pompe disease with enzyme replacement therapy: Current strategies and clinical evidence. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2025, 26, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, L.; Puertollano, R.; Raben, N. Pompe disease: From basic science to therapy. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2018, 15, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Yang, H.W.; Pennybacker, M.; Ichihara, N.; Mizutani, M.; Van Hove, J.L.; Chen, Y. Clinical and metabolic correction of Pompe disease by enzyme therapy in acid maltase-deficient quail. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


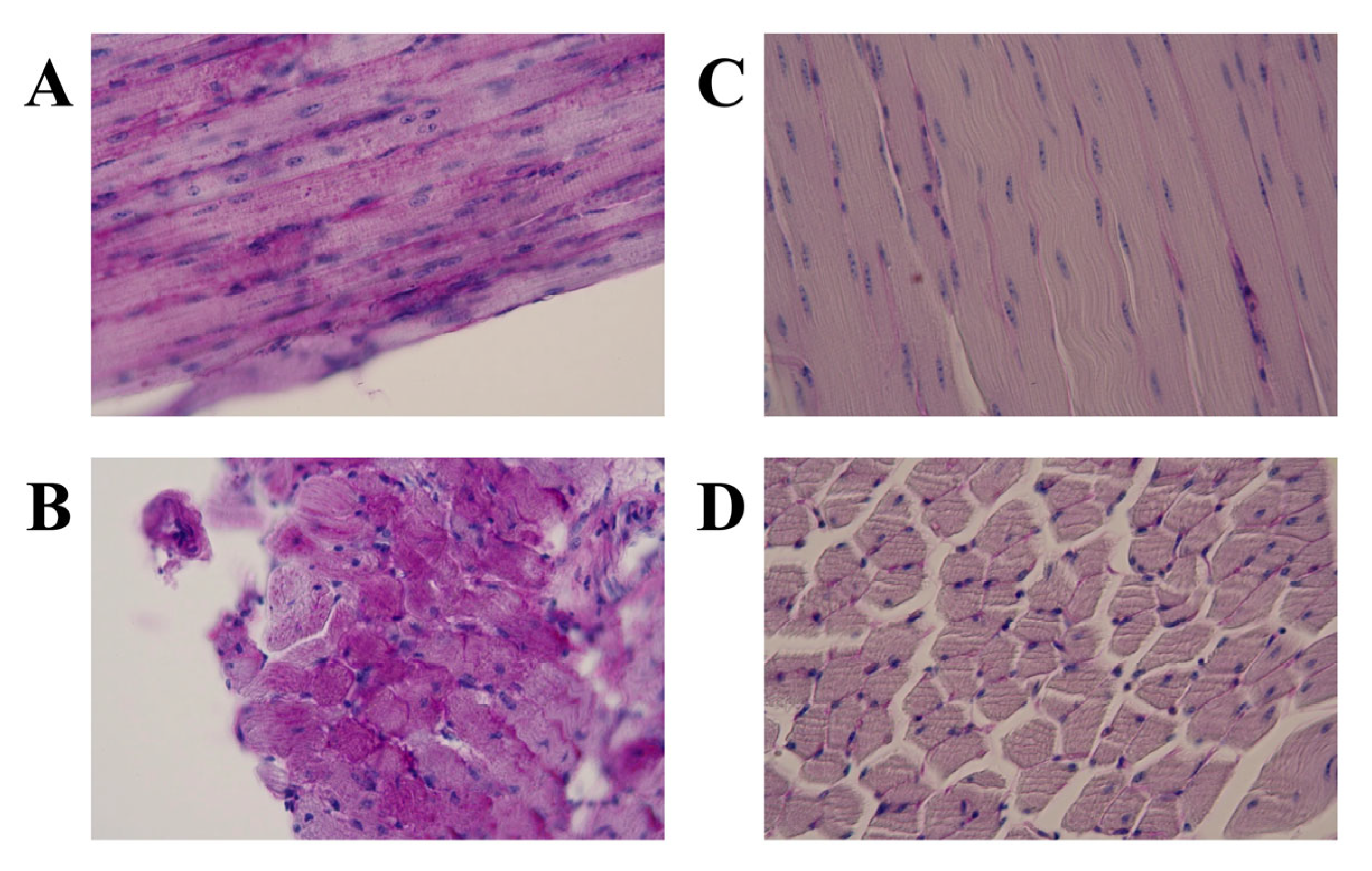
| JQ | Glycogen Accumulation | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive * | Negative ** | |
| PD | 3 (100%) | 0 (0%) |
| Control | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) |
| Exon | Variant (Nucleotide) * | Variant (Amino Acid) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 1 | c.150T>C | p.T50T | synonymous |
| Exon 2 | c.546C>T | p.T182T | synonymous |
| Exon 2 | c.642T>C | p.D214D | synonymous |
| Exon 4 | c.918C>T | p.H306H | synonymous |
| Exon 6 | c.1096delG | p.A366Hfs*23 | deletion (deleterious) |
| Exon 13 | c.1944C>T | p.S648S | synonymous |
| JQ | Number Examined | GAA I:c.1096delG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutant Homozygote | Heterozygote | Wild-Type Homozygote | ||
| New-hatched JQ | 70 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 70 (100%) |
| Egg | 10 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faruq, A.A.; Matsui, T.; Maki, S.; Arakawa, N.; Watanabe, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Rakib, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Yabuki, A.; Yamato, O. Identification of a Pathogenic Mutation for Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease) in Japanese Quails (Coturnix japonica). Genes 2025, 16, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080975
Faruq AA, Matsui T, Maki S, Arakawa N, Watanabe K, Kobayashi Y, Rakib TM, Islam MS, Yabuki A, Yamato O. Identification of a Pathogenic Mutation for Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease) in Japanese Quails (Coturnix japonica). Genes. 2025; 16(8):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080975
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaruq, Abdullah Al, Takane Matsui, Shinichiro Maki, Nanami Arakawa, Kenichi Watanabe, Yoshiyasu Kobayashi, Tofazzal Md Rakib, Md Shafiqul Islam, Akira Yabuki, and Osamu Yamato. 2025. "Identification of a Pathogenic Mutation for Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease) in Japanese Quails (Coturnix japonica)" Genes 16, no. 8: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080975
APA StyleFaruq, A. A., Matsui, T., Maki, S., Arakawa, N., Watanabe, K., Kobayashi, Y., Rakib, T. M., Islam, M. S., Yabuki, A., & Yamato, O. (2025). Identification of a Pathogenic Mutation for Glycogen Storage Disease Type II (Pompe Disease) in Japanese Quails (Coturnix japonica). Genes, 16(8), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080975









