Molecular Genetic Basis of Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
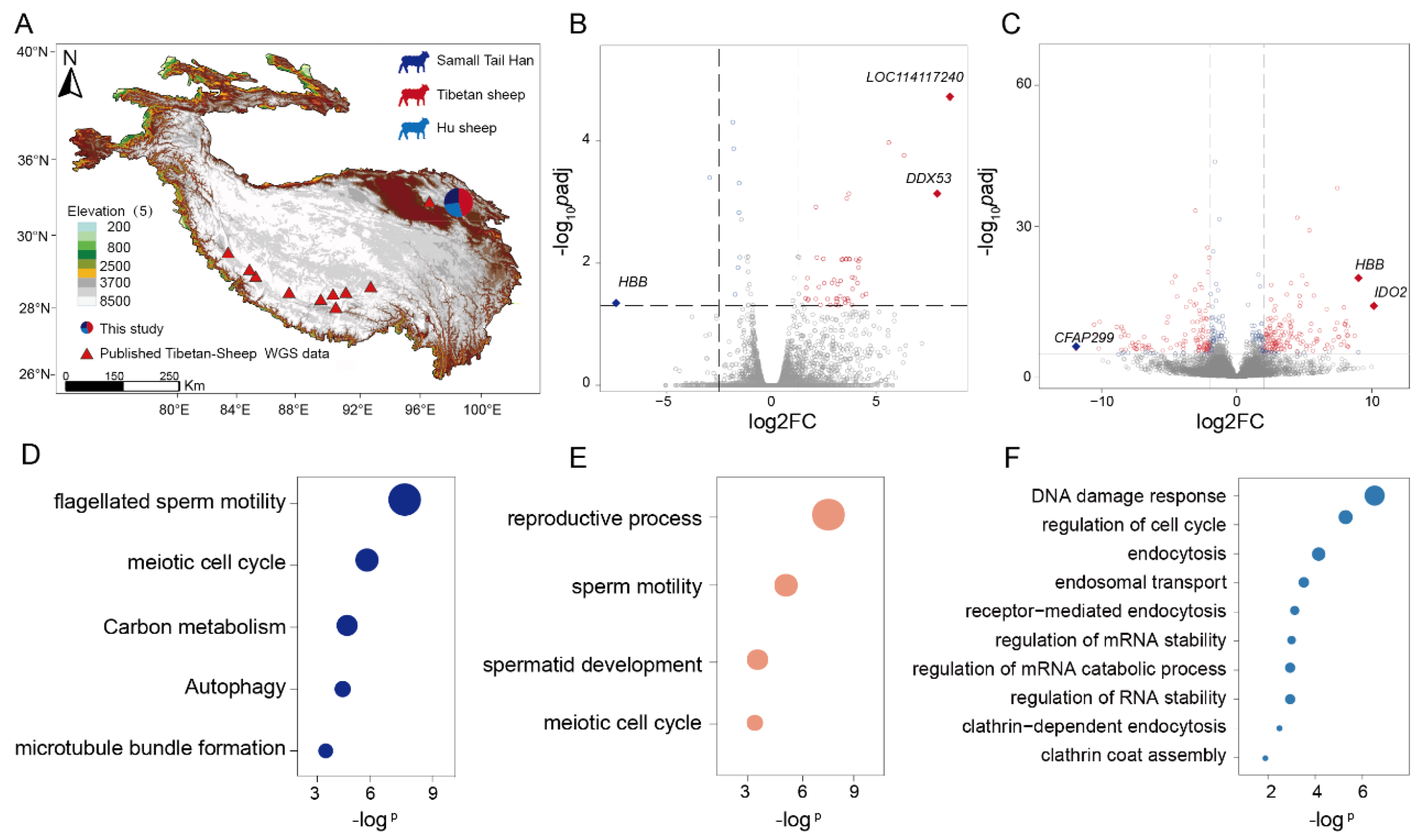
2.1. Sampling, Transcriptomic and Genomic Sequencing
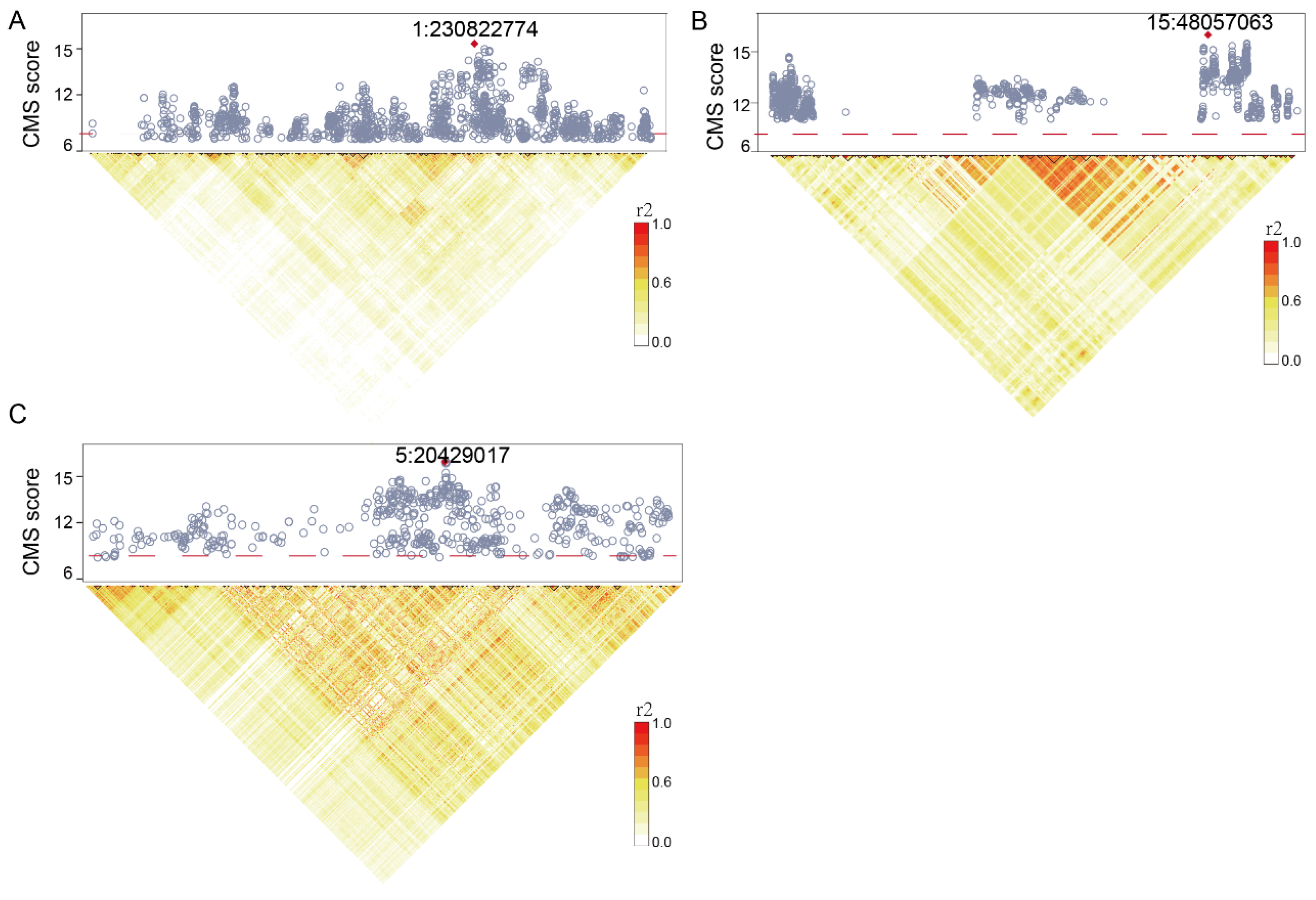
2.2. Genome-Wide Natural Selection Signatures Scanned in Tibetan Sheep
2.3. Identification of Genes Underpinning Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep
3. Discussion
4. Data and Method
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Transcriptome Analysis
4.2.1. Data Preprocessing
4.2.2. Differential Expression Analysis
4.2.3. Functional Enrichment
4.3. Genomic Analysis
4.3.1. Data Preprocessing
4.3.2. Variant Calling
4.4. Variant Quality Control
4.4.1. Primary Filtering
4.4.2. Sample-Level QC
4.4.3. Variant-Level QC
- ①
- Removal of 2,808,163 singleton variants;
- ②
- Exclusion of 4,712,207 SNVs with >5% missing genotypes;
- ③
- Elimination of 983,635 SNVs violating Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium exact test (p < 1 × 10−6).
4.4.4. Functional Annotation
4.5. Genome-Wide Natural Selection Signature Detection
4.5.1. Population Branch Statistic (PBS)
4.5.2. ΔDAF
4.5.3. XPEHH and iHS
4.5.4. CMS Implementation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, S.; Hansen, M.E.; Lo, Y.; Tishkoff, S.A. Going global by adapting local: A review of recent human adaptation. Science 2016, 354, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.G. Human Genetic Adaptation to High Altitudes: Current Status and Future Prospects. Quat. Int. 2017, 461, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yue, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Feng, Z.; Ouzhuluobu; Cui, C.; Liu, K.; et al. Polygenic adaptation leads to a higher reproductive fitness of native Tibetans at high altitude. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 4037–4051.e4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieson, I. Human genetics: An extreme fitness landscape. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R1064–R1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, D. Darwin’s two theories, 1844 and 1859. J. Hist Biol. 2018, 51, 563–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.G.; Young, D.; McCullough, R.E.; Droma, T.; Zamudio, S. Tibetan protection from intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) and reproductive loss at high altitude. Am. J. Hum Biol. 2001, 13, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.; Guo, Y.; Qi, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, X.; He, Y.; et al. Sex-biased regulatory changes in the placenta of native highlanders contribute to adaptive fetal development. eLife 2024, 12, RP89004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; He, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yue, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, X.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; et al. Large-scale genome sequencing redefines the genetic footprints of high-altitude adaptation in Tibetans. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, F.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing to investigate the genetic diversity and mechanisms of plateau adaptation in Tibetan sheep. J. Anim Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.D.; Yang, C.P.; Wang, M.S.; Dong, K.Z.; Yan, D.W.; Hao, Z.Q.; Fan, S.Q.; Chu, S.Z.; Shen, Q.S.; Jiang, L.P.; et al. Convergent genomic signatures of high-altitude adaptation among domestic mammals. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yao, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L. Genetic Adaptations of the Tibetan Pig to High-Altitude Hypoxia on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.G.; Charles, S.M.; Julian, C.G. Humans at high altitude: Hypoxia and fetal growth. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 178, 81–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Duan, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Mao, L.; An, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Genomic structural variation contributes to evolved changes in gene expression in high-altitude Tibetan sheep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2322291121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Li, T.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Lang, X.; Ma, Y. Whole genome sequencing revealed genetic diversity, population structure, and selective signature of Panou Tibetan sheep. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, L.; Han, X.; Zhao, N.; Xu, T.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, S.; Zhao, X.; et al. Tibetan Sheep Adapt to Plant Phenology in Alpine Meadows by Changing Rumen Microbial Community Structure and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 587558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Adjei, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Cisang, Z.; Song, T. The role of GnRH in Tibetan male sheep and goat reproduction. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2023, 58, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, C.; An, X.; Guo, T.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J. Transcriptome and metabolome revealed the effects of hypoxic environment on ovarian development of Tibetan sheep. Genomics 2025, 117, 110973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Han, B.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Pei, Q.; Zhao, K. Genetic diversity and selection of Tibetan sheep breeds revealed by whole-genome resequencing. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.; Braz, C.U.; Taylor, T.; Khatib, H. Effects of paternal methionine supplementation on sperm DNA methylation and embryo transcriptome in sheep. Environ. Epigenet. 2023, 9, dvac029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Cai, Y.; Guo, J.; Leonard, A.S.; Kalds, P.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; et al. Markhor-derived Introgression of a Genomic Region Encompassing PAPSS2 Confers High-altitude Adaptability in Tibetan Goats. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Ma, M.; Wang, X. Transcriptomic Study of Testicular Hypoxia Adaptation in Tibetan Sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2025, 60, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, S.R.; Shlyakhter, I.; Karlsson, E.K.; Byrne, E.H.; Morales, S.; Frieden, G.; Hostetter, E.; Angelino, E.; Garber, M.; Zuk, O.; et al. A composite of multiple signals distinguishes causal variants in regions of positive selection. Science 2010, 327, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yengo, L.; Vedantam, S.; Marouli, E.; Sidorenko, J.; Bartell, E.; Sakaue, S.; Graff, M.; Eliasen, A.U.; Jiang, Y.; Raghavan, S.; et al. A saturated map of common genetic variants associated with human height. Nature 2022, 610, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.S.; He, W.M.; Ji, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.L. LDBlockShow: A fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, C. Genetic basis of congenital erythrocytosis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 40 (Suppl. S1), 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, B.; Langda, S.; Pu, P.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, S.; Kalds, P.; Zhang, K.; Bhati, M.; Leonard, A.; et al. Multi-omic Analyses Shed Light on The Genetic Control of High-altitude Adaptation in Sheep. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2024, 22, qzae030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astle, W.J.; Elding, H.; Jiang, T.; Allen, D.; Ruklisa, D.; Mann, A.L.; Mead, D.; Bouman, H.; Riveros-Mckay, F.; Kostadima, M.A.; et al. The Allelic Landscape of Human Blood Cell Trait Variation and Links to Common Complex Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1415–1429.e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, B.; Gao, R.; Wang, X. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal High-Altitude Adaptation Mechanism of Epididymis Sperm Maturation in Tibetan Sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bai, C.; Pu, Y.; Kong, Q.; Guo, Y.; Ouzhuluobu; Gengdeng; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Genetic adaptation of skin pigmentation in highland Tibetans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200421119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Tian, D.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Tian, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, K. Multiomics Analyses Provide New Insight into Genetic Variation of Reproductive Adaptability in Tibetan Sheep. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. Imeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpiech, Z.A.; Hernandez, R.D. Selscan: An efficient multithreaded program to perform EHH-based scans for positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, K.; Gao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ge, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Prioritizing natural-selection signals from the deep-sequencing genomic data suggests multi-variant adaptation in Tibetan highlanders. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Members, C.-N. Partners, Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D18–D32. [Google Scholar]

| CHR | SNVID | CMS | XPEHH | iHS | PBS | MDAF | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10:32335294 | 16.82 | 3.91 | 2.91 | 0.41 | 0.42 | URAD |
| 1 | 1:103177691 | 15.28 | 3.55 | 2.40 | 0.37 | 0.43 | LOC114116898 |
| 4 | 4:11649074 | 14.98 | 5.93 | 1.97 | 0.48 | 0.37 | CALCR |
| 1 | 1:230822774 | 14.98 | 3.80 | 4.52 | 0.23 | 0.33 | VEPH1 |
| 5 | 5:20429017 | 14.66 | 4.38 | 3.70 | 0.14 | 0.43 | MEIKIN |
| 19 | 19:31783794 | 14.44 | 4.86 | 2.20 | 0.37 | 0.36 | MITF |
| 2 | 2:139020738 | 14.23 | 3.95 | 4.25 | 0.27 | 0.29 | MYO3B |
| 15 | 15:48057063 | 14.17 | 9.95 | 3.80 | 0.15 | 0.31 | HBB |
| 5 | 5:16451067 | 14.07 | 4.08 | 2.01 | 0.35 | 0.39 | HSD11B1L |
| 1 | 1:186064886 | 14.03 | 5.01 | 3.63 | 0.21 | 0.34 | FSTL1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Leng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, X.; Wang, X. Molecular Genetic Basis of Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Genes 2025, 16, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080909
Zheng W, Ge S, Zhang Z, Li Y, Li Y, Leng Y, Wang Y, Kang X, Wang X. Molecular Genetic Basis of Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Genes. 2025; 16(8):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080909
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Wangshan, Siyu Ge, Zehui Zhang, Ying Li, Yuxing Li, Yan Leng, Yiming Wang, Xiaohu Kang, and Xinrong Wang. 2025. "Molecular Genetic Basis of Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Genes 16, no. 8: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080909
APA StyleZheng, W., Ge, S., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Li, Y., Leng, Y., Wang, Y., Kang, X., & Wang, X. (2025). Molecular Genetic Basis of Reproductive Fitness in Tibetan Sheep on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Genes, 16(8), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080909






