BIM-Ken: Identifying Disease-Related miRNA Biomarkers Based on Knowledge-Enhanced Bio-Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
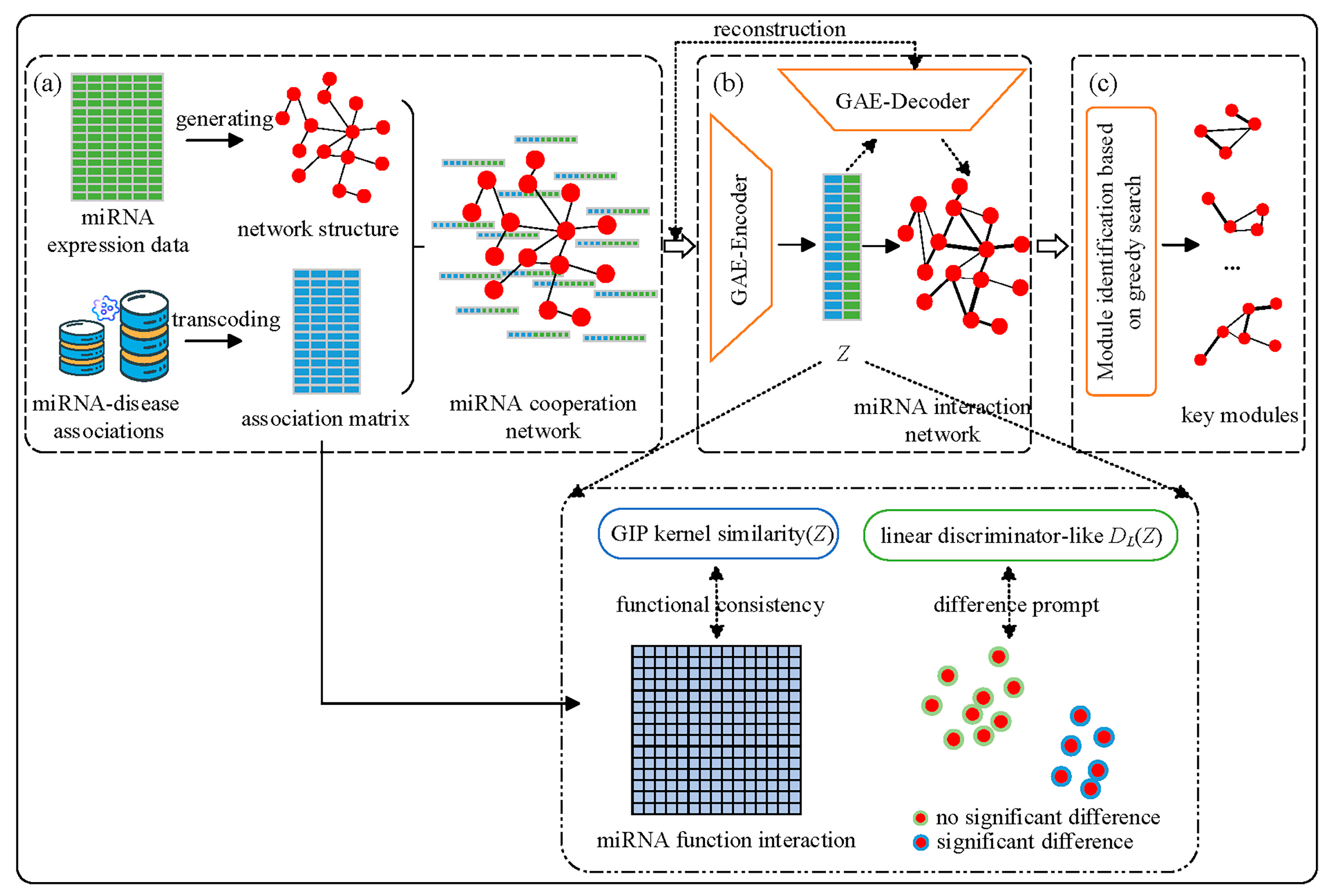
2.2. BIM-Ken Method
2.2.1. MiRNA Cooperation Network Generation
2.2.2. MiRNA Cooperation Network Enhancement
- (1)
- The reconstruction loss
- (2)
- Functional consistency constraint
- (3)
- Difference prompt constraint
2.2.3. Key miRNA Module Identification
3. Experimental Settings
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Performance Comparison
4.2. Ablation Study
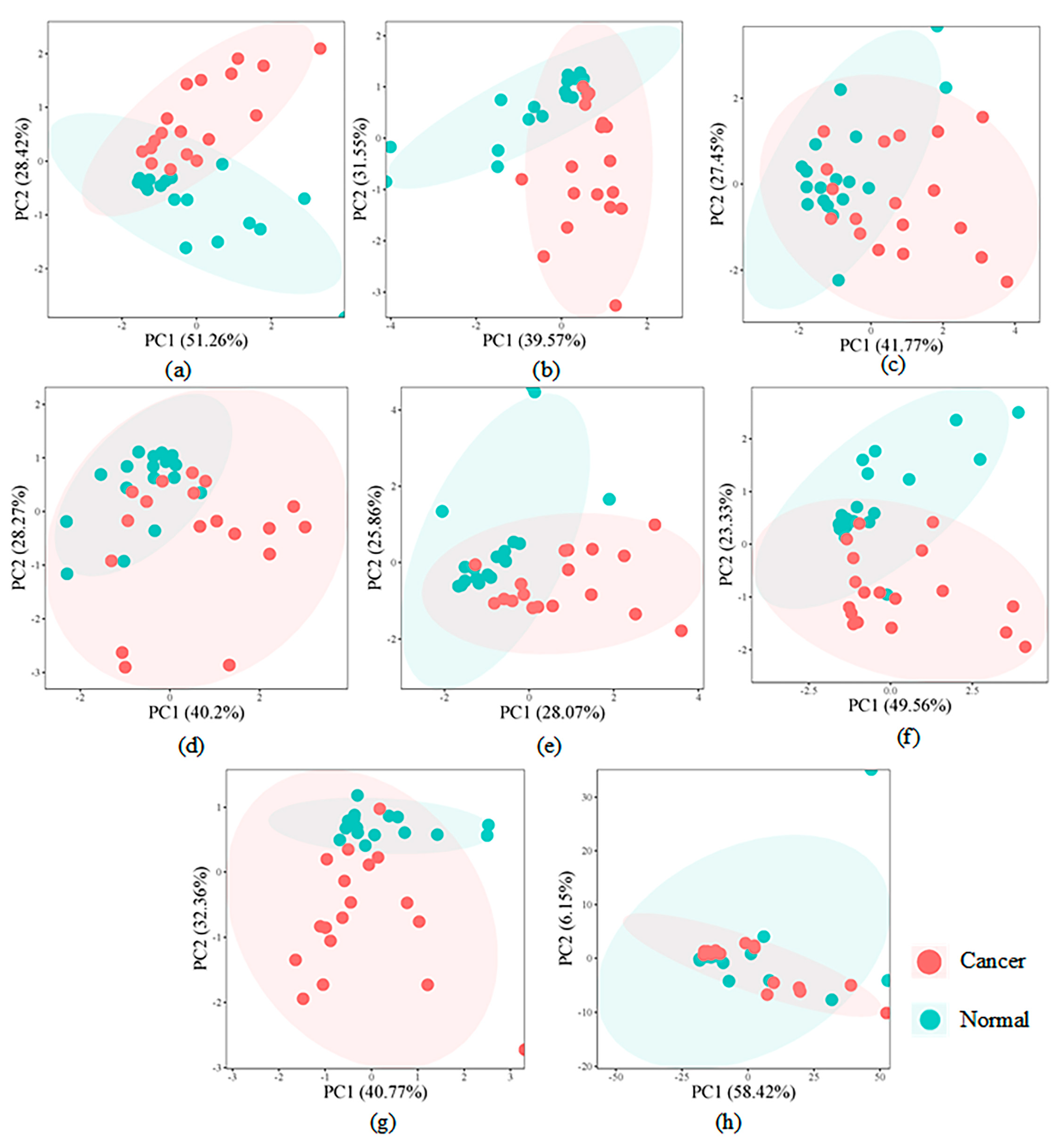
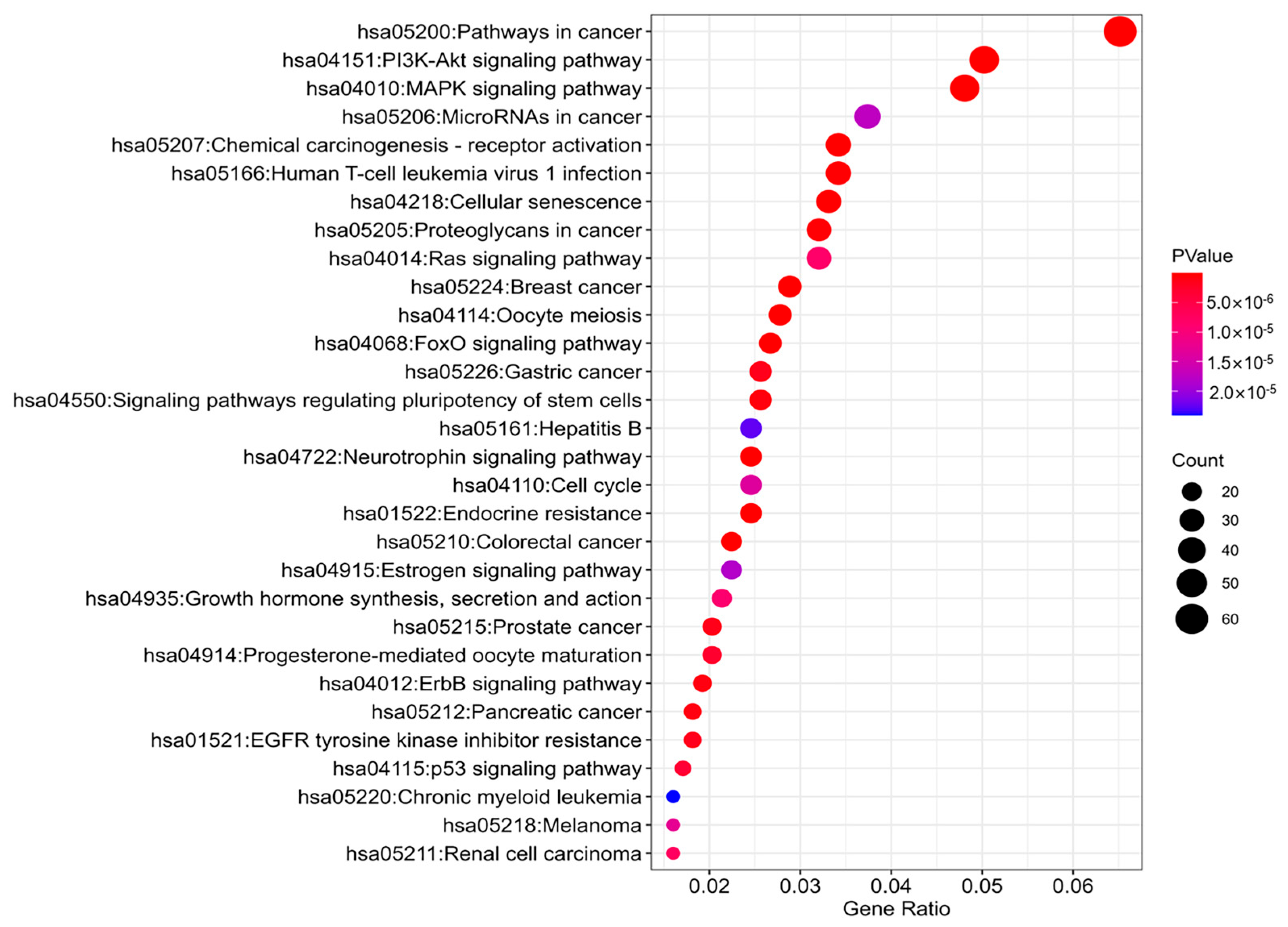
4.3. Module Biomarker Detected by BIM-Ken for the Renal Cell Carcinoma
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Dai, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Q.K.; Peng, S.L.; Wei, X.Y.; Qiu, J.F.; Salahub, D.R.; Xiong, Y.; et al. MDA-GCNFTG: Identifying miRNA-disease associations based on graph convolutional networks via graph sampling through the feature and topology graph. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Qiao, W.; Fang, H.; Bao, Y. Improving the identification of miRNA-disease associations with multi-task learning on gene-disease networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.D.; Lv, J.; Wei, K.L.; Feng, Z.B.; Chen, J.T.; Liu, K.C.; Chen, G.; Luo, D.Z. A nine-miRNA signature as a potential diagnostic marker for breast carcinoma: An integrated study of 1110 cases. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewarchuk, M.E.; Barros-Filho, M.C.; Minatel, B.C.; Cohn, D.E.; Guisier, F.; Sage, A.P.; Marshall, E.A.; Stewart, G.L.; Rock, L.D.; Garnis, C.; et al. Upgrading the repertoire of miRNAs in gastric adenocarcinoma to provide a new resource for biomarker discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.T.; Wang, G.J.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y.J.; Jin, X.Y.; Bai, J.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. Survey of miRNA-miRNA cooperative regulation principles across cancer types. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1621–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dou, P.; Wang, T.X.; Lu, X.; Xu, G.W.; Lin, X.H. Defining disease-related modules based on weighted miRNA synergistic network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-R.; Hu, X.H. Network-based approaches in bioinformatics and biomedicine. Methods 2022, 198, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.M.; Cui, Y.; Di Poto, C.; Varghese, R.S.; Yu, G.Q.; Li, R.J.; Ressom, H.W. INDEED: Integrated differential expression and differential network analysis of omic data for biomarker discovery. Methods 2016, 111, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.Y.; Rao, N.N.; Liu, D.Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.M.; Gan, T.; Ding, H.; Lin, H. Analysis of connection networks among miRNAs differentially expressed in early gastric cancer for disclosing some biological features of disease development. Gene 2014, 548, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.N.; Dudemaine, P.L.; Fomenky, B.E.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Integration of miRNA weighted gene co-expression network and miRNA-mRNA co-expression analyses reveals potential regulatory functions of miRNAs in calf rumen development. Genomics 2019, 111, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.D.; Cui, S.D.; Huang, Y.X.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.T.; Bao, J.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.L.; et al. miRTarBase update 2022: An informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.M.; Zhong, B.T.; Fan, R.; Cui, Q.H. HMDD v4.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1327–D1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Y.F.; Ling, Y.C.; Zhou, C.F.; Wang, H.Z.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.T.; He, Y.G.; Zhang, G.Q.; et al. dbDEMC 3.0: Functional exploration of differentially expressed miRNAs in cancers of human and model organisms. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.Y.; Ding, Q.; Han, H.J.; Wu, D. miRCancer: A microRNA-cancer association database constructed by text mining on literature. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laarhoven, T.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Marchiori, E. Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug-target interaction. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3036–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Li, T.H.; Huang, L.; Chen, X. Prediction of potential miRNA-disease associations based on stacked autoencoder. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lin, H.; Huang, L.; Peng, L.; Tang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L. Identification of miRNA–disease associations via deep forest ensemble learning based on autoencoder. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.Z.; Wang, W.W.; Lin, X.H.; Liu, S.L.; Huang, X. Identifying the potential miRNA biomarkers based on multi-view networks and reinforcement learning for diseases. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbad427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.M.; Cui, Y.; Yu, G.Q.; Li, R.J.; Ressom, H.W. Incorporating prior biological knowledge for network-based differential gene expression analysis using differentially weighted graphical LASSO. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, R.; Amirkhani, H.; Bosaghzadeh, A. Multi-view graph structure learning using subspace merging on grassmann manifold. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 17135–17157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Pan, S.R.; Chen, F.W.; Long, G.D.; Zhang, C.Q.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, P.; Gao, L.; Sheng, N.; Zhang, T.G.; Nakaguchi, T. Graph convolutional autoencoder and fully-connected autoencoder with attention mechanism based method for predicting drug-disease associations. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.L.; Liu, J.H.; Ou-Yang, L. scMIC: A deep multi-level information fusion framework for clustering single-cell multi-omics data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 6121–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappan, S.; Rayan, A.X.A.; Varrieth, G.T. EGeRepDR: An enhanced genetic-based representation learning for drug repurposing using multiple biomedical sources. J. Biomed. Inform. 2023, 147, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Variational graph auto-encoders. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haunsberger, S.J.; Connolly, N.M.C.; Prehn, J.H.M. miRNAmeConverter: An R/bioconductor package for translating mature miRNA names to different miRBase versions. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, B.E.; Guyon, I.M.; Vapnik, V.N. A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual ACM Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–29 July 1992; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevert, D.-A.; Unterthiner, T.; Hochreiter, S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernett, J.; Krupke, D.; Sadegh, S.; Baumbach, J.; Fekete, S.P.; Kacprowski, T.; List, M.; Blumenthal, D.B. Robust disease module mining via enumeration of diverse prize-collecting steiner trees. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Guan, Q.; Zheng, C.H. An integrated method based on wasserstein distance and graph for cancer subtype discovery. IEEE-ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 3499–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, M.Q.; Bo, D.Y.; Cui, P.; Shi, C.; Pei, J. AM-GCN: Adaptive multi-channel graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Virtual Event, CA, USA, 23–27 August 2020; pp. 1243–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.L.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.W. DiffuSum: Generation enhanced extractive summarization with diffusion. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 13089–13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Weiss, S.T.; Liu, Y.Y. Graph convolutional network-based feature selection for high-dimensional and low-sample size data. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddouri, O.; Qian, X.N.; Yoon, B.J. Deep graph representations embed network information for robust disease marker identification. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fatlawi, A.; Rusadze, E.; Shmelkin, A.; Malekian, N.; Ozen, C.; Pilarsky, C.; Schroeder, M. Netrank: Network-based approach for biomarker discovery. Bmc Bioinformatics 2023, 24, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.J.; Pederson, S. On robustness in the logistic regression model. J. R. Statist. Soc. 1993, 55, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Shen, Z.Y.; Mo, S.C.; Dai, L.J.; Song, B.; Gu, W.C.; Ding, X.Q.; Zhang, X.Y. Construction and validation of a novel ten miRNA-pair based signature for the prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 25, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Ye, Y.Q.; Chang, D.W.; Lin, S.H.; Huang, M.S.; Tannir, N.M.; Matin, S.; Karam, J.A.; Wood, C.G.; Chen, Z.N.; et al. Global and targeted miRNA expression profiling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma tissues potentially links miR-155-5p and miR-210-3p to both tumorigenesis and recurrence. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.H.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokar, T.; Pastrello, C.; Rossos, A.E.M.; Abovsky, M.; Hauschild, A.C.; Tsay, M.; Lu, R.; Jurisica, I. mirDIP 4.1-integrative database of human microRNA target predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D360–D370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.L.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W.Z. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Zou, X.F.; Zou, J.R.; Zhang, G.X. A review of recent research on the role of microRNAs in renal cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e930639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.F.; German, P.; Bai, S.S.; Barnes, S.; Guo, W.; Qi, X.J.; Lou, H.X.; Liang, J.Y.; Jonasch, E.; Mills, G.B.; et al. The PI3K/AKT pathway and renal cell carcinoma. J. Genet. Genom. 2015, 42, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Li, Y.F.; He, T.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.J.; Chen, M.W.; Zhang, Z.; Gui, Y.T.; Mao, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; et al. MiR-15a-5p acts as an oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q. An increased level of MiR-222-3p is associated with TMP2 suppression, ERK activation and is associated with metastasis and a poor prognosis in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 28, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.M.; Chen, D.Q.; Zhang, E.P.; Li, Y.F.; Yu, Z.H.; Shi, M.; Jiang, Z.M.; Ni, L.C.; Yang, S.Q.; Gui, Y.T.; et al. MicroRNA-509-3p inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Datasets | Disease Types | Features | Samples | Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE34496 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | 812 | 69 | 2 |
| GSE36802 | Prostate cancer | 812 | 42 | 2 |
| GSE41922 | Breast cancer | 264 | 54 | 2 |
| GSE67139 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 812 | 115 | 2 |
| GSE76260 | Prostate cancer | 787 | 64 | 2 |
| GSE78775 | Gastric cancer | 818 | 56 | 2 |
| GSE116251 | Renal cell carcinoma | 769 | 36 | 2 |
| GSE142699 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 769 | 48 | 2 |
| GSE158284 | Glioblastoma | 214 | 41 | 2 |
| Datasets | BIM-Ken | SVM-RFE | INDEED | GRACES | t-Test | GCNCC | NetRank | DDRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE34496 | 94.50 ± 1.90 | 87.36 ± 3.70 * | 91.62 ± 2.70 * | 91.38 ± 2.02 * | 93.64 ± 2.61 | 85.43 ± 4.46 * | 91.86 ± 1.84 * | 89.98 ± 1.86 * |
| GSE36802 | 93.10 ± 3.89 | 82.50 ± 5.90 * | 87.40 ± 1.82 * | 91.95 ± 3.83 | 87.55 ± 3.60 * | 84.85 ± 4.96 * | 91.95 ± 2.66 | 89.50 ± 3.79 |
| GSE41922 | 90.57 ± 1.46 | 85.70 ± 2.28 * | 84.73 ± 3.31 * | 91.43 ± 2.89 | 86.07 ± 3.15 * | 87.00 ± 4.11 * | 86.77 ± 2.01 * | 85.83 ± 3.56 * |
| GSE67139 | 87.17 ± 1.84 | 77.35 ± 1.73 * | 82.92 ± 1.83 * | 81.48 ± 3.09 * | 84.14 ± 1.72 * | 83.52 ± 2.67 * | 85.18 ± 2.94 | 81.06 ± 2.04 * |
| GSE76260 | 79.38 ± 2.92 | 72.57 ± 5.67 * | 74.88 ± 3.76 * | 71.67 ± 2.59 * | 73.10 ± 3.09 * | 71.17 ± 3.62 * | 74.74 ± 4.24 * | 72.07 ± 3.24 * |
| GSE78775 | 80.23 ± 2.64 | 74.37 ± 5.57 * | 74.33 ± 4.85 * | 68.80 ± 6.08 * | 77.50 ± 3.21 | 58.97 ± 3.62 * | 79.87 ± 3.42 | 69.10 ± 4.59 * |
| GSE116251 | 85.33 ± 4.40 | 78.33 ± 3.97 * | 80.42 ± 2.95 * | 73.58 ± 4.55 * | 83.25 ± 4.15 | 64.00 ± 11.55 * | 82.83 ± 4.07 | 79.25 ± 3.63 * |
| GSE142699 | 97.40 ± 0.91 | 91.80 ± 2.54 * | 91.75 ± 3.08 * | 94.80 ± 1.44 * | 93.95 ± 3.18 * | 94.60 ± 3.55 * | 94.50 ± 1.97 * | 95.55 ± 3.02 |
| GSE158284 | 92.20 ± 3.12 | 83.85 ± 1.86 * | 86.05 ± 2.58 * | 85.95 ± 3.82 * | 84.70 ± 3.05 * | 85.30 ± 4.46 * | 82.85 ± 3.35 * | 87.95 ± 2.90 * |
| Ave | 88.88 | 81.54 | 83.79 | 83.45 | 84.88 | 79.43 | 85.62 | 83.37 |
| W/T/L | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 8/0/1 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 |
| Datasets | BIM-Ken | SVM-RFE | INDEED | GRACES | t-Test | GCNCC | NetRank | DDRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE34496 | 94.60 ± 1.79 | 89.05 ± 4.56 * | 91.45 ± 2.31 * | 92.05 ± 2.93 * | 93.60 ± 1.87 | 92.40 ± 3.92 | 91.40 ± 2.65 * | 91.55 ± 2.95 * |
| GSE36802 | 89.17 ± 5.57 | 76.00 ± 9.00 * | 86.17 ± 3.93 | 91.33 ± 5.32 | 84.83 ± 3.55 | 89.17 ± 4.25 | 90.33 ± 3.91 | 88.17 ± 5.47 |
| GSE41922 | 90.67 ± 2.22 | 85.25 ± 3.38 * | 86.92 ± 5.11 | 92.17 ± 3.50 | 85.08 ± 4.88 * | 92.75 ± 4.36 | 87.08 ± 3.65 * | 86.75 ± 2.87 * |
| GSE67139 | 84.93 ± 2.14 | 73.67 ± 1.85 * | 80.57 ± 2.72 * | 78.67 ± 3.09 * | 81.00 ± 2.01 * | 86.03 ± 2.83 | 85.20 ± 3.92 | 80.00 ± 3.23 * |
| GSE76260 | 76.00 ± 4.81 | 70.25 ± 6.57 * | 74.42 ± 7.73 | 73.33 ± 6.21 | 72.83 ± 6.14 | 73.50 ± 4.76 | 72.83 ± 7.83 | 70.42 ± 6.10 * |
| GSE78775 | 79.17 ± 3.54 | 75.00 ± 6.48 | 75.67 ± 4.73 | 67.00 ± 9.78 * | 77.00 ± 4.43 | 62.00 ± 4.89 * | 82.67 ± 6.68 | 67.33 ± 5.89 * |
| GSE116251 | 79.50 ± 7.62 | 73.50 ± 7.84 | 76.50 ± 10.01 | 73.50 ± 5.80 | 78.00 ± 8.56 | 69.00 ± 9.94 * | 79.00 ± 6.99 | 79.50 ± 5.99 |
| GSE142699 | 94.50 ± 2.09 | 90.00 ± 2.36 * | 92.67 ± 4.39 | 92.33 ± 2.96 | 93.00 ± 4.29 | 93.00 ± 4.29 | 91.00 ± 3.06 * | 92.33 ± 5.73 |
| GSE158284 | 97.17 ± 3.34 | 87.00 ± 2.05 * | 90.17 ± 3.55 * | 89.00 ± 5.73 * | 88.83 ± 4.01 * | 90.33 ± 6.18 * | 85.33 ± 2.46 * | 89.83 ± 2.77 * |
| Ave | 87.30 | 79.97 | 83.84 | 83.26 | 83.80 | 83.13 | 84.98 | 82.88 |
| W/T/L | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 7/0/2 | 9/0/0 | 6/1/2 | 6/0/3 | 8/1/0 |
| Datasets | BIM-Ken | SVM-RFE | INDEED | GRACES | t-Test | GCNCC | NetRank | DDRM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE34496 | 94.17 ± 2.86 | 84.50 ± 6.67 * | 92.33 ± 5.10 | 89.67 ± 4.07 * | 93.67 ± 3.83 | 73.83 ± 6.76 * | 92.67 ± 2.96 | 86.67 ± 3.69 * |
| GSE36802 | 96.83 ± 4.68 | 88.50 ± 8.29 * | 89.00 ± 5.34 * | 92.50 ± 3.54 * | 90.33 ± 4.96 * | 81.00 ± 6.54 * | 93.67 ± 4.83 | 90.83 ± 4.39 * |
| GSE41922 | 90.83 ± 3.36 | 86.17 ± 4.01 * | 82.17 ± 4.72 * | 90.50 ± 5.78 | 87.50 ± 4.32 | 79.67 ± 6.47 * | 87.00 ± 3.31 * | 84.00 ± 6.05 * |
| GSE67139 | 89.50 ± 2.17 | 81.03 ± 4.57 * | 85.40 ± 2.11 * | 84.67 ± 4.22 * | 87.37 ± 2.49 | 81.43 ± 3.45 * | 85.30 ± 3.63 * | 81.93 ± 2.32 * |
| GSE76260 | 82.58 ± 3.59 | 74.83 ± 6.26 * | 75.08 ± 5.59 * | 69.75 ± 2.83 * | 73.42 ± 3.25 * | 69.17 ± 3.26 * | 76.08 ± 6.16 * | 73.92 ± 4.16 * |
| GSE78775 | 81.50 ± 2.99 | 74.00 ± 6.81 * | 73.17 ± 7.68 * | 70.50 ± 6.19 * | 77.83 ± 5.21 | 56.33 ± 7.06 * | 76.50 ± 5.90 * | 70.33 ± 6.23 * |
| GSE116251 | 90.50 ± 4.97 | 84.50 ± 5.50 * | 84.00 ± 8.76 | 74.00 ± 5.16 * | 88.00 ± 4.83 | 62.00 ± 13.58 * | 86.50 ± 5.30 | 78.00 ± 4.83 * |
| GSE142699 | 100.00 ± 0.00 | 93.33 ± 4.51 * | 90.33 ± 5.02 * | 97.50 ± 2.26 * | 94.67 ± 3.58 * | 97.33 ± 3.06 * | 97.83 ± 2.84 * | 99.33 ± 1.41 |
| GSE158284 | 79.50 ± 5.99 | 76.00 ± 4.59 | 76.50 ± 6.26 | 77.50 ± 5.89 | 76.00 ± 6.58 | 77.00 ± 4.22 | 77.00 ± 10.06 | 85.00 ± 7.45 |
| Ave | 89.49 | 82.54 | 83.11 | 82.95 | 85.42 | 75.31 | 85.84 | 83.33 |
| W/T/L | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 9/0/0 | 8/0/1 |
| Module id | Classification Accuracy Rate | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|
| M_1 | 97.10 ± 0.30 | 97.51 ± 0.39 | 95.71 ± 0.00 |
| M_2 | 94.82 ± 0.32 | 96.35 ± 0.17 | 89.57 ± 1.79 |
| M_3 | 97.33 ± 0.22 | 97.51 ± 0.34 | 96.71 ± 0.69 |
| M_4 | 92.31 ± 0.24 | 95.15 ± 0.28 | 82.57 ± 0.60 |
| M_5 | 97.11 ± 0.34 | 97.72 ± 0.22 | 95.00 ± 1.01 |
| M_6 | 96.11 ± 0.35 | 96.63 ± 0.41 | 94.29 ± 1.17 |
| M_7 | 87.49 ± 0.44 | 94.39 ± 0.35 | 63.71 ± 1.20 |
| Module id | Pathway | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| M_1 | hsa04010:MAPK signaling pathway | 2.45 × 10−3 |
| M_2 | hsa05211:Renal cell carcinoma | 7.71 × 10−4 |
| M_3 | hsa05211:Renal cell carcinoma | 2.15 × 10−3 |
| M_4 | hsa04350:TGF-beta signaling pathway | 1.20 × 10−3 |
| M_5 | hsa05211:Renal cell carcinoma | 4.36 × 10−3 |
| M_6 | hsa05211:Renal cell carcinoma | 7.51 × 10−6 |
| M_7 | hsa04350:TGF-beta signaling pathway | 8.72 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Dong, K.; Sun, W.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X. BIM-Ken: Identifying Disease-Related miRNA Biomarkers Based on Knowledge-Enhanced Bio-Network. Genes 2025, 16, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080902
Zhang Y, Dong K, Sun W, Gao Z, Zhang J, Lin X. BIM-Ken: Identifying Disease-Related miRNA Biomarkers Based on Knowledge-Enhanced Bio-Network. Genes. 2025; 16(8):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080902
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanhui, Kunjie Dong, Wenli Sun, Zhenbo Gao, Jianjun Zhang, and Xiaohui Lin. 2025. "BIM-Ken: Identifying Disease-Related miRNA Biomarkers Based on Knowledge-Enhanced Bio-Network" Genes 16, no. 8: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080902
APA StyleZhang, Y., Dong, K., Sun, W., Gao, Z., Zhang, J., & Lin, X. (2025). BIM-Ken: Identifying Disease-Related miRNA Biomarkers Based on Knowledge-Enhanced Bio-Network. Genes, 16(8), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080902






