Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Genetic Analysis Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case–Control Comparisons
3.1.1. Overall Population
3.1.2. Sex-Stratified Analysis Results
3.2. Gene–Gene Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, M.E.; Ratay, J.S.; Marazita, M.L. Asian Oral-Facial Cleft Birth Prevalence. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2006, 43, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wornom, I.L.; Will, L.A.; Burdi, A.R.; Berkowitz, S.; Breen, M.L.; Clarke-Sheehan, N.; Curtin, V.M.; D’Antonio, L.L.; Friedman, C.D.; Gleason, A.T.; et al. Core Curriculum for Cleft Lip/Palate and other Craniofacial Anomalies. In Cleft Lip and Palate; Berkowitz, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.J.; Marazita, M.L.; Beaty, T.H.; Murray, J.C. Cleft lip and palate: Understanding genetic and environmental influences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Natsume, N.; Kinoshita, H.; Tsunoda, N.; Takahashi, H.; Kawai, T. Experimental Study on Cleft Lip and/or Palate: Fetuses of A/J Mice in Uteri of F1 Hybrid Mothers Using Ovarian Transplantation. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1996, 33, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, J.; Natsume, N.; Kawai, T. Transplantation of Fertilized Ova of cleft lip and palate-Resistant C57BL/6 Strain Mice to Pseudopregnant cleft lip and palate-Prone A/J Strain Mice. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 2625–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaty, T.H.; Murray, J.C.; Marazita, M.L.; Munger, R.G.; Ruczinski, I.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Liang, K.Y.; Wu, T.; Murray, T.; Fallin, M.D.; et al. A genome-wide association study of cleft lip with and without cleft palate identifies risk variants near MAFB and ABCA4. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cvekl, A. Large Maf transcription factors: Cousins of AP-1 proteins and important regulators of cellular differentiation. Einstein J. Biol. Med. 2007, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liang, X.; Ou, Y.; Tang, S.; He, Y. Association between 20q12 rs13041247 polymorphism and risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate: A meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Duan, S.; Shi, J.; Jiang, S.; Feng, F.; Shi, B.; Jia, Z. Family-based study of association between MAFB gene polymorphisms and NSCL/P among Western Han Chinese population. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, H.D.B.; Phuong, L.H.; Vu, H.A. Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of MAFB Gene with Nonsyndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in Kinh Vietnamese Patients. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 55, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, C.J.; Birkeland, A.C.; Nuñez, J.A.P.; Su, G.H.; Lanzano, P.; Guzman, E.; Celis, K.; Eisig, S.B.; Hoffman, D.; Rendon, M.T.G.; et al. Association of candidate genes with nonsyndromic clefts in Honduran and Colombian populations. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallonet, M.; Hollemann, T.; Pieler, T.; Gruss, P. Vax1, a novel homeobox-containing gene, directs development of the basal forebrain and visual system. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3106–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoghegan, F.; Xavier, G.M.; Birjandi, A.A.; Seppala, M.; Cobourne, M.T. Vax1 Plays an Indirect Role in the Etiology of Murine Cleft Palate. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, S.; Ludwig, K.U.; Reutter, H.; Herms, S.; Steffens, M.; Rubini, M.; Baluardo, C.; Ferrian, M.; Almeida de Assis, N.; Alblas, M.A.; et al. Key susceptibility locus for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on chromosome 8q24. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butali, A.; Suzuki, S.; Cooper, M.E.; Mansilla, A.M.; Cuenco, K.; Leslie, E.J.; Suzuki, Y.; Niimi, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Ayanga, G.; et al. Replication of Genome Wide Association Identified Candidate Genes Confirm the Role of Common and Rare Variants in PAX7 and VAX1 in the Etiology of Nonsyndromic CL(P). Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2013, 161, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, S.; Song, Q.; Hu, H.; An, J.; Liu, J. The risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate and Vax1 rs7078160 polymorphisms in southern Han Chinese. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 87, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.H.; Shi, J.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Shi, B.; Jia, Z.L. VAX1 gene associated non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate in Western Han Chinese. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 95, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, K.E.; Nusse, R.; van Amerongen, R. Wnt signalling: Conquering complexity. Development 2018, 145, dev165902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, P.; Jarrell, A.; Myers, J.; Atit, R. Visualizing canonical Wnt signaling during mouse craniofacial development. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Gregorieff, A.; Leucht, P.; ten Berge, D.; Fuerer, C.; Clevers, H.; Nusse, R.; Helms, J.A. Wnt signaling mediates regional specification in the vertebrate face. Development 2007, 134, 3283–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Chen, Y. Wnt Signaling in Lip and Palate Development. In Cleft Lip and Palate: Epidemiology, Aetiology and Treatment; Cobourne, M.T., Ed.; S.Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Mostowska, A.; Hozyasz, K.K.; Biedziak, B.; Wojcicki, P.; Lianeri, M.; Jagodzinski, P.P. Genotype and haplotype analysis of WNT genes in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Eur. J. Oral. Sci. 2012, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, R.; Letra, A.; Kim, A.H.; Küchler, E.C.; Day, A.; Tannure, P.N.; da Motta, L.G.; Paiva, K.B.S.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Vieira, A.R. Studies with Wnt genes and nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.P.; Han, W.T.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.X.; Li, Z.J.; Jiang, M.; Xu, W. Variations in WNT3 gene are associated with incidence of non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in a northeast Chinese population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 12646–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, G.; Antona, V.; Giuffré, M.; Li Pomi, F.; Lo Scalzo, L.; Piro, E.; Schierz, I.A.M.; Corsello, G. Novel missense mutation of the TP63 gene in a newborn with Hay-Wells/Ankyloblepharon-Ectodermal defects-Cleft lip/palate (AEC) syndrome: Clinical report and follow-up. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamada, A.; Aoki, Y.; Kure, S.; Matsubara, Y. Association between nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate and the glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 gene in the Japanese population. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2004, 127a, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibano, M.; Watanabe, A.; Takano, N.; Mishima, H.; Kinoshita, A.; Yoshiura, K.-i.; Shibahara, T. Target Capture/Next-Generation Sequencing for Nonsyndromic Cleft Lip and Palate in the Japanese Population. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2020, 57, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, E.; Watanabe, A.; Nakano, Y.; Akita, S.; Hirano, A.; Kinoshita, A.; Kondo, S.; Kishino, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Niikawa, N.; et al. PAX9 and TGFB3 are linked to susceptibility to nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Japanese: Population-based and family-based candidate gene analyses. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 51, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangold, E.; Ludwig, K.U.; Birnbaum, S.; Baluardo, C.; Ferrian, M.; Herms, S.; Reutter, H.; de Assis, N.A.; Chawa, T.A.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies two susceptibility loci for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zeng, X.; Guo, Z. Is a polymorphism in 10q25 associated with non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate? A meta-analysis based on limited evidence. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavec, L.; Karas Kuželički, N.; Locatelli, I.; Geršak, K. Genetic markers for non-syndromic orofacial clefts in populations of European ancestry: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, H.J.; Innes, N.P.T.; Edris Ahmed, S.; Butali, A.; Alnamnakani, E.A.; Rabah, S.M.; Hamdan, M.A.; Alhamlan, N.H.; Abdulhameed, F.D.; Hassan, M.H.A.; et al. Molecular Screening of VAX1 Gene Polymorphisms Uncovered the Genetic Heterogeneity of Nonsyndromic Orofacial Cleft Among Saudi Arabian Patients. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2019, 23, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikopensius, T.; Birnbaum, S.; Ludwig, K.U.; Jagomägi, T.; Saag, M.; Herms, S.; Knapp, M.; Hoffmann, P.; Nöthen, M.M.; Metspalu, A.; et al. Susceptibility locus for non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on chromosome 10q25 confers risk in Estonian patients. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 118, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Martinez, A.; Reutter, H.; Chacon-Camacho, O.; Leon-Cachon, R.B.; Munoz-Jimenez, S.G.; Nowak, S.; Becker, J.; Herberz, R.; Ludwig, K.U.; Paredes-Zenteno, M.; et al. Genetic risk factors for nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in a Mesoamerican population: Evidence for IRF6 and variants at 8q24 and 10q25. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostowska, A.; Hozyasz, K.K.; Wojcicka, K.; Biedziak, B.; Jagodzinski, P.P. Polymorphic variants at 10q25.3 and 17q22 loci and the risk of non-syndromic cleft lip and palate in the polish population. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salagovic, J.; Klimcakova, L.; Zabavnikova, M.; Behunova, J.; Hudakova, T.; Fedeles, J.; Molnarova, A.; Podracka, L. Polymorphisms at 1q32, 8q24, and 17q22 loci are associated with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate risk in the Slovak population. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2017, 161, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Guo, Q.; Shi, J.; Hao, Y.; Jiao, X.; Lv, K.; Song, T. Polymorphic variants in VAX1 and the risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in a population from northern China. Medicine 2017, 96, e6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. Replication of two novel susceptibility loci for non-syndromic orofacial clefts in a Chinese population. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis Machado, R.; de Toledo, I.P.; Martelli-Júnior, H.; Reis, S.R.; Neves Silva Guerra, E.; Coletta, R.D. Potential genetic markers for nonsyndromic oral clefts in the Brazilian population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Birth Defects Res. 2018, 110, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Shi, J.; Shi, B.; Jia, Z. Target sequencing reveals the association between variants in VAX1 and NSCL/P in Chinese population. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yin, A.; Shi, B.; Du, X.; Ma, L.; Lan, F.; Jiang, M.; et al. Validation of a genome-wide association study implied that SHTIN1 may involve in the pathogenesis of NSCL/P in Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Pan, Y.; Tan, Q. Associations of genetic variants in endocytic trafficking of epidermal growth factor receptor super pathway with risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanasio, C.; Nord, A.S.; Zhu, Y.; Blow, M.J.; Li, Z.; Liberton, D.K.; Morrison, H.; Plajzer-Frick, I.; Holt, A.; Hosseini, R.; et al. Fine tuning of craniofacial morphology by distant-acting enhancers. Science 2013, 342, 1241006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Wei, B.; Xie, X.; Li, P.; Shen, X. The potential up-regulation risk of 3′ UTR SNP (rs10787760 G > A) for the VAX1 gene is associated with NSCLP in the northwest Chinese population. Gene 2024, 922, 148458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.U.; Mangold, E.; Herms, S.; Nowak, S.; Reutter, H.; Paul, A.; Becker, J.; Herberz, R.; AlChawa, T.; Nasser, E.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analyses of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate identify six new risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awotoye, W.; Comnick, C.; Pendleton, C.; Zeng, E.; Alade, A.; Mossey, P.A.; Gowans, L.J.J.; Eshete, M.A.; Adeyemo, W.L.; Naicker, T.; et al. Genome-wide Gene-by-Sex Interaction Studies Identify Novel Nonsyndromic Orofacial Clefts Risk Locus. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.C.; Nidey, N.L.; Butali, A.; Buxo, C.J.; Christensen, K.; Deleyiannis, F.W.; Hecht, J.T.; Field, L.L.; Moreno-Uribe, L.M.; Orioli, I.M.; et al. Genome-wide interaction studies identify sex-specific risk alleles for nonsyndromic orofacial clefts. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 42, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loh, B.M.; Yaw, A.M.; Breuer, J.A.; Jackson, B.; Nguyen, D.; Jang, K.; Ramos, F.; Ho, E.V.; Cui, L.J.; Gillette, D.L.M.; et al. The transcription factor VAX1 in VIP neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus impacts circadian rhythm generation, depressive-like behavior, and the reproductive axis in a sex-specific manner in mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1269672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, L.; Nicolì, V.; Stoccoro, A. Gender Specific Differences in Disease Susceptibility: The Role of Epigenetics. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.O.; Evans, K.A. Inheritance of congenital pyloric stenosis. J. Med. Genet. 1969, 6, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiślak, A.; Woźniak, K.; Tartaglia, G.; Kawala, B.; Gupta, S.; Znamirowska-Bajowska, A.; Grocholewicz, K.; Lubiński, J.; Jakubowska, A. Testing Reported Associations of Gene Variants with Non-Syndromic Orofacial Clefts in the Polish Population. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontoura, C.; Silva, R.M.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Letra, A. Further evidence of association of the ABCA 4 gene with cleft lip/palate. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 120, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, M.M.; Lopez-Jornet, P.; Pons-Fuster López, E.; Sadeghi, M. Polymorphic Variants of V-Maf Musculoaponeurotic Fibrosarcoma Oncogene Homolog B (rs13041247 and rs11696257) and Risk of Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip/Palate: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, N.L.; Dixon, M.J. Revisiting the embryogenesis of lip and palate development. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 1306–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurano, M.T.; Humbert, R.; Rynes, E.; Thurman, R.E.; Haugen, E.; Wang, H.; Reynolds, A.P.; Sandstrom, R.; Qu, H.; Brody, J.; et al. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 2012, 337, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiślak, A.; Woźniak, K.; Tartaglia, G.; Agirre, X.; Gupta, S.; Kawala, B.; Znamirowska-Bajowska, A.; Grocholewicz, K.; Prosper, F.; Lubiński, J.; et al. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in WNT Genes in Patients with Non-Syndromic Orofacial Clefts in a Polish Population. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Q.; Gao, S.T.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.Q.; Sun, J.M.; Xia, Y.; Lv, Z.T. Association of the WNT3 polymorphisms and non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi Karibozorg, H.; Masoudian, N.; Saliminejad, K.; Ebadifar, A.; Kamali, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R. Association of the WNT3 Variations and the Risk of Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip and Palate in a Population of Iranian Infants. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2018, 10, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R.; Varmus, H.E. Wnt genes. Cell 1992, 69, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Kawakami, C.; Kawakami, K.; Ito, S. Maternal multivitamin intake and orofacial clefts in offspring: Japan Environment and Children’s Study (JECS) cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.C.; Raynes-Greenow, C.; Turner, R.M.; Bower, C.; Nassar, N.; O’Leary, C.M. Maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy and the risk of orofacial clefts in infants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2014, 28, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, H.; Motoki, N.; Inaba, Y.; Misawa, Y.; Ohira, S.; Kanai, M.; Tsukahara, T.; Nomiyama, T.; Kamijima, M.; Yamazaki, S.; et al. Maternal alcohol consumption and risk of offspring with congenital malformation: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaty, T.H.; Ruczinski, I.; Murray, J.C.; Marazita, M.L.; Munger, R.G.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Murray, T.; Redett, R.J.; Fallin, M.D.; Liang, K.Y.; et al. Evidence for gene-environment interaction in a genome wide study of nonsyndromic cleft palate. Genet. Epidemiol. 2011, 35, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Venkataraghavan, S.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Leslie, E.J.; Marazita, M.L.; Feingold, E.; Weinberg, S.M.; Ruczinski, I.; Taub, M.A.; Scott, A.F. Detecting gene-environment interaction for maternal exposures using case-parent trios ascertained through a case with non-syndromic orofacial cleft. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 621018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Liang, K.Y.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Ruczinski, I.; Fallin, M.D.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Wang, H.; Huang, S.; Ye, X.; Wu-Chou, Y.-H.; et al. Evidence of gene–environment interaction for the IRF6 gene and maternal multivitamin supplementation in controlling the risk of cleft lip with/without cleft palate. Hum. Genet. 2010, 128, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y. Advances in CRISPR/Cas9. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9978571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, K.; Maki, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Kaji, S.; Toyokawa, M.; Nishigori, R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Ono, Y.; Kinoshita, A.; Takahashi, R. Sex-specific differences in transcriptomic profiles and cellular characteristics of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 46, 101866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| NSCLO | NSCLP | NSCL/P | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 57 | 115 | 172 | 136 |
| Female | 58 | 80 | 138 | 172 |
| Total | 115 | 195 | 310 | 308 |
| Chr | Gene | SNP | Allele | HWE p | MAF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | NSCLO | NSCLP | NSCL/P | |||||
| 10 | VAX1 | rs7078160 | G > A | 0.9987 | 0.459 | 0.600 | 0.579 | 0.587 |
| 20 | MAFB | rs13041247 | T > C | 0.9742 | 0.406 | 0.296 | 0.410 | 0.368 |
| 17 | WNT3 | rs3809857 | G > T | 0.070 | 0.231 | 0.230 | 0.233 | 0.232 |
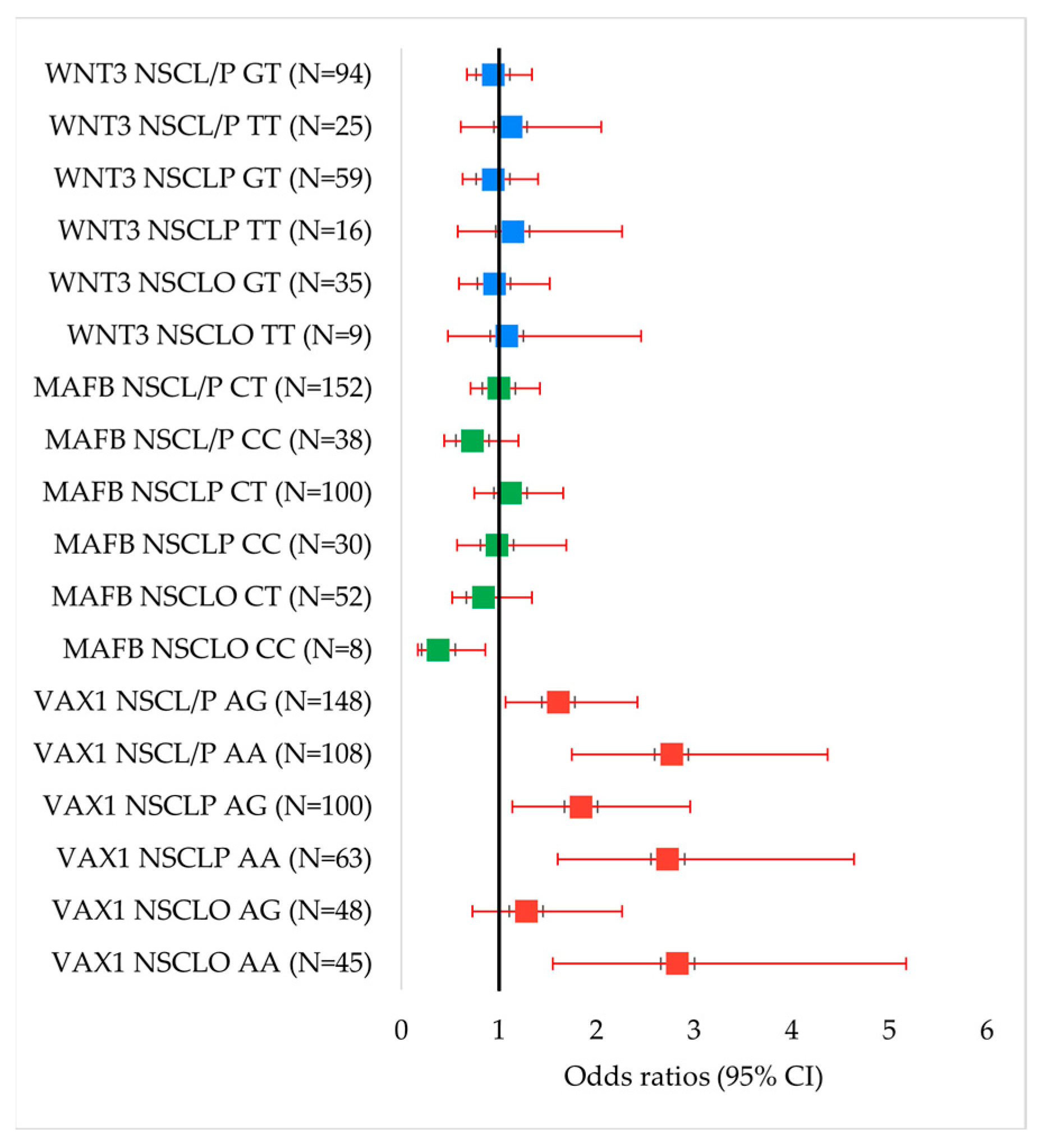
| Genotype/Allele | Control (n = 308) | NSCLO (n = 115) | OR (95% CI) | p Value | NSCLP (n = 195) | OR (95% CI) | p Value | NSCL/P (n = 310) | OR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAX1 rs7078160 | ||||||||||
| GG | 90 | 22 | Reference | 32 | Reference | 54 | Reference | |||
| AG | 153 | 48 | 1.28 (0.73–2.26) | 0.388 | 100 | 1.84 (1.14–2.96) | 0.012 | 148 | 1.61 (1.07–2.42) | 0.021 |
| AA | 65 | 45 | 2.83 (1.55–5.17) | 0.0006 | 63 | 2.73 (1.60–4.64) | 0.0002 | 108 | 2.77 (1.75–4.37) | <0.00001 |
| Dominant model | 218 | 93 | 1.75 (1.03–2.95) | 0.036 | 163 | 2.10 (1.34–3.30) | 0.0011 | 256 | 1.96 (1.33–2.87) | 0.0005 |
| Recessive model | 243 | 70 | 2.40 (1.51–3.82) | 0.0002 | 132 | 1.78 (1.19–2.68) | 0.005 | 202 | 1.58 (1.11–2.25) | 0.011 |
| A | 283 | 138 | 1.77 (1.30–2.40) | 0.0003 | 226 | 1.62 (1.26–2.09) | 0.0002 | 364 | 1.67 (1.34–2.1) | <0.00001 |
| G | 333 | 92 | Reference | 164 | Reference | 256 | Reference | |||
| MAFB rs13041247 | ||||||||||
| TT | 108 | 45 | Reference | 65 | Reference | 110 | Reference | |||
| CT | 149 | 52 | 0.84 (0.52–1.34) | 0.459 | 100 | 1.12 (0.75–1.66) | 0.592 | 152 | 1.00 (0.71–1.42) | 0.993 |
| CC | 51 | 8 | 0.38 (0.17–0.86) | 0.017 * | 30 | 0.98 (0.57–1.69) | 0.935 | 38 | 0.73 (0.44–1.20) | 0.217 |
| Dominant model | 200 | 60 | 0.72 (0.45–1.13) | 0.153 | 130 | 1.08 (0.74–1.58) | 0.690 | 190 | 0.93 (0.67–1.30) | 0.680 |
| Recessive model | 257 | 97 | 0.42 (0.19–0.91) | 0.024 * | 165 | 0.92 (0.56–1.50) | 0.727 | 162 | 1.18 (0.74–1.88) | 0.479 |
| C | 251 | 68 | 0.70 (0.50–0.97) | 0.032 * | 160 | 1.01 (0.78–1.31) | 0.930 | 228 | 0.89 (0.71–1.12) | 0.327 |
| T | 365 | 142 | Reference | 230 | Reference | 372 | Reference | |||
| WNT3 rs3809857 | ||||||||||
| GG | 188 | 71 | Reference | 120 | Reference | 191 | Reference | |||
| GT | 98 | 35 | 0.95 (0.59–1.52) | 0.817 | 59 | 0.94 (0.63–1.40) | 0.772 | 94 | 0.94 (0.67–1.34) | 0.746 |
| TT | 22 | 9 | 1.08 (0.48–2.46) | 0.849 | 16 | 1.14 (0.58–2.26) | 0.708 | 25 | 1.12 (0.61–2.05) | 0.718 |
| Dominant model | 120 | 44 | 0.97 (0.63–1.51) | 0.895 | 75 | 0.98 (0.68–1.42) | 0.911 | 119 | 0.98 (0.71–1.35) | 0.884 |
| Recessive model | 298 | 106 | 1.15 (0.51–2.58) | 0.734 | 179 | 1.21 (0.62–2.37) | 0.575 | 285 | 1.19 (0.66–2.16) | 0.567 |
| T | 142 | 53 | 1.02 (0.71–1.46) | 0.911 | 91 | 1.04 (0.77–1.40) | 0.811 | 144 | 1.03 (0.79–1.34) | 0.820 |
| G | 474 | 177 | Reference | 299 | Reference | 476 | Reference | |||
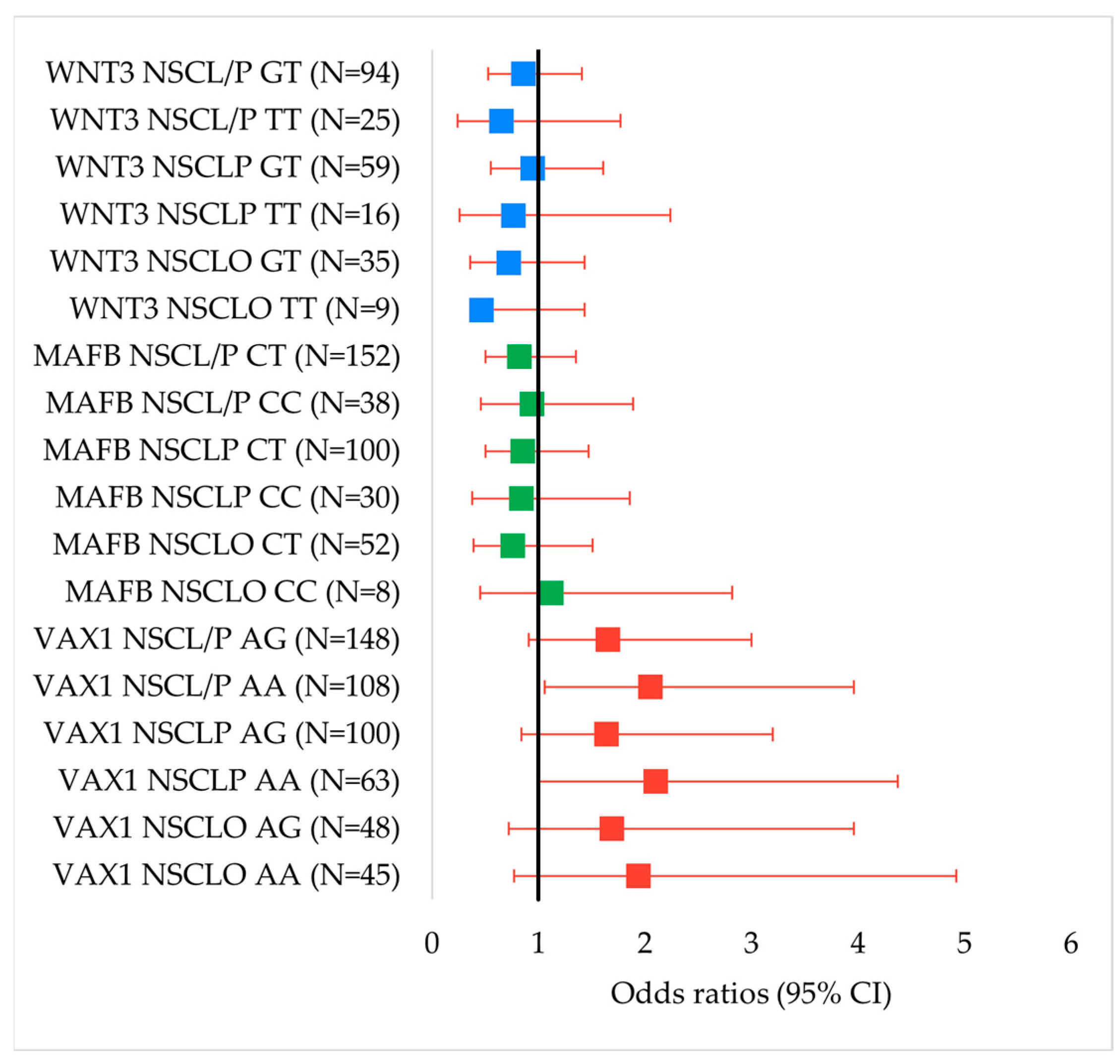
| Genotype/Allele | Control (F/M) | NSCLO (F/M) | OR (95% CI) (F/M) | p Value (F/M) | NSCLP (F/M) | OR (95% CI) (F/M) | p Value (F/M) | NSCL/P (F/M) | OR (95% CI) (F/M) | p Value (F/M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAX1 rs7078160 | ||||||||||
| GG | 56/34 | 13/9 | Reference | 14/18 | Reference | 27/27 | Reference | |||
| AG | 86/67 | 18/30 | 0.90 (0.41–1.98) /1.69 (0.72–3.96) | 0.797 /0.223 | 42/58 | 1.95 (0.98–3.90) /1.64 (0.84–3.20) | 0.056 /0.149 | 60/88 | 1.45 (0.82–2.55) /1.65 (0.91–3.00) | 0.199 /0.097 |
| AA | 30/35 | 27/18 | 3.88 (1.75–8.60) /1.94 (0.77–4.92) | 0.0006 /0.160 | 24/39 | 3.2 (1.45–7.08) /2.10 (1.01–4.37) | 0.0034 /0.045 | 51/57 | 3.53 (1.85–6.71) /2.05 (1.06–3.96) | <0.00001 /0.031 |
| Dominant model | 116/102 | 45/48 | 1.67 (0.83–3.35) /1.78 (0.79–4.00) | 0.145 /0.161 | 66/97 | 2.28 (1.18–4.40) /1.80 (0.95–3.39) | 0.013 /0.069 | 111/145 | 1.98 (1.17–3.36) /1.79 (1.02–3.15) | 0.010 /0.042 |
| Recessive model | 142/101 | 31/39 | 4.12 (2.15–7.89) /1.33 (0.68–2.62) | <0.00001 /0.407 | 56/76 | 2.03 (1.09–3.77) /1.48 (0.86–2.55) | 0.024 /0.159 | 87/115 | 2.77 (1.64–4.69) /1.43 (0.87–2.35) | 0.0001 /0.159 |
| A | 146/137 | 72/66 | 2.22 (1.44–3.42)/ 1.35 (0.87–2.11) | 0.0003 /0.177 | 90/136 | 1.74 (1.19–2.55) /1.43 (1.00–2.03) | 0.0038 /0.05 | 162/202 | 1.93 (1.40–2.66) /1.40 (1.02–1.93) | <0.00001 /0.039 |
| G | 198/135 | 44/48 | Reference | 70/94 | Reference | 114/142 | Reference | |||
| MAFB rs13041247 | ||||||||||
| TT | 61/47 | 23/22 | Reference | 21/44 | Reference | 44/66 | Reference | |||
| CT | 79/70 | 27/25 | 0.91 (0.47–1.73) /0.76 (0.39–1.51) | 0.767 /0.436 | 44/56 | 1.62 (0.87–3.00) /0.85 (0.50–1.47) | 0.126 /0.569 | 71/81 | 1.25 (0.75–2.06) /0.82 (0.50–1.35) | 0.391 /0.441 |
| CC | 32/19 | 8/10 | 0.66 (0.27–1.65) /1.12 (0.45–2.82) | 0.375 /0.802 | 15/15 | 1.36 (0.62–3.00) /0.84 (0.38–1.86) | 0.442 /0.673 | 23/25 | 0.73 (0.44–1.20) /0.94 (0.46–1.89) | 0.217 /0.856 |
| Dominant model | 111/89 | 35/47 | 0.84 (0.45–1.54) /0.84 (0.44–1.59) | 0.567 /0.593 | 59/71 | 1.54 (0.86–2.78) /0.85 (0.51–1.43) | 0.146 /0.543 | 94/106 | 1.17 (0.73–1.89) /0.85 (0.53–1.35) | 0.508 /0.490 |
| Recessive model | 140/117 | 50/47 | 0.7 (0.30–1.62) /1.31 (0.57–3.03) | 0.403 /0.526 | 65/100 | 1.01 (0.51–1.99) /0.92 (0.45–1.91) | 0.978 /0.831 | 115/147 | 0.88 (0.49–1.58) /1.05 (0.55–1.99) | 0.657 /0.888 |
| C | 143/108 | 43/45 | 0.83 (0.54–1.28) /0.99 (0.63–1.55) | 0.393 /0.966 | 74/86 | 1.21 (0.83–1.76) /0.91 (0.63–1.30) | 0.323 /0.596 | 117/131 | 1.03 (0.75–1.43) /0.93 (0.67–1.29) | 0.837 /0.681 |
| T | 201/164 | 73/69 | Reference | 86/144 | Reference | 159/213 | Reference | |||
| WNT3 rs3809857 | ||||||||||
| GG | 107/81 | 32/39 | Reference | 49/71 | Reference | 81/110 | Reference | |||
| GT | 52/46 | 19/16 | 1.22 (0.63–2.36) /0.72 (0.36–1.43) | 0.550 /0.351 | 21/38 | 0.88 (0.48–1.62) /0.94 (0.55–1.61) | 0.686 /0.828 | 40/54 | 1.02 (0.61–1.68) /0.86 (0.53–1.41) | 0.950 /0.557 |
| TT | 13/9 | 7/2 | 1.80(0.66–4.89) /0.46 (0.10–2.24) | 0.244 /0.501 | 10/6 | 1.68 (0.69–4.09) /0.76 (0.26–2.24) | 0.250 /0.619 | 17/8 | 1.73 (0.79–3.76) /0.65 (0.24–1.77) | 0.165 /0.400 |
| Dominant model | 65/55 | 26/18 | 1.34 (0.73–2.44) /0.68 (0.35–1.31) | 0.343 /0.247 | 31/44 | 1.04 (0.60–1.80) /0.91 (0.55–1.52) | 0.884 /0.724 | 57/62 | 1.16 (0.73–1.83) /0.83 (0.52–1.32) | 0.529 /0.430 |
| Recessive model | 159/127 | 51/55 | 1.68 (0.63–4.44) /0.51 (0.11–2.45) | 0.292 /0.512 | 70/109 | 1.75 (0.73–4.17) /0.78 (0.27–2.25) | 0.205 /0.641 | 121/164 | 1.72 (0.80–3.67) /0.69 (0.26–1.83) | 0.159 /0.453 |
| T | 78/64 | 33/20 | 1.36 (0.84–2.18) /0.69 (0.40–1.21) | 0.209 /0.194 | 41/50 | 1.17 (0.76–1.82) /0.90 (0.59–1.37) | 0.468 /0.633 | 74/70 | 1.25 (0.87–1.80) /0.83 (0.57–1.22) | 0.234 /0.342 |
| G | 266/208 | 83/94 | Reference | 119/180 | Reference | 202/274 | Reference | |||
| Control | NSCLO | p Value | OR (95%CI) | NSCLP | p Value | OR (95%CI) | NSCL/P | p Value | OR (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both VAX1 and MAFB | 138 | 58 | 113 | 171 | ||||||
| VAX1 only | 80 | 35 | 0.8754 | 0.96 (0.58–1.59) | 50 | 0.2199 | 1.31 (0.85–2.02) | 85 | 0.4261 | 1.17 (0.80–1.70) |
| MAFB only | 62 | 12 | 0.0253 | 2.17 (1.09–4.33) | 17 | 0.0002 | 2.99 (1.65–5.39) | 29 | 0.00008 | 2.65 (1.61–4.34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thao, T.P.; Niimi, T.; Suzuki, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Sakuma, C.; Kitagawa, K.; Imura, H.; Kondo, H.; Tu, N.H.; Son, T.M.; et al. Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population. Genes 2025, 16, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080862
Thao TP, Niimi T, Suzuki S, Hayakawa T, Sakuma C, Kitagawa K, Imura H, Kondo H, Tu NH, Son TM, et al. Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population. Genes. 2025; 16(8):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080862
Chicago/Turabian StyleThao, Tran Phuong, Teruyuki Niimi, Satoshi Suzuki, Toko Hayakawa, Chisato Sakuma, Ken Kitagawa, Hideto Imura, Hisataka Kondo, Nguyen Huu Tu, Tong Minh Son, and et al. 2025. "Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population" Genes 16, no. 8: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080862
APA StyleThao, T. P., Niimi, T., Suzuki, S., Hayakawa, T., Sakuma, C., Kitagawa, K., Imura, H., Kondo, H., Tu, N. H., Son, T. M., Ngoc, V. T. N., Anh, L. K., Loc, P. N. G., Furukawa, H., Natsume, N., & Natsume, N. (2025). Association of VAX1, MAFB, WNT3 with Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate in a Japanese Population. Genes, 16(8), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080862






