Characterization of the Four Rosa L. Species from Kazakhstan Based on Complete Plastomes and Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing of the Internal Transcribed Spacer
2.3. Plastome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.4. Identification of the Simple Sequence Repeats
2.5. Plastome Comparison
2.6. Sliding Window Analysis and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
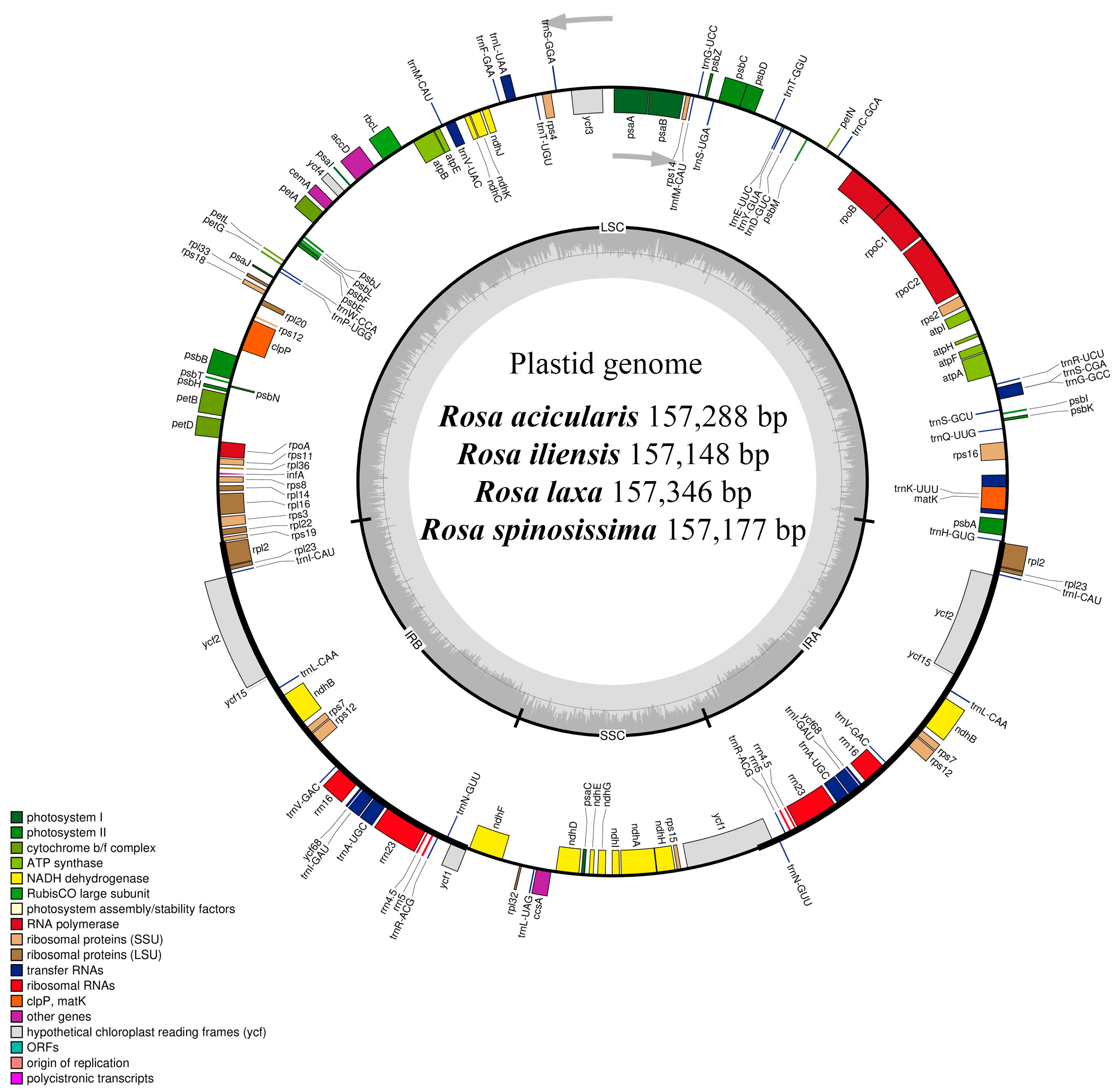
3.1. General Characteristics of the Four Rosa Plastomes
3.2. Simple Sequence Repeat Analysis
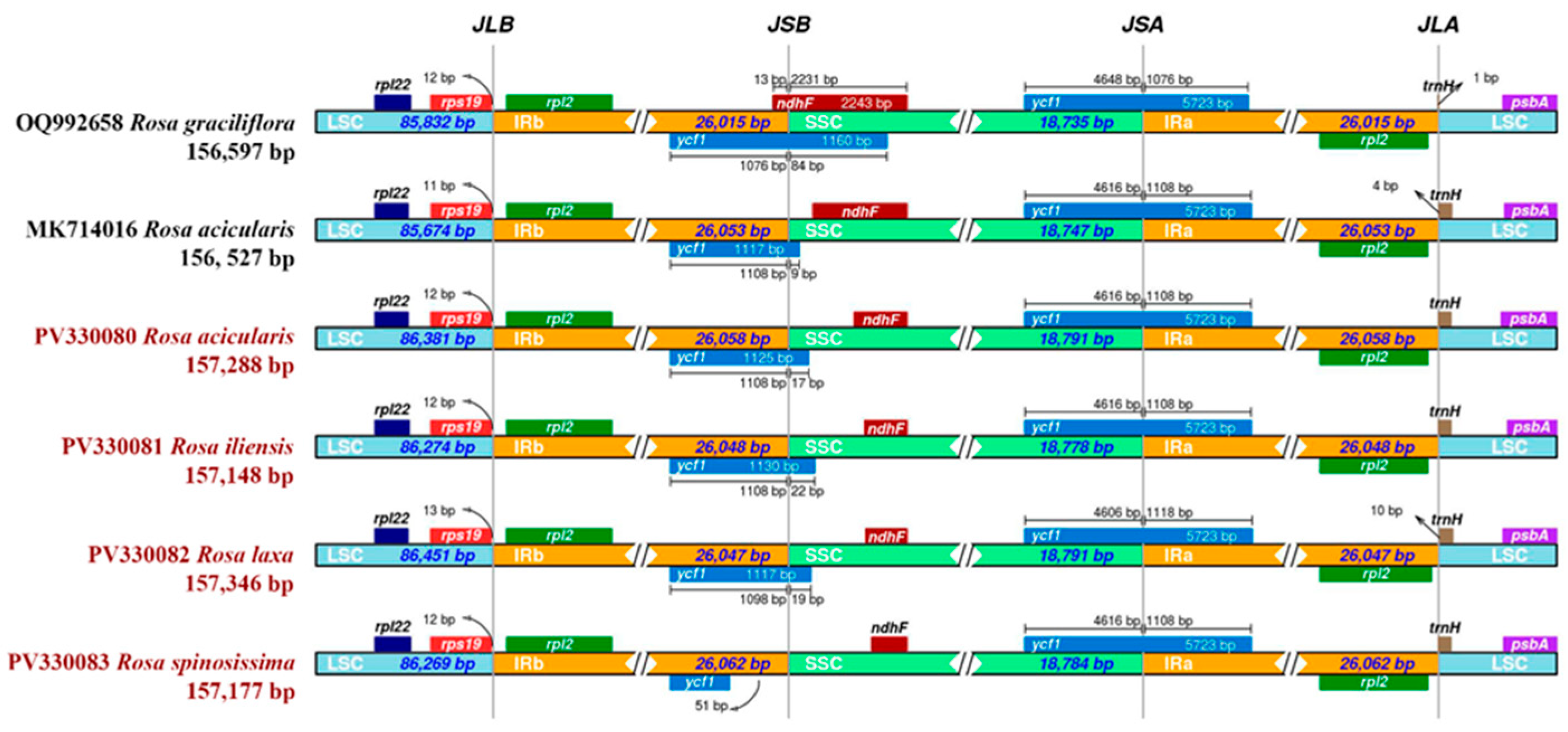
3.3. Comparative Analysis of the Plastomes of Four Rosa Species
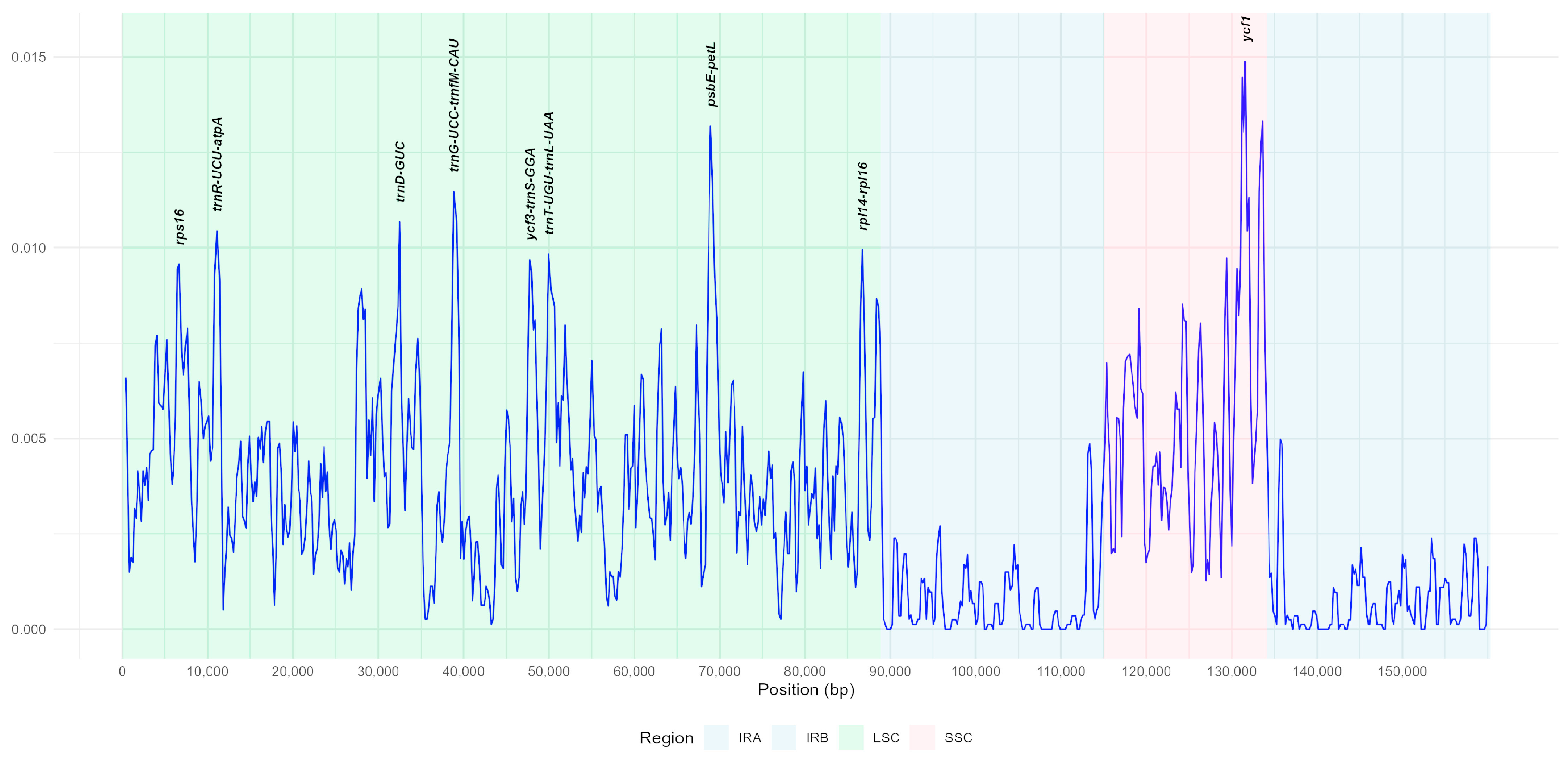
3.4. Nucleotide Diversity Analysis by Sliding Window
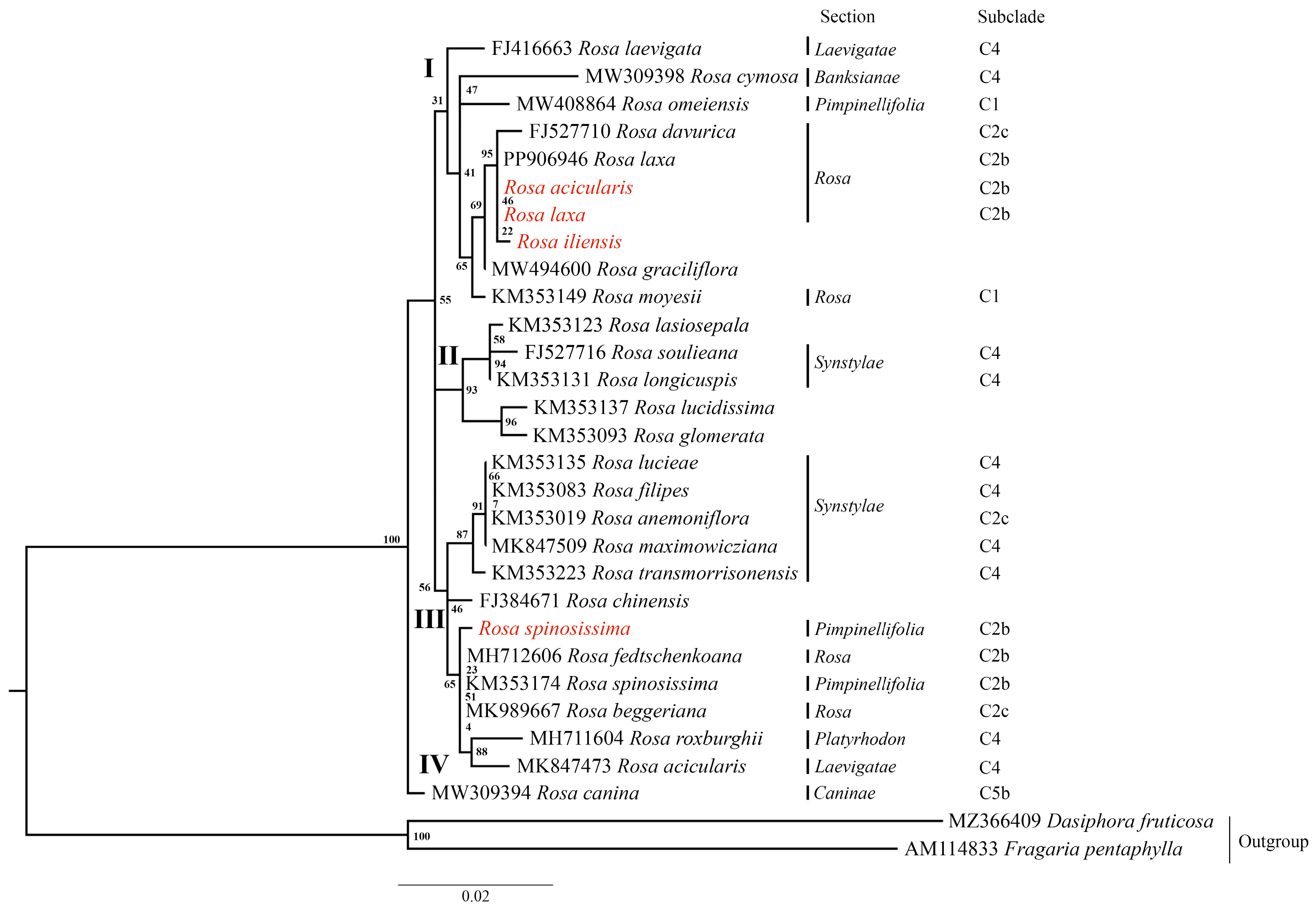
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wissemann, V.; Ritz, C.M. The genus Rosa (Rosoideae, Rosaceae) revisited: Molecular analysis of nrITS-1 and atpB–rbcL intergenic spacer (IGS) versus conventional taxonomy. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2005, 147, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, A. Bibliography of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs Hardy in the Cooler Temperate Regions of the Northern Hemisphere; The Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University: Boston, MA, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, N.V. (Ed.) Flora of Kazakhstan; Publishing House of the Academy of Sciences of the Kazakh SSR: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 1961; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Childibayeva, A.; Ametov, A.; Kurbatova, N.V.; Akhmetova, A.; Tynybekov, B.M.; Mukanova, G.A. Structural characteristics of Rosa iliensis Chrshan. under conditions of the floodplains of the Rivers Ili and Sharyn. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissemann, V. Conventional Taxonomy (Wild Roses). 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312015123_Conventional_Taxonomy_Wild_Roses (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Rehder, A. Rosa L. In Manual of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs Hardy in North America; Collier MacMillan Ltd.: London, UK, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Fougère-Danezan, M.; Joly, S.; Bruneau, A.; Gao, X.F.; Zhang, L.B. Phylogeny and biogeography of wild roses with specific attention to polyploids. Ann. Bot. 2015, 115, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Xia, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Y. Phylogenetic relationships in the genus Rosa revisited based on rpl16, trnL-F, and atpB–rbcL sequences. HortScience 2015, 50, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, K.; Le Paslier, M.C.; Bérard, A.; Thouroude, T.; Michel, G.; Marie-Magdelaine, J.; Bruneau, A.; Foucher, F.; Malécot, V. Unveiling the patterns of reticulated evolutionary processes with phylogenomics: Hybridization and polyploidy in the genus. Rosa. Syst. Biol. 2022, 71, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederick, C.; Wagner, A.; Morvillo, N. Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of the musk roses (Rosa moschata). Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2002, 115, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, A.; Hameed, M.; Khan, A.I.; Younis, A.; Awan, F.S. Assessment of biodiversity based on morphological characteristics and RAPD markers among genotypes of wild rose species. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12520–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Riek, J.; De Cock, K.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Nybom, H. AFLP-based population structure analysis as a means to validate the complex taxonomy of dogroses (Rosa section Caninae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 67, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopman, W.J.M.; Wissemann, V.; De Cock, K.; Van Huylenbroeck, J.; De Riek, J.; Sabatino, G.J.; Visser, D.; Vosman, B.; Ritz, C.M.; Maes, B.; et al. AFLP markers as a tool to reconstruct complex relationships: A case study in Rosa (Rosaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akond, M.; Jin, S.; Wang, X. Molecular characterization of selected wild species and miniature roses based on SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 147, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, A.K.; Namita; Raju, D.V.S.; Ramkumar, M.K.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, B.; Krishnan, S.G.; Panwar, S.; Sevanthi, A.M. Genetic diversity analysis of wild and cultivated Rosa species of India using microsatellite markers and their comparison with morphology-based diversity. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhou, L.; Yu, C.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Q. Molecular evidence for hybrid origin and phenotypic variation of Rosa section Chinenses. Genes 2020, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M.S.; Han, K.; Kwon, J.K.; Kang, B.C. Development of SNP markers using genotyping-by-sequencing for cultivar identification in rose (Rosa hybrida). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2017, 58, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.N.; Yang, A.A.; Meng, X.S.; Dong, G.Z.; Tang, X.J.; Lei, S.M.; Liu, Y.G. Development and application of rose (Rosa chinensis Jacq.) SNP markers based on SLAF-seq technology. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Gao, X.F.; Fougère-Danezan, M. Phylogeny of Rosa sections Chinenses and Synstylae (Rosaceae) based on chloroplast and nuclear markers. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 87, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.V. Relationship between species in the genus Rosa, section Pimpinellifoliae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1977, 74, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Kim, S.C. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome sequences of three closely related East-Asian wild roses (Rosa sect. Synstylae; Rosaceae). Genes 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Huang, X. Phylogenetic relationships and characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Rosa sterilis. Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 1544–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Liao, B.; Guo, S.; Liang, C.; Pei, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. The chloroplasts genomic analyses of Rosa laevigata, R. rugosa and R. canina. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wu, M.; Lian, Y.; Li, Z. Comparative analysis of the chloroplast genomes of Rosa species and RNA editing analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelhans, M.S.; Bayly, M.J.; Heslewood, M.M.; Groppo, M.; Verboom, G.A.; Forster, P.I.; Kallunki, J.A.; Duretto, M.F. A new subfamily classification of the Citrus family (Rutaceae) based on six nuclear and plastid markers. Taxon 2021, 70, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Feng, C.; Kou, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H. Phylogeny and divergence time estimation of the genus Didymodon (Pottiaceae) based on nuclear and chloroplast markers. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.; Peakall, R. Chloroplast simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs): Technical resources and recommendations for expanding cpSSR discovery and applications to a wide array of plant species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.L.; Lim, P.E.; Phang, S.M.; Lee, W.W.; Hong, D.D.; Prathep, A. Development of chloroplast simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs) for the intraspecific study of Gracilaria tenuistipitata (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta) from different populations. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodner, R.; Tewari, K.K. Inverted repeats in chloroplast DNA from higher plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Brozynska, M.; Furtado, A.; Waters, D.L.; Henry, R.J. Relationships of wild and domesticated rices (Oryza AA genome species) based upon whole chloroplast genome sequences. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almerekova, S.; Yermagambetova, M.; Ivaschenko, A.; Turuspekov, Y.; Abugalieva, S. Comparative analysis of plastome sequences of seven Tulipa L. (Liliaceae Juss.) species from section Kolpakowskianae Raamsd. ex Zonn and Veldk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyamgerel, N.; Baasanmunkh, S.; Munkhtulga, D.; Tugsbilguun, T.; Oyuntsetseg, B.; Xiang, C.L.; Choi, H.J. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Dracocephalum ruyschiana (Lamiaceae) and its phylogenetic analysis. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2025, 55, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Gairola, S. Nutritional Potential of Wild Edible Rose Hips in India for Food Security. In Wild Food Plants for Zero Hunger and Resilient Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Pekamwar, S.S.; Kalyankar, T.M.; Jadhav, A.C. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis: A review on ornamental plant. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. (WJPPS) 2013, 2, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N. Rose (Rosa sp.) More Than Just Beautiful: Exploring the Therapeutic Properties of the Rose Species. In Advances in Medicinal and Aromatic Plants; Apple Academic Press: Oakville, 2025; Volume 2, p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Butkevičiūtė, A.; Urbštaitė, R.; Liaudanskas, M.; Obelevičius, K.; Janulis, V. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity in fruit of the genus Rosa L. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 912. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrubasik, C.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Chrubasik, S. A systematic review on the Rosa canina effect and efficacy profiles. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Mirza, B. Phytochemical analysis and comprehensive evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of 61 medicinal plant species. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagle, P.; Idassi, O.; Carpenter, J.; Minor, R.; Goktepe, I.; Martin, P. Effect of rosehip (Rosa canina) extracts on human brain tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis. J. Cancer Ther. 2012, 3, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Lu, W.; Tang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, H. Study on the anti-atherosclerosis effect of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2015, 11, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Wei, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhao, J.; Shang, H. Extraction optimization, physicochemical properties and antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from roxburgh rose (Rosa roxburghii Tratt.) leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaudanskas, M.; Noreikienė, I.; Zymonė, K.; Juodytė, R.; Žvikas, V.; Janulis, V. Composition and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in fruit of the genus Rosa L. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chroho, M.; Bouymajane, A.; Oulad El Majdoub, Y.; Cacciola, F.; Mondello, L.; Aazza, M.; Zair, T.; Bouissane, L. Phenolic composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of extract from flowers of Rosa damascena from Morocco. Separations 2022, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Chen, J.; Fu, M.; Li, H.; Bu, S.; Hao, X.; Gu, W. UPLC-ESI-MS/MS-based analysis of various edible Rosa fruits concerning secondary metabolites and evaluation of their antioxidant activities. Foods 2024, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Chemposov, V.V.; Chirikova, N.K. Metabolites of prickly rose: Chemodiversity and digestive-enzyme-inhibiting potential of Rosa acicularis and the main ellagitannin rugosin D. Plants 2021, 10, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Li, A.; Feng, Q.; Tian, L. Research on the pharmacognostic characteristics, physicochemical properties and in vitro antioxidant potency of Rosa laxa Retz. flos. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 2487–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, O.O.; Pisarev, D.I.; Zhilyakova, E.T.; Novikova, M.U.; Bondarenko, E.V.; Fadeeva, D.A.; Bezmenova, M.D. Phytochemical study of the north caucasian Rosa spinossima L. fruit. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 152, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özek, G.; Chidibayeva, A.; Ametov, A.; Nurmahanova, A.; Özek, T. Chemical composition of flower volatiles and seeds fatty acids of Rosa iliensis Chrshan, an endemic species from Kazakhstan. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2022, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): A tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Curr. Genet. 2007, 52, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozas, J.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Messeguer, X.; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.N.L.; Doan, T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Phạm, M.H.; Le, T.L.; Sy, D.T.; Chu, H.H.; Chu, H.M. Complete chloroplast genome of novel Adrinandra megaphylla Hu species: Molecular structure, comparative and phylogenetic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyuntsetseg, D.; Nyamgerel, N.; Baasanmunkh, S.; Oyuntsetseg, B.; Bayarmaa, G.A.; Choi, H.J. The complete chloroplast genome of Swertia obtusa (Gentianaceae) in Mongolia. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Cai, H.W.; Zhu, Z.M. Characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of Rosa glomerata (Rosaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2022, 7, 1579–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, X.; Yan, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Tang, K. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of a critically endangered decaploid rose species, Rosa praelucens (Rosaceae). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2018, 10, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, C. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Rosa minutifolia. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 3320–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, M.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, A.; Li, Z. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast genome for Rosa xanthina. Mitochondrial DNA B 2020, 5, 2922–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yan, H.J.; Qiu, X.Q.; Wang, Q.G.; Li, S.B.; Wang, Q.-G.; Tang, K.-X. The complete chloroplast genome of a key ancestor of modern roses, Rosa chinensis var. spontanea, and a comparison with congeneric species. Molecules 2018, 23, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Sahu, S.K.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Mu, W.; Liu, X.; Strube, M.L.; Liu, H.; Zhong, B. Comparative analyses of 3,654 plastid genomes unravel insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogenetic discordance of green plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 808156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millen, R.S.; Olmstead, R.G.; Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Lao, N.T.; Heggie, L.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C.; Morden, C.W.; et al. Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Q.; Lin, G.; Fu, C.; Kang, T.; Zeng, H. Assembly and comparative analyses of the chloroplast genomes of the threatened plant Rosa anemoniflora. Forests 2024, 15, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Saski, C.; Lee, S.B.; Hansen, A.K.; Daniell, H. Complete plastid genome sequences of three rosids (Castanea, Prunus, Theobroma): Evidence for at least two independent transfers of rpl22 to the nucleus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangphatsornruang, S.; Uthaipaisanwong, P.; Sangsrakru, D.; Chanprasert, J.; Yoocha, T.; Jomchai, N.; Tragoonrung, S. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Hevea brasiliensis reveals genome rearrangement, RNA editing sites and phylogenetic relationships. Gene 2011, 475, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yan, H.F.; Zhang, L.; Ge, X.J.; Hao, G. Complete plastid genome sequence of Primula sinensis (Primulaceae): Structure comparison, sequence variation and evidence for accD transfer to nucleus. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Deng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Da, Q. Comparative chloroplast genomics of 34 species in subtribe Swertiinae (Gentianaceae) with implications for its phylogeny. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Ni, D.; Wang, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, C. Intraspecific and heteroplasmic variations, gene losses and inversions in the chloroplast genome of Astragalus membranaceus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cai, C.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, M.; Chen, L.; Li, J. Variation and evolution of the whole chloroplast genomes of Fragaria spp. (Rosaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 754209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tong, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, Y. Complete plastid genome structure of 13 Asian Justicia (Acanthaceae) species: Comparative genomics and phylogenetic analyses. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, M.A.; Shahzad, R.; Lubna; Kang, S.M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Lee, I.-J.; Budak, H. Complete chloroplast genome sequence and comparative analysis of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) with related species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazareno, A.G.; Carlsen, M.; Lohmann, L.G. Complete chloroplast genome of Tanaecium tetragonolobum: The first Bignoniaceae plastome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, P. Molecular markers from the chloroplast genome of rose provide a complementary tool for variety discrimination and profiling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Lu, T.; Shi, W. Development of SSR markers and evaluation of genetic diversity of endangered plant Saussurea involucrata. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yermagambetova, M.; Almerekova, S.; Turginov, O.; Sultangaziev, O.; Abugalieva, S.; Turuspekov, Y. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juniperus seravschanica Kom. collected in Central Asia. Plants 2023, 12, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Shavvon, R.S.; Qi, H.; Wu, H.; Fan, P.; Shalizi, M.N.; Khurram, S.; Davletbek, M.; Turuspekov, Y.; Liu, J. Population genetic insights into the conservation of common walnut (Juglans regia) in Central Asia. Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, J.C.; Poletto, T.; Muniz, M.F.B.; Poletto, I.; de Oliveira, J.N.M.; Stefenon, V.M. Species-specific plastid SSR markers reveal evidence of cultivar misassignments in Brazilian pecan [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch] orchards. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2023, 70, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, J.; Caré, O.; Beck, W.; Gailing, O.; Hosius, B.; Leinemann, L. A novel set of chloroplast SSR markers for the genus Juglans reveals within species differentiation. Silvae Genet. 2024, 73, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, J.; Leinemann, L.; Gailing, O.; Hardtke, A.; Caré, O. Development of a highly polymorphic chloroplast SSR set in Abies grandis with transferability to other conifer species—A promising toolkit for gene flow investigations. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jacquemyn, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W. Comparative analysis of the chloroplast genomes of Cypripedium: Assessing the roles of SSRs and TRs in the non-coding regions of LSC in shaping chloroplast genome size. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.A.; Albokhari, E.J. Complete chloroplast genomes of Desmidorchis penicillata (Deflers) Plowes and Desmidorchis retrospiciens Ehrenb.: Comparative and phylogenetic analyses among subtribe Stapeliinae (Ceropegieae, Asclepiadoideae, Apocynaceae). Nord. J. Bot. 2025, 2025, e04526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almerekova, S.; Yermagambetova, M.; Osmonali, B.; Vesselova, P.; Turuspekov, Y.; Abugalieva, S. Complete plastid genome sequences of four Salsoleae s.l. species: Comparative and phylogenetic analyses. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almerekova, S.; Shchegoleva, N.; Abugalieva, S.; Turuspekov, Y. The molecular taxonomy of three endemic Central Asian species of Ranunculus (Ranunculaceae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antil, S.; Abraham, J.S.; Sripoorna, S.; Maurya, S.; Dagar, J.; Makhija, S.; Bhagat, P.; Gupta, R.; Sood, U.; Lal, R.; et al. DNA barcoding, an effective tool for species identification: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamdade, R.; Mosa, K.A.; El-Keblawy, A.; Al Shaer, K.; Al Harthi, E.; Al Sallani, M.; Al Jasmi, M.; Gairola, S.; Shabana, H.; Mahmoud, T. DNA barcodes for accurate identification of selected medicinal plants (Caryophyllales): Toward barcoding flowering plants of the United Arab Emirates. Diversity 2022, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabelin, V.L.D.; Santor, P.J.S.; Alejandro, G.J.D. Evaluation of DNA barcoding efficiency of cpDNA barcodes in selected Philippine Leea L. (Vitaceae). Acta Bot. Gall. 2015, 162, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevindik, E.; Korkom, Y.; Murathan, Z.T. Evaluating DNA barcoding using cpDNA matK and rbcL for species identification and phylogenetic analysis of Prunus armeniaca L. (Rosaceae) genotypes. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Tyagi, A.; Shukla, V.; Kumar, A.; Singh, U.M.; Chaudhary, L.B.; Datt, B.; Bag, S.K.; Singh, P.K.; Nair, N.K.; et al. Universal plant DNA barcode loci may not work in complex groups: A case study with Indian Berberis species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Yan, H.F.; Wei, L.; Liu, T.J.; Chen, L.; Hao, G.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.L. Plastid genome and its phylogenetic implications of Asiatic Spiraea (Rosaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Chen, X.; Deng, Y.; Geng, L.; Ma, J.; Wei, X. Complete chloroplast genomes of Sorbus sensu stricto (Rosaceae): Comparative analyses and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Tian, Q.; Gu, W.; Yang, C.X.; Wang, D.J.; Yi, T.S. Comparative genomics on chloroplasts of Rubus (Rosaceae). Genomics 2024, 116, 110845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Ueda, Y.; Nishihara, S.; Matsumoto, S. Phylogenetic analysis of Japanese Rosa species using DNA sequences of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers (ITS). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuong, L.Q.; Tam, T.V.; Dong, D.V.; Duong, T.D.; Cuc, D.T.K.; Thu, P.T.L.; Luong, D.T.; Tuyen, V.T.M.; Giang, N.V.; Tuan, N.T. Identification of Vietnamese native rose species by using internal transcribed spacers (ITS) sequencing. Plant Cell Biotech. Mol. Biol. 2020, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Xu, K.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Liao, W.B.; Zhang, Y.H. Molecular phylogenetic analyses based on the complete plastid genomes and nuclear sequences reveal Daphne (Thymelaeaceae) to be non-monophyletic as current circumscription. Plant Divers. 2022, 44, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Direction | Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS1nF | AGAAGTCGTAACAAGGTTTCCGTAGG | Forward | 58 | [50] |
| ITS4nR | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | Reverse | 58 | [50] |
| Species | Rosa acicularis | Rosa iliensis | Rosa laxa | Rosa spinosissima |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank accession number | PV330080 | PV330081 | PV330082 | PV330083 |
| Genome size (bp) | 157,288 | 157,148 | 157,346 | 157,177 |
| LSC length (bp) | 86,381 | 86,274 | 86,461 | 86,269 |
| SSC length (bp) | 18,791 | 18,778 | 18,791 | 18,784 |
| IRA length (bp) | 26,058 | 26,048 | 26,047 | 26,062 |
| IRB length (bp) | 26,058 | 26,048 | 26,047 | 26,062 |
| Total GC content (%) | 37.20 | 37.20 | 37.20 | 37.20 |
| Number of total genes (unique) | 136 (116) | 136 (116) | 136 (116) | 136 (116) |
| Total protein-coding genes (unique) | 90 (81) | 90 (81) | 90 (81) | 90 (81) |
| Total tRNA genes (unique) | 38 (31) | 38 (31) | 38 (31) | 38 (31) |
| Total rRNA genes (unique) | 8 (4) | 8 (4) | 8 (4) | 8 (4) |
| Group of Genes | Name of Genes |
|---|---|
| Self-replication | |
| Ribosomal RNA | rrn4.5 (×2), rrn5 (×2), rrn16 (×2), rrn23 (×2) |
| Transfer RNA | trnA-UGC * (×2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnfM-CAU, trnG-GCC *, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU (×2), trnI-GAU * (×2), trnK-UUU *, trnL-CAA (×2), trnL-UAA *, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU (×2), trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG (×2), trnR-UCU, trnS-CGA *, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC (×2), trnV-UAC *, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA |
| Small subunit of ribosome | rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7 (×2), rps8, rps11, rps12 ** (×2), rps14, rps15, rps16 *, rps18, rps19 |
| Large subunit of ribosome | rpl2 * (×2), rpl14, rpl16 *, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23 (×2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1 *, rpoC2 |
| Translation initiation factor | infA |
| Photosynthesis | |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF, atpH, atpI |
| NADH dehydrogenase | ndhA *, ndhB * (×2), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK |
| Subunits of cytochrome | petA, petB *, petD *, petG, petL, petN |
| Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ |
| Rubisco | rbcL |
| Other genes | |
| Maturase | matK |
| Protease | clpP ** |
| Envelope membrane protein | cemA |
| Subunit of acetyl-CoA-carboxylase | accD |
| C-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA |
| Genes of unknown function | |
| Conserved hypothetical chloroplast ORF | ycf1 (×2), ycf2 (×2), ycf3 **, ycf4, ycf15 (×2), ycf68 (×2) |
| Type | Repeat Unit | Rosa acicularis | Rosa iliensis | Rosa laxa | Rosa spinosissima | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono- | A/T | 138 | 144 | 138 | 143 | 563 | 66.41 |
| C/G | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 38 | ||
| Di- | AT/AT | 39 | 39 | 39 | 38 | 155 | 24.64 |
| AG/CT | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 64 | ||
| AC/GT | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||
| Tri- | AAT/ATT | 7 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 26 | 2.98 |
| AGC/CTG | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Tetra- | AAAT/ATTT | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 24 | 4.75 |
| AATT/AATT | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 7 | ||
| ACAT/ATGT | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||
| ACCT/AGGT | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | ||
| Penta- | AATAT/ATATT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.33 |
| AAAAG/CTTTT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Hexa- | AAGTAG/ACTTCT | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 0.88 |
| Total | 224 | 227 | 225 | 229 | 905 | 100.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yermagambetova, M.; Imanbayeva, A.; Ishmuratova, M.; Sumbembayev, A.; Almerekova, S. Characterization of the Four Rosa L. Species from Kazakhstan Based on Complete Plastomes and Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequences. Genes 2025, 16, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080852
Yermagambetova M, Imanbayeva A, Ishmuratova M, Sumbembayev A, Almerekova S. Characterization of the Four Rosa L. Species from Kazakhstan Based on Complete Plastomes and Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequences. Genes. 2025; 16(8):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080852
Chicago/Turabian StyleYermagambetova, Moldir, Akzhunis Imanbayeva, Margarita Ishmuratova, Aidar Sumbembayev, and Shyryn Almerekova. 2025. "Characterization of the Four Rosa L. Species from Kazakhstan Based on Complete Plastomes and Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequences" Genes 16, no. 8: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080852
APA StyleYermagambetova, M., Imanbayeva, A., Ishmuratova, M., Sumbembayev, A., & Almerekova, S. (2025). Characterization of the Four Rosa L. Species from Kazakhstan Based on Complete Plastomes and Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Sequences. Genes, 16(8), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080852






