Brain and CSF Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Are Associated with SERPINE1 Gene Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants from the Douglas-Bell Canada Brain Bank Cohort
2.2. Study Participants from the Mayo Clinic/Banner Brain Bank Cohort
2.3. Study Participants from the Asymptomatic PREVENT-AD Cohort
2.3.1. Cerebrospinal Fluid Measurements of the PREVENT-AD Cohort
2.3.2. Hippocampus Volume of the PREVENT-AD Cohort
2.3.3. APOE Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Data Availability
3. Results
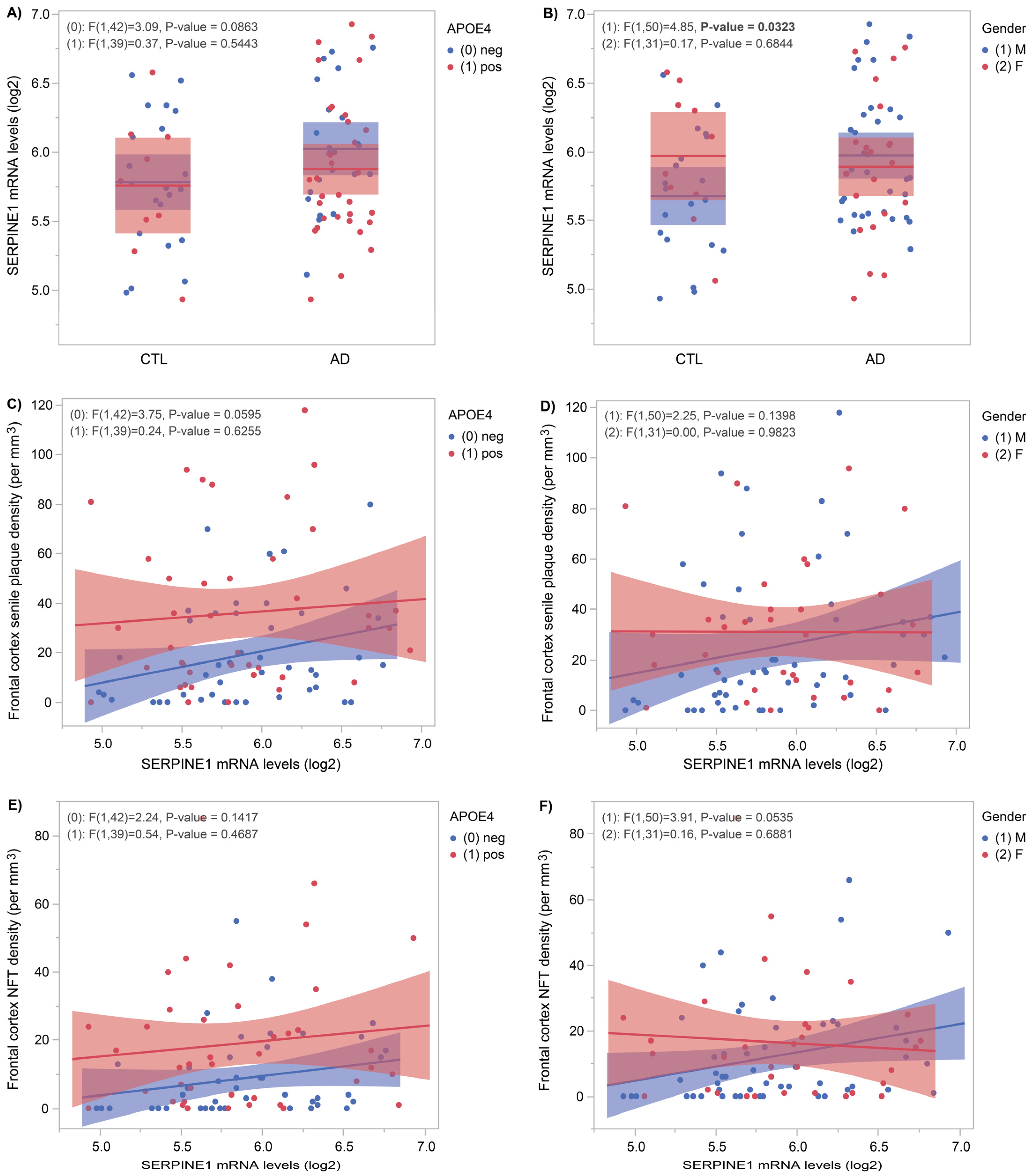
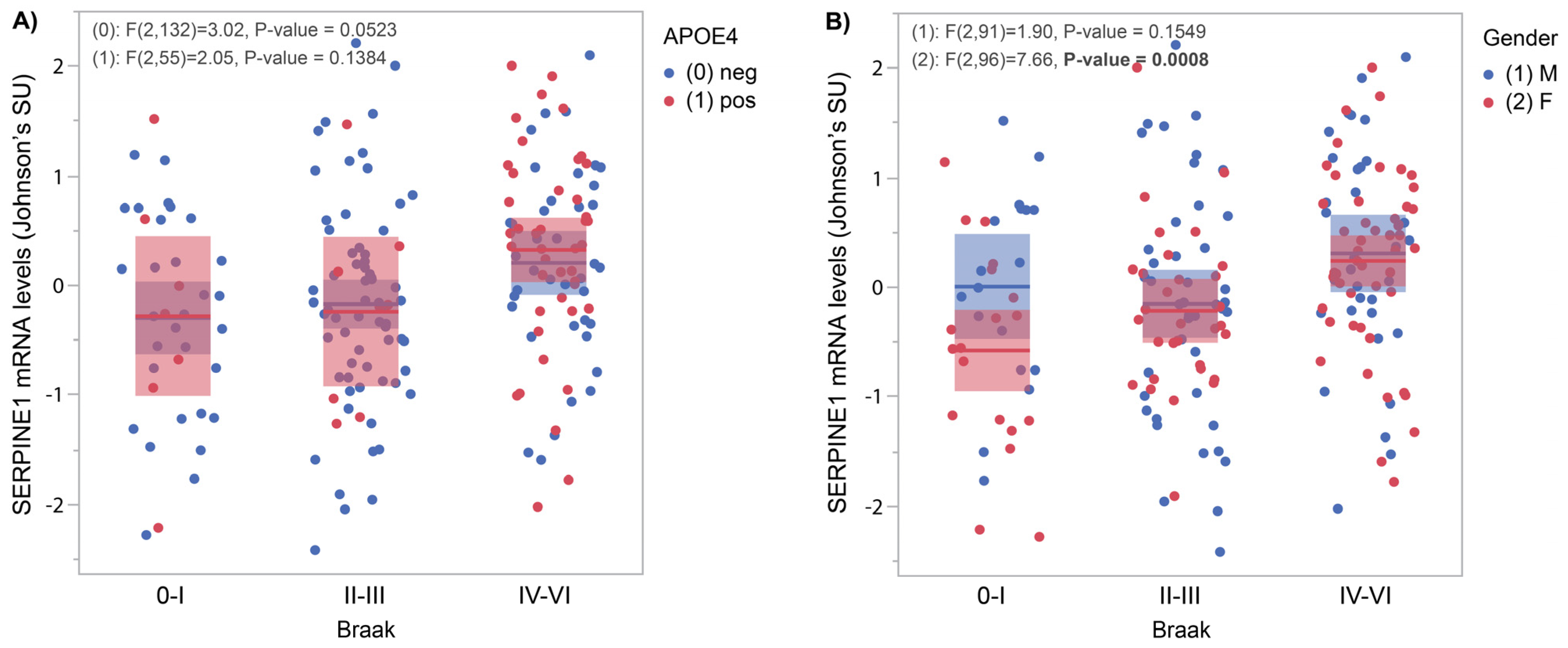
3.1. SERPINE1 mRNA Levels Correlate with AD Pathology
3.2. CSF SERPINE1 Protein Levels Correlate Positively with AD Biomarkers
3.3. SERPINE1 Protein Levels Correlate Negatively with Hippocampus Volume
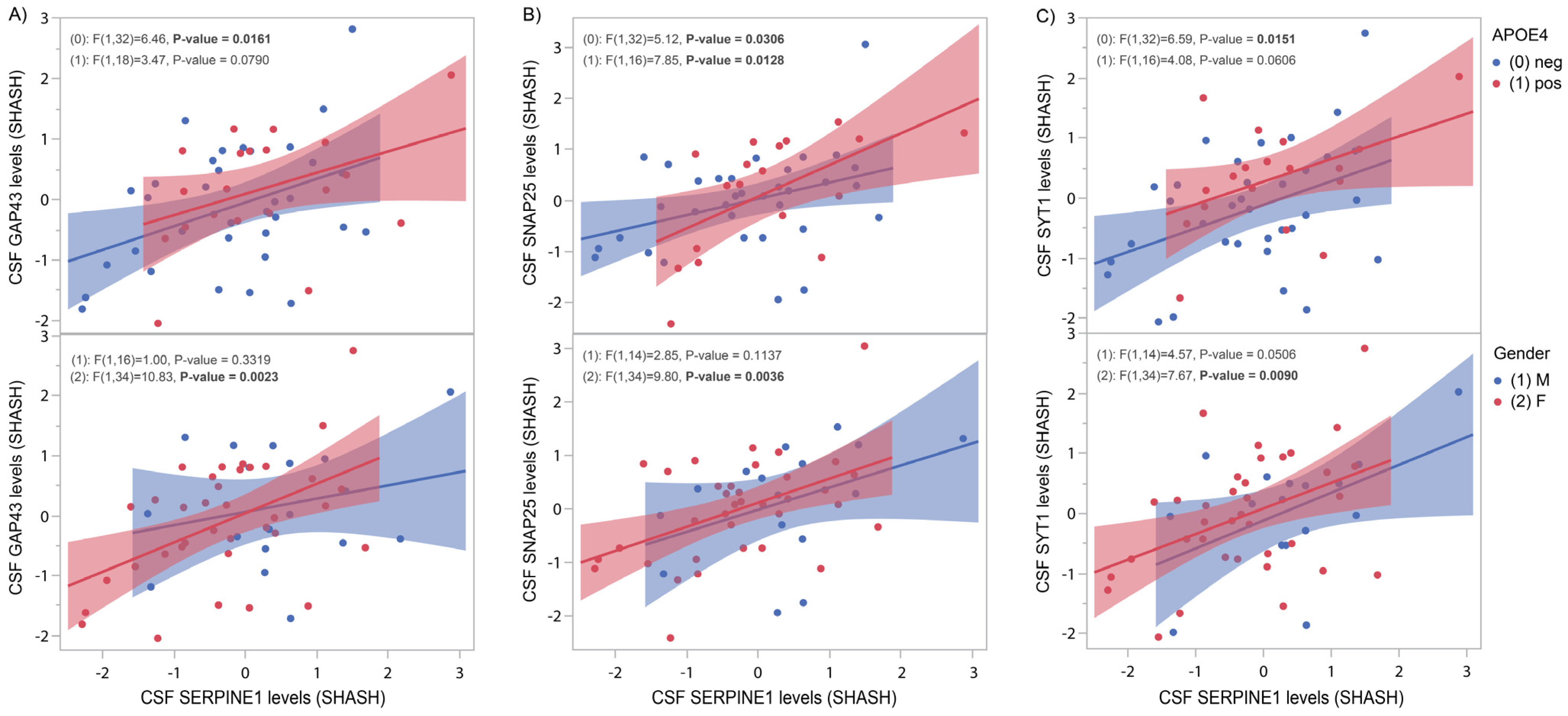
3.4. SERPINE1 Protein Levels Correlate Positively with Synaptic Markers
3.5. Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis of CSF SERPINE1 Levels Identifies Naturally Occurring Polymorphisms in the SERPINE1 and VAT1L Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| PAI | Plasminogen activator inhibitor |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| PREVENT-AD | The PRe-symptomatic EValuation of Experimental or Novel Treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADNI | The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| DBCBB | Douglas-Bell Canada Brain Bank |
| tPA | Tissue plasminogen activator |
| uPA | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| PSP | Progressive supranuclear palsy |
| CU | Cognitively unimpaired |
| GAP43 | Growth-associated protein 43 |
| SNAP25 | Synaptosome-associated protein 25 |
| SYT1 | Synaptotagmin 1 |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E |
| CTL | Controls |
| NFT | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| pQTL | Protein quantitative trait loci |
| VAT1L | Vesicle amine transport 1 like |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| PLAT | Plasminogen activator, tissue type |
| TP53 | Tumour protein p53 |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| GSK3B | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
References
- Cesari, M.; Pahor, M.; Incalzi, R.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): A key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28, e72–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Seiffert, D.; Fowler, B.J.; Jenkins, G.R.; Thinnes, T.C.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Parmer, R.J.; Miles, L.A. Plasminogen has a broad extrahepatic distribution. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 493–501. [Google Scholar]
- Kjoller, L.; Kanse, S.M.; Kirkegaard, T.; Rodenburg, K.W.; Ronne, E.; Goodman SLPreissner, K.T.; Ossowski, L.; Andreasen, P.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 represses integrin- and vitronectin-mediated cell migration independently of its function as an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 232, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzha, Y.; Ni, J.; Quan, Z.; Li, H.; Qing, H. Role of Vitronectin and Its Receptors in Neuronal Function and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, H.M.; Kihiko, M.; Caldwell, J.N.; Wright, S.; Kawarabayashi, T.; Price, D.; Walker, D.; Scheff, S.; McGillis, J.P.; Rydel, R.E.; et al. The plasmin system is induced by and degrades amyloid-beta aggregates. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3937–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, M.D.; Da Silva, J.S.; Crassaerts, K.; Delacourte, A.; De Strooper, B.; Dotti, C.G. Brain plasmin enhances APP alpha-cleavage and Abeta degradation and is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease brains. EMBO Rep. 2000, 1, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Lee, H.J.; Song, J.H.; Park, S.I.; Kim, H. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as an early potential diagnostic marker for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 60, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistri, M.; Velmeshev, D.; Makhmutova, M.; Faghihi, M.A. Transcriptomics Profiling of Alzheimer’s Disease Reveal Neurovascular Defects, Altered Amyloid-beta Homeostasis, and Deregulated Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Funk, C.; Heavner, B.D.; Zou, F.; Younkin, C.S.; Burgess, J.D.; Chai, H.S.; Crook, J.; Eddy, J.A.; et al. Human whole genome genotype and transcriptome data for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Madjar, C.; Das, S.; Pichet Binette, A.; Dyke, S.O.M.; Étienne, P.; Lafaille-Magnan, M.E.; Remz, J.; Bellec, P.; Louis Collins, D.; et al. Open science datasets from PREVENT-AD, a longitudinal cohort of pre-symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 31, 102733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmalm, A.; Brinkmalm, G.; Honer, W.G.; Frölich, L.; Hausner, L.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Wallin, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. SNAP-25 is a promising novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for synapse degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, P.; Madjar, C.; Savard, M.; Dansereau, C.; Tam, A.; Das, S.; Evans, A.C.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Breitner, J.; Bellec, P. Test-retest resting-state fMRI in healthy elderly persons with a family history of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Data. 2015, 2, 150043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.W.; Vachon-Presseau, E.; Pichet Binette, A.; Tam, A.; Orban, P.; La Joie, R.; Savard, M.; Picard, C.; Poirier, J.; Bellec, P.; et al. Brain properties predict proximity to symptom onset in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2018, 141, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage 2007, 38, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupe, P.; Manjon, J.V.; Fonov, V.; Pruessner, J.; Robles, M.; Collins, D.L. Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: Application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, D.; Zeheb, R.; Yang, A.Y.; Rafferty, U.M.; Andreasen, P.A.; Nielsen, L.; Dano, K.; Lebo, R.V.; Gelehrter, T.D. cDNA cloning of human plasminogen activator-inhibitor from endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.; Kallin, B.; van ‘t Hooft, F.M.; Bavenholm, P.; Hamsten, A. Allele-specific increase in basal transcription of the plasminogen-activator inhibitor 1 gene is associated with myocardial infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, P. Myocardial Infarction Predisposes Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santisteban, M.M.; Iadecola, C. The pathobiology of neurovascular aging. Neuron 2025, 113, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, M.; Woo, Y.; Martin-Jimenez, C. Plasminogen Activators in Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelucci, F.; Veverova, K.; Katonova, A.; Vyhnalek, M.; Hort, J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 serum levels in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherva, R.; Tripodis, Y.; Bennett, D.A.; Chibnik, L.B.; Crane, P.K.; de Jager, P.L.; Farrer, L.A.; Saykin, A.J.; Shulman, J.M.; Naj, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study of the rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Dong, N.Z.; Bai, X.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, C.G. A case of deficiency of plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 related to Ala15Thr mutation in its signal peptide. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2005, 16, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Kawarai, T.; Meng, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Wakutani, Y.; Shibata, E.; Pathan, N.; Bi, A.; Sato, C.; et al. Association studies between the plasmin genes and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekih-Mrissa, N.; Mansour, M.; Sayeh, A.; Bedoui, I.; Mrad, M.; Riahi, A.; Mrissa, R.; Nsiri, B. The Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 4G/5G Polymorphism and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2017, 32, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.L.; Ganaraja, B.; Murlimanju, B.V.; Joy, T.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Agrawal, A. Hippocampus and its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease: A review. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleó, A.; Núñez-Llaves, R.; Alcolea, D.; Chiva, C.; Balateu-Paños, D.; Colom-Cadena, M.; Gomez-Giro, G.; Muñoz, L.; Querol-Vilaseca, M.; Pegueroles, J.; et al. Changes in Synaptic Proteins Precede Neurodegeneration Markers in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K. Cerebrospinal fluid protein biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrfelt, A.; Brinkmalm, A.; Dumurgier, J.; Brinkmalm, G.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Bouaziz-Amar, E.; Hugon, J.; Paquet, C.; Blennow, K. The pre-synaptic vesicle protein synaptotagmin is a novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepes, M. The plasminogen activating system in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| DBCBB | Mayo | PREVENT-AD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL (n = 30) | AD (n = 55) | non AD (n = 111) | AD (n = 82) | CU at risk (n = 125) | |
| Age (mean ± SEM) | 77.4 ± 2.1 | 80.7 ± 0.9 | >78 * | >83 * | 59.9 ± 1.1 |
| Gender F (%) | 33.3 | 41.8 | 45 | 59.8 | 69.6 |
| APOE4 (%) | 30 | 58.2 | 13.5 | 52.4 | 38.4 |
| SNP | Cohort | Freq CTL | Freq AD | CTL vs. AD p Value | SERPINE1 QTL p Value | Aβ42 CSF | pTau181 CSF | tTau CSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs17705051 (VAT1L) | PREVENT-AD | 0.05 | - | - | p = 5 × 10−8 (CSF) | p = 0.421 | p = 6 × 10−3 | p = 5 × 10−3 |
| ADNI | 0.04 | 0.04 | p = 0.801 | p = 0.654 (CSF) | p = 0.642 | p = 0.663 | p = 0.629 | |
| DBCBB | 0.08 | 0.08 | p = 0.972 | p = 0.420 (Brain) | ||||
| MAYO | 0.04 | 0.05 | p = 0.703 | p = 0.413 (Brain) | ||||
| rs6092 (SERPINE1) | PREVENT-AD | 0.12 | - | - | p = 2.5 × 10−2 (CSF) | p = 0.067 | p = 0.674 | p = 0.870 |
| ADNI | 0.09 | 0.12 | p = 0.537 | p = 7 × 10−4 (CSF) | p = 0.322 | p = 0.461 | p = 0.381 | |
| DBCBB | 0.13 | 0.22 | p = 0.184 | p = 0.792 (Brain) | ||||
| MAYO | 0.14 | 0.11 | p = 0.311 | p = 4.1 × 10−2 (Brain) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picard, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Villeneuve, S.; Poirier, J.; on behalf of the PREVENT-AD Research Group. Brain and CSF Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Are Associated with SERPINE1 Gene Expression. Genes 2025, 16, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070818
Picard C, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Villeneuve S, Poirier J, on behalf of the PREVENT-AD Research Group. Brain and CSF Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Are Associated with SERPINE1 Gene Expression. Genes. 2025; 16(7):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070818
Chicago/Turabian StylePicard, Cynthia, Henrik Zetterberg, Kaj Blennow, Sylvia Villeneuve, Judes Poirier, and on behalf of the PREVENT-AD Research Group. 2025. "Brain and CSF Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Are Associated with SERPINE1 Gene Expression" Genes 16, no. 7: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070818
APA StylePicard, C., Zetterberg, H., Blennow, K., Villeneuve, S., Poirier, J., & on behalf of the PREVENT-AD Research Group. (2025). Brain and CSF Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Are Associated with SERPINE1 Gene Expression. Genes, 16(7), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070818






