Gene-Based Burden Testing of Rare Variants in Hemiplegic Migraine: A Computational Approach to Uncover the Genetic Architecture of a Rare Brain Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Rare Variant Association Tests
1.2. Population Stratification
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohorts
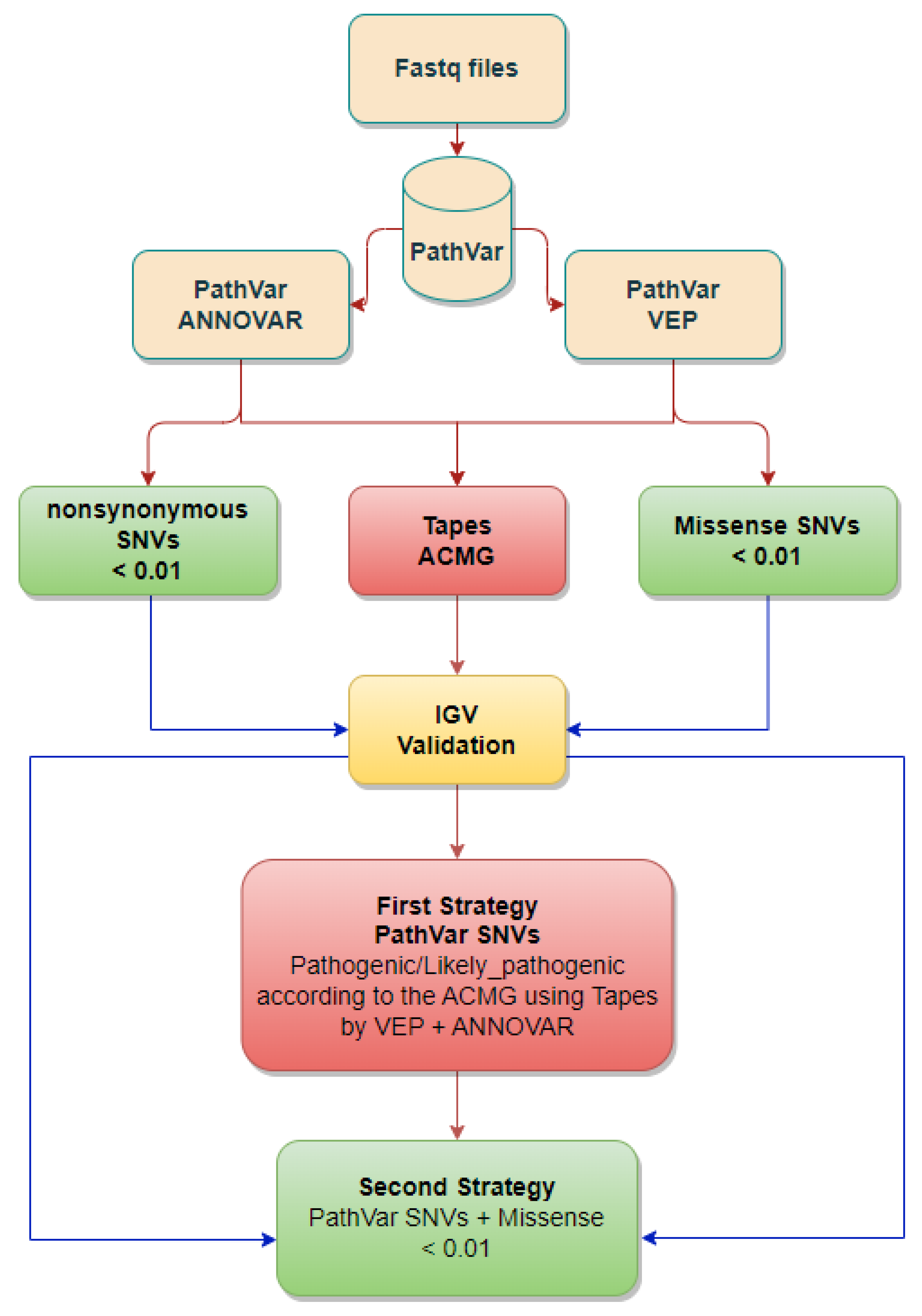
2.2. Qualifying SNVs Selection
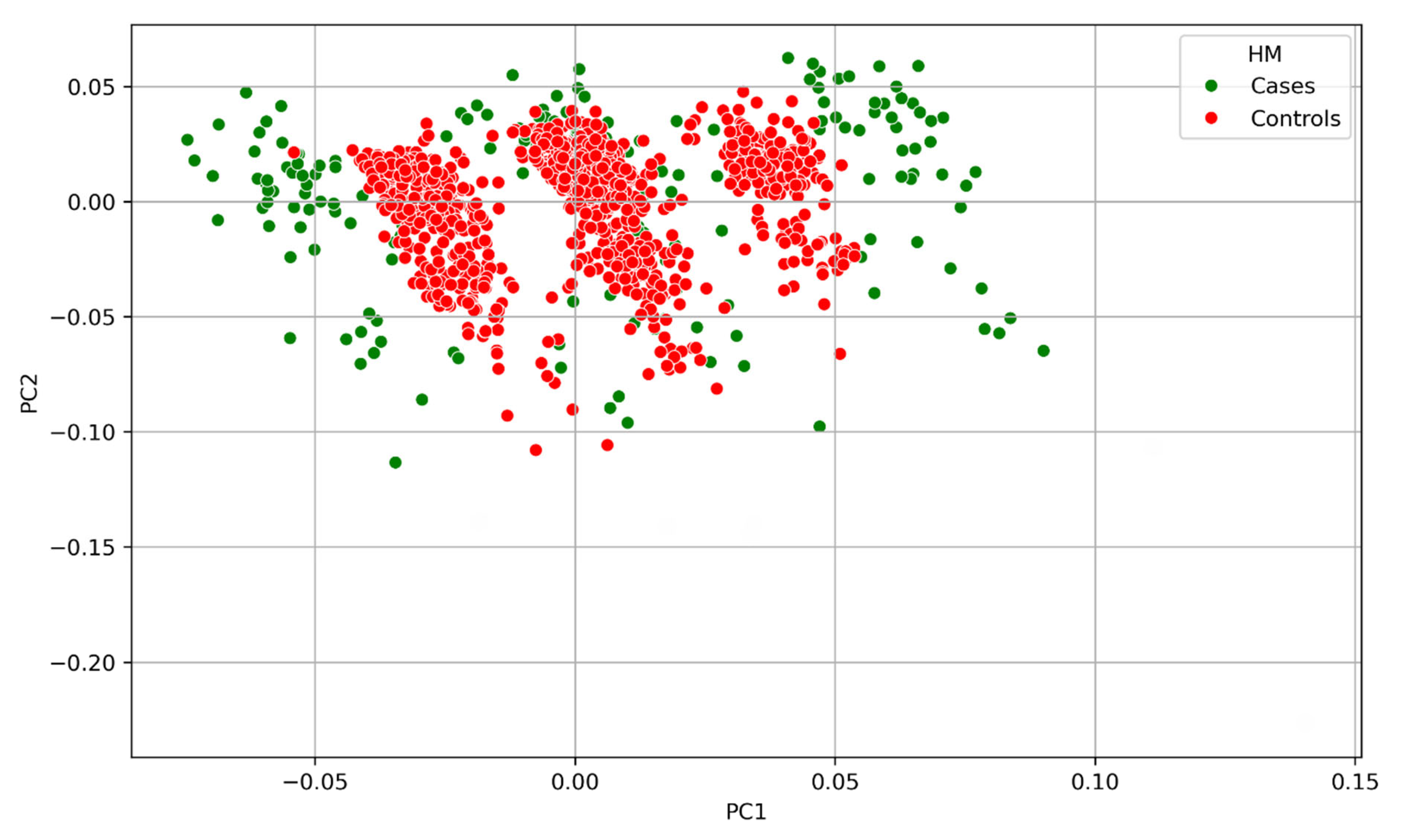
2.3. Population Stratification Investigation
3. Results
3.1. SNVs and Genes Tested
3.2. Principal Component Analysis
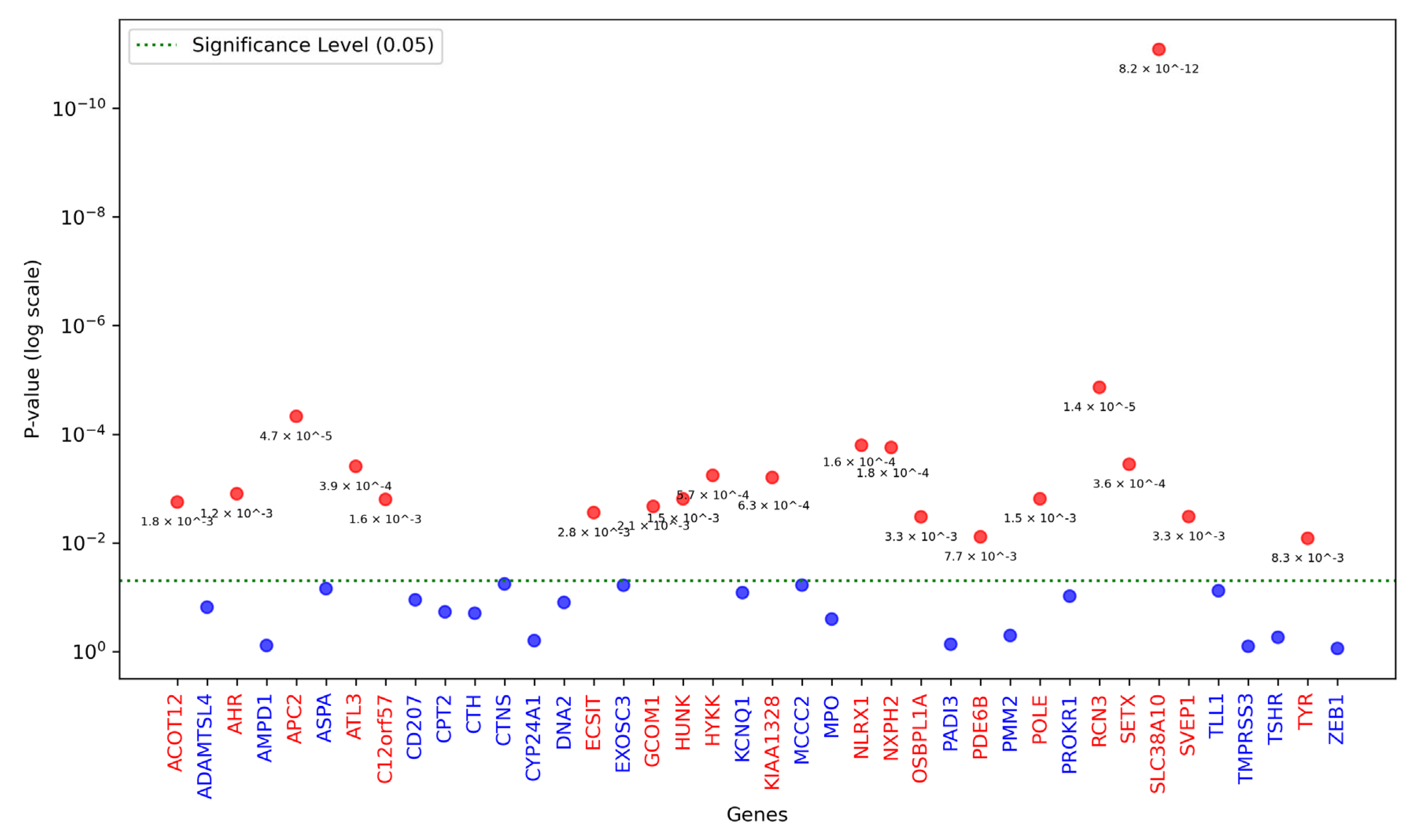
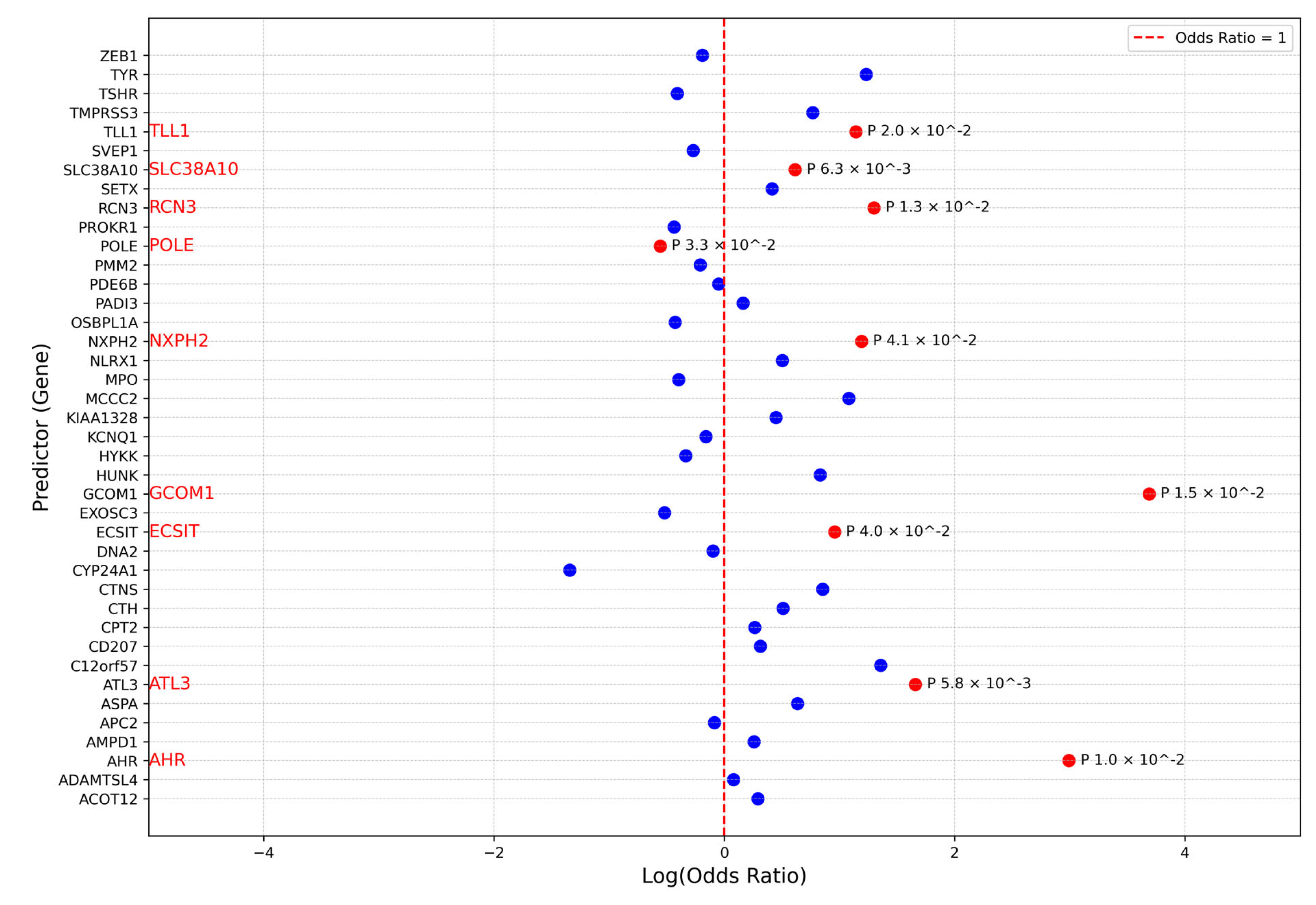
3.3. Association Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HM | Hemiplegic Migraine |
| WES | Whole Genome Sequencing |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| SNVs | Single Nucleotide Variants |
| MA | Migraine with Aura |
| MO | Migraine without Aura |
| FHM | Familial Hemiplegic Migraine |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
| GWASs | Genome-Wide Association Studies |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| ACMGs | American College of Medical Genetics |
| PCs | Principal Components |
References
- Anonymous. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, B.K.; Olesen, J. Migraine with aura and migraine without aura: An epidemiological study. Cephalalgia 1992, 12, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelzer, N.; Stam, A.H.; Haan, J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Terwindt, G.M. Familial and sporadic hemiplegic migraine: Diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2013, 15, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, M.B.; Ducros, A. Sporadic and familial hemiplegic migraine: Pathophysiological mechanisms, clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.C.; Baca, S.M. Cortical spreading depression and migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Yuzawa, I.; Qin, T.; Wang, Y.; Baek, K.; Kim, Y.R.; Hoffmann, U.; Dilekoz, E.; Waeber, C.; Ferrari, M.D.; et al. Enhanced subcortical spreading depression in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 mutant mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5755–5763. [Google Scholar]
- Alfayyadh, M.M.; Maksemous, N.; Sutherland, H.G.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.R. Unravelling the Genetic Landscape of Hemiplegic Migraine: Exploring Innovative Strategies and Emerging Approaches. Genes 2024, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobon, D. Familial hemiplegic migraine. Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, B.; Freilinger, T.; Vanmolkot, K.R.; Koenderink, J.B.; Stam, A.H.; Terwindt, G.M.; Babini, E.; van den Boogerd, E.H.; van den Heuvel, J.J.; Frants, R.R.; et al. Systematic analysis of three FHM genes in 39 sporadic patients with hemiplegic migraine. Neurology 2007, 69, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; Rispoli, M.G.; Pellegrino, N.; Graziosi, A.; Rotondo, E.; Napoli, C.; Pietrobon, D.; Brighina, F.; Parisi, P. Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of hemiplegic migraine. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzer, N.; Haan, J.; Stam, A.H.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Koelewijn, S.C.; Smagge, A.; de Vries, B.; Ferrari, M.D.; van den Maagdenberg, A.; Terwindt, G.M. Clinical spectrum of hemiplegic migraine and chances of finding a pathogenic mutation. Neurology 2018, 90, e575–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, L.L.; Eriksen, M.K.; Roemer, S.F.; Andersen, I.; Olesen, J.; Russell, M.B. A population-based study of familial hemiplegic migraine suggests revised diagnostic criteria. Brain 2002, 125 Pt 6, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Haan, J.; Terwindt, G.M.; Ferrari, M.D. Migraine: Gene mutations and functional consequences. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2007, 20, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veltman, J.A.; Brunner, H.G. De novo mutations in human genetic disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 565–575. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, H.G.; Maksemous, N.; Albury, C.L.; Ibrahim, O.; Smith, R.A.; Lea, R.A.; Haupt, L.M.; Jenkins, B.; Tsang, B.; Griffiths, L.R. Comprehensive Exonic Sequencing of Hemiplegic Migraine-Related Genes in a Cohort of Suspected Probands Identifies Known and Potential Pathogenic Variants. Cells 2020, 9, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksemous, N.; Harder, A.V.; Ibrahim, O.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Sutherland, H.; Pelzer, N.; de Boer, I.; Terwindt, G.M.; Lea, R.A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; et al. Whole exome sequencing of hemiplegic migraine patients shows an increased burden of missense variants in CACNA1H and CACNA1I genes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 3034–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Schork, N.J.; Murray, S.S.; Frazer, K.A.; Topol, E.J. Common vs. rare allele hypotheses for complex diseases. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotou, O.A.; Evangelou, E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Genome-wide significant associations for variants with minor allele frequency of 5% or less—An overview: A HuGE review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 869–889. [Google Scholar]
- Hautakangas, H.; Winsvold, B.S.; Ruotsalainen, S.E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Harder, A.V.; Kogelman, L.J.; Thomas, L.F.; Noordam, R.; Benner, C.; Gormley, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of 102,084 migraine cases identifies 123 risk loci and subtype-specific risk alleles. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, G. Rare and common variants: Twenty arguments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, D.G.; Balasubramanian, S.; Frankish, A.; Huang, N.; Morris, J.; Walter, K.; Jostins, L.; Habegger, L.; Pickrell, J.K.; Montgomery, S.B.; et al. A systematic survey of loss-of-function variants in human protein-coding genes. Science 2012, 335, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 2012, 491, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, M.A.; Beaudoin, M.; Gardet, A.; Stevens, C.; Sharma, Y.; Zhang, C.K.; Boucher, G.; Ripke, S.; Ellinghaus, D.; Burtt, N.; et al. Deep resequencing of GWAS loci identifies independent rare variants associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, T.; Atwal, J.K.; Steinberg, S.; Snaedal, J.; Jonsson, P.V.; Bjornsson, S.; Stefansson, H.; Sulem, P.; Gudbjartsson, D.; Maloney, J.; et al. A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. Nature 2012, 488, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Bamshad, M.J.; Ng, S.B.; Bigham, A.W.; Tabor, H.K.; Emond, M.J.; Nickerson, D.A.; Shendure, J. Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.B.; Buckingham, K.J.; Lee, C.; Bigham, A.W.; Tabor, H.K.; Dent, K.M.; Huff, C.D.; Shannon, P.T.; Jabs, E.W.; Nickerson, D.A.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.B.; Bigham, A.W.; Buckingham, K.J.; Hannibal, M.C.; McMillin, M.J.; Gildersleeve, H.I.; Beck, A.E.; Tabor, H.K.; Cooper, G.M.; Mefford, H.C.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies MLL2 mutations as a cause of Kabuki syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, C.; Guerreiro, R.; Gibbs, R.; Ding, J.; Lupton, M.; Troakes, C.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Niblock, M.; Gallo, J.; Adnan, J.; et al. Investigating the role of rare coding variability in Mendelian dementia genes (APP, PSEN1, PSEN2, GRN, MAPT, and PRNP) in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2014, 35, e1-2881.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, L.A.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Tang, Z.Z.; Bizon, C.; Lange, E.M.; Smith, J.D.; Turner, E.H.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies rare and low-frequency coding variants associated with LDL cholesterol. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Leal, S.M. A novel adaptive method for the analysis of next-generation sequencing data to detect complex trait associations with rare variants due to gene main effects and interactions. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001156. [Google Scholar]
- Asimit, J.; Zeggini, E. Rare variant association analysis methods for complex traits. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, A.L.; Kryukov, G.V.; de Bakker, P.I.; Purcell, S.M.; Staples, J.; Wei, L.-J.; Sunyaev, S.R. Pooled association tests for rare variants in exon-resequencing studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Leal, S.M. Discovery of rare variants via sequencing: Implications for the design of complex trait association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000481. [Google Scholar]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Lasseigne, B.N.; Petrovski, S.; Sapp, P.C.; Dion, P.A.; Leblond, C.S.; Couthouis, J.; Lu, Y.-F.; Wang, Q.; Krueger, B.J.; et al. Exome sequencing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identifies risk genes and pathways. Science 2015, 347, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Leal, S.M. Methods for detecting associations with rare variants for common diseases: Application to analysis of sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, B.E.; Browning, S.R. A groupwise association test for rare mutations using a weighted sum statistic. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000384. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenthaler, S.; Thilly, W.G. A strategy to discover genes that carry multi-allelic or mono-allelic risk for common diseases: A cohort allelic sums test (CAST). Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2007, 615, 28–56. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, B.M.; Rivas, M.A.; Voight, B.F.; Altshuler, D.; Devlin, B.; Orho-Melander, M.; Kathiresan, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Roeder, K.; Daly, M.J. Testing for an unusual distribution of rare variants. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001322. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Wu, M.C.; Lin, X. Optimal tests for rare variant effects in sequencing association studies. Biostatistics 2012, 13, 762–775. [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur, M.; Dastani, Z.; Aulchenko, Y.S.; Greenwood, C.M.; Richards, J.B. The empirical power of rare variant association methods: Results from sanger sequencing in 1,998 individuals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002496. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.C.; Lee, S.; Cai, T.; Li, Y.; Boehnke, M.; Lin, X. Rare-variant association testing for sequencing data with the sequence kernel association test. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, W. Asymptotic tests of association with multiple SNPs in linkage disequilibrium. Genet. Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derkach, A.; Lawless, J.F.; Sun, L. Robust and powerful tests for rare variants using Fisher’s method to combine evidence of association from two or more complementary tests. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, Y.; Hsu, L. A unified mixed-effects model for rare-variant association in sequencing studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.; Jin, J. Higher criticism for detecting sparse heterogeneous mixtures. Ann. Stat. 2004, 32, 962–994. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, I.; Mukherjee, R.; Lin, X. The generalized higher criticism for testing SNP-set effects in genetic association studies. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2017, 112, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Morrison, A.C.; Boerwinkle, E.; Lin, X. ACAT: A fast and powerful p value combination method for rare-variant analysis in sequencing studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 410–421. [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis, J.; Silk, M.; Wang, Q.; Berkovic, S.F.; Liu, L.; Ascher, D.B.; Balding, D.J.; Petrovski, S. Optimizing genomic medicine in epilepsy through a gene-customized approach to missense variant interpretation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1715–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Hayeck, T.J.; Stong, N.; Wolock, C.J.; Copeland, B.; Kamalakaran, S.; Goldstein, D.B.; Allen, A.S. Improved pathogenic variant localization via a hierarchical model of sub-regional intolerance. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Price, A.L.; Zaitlen, N.A.; Reich, D.; Patterson, N. New approaches to population stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Reich, D. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e190. [Google Scholar]
- Novembre, J.; Stephens, M. Interpreting principal component analyses of spatial population genetic variation. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Boehnke, M.; Lin, X. Rare-variant association analysis: Study designs and statistical tests. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Willer, C.J.; Ding, J.; Scheet, P.; Abecasis, G.R. MaCH: Using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 816–834. [Google Scholar]
- McVean, G. A genealogical interpretation of principal components analysis. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000686. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, D.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T. A penalized matrix decomposition, with applications to sparse principal components and canonical correlation analysis. Biostatistics 2009, 10, 515–534. [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell, J.; Pritchard, J. Inference of population splits and mixtures from genome-wide allele frequency data. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002967. [Google Scholar]
- Maksemous, N.; Blayney, C.D.; Sutherland, H.G.; Smith, R.A.; Lea, R.A.; Tran, K.N.; Ibrahim, O.; McArthur, J.R.; Haupt, L.M.; Cader, M.Z.; et al. Investigation of CACNA1I Cav3.3 Dysfunction in Hemiplegic Migraine. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 892820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfayyadh, M.M.; Maksemous, N.; Sutherland, H.G.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.R. PathVar: A Customisable NGS Variant Calling Algorithm Implicates Novel Candidate Genes and Pathways in Hemiplegic Migraine. Clin. Genet. 2024, 107, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Maksemous, N.; Smith, R.A.; Sutherland, H.G.; Maher, B.H.; Ibrahim, O.; Nicholson, G.A.; Carpenter, E.P.; Lea, R.A.; Cader, M.Z.; Griffiths, L.R. Targeted next generation sequencing identifies a genetic spectrum of DNA variants in patients with hemiplegic migraine. Cephalalgia Rep. 2019, 2, 2515816319881630. [Google Scholar]
- Halldorsson, B.V.; Eggertsson, H.P.; Moore, K.H.; Hauswedell, H.; Eiriksson, O.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Palsson, G.; Hardarson, M.T.; Oddsson, A.; Jensson, B.O.; et al. The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank. Nature 2022, 607, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.; Scott, R.J.; Talseth-Palmer, B.A. TAPES: A tool for assessment and prioritisation in exome studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar]
- Roginski, R.S.; Lau, C.W.; Santoiemma, P.P.; Weaver, S.J.; Du, P.; Soteropoulos, P.; Yang, J. The human GCOM1 complex gene interacts with the NMDA receptor and internexin-alpha. Gene 2018, 648, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, A.; Cuartas, J.; Gangwani, P.; Branzei, D.; Gangwani, L. Mutation in senataxin alters the mechanism of R-loop resolution in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 4. Brain 2022, 145, 3072–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Aggarwal, T.; Lindberg, F.A.; Klemm, A.H.; Fredriksson, R. SLC38A10 Regulate Glutamate Homeostasis and Modulate the AKT/TSC2/mTOR Pathway in Mouse Primary Cortex Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 854397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinde, K.E.; Browning, B.L.; Reiner, A.P.; Thornton, T.A.; Browning, S.R. Adjusting for principal components can induce spurious associations in genome-wide association studies in admixed populations. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.H.; Plummer, L.; Chan, Y.-M.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Lippincott, M.F. Burden testing of rare variants identified through exome sequencing via publicly available control data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The gene ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar]
- Greenacre, M.; Groenen, P.J.; Hastie, T.; d’Enza, A.I.; Markos, A.; Tuzhilina, E. Principal component analysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Elhaik, E. Principal Component Analyses (PCA)-based findings in population genetic studies are highly biased and must be reevaluated. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14683. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mehler, M.F. Understanding neurological disease mechanisms in the era of epigenetics. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 703–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Need, A.C.; Petrovski, S.; Goldstein, D.B. One gene, many neuropsychiatric disorders: Lessons from Mendelian diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 773–781. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjinicolaou, A.; Ngo, K.J.; Conway, D.Y.; Provias, J.P.; Baker, S.K.; Brady, L.I.; Bennett, C.L.; La Spada, A.R.; Fogel, B.L.; Yoon, G. De novo pathogenic variant in SETX causes a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disorder of early childhood-onset with severe axonal polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanetti, L.; Cavalieri, S.; Pensato, V.; Erbetta, A.; Pareyson, D.; Panzeri, M.; Zorzi, G.; Antozzi, C.; Moroni, I.; Gellera, C.; et al. SETX mutations are a frequent genetic cause of juvenile and adult onset cerebellar ataxia with neuropathy and elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, C.F.; Griffiths, L.R. The biology of the glutamatergic system and potential role in migraine. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mormile, R.; Mazzei, G.; Vittori, G.; De Michele, M.; Squarcia, U. Insomnia and shift-work sleep disorder: A crosstalk between glutamate excitotoxicity and decreased GABAergic neurotransmission? Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2012, 10, 340–341. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, R.; Aggarwal, T.; Fredriksson, R. SLC38A10 Transporter Plays a Role in Cell Survival Under Oxidative Stress and Glutamate Toxicity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 671865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Charles, A. Glutamate and its receptors as therapeutic targets for migraine. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Vikelis, M.; Mitsikostas, D.D. The role of glutamate and its receptors in migraine. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2007, 6, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Anttila, V.; Stefansson, H.; Kallela, M.; Todt, U.; Terwindt, G.M.; Calafato, M.S.; Nyholt, D.R.; Dimas, A.S.; Freilinger, T.; Müller-Myhsok, B. Genome-wide association study of migraine implicates a common susceptibility variant on 8q22.1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 869–873. [Google Scholar]


| Method | Type | Key Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burden Tests | Collapsing | Aggregates rare variants into a single score for analysis | High power when all variants affect trait in same direction | Loses power with bidirectional or non-causal variants |
| SKAT (Sequence Kernel Association Test) | Kernel-based | Models distribution of variant effects; allows covariate adjustment | Handles bidirectional effects; flexible modeling | Lower power if all variants affect in same direction |
| SKAT-O | Omnibus (Hybrid) | Combines SKAT and burden tests using Fisher’s method | Balances power across different genetic architectures | May lose power when few trait-associated variants exist |
| C-alpha Test | Distribution-based | Tests for variability in effect direction among variants | Detects both risk-increasing and protective variants | Lower power when effects are unidirectional |
| SSU Test (Sum of Squared Score) | Distribution-based | Captures total variance in genetic effects | Useful for mixed-direction effects | Sensitive to number of causal variants |
| KBAC (Kernel-Based Adaptive Cluster) | Kernel-based | Clusters similar genotypes; adaptive weighting | Effective for complex genotype-phenotype relationships | Computationally intensive |
| CMC (Combined Multivariate and Collapsing) | Hybrid | Combines rare and common variants; uses Hotelling’s T2 test | Incorporates broad variant spectrum | Assumes consistent direction of effect |
| ACAT (Aggregated Cauchy Association Test) | p-value Combination | Combines p-values using Cauchy distribution | Good power when few strong-effect variants are present | May underperform with many weak signals |
| Sub-regional Collapsing | Collapsing | Targets functionally intolerant genomic sub-regions | Enhances detection of clustered pathogenic variants | Requires accurate regional intolerance annotation |
| PathVar SNVs + (Missense SNVs < 0.01) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHR | Gene | SKAT_Burden | Logistic Regression | ||||
| Cases SNVs% | Controls SNVs% | Buden_Pvalue | Odds Ratio | log_Pvalue | Coefficient | ||
| 2 | NXPH2 | 0.02 | 0.007 | 0.02 | 3.29 | 0.04 | 1.18 |
| 7 | AHR | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 19.93 | 0.009 | 2.99 |
| 11 | ATL3 | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 5.25 | 0.005 | 1.65 |
| 11 | TYR | 0.02 | 0.006 | 0.04 | 3.42 | 0.05 | 1.23 |
| 15 | GCOM1 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.002 | 39.94 | 0.01 | 3.68 |
| 17 | SLC38A10 | 0.10 | 0.076 | 0.006 | 1.85 | 0.006 | 0.61 |
| 19 | ECSIT | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.60 | 0.03 | 0.95 |
| 19 | RCN3 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.66 | 0.01 | 1.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfayyadh, M.M.; Maksemous, N.; Sutherland, H.G.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.R. Gene-Based Burden Testing of Rare Variants in Hemiplegic Migraine: A Computational Approach to Uncover the Genetic Architecture of a Rare Brain Disorder. Genes 2025, 16, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070807
Alfayyadh MM, Maksemous N, Sutherland HG, Lea RA, Griffiths LR. Gene-Based Burden Testing of Rare Variants in Hemiplegic Migraine: A Computational Approach to Uncover the Genetic Architecture of a Rare Brain Disorder. Genes. 2025; 16(7):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070807
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfayyadh, Mohammed M., Neven Maksemous, Heidi G. Sutherland, Rodney A. Lea, and Lyn R. Griffiths. 2025. "Gene-Based Burden Testing of Rare Variants in Hemiplegic Migraine: A Computational Approach to Uncover the Genetic Architecture of a Rare Brain Disorder" Genes 16, no. 7: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070807
APA StyleAlfayyadh, M. M., Maksemous, N., Sutherland, H. G., Lea, R. A., & Griffiths, L. R. (2025). Gene-Based Burden Testing of Rare Variants in Hemiplegic Migraine: A Computational Approach to Uncover the Genetic Architecture of a Rare Brain Disorder. Genes, 16(7), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070807





