Abstract
ABCC6, a key regulator in ectopic calcification, plays a crucial role in mineralization through the modulation of extracellular purinergic pathways and production of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), which inhibits calcification. Inherited deficiencies in ABCC6 lead to pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) and related conditions, characterized by calcification in various tissues, particularly affecting the skin, eyes, and cardiovascular system. Although PXE does not directly impact the nervous system, secondary neurological issues arise from cerebrovascular complications, increasing the risk of strokes linked to arterial blockages resembling atherosclerosis. This review investigates the connection between ABCC6 mutations and cerebral small vessel disease (SVD), expanding the understanding of PXE and related phenotypes. Mutations in ABCC6, identified as causing PXE, contribute to systemic metabolic dysfunction, with significant implications for cerebrovascular health. An association between ABCC6 mutations and cerebral SVD has been suggested in various studies, particularly in populations with distinct genetic backgrounds. Emerging evidence indicates that pathogenic mutations increase the risk of ischemic strokes, with both homozygous and heterozygous carriers showing susceptibility. Mechanistically, ABCC6 deficiency is implicated in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis, further exacerbating cerebrovascular risks. Increased arterial pulsatility, linked to carotid siphon calcification, may also contribute to microvascular damage and subsequent brain injury. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for developing targeted diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for managing cerebrovascular risks in PXE patients. This review emphasizes the need for comprehensive genetic screening and the consideration of traditional vascular risk factors in patient management, highlighting the complex interplay between genetic mutations and environmental influences affecting cerebrovascular health. Future research should focus on longitudinal studies to elucidate the causal pathways linking arterial calcification, pulsatility, and brain damage in PXE.
1. Introduction
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 (ABCC6) belongs to the ATP-binding cassette superfamily [1] and plays a critical role in regulating ectopic calcification [2,3]. This protein influences mineralization by modulating the extracellular purinergic pathway through several essential enzymes that generate inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) and inhibit its degradation [4,5,6]. Notably, PPi serves as a strong inhibitor of ectopic calcification [7]. The activity of ABCC6 contributes to around 60% of plasma PPi levels in both humans and mice [8,9]. The liver and kidneys exhibit the highest levels of ABCC6 expression, although this protein is also present in various other cell types [10,11]. A deficiency in ABCC6 due to genetic inheritance can result in calcification of the dermis, eyes, and cardiovascular system in individuals with pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) [3], and is implicated in some instances of generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) [12]. Additionally, it may be a contributing factor to PXE-like symptoms in patients with β-thalassemia [13,14]. Besides arterial calcifications, PXE does not have a direct impact on the nervous system; however, secondary neurological issues due to cerebrovascular limitations are well established, although present in a variable proportion of patients. Older patients with PXE are at a higher risk for developing cerebrovascular events, which often stem from the gradual narrowing and blockage of one or several cerebral arteries [15]. The angiographic characteristics of PXE are similar to those seen in severe atherosclerosis, exhibiting features such as arterial stenosis, tortuosity, and occlusion, particularly affecting the internal carotid or vertebral arteries. Carotid artery stenosis, accompanied by significant collateral circulation, bears a resemblance to moyamoya syndrome in angiographic findings [16,17]. Findings similar to those of fibromuscular dysplasia have also been reported [18]. There is a slightly elevated incidence of intracranial arterial aneurysms among individuals with PXE, likely due to their abnormal elastic lamina [19]. These aneurysms frequently occur in the intracranial segment of the internal carotid artery [20,21,22], while aneurysms in other intracranial vessels are rarer. A case was noted where a woman experienced subarachnoid hemorrhage and spinal cord dysfunction due to an aneurysm in the anterior spinal artery [23]. Both intracerebral and subarachnoid bleeding have been observed in PXE patients without the presence of an aneurysm [24,25].
In recent years, the association of some pathogenic mutations of ABCC6 with a microvascular cerebral lesion pattern, or with a neuroimaging pattern consistent with a cerebral Small Vessel Disease (SVD), has been reported, albeit occasionally [25,26,27,28]. Furthermore, some similar reports, both in the European and Asian populations, concern one of the manifestations of SVD, namely lacunar ischemic stroke. This association may be due to different mechanisms and can be either direct or mediated by the co-presence of some vascular risk factors.
The aim of this review is to explore the association between ABCC6 mutations and SVD and to illustrate the mechanisms of this, substantially expanding the range of PXE and PXE-like phenotypes.
2. ABCC6 and PXE
PXE is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by mutations in the ABCC6 gene on chromosome 16 16p13.1, identified in 2000 [3,29,30,31,32,33], which codes for a transmembrane transporter protein of the ATP binding ABC family. The prevalence of PXE is around 1 in 25,000 people, but some individuals with milder phenotypes probably remain undiagnosed. This gene consists of 31 exons and encodes a 1503-amino-acid protein (molecular weight: 165 kDa). The literature encompasses 48 ABC (“adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette”) genes, categorized into seven subfamilies (A to G). The ABCC subfamily includes 12 genes, among which are ABCC6 and ABCC7 (CFTR, linked to cystic fibrosis), along with a pseudogene (ABCC13). Due to structural similarities, the protein encoded by ABCC6 is classified within the multidrug resistance protein subfamily, known for exporting organic ions from external sources (e.g., cancer drug metabolites) [34]. In fact, older studies may refer to ABCC6 as MRP6. The ABCC4, ABCC5, ABCC11, and ABCC12 proteins possess two membrane-spanning domains and two nucleotide-binding domains. SUR1 and SUR2 (from ABCC8 and ABCC9) also exhibit four domains, while ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCC6, and ABCC10 have an additional N-terminal domain. A three-dimensional model of ABCC6 has been proposed based on homology, with high-resolution structures of other ABC proteins [35], but its accuracy remains uncertain. ABCC6 gene expression is tissue-specific [36], with indications that a primate-specific sequence (+629/+688) in the first intron might play a role [37]. The binding of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 α (HNF4α) to a conserved promoter region (−209/−145) may explain the gene’s predominant expression in the liver [38]. The transport mechanism of endogenous or exogenous substrates by ABCC6 is poorly characterized. Despite its classification in the MRP family, the molecular pathways for drug or metabolite transport by ABCC6 remain undefined, suggesting it has limited involvement in clinical multidrug resistance. In vitro studies indicated that ABCC6-transfected cells did not show significant resistance to various chemotherapeutic agents [39]. In autosomal recessive disorders, heterozygous carriers of a mutation in one ABCC6 allele typically do not exhibit PXE symptoms [40,41]. However, some heterozygotes may display clinical and histopathological PXE characteristics [42,43,44]. The observation of mineralized skin in a woman with ABCC6 and GGCX mutations raised the possibility of a milder PXE form (OMIM #177850). It is plausible that undetected mutations could affect the other allele, maintaining the recessive inheritance pattern [45]. Additionally, heterozygotes for ABCC6 mutations may have an increased risk of cardiovascular calcification [46].
While PXE’s genetic basis is acknowledged, its pathophysiological mechanisms are not fully understood. Although ATP secretion from the liver is ABCC6-dependent, ATP is not transported by the protein. This ABCC6-dependent ATP secretion is a primary source of circulating pyrophosphate (PPi) [4,8]. In Abcc6 (−/−) mice, plasma PPi levels are about 40% of those in wild-type mice, and PXE patients show a low plasma PPi/Pi ratio [4,8]. Thus, PPi is proposed as a key circulating factor in PXE metabolic disorder [8,47]. Despite ABCC6 being primarily expressed in the liver, kidney, and intestine, damage to PXE occurs at distant sites. Two main hypotheses exist: the cell-based hypothesis, suggesting that dysfunctional ABCC6 at peripheral sites leads to ectopic mineralization [48], and a systemic metabolic hypothesis positing that insufficient circulating factors from the liver result in mineralization elsewhere. One variant of this hypothesis indicates that these circulating factors normally inhibit mineralization, and their absence leads to dystrophic calcification in tissues like skin, eyes, and arteries. Experimental evidence in Abcc6-deficient mice supports this metabolic hypothesis, as pairing these mice with wild-type mice halted connective tissue mineralization, likely due to the introduction of critical anti-mineralization factors from the wild-type circulation [49]. PPi remains a strong candidate for the anti-mineralization factor in PXE [8,47]. Elevated Pi levels have been implicated in calcification based on dietary experiments in Abcc6 (−/−) mice [47], yet PXE patients maintain normal parathyroid hormone levels, and a clinical trial of sevelamer hydrochloride showed no significant effects on calcification [50]. The results may have been influenced by excipient components. If Pi plays a role in PXE, it may be through a reduced PPi/Pi ratio [4,8]. Other potential players in PXE include the anti-mineralization proteins matrix Gla-protein (MGP) and fetuin-A, which were found to be moderately low in PXE patients and significantly low in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients [51,52]. MGP knockout mice exhibit spontaneous arterial and cartilage calcification [53]. A CKD model showed low Abcc6 protein levels despite normal mRNA levels, suggesting post-transcriptional or post-translational deficiencies [54]. Additionally, it has been hypothesized that impaired vitamin K export from the liver decreases the γ-carboxylation of anti-mineralization proteins [55,56]. MGP is not carboxylated in PXE patients’ elastic fibers [57], and PXE-like calcification is observed in GGCX mutation patients [57]. However, failed supplementation trials in PXE mouse models challenge the vitamin K hypothesis [58,59,60]. Adenosine is another candidate circulating factor, given the parallels between PXE and “arterial calcification due to deficiency of CD73” (ACDC), where extracellular adenosine monophosphate cannot convert to adenosine [61,62]. Patients with ACDC and CD73-deficient mice develop dystrophic calcification [63,64], but this hypothesis is weakened by the lack of adenosine transport by ABCC6 in vitro [65]. Oxidative stress is also considered a potential factor in PXE, as some patients show biochemical signs of stress [66], and conditions like β-thalassemia or sickle cell anemia (characterized by elevated free radical levels) can present PXE-like symptoms [67,68,69,70]. Furthermore, oxidative stress may inhibit ABCC6 expression in human cell lines. One study reported abcc6 localization to mitochondria-associated membranes in mice [71], but other studies confirmed its primary basolateral membrane localization in human and mouse liver [72]. Gene expression analyses in wild-type, Abcc6-deficient, and Abcc6-transgenic mice indicated that impaired substrate export from hepatocytes alters the regulation of systemic anti-mineralization factors (the “hepatic intoxication” hypothesis). However, differences in gene expression were minor and not statistically significant after correction [73], with metabolic changes in the liver not reflected in plasma profiles [73]. Liver function remains intact in PXE patients. Most experimental data on PXE’s pathophysiology derives from Abcc6-deficient zebrafish [74,75] and mouse models [76,77,78,79,80]. In mice, all Abcc6 −/− models develop dystrophic mineralization, with calcium deposits in the skin, retina, and arteries mirroring human PXE. For instance, arterial calcium accumulation is significantly higher in Abcc6 −/− mice compared to wild-type [81]. One study highlighted the activation of the BMP2-SMAD-RUNX2 signaling pathway, critical for vascular calcification, in Abcc6-deficient mice [82].
The main molecular mechanisms involved in PXE manifestations are summarized in the following table (Table 1).

Table 1.
Main molecular mechanisms of ABCC6’s role in PXE manifestations.
Different hypotheses were proposed for the factors pathologically involved with PXE, which are the main ABCC6 expression in the liver and the main PXE manifestations outside the liver, as follows: (I) the metabolic hypothesis (the decrease or loss of ABCC6 functionality, especially in the liver, may lead to a decrease in circulating factors in the bloodstream, whose role is to prevent the ectopic mineralization of soft tissues); (II) the PXE cell hypothesis (the absence of ABCC6 in PXE tissues alters cell proliferation and changes in the biosynthetic pathway affect cell interactions with the extracellular matrix); (III) the ATP release hypothesis (ABCC6 mediates the efflux of ATP into the extracellular milieu; ATP is hydrolyzed into AMP and pyrophosphate and this process prevents the mineralization of soft tissues).
Genotype–phenotype correlations are generally weak [83]. The nonsense mutation p. Arg1141* may predispose individuals to cardiovascular disease independent of hyperlipidemia [84,85], while the ABCC6 p. Arg1268Gln polymorphism [30,86] is associated with early onset of angioid streaks [87,88]. ABCC6 mutations have also been connected to generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI; OMIM 173335), which is linked to ENPP1 mutations that regulate bone mineralization [89]. GACI is often lethal in utero or within months of birth, with ENPP1 mutations found in most affected patients [90].
At present, there are no universally recognized international guidelines for the clinical and genetic diagnosis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). In the past, before the identification of the ABCC6 gene’s involvement in PXE, diagnosis was based on three major and two minor criteria [91]. The major criteria were as follows: (i) the presence of distinctive skin manifestations characterized by yellow cobblestone lesions in flexural areas, (ii) specific histopathological features of lesional skin evaluated with elastic tissue or von Kossa stains, and (iii) ocular complications, including angioid streaks, peau d’orange lesions, or maculopathy in individuals aged over 20. The minor criteria encompassed histopathological characteristics of non-lesional skin and a family history of PXE among first-degree relatives. However, this classification often does not correlate well with molecular findings related to ABCC6 [92]. In 2010, a revised classification system was proposed [93] (see Table 2). This semi-standardized method includes the following: (i) a comprehensive skin examination conducted by a dermatologist or physician familiar with PXE, (ii) histological analysis using hematoxylin–eosin, Verhoeff–van Gieson (to assess elastin), and von Kossa (to detect calcium) staining of a biopsy from an affected lesion or, if necessary, from the lateral neck, and (iii) fundoscopy of both eyes by a skilled ophthalmologist to evaluate for peau d’orange, angioid streaks, macular degeneration, comets, and wing signs, with optional fluorescein or indocyanine green angiography and fundus autofluorescence for angioid streaks [93]. In clinical practice, the identification of characteristic yellow cobblestone skin lesions typically prompts screening for ABCC6 mutations.

Table 2.
New diagnostic criteria for PXE [93].
As previously mentioned, testing for ABCC6 mutations is conducted in patients unless the clinical presentation is unequivocal. So far, over 2000 unique DNA sequence variants of the ABCC6 gene have been recorded, with the majority being missense mutations [94]. Among these variants, there are 76 classified as conflicting, 103 as benign, 549 as likely benign, 826 as variants of uncertain significance, 232 as likely pathogenic, and 333 as pathogenic mutations. Approximately 90% of patients diagnosed with clinical PXE have mutations in both alleles of the gene. Notably, the mutation profile varies across different ethnic groups [95]. For example, the p.Arg1141* (p.R1141X) mutation is commonly found in European populations [95] but is less prevalent in North American groups [2,3], and was completely absent in a study of 22 Chinese patients, who instead exhibited 15 previously unreported mutations [96]. The del23-29 mutation is particularly common in Northern Europe and the northern Mediterranean, while the p.Gly1321Ser mutation is frequently observed in North America but is rare in Europe [2,3]. The p.Arg1138Trp missense mutation may act as a genetic marker for individuals of French ancestry, being present in France and French-speaking Canada, whereas the 2542delG frameshift mutation is mainly found in Japanese patients [95]. In contrast, mutations such as p.Gln378* and p.Arg1339Cys appear to have a similar distribution globally, suggesting recurrent mutational events. Generally, disease-associated missense mutations tend to cluster at domain–domain interfaces, exhibiting a mutation rate that is 4.25 times higher [97]. Copy number variations in the ABCC6 pseudogenes, ABCC6Ψ1 and ABCC6Ψ2 [98,99], have been found more frequently in PXE patients than in controls, although the clinical relevance of these variations remains unclear [100,101]. Furthermore, non-pathogenic polymorphisms have also been identified; for instance, an individual homozygous for the ABCC6 p.Arg1268Gln polymorphism did not show any PXE symptoms, and the Gln1268 (Q1268) allele was present at a frequency of 0.19 among healthy controls [31].
However, the estimated prevalence of PXE, at between 1 in 25,000 and 1 in 50,000, suggests a significant number of heterozygous carriers in the general population [102], irrespective of whether the full clinical spectrum of PXE is observed, leading to diagnostic tests [93,103]. It is possible that a genetic diagnosis may be even wider than a diagnosis triggered by clinical issues, as defined in the first and revised diagnostic criteria [104]. A recent study analyzed a French cohort of PXE patients, aiming to identify genotype-phenotype correlations, specifically through a comprehensive molecular analysis of the ABCC6 gene [105]. The study involved 458 French PXE probands referred for molecular analysis and a modified Phenodex score was used to evaluate the severity of symptoms [103]. The genetic analysis included sequencing of the ABCC6 gene and its pseudogenes, focusing on identifying both known and novel variants. Among the 306 PXE patients analyzed, the majority were women (63.1%) and Caucasian (79.4%), with a median age of 43.5 years. Neurovascular manifestations, such as strokes, were noted in 10% of cases, while renal lithiasis was detected in 12.9% [106]. A total of 538 mutational events were identified, with a detection rate of 87.7%. This included 142 distinct variants, of which 66 were novel. The most common variants identified were the nonsense variant p.Arg1141Ter and the del23-29 deletion, which were particularly prevalent among Caucasian patients [86,103]. Among the 306 cases, 81.7% had two identifiable variants, with many patients showing a homozygous status for certain variants. Two families exhibited pseudodominant inheritance patterns, which confirmed the recessive nature of PXE. Most missense variants were located in intracellular domains of the ABCC6 protein. The study highlighted specific regions within the protein that were enriched with pathogenic variants, particularly in the nucleotide-binding fold regions [8]. The analysis of 220 cases with complete Phenodex scores showed that skin lesions were the most common manifestation, present in over 90% of cases with two variants. The severity of ocular and vascular manifestations was significantly associated with the presence of loss-of-function variants [93]. The severity of PXE was influenced by the number and type of variants. Cases with two loss-of-function variants exhibited more severe eye and vascular complications compared to those with missense variants. Ethnic background also played a role, with Caucasian patients experiencing more severe ocular complications than North African patients [30]. This study found a high detection rate of causative variants in the ABCC6 gene, similar to previous studies [103]. However, it also highlighted the need for complementary diagnostic methods, such as array comparative genomic hybridization, to improve variant detection. The findings confirmed that the most common variants were consistent with previous reports, while new correlations were identified regarding the ethnic background of patients. The phenotype variability observed in PXE suggests the influence of additional genetic and environmental modifiers. The study proposed modifications to the Phenodex score to include additional clinical features, such as nephrolithiasis and stroke, which are prevalent yet overlooked in the standard assessment.
3. Small Vessel Disease Phenotype and ABCC6 Mutations
Cerebral SVD accounts for approximately 25% of strokes, manifesting as lacunar strokes and deep intracerebral hemorrhages (ICH) [107,108], and serves as the primary pathology behind vascular cognitive impairment [109]. Cerebral SVD is characterized by various neuroimaging findings, such as lacunar infarctions (LIs), enlarged perivascular spaces (EPVS), microbleeds (MBs), and white matter hyperintensities (WMHs). It is a significant cause of dementia and gait disturbances [110]. While traditional risk factors include aging and hypertension, the pathogenesis of SVD is still not fully understood. In most instances, it is a sporadic age-related condition associated with hypertension and subsequent arteriosclerosis, although a minority of cases can be attributed to rare genetic variants [111]. More than 10 genes are implicated in monogenic forms of cerebral SVD, including NOTCH3 and HTRA1, which have been increasingly recognized in the recent literature [112]. Diagnosing monogenic cerebral SVD (mgCSVD) is often challenging due to the absence of distinct clinical features in some patients and the potential for the disease to occur without a family history. This necessitates genetic screening to identify cases of mgCSVD even when familial patterns are not evident. The most prevalent inherited form of SVD is cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), which is caused by NOTCH3 variants [113]. Recently, additional genes have been identified that can lead to similar phenotypes, including HTRA1, COL4A1, COL4A2, TREX1, GLA, and FOXC1 [114]. However, the prevalence of these variants in populations with presumed sporadic SVD remains unknown and several other variants of different genes which are not routinely searched for could be at least equally prevalent. As the understanding of monogenic SVD broadens, a gene-by-gene testing approach becomes less cost- and time-effective. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) panels utilizing next-generation sequencing technologies facilitate the simultaneous testing of multiple genes associated with a single disease phenotype in a more economical manner and are increasingly adopted in clinical settings. In a recent description [115], an HTS panel that includes 15 genes associated with the SVD phenotype was evaluated for its effectiveness in disease diagnosis and to ascertain the frequency of monogenic disease-causing variants in a well-defined population with MRI-confirmed younger-onset lacunar stroke. This investigation assesses both known disease-causing mutations and novel, potentially pathogenic variants. The gene panel was crafted to encompass seven genes established as causal for SVD (NOTCH3, HTRA1, FOXC1, COL4A1, COL4A2, TREX1, GLA), alongside eight genes linked to disorders that exhibit SVD-related phenotypes. These include familial cerebral amyloid angiopathy (APP, CST3, ITM2B), familial hemiplegic migraine (ATP1A2, CACNA1A, SCN1A), and connective tissue disorders (ABCC6, COL3A1). These conditions share clinical features with monogenic forms of SVD (for instance, lacunar stroke, MRI WMHs, dementia, migraine with aura, and encephalopathy) and may thus present similarly. In the above-mentioned study [115], the study population consisted of patients from the UK DNA Lacunar Stroke Study, collecting unrelated patients of European ancestry with MRI-confirmed lacunar stroke occurring at or before the age of 70 [116]. Interestingly, no ABCC6 mutations were identified in this cohort. The same finding was proposed by a more recent study analyzing a cohort of 257 patients with suspected familial cerebral SVD and 13,086 controls [117]. Besides these cohorts, single case reports and small case series have noted an association between ABCC6 mutations and SVD [26].
Conversely, in a Japanese study in patients with adult-onset SVD [118], more than 90% of monogenic cerebral SVD (mgCSVDs) were diagnosed by screening for NOTCH3, HTRA1, and ABCC6, concluding that the target sequences for these three genes could be used to efficiently diagnose mgCSVD in Japanese patients. The study focuses on the role of these genetic factors in Japanese patients, emphasizing the need for effective genetic screening. The study recruited patients with adult-onset severe CSVD characterized by significant WMHs. Group 1 included patients aged 55 or younger, while Group 2 consisted of those older than 55 with a family history of CSVD. Genetic testing was performed for NOTCH3 and HTRA1, followed by whole-exome sequencing (WES) for undiagnosed cases. The study also included measuring HTRA1 protease activity and assessing clinical and imaging features through statistical analyses. A total of 106 patients were initially recruited, with 75 in Group 1 and 31 in Group 2. The study identified various mutations: 30 patients had NOTCH3 mutations, 11 had HTRA1 mutations, and 6 had ABCC6 mutations. Notably, the total mutation frequency for NOTCH3, HTRA1, and ABCC6 was 94% in patients with mgCSVD. Significant differences were observed in family history, hypertension prevalence, and multiple LIs between monogenic and undetermined cases. In Group 1, 54.7% of patients had mgCSVD, while in Group 2, the frequency was 29.0%. Among the mgCSVD cases, mutations in NOTCH3 accounted for 56.1%, HTRA1 for 24.4%, and ABCC6 for 12.2%. The findings suggested that screening these three genes could efficiently diagnose mgCSVD in the Japanese population. The results showed that HTRA1 and ABCC6 mutations significantly contribute to severe cerebral SVD in Japanese patients. While CADASIL was prevalent, the study highlighted the role of HTRA1 and ABCC6, even in heterozygous states, as important genetic risk factors. The neuroradiological selection criteria for the study are a relevant issue. The study recruited patients with adult-onset severe symmetrical WMHs corresponding to Fazekas grade 3 and various conditions, like LIs or MBs, on MRI. Genetic testing identified CADASIL in 30 patients, with several novel mutations in the NOTCH3 gene noted. Additionally, mutations in HTRA1 were found in nine patients, with two being novel. Among the undiagnosed patients assessed through WES, several mutations in ABCC6 were identified, including one with a heterozygous mutation resulting in PXE. When the clinical features of mgCSVD patients were compared to those of undetermined patients, the former had a higher frequency of family history, LIs, and non-lobar MB distributions. Statistical analysis indicated that family history, hypertension, and multiple LIs were significant predictors for mgCSVD diagnosis. This study demonstrated that over 50% of patients with severe CSVD who developed symptoms before 55 years had identifiable genetic mutations, with CADASIL being the most prevalent. Notably, HTRA1 and ABCC6 mutations were significant contributors to mgCSVD cases. The results indicate that these mutations can occur even in heterozygotes, emphasizing the necessity of genetic testing in diagnosing severe CSVD in Japanese patients, regardless of family history. The high frequency of ABCC6 mutations in this cohort suggests a potential link between these genetic factors and severe CSVD. The findings advocate for targeted genetic testing strategies, focusing on NOTCH3, HTRA1, and ABCC6, to enhance diagnostic efficiency for mgCSVD in Japan. Unfortunately, similar information in different populations is not currently available.
Two examples of severe SVD in patients with ABCC6 mutations are illustrated in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
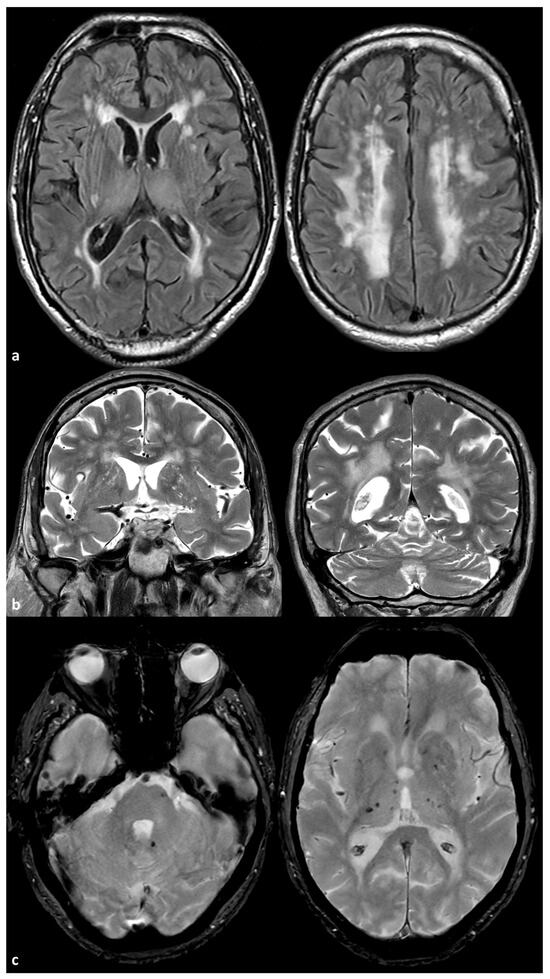
Figure 1.
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of a 72-year-old man with a mutation ABCC6(NM_001351800.1):c.3840delG:(p.Lys1280AsnfsTer9) in heterozygosis. The patient has a very mild arterial hypertension and was sent to the neurological attention because of the occurrence of transient neurological deficit. In panel (a), some examples of axial Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) images are provided at basal ganglia level (left image) and at centrum semiovale level (right image), showing symmetric, extensive, confluent white matter hyperintensities that are prevalent in the centrum semiovale. In panel (b), coronal T2W images show the enlarged perivasculae spaces in the basal ganglia on both sides. In panel (c), Gradient Recalled Echo (GRE) images show isolated pontine and deep, supratentorial, hypointense rounded signals similar to those observed for microbleeds.
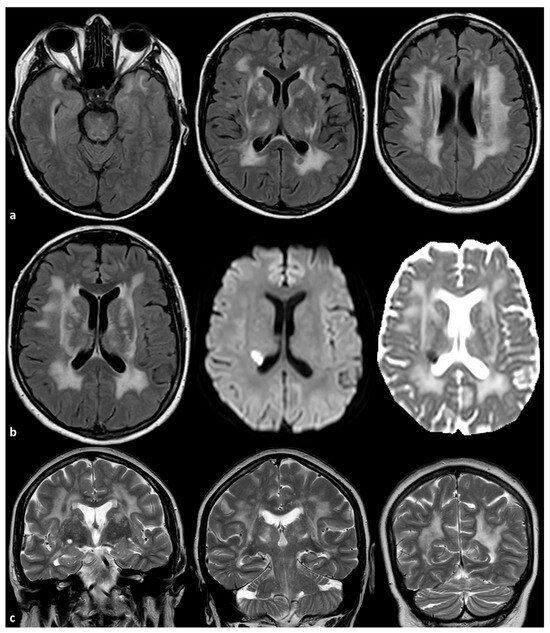
Figure 2.
Brain MRI of a 56-year-old woman with a mutation ABCC6 (NM_001351800.1):c.3071G>A:p.(Arg1024Gln) in heterozygosis. The patient had no relevant vascular risk factors and no systemic signs of PXE. In panel (a), axial FLAIR images are provided, showing symmetric, extensive, confluent white matter hyperintensities involving the anterior temporal pole, the external and extrema capsula, the thalamus and the centrum semiovale on both sides (the other known genes responsible for SVD were tested and no mutations were identified). In panel (b), axial FLAIR, axial Diffusion Weighted Imaging and axial Apparent Diffusion Coefficient map images show an acute subcortical ischemia in the corona radiata close to the occipital pole of the right lateral ventricle. In panel (c), coronal T2W images show the enlarged perivascular spaces in the basal ganglia on both sides.
4. Mechanisms Linking ABCC6 Mutations to Small Vessel Disease
At least one cohort study raised noted pathogenic mutations of ABCC6 and the risk of stroke [119]. That study highlighted the increased incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with PXE, including patients with monoallelic and biallelic pathogenic ABCC6 variants. Interestingly, the authors found that heterozygous ABCC6 variants significantly increase the risk of ischemic stroke. The study involved two main cohorts: a multigenerational family with a history of ischemic cerebrovascular events and an independent cohort of 424 ischemic stroke patients compared to 250 healthy controls. A genetic analysis of the ABCC6 gene was performed to identify pathogenic variants, including the recurrent multi-exon deletion. Clinical evaluations included a complete cardiovascular examination and neuroimaging to classify stroke types. In a large multigenerational family, the pathogenic ABCC6 variant (p.[Arg1314Gln]) was segregated alongside cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases. This family exhibited an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, with multiple family members affected by ischemic events at a relatively young age. The case–control study revealed that pathogenic ABCC6 variants were found in 16 out of 424 ischemic stroke patients (3.8%) compared to 2 out of 250 controls (0.8%), resulting in an odds ratio of 4.9 (p = 0.036). This suggests that carriers of pathogenic ABCC6 variants have a significantly higher risk of developing ischemic stroke. Additionally, Abcc6-deficient mice show Bmp (bone morphogenetic protein) and Tgfβ (transforming growth factor β) dysfunction in induced acute cardiac ischemia [120,121,122]. Similar BMP and TGFβ dysfunction was observed by us in PXE patients [123]. The immunostaining of brain tissues from Abcc6-deficient mice indicated dysregulation of Bmp and Tgfβ signaling pathways, suggesting a pro-ischemic state that may contribute to the increased risk of ischemic events in patients with ABCC6 mutations. The results advocate for the inclusion of molecular analyses of the ABCC6 gene in the diagnostic workup for patients with cryptogenic ischemic stroke, as early identification could influence management strategies. Interestingly, in the case–control study, only one out of sixteen patients had an SVD-related stroke pattern, and Del23-29 (Exon 23-29) was found in ABCC6 gene. In fact, the stroke phenotypes linked to pathogenic ABCC6 variants are varied, primarily including large vessel disease, followed by cardioembolic stroke and SVD, aligning with previous findings in PXE patients [45,46]. This heterogeneity complicates the identification of a specific subgroup of ischemic stroke patients predisposed to these variants; however, a negative family history should not dismiss the possibility of genetic influence. In an independent stroke patient cohort, none exhibited the significant intracerebral vascular calcifications or anatomical malformations previously noted in PXE patients [124]. In addition, the increased cardiovascular risk in heterozygous carriers of pathogenic ABCC6 variants may be due to other members of the ABC transporter superfamily that are involved in brain disease [125,126,127]. After stroke, increased ABCB1 expression was observed, negatively affecting neuroprotective agents [127]. In contrast, variants in ABCA1 linked to a reduced risk of ischemic stroke were identified [125]. Immunostaining on targets within the Bmp and Tgfβ signaling pathways (Bmp4, Bmp9, Alk2, Eng) in the Abcc6-deficient brain found the upregulation of Bmp4, a protein with confirmed pro-apoptotic properties [128]. Additionally, the downregulation of Alk2, which also leads to increased apoptosis, was noted [129]. Furthermore, the upregulation of Eng was observed; this pathway is crucial for VEGF-induced angiogenesis in ischemic conditions [129,130]. Overall, this suggests a pro-ischemic state is present in the brain tissue of Abcc6-deficient mice, potentially explaining the higher risk of ischemic stroke in patients with pathogenic ABCC6 variants. The primary limitations of this study include the relatively small sample size and the heterogeneity of the patient group suffering from various stroke subtypes, complicating the demonstration of minor differences between groups, as reflected in the wide confidence interval of the odds ratio. Nevertheless, a significantly higher presence of pathogenic ABCC6 variants in the stroke patient cohort compared to healthy age- and sex-matched controls was demonstrated, independently of other risk factors. Given that even minor triggers could lead to acute ischemic events in these patients, stricter management of other cerebrovascular and cardiovascular risk factors, such as tobacco use, obesity, and hypercholesterolemia, is advisable to minimize the risk of ischemic stroke or cardiovascular issues.
Another potential mechanism linking ABCC6 with stroke comes from animal studies suggesting there is an indirect pathway involving the classic vascular risk factors [131]. In fact, the study reveals that ABCC6 deficiency contributes significantly to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis in both mice and humans. Mice lacking the ABCC6 gene exhibited altered lipoprotein profiles, specifically decreased HDL cholesterol and increased LDL levels, which corresponded with enhanced atherosclerotic plaque formation [8,132]. The absence of ABCC6 was linked to decreased cholesterol efflux from macrophages and increased systemic inflammation, indicated by elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and CCL-2 [85,133]. These factors likely exacerbate the atherosclerotic phenotype observed in both Abcc6-deficient mice and PXE patients [2,134,135]. Despite the noted dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis, the study found that ABCC6 deficiency did not significantly affect vascular calcification associated with atherosclerosis. The vascular mineralization appeared to be a consequence of atherosclerotic plaque rather than a direct effect of ABCC6 genotype [136]. In a cohort of PXE patients, significant reductions in HDL levels were observed, mirroring the findings in the ABCC6-deficient mice. However, total cholesterol levels did not differ significantly from healthy controls, suggesting a complex interplay between ABCC6 deficiency and lipid metabolism [2,3,137,138]. Overall, the findings establish that ABCC6 plays a crucial role in modulating plasma lipoproteins and the hapolinsufficient development of atherosclerosis, with implications for understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with ABCC6 mutations. The study emphasizes that further investigation into cellular and molecular mechanisms is necessary to fully elucidate the pathways involved in these processes. These putative mechanisms are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Main molecular mechanisms underlying ABCC6’s role in SVD.
Other potentially relevant factors were provided by a neuroradiological study [139]. This study investigated the neuroradiological findings associated with PXE, particularly focusing on increased intracranial arterial pulsatility and microvascular brain damage, using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT)-based techniques (Table 4).

Table 4.
Neuroradiological protocol employed in the above reported study [139].
Patients with PXE demonstrated significantly higher pulsatility indexes (1.05) compared to controls (0.94) (p = 0.02), indicating increased arterial flow pulsatility in the intracranial arteries. This elevated pulsatility is likely a consequence of carotid siphon calcification, which contributes to the high prevalence of cerebrovascular disease observed in PXE patients [140,141]. The findings suggest that increased pulsatility may lead to microvascular damage in the brain, contributing to structural changes such as lower gray matter volumes (597 mL vs. 632 mL in controls, p < 0.01), more white matter lesions (2.6 mL vs. 1.1 mL, p = 0.05), and a higher number of lacunar infarctions (64 vs. 8, p = 0.04) [124,142,143]. These results align with the pulsatility hypothesis, which posits that increased pulsatility damages brain tissue by leading to stress on the microvasculature, including the role of vascular calcifications [144]. The presence of carotid siphon calcification is associated with increased flow pulsatility, which in turn correlates with microvascular brain damage, including infarctions and white matter lesions [145,146].
5. Potential Implications for Future Studies
These findings underscore the need for further research to elucidate the mechanisms linking arterial calcification and increased pulsatility to brain damage in PXE. Longitudinal studies that monitor changes in pulsatility and calcification over time could provide insights into the causal pathways involved in cerebrovascular events among PXE patients [147]. Understanding the relationship between pulsatility and small-vessel disease could also inform therapeutic strategies aimed at reducing vascular risk in this population, potentially focusing on interventions that modify arterial stiffness or pulsatility [8]. Additionally, the study highlights the importance of evaluating traditional vascular risk factors in the context of PXE. A prevalence of hypertension and hypercholesterolemia was noted in the patient cohort, with 44% of PXE patients exhibiting hypertension and 86% having hypercholesterolemia [148,149]. These factors may exacerbate microvascular damage and warrant consideration in the management of patients with PXE. The interplay between genetic factors like ABCC6 mutations and environmental factors such as lifestyle and comorbidities may present a multifaceted challenge in understanding and addressing cerebrovascular risk in these patients [150,151].
Another less-explored issue in the ABCC6 literature is the association between biomarkers of extracellular matrix degradation, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors, and the progression of vascular diseases. Elevated levels of some of these biomarkers have been linked to increased vascular inflammation and remodeling, which are critical factors in conditions like atherosclerosis and hypertension and could be enhanced by the decrease or loss of function of the ABCC6 gene product. Table 5 summarizes some of these biomarkers and their potential role in vascular diseases.

Table 5.
Main extracellular matrix degradation biomarkers and their role in vascular diseases [152,153,154,155,156].
From a personal perspective, integrating these biomarkers into clinical practice could enhance risk stratification and therapeutic monitoring, ultimately improving patient outcomes in vascular disease management.
6. Conclusions
ABCC6 is a pivotal regulator of ectopic calcification, primarily through its influence on the extracellular purinergic pathway and the modulation of PPi levels. Its deficiency is implicated in conditions such as PXE, underscoring the importance of this gene in mineralization processes. Patients with ABCC6 mutations exhibit an increased risk of cerebrovascular events, including ischemic strokes. The mechanisms linking these mutations to cerebrovascular complications involve dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and potentially altered hemodynamics, such as increased arterial pulsatility.
There is a pressing need for standardized genetic screening protocols to identify ABCC6 mutations in patients presenting with PXE and cerebrovascular manifestations. The current diagnostic criteria should be refined to incorporate genetic testing as a routine part of evaluation, especially for individuals with unexplained vascular conditions.
The clinical manifestations of ABCC6 mutations show significant variability, influenced by genetic background and environmental factors. This variability suggests the presence of additional genetic modifiers and highlights the need for personalized approaches to diagnosis and management.
Future research should involve longitudinal studies to track changes in cerebrovascular health in PXE patients over time. These studies could help establish causal relationships between ABCC6 mutations, arterial calcification, and the development of cerebrovascular complications. Investigating the broader genetic landscape surrounding ABCC6, including potential interactions with other genes implicated in vascular health, will provide deeper insights into the mechanisms underlying PXE and associated phenotypes. High-throughput sequencing technologies could facilitate this exploration. Detailed mechanistic studies are warranted to clarify how ABCC6 deficiency leads to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Understanding these pathways could inform therapeutic strategies aimed at mitigating cerebrovascular risks in affected individuals. Employing advanced neuroimaging techniques to assess microvascular damage and arterial pulsatility in PXE patients could provide critical insights into the relationship between vascular changes and neurological outcomes, enhancing our understanding of the disease’s impact on the nervous system.
Finally, clinical trials targeting vascular risk factors in PXE patients, such as hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, should be conducted. These trials can help determine the efficacy of various interventions in reducing cerebrovascular events in this population. By addressing these research issues, we can improve our understanding of the complex interplay between ABCC6 mutations, ectopic calcification, and cerebrovascular health, ultimately leading to enhanced patient care and management strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. and R.P.; methodology, M.Z.; validation, R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.Z. and R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Iliás, A.; Urbán, Z.; Seidl, T.L.; Le Saux, O.; Sinkó, E.; Boyd, C.D.; Sarkadi, B.; Váradi, A. Loss of ATP-dependent Transport Activity in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum-associated Mutants of Human ABCC6 (MRP6). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16860–16867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Saux, O.; Martin, L.; Aherrahrou, Z.; Leftheriotis, G.; Váradi, A.; Brampton, C.N. The molecular and physiological roles of ABCC6: More than meets the eye. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Saux, O.; Urban, Z.; Tschuch, C.; Csiszar, K.; Bacchelli, B.; Quaglino, D.; Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; Pope, F.M.; Richards, A.; Terry, S.; et al. Mutations in a gene encoding an ABC transporter cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.S.; Küçükosmanoğlu, A.; de Haas, M.; Sapthu, S.; Otero, J.A.; Hegman, I.E.M.; Bergen, A.A.B.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Borst, P.; van de Wetering, K. ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20206–20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffenstein, G.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Khiati, S.; Pomozi, V.; Le Saux, O.; Leftheriotis, G.; Lenaers, G.; Henrion, D.; Martin, L. Alteration of Extracellular Nucleotide Metabolism in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.G.; Ferreira, C.R.; MacFarlane, E.G.; Riddle, R.C.; Tomlinson, R.E.; Chew, E.Y.; Martin, L.; Ma, C.-T.; Sergienko, E.; Pinkerton, A.B.; et al. Ectopic calcification in pseudoxanthoma elasticum responds to inhibition of tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orriss, I.R.; Arnett, T.R.; Russell, R.G.G. Pyrophosphate: A key inhibitor of mineralisation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 28, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.S.; Duijst, S.; Mahakena, S.; Sommer, D.; Szeri, F.; Váradi, A.; Plomp, A.; Bergen, A.A.; Elferink, R.P.O.; Borst, P.; et al. ABCC6–Mediated ATP Secretion by the Liver Is the Main Source of the Mineralization Inhibitor Inorganic Pyrophosphate in the Systemic Circulation—Brief Report. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomozi, V.; Brampton, C.; van de Wetering, K.; Zoll, J.; Calio, B.; Pham, K.; Owens, J.B.; Marh, J.; Moisyadi, S.; Váradi, A.; et al. Pyrophosphate Supplementation Prevents Chronic and Acute Calcification in ABCC6-Deficient Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1258–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.; Hayashi, K.; Dang, K.; Hayashi, M.; Boyd, C.D. Analysis of ABCC6 (MRP6) in normal human tissues. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2005, 123, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.; Hayashi, K.; Nishiguchi, B.; Le Saux, O.; Hayashi, M.; Boyd, C.D. The Distribution of Abcc6 in Normal Mouse Tissues Suggests Multiple Functions for this ABC Transporter. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2003, 51, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, Y.; Baujat, G.; Botschen, U.; Wittkampf, T.; du Moulin, M.; Stella, J.; Le Merrer, M.; Guest, G.; Lambot, K.; Tazarourte-Pinturier, M.-F.; et al. Generalized Arterial Calcification of Infancy and Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Can Be Caused by Mutations in Either ENPP1 or ABCC6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, N.; Beck, K.; Bacchelli, B.; Cianciulli, P.; Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; Le Saux, O. Acquired Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like syndrome in beta-thalassaemia patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Douet, V.; VanWart, C.M.; Heller, M.B.; Le Saux, O. A Mouse Model of β-Thalassemia Shows a Liver-Specific Down-Regulation of Abcc6 Expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Montenegro, E.N.; Behrens, M.M.; Hoyt, W.F. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Arch. Neurol. 1972, 26, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, T.; Sugiu, K.; Kakishita, M.; Date, I. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum with carotid rete mirabile. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2004, 106, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Zotto, E.; Ritelli, M.; Pezzini, A.; Drera, B.; Gamba, M.; Giossi, A.; Volonghi, I.; Costa, P.; Barlati, S.; Gasparotti, R.; et al. Clinical, neuroradiological and molecular features of a patient affected by pseudoxhantoma elasticum associated to carotid rete mirabile: Case report. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2012, 114, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prick, J.; Thijssen, H. Radiodiagnostic signs in pseudoxanthoma elasticum generalisatum (dysgenesis elastofibrillaris mineralisans). Clin. Radiol. 1977, 28, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Alter, M.; Lee, S.H. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: A review of neurological complications. Ann. Neurol. 1978, 4, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.M. Angioid streaks and pseudoxanthoma elasticum with aneurysm of the internal carotid artery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1951, 34, 1322–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheie, H.G.; Hogan, T.F. Angioid Streaks and Generalized Arterial Disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1957, 57, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyer, T.; Margulis, A. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum with internal carotid artery aneurysm. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1981, 136, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kito, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Mori, N.; Kohno, H. Ruptured aneurysm of the anterior spinal artery associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Neurosurg. 1983, 58, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.G.K.; Beohar, P.C.; Ghosh, S.K.; Gupta, P.S. Subarachnoid haemorrhage in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Postgrad. Med. J. 1974, 50, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Schwegler, G. Intracerebral haemorrhage as first manifestation of Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2008, 110, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, A.M.; Zidverc-Trajkovic, J.; Milovic, M.M.; Pavlovic, D.M.; Jovanovic, Z.; Mijajlovic, M.; Petrovic, M.; Kostic, V.S.; Sternic, N. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Three Cases. Can. J. Neurol. Sci./J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2005, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalloz, M.-A.; Debs, R.; Bensa, C.; Alamowitch, S. Hypersignaux de la substance blanche révélant un pseudoxanthome élastique. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 166, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kimura, K.; Uchino, M. Lacunar brain infarction in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1996, 36, 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Germain, D.P.; Perdu, J. Identification of novel polymorphisms in the pM5 and MRP1 (ABCC1) genes at locus 16p13.1 and exclusion of both genes as responsible for pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 17, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, A.A.; Plomp, A.S.; Schuurman, E.J.; Terry, S.; Breuning, M.; Dauwerse, H.; Swart, J.; Kool, M.; van Soest, S.; Baas, F.; et al. Mutations in ABCC6 cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringpfeil, F.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Christiano, A.M.; Uitto, J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Mutations in the MRP6 gene encoding a transmembrane ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6001–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, D.P.; Perdu, J.; Remones, V.; Jeunemaitre, X. Homozygosity for the R1268Q Mutation in MRP6, the Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Gene, Is Not Disease-Causing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 274, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struk, B.; Cai, L.; Zäch, S.; Ji, W.; Chung, J.; Lumsden, A.; Stumm, M.; Huber, M.; Schaen, L.; Kim, C.-A.; et al. Mutations of the gene encoding the transmembrane transporter protein ABC-C6 cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Mol. Med. 2000, 78, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tiwari, A.K. Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs/ABCCs) in cancer chemotherapy and genetic diseases. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3226–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fülöp, K.; Barna, L.; Symmons, O.; Závodszky, P.; Váradi, A. Clustering of disease-causing mutations on the domain–domain interfaces of ABCC6. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arányi, T.; Bacquet, C.; de Boussac, H.; Ratajewski, M.; Pomozi, V.; Fülöp, K.; Brampton, C.N.; Pulaski, L.; Le Saux, O.; Váradi, A.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of the ABCC6 gene and the background of impaired function of missense disease-causing mutations. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 39319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajewski, M.; de Boussac, H.; Sachrajda, I.; Bacquet, C.; Kovács, T.; Váradi, A.; Pulaski, L.; Arányi, T. ABCC6 Expression Is Regulated by CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Activating a Primate-Specific Sequence Located in the First Intron of the Gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boussac, H.; Ratajewski, M.; Sachrajda, I.; Köblös, G.; Tordai, A.; Pulaski, L.; Buday, L.; Váradi, A.; Arányi, T. The ERK1/2-hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha axis regulates human ABCC6 gene expression in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22800–22808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, M.G.; Chen, Z.-S.; Shchaveleva, I.; Zeng, H.; Kruh, G.D. Characterization of the drug resistance and transport properties of multidrug resistance protein 6 (MRP6, ABCC6). Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6172–6177. [Google Scholar]
- Miksch, S.; Lumsden, A.; Guenther, U.P.; Foernzler, D.; Christen-Zäch, S.; Daugherty, C.; Ramesar, R.K.S.; Lebwohl, M.; Hohl, D.; Neldner, K.H.; et al. Molecular genetics of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Type and frequency of mutations in ABCC6. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 26, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen-Zach, S.; Huber, M.; Struk, B.; Lindpaintner, K.; Munier, F.; Panizzon, R.G.; Hohl, D. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Evaluation of diagnostic criteria based on molecular data. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfendner, E.G.; Vanakker, O.M.; Terry, S.F.; Vourthis, S.; McAndrew, P.E.; McClain, M.R.; Fratta, S.; Marais, A.-S.; Hariri, S.; Coucke, P.J.; et al. Mutation detection in the ABCC6 gene and genotype phenotype analysis in a large international case series affected by pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 44, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornstrup, L.S.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Haase, C.L.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Sillesen, H.; Grande, P.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Heterozygosity for R1141X in ABCC6 and Risk of Ischemic Vascular Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoglu, G.; Li, Q.; Gokoz, O.; Gazyagci, A.S.; Uitto, J. Clinical and histopathological characteristics of a family with R1141X mutation of pseudoxanthoma elasticum—Presymptomatic testing and lack of carrier phenotypes. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanakker, O.M.; Leroy, B.P.; Coucke, P.; Bercovitch, L.G.; Uitto, J.; Viljoen, D.; Terry, S.F.; Van Acker, P.; Matthys, D.; Loeys, B.; et al. Novel clinico-molecular insights in pseudoxanthoma elasticum provide an efficient molecular screening method and a comprehensive diagnostic flowchart. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, N.; Martin, L.; Calvas, P.; Le Bert, M.; Hovnanian, A. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: A clinical, pathophysiological and genetic update including 11 novel ABCC6 mutations. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Arányi, T.; Váradi, A.; Terry, S.F.; Uitto, J. Research Progress in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum and Related Ectopic Mineralization Disorders. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzaj, P.; Kuhn, J.; Michalek, R.D.; Karoly, E.D.; Faust, I.; Dabisch-Ruthe, M.; Knabbe, C.; Hendig, D.; Dardis, A. Large-Scaled Metabolic Profiling of Human Dermal Fibroblasts Derived from Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Patients and Healthy Controls. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Oldenburg, R.; Otsuru, S.; Grand-Pierre, A.E.; Horwitz, E.M.; Uitto, J. Parabiotic heterogenetic pairing of Abcc6−/−/Rag1−/− mice and their wild-type counterparts halts ectopic mineralization in a murine model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Blum, R.R.; Singer, G.K.; Stern, D.K.; Emanuel, P.O.; Fuchs, W.; Phelps, R.G.; Terry, S.F.; Lebwohl, M.G. A randomized controlled trial of oral phosphate binders in the treatment of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendig, D.; Schulz, V.; Arndt, M.; Szliska, C.; Kleesiek, K.; Gotting, C. Role of serum fetuin-A, a major inhibitor of systemic calcifi-cation, in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, M.E.; Garcia-Lopez, E.; Anderstam, B.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Vascular calcification inhibitors in relation to cardiovascular disease with special emphasis on fetuin-A in chronic kidney disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2008, 46, 217–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Ducy, P.; McKee, M.D.; Pinero, G.J.; Loyer, E.; Behringer, R.R.; Karsenty, G. Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature 1997, 386, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.L.; Liu, S.; Vaziri, N.D. Chronic Kidney Disease Results in Deficiency of ABCC6, the Novel Inhibitor of Vascular Calcification. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Uitto, J.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla-protein: A crucial switch to control ectopic mineralization. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, E.W.; Apschner, A.; Schulte-Merker, S. Vitamin K reduces hypermineralisation in zebrafish models of PXE and GACI. Development 2015, 142, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminejad, A.; Bozorgmehr, B.; Najafi, A.; Khoshaeen, A.; Ghalandari, M.; Najmabadi, H.; Kariminejad, M.H.; Vanakker, O.M.; Hosen, M.J.; Malfait, F.; et al. Retinitis pigmentosa, cutis laxa, and pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like skin manifestations associated with GGCX mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Q.; Grand-Pierre, A.E.; Schurgers, L.J.; Uitto, J. Administration of vitamin K does not counteract the ectopic minerali-zation of connective tissues in Abcc6 (−/−) mice, a model for pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brampton, C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Vanakker, O.; Van Laer, L.; Chen, L.-H.; Thakore, M.; De Paepe, A.; Pomozi, V.; Szabó, P.T.; Martin, L.; et al. Vitamin K does not prevent soft tissue mineralization in a mouse model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Waarsing, J.H.; Herfs, M.; Versteeg, D.; Schoensiegel, F.; Sato, T.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Ivandic, B.; Vermeer, C.; Schurgers, L.J.; et al. Vitamin K supplementation increases vitamin K tissue levels but fails to counteract ectopic calcification in a mouse model for pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Hilaire, C.; Ziegler, S.G.; Markello, T.C.; Brusco, A.; Groden, C.; Gill, F.; Carlson-Donohoe, H.; Lederman, R.J.; Chen, M.Y.; Yang, D.; et al. NT5E mutations and arterial calcifications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markello, T.C.; Pak, L.K.; Hilaire, C.S.; Dorward, H.; Ziegler, S.G.; Chen, M.Y.; Chaganti, K.; Nussbaum, R.L.; Boehm, M.; Gahl, W.A. Vascular pathology of medial arterial calcifications in NT5E deficiency: Implications for the role of adenosine in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 103, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vilder, E.Y.; Vanakker, O.M. From variome to phenome: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of ectopic mineralization disorders. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Price, T.P.; Sundberg, J.P.; Uitto, J. Juxta-articular joint-capsule mineralization in CD73 deficient mice: Similarities to patients with NT5E mutations. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, Z.; Váradi, A.; Li, Q.; Uitto, J. ABCC6 does not transport adenosine—Relevance to pathomechanism of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fernandez, M.I.; Gheduzzi, D.; Boraldi, F.; Paolinelli, C.D.; Sanchez, P.; Valdivielso, P.; Morilla, M.J.; Quaglino, D.; Guerra, D.; Casolari, S.; et al. Parameters of oxidative stress are present in the circulation of PXE patients. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskou, S.; Aslan, M.; Fanis, P.; Phylactides, M.; Kleanthous, M. Oxidative stress in β-thalassaemia and sickle cell disease. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani-Contri, M.; Bacchelli, B.; Boraldi, F.; Quaglino, D.; Taparelli, F.; Carnevalia, E.; Francomano, M.A.; Seidenari, S.; Bettoli, V.; De Sanctis, V.; et al. Characterization of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like lesions in the skin of patients with ?-thalassemia. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 44, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Pfendner, E.; Váradi, A.; Uitto, J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Clinical phenotypes, molecular genetics and putative pathomechanisms. Exp Dermatol. 2009, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Forni, G.L.; Guerrini, G.; Borgna-Pignatti, C. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like syndrome and thalassemia: An update. Dermatol. Online J. 2009, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Lau, E.; Singh, H.; Vergnes, L.; Tarling, E.J.; Mehrabian, M.; Mungrue, I.; Xiao, S.; Shih, D.; Castellani, L.; et al. ABCC6 localizes to the mitochondria-associated mem-brane. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferré, M.; Reynier, P.; Chevrollier, A.; Prunier-Mirebeau, D.; Lefthériotis, G.; Henrion, D.; Bonneau, D.; Procaccio, V.; Martin, L. Is ABCC6 a genuine mitochondrial protein? BMC Res Notes. 2013, 6, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.S.M.; Moestrup, S.K. Is classical pseudoxanthoma elasticum a consequence of hepatic ‘intoxication’ due to ABCC6 substrate accumulation in the liver? Expert Rev. Endocr. Metabol. 2013, 8, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Frank, M.; Thisse, C.I.; Thisse, B.V.; Uitto, J. Zebrafish: A Model System to Study Heritable Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sadowski, S.; Frank, M.; Chai, C.; Varadi, A.; Ho, S.Y.; Lou, H.; Dean, M.; Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; et al. The abcc6a gene expression is required for normal zebrafish development. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Chou, D.W.; Berndt, A.; Sundberg, J.P.; Uitto, J.; Sato, M. Mouse Models for Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Genetic and Dietary Modulation of the Ectopic Mineralization Phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgels, T.G.; Hu, X.; Scheffer, G.L.; van der Wal, A.C.; Toonstra, J.; de Jong, P.T.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Levelt, C.N.; de Wolf, A.; Loves, W.J.; et al. Disruption of Abcc6 in the mouse: Novel insight in the pathogenesis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, J.F.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Jiang, Q.-J.; Terlizzi, J.; Choi, H.Y.; Fujimoto, N.; Li, K.; Pulkkinen, L.; Birk, D.E.; Sundberg, J.P.; et al. Targeted Ablation of the Abcc6 Gene Results in Ectopic Mineralization of Connective Tissues. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8299–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heston, W.E.; Vlahakis, G. Mammary tumors, plaques, and hyperplastic alveolar nodules in various combinations of mouse inbred strains and the different lines of the mammary tumor virus. Int. J. Cancer 1971, 7, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherrahrou, Z.; Doehring, L.C.; Ehlers, E.-M.; Liptau, H.; Depping, R.; Linsel-Nitschke, P.; Kaczmarek, P.M.; Erdmann, J.; Schunkert, H. An Alternative Splice Variant in Abcc6, the Gene Causing Dystrophic Calcification, Leads to Protein Deficiency in C3H/He Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7608–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffenstein, G.; Pizard, A.; Le Corre, Y.; Vessières, E.; Grimaud, L.; Toutain, B.; Labat, C.; Mauras, Y.; Gorgels, T.; Bergen, A.; et al. Disseminated Arterial Calcification and Enhanced Myogenic Response Are Associated With Abcc6 Deficiency in a Mouse Model of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, M.J.; Coucke, P.J.; Le Saux, O.; De Paepe, A.; Vanakker, O.M. Perturbation of specific pro-mineralizing signalling pathways in human and murine pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeri, F.; Miko, A.; Navasiolava, N.; Kaposi, A.; Verschuere, S.; Molnar, B.; Li, Q.; Terry, S.F.; Boraldi, F.; Uitto, J.; et al. The pathogenic c.1171A>G (p.Arg391Gly) and c.2359G>A (p.Val787Ile) ABCC6 variants display incomplete penetrance causing pseudoxanthoma elasticum in a subset of individuals. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köblös, G.; Andrikovics, H.; Prohászka, Z.; Tordai, A.; Váradi, A.; Arányi, T. The R1141X Loss-of-Function Mutation of the ABCC6 Gene Is a Strong Genetic Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2010, 14, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisciotta, L.; Tarugi, P.; Borrini, C.; Bellocchio, A.; Fresa, R.; Guerra, D.; Quaglino, D.; Ronchetti, I.; Calandra, S.; Bertolini, S. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum and familial hypercholes-terolemia: A deleterious combination of cardiovascular risk factors. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, D.P. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Nakayama, T.; Mizutani, Y.; Yuzawa, M. Novel mutations of ABCC6 gene in Japanese patients with Angioid streaks. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sadowski, S.; Uitto, J. Angioid Streaks in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Role of the p.R1268Q Mutation in the ABCC6 Gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omarjee, L.; Nitschke, Y.; Verschuere, S.; Bourrat, E.; Vignon, M.D.; Navasiolava, N.; Leftheriotis, G.; Kauffenstein, G.; Rutsch, F.; Vanakker, O.M.; et al. Severe early-onset manifestations of pseudoxanthoma elasticum resulting from the cumulative effects of several deleterious mutations in ENPP1, ABCC6 and HBB: Transient improvement in ectopic calcification with sodium thiosulfate. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalal, I.G.; Seetha, D.; Panda, A.; Nitschke, Y.; Rutsch, F. Molecular diagnosis of generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI). J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Res. 2012, 3, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, M.; Neldner, K.; Pope, F.M.; De Paepe, A.; Christiano, A.M.; Boyd, C.D.; Uitto, J.; McKusick, V.A. Classification of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Report of a consensus conference. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Bercovitch, L.; Terry, S.F.; Terry, P.F. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Progress in diagnostics and research towards treatment: Summary of the 2010 PXE International Research Meeting. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomp, A.S.; Toonstra, J.; Bergen, A.A.; van Dijk, M.R.; de Jong, P.T. Proposal for updating the pseudoxanthoma elasticum classification system and a review of the clinical findings. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part. A 2010, 152, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/?term=ABCC6[gene] (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Larusso, J.; Ringpfeil, F.; Uitto, J. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: A streamlined, ethnicity-based mutation detection strategy. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2010, 3, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Shao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Uitto, J.; Wang, G. Genetic Heterogeneity of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: The Chinese Signature Profile of ABCC6 and ENPP1 Mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomozi, V.; Brampton, C.; Fülöp, K.; Chen, L.H.; Apana, A.; Li, Q.; Uitto, J.; Le Saux, O.; Váradi, A. Analysis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing missense mutants of ABCC6 in vivo; pharmacological correction of the mislocalized proteins. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, D.P. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: Evidence for the existence of a pseudogene highly homologous to the ABCC6 gene. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 38, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, L.; Nakano, A.; Ringpfeil, F.; Uitto, J. Identification of ABCC6 pseudogenes on human chromosome 16p: Implications for mutation detection in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Hum. Genet. 2001, 109, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringen, M.K.; Stormo, C.; Grimholt, R.M.; Berg, J.P.; Piehler, A.P. Copy number variations of the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC6 gene and its pseudogenes. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringen, M.K.; Stormo, C.; Berg, J.P.; Terry, S.F.; Vocke, C.M.; Rizvi, S.; Hendig, D.; Piehler, A.P. Copy number variation in the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC6 gene and ABCC6 pseudogenes in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2015, 3, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunier, F.; Terrien, G.; Le Corre, Y.; Apana, A.L.Y.; Bière, L.; Kauffenstein, G.; Furber, A.; Bergen, A.A.B.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Le Saux, O.; et al. Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Cardiac Findings in Patients and Abcc6-Deficient Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendig, D.; Knabbe, C.; Götting, C. New insights into the pathogenesis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum and related soft tissue calcification disorders by identifying genetic interactions and modifiers. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 43253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Terry, S.F.; Terry, P.F.; Bercovitch, L.G.; Gerard, G.F. Development of a Rapid, Reliable Genetic Test for Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.; Cornez, L.; Samkari, W.; Mazzella, J.-M.; Venisse, A.; Boccio, V.; Auribault, K.; Keren, B.; Benistan, K.; Germain, D.P.; et al. Mutation spectrum in the ABCC6 gene and genotype–phenotype correlations in a French cohort with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 19, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campens, L.; Vanakker, O.M.; Trachet, B.; Segers, P.; Leroy, B.P.; De Zaeytijd, J.; Voet, D.; De Paepe, A.; De Backer, T.; De Backer, J. Characterization of Cardiovascular Involvement in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Families. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duering, M.; Biessels, G.J.; Brodtmann, A.; Chen, C.; Cordonnier, C.; de Leeuw, F.-E.; Debette, S.; Frayne, R.; Jouvent, E.; Rost, N.S.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease—Advances since 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.T.; Thomas, A. Vascular dementia. Lancet 2015, 386, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Schilling, S.; Duperron, M.-G.; Larsson, S.C.; Markus, H.S. Clinical Significance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Markers of Vascular Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Traylor, M.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Markus, H. New insights into mechanisms of small vessel disease stroke from genetics. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M.; Nozaki, H.; Kato, T.; Koyama, A.; Sakai, N.; Ando, S.; Kanazawa, M.; Hishikawa, N.; Nishimoto, Y.; Polavarapu, K.; et al. HTRA1-Related Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabriat, H.; Joutel, A.; Dichgans, M.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Bousser, M.-G. CADASIL. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.Y.Y.; Markus, H.S. Monogenic causes of stroke: Now and the future. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2601–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.Y.; Traylor, M.; Megy, K.; Duarte, D.; Deevi, S.V.; Shamardina, O.; Mapeta, R.P.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Gräf, S.; Downes, K.; et al. How common are single gene mutations as a cause for lacunar stroke? Neurology 2019, 93, e2007–e2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilarski, L.L.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.; Bevan, S.; Baker, R.; Hassan, A.; Hughes, D.A.; Markus, H.S.; UK Young Lacunar Stroke DNA Study. Prevalence of CADASIL and Fabry disease in a cohort of MRI defined younger onset lacunar stroke. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.P.H.; Auckland, K.; Gräf, S.; Markus, H.S. Rare Sequence Variation Underlying Suspected Familial Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2024, 13, e035771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, M.; Hatano, Y.; Nozaki, H.; Ando, S.; Kondo, H.; Hanazono, A.; Iwanaga, A.; Murota, H.; Osakada, Y.; Osaki, M.; et al. High frequency of HTRA1 and ABCC6 mutations in Japanese patients with adult-onset cerebral small vessel disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 94, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vilder, E.Y.; Cardoen, S.; Hosen, M.J.; Le Saux, O.; De Zaeytijd, J.; Leroy, B.P.; De Reuck, J.; Coucke, P.J.; De Paepe, A.; Hemelsoet, D.; et al. Pathogenic variants in the ABCC6 gene are associated with an increased risk for ischemic stroke. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Issa, R.; Kumar, P.; Hampson, I.N.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Bernabeu, C.; Kumar, S. CD105 prevents apoptosis in hypoxic endothelial cells. J. Cell. Sci. 2003, 116, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungrue, I.N.; Zhao, P.; Yao, Y.; Meng, H.; Rau, C.; Havel, J.V.; Gorgels, T.G.; Bergen, A.A.; MacLellan, W.R.; Drake, T.A.; et al. Abcc6 deficiency causes increased infarct size and apoptosis in a mouse cardiac ischemia-reperfusion model. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Dattilo, L.K.; Kaartinen, V.; Deng, C.X.; Umans, L.; Zwijsen, A.; Roberts, A.B.; Bottinger, E.P.; Beebe, D.C. Functions of the type 1 BMP receptor Acvr1 (Alk2) in lens development: Cell proliferation, terminal differentiation, and survival. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheduzzi, D.; Boraldi, F.; Annovi, G.; DeVincenzi, C.P.; Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C.; Quaglino, D.; Ronchetti, I.P. Matrix Gla protein is involved in elastic fiber calcification in the dermis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 87, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauw, F.; Kranenburg, G.; Kappelle, L.J.; Hendrikse, J.; Koek, H.L.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Mali, W.P.T.; de Jong, P.A.; Spiering, W. Cerebral disease in a nationwide Dutch pseudoxanthoma elasticum cohort with a systematic review of the literature. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 15, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikovics, H.; Pongrácz, E.; Kalina, E.; Szilvási, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Schmitz, G.; Tordai, A. Decreased frequencies of ABCA1 polymorphisms R219K and V771M in Hungarian patients with cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 21, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.M.; Lin, W.; Harding, B.N.; Squier, M.V.; Thom, M. Drug resistance in epilepsy: Expression of drug resistance proteins in common causes of refractory epilepsy. Brain 2002, 125, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, A.; Kilic, E.; Xing, H.; Kilic, U.; Rentsch, K.M.; Wunderli-Allenspach, H.; Bassetti, C.L.; Hermann, D.M. Inhibition of multidrug resistance transporter-1 facilitates neuroprotective therapies after focal cerebral ischemia. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, A.S.; Custer, L.; Hansen, D.; Clapp, S.; Kemppa, E.; Klingensmith, J. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 mediates myocardial ischemic injury through JNK-dependent signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 48, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, M.; Shore, E.M. Common mutations in ALK2/ACVR1, a multi-faceted receptor, have roles in distinct pediatric musculoskeletal and neural orphan disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 27, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xie, L.; Jin, K.; Sheibani, N.; Greenberg, D.A. Hypoxic Induction of Endoglin via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Mouse Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Stroke 2003, 34, 2483–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brampton, C.; Pomozi, V.; Chen, L.-H.; Apana, A.; McCurdy, S.; Zoll, J.; Boisvert, W.A.; Lambert, G.; Henrion, D.; Blanchard, S.; et al. ABCC6 deficiency promotes dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Peek, R.; Plomp, A.; Brink, J.T.; Scheffer, G.; van Soest, S.; Leys, A.; de Jong, P.T.V.M.; Bergen, A.A.B. Analysis of the Frequent R1141X Mutation in the ABCC6 Gene in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzaj, P.; Kuhn, J.; Dabisch-Ruthe, M.; Faust, I.; Götting, C.; Knabbe, C.; Hendig, D. ABCC6- a new player in cellular cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism? Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Near, S.; Young, K.; Connelly, P.W.; Hegele, R.A. ABCC6 gene polymorphism associated with variation in plasma lipoproteins. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 46, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglionico, R.; Armentano, M.F.; Carmosino, M.; Salvia, A.M.; Cuviello, F.; Bisaccia, F.; Ostuni, A. Dysregulation of gene expression in ABCC6 knockdown HepG2 cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, M.J.; Mahn, T.; Steinmetz, M.; Fimmers, R.; Pizarro, C.; Nickenig, G.; Skowasch, D.; Schahab, N.; Schaefer, C.A. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum—Also a microvascular disease. Vasa 2020, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglionico, R.; Ostuni, A.; Armentano, M.F.; Milella, L.; Crescenzi, E.; Carmosino, M.; Bisaccia, F. ABCC6 knockdown in HepG2 cells induces a senescent-like cell phenotype. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Martin, L.J.; Schadt, E.E.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Ingram-Drake, L.; Nebohacova, M.; Mehrabian, M.; Drake, T.A.; et al. Disruption of the Aortic Elastic Lamina and Medial Calcification Share Genetic Determinants in Mice. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartstra, J.W.; van den Beukel, T.; Kranenburg, G.; Geurts, L.J.; den Harder, A.M.; Witkamp, T.; Wolterink, J.M.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M.; van Valen, E.; Koek, H.L.; et al. Increased Intracranial Arterial Pulsatility and Micro-vascular Brain Damage in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024, 45, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, G.; De Jong, P.A.; Mali, W.P.; Attrach, M.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Spiering, W. Prevalence and severity of arterial calcifications in pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) compared to hospital controls. Novel insights into the vascular phenotype of PXE. Atherosclerosis 2017, 256, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tuijl, R.J.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Geurts, L.J.; van der Schaaf, I.C.; Biessels, G.J.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Velthuis, B.K.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M. Does the Internal Carotid Artery Attenuate Blood-Flow Pulsatility in Small Vessel Disease? A 7 T 4D-Flow MRI Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risseeuw, S.; Ossewaarde-van Norel, J.; van Buchem, C.; Spiering, W.; Imhof, S.M.; van Leeuwen, R. The Extent of Angioid Streaks Correlates With Macular Degeneration in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 220, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.F. Aortic stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility, and target organ damage. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedde, M.; Pascarella, R. Arterial Calcification as a Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum-like Manifestation in Beta-Thalassemia: Molecular Mechanisms and Significance. Hemato 2025, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leftheriotis, G.; Kauffenstein, G.; Hamel, J.F.; Abraham, P.; Le Saux, O.; Willoteaux, S.; Henrion, D.; Martin, L.; Eller, P. The Contribution of Arterial Calcification to Peripheral Arterial Disease in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartstra, J.W.; Spiering, W.; Ouweland, J.M.W.v.D.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Janssen, R.; de Jong, P.A. Increased Elastin Degradation in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Independent of Calcification. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Pencina, K.M.; Massaro, J.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Hoffmann, U.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Mitchell, G.F. Cross-Sectional Relations of Arterial Stiffness, Pressure Pulsatility, Wave Reflection, and Arterial Calcification. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, N.R.; Seo, H.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Seol, H.Y.; Lee, N.J.; Suh, S.-I. The correlation between carotid siphon calcification and lacunar infarction. Neuroradiology 2011, 53, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo, J.D.; Vernooij, M.W.; Ikram, M.A.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Bos, D. Intracranial Carotid Arteriosclerosis Mediates the Association Between Blood Pressure and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Hypertension 2023, 80, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omarjee, L.; Fortrat, J.-O.; Larralde, A.; Le Pabic, E.; Kauffenstein, G.; Laot, M.; Navasiolava, N.; Mention, P.-J.; Linares, J.L.C.; Valdivielso, P.; et al. Internal Carotid Artery Hypoplasia: A New Clinical Feature in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mention, P.-J.; Lacoeuille, F.; Leftheriotis, G.; Martin, L.; Omarjee, L. 18F-Flurodeoxyglucose and 18F-Sodium Fluoride Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Imaging of Arterial and Cutaneous Alterations in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Valasciuc, E.; Anton, I.-B.; Gosav, E.M.; Dima, N.; Cucu, A.I.; Costea, C.F.; Floria, D.E.; Hurjui, L.L.; Tarniceriu, C.C.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Pathophysiologic Implications and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolosowicz, M.; Prokopiuk, S.; Kaminski, T.W. The Complex Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nubila, A.; Dilella, G.; Simone, R.; Barbieri, S.S. Vascular Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Poștaru, M.; Rotariu, M.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D. Hydrogen Sulfide Modulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases and CD147/EMMPRIN: Mechanistic Pathways and Impact on Atherosclerosis Progression. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).