The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ⮚
- elevated waist circumference (WC) (≥102 cm for men, ≥88 cm for women);
- ⮚
- elevated fasting glucose (≥100 mg/dL) or ongoing treatment for dysglycemia;
- ⮚
- elevated triglycerides (≥150 mg/dL) or ongoing treatment for hypertriglyceridemia;
- ⮚
- reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (<40 mg/dL for men, <50 mg/dL for women) or ongoing treatment for low HDL-C;
- ⮚
- elevated blood pressure (≥130/≥85 mm Hg) or ongoing treatment for hypertension [8].
2. Adiponectin: Discovery, Structure, and Receptors
3. Adiponectin and Metabolic Syndrome Components: Clinical Associations and Genetic Variants
3.1. Central Obesity
Adiponectin Gene Variants and Obesity Risk
3.2. Glucose and Lipid Profile
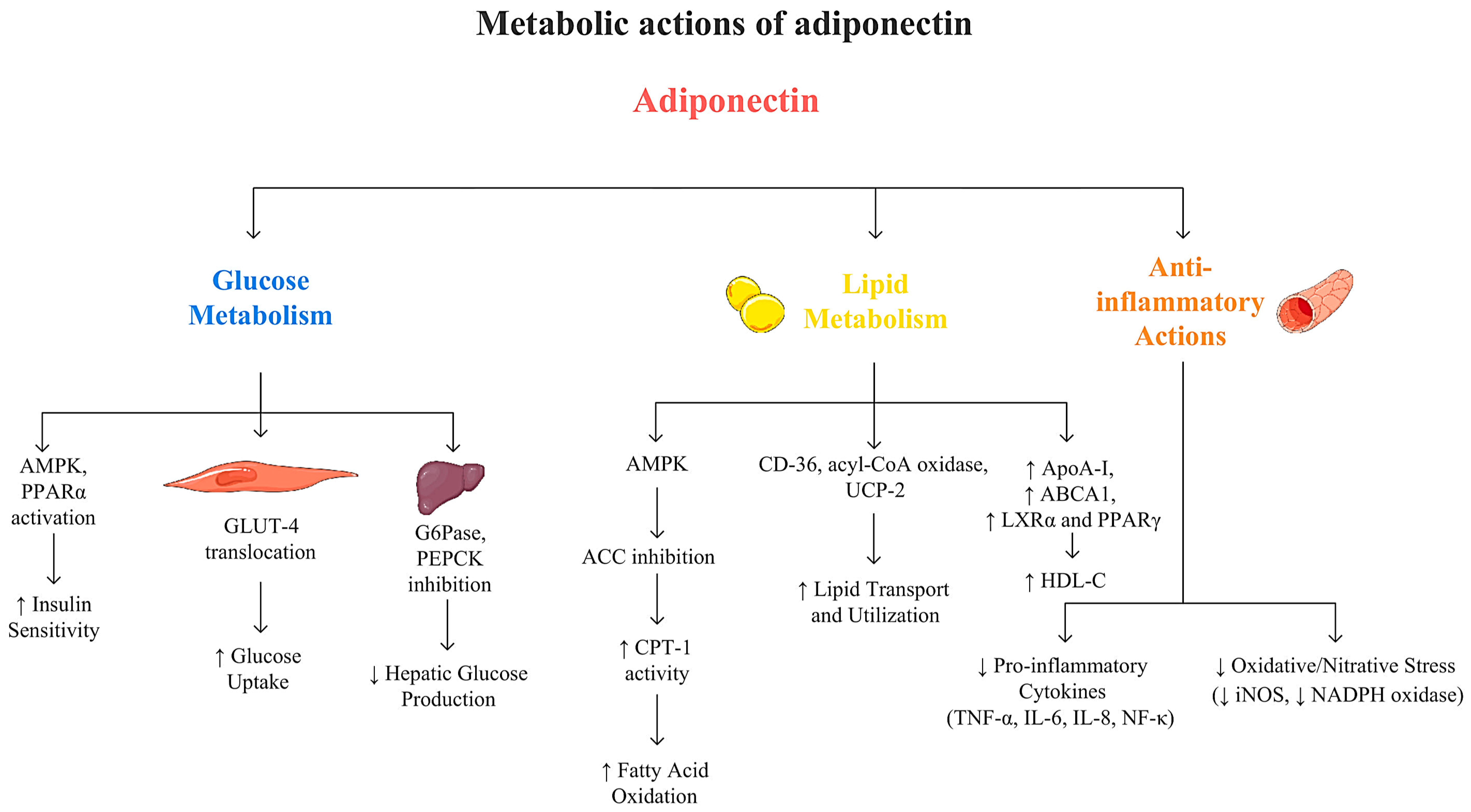
3.2.1. Adiponectin and Glucose Metabolism
3.2.2. Adiponectin and Lipid Metabolism
3.2.3. Adiponectin and Cardiovascular Health
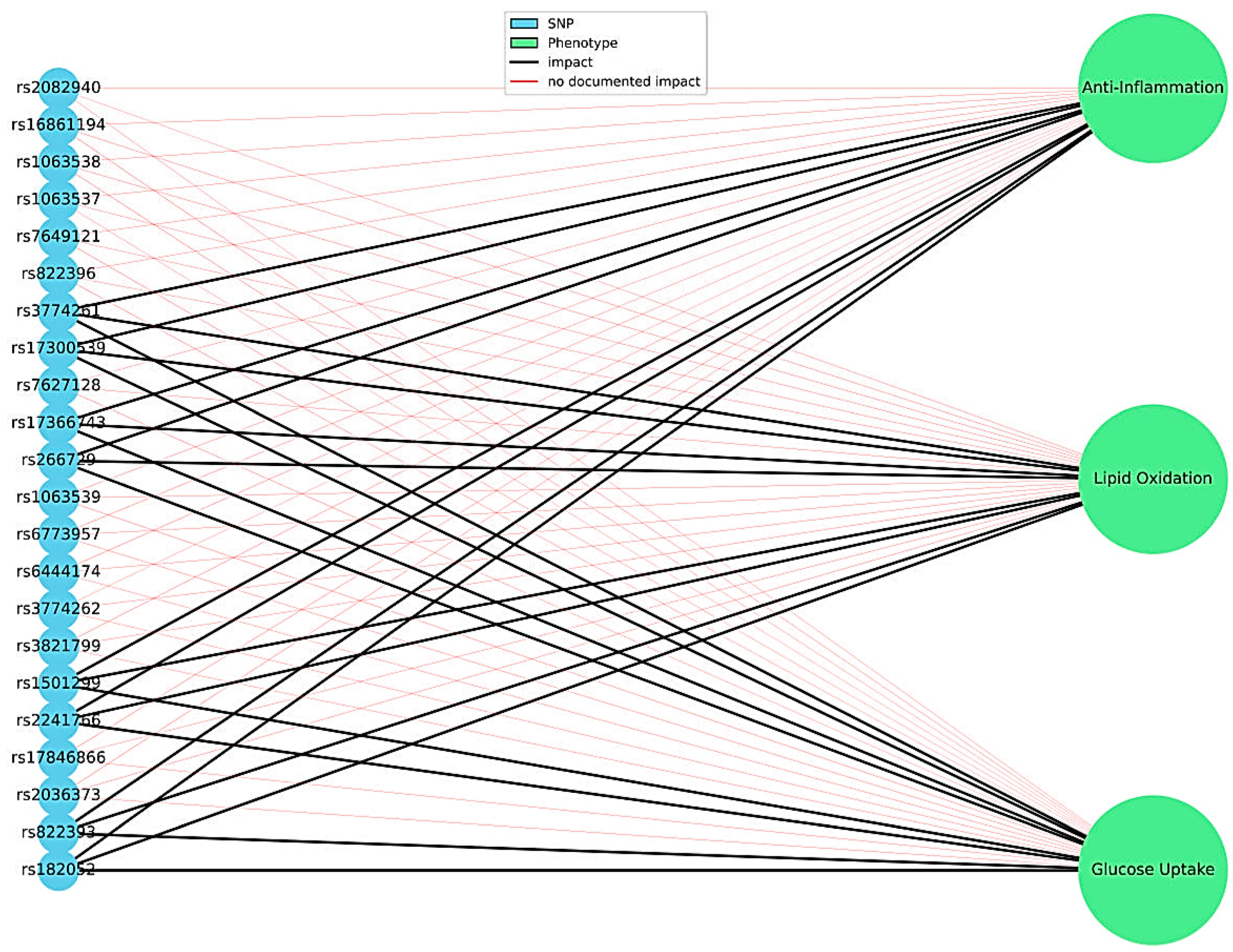
3.2.4. The Role of Adiponectin Gene Variants in Modulating Lipid and Carbohydrate Profiles
| rsID | Allele Change | Variant Location/Molecular Consequences | Observed Associations | Study Population | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1501299 | G > T | Intron |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] | |||
|
| [158] | |||
|
| [159] | |||
|
| [160] | |||
|
| [161] | |||
|
| [92] | |||
|
| [162] | |||
| rs2241766 | T > G | Exon/synonymous variant |
|
| [163] |
|
| [157] | |||
|
| [164] | |||
|
| [158] | |||
|
| [153] | |||
|
| [159] | |||
|
| [165] | |||
|
| [85] | |||
| rs266729 | C > G | Promoter |
|
| [166] |
|
| [157] | |||
|
| [167] | |||
|
| [168] | |||
|
| [92] | |||
| rs17366743 | T > C | Exon/missense variant |
|
| [114] |
|
| [19] | |||
| rs7627128 | C > A | Intron |
|
| [117] |
|
| [161] | |||
| rs17300539 | G > A | Promoter |
|
| [163] |
| No significant association with T2DM |
| [157] | |||
|
| [19] | |||
| Spanish adults (n = 180) | [169] | |||
|
| [168] | |||
|
| [92] | |||
| rs182052 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [170] |
| Chinese adults: T2DM cases (n = 340) and controls (n = 340) | [161] | |||
| African-American adults: T2DM with ESRD (n = 851), T2DM without nephropathy (n = 317) and controls (n = 871) | [171] | |||
| rs17846866 | T > G | 3′UTR |
| Kazakh adults: T2DM cases (n = 136) and controls (n = 577) | [103] |
| Asian-Indian adults: T2DM cases (n = 2000) and controls (n = 2000) | [94] | |||
| Both heterozygous (TG vs. TT; OR = 1.92; 95% CI 1.01–3.66; p = 0.004) and homozygous variant (GG vs. TT; OR = 4.83; 95% CI 1.50–15.55; p = 0.004) was associated in T2DM | Saudi adults: T2DM cases (n = 96) and controls (n = 96) | [162] | |||
| rs3774261 | A > G | Intron |
| European-Australian adults from a meta-analysis combining BHS, CUDAS, and FDS: T2DM cases (n = 967) and controls (n = 2355) | [172] |
| South-Indian adults: T2DM cases (n = 1100) and controls (n = 1100) | [92] | |||
| Chinese Han adults from northeast China: T2DM cases (n = 993) and controls (n = 966)—total n = 1959 | [173] | |||
| rs822393 | C > T | Intron |
| South-Indian adults: T2DM cases (n = 1100) and controls (n = 1100) | [92] |
|
| [174] | |||
| Caucasian obese adults from Spain (n = 1004) | [175] | |||
|
| [176] | |||
|
| [173] | |||
| rs822395 | C > A | Intron | A allele was associated with lower ApoA1 under dominant (p = 0.00234), codominant (p = 0.00123), recessive (p = 0.00314), and additive models (p = 0.00027); A allele was also associated with higher CVD risk under recessive (p = 0.00234) and additive models (p = 0.00238) | European adolescents aged 12–18 years (n = 1057) | [176] |
| rs822396 | G > A | Intron |
| North-African Tunisian Arab adults: T2DM cases (n = 917) and controls (n = 748) | [168] |
| North-Indian Punjabi adults: T2DM cases (n = 316) and controls (n = 300) | [177] | |||
| South-Indian adults: T2DM cases (n = 1100) and controls (n = 1100) | [92] | |||
| rs16861205 | G > A | Intron |
| African-American adults: T2DM cases (n = 586) and controls (n = 2434) | [117] |
| rs7649121 | A > T | Intron |
| Chinese Han adults: T2DM cases (n = 1105) and controls (n = 1107) | [178] |
| European adolescents aged 12–18 years (n = 1 057) | [176] | |||
| rs1063537 | C > T | 3′UTR |
| Chinese Han adults: T2DM cases (n = 188) and controls (n = 176) | [150] |
| Taiwanese adults with T2DM and normoalbuminuria at baseline, prospective cohort (n = 566; 263 men, 303 women; 6-year follow-up) | [154] | |||
| rs1063538 | T > C | 3′UTR |
| Taiwanese adults: T2DM cases (n = 570) and controls (n = 1700) | [153] |
| North-African Tunisian Arab adults: T2DM cases (n = 917) and controls (n = 748) | [168] | |||
| rs16861194 | A > G | Promoter |
| European and Asian adults from a meta-analysis of 39 studies: T2DM cases (n = 3176) and controls (n = 4007) | [163] |
| North-African Tunisian Arab adults: T2DM cases (n = 917) and controls (n = 748) | [168] | |||
| rs2082940 | T > C | 3′UTR |
|
| [85] |
3.3. Hypertension
The Influence of Adiponectin Gene Variations on Hypertension
4. Epigenetic Regulation of ADIPOQ Gene
4.1. ADIPOQ Promoter Hypermethylation
4.2. MicroRNA Regulation of ADIPOQ
5. Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Determinants of Adiponectin Concentrations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| SNV | Single-nucleotide variant |
| TGs | Triglycerides |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| NHLBI | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute |
| WHF | World Heart Federation |
| IAS | International Atherosclerosis Society |
| IASO | International Association for the Study of Obesity |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| C1q | Complement component 1q |
| Acrp30 | Adipocyte complement-related protein of 30 kDa |
| AdipoQ | Adipocyte-derived Protein Q |
| ApM1 | Adipose most abundant gene transcript |
| GBP28 | Gelatin-binding protein of 28 kDa |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| HMW | High molecular weight |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| iPSCs | Induced pluripotent stem cells |
| NAS | NAFLD Activity Scores |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| FFA | Free fatty acids |
| VAT | Visceral adipose tissue |
| SAT | Subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| GLP-1RA | Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist |
| GPI-PLD | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase D |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| SAA | Serum amyloid A |
| MHR | Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio |
| ECW/ICW | Extracellular to intracellular water ratio |
| AMPK | Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| PPAR-α | Proliferator-activated receptor-alpha |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| G6Pase | Glucose-6-phosphatase |
| PEPCK | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| GLUT-4 | Glucose transporter-4 |
| S1P | Sphingosine 1 phosphate |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| iNOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 |
| CD-36 | Increasing cluster of differentiation 36 |
| UCP-2 | uncoupling protein-2 |
| Acyl-CoA | Acyl-coenzyme A |
| ApoAI | Apolipoprotein AI |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| LXRα | Liver X receptor alpha |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| HL | Hepatic lipase |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoprotein |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase |
| ApoC-III | Apolipoprotein C-III |
| VLDLr | Very low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| IGT | Impaired glucose tolerance |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| VCAM | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| RAAs | Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| PRC2 | Polycomb repressive complex 2 |
| DASH | Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension |
References
- Wu, S.H.; Liu, Z.; Ho, S.C. Metabolic Syndrome and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J. A Comprehensive Review on Metabolic Syndrome. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 943162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, N.W.S.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Kong, G.; Lin, C.; Chin, Y.H.; Lim, W.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Quek, J.; Fu, C.E.; et al. The Global Burden of Metabolic Disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 414–428.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorout, J.; Kacker, S.; Saboo, N. Metabolic Syndrome and Possible Treatments (Consecutive Therapies): A Literature Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, V. Metabolic Syndrome: What Are the Risks for Humans? Biosci. Trends 2010, 4, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Noubiap, J.J.; Nansseu, J.R.; Lontchi-Yimagou, E.; Nkeck, J.R.; Nyaga, U.F.; Ngouo, A.T.; Tounouga, D.N.; Tianyi, F.-L.; Foka, A.J.; Ndoadoumgue, A.L.; et al. Geographic Distribution of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in the General Adult Population: A Meta-Analysis of Global Data from 28 Million Individuals. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 188, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milici, N.; Rainer, F.I. A short history of the metabolic syndrome definitions. Proc. Rom. Acad. Ser. B 2010, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C.J. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-Function Studies of the Adipocyte-Secreted Hormone Acrp30/Adiponectin. Implications Fpr Metabolic Regulation and Bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmalayam, I.; Suto, M. Role of Adiponectin in the Metabolic Syndrome: Current Perspectives on Its Modulation as a Treatment Strategy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5755–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerre-Millo, M. Adiponectin: An Update. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin--Journey from an Adipocyte Secretory Protein to Biomarker of the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, M.; Sultana, M.I.; Akter, F.; Hossain, M.M. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms Associated with Diabetes Mellitus: A Descriptive Review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, D.R.; Hurel, S.J.; Humphries, S.E. Adiponectin and Its Gene Variants as Risk Factors for Insulin Resistance, the Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkić, A.; Jahić, R.; Ejubović, M.; Đešević, M.; Ejubović, A.J.; Lepara, O. The Trend of Changes in Adiponectin, Resistin, and Adiponectin-Resistin Index Values in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with the Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina 2024, 60, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzie, A.G.; Funahashi, T.; Sonnenberg, G.; Martin, L.J.; Jacob, H.J.; Black, A.E.; Maas, D.; Takahashi, M.; Kihara, S.; Tanaka, S.; et al. The Genetic Basis of Plasma Variation in Adiponectin, a Global Endophenotype for Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, F.; Helbecque, N.; Dina, C.; Lobbens, S.; Delannoy, V.; Gaget, S.; Boutin, P.; Vaxillaire, M.; Leprêtre, F.; Dupont, S.; et al. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Haplotypes in the Both Proximal Promoter and Exon 3 of the APM1 Gene Modulate Adipocyte-Secreted Adiponectin Hormone Levels and Contribute to the Genetic Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzaghi, C.; Trischitta, V.; Doria, A. Genetic Influences of Adiponectin on Insulin Resistance, Type 2 Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissebah, A.H.; Sonnenberg, G.E.; Myklebust, J.; Goldstein, M.; Broman, K.; James, R.G.; Marks, J.A.; Krakower, G.R.; Jacob, H.J.; Weber, J.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci on Chromosomes 3 and 17 Influence Phenotypes of the Metabolic Syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14478–14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Waterworth, D.M.; Stirnadel, H.A.; Pollin, T.I.; Barter, P.J.; Kesäniemi, Y.A.; Mahley, R.W.; McPherson, R.; Waeber, G.; Bersot, T.P.; et al. Genome-Wide Linkage and Association Analyses to Identify Genes Influencing Adiponectin Levels: The GEMS Study. Obesity 2009, 17, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Saad, M.F.; Langefeld, C.D.; Williams, A.H.; Cui, J.; Taylor, K.D.; Norris, J.M.; Jinagouda, S.; Darwin, C.H.; Mitchell, B.D.; et al. Genome-Wide Linkage of Plasma Adiponectin Reveals a Major Locus on Chromosome 3q Distinct from the Adiponectin Structural Gene: The IRAS Family Study. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsani, V.; Brotman, S.M.; Xianyong, Y.; Fernandes Silva, L.; Laakso, M.; Spracklen, C.N. A Cross-Ancestry Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis, Fine-Mapping, and Gene Prioritization Approach to Characterize the Genetic Architecture of Adiponectin. HGG Adv. 2024, 5, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Ding, D.; Huang, J.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q. Association of Genetic Variants in the Adiponectin Gene with Metabolic Syndrome: A Case-Control Study and a Systematic Meta-Analysis in the Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monda, K.L.; North, K.E.; Hunt, S.C.; Rao, D.C.; Province, M.A.; Kraja, A.T. The Genetics of Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 10, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of Adiponectin Receptors That Mediate Antidiabetic Metabolic Effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Klein, R.L.; El-Shewy, H.M.; Luttrell, D.K.; Luttrell, L.M. The Adiponectin Receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Activate ERK1/2 through a Src/Ras-Dependent Pathway and Stimulate Cell Growth. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 11682–11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted Disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Causes Abrogation of Adiponectin Binding and Metabolic Actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, E.; Rostamkhani, F.; Abdollahi, M.; Ahmadifard, M. Targeting the UCP1-Dependent Thermogenesis Pathway with CRISPR/Cas9: A New Approach to Obesity Management. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2025, 9, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, K.; Ramachandiran, I.; Chechi, A.; Khan, K.; Khan, D.; Kaufman, R.; Fox, P.L. Translational Control of Murine Adiponectin Expression by an Upstream Open Reading Frame Element. RNA Biol. 2023, 20, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Laurindo, L.F. AdipoRon and ADP355, Adiponectin Receptor Agonists, in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 218, 115871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Asaba, S.; Tanaka, M.; Matsui, T. Oral Administration of the Adiponectin Receptor 1 Agonistic Dipeptide Tyr-Pro Prevents Hyperglycemia in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii Rats. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, S.; Sweeney, G.; Perry, C.G.R. Recent Advances in Pre-Clinical Development of Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sung, H.K.; Yan, X.; He, S.; Jin, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Hsu, H.H.; Pignalosa, A.; Crawford, K.; et al. The Adiponectin-Derived Peptide ALY688 Protects against the Development of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Castro, C.; Fu, Y.; Chung, B.H.; Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin and the Metabolic Syndrome: Mechanisms Mediating Risk for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2007, 18, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.; Movahedian, A.; Baranchi, M.; Goodarzi, M.T. Adiponectin: An Adipokine with Protective Features against Metabolic Syndrome. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 430–442. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, M.C.; Barros, A.J.D.; Ferreira, D.L.S.; Casas, J.P.; Horta, B.L.; Kivimaki, M.; Kumari, M.; Menon, U.; Gaunt, T.R.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; et al. Metabolic Profiling of Adiponectin Levels in Adults: Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2017, 10, e001837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafraniec-Porada, A.; Porada, D.; Konopeklo, M.; Przybylska, D.; Pucułek, M. The Importance of Adiponectin in the Human Body. J. Educ. Health Sport. 2018, 8, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Szydełko, J.; Dąbrowska, I. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Adiponectin and Its Receptors’ Genes as Potential Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—An up-to-Date Overview. J. Educ. Health Sport 2021, 11, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Shibazaki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nagai, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T. Adiponectin as a Biomarker of the Metabolic Syndrome. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, K.; Bhattacharyya, M. Adiponectin: Probe of the Molecular Paradigm Associating Diabetes and Obesity. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin/AdipoR Research and Its Implications for Lifestyle-Related Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Pathophysiology of Human Visceral Obesity: An Update. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 359–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paley, C.A.; Johnson, M.I. Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Exercise as Medicine? BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, the Past Two Decades. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.; Jain, S. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Huenchullan, S.F.; Tam, C.S.; Ban, L.A.; Ehrenfeld-Slater, P.; Mclennan, S.V.; Twigg, S.M. Skeletal Muscle Adiponectin Induction in Obesity and Exercise. Metabolism 2020, 102, 154008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y. Establishment of a Concept of Visceral Fat Syndrome and Discovery of Adiponectin. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2010, 86, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; Palmieri, A.; Mazzarella, G.; Costagliola, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. New Insight into Adiponectin Role in Obesity and Obesity-Related Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 658913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. New Advances of Adiponectin in Regulating Obesity and Related Metabolic Syndromes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 14, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Bunt, A.E.; Alemán, G.; Marquez-Mota, C.C.; Diaz-Villaseñor, A.; Noriega, L.G.; Estrada, I.; Figueroa-Juárez, E.; Tovar-Palacio, C.; Rodriguez-López, L.A.; et al. Adiponectin Synthesis and Secretion by Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Impaired during Obesity by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 5970–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, R.; Bélanger, C.; Fortier, M.; Huot, C.; Mailloux, J.; Légaré, D.; Tchernof, A. Fat Depot-Specific Impact of Visceral Obesity on Adipocyte Adiponectin Release in Women. Obesity 2009, 17, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.K.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wittgrove, A.C.; Phillips, S.A. Adipose Tissue Depot and Cell Size Dependency of Adiponectin Synthesis and Secretion in Human Obesity. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, M.; James, R.; Marks, J.; Zhao, S.; Szabo, A.; Kidambi, S. Adiposity Distribution Influences Circulating Adiponectin Levels. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, P. The Role of Adiponectin in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Effects of Nutritional Interventions. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 422S–426S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Chao, C.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Tai, T.-Y.; Chuang, L.-M. Weight Reduction Increases Plasma Levels of an Adipose-Derived Anti-Inflammatory Protein, Adiponectin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 3815–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzano, A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ambrosi, A.; Tafuri, D.; Monda, M.; Messina, A.; Sessa, F.; Campanozzi, A.; Monda, V.; Cibelli, G.; et al. The Metabolic Rearrangements of Bariatric Surgery: Focus on Orexin-A and the Adiponectin System. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Sánchez-García, A.; Linden-Torres, E.; Simental-Mendía, M. Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Adiponectin Concentrations: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4140–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Li, T.; An, P.; Yan, W.; Zheng, H.; Wang, B.; Mu, Y. Exendin-4 Upregulates Adiponectin Level in Adipocytes via Sirt1/Foxo-1 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.T.K.; Hosaka, T.; Yoshida, M.; Harada, N.; Sakaue, H.; Sakai, T.; Nakaya, Y. Exendin-4, a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, Directly Induces Adiponectin Expression through Protein Kinase A Pathway and Prevents Inflammatory Adipokine Expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, A.Y.; Scherer, P.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Koh, K.K. Adiponectin and Cardiometabolic Trait and Mortality: Where Do We Go? Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizer, J.R. Adiponectin, Cardiovascular Disease, and Mortality: Parsing the Dual Prognostic Implications of a Complex Adipokine. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-Leptin Ratio: A Promising Index to Estimate Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Relation with Obesity-Associated Cardiometabolic Risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-Leptin Ratio Is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabeih, N.; Kalinkovich, A.; Ashkenazi, S.; Cherny, S.S.; Shalata, A.; Livshits, G. Relationships between Circulating Biomarkers and Body Composition Parameters in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Community-Based Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A Small-Molecule AdipoR Agonist for Type 2 Diabetes and Short Life in Obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Tanabe, H.; Ohuchi, N.; Miyata, K.; Kobori, T.; Odawara, S.; Kadowaki, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamauchi, T.; et al. AdipoR Agonist Increases Insulin Sensitivity and Exercise Endurance in AdipoR-Humanized Mice. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvais, C.M.; Davis-López De Carrizosa, M.A.; Nachit, M.; Versele, R.; Dubuisson, N.; Noel, L.; Gillard, J.; Leclercq, I.A.; Brichard, S.M.; Abou-Samra, M. AdipoRon Enhances Healthspan in Middle-aged Obese Mice: Striking Alleviation of Myosteatosis and Muscle Degenerative Markers. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Xie, M.; Song, L.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. AdipoRon Ameliorates the Progression of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction via Mitigating Lipid Accumulation and Fibrosis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 68, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, S.; Debayle, D.; Béchade, C.; Maroteaux, L.; Gay, A.-S.; Bayer, P.; Heurteaux, C.; Guyon, A.; Chabry, J. Adiporon, an Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Acts as an Antidepressant and Metabolic Regulator in a Mouse Model of Depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Wu, H.; Hu, Z.; Wu, X.; Tu, M.; Fang, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lian, J.; Valverde, P.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Adipo Anti-inflammation Agonist and Its Anti-inflammatory Effects in Vitro and in Vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindfors, S.; Polianskyte-Prause, Z.; Bouslama, R.; Lehtonen, E.; Mannerla, M.; Nisen, H.; Tienari, J.; Salmenkari, H.; Forsgård, R.; Mirtti, T.; et al. Adiponectin Receptor Agonist AdipoRon Ameliorates Renal Inflammation in Diet-Induced Obese Mice and Endotoxin-Treated Human Glomeruli Ex Vivo. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, N.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Iwabu, M.; Wada, K.; Oka, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. A Monoclonal Antibody Activating AdipoR for Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.; Zboinski, E.; das, S.; Zhu, X.; Ma, Q.; Xie, Y.; Tu, Q.; Chen, J. Antidiabetic Features of AdipoAI, a Novel AdipoR Agonist. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana Swamy, A.; Valasala, H.; Kamma, S. In Silico Evaluation of Nonsynonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the ADIPOQ Gene Associated with Diabetes, Obesity, and Inflammation. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2015, 7, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Jungtrakoon, P.; Plengvidhya, N.; Tangjittipokin, W.; Chimnaronk, S.; Salaemae, W.; Chongjaroen, N.; Chanprasert, K.; Sujjitjoon, J.; Srisawat, C.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T. Novel Adiponectin Variants Identified in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Reveal Multimerization and Secretion Defects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.C.P.D.; Ochioni, A.C.; Martins, R.D.S.; Zembrzuski, V.M.; Campos Junior, M.; Ramos, V.G.; Carneiro, J.R.I.; Nogueira Neto, J.F.; Cabello, P.H.; Cabello, G.M.K. Adiponectin, Retinoic Acid Receptor Responder 2, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor- γ Coativator-1 Genes and the Risk for Obesity. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 5289120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassel, C.L.; Pankow, J.S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Steffes, M.W.; Li, N.; Schreiner, P.J. Variants in the Adiponectin Gene and Serum Adiponectin: The Coronary Artery Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Obesity 2010, 18, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, B.S.; Weinert, S.; Langefeld, C.D.; Williams, A.H.; Campbell, J.K.; Saad, M.F.; Haffner, S.M.; Norris, J.M.; Bowden, D.W. Genetic Analysis of Adiponectin and Obesity in Hispanic Families: The IRAS Family Study. Hum. Genet. 2005, 117, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayani, N.; Omezzine, A.; Boumaiza, I.; Achour, O.; Rebhi, L.; Rejeb, J.; Ben Rejeb, N.; Ben Abdelaziz, A.; Bouslama, A. Association of ADIPOQ, Leptin, LEPR, and Resistin Polymorphisms with Obesity Parameters in Hammam Sousse Sahloul Heart Study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 31, e22148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siitonen, N.; Pulkkinen, L.; Lindström, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Eriksson, J.G.; Venojärvi, M.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Uusitupa, M. Association of ADIPOQ Gene Variants with Body Weight, Type 2 Diabetes and Serum Adiponectin Concentrations: The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.S.; Gammon, M.D.; North, K.E.; Millikan, R.C.; Lange, E.M.; Williams, S.M.; Zheng, W.; Cai, Q.; Long, J.; Smith, J.R.; et al. ADIPOQ, ADIPOR1, and ADIPOR2 Polymorphisms in Relation to Serum Adiponectin Levels and BMI in Black and White Women. Obesity 2011, 19, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.S.; Hanley, A.J.G.; Ziegler, J.T.; Brown, W.M.; Haffner, S.M.; Norris, J.M.; Rotter, J.I.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; et al. Association between ADIPOQ SNPs with Plasma Adiponectin and Glucose Homeostasis and Adiposity Phenotypes in the IRAS Family Study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riestra, P.; Gebreab, S.Y.; Xu, R.; Khan, R.J.; Bidulescu, A.; Correa, A.; Tekola-Ayele, F.; Davis, S.K. Gender-Specific Associations between ADIPOQ Gene Polymorphisms and Adiponectin Levels and Obesity in the Jackson Heart Study Cohort. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe-Dimmer, J.L.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Cooney, K.A. Genetic Variation in Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) and the Type 1 Receptor (ADIPOR1), Obesity and Prostate Cancer in African Americans. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010, 13, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Badaruddoza, B.; Bains, V.; Kaur, A. Genetic Association of ADIPOQ Gene Variants (-3971A>G and +276G>T) with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in North Indian Punjabi Population. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Chavez, L.A.; Rosales-Gomez, R.C.; Rubio-Chavez, K.-H.L.; Ramos-Nuñez, J.L.; Garcia-Cobian, T.A.; Camargo-Hernandez, G.; Sanchez-Corona, J.; Gutierrez-Rubio, S.A. The Rs822396 Polymorphism of the ADIPOQ Gene Is Associated with Anthropometric, Clinical, and Biochemical Alterations Related to the Metabolic Syndrome in the Mexican Population. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2020, 18, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, K.; Ayyappa, K.A.; Ghosh, S.; Mohan, V.; Radha, V. Genetic Association of ADIPOQ Gene Variants with Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity and Serum Adiponectin Levels in South Indian Population. Gene 2013, 532, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Rampal, S.; Salim, A.; Moy, F.M.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Association of ADIPOQ Gene with Obesity and Adiponectin Levels in Malaysian Malays. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimaleswaran, K.S.; Radha, V.; Ramya, K.; Babu, H.N.S.; Savitha, N.; Roopa, V.; Monalisa, D.; Deepa, R.; Ghosh, S.; Majumder, P.P.; et al. A Novel Association of a Polymorphism in the First Intron of Adiponectin Gene with Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity and Hypoadiponectinemia in Asian Indians. Hum. Genet. 2008, 123, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, S.P.; Patel, R.; Jadeja, S.D.; Rathwa, N.; Mahajan, A.; Ramachandran, A.V.; Dhar, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Begum, R. A Genetic Analysis Identifies a Haplotype at Adiponectin Locus: Association with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazizadeh, F.; Afshari-Moez, S.; Alinaghian, N.; Torab, M.; Rahimi-Moghaddam, P. Association of Adiponectin 45T/G (Rs2241766) and Visfatin 4689G/T (Rs2110385) Gene Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Obesity. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2023, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, C.; Farias, D.R.; Carrilho, T.R.B.; Kac, G.; Mastroeni, M.F. Association of ADIPOQ-Rs2241766 and FTO-Rs9939609 Genetic Variants with Body Mass Index Trajectory in Women of Reproductive Age over 6 Years of Follow-up: The PREDI Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, A.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Moreno-Macías, H.; Espinosa Fematt, J.; Pérez-Morales, R. LEP Rs7799039, LEPR Rs1137101, and ADIPOQ Rs2241766 and 1501299 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Obesity and Chemotherapy Response in Mexican Women with Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2017, 17, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergören, M.C.; Söyler, G.; Sah, H.; Becer, E. Investigation of Potential Genomic Biomarkers for Obesity and Personalized Medicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumvoll, M.; Tschritter, O.; Fritsche, A.; Staiger, H.; Renn, W.; Weisser, M.; Machicao, F.; Häring, H. Association of the T-G Polymorphism in Adiponectin (Exon 2) with Obesity and Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes 2002, 51, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Meng, K.; Zhang, L. Association of Adiponectin Gene (ADIPOQ) Rs2241766 Polymorphism with Obesity in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Yang, M.; Guo, H.; Ji, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Genetic Analysis Identifies Haplotype at Adiponectin Locus: Association with the Metabolic Health and Obesity Phenotypes. Gene 2021, 784, 145593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikhayeva, N.; Bolatov, A.; Zholdybayeva, E.; Akhmetollayev, I.; Iskakova, A. Association of ADIPOQ Gene Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Risk in the Kazakh Population: A Case–Control and Population-Based Study. Genes 2024, 15, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqlain, M.; Khalid, M.; Fiaz, M.; Saeed, S.; Mehmood Raja, A.; Mobeen Zafar, M.; Fatima, T.; Bosco Pesquero, J.; Maglio, C.; Valadi, H.; et al. Risk Variants of Obesity Associated Genes Demonstrate BMI Raising Effect in a Large Cohort. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shramko, I.I.; Ageeva, E.S.; Maliy, K.D.; Repinskaya, I.N.; Tarimov, C.O.; Fomochkina, I.I.; Kubishkin, A.V.; Ostapenko, O.V.; Gurtovaya, A.K.; Shekhar, S. Association between Adiponectin and Leptin Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms and Clinical Manifestations of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 9881422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Jiang, H.; Hu, B.; Qin, S. Association of ADIPOQ Polymorphisms with Obesity Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozarova de Courten, B.; Hanson, R.L.; Funahashi, T.; Lindsay, R.S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Thameem, F.; Gruber, J.D.; Froguel, P.; Wolford, J.K. Common Polymorphisms in the Adiponectin Gene ACDC Are Not Associated with Diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2005, 54, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.K.; Schneider, J.; Fourcaudot, M.J.; Rodriguez, L.M.; Arya, R.; Dyer, T.D.; Almasy, L.; Blangero, J.; Stern, M.P.; Defronzo, R.A.; et al. Association between Variants in the Genes for Adiponectin and Its Receptors with Insulin Resistance Syndrome (IRS)-Related Phenotypes in Mexican Americans. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2317–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakou, T.; Collins, L.J.; Spencer-Jones, N.J.; Malcolm, C.; Wang, X.; Snieder, H.; Swaminathan, R.; Burling, K.A.; Hart, D.J.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Adiponectin Gene ADIPOQ SNP Associations with Serum Adiponectin in Two Female Populations and Effects of SNPs on Promoter Activity. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, S.; Peeters, A.V.; de Freitas, F.; Mertens, I.L.; Verhulst, S.L.; Haentjens, D.; Desager, K.N.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Van Hul, W. Association Study and Mutation Analysis of Adiponectin Shows Association of Variants in APM1 with Complex Obesity in Women. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2009, 73, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchia, C.; Scott, K.; Fortina, P.; Devoto, M.; Falkner, B. Association of a Polymorphic Variant of the Adiponectin Gene with Insulin Resistance in African Americans. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2008, 1, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiang, Y.-B.; Long, J.-R.; Cai, H.; Cai, Q.; Cheng, J.; Wen, W.; Gao, Y.-T.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.-O. Genetic Polymorphisms in Obesity-Related Genes and Endometrial Cancer Risk. Cancer 2012, 118, 3356–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbi, G.; Polito, R.; Monaco, M.L.; Cacciatore, F.; Scioli, M.; Ferrara, N.; Daniele, A.; Nigro, E. Adiponectin Expression and Genotypes in Italian People with Severe Obesity Undergone a Hypocaloric Diet and Physical Exercise Program. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hivert, M.-F.; Manning, A.K.; McAteer, J.B.; Florez, J.C.; Dupuis, J.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Meigs, J.B. Common Variants in the Adiponectin Gene (ADIPOQ) Associated with Plasma Adiponectin Levels, Type 2 Diabetes, and Diabetes-Related Quantitative Traits: The Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhong, L.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, L.; et al. Genetic Variations in Adiponectin Levels and Dietary Patterns on Metabolic Health among Children with Normal Weight versus Obesity: The BCAMS Study. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Escalante, V.M.; Nava-Gonzalez, E.J.; Voruganti, V.S.; Kent, J.W.; Haack, K.; Laviada-Molina, H.A.; Molina-Segui, F.; Gallegos-Cabriales, E.C.; Lopez-Alvarenga, J.C.; Cole, S.A.; et al. Replication of Obesity and Diabetes-Related SNP Associations in Individuals from Yucatán, México. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.K.; Xu, R.; Gebreab, S.Y.; Riestra, P.; Gaye, A.; Khan, R.J.; Wilson, J.G.; Bidulescu, A. Association of ADIPOQ Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Related Phenotypes in African American Men and Women: The Jackson Heart Study. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouatia-Naji, N.; Meyre, D.; Lobbens, S.; Séron, K.; Fumeron, F.; Balkau, B.; Heude, B.; Jouret, B.; Scherer, P.E.; Dina, C.; et al. ACDC/Adiponectin Polymorphisms Are Associated with Severe Childhood and Adult Obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, A.; Maffeis, C.; Lobbens, S.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Heude, B.; Pinelli, L.; Meyre, D.; Froguel, P. Early Detrimental Metabolic Outcomes of Rs17300539-A Allele of ADIPOQ Gene despite Higher Adiponectinemia. Obesity 2010, 18, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaiza, I.; Omezzine, A.; Rejeb, J.; Rebhi, L.; Rejeb, N.B.; Nabli, N.; Abdelaziz, A.B.; Bouslama, A. Association between Eight Adiponectin Polymorphisms, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome Parameters in Tunisian Volunteers. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2011, 9, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Park, J.; Jee, S.H. ADIPOQ Gene Variants Associated with Susceptibility to Obesity and Low Serum Adiponectin Levels in Healthy Koreans. Epidemiol. Health 2011, 33, e2011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomani, H.; Hesami, O.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Tanhapour, M.; Bahrehmand, F.; Rahimi, Z.; Kiani, A.; Shakiba, E.; Pourmotabbed, T. Association between the -11377 C/G and -11391 G/A Polymorphisms of Adiponectin Gene and Adiponectin Levels with Susceptibility to Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Population from the West of Iran, Correlation with Lipid Profile. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3574–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshaghani, H.; Kokhaei, P.; Barati, M.; Pakdel, A.; Mohammadzadeh, G.; Bandegi, N.; Bandegi, A. Association of Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms and Their Haplotypes with Type 2 Diabetes and Related Metabolic Traits in an Iranian Population. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2020, 40, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, R.-W.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Chowdhury, R.; Yuan, J.-M.; Koh, W.-P.; Pan, A. Plasma Adiponectin Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: A Nested Case-Control Study in a Chinese Population and an Updated Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Noda, M.; Mizoue, T. Circulating Adiponectin Levels and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Japanese. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Jensen, J.S.; Bjerre, M.; Pedersen, S.H.; Frystyk, J.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Galatius, S.; Jeppesen, J.; Mogelvang, R. Adiponectin, Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Endogenous Glucose Production Is Inhibited by the Adipose-Derived Protein Acrp30. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Roles of Adiponectin and Oxidative Stress in Obesity-Associated Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular Adiponectin Increases GLUT4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake but Reduces Glycogen Synthesis in Rat Skeletal Muscle Cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowska, J.; Kochan, Z. Role of Adiponectin in the Regulation of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57 (Suppl. 6), 103–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Sifuentes, A.; Holland, W.L. Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis by Adiponectin: Effects on Hepatocytes, Pancreatic β Cells and Adipocytes. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Miller, R.A.; Wang, Z.V.; Sun, K.; Barth, B.M.; Bui, H.H.; Davis, K.E.; Bikman, B.T.; Halberg, N.; Rutkowski, J.M.; et al. Receptor-Mediated Activation of Ceramidase Activity Initiates the Pleiotropic Actions of Adiponectin. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hirose, H.; Saito, I.; Tomita, M.; Taniyama, M.; Matsubara, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Ishii, T.; Nishikai, K.; Saruta, T. Correlation of the Adipocyte-Derived Protein Adiponectin with Insulin Resistance Index and Serum High-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol, Independent of Body Mass Index, in the Japanese Population. Clin. Sci. 2002, 103, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas-Kontio, T.; Huotari, A.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Herzig, K.-H.; Tamminen, M.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Savolainen, M.J.; Kakko, S. Genetic and Environmental Determinants of Total and High-Molecular Weight Adiponectin in Families with Low HDL-Cholesterol and Early Onset Coronary Heart Disease. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, G.A.; Kiortsis, D.N. Adiponectin and Lipoprotein Metabolism. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kusunoki, M.; Murase, Y.; Kawashiri, M.; Higashikata, T.; Miwa, K.; Katsuda, S.; Takata, M.; Asano, A.; Nohara, A.; et al. Relationship of Lipoprotein Lipase and Hepatic Triacylglycerol Lipase Activity to Serum Adiponectin Levels in Japanese Hyperlipidemic Men. Horm. Metab. Res. 2005, 37, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, C. The Role of Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2023, 64, 107514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- null, null Global Effect of Modifiable Risk Factors on Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1273–1285. [CrossRef]
- Timmis, A.; Aboyans, V.; Vardas, P.; Townsend, N.; Torbica, A.; Kavousi, M.; Boriani, G.; Huculeci, R.; Kazakiewicz, D.; Scherr, D.; et al. European Society of Cardiology: The 2023 Atlas of Cardiovascular Disease Statistics. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4019–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Cao, L.; Sun, G. Role of Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Diseases Related to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mado, H.; Szczurek, W.; Gąsior, M.; Szyguła-Jurkiewicz, B. Adiponectin in Heart Failure. Future Cardiol. 2021, 17, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Qiu, S.; Yang, G.; Wu, Q. Adiponectin and Metabolic Cardiovascular Diseases: Therapeutic Opportunities and Challenges. Genes Dis. 2023, 10, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Sato, K.; Inoue, T.; Funahashi, T.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin Stimulates Angiogenesis by Promoting Cross-Talk between AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Akt Signaling in Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q.; Duan, M.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, T.; Shou, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y. Adiponectin Improves NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation and Abates Atherosclerosis Progression in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.B.; Çolak, Y.; Benn, M.; Mason, A.; Burgess, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Plasma Adiponectin Levels and Risk of Heart Failure, Atrial Fibrillation, Aortic Valve Stenosis, and Myocardial Infarction: Large-Scale Observational and Mendelian Randomization Evidence. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-Mapping Type 2 Diabetes Loci to Single-Variant Resolution Using High-Density Imputation and Islet-Specific Epigenome Maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathophysiolo; Dyslipidaemia, M.; Bereda, G. Pathophysiology and Management of Dyslipidaemia. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2022, 43, 34369–34375. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Li, M. Association between Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism and Environmental Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among the Chinese Population in Hohhot. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6383906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Association of Four Insulin Resistance Genes with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension in the Chinese Han Population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z. Effect of Adiponectin Variant on Lipid Profile and Plasma Adiponectin Levels: A Multicenter Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 4395266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanu, J.S.; Qiu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, R.; Kou, C.; Gu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Associations between Three Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (Rs266729, Rs2241766, and Rs1501299) of ADIPOQ and Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Chan, C.-J.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chen, S.-Y. Genetic and Functional Effects of Adiponectin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.-F.; Long, K.Z.; Hsu, C.-C.; Mamun, A.A.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Tu, H.-P.; Chen, P.-S.; Jhang, H.-R.; Hwang, S.-J.; Huang, M.-C. Adiponectin Gene (ADIPOQ) Polymorphisms Correlate with the Progression of Nephropathy in Taiwanese Male Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shramko, I.; Ageeva, E.; Krutikov, E.; Maliy, K.; Repinskaya, I.; Fomochkina, I.; Kubishkin, A.; Gurtovaya, A.; Tarimov, C.; Shekhar, S. Polymorphism in Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptor Genes in Diabetes Mellitus Pathogenesis. Pathophysiology 2022, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Fan, G.; Yang, P.; Lai, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Yu, X.; et al. Assessment of Type 2 Diabetes Risk Conferred by SNPs Rs2241766 and Rs1501299 in the ADIPOQ Gene, a Case/Control Study Combined with Meta-Analyses. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 396, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Jiao, M.L.; Hao, Y.H.; Liang, L.B.; Gao, L.J.; Legge, D.G.; Quan, H.; Zhao, M.M.; Ning, N.; et al. Associations between Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (+45T>G, +276G>T, −11377C>G, −11391G>A) of Adiponectin Gene and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Boutin, P.; Mori, Y.; Tobe, K.; Dina, C.; Yasuda, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Otabe, S.; Okada, T.; Eto, K.; et al. Genetic Variation in the Gene Encoding Adiponectin Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the Japanese Population. Diabetes 2002, 51, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, J.L.; Zabena, C.A.; Martínez-Larrad, M.T.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Pérez-Barba, M.; Laakso, M.; Serrano-Ríos, M. An SNP in the Adiponectin Gene Is Associated with Decreased Serum Adiponectin Levels and Risk for Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Chae, J.S.; Kim, O.Y.; Koh, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.E.; Ordovas, J.M. Association of the 276G->T Polymorphism of the Adiponectin Gene with Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Nondiabetic Koreans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-P.; Zhang, M.; Gao, J.; Zhou, G.-Y.; Li, S.-Q.; An, Z.-M. Relation between ADIPOQ Gene Polymorphisms and Type 2 Diabetes. Genes 2015, 6, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nbaheen, M.S. Effect of Genetic Variations in the ADIPOQ Gene on Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhong, D.; Shi, D.; Ma, L.; Tong, N.; Zhang, Z. AdipoQ Polymorphisms Are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis Study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2013, 29, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, K.; Chatterjee, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Sengupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, M. Adiponectin Genetic Variant and Expression Coupled with Lipid Peroxidation Reveal New Signatures in Diabetic Dyslipidemia. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.K.; Deli, F.A.; Algenabi, A.H.A.; Abdul-Rudha, K.H. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms as a Predictor for Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Iraqi Population. Gene 2018, 662, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, L.; Imam, M.U.; Chen, Y.; Pei, X.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; et al. The Polymorphism of Rs266729 in Adiponectin Gene and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Yang, Z.-J.; Zhou, C.-W.; Wang, X.-M.; Qian, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, J. Adiponectin-11377CG Gene Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Chinese Population: A Meta-Analysis of 6425 Subjects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mtiraoui, N.; Ezzidi, I.; Turki, A.; Chaieb, A.; Mahjoub, T.; Almawi, W.Y. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Haplotypes in the Adiponectin Gene Contribute to the Genetic Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in Tunisian Arabs. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyenechea, E.; Collins, L.J.; Parra, D.; Abete, I.; Crujeiras, A.B.; O’Dell, S.D.; Martínez, J.A. The - 11391 G/A Polymorphism of the Adiponectin Gene Promoter Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Traits and the Outcome of an Energy-Restricted Diet in Obese Subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. 2009, 41, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastani, Z.; Hivert, M.-F.; Timpson, N.; Perry, J.R.B.; Yuan, X.; Scott, R.A.; Henneman, P.; Heid, I.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; et al. Novel Loci for Adiponectin Levels and Their Influence on Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Traits: A Multi-Ethnic Meta-Analysis of 45,891 Individuals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, M.A.; Freedman, B.I.; Langefeld, C.D.; Liu, L.; Hicks, P.J.; Bowden, D.W. Association of Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes in an African American Population Enriched for Nephropathy. Diabetes 2009, 58, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.E.; Beilby, J.; Cadby, G.; Warrington, N.M.; Bruce, D.G.; Davis, W.A.; Davis, T.M.; Wiltshire, S.; Knuiman, M.; McQuillan, B.M.; et al. A Comprehensive Investigation of Variants in Genes Encoding Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) and Its Receptors (ADIPOR1/R2), and Their Association with Serum Adiponectin, Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Q.; Sun, L.; Li, T.; Qiao, H. Association of ADIPOQ Variants with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Susceptibility in Ethnic Han Chinese from Northeast China. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen-Torvik, L.J.; Pankow, J.S.; Jacobs, D.R.J.; Steinberger, J.; Moran, A.; Sinaiko, A.R. The Association of SNPs in ADIPOQ, ADIPOR1, and ADIPOR2 with Insulin Sensitivity in a Cohort of Adolescents and Their Parents. Hum. Genet. 2009, 125, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.; Izaola, O.; Primo, D.; Aller, R. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of ADIPOQ Gene (Rs822393) Is Associated with Lipid Profile, Adiponectin Levels and Ratio of Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Adult Obese Subjects. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 5, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Tortosa, D.F.; Pascual-Gamarra, J.M.; Labayen, I.; Rupérez, A.I.; Censi, L.; Béghin, L.; Michels, N.; González-Gross, M.; Manios, Y.; Lambrinou, C.-P.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of ADIPOQ Gene Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in European Adolescents: The Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence Study. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, V.; Kaur, H. Badaruddoza Association Study of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms -3971G/A and +276G/T in the Adiponectin Gene with Type 2 Diabetes in a North Indian Punjabi Population. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2020, 84, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Yu, X.; Ye, X.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Cheng, J.; Cao, Y.; Du, J.; et al. Genetic Variants in ADIPOQ Gene and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study of Chinese Han Population. Endocrine 2011, 40, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Comparative Risk Assessment of 84 Behavioural, Environmental and Occupational, and Metabolic Risks or Clusters of Risks for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, L.; Mahfoud, F.; Azizi, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Ewen, S.; Kario, K.; Parati, G.; Rossignol, P.; Schlaich, M.P.; Teo, K.K.; et al. Hypertension Management in Patients with Cardiovascular Comorbidities. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 44, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaqeeh, M.; Alfian, S.D.; Abdulah, R. Factors Associated with Hypertension Among Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Indonesian Family Life Survey. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, C.; Ding, E.L.; Townsend, M.K.; Lipsitz, L.A. Adiponectin Levels and the Risk of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2013, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri-Okonny, P.A.; Ayers, C.; Maalouf, N.; Das, S.R.; de Lemos, J.A.; Berry, J.D.; Turer, A.T.; Neeland, I.J.; Scherer, P.E.; Vongpatanasin, W. Adiponectin Protects against Incident Hypertension Independent of Body Fat Distribution: Observations from the Dallas Heart Study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.-S.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Tso, A.W.K.; Xu, A.; Wat, N.M.S.; Fong, C.H.Y.; Ong, L.H.Y.; Tam, S.; Tan, K.C.B.; Janus, E.D.; et al. Hypoadiponectinemia as a Predictor for the Development of Hypertension: A 5-Year Prospective Study. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Hwu, C.-M.; Sheu, W.H.-H.; Hung, Y.-J.; Fujimoto, W.; Quertermous, T.; Curb, J.D.; Tai, T.-Y.; Chuang, L.-M. The Negative Correlation between Plasma Adiponectin and Blood Pressure Depends on Obesity: A Family-Based Association Study in SAPPHIRe. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, E.; Rodríguez-Molina, D.; Bolli, P.; Israili, Z.H.; Faría, J.; Fidilio, E.; Bermúdez, V.; Velasco, M. The Role of Adiponectin in Endothelial Dysfunction and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, N.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, D. New Horizons in the Roles and Associations of COX-2 and Novel Natural Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Diseases. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Ura, N.; Higashiura, K.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, M.; Moniwa, N.; Yoshida, D.; Shimamoto, K. Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System Increases Adiponectin Concentrations in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 42, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agata, J.; Nagahara, D.; Kinoshita, S.; Takagawa, Y.; Moniwa, N.; Yoshida, D.; Ura, N.; Shimamoto, K. Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Prevents Increased Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, V.; de Faria, A.P.C.; Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Silva, P.S.; Biagi, C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Moreno, H. Effects of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition on Leptin and Adiponectin Levels in Essential Hypertension. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Cao, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, W.; et al. Associations between Polymorphisms of the ADIPOQ Gene and Hypertension Risk: A Systematic and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Y.; Yao, Y. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in ADIPOQ Gene with Risk of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2021, 12, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; He, D.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J.; Liu, M.; Li, J. Common Polymorphisms (Rs2241766 and Rs1501299) in the ADIPOQ Gene Are Not Associated with Hypertension Susceptibility among the Chinese. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8771–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, K.-Y.; Yan, D.-Y.; Guo, T.-S.; Zheng, W.-L.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Mu, J.-J. Genetic Variants in Adiponectin and Blood Pressure Responses to Dietary Sodium or Potassium Interventions: A Family-Based Association Study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.L.; Li, M.; Tso, A.W.K.; Xu, A.; Cherny, S.S.; Sham, P.C.; Tse, H.F.; Lam, T.H.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Lam, K.S.L. Association of Genetic Variants in the Adiponectin Gene with Adiponectin Level and Hypertension in Hong Kong Chinese. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 163, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuo, S.-J.; Tsai, W.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Lin, T.-H.; Lee, K.-T.; Lai, W.-T. Association between Adiponectin T94G Polymorphism and Resistant Hypertension in Young-Onset Taiwanese Patients. Gene 2019, 689, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xi, Y.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J.; Dong, L.; Liang, H.; Sun, Z.; Lei, L.; Fan, G.; et al. Polymorphisms of Adiponectin Gene and Gene-Lipid Interaction with Hypertension Risk in Chinese Coal Miners: A Matched Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, H.-B.; Chung, C.-M.; Lin, S.-J.; Jong, Y.-S.; Pan, W.-H.; Chen, J.-W. Adiponectin Gene Polymorphism Is Selectively Associated with the Concomitant Presence of Metabolic Syndrome and Essential Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, S.; et al. Essential Hypertension in Patients Exposed to High-Arsenic Exposed Areas in Western China: Genetic Susceptibility and Urinary Arsenic Metabolism Characteristics. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 67, 126778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, D.; Shibata, R.; Izawa, H.; Hirashiki, A.; Asano, H.; Murase, Y.; Miyata, S.; Nakatochi, M.; Ouchi, N.; Ichihara, S.; et al. Relation of a Common Variant of the Adiponectin Gene to Serum Adiponectin Concentration and Metabolic Traits in an Aged Japanese Population. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.; Morais, T.; Sandovici, I.; Seabra, A.L.; Constância, M.; Monteiro, M.P. Adipose Tissue Epigenetic Profile in Obesity-Related Dysglycemia—A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 681649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Park, Y.J.; Pan, X.; Shin, K.C.; Kwak, S.-H.; Bassas, A.F.; Sallam, R.M.; Park, K.S.; Alfadda, A.A.; Xu, A.; et al. Obesity-Induced DNA Hypermethylation of the Adiponectin Gene Mediates Insulin Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, L.; Hivert, M.-F.; Guay, S.-P.; St-Pierre, J.; Perron, P.; Brisson, D. Placental Adiponectin Gene DNA Methylation Levels Are Associated with Mothers’ Blood Glucose Concentration. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.A.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Ann, S.; Lee, J.; Han, J.-W. S6K1 Controls Adiponectin Expression by Inducing a Transcriptional Switch: BMAL1-to-EZH2. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Yagi, S.; Nishimoto, S.; Kozuka, C.; Fukuda, D.; Soeki, T.; Masuzaki, H.; Tsutsui, M.; Sata, M. MicroRNA-378 Regulates Adiponectin Expression in Adipose Tissue: A New Plausible Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, C.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.-H. MicroRNAs in Adipose Tissue Metabolism and Inflammation. Drug Targets Ther. 2025, 4, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, I.M.; Wagner, S.A.; Gohlke, H.; Iglseder, B.; Mueller, J.C.; Cip, P.; Ladurner, G.; Reiter, R.; Stadlmayr, A.; Mackevics, V.; et al. Genetic Architecture of the APM1 Gene and Its Influence on Adiponectin Plasma Levels and Parameters of the Metabolic Syndrome in 1,727 Healthy Caucasians. Diabetes 2006, 55, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, F.; Helbecque, N.; Lobbens, S.; Vasseur-Delannoy, V.; Dina, C.; Clément, K.; Boutin, P.; Kadowaki, T.; Scherer, P.E.; Froguel, P. Hypoadiponectinaemia and High Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Are Associated with Adiponectin-Encoding (ACDC) Gene Promoter Variants in Morbid Obesity: Evidence for a Role of ACDC in Diabesity. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Ha, X.; Li, W.; Xu, P.; Gu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. DNA Methylation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1, and Adiponectin Genes in Visceral Adipose Tissue Is Related to Type 2 Diabetes in the Xinjiang Uygur Population. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houshmand-Oeregaard, A.; Hansen, N.S.; Hjort, L.; Kelstrup, L.; Broholm, C.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Clausen, T.D.; Damm, P.; Vaag, A. Differential Adipokine DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue from Adult Offspring of Women with Diabetes in Pregnancy. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, R.; Stupin, J.H.; Melchior, K.; Schellong, K.; Ziska, T.; Dudenhausen, J.W.; Henrich, W.; Rancourt, R.C.; Plagemann, A. Alterations of Adiponectin Gene Expression and DNA Methylation in Adipose Tissues and Blood Cells Are Associated with Gestational Diabetes and Neonatal Outcome. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houde, A.-A.; Légaré, C.; Biron, S.; Lescelleur, O.; Biertho, L.; Marceau, S.; Tchernof, A.; Vohl, M.-C.; Hivert, M.-F.; Bouchard, L. Leptin and Adiponectin DNA Methylation Levels in Adipose Tissues and Blood Cells Are Associated with BMI, Waist Girth and LDL-Cholesterol Levels in Severely Obese Men and Women. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Peng, J. miR-221 Negatively Regulates Inflammation and Insulin Sensitivity in White Adipose Tissue by Repression of Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6418–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, A.; Traurig, M.; Ossowski, V.; Fleming, J.M.; Mullins, M.; Baier, L.J. Human Adipose microRNA-221 Is Upregulated in Obesity and Affects Fat Metabolism Downstream of Leptin and TNF-α. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belarbi, Y.; Mejhert, N.; Lorente-Cebrián, S.; Dahlman, I.; Arner, P.; Rydén, M.; Kulyté, A. MicroRNA-193b Controls Adiponectin Production in Human White Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1084–E1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hui, X.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Ye, D.; Chan, C.Y.C.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A. Adipocyte-Secreted Exosomal microRNA-34a Inhibits M2 Macrophage Polarization to Promote Obesity-Induced Adipose Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Trajkovski, M. MiR-27 Orchestrates the Transcriptional Regulation of Brown Adipogenesis. Metabolism 2014, 63, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Jin, L. 1510-P: Adipocyte MicroRNA-802 Promotes Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Modulating Macrophages in Obesity. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1510-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, L.; Fiedorczuk, J.; Adamska, E. Effect of Diet and Other Factors on Serum Adiponectin Concentrations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Rocz. Państwowego Zakładu Hig. Ann. Natl. Inst. Hyg. 2013, 64, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Janiszewska, J.; Ostrowska, J.; Szostak-Węgierek, D. The Influence of Nutrition on Adiponectin—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.P.; Milne, K.J.; Hawke, T.J. Adiponectin-Consideration for Its Role in Skeletal Muscle Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of Adiponectin to Body Fat Distribution, Insulin Sensitivity and Plasma Lipoproteins: Evidence for Independent Roles of Age and Sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.M.; de Almeida, J.C.; Feoli, A.M. Effect of Diet on Adiponectin Levels in Blood. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Mediterranean Dietary Pattern, Inflammation and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Intervention Trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.; Halvardsson, P.; Kadi, F. Adherence to DASH-Style Dietary Pattern Impacts on Adiponectin and Clustered Metabolic Risk in Older Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlEssa, H.B.; Malik, V.S.; Yuan, C.; Willett, W.C.; Huang, T.; Hu, F.B.; Tobias, D.K. Dietary Patterns and Cardiometabolic and Endocrine Plasma Biomarkers in US Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Izadi, V.; Azadbakht, L. The Effect of Low Calorie Diet on Adiponectin Concentration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemirani, F.; Golzarand, M.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Effect of Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Adiponectin Level in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becic, T.; Studenik, C. Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on Adipocytokines in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, M.; Yoneda, M.; Maeda, N.; Ohno, H.; Oki, K.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I.; Hattori, N. Westernization of Lifestyle Affects Quantitative and Qualitative Changes in Adiponectin. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Ruan, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials on the Effect of Exercise on Serum Leptin and Adiponectin in Overweight and Obese Individuals. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 49, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| rsID | Allele Change | Variant Location/Molecular Consequences | Observed Associations | Study Population | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs182052 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] | |||
|
| [83] | |||
| rs822393 | C > T | Intron |
|
| [84] |
| rs16861210 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] | |||
| rs822394 | A > C | Intron |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] | |||
| rs822395 | C > A | Intron |
|
| [89] |
| rs822396 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] | |||
|
| [92] | |||
|
| [86] | |||
| rs12495941 | G > T | Intron |
|
| [88] |
|
| [87] | |||
|
| [86] | |||
| rs2036373 | T > G | Intron |
|
| [87] |
| rs17366568 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] | |||
|
| [87] | |||
|
| [93] | |||
|
| [84] | |||
| rs17846866 | T > G | Intron |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] | |||
| rs2241766 | T > G | Exon/synonymous variant |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] | |||
|
| [98] | |||
|
| [99] | |||
|
| [100] | |||
|
| [101] | |||
|
| [102] | |||
|
| [103] | |||
|
| [84] | |||
|
| [104] | |||
|
| [105] | |||
|
| [106] | |||
| rs1501299 | G > T | Intron |
|
| [85] |
|
| [89] | |||
|
| [107] | |||
| rs2241767 | A > G | Intron |
|
| [92] |
|
| [108] | |||
| rs3821799 | T > C | Intron |
|
| [85] |
|
| [109] | |||
| rs3774261 | A > G | Intron |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] | |||
|
| [92] | |||
|
| [93] | |||
| rs3774262 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [112] |
| rs62625753 | G > A | Intron |
|
| [113] |
| rs17366743 | T > C | Exon/missense variant |
|
| [85] |
|
| [113] | |||
|
| [114] | |||
| rs6444174 | C > T | 3′UTR |
|
| [88] |
| rs6773957 | A > G | 3′UTR |
|
| [85] |
|
| [115] | |||
| rs2082940 | T > C | 3′UTR |
|
| [85] |
| rs1063538 | T > C | 3′UTR |
|
| [107] |
| rs1063539 | G > C | 3′UTR |
|
| [116] |
|
| [86] | |||
|
| [112] | |||
| rs9842733 | A > T | 3′UTR |
|
| [86] |
|
| [117] | |||
| rs17300539 | G > A | Promoter |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] | |||
|
| [120] | |||
| rs266729 | C > G | Promoter |
|
| [85] |
|
| [121] | |||
|
| [118] |
| rsID | Allele Change | Variant Location/Molecular Consequences | Observed Associations | Study Population | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs12495941 | G > T | Intron |
| Chinese adults (n = 334) | [196] |
| Chinese adults (n = 1616) | [197] | |||
| rs182052 | G > A | Intron |
| Chinese adults (n = 334) | [196] |
| Chinese adults (n = 1 616) | [197] | |||
| rs2241766 | T > G | Exon/synonymous variant |
|
| [150] |
|
| [198] | |||
|
| [199] | |||
| rs1501299 | G > T | Intron |
|
| [195] |
|
| [194] | |||
|
| [193] | |||
|
| [199] | |||
|
| [200] | |||
| rs822394 | A > C | Intron |
|
| [196] |
| rs266729 | C > G | Intergenic |
|
| [199] |
|
| [197] | |||
|
| [150] | |||
|
| [201] | |||
| rs1656930 | A > G | Intergenic |
|
| [202] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Błażejewska, W.; Dąbrowska, J.; Michałowska, J.; Bogdański, P. The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Genes 2025, 16, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060699
Błażejewska W, Dąbrowska J, Michałowska J, Bogdański P. The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Genes. 2025; 16(6):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060699
Chicago/Turabian StyleBłażejewska, Wiktoria, Justyna Dąbrowska, Joanna Michałowska, and Paweł Bogdański. 2025. "The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review" Genes 16, no. 6: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060699
APA StyleBłażejewska, W., Dąbrowska, J., Michałowska, J., & Bogdański, P. (2025). The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Genes, 16(6), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060699







