Comparative Analysis of Plastomes of Artemisia and Insights into the Infra-Generic Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Genus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxa Sampling, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing
| Taxon | Genbank Accession Number | Nucleotide Length (bp) | Number of Genes | GC Content | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | LSC | SSC | IR | Protein-Coding Genes | rRNA Genes | tRNA Genes | (%) | ||
| A. sichuanensis | PP898074 | 151,230 | 82,935 | 18,375 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. adamsii | PP898105 | 151,231 | 82,955 | 18,337 | 24,969 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. bhutanica | PP898085 | 151,269 | 82,949 | 18,398 | 24,961 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. blepharolepis | PP898101 | 150,908 | 82,963 | 18,019 | 24,963 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. comaiensis | PP898079 | 151,298 | 82,930 | 18,448 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. fulgens var. meiguensis | PP898075 | 151,201 | 82,856 | 18,425 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. gyitangensis | PP898091 | 151,199 | 82,810 | 18,471 | 24,959 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. integrifolia | PP898104 | 151,117 | 82,912 | 18,285 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. jilongensis | PP898086 | 151,275 | 82,538 | 18,883 | 24,927 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. linyoureunensis | PP898096 | 151,174 | 82,718 | 18,594 | 24,931 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. mairei | PP898080 | 151,045 | 82,911 | 18,200 | 24,967 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. mattfeldii var. etomentosa | PP898076 | 151,087 | 82,929 | 18,238 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. minor | PP898083 | 151,083 | 82,556 | 18,673 | 24,927 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. mongolica | PP898103 | 151,193 | 82,795 | 18,478 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. neosinensis | PP898094 | 151,172 | 82,832 | 18,422 | 24,959 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. nortonii | PP898084 | 151,028 | 82,873 | 18,235 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. phyllobotrys | PP898077 | 151,171 | 82,931 | 18,312 | 24,964 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. qinlingensis | PP898098 | 151,181 | 82,921 | 18,326 | 24,967 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. selengensis-1 | PP898102 | 151,228 | 82,902 | 18,406 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. sericea | PP898073 | 150,870 | 82,852 | 18,094 | 24,962 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. smithii | PP898097 | 151,225 | 83,037 | 18,272 | 24,958 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. stracheyi | PP898081 | 151,327 | 82,937 | 18,470 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. stricta | PP898082 | 150,770 | 82,911 | 17,939 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. sylvatica | PP898100 | 151,200 | 82,982 | 18,296 | 24,961 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
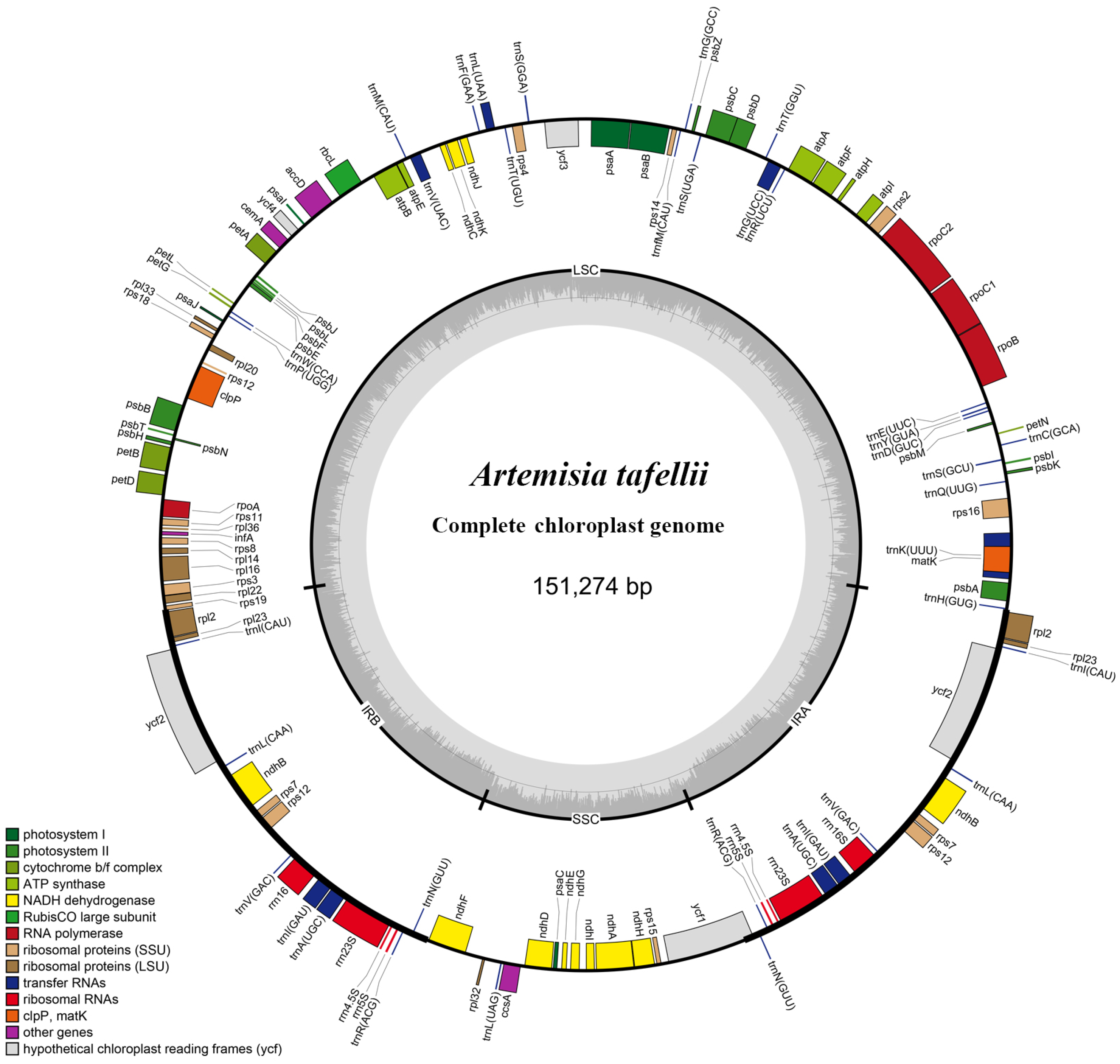
| A. tafellii | PP898088 | 151,274 | 82,937 | 18,417 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. tangutica | PP898099 | 151,191 | 82,833 | 18,452 | 24,953 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. tournefortiana | PP898072 | 151,106 | 82,600 | 18,606 | 24,950 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. tridactyla | PP898095 | 150,654 | 82,810 | 17,946 | 24,949 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. viscidissima | PP898078 | 151,241 | 82,655 | 18,622 | 24,982 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. waltonii | PP898087 | 151,038 | 82,909 | 18,209 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.50% |
| A. waltonii var. yushuensis | PP898092 | 150,636 | 82,981 | 17,735 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. youngii | PP898089 | 151,249 | 82,948 | 18,363 | 24,969 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. yunnanensi-1 | PP898090 | 151,190 | 82,987 | 18,283 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
| A. yunnanensis-2 | PP898093 | 151,232 | 82,977 | 18,335 | 24,960 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 37.40% |
2.2. Plastome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Comparative Analyses, Identification of Divergence Hotspots, and Simple Sequence Repeats
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plastome Features of Artemisia Species
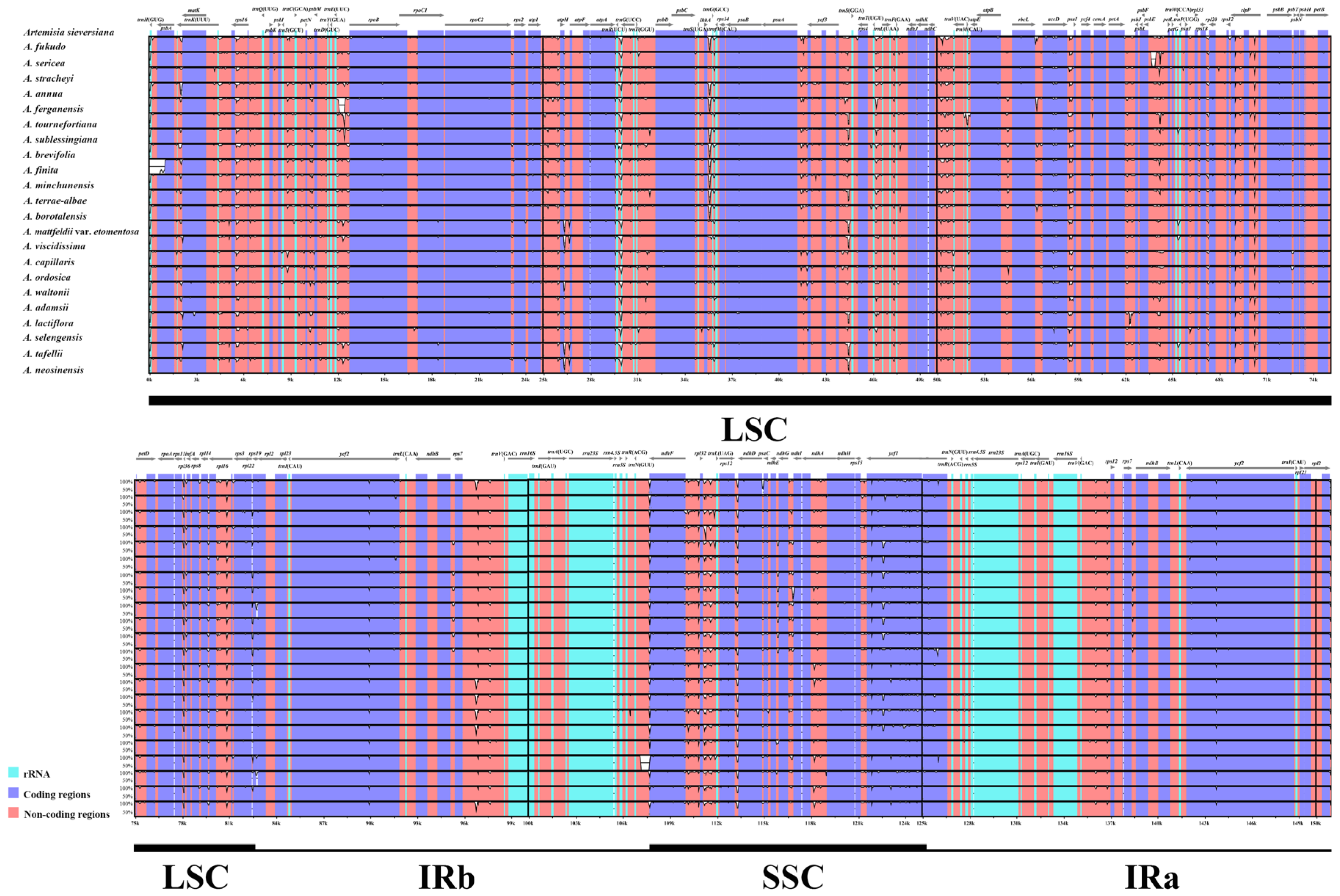
3.2. Plastome Sequence Divergence
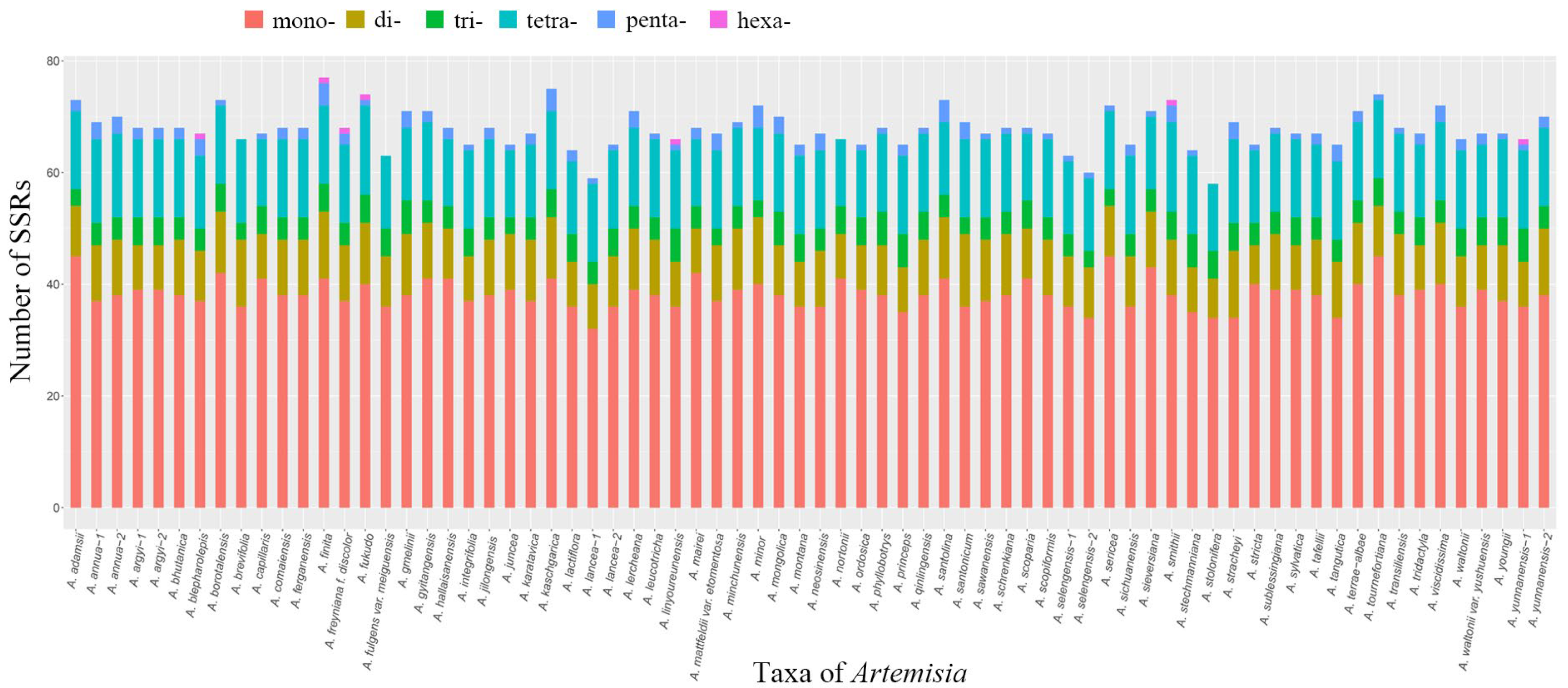
3.3. Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) in Artemisia Plastomes
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Plastomes and Genetic Variations in Artemisia
4.2. Phylogenetic Relationships of Artemisia
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDS | protein-coding sequences |
| LSC | large single-copy region |
| SSC | small single-copy region |
| IR | inverted repeat region |
References
- Ling, Y.R.; Humphries, C.J.; Gilbert, M.G. Artemisia Linnaeus. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; Volume 20–21, pp. 676–737. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Y.R. Artemisia L. In Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Ling, Y., Ling, Y.R., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991; Volume 76, pp. 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Shulz, L.M. Artemisia L. In Flora of North America; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 19–21, pp. 503–534. [Google Scholar]
- Vallès, J.; McArthur, E.D. Artemisia systematics and phylogeny: Cytogenetic and molecular in sights. In Proceedings of Shrubland Ecosystem, Genetics and Biodiversity; US Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 2001; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, C.R.; Baldwin, B.G. Asian origin and upslope migration of Hawaiian Artemisia (Compositae-Anthemideae). J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, N.V.; Hoffmann, M.H.; Röser, M.; Korobkov, A.A.; Hagen, K.B. Parallel evolutionary patterns in multiple lineages of arctic Artemisia L. (Asteraceae). Evolution 2008, 62, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, J.; Saslis-Lagoudakis, C.H.; Carrió, E.; Ernst, M.; Garnatje, T.; Grace, O.M.; Gras, A.; Mumbrú, M.; Vallès, J.; Vitales, D.; et al. A phylogenetic road map to antimalarial Artemisia species. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normile, D. DRUG DISCOVERY. Nobel for antimalarial drug highlights East-West divide. Science 2015, 350, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.R. The Chinese Artemisia Linn.—The classification, distribution and application of Artemisia Linn. in China. Bull. Bot. Res. 1988, 8, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, W.S. Lettre de Mr. le Dr. Besser au directeur monsieur le directeur. Bull. Soc. Imp. Nat. Moscou 1829, 1, 219–265. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, W.S. Tentamen de Abrotanis seu de sectione IIa Artemisiarum Linnaei. Nouv. Mém. Soc. Imp. Nat. Moscou 1832, 3, 3–89. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, W.S. De Seriphidiis seu de sectione IIIa Artemisiarum Linnaei. Bull. Soc. Imp. Nat. Moscou 1934, 7, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, W.S. Dracunculi, seu de sectione quarta et ultima Artemisiarum Linnaei. Bull. Soc. Imp. Nat. Moscou 1835, 8, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, S. A classification of Artemisia. Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 1939, 8, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Poljakov, P.P. Artemisia L. In Flora U.S.S.R.; Akademiya Nauk SSSR: Leninggrad, Russia, 1961; Volume 26, pp. 425–631. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S.; McArthur, E.D.; Pellicer, J.; Sanderson, S.C.; Vallès, J.; Garnatje, T. A molecular phylogenetic approach to western North America endemic Artemisia and allies (Asteraceae): Untangling the sagebrushes. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Vitales, D.; Hayat, M.Q.; Korobkov, A.A.; Garnatje, T.; Vallès, J. Phylogeny and biogeography of Artemisia subgenus Seriphidium (Asteraceae: Anthemideae). Taxon 2017, 66, 934–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, J.; Garnatje, T.; Korobkov, A.A.; Garnatje, T. Phylogenetic relationships of subgenus Dracunculus (genus Artemisia, Asteraceae) based on ribosomal and chloroplast DNA sequences. Taxon 2011, 60, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.E.; Bates, P.L.; Evans, T.M.; Unwin, M.W.; Estes, J.R. Molecular phylogeny of subtribe Artemisiinae (Asteraceae), including Artemisia and its allied and segregate genera. BMC Evol. Biol. 2002, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, B.H.; Chen, C.; Wei, M.; Niu, G.H.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Shen, J.H.; Vitales, D.; Vallès, J.; Verloove, F.; et al. Phylogenomics and morphological evolution of the mega-diverse genus Artemisia (Asteraceae: Anthemideae): Implications for its circumscription and infrageneric taxonomy. Am. J. Bot. 2023, 131, 867–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Xi, Z.X.; Mathews, S. Plastid phylogenomics and green plant phylogeny: Almost full circle but not quite there. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, B.; Torres-Montilla, S.; Morelli, L.; Florez-Sarasa, I.; Matus, J.T.; Ezquerro, M.; D’Andrea, L.; Houhou, F.; Majer, E.; Picó, B.; et al. Synthetic conversion of leaf chloroplasts into carotenoidrich plastids reveals mechanistic basis of natural chromoplast development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21796–21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Puche, L.; Tan, H.; Dogra, V.; Wu, M.; Rosas-Diaz, T.; Wang, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, D.; Fu, X.; Kim, C.; et al. A defense pathway linking plasma membrane and chloroplasts and coopted by pathogens. Cell 2020, 182, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitzendanner, M.A.; Soltis, P.S.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z.; Soltis, D.E. Plastome phylogenetics: 30 years of inferences into plant evolution. Adv. Bot. Res. 2018, 85, 293–313. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, S.E.; Smith, J.F.; Davidson, C.; Buerki, S. Phylogenetics and comparative plastome genomics of two of the largest genera of angiosperms, Piper and Peperomia (Piperaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 163, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; Luo, Y.; Gan, L.; Ma, P.F.; Gao, L.M.; Yang, J.B.; Cai, J.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Zhang, T.; et al. Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Hao, G.Q.; Zhang, L.; Mao, K.S.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, T.; Hu, Q.J.; Al-Shehbaz, I.A.; et al. Plastome phylogeny and early diversification of Brassicaceae. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.Z.; Liu, K.J.; Deng, R.Y.; Gao, Y.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Dong, W.P.; Zhang, Z.X. Insights into the phylogeny and chloroplast genome evolution of Eriocaulon (Eriocaulaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Odago, W.O.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.X.; Hu, G.W.; Wang, Q.F. Evolution of 101 Apocynaceae plastomes and phylogenetic implications. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2023, 180, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Forrest, L.L.; Spouge, J.L.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ratnasingham, S.; van der Bank, M.; Chase, M.W.; Cowan, R.S.; Erickson, D.L.; Fazekas, A.J. A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12794–12797. [Google Scholar]
- Riggins, C.W.; Seigler, D.S. The genus Artemisia (Asteraceae: Anthemideae) at a continental crossroads: Molecular insights into migrations, disjunctions, and reticulations among Old and New World species from a Beringian perspective. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2012, 64, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Liu, D.H.; Zhu, S.X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Q.R. Phylogeny of Trigonotis in Chinadwith a special reference to its nutlet morphology and plastid genome. Plant Divers. 2023, 45, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.B. Phylogeny, character evolution, and systematics of the fern family Ophioglossaceae based on Sanger sequence data, plastomes, and morphology. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2022, 173, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.B.; Lim, C.E.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, H.J.; Mun, J.H. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of Artemisia (Asteraceae) in East Asia: Insights into evolutionary divergence and phylogenomic implications. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 21, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Z.; Li, W.J.; Song, F.; Yang, L.; Wen, Z.B.; Feng, Y. Comparative analysis of complete Artemisia subgenus Seriphidium (Asteraceae: Anthemideae) chloroplast genomes: Insights into structural divergence and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualisation of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, C.; Brudno, M.; Schwartz, J.R.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.S.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Visualizing Global DNA Sequence Alignments of Arbitrary Length. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. CPJSdraw: Analysis and visualization of junction sites of chloroplast genomes. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large data sets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandros, S. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Stöver, B.C.; Müller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Miao, Y.H.; Luo, D.D.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Luo, M.; Zhao, T.T.; Liu, D.H. Sequence Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Artemisia argyi Chloroplast Genome. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 906725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.H.; Shi, Y.H.; Yin, Q.G.; Gao, R.R.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, W.T.; Tian, X.F.; Liu, J.W.; Nong, Y.Y.; Xiang, L.; et al. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genomes from five Artemisia species. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1049209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenberg, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Li, W.T. Partial correlation analysis indicates causal relationships between GC-content, exon density and recombination rate in the human genome. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Ming, R.; Yu, Q.Y. Comparative analysis of GC content variations in plant genomes. Trop. Plant Biol. 2016, 9, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glémin, S.; Clémin, Y.; David, J.; Ressayre, A. GC content evolution in coding regions of angiosperm genomes: A unifying hypothesis. Trend. Genet. 2014, 30, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre-Walker, A.; Hurst, L.D. The evolution of isochores. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.M.; Wang, J.R.; Feng, L.; Liu, S.; Pang, H.B.; Qi, L.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. Inferring the evolutionary mechanism of the chloroplast genome size by comparing whole-chloroplast genome sequences in seed plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1555. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.; Shafer, H.L.; Leonard, O.R.; Kovach, M.J.; Schorr, M.; Morris, A.B. Chloroplast DNA sequence utility for the lowest phylogenetic and phylogeographic inferences in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare IV. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1987–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.R. Taxa nova generum Artemisiae et Seriphidii xizangensis. Acta Phytotax. Sin. 1980, 18, 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Soltis, E.D.; Soltis, P.S. Contributions of plant molecular systematics to studies of molecular evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 42, 45–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.H.; Ge, S. Conflicting gene trees and phylogenomics. J. Syst. Evol. 2008, 46, 795–807. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, J.; Besansky, N.; Hahn, M.W. How reticulated are species? BioEssays 2016, 38, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.F.; Yuan, S.; Crowl, A.A.; Liang, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; An, Q.Q.; Kang, M.; Manos, P.S.; Wang, B.S. Phylogenomic analyses highlight innovation and introgression in the continental radiations of Fagaceae across the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.J.; Hegarty, M.J.; Hiscock, S.J.; Brennan, A.C. Homoploid hybrid speciation in action. Taxon 2010, 59, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.B. Compositae Indicae; Thacker, Spink and Co.: Calcutta, India, 1876; pp. 1–347. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, A. Artemisiella: A new genus of Compositae based on Artemisia stracheyii Hook. F. & Thoms. ex Clarke. Candollea 1992, 47, 635–643. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Xue, D.; Wu, Y. Comparative Analysis of Plastomes of Artemisia and Insights into the Infra-Generic Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Genus. Genes 2025, 16, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060659
Guo X, Huang W, Zhao Z, Xue D, Wu Y. Comparative Analysis of Plastomes of Artemisia and Insights into the Infra-Generic Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Genus. Genes. 2025; 16(6):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060659
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xinqiang, Weiquan Huang, Zhiyi Zhao, Dawei Xue, and Yuhuan Wu. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Plastomes of Artemisia and Insights into the Infra-Generic Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Genus" Genes 16, no. 6: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060659
APA StyleGuo, X., Huang, W., Zhao, Z., Xue, D., & Wu, Y. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Plastomes of Artemisia and Insights into the Infra-Generic Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Genus. Genes, 16(6), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060659






