Exploring the Association Between CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Non-Contact Tissue Injuries in Moroccan Elite Cyclists and Field Hockey Players: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Design and Participants
2.3. Injury Collection
2.4. Genotyping
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD36 | cluster of differentiation 36 |
| FAT | fatty acid translocase |
| IOC | International Olympic Committee |
| LCFAs | long-chain fatty acids |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| VO2 peak | peak oxygen uptake |
References
- Ekstrand, J.; Hägglund, M.; Waldén, M. Epidemiology of muscle injuries in professional football (soccer). Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delecroix, B.; McCall, A.; Dawson, B.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. Workload and non-contact injury incidence in elite football players competing in European leagues. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, A.; Dupont, G.; Ekstrand, J. Internal workload and non-contact injury: A one-season study of five teams from the UEFA Elite Club Injury Study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, L.; Silva, D.D.O.; Whalan, M.; McKay, M.J.; Sullivan, J.; Fuller, C.W.; Pappas, E. Non-contact Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Epidemiology in Team-Ball Sports: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis by Sex, Age, Sport, Participation Level, and Exposure Type. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2447–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkodi, B.; Bardoni, R.; Poór, G. Osteoporosis in Light of a New Mechanism Theory of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness and Non-Contact Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnoodi, P.; Tehranzadeh, A.D.; Dunn, J.M.; Tehranzadeh, J. Semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture of the posteromedial tibial plateau associated with posterior cruciate ligament tear and capsular rupture. Skelet. Radiol. 2014, 43, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prien, A.; Feddermann-Demont, N.; Verhagen, E.; Twisk, J.; Junge, A. Neurocognitive performance and mental health of retired female football players compared to non-contact sport athletes. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuglov, E.; Talibov, O.; Butovskiy, M.; Lyubushkina, A.; Khaitin, V.; Lazarev, A.; Achkasov, E.; Waśkiewicz, Z.; Rosemann, T.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; et al. The prevalence of non-contact muscle injuries of the lower limb in professional soccer players who perform Salah regularly: A retrospective cohort study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerson, S.; Hemingway, H.; Budget, R.; Martin, J.; Humphries, S.; Montgomery, H. Human angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene and endurance performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindpaintner, K.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Kreutz, R.; Stampfer, M.J.; Grodstein, F.; LaMotte, F.; Buring, J.; Hennekens, C.H. A prospective evaluation of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme gene polymorphism and the risk of ischemic heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Kiely, J.; Suraci, B.; Collins, D.; de Lorenzo, D.; Pickering, C.; Grimaldi, K. A genetic-based algorithm for personalized resistance training. Biol. Sport 2016, 33, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; Hall, E.C.R.; Semenova, E.A.; Pranckevičienė, E.; Ginevičienė, V. Chapter Five—Advances in sports genomics. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 107, pp. 215–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, A.; Carling, C.; Nedelec, M.; Davison, M.; Le Gall, F.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. Risk factors, testing and preventative strategies for non-contact injuries in professional football: Current perceptions and practices of 44 teams from various premier leagues. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, D.B.; Pimenta, E.M.; Rosse, I.C.; Veneroso, C.; Pussieldi, G.D.A.; Becker, L.K.; Oliveira, E.C.; Carvalho, M.R.; Silami-Garcia, E. α-Actinin-3 R577x Polymorphism Influences Muscle Damage and Hormonal Responses After a Soccer Game. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massidda, M.; Bachis, V.; Corrias, L.; Piras, F.; Scorcu, M.; Culigioni, C.; Masala, D.; Calò, C.M. ACTN3 R577X polymorphism is not associated with team sport athletic status in Italians. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massidda, M.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Kumagai, H.; Ikeda, H.; Shimasaki, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Cugia, P.; Piras, F.; Scorcu, M.; Kikuchi, N.; et al. Association between the ACE I/D polymorphism and muscle injuries in Italian and Japanese elite football players. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HKumagai, H.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Hirata, K.; Kikuchi, N.; Kamiya, N.; Hoshikawa, S.; Zempo, H.; Naito, H.; Miyamoto, N.; Fuku, N. ESR1 rs2234693 Polymorphism Is Associated with Muscle Injury and Muscle Stiffness. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.-W.; Liao, M.-F.; Liu, L.; Xiong, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.-R.; Meng, Z.-Y.; Gong, C.-X.; et al. CD36 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Intracerebral Hemorrhage Susceptibility in a Han Chinese Population. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5352071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, B.; Yao, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, W. CD36 genotype associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese Han. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 16149–16157. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Ruiz, E.; Armesilla, A.L.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Vega, M.A. Gene Encoding the Collagen Type I and Thrombospondin Receptor CD36 Is Located on Chromosome 7q11.2. Genomics 1993, 17, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rać, M.E.; Safranow, K.; Poncyljusz, W. Molecular basis of human CD36 gene mutations. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, U.; Elumalai, S.; Moon, J.-S.; Won, K.-C. CD36 Signal Transduction in Metabolic Diseases: Novel Insights and Therapeutic Targeting. Cells 2021, 10, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Abumrad, N.A. Cellular fatty acid uptake: A pathway under construction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahimi, A.; Bonen, A.; Blinn, W.D.; Hajri, T.; Li, X.; Zhong, K.; Cameron, R.; Abumrad, N.A. Muscle-specific overexpression of FAT/CD36 enhances fatty acid oxidation by contracting muscle, reduces plasma triglycerides and fatty acids, and increases plasma glucose and insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26761–26766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonen, A.; Han, X.-X.; Habets, D.D.J.; Febbraio, M.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P. A null mutation in skeletal muscle FAT/CD36 reveals its essential role in insulin- and AICAR-stimulated fatty acid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1740–E1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Watanabe, I.; Ishii, K.; Morimoto, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Yoshida, S.; Hui, S.-P.; Matsuno, K.; Chiba, H. Attenuated aerobic exercise capacity in CD36 deficiency. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 44, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscella, A.; Stefàno, E.; Lunetti, P.; Capobianco, L.; Marsigliante, S. The Regulation of Fat Metabolism during Aerobic Exercise. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, J.F.; Nabben, M.; Luiken, J.J. CD36 (SR-B2) as master regulator of cellular fatty acid homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2022, 33, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouali, E.M.; Bosquet, L.; Elgharbaoui, B.; Laziri, F.; Laher, I.; Hackney, A.C.; Ibrahimi, A.; Taib, B.; El Harane, S.; Weiss, K.; et al. Association between “cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36)” and adipose tissue lipolysis during exercise training: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1256440. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2023.1256440 (accessed on 30 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.F. Mitochondrial basis for sex-differences in metabolism and exercise performance. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, R848–R849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, N.S.; Snook, L.A.; Jain, S.S.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Bonen, A.; Spriet, L.L. Acute endurance exercise increases plasma membrane fatty acid transport proteins in rat and human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E183–E189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhry, M.M.; Abdel-Hamed, A.R.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Mesbah, N.M.; Al-Sawaf, A.; Ezzat, O.; Al-Sawaf, H. A possible novel co-relation of locus 7q11 rs1761667 polymorphism with the severity of preeclampsia in Egyptian pregnant women. Meta Gene 2020, 24, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouali, E.M.; Kartibou, J.; Del Coso, J.; El Makhzen, B.; Bouguenouch, L.; El Harane, S.; Taib, B.; Weiss, K.; Knechtle, B.; Mesfioui, A.; et al. Genotypic and Allelic Distribution of the CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism in High-Level Moroccan Athletes: A Pilot Study. Genes 2024, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MMelis, M.; Carta, G.; Pintus, S.; Pintus, P.; Piras, C.A.; Murru, E.; Manca, C.; Di Marzo, V.; Banni, S.; Barbarossa, I.T. Polymorphism rs1761667 in the CD36 Gene Is Associated to Changes in Fatty Acid Metabolism and Circulating Endocannabinoid Levels Distinctively in Normal Weight and Obese Subjects. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrizak, I.; Šerý, O.; Plesnik, J.; Arfa, A.; Fekih, M.; Bouslema, A.; Zaouali, M.; Tabka, Z.; Khan, N.A. The A allele of cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) SNP 1761667 associates with decreased lipid taste perception in obese Tunisian women. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, K.; Kuwasako, T.; Hirano, K.-I.; Nozaki, S.; Yamashita, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. CD36 deficiency associated with insulin resistance. Lancet 2001, 357, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Hirano, K.-I.; Kuwasako, T.; Janabi, M.; Toyama, Y.; Ishigami, M.; Sakai, N. Physiological and pathological roles of a multi-ligand receptor CD36 in atherogenesis; insights from CD36-deficient patients. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2007, 299, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanisawa, K.; Wang, G.; Seto, J.; Verdouka, I.; Twycross-Lewis, R.; Karanikolou, A.; Tanaka, M.; Borjesson, M.; Di Luigi, L.; Dohi, M.; et al. Sport and exercise genomics: The FIMS 2019 consensus statement update. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Pluim, B.M.; Moreno-Pérez, V.; Bigard, X.; Blauwet, C.; Del Coso, J.; Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Grimm, K.; Jones, N.; Kolman, N.; et al. Methods for epidemiological studies in competitive cycling: An extension of the IOC consensus statement on methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, R.; Clarsen, B.; Derman, W.; Dvorak, J.; Emery, C.A.; Finch, C.F.; Hägglund, M.; Junge, A.; Kemp, S.; Khan, K.M.; et al. International Olympic Committee consensus statement: Methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020 (including STROBE Extension for Sport Injury and Illness Surveillance (STROBE-SIIS)). Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssaini, T.; Jaafour, S.; Ouldim, K.; Squali, F.-Z. CD36 Gene Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Nephropathies. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 9798–9804. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Wu, F.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; You, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wei, L.; Ruan, X.Z.; Zhao, L.; et al. Inhibition of Fatty Acid Translocase (FAT/CD36) Palmitoylation Enhances Hepatic Fatty Acid β-Oxidation by Increasing Its Localization to Mitochondria and Interaction with Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 1. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2022, 36, 1081–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momeni-Moghaddam, M.A.; Asadikaram, G.; Akbari, H.; Abolhassani, M.; Masoumi, M.; Nadimy, Z.; Khaksari, M. CD36 gene polymorphism rs1761667 (G > A) is associated with hypertension and coronary artery disease in an Iranian population. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBajit, H.; Mohammed, O.A.S.; Guennoun, Y.; Benaich, S.; Bouaiti, E.; Belghiti, H.; Mrabet, M.; Elfahime, E.M.; El Haloui, N.E.; Saeid, N.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs1761667 in the CD36 gene is associated with orosensory perception of a fatty acid in obese and normal-weight Moroccan subjects. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 9, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massidda, M.; Scorcu, M.; Calò, C.M. New Genetic Model for Predicting Phenotype Traits in Sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.C.; Day, S.H.; Ahmetov, I.I.; Williams, A.G. Genetics of muscle strength and power: Polygenic profile similarity limits skeletal muscle performance. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.; Folland, J.P. Similarity of polygenic profiles limits the potential for elite human physical performance. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Athletes | Injured | Non-Injured | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 20 (18–23) | 21.83 ± 3.86 | 20 (18–23) | 0.80 |
| Weight (kg) | 64.30 ± 6.23 | 65.83 ± 4.59 | 64 (60–67) | 0.22 |
| Height (m) | 1.77 ± 0.05 | 1.78 ± 0.04 | 1.76 ± 0.05 | 0.65 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.64 ± 1.93 | 20.87 ± 1.43 | 20.55 ± 2.11 | 0.89 |
| Groups | Cyclists | Field Hockey Players | All Athletes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 18 | n = 24 | n = 42 | |||
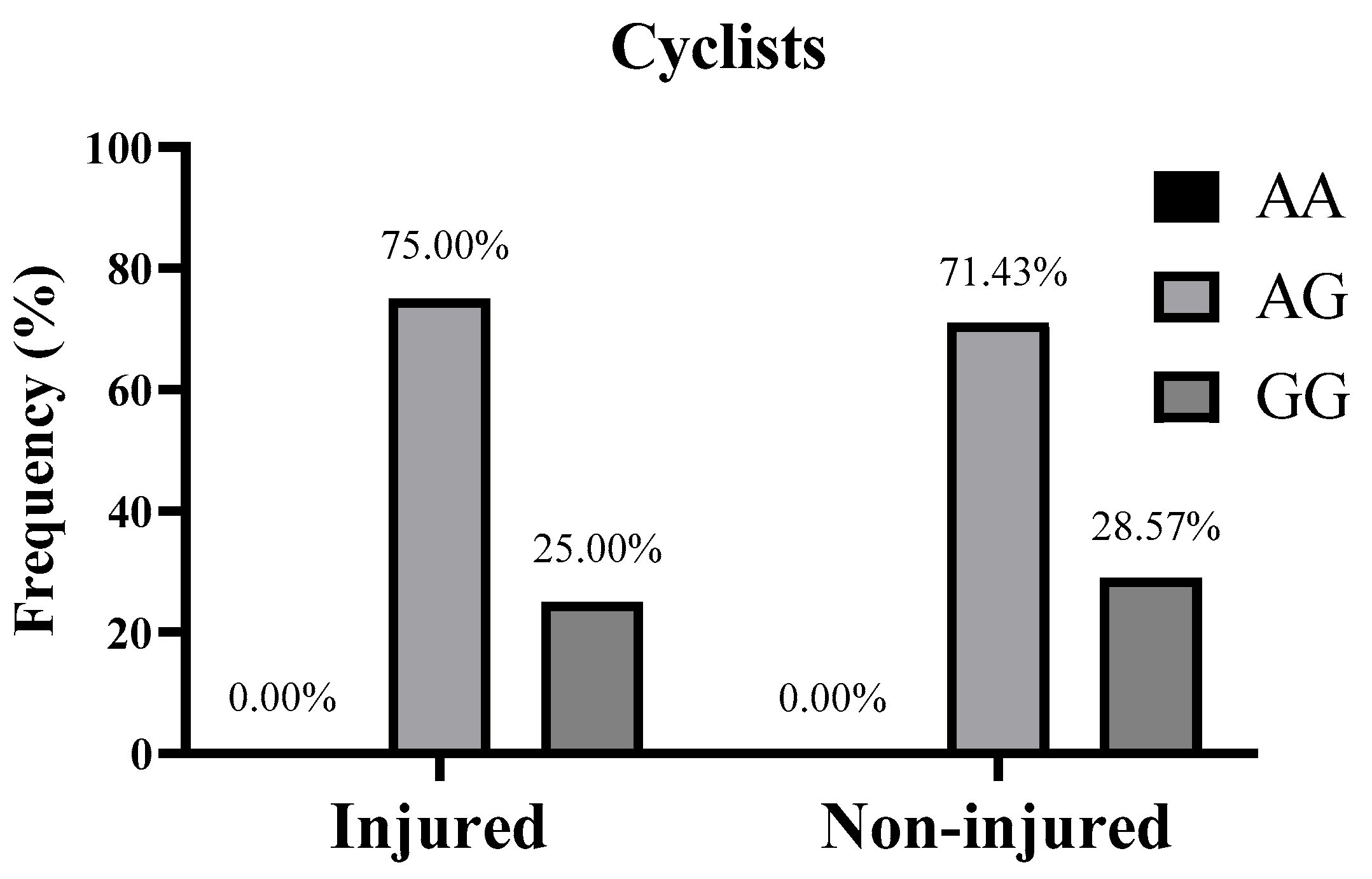
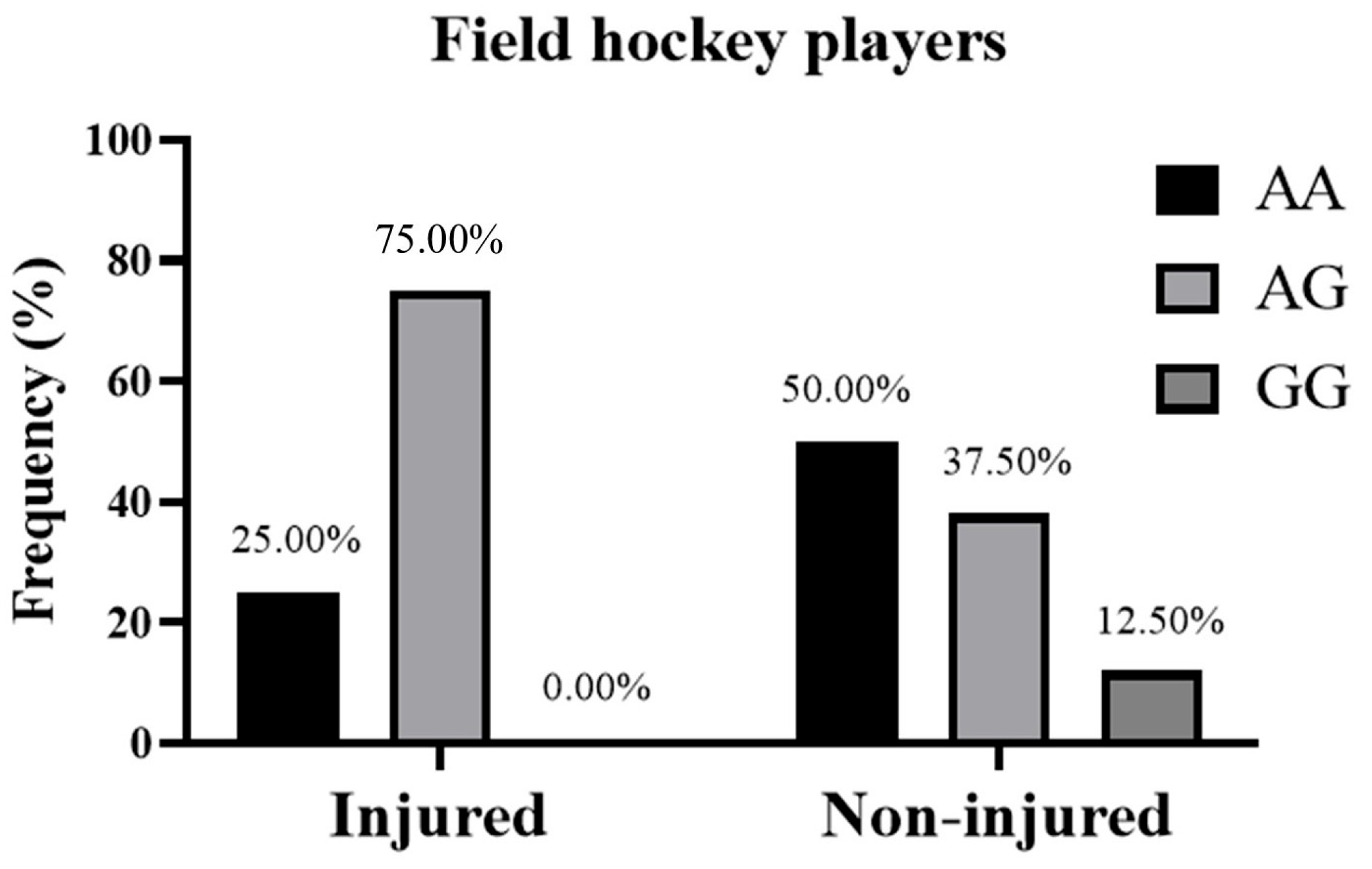
| Injured | Genotype n (%) | AA | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (25.00%) | 2 (16.67%) |
| AG | 3 (75.00%) | 6 (75.00%) | 9 (75.00%) | ||
| GG | 1 (25.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (8.33%) | ||
| Allele n (%) | A | 3 (37.50%) | 10 (62.50%) | 13 (54.17%) | |
| G | 5 (62.50%) | 6 (37.50%) | 11 (45.83%) | ||
| Non-injured | Genotype n (%) | AA | 0 (0.00%) | 8 (50.00%) | 8 (26.67%) |
| AG | 10 (71.43%) | 6 (37.50%) | 16 (53.33%) | ||
| GG | 4 (28.57%) | 2 (12.50%) | 6 (20.00%) | ||
| Allele n (%) | A | 10 (35.71%) | 22 (68.75%) | 32 (53.33%) | |
| G | 18 (64.29%) | 10 (31.25%) | 28 (46.67%) |
| Groups | Injured vs. Non-Injured | Dominant (AA+AG vs. GG) | Recessive (AA vs. AG+GG) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | df | p-Value | OR [95% CI] | p-Value | OR [95% CI] | p-Value | |
| Cyclists | - | - | - | 1.20 [0.13–19.09] | >0.9999 | - | >0.9999 |
| Field hockey players | 3.3 | 2 | 0.19 | infinity [0.23–infinity] | 0.53 | 0.33 [0.05–2.40] | 0.38 |
| All athletes | 1.73 | 2 | 0.41 | 2.75 [0.32–34.12] | 0.65 | 0.55 [0.10–2.60] | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Ouali, E.M.; Kartibou, J.; Del Coso, J.; El Makhzen, B.; Bouguenouch, L.; El Akbir, R.; El Haboussi, A.; Akhouayri, O.; Ibrahimi, A.; Mesfioui, A.; et al. Exploring the Association Between CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Non-Contact Tissue Injuries in Moroccan Elite Cyclists and Field Hockey Players: A Pilot Study. Genes 2025, 16, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060651
El Ouali EM, Kartibou J, Del Coso J, El Makhzen B, Bouguenouch L, El Akbir R, El Haboussi A, Akhouayri O, Ibrahimi A, Mesfioui A, et al. Exploring the Association Between CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Non-Contact Tissue Injuries in Moroccan Elite Cyclists and Field Hockey Players: A Pilot Study. Genes. 2025; 16(6):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060651
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Ouali, El Mokhtar, Jihan Kartibou, Juan Del Coso, Badreddine El Makhzen, Laila Bouguenouch, Ramzi El Akbir, Abdelmoujoud El Haboussi, Omar Akhouayri, Azeddine Ibrahimi, Abdelhalem Mesfioui, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Association Between CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Non-Contact Tissue Injuries in Moroccan Elite Cyclists and Field Hockey Players: A Pilot Study" Genes 16, no. 6: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060651
APA StyleEl Ouali, E. M., Kartibou, J., Del Coso, J., El Makhzen, B., Bouguenouch, L., El Akbir, R., El Haboussi, A., Akhouayri, O., Ibrahimi, A., Mesfioui, A., & Zouhal, H. (2025). Exploring the Association Between CD36 rs1761667 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Non-Contact Tissue Injuries in Moroccan Elite Cyclists and Field Hockey Players: A Pilot Study. Genes, 16(6), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060651








