Advancements in Gene Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Landscape of NSCLC
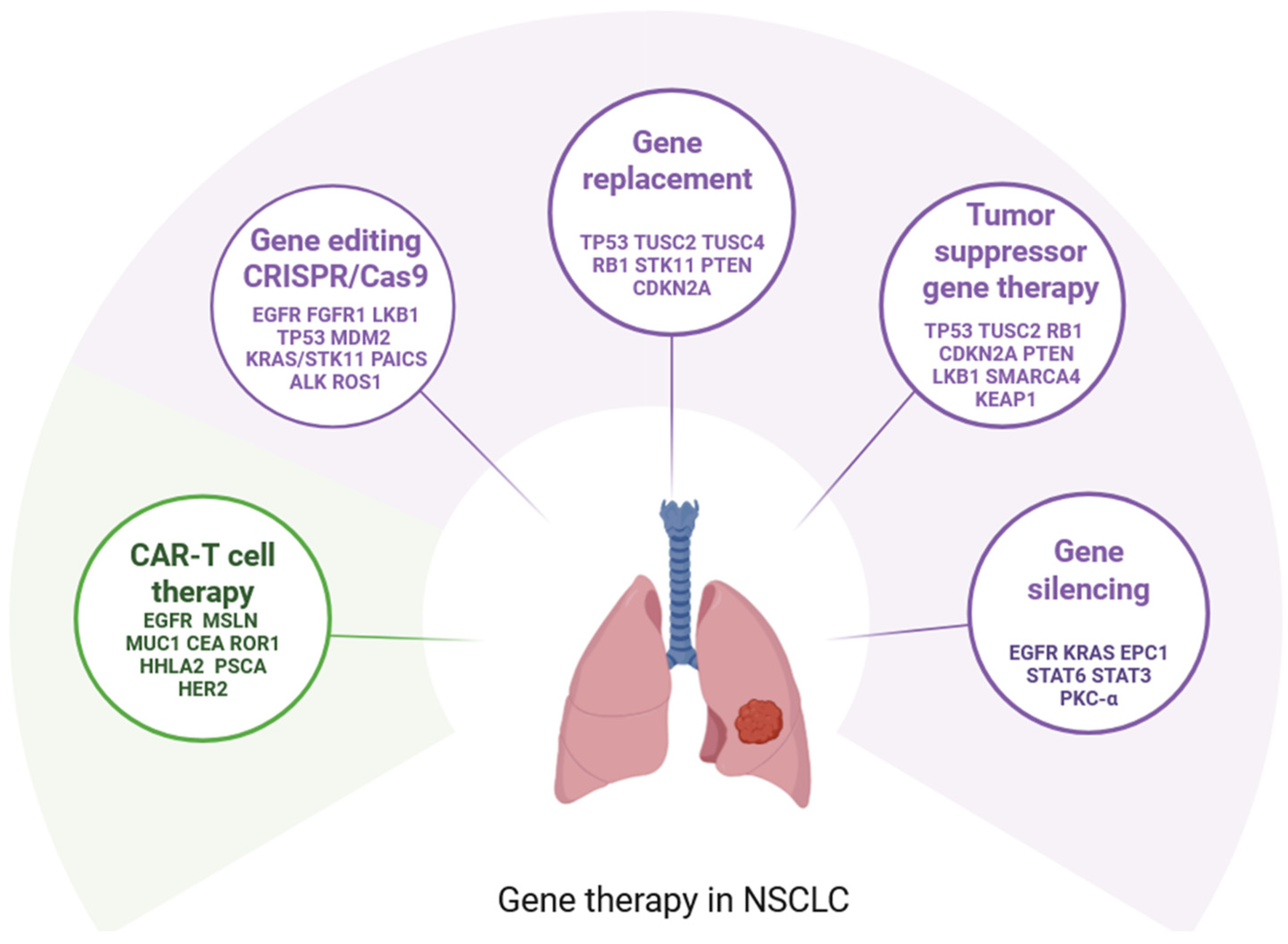
3. General Mechanisms of Gene Therapy in NSCLC
4. Gene Replacement
5. Gene Silencing
6. Gene Editing: CRISPR/Cas9 in NSCLC
7. Chimeric Antigen Receptor CAR-T Cell Therapy in NSCLC
8. Challenges in Gene Therapy for NSCLC
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Adp53 | adenoviral p53 vector |
| ASO | antisense oligonucleotide therapies |
| BRAF | v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly-Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| c-ROS1 | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| EPC1 | enhancer of polycomb 1 |
| ERBB2 | otherwise HER2: human epidermal growth factor 2 |
| hRT | hypofractionated radiotherapy |
| MET | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| MSLN | mesothelin |
| MUC1 | mucin 1 |
| NGR1 | neuregulin-1 |
| NPRL2 | Nitrogen Permease Regulator-Like 2 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| NTRK1 | neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase |
| PKC-α | Protein Kinase C-alpha prostate stem cell antigen |
| PSCA | phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase |
| PAICS | phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinylcarboxamide synthetase |
| rAd-p53 | recombinant adenoviral p53 gene |
| RNAi | including RNA interference |
| ROR1 | receptor tyrosine kinase type 1 |
| TKIs | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| TUSC2 | Tumor Suppressor Candidate 2 gene |
| siRNAs | small interfering RNAs |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| STAT6 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 147, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2023-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Sereno, M.; Hernandez de Cordoba, I.; Gutierrez-Gutierrez, G.; Casado, E. Brain metastases and lung cancer: Molecular biology, natural history, prediction of response and efficacy of immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1297988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, P.M.; Vandermeer, R. Delays in the diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2011, 3, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Mockus, S.M.; Spotlow, V.; Reddi, H.V.; Malcolm, J.; Huberman, M.S.; Joseph, L.J.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Mutations in TP53, PIK3CA, PTEN and other genes in EGFR mutated lung cancers: Correlation with clinical outcomes. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Planchard, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, C.K.; Valdiviezo, N.; Laktionov, K.; Yang, T.Y.; Yu, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. A plain language summary of results from the FLAURA2 study: Effects of initial (first-line) osimertinib plus chemotherapy on the brain in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2025, 21, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guerin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; Voegeli, A.C.; Vallat, L.; Mascaux, C.; Beau-Faller, M. Direct Targeting KRAS Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Shin, S.C.; Oh, Y.; Kim, J.; Hwang, I.; Kim, E.E.; Choo, H.; Song, E.J. Targeting USP47 enhances the efficacy of KRAS inhibitor in KRAS(G12C) mutated non-small cell lung cancer by controlling deubiquitination of c-Myc. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 215, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Alcon, C.; Marin, E.; Morales-Sanchez, P.; Manzano-Munoz, A.; Diaz, S.; Garcia, M.; Samitier, J.; Lu, A.; Villanueva, A.; et al. Novel selective strategies targeting the BCL-2 family to enhance clinical efficacy in ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Noronha, V.; Patil, V.; Singh, A.K.; Menon, N.; Goud, S.; Shah, S.; More, S.; Kapoor, A.; Mishra, B.K.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Driver Gene Alterations in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Patterns of Treatment and Impact on Survival Outcomes: A Single Center Experience of More Than 1200 Patients. Clin. Lung Cancer 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Patel, S.; Drusbosky, L.M.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, R.; Geng, R.; Heeke, S.; Nilsson, M.; Wu, J.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Molecular landscape of ERBB2 alterations in 3000 advanced NSCLC patients. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, D.H.; Jang, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Yoon, S.; Lee, D.H. Comparison of Clinicopathogenomic Features and Treatment Outcomes of EGFR and HER2 Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Single-Institution Experience. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Inaba Higashiyama, R.; Yoshida, T.; Satozono, Y.; Ohe, Y. Response to dabrafenib plus trametinib on a rare BRAF mutation (V600_W604 deletion-insertion R) in an advanced non-small cell lung cancer patient. Thorac. Cancer 2024, 15, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Ota, M.; Iwama, E.; Sugawara, S.; Shukuya, T.; Umemura, S.; Tanaka, H.; Oki, M.; Takahama, T.; Masuda, T.; et al. A Phase II, Open Label, Single-Arm Study on the Efficacy of Cabozantinib in Patients With Advanced/Metastatic Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Harboring MET Exon 14 Alterations who Developed Acquired Resistance to Tepotinib or Capmatinib (CAPTURE Trial). Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 26, e232–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, M.S.; Riess, J.W.; Goldman, J.W.; Jiang, F.; Bivona, T.G.; Blakely, C.M. Current Trial Report: A Multicenter Phase I/Ib study of Capmatinib Plus Trametinib in Patients With Metastatic Nonsmall Cell Lung Center Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations and Other MET-Alterations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 25, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.R.; Dixon, C.B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Ruiz, J.; Oliver, G.; Miller, L.D.; Topaloglu, U.; Chan, M.D.; et al. Targeting NTRK1 Enhances Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Efficacy in NTRK1 Wild-Type Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 4002–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Massarelli, E.; Buchschacher, G.L.; Goto, K.; Overbeck, T.R.; Loong, H.H.F.; Chee, C.E.; Garrido, P.; Dong, X.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety of entrectinib in NTRK fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2024, 188, 107442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.; Borgeaud, M.; Addeo, A.; Friedlaender, A. Oncogenic driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: Past, present and future. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lu, X. Live or let die: The cell’s response to p53. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A.; Swisher, S.G.; Merritt, J.A.; Lawrence, D.D.; Kemp, B.L.; Carrasco, C.H.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Fossella, F.V.; Glisson, B.S.; Hong, W.K.; et al. Gene therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary report of a phase I trial of adenoviral p53 gene replacement. Semin. Oncol. 1998, 25, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Swisher, S.G.; Roth, J.A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Lawrence, D.D.; Kemp, B.L.; Carrasco, C.H.; Connors, D.G.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Fossella, F.; Glisson, B.S.; et al. Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Herrmann, R.; De Greve, J.L.; Stewart, A.K.; Gatzemeier, U.; Stewart, D.J.; Laufman, L.; Gralla, R.; Kuball, J.; Buhl, R.; et al. Adenovirus-mediated wild-type p53 gene transfer in patients receiving chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a multicenter phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Tang, B.; Tao, S.; Kang, P.; Qian, K.; Jiang, B.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Zhou, J.; et al. Surgery combined with adenoviral p53 gene therapy for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A phase II study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107089–107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, L. The Development of p53-Targeted Therapies for Human Cancers. Cancers 2023, 15, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, M.; Ji, L.; Kamibayashi, C.; Tomizawa, Y.; Randle, D.; Sekido, Y.; Yokota, J.; Kashuba, V.; Zabarovsky, E.; Kuzmin, I.; et al. Overexpression of candidate tumor suppressor gene FUS1 isolated from the 3p21.3 homozygous deletion region leads to G1 arrest and growth inhibition of lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6258–6262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Nishizaki, M.; Gao, B.; Burbee, D.; Kondo, M.; Kamibayashi, C.; Xu, K.; Yen, N.; Atkinson, E.N.; Fang, B.; et al. Expression of several genes in the human chromosome 3p21.3 homozygous deletion region by an adenovirus vector results in tumor suppressor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2715–2720. [Google Scholar]
- Thu, K.L.; Vucic, E.A.; Chari, R.; Zhang, W.; Lockwood, W.W.; English, J.C.; Fu, R.; Wang, P.; Feng, Z.; MacAulay, C.E.; et al. Lung adenocarcinoma of never smokers and smokers harbor differential regions of genetic alteration and exhibit different levels of genomic instability. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Guerra, H.; Roth, J.A. Gene Therapy for Lung Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2016, 21, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Stewart, D.J.; Lee, J.J.; Ji, L.; Ramesh, R.; Jayachandran, G.; Nunez, M.I.; Wistuba, I.I.; Erasmus, J.J.; Hicks, M.E.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of systemically administered TUSC2(FUS1)-nanoparticles mediating functional gene transfer in humans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, M.I.; Minna, J.D. The 630-kb lung cancer homozygous deletion region on human chromosome 3p21.3: Identification and evaluation of the resident candidate tumor suppressor genes. The International Lung Cancer Chromosome 3p21.3 Tumor Suppressor Gene Consortium. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6116–6133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Kawashima, H.; Ohtani, S.; Deng, W.G.; Ravoori, M.; Bankson, J.; Gao, B.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Roth, J.A.; et al. The 3p21.3 tumor suppressor NPRL2 plays an important role in cisplatin-induced resistance in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9682–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraz, I.M.; Majidi, M.; Song, R.; Meng, F.; Gao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shpall, E.J.; Roth, J.A. NPRL2 gene therapy induces effective antitumor immunity in KRAS/STK11 mutant anti-PD1 resistant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in a humanized mouse model. eLife 2025, 13, RP98258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Kronenberger, P.; Teugels, E.; Umelo, I.A.; De Greve, J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells: The effect of combining RNA interference with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or cetuximab. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Deng, Z.J.; Roy, S.; Hammond, P.T. A Combination RNAi-Chemotherapy Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticle for Systemic Targeting of KRAS/P53 with Cisplatin to Treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7312–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Middleton, J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Magee, P.; Veneziano, D.; Lagana, A.; Leong, H.S.; Sahoo, S.; Fassan, M.; Booton, R.; et al. KRAS induces lung tumorigenesis through microRNAs modulation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cina, C.; Majeti, B.; O’Brien, Z.; Wang, L.; Clamme, J.P.; Adami, R.; Tsang, K.Y.; Harborth, J.; Ying, W.; Zabludoff, S. A Novel Lipid Nanoparticle NBF-006 Encapsulating Glutathione S-Transferase P siRNA for the Treatment of KRAS-Driven Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2025, 24, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Zhang, L.; Huo, J.; Zhang, Y. RNA interference targeting enhancer of polycomb1 exerts anti-tumor effects in lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Barsoumian, H.B.; Puebla-Osorio, N.; Hu, Y.; Sezen, D.; Wasley, M.D.; Bertolet, G.; Zhang, J.; Leuschner, C.; Yang, L.; et al. Inhibition of STAT6 with Antisense Oligonucleotides Enhances the Systemic Antitumor Effects of Radiotherapy and Anti-PD-1 in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Kurzrock, R.; Kim, Y.; Woessner, R.; Younes, A.; Nemunaitis, J.; Fowler, N.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, J.; Jo, M.; et al. AZD9150, a next-generation antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of STAT3 with early evidence of clinical activity in lymphoma and lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 314ra185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hartley, G.P.; Couillault, C.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, H.; Nicholas, C.; Srinivasamani, A.; Dai, J.; Dumbrava, E.E.I.; Fu, S.; et al. Preclinical study and parallel phase II trial evaluating antisense STAT3 oligonucleotide and checkpoint blockade for advanced pancreatic, non-small cell lung cancer and mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer. BMJ Oncol. 2024, 3, e000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, N.M.; McKay, R.; Condon, T.P.; Bennett, C.F. Inhibition of protein kinase C-α expression in human A549 cells by antisense oligonucleotides inhibits induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) mRNA by phorbol esters. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16416–16424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Ritch, P.; Figueroa, J.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Belt, R.; Dow, E.; George, S.; Leonardo, J.; McCachren, S.; Miller, G.L.; et al. A phase I/II study of LY900003, an antisense inhibitor of protein kinase C-α, in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6086–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritch, P.; Rudin, C.M.; Bitran, J.D.; Edelman, M.J.; Makalinao, A.; Irwin, D.; Lilenbaum, R.; Peterson, P.; John, W.J. Phase II study of PKC-α antisense oligonucleotide aprinocarsen in combination with gemcitabine and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 52, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Canon, J.L.; Riska, H.; Pirker, R.; Peterson, P.; John, W.; Mali, P.; Lahn, M. Randomized phase II evaluation of aprinocarsen in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin for patients with advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2005, 23, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Douillard, J.Y.; Koralewski, P.; Manegold, C.; Smit, E.F.; Reyes, J.M.; Chang, G.C.; John, W.J.; Peterson, P.M.; Obasaju, C.K.; et al. Phase III study of gemcitabine and cisplatin with or without aprinocarsen, a protein kinase C-α antisense oligonucleotide, in patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.; Yoon, A.R.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, S.; Yun, C.O.; Kim, J.S. Selective disruption of an oncogenic mutant allele by CRISPR/Cas9 induces efficient tumor regression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7897–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.H.; Chow, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Ng, K.C.; Or, T.C.; Yao, Y.Y.; Dong, Y.; Fung, J.M.; et al. Specific targeting of point mutations in EGFR L858R-positive lung cancer by CRISPR/Cas9. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, S.Q.; Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Bruggmann, R.; Gao, Y.; Deng, H.; Berezowska, S.; Hall, S.R.R.; Marti, T.M.; et al. CRISPR-Mediated Kinome Editing Prioritizes a Synergistic Combination Therapy for FGFR1-Amplified Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3121–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, M.B.; Morelli, A.P.; Pavan, I.C.B.; Mancini, M.C.S.; Gois, M.M.; Borges, R.J.; Braga, R.R.; da Silva, L.G.S.; Quintero-Ruiz, N.; Costa, M.M.; et al. A CRISPR-edited isoform of the AMPK kinase LKB1 improves the response to cisplatin in A549 lung cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Mao, J.; Duan, C.; Liang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, F.; et al. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening for therapeutic targets in NSCLC carrying wild-type TP53 and receptor tyrosine kinase genes. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.; Ranieri, M.; Li, S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Guidry, K.; Hu, H.; et al. Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 4095–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, M.; Brammeld, J.S.; Price, S.; Pilling, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Farcas, A.; Bateson, J.; Sundarrajan, A.; Miragaia, R.J.; Guan, N.; et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify the YAP/TEAD axis as a driver of persister cells in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Mao, J.; Zheng, H.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Mao, T.; Zhou, T.; Cao, P.; Wu, H.; et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen identifies PAICS as a therapeutic target for EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung cancer. MedComm (2020) 2024, 5, e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddalo, D.; Manchado, E.; Concepcion, C.P.; Bonetti, C.; Vidigal, J.A.; Han, Y.C.; Ogrodowski, P.; Crippa, A.; Rekhtman, N.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. In vivo engineering of oncogenic chromosomal rearrangements with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Nature 2014, 516, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrones, M.; Deben, C.; Rodrigues-Fortes, F.; Schepers, A.; de Beeck, K.O.; Van Camp, G.; Vandeweyer, G. CRISPR/Cas9-edited ROS1 + non-small cell lung cancer cell lines highlight differential drug sensitivity in 2D vs 3D cultures while reflecting established resistance profiles. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.Y.; Das, J.; Prendergast, C.; De Jong, D.; Braumuller, B.; Paily, J.; Huang, S.; Liou, C.; Giarratana, A.; Hosseini, M.; et al. Advances in CAR T Cell Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9019–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Guo, Y.; Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, H.; Han, W. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the immunotherapy of patients with EGFR-expressing advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chu, W.; Jin, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Lou, J.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachala, S.S.; Bograd, A.J.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Suzuki, K.; Servais, E.L.; Kadota, K.; Chou, J.; Sima, C.S.; Vertes, E.; Rusch, V.W.; et al. Mesothelin overexpression is a marker of tumor aggressiveness and is associated with reduced recurrence-free and overall survival in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenito, C.; Milone, M.C.; Hassan, R.; Simonet, J.C.; Lakhal, M.; Suhoski, M.M.; Varela-Rohena, A.; Haines, K.M.; Heitjan, D.F.; Albelda, S.M.; et al. Control of large, established tumor xenografts with genetically retargeted human T cells containing CD28 and CD137 domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Lou, Y.; Lu, L.; Fan, X. Mesothelin-targeted second generation CAR-T cells inhibit growth of mesothelin-expressing tumors in vivo. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.Y.; Kwon, T.; Bak, Y.; Yu, J.H.; Hong, J.; Lee, S.K.; Yu, D.Y.; Yoon, D.Y. Mucin 1-mediated chemo-resistance in lung cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lai, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, B.; Lin, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. PSCA and MUC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer as targets of chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1284722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallstabe, L.; Gottlich, C.; Nelke, L.C.; Kuhnemundt, J.; Schwarz, T.; Nerreter, T.; Einsele, H.; Walles, H.; Dandekar, G.; Nietzer, S.L.; et al. ROR1-CAR T cells are effective against lung and breast cancer in advanced microphysiologic 3D tumor models. JCI Insight 2019, 4, 126345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Current challenges and therapeutic advances of CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kitano, M.; Dudley, M.E.; Laurencot, C.M.; Rosenberg, S.A. Case report of a serious adverse event following the administration of T cells transduced with a chimeric antigen receptor recognizing ERBB2. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, L.; Mezosi-Csaplar, M.; Rebenku, I.; Vereb, G.; Szoor, A. Universal CAR T cells targeted to HER2 with a biotin-trastuzumab soluble linker penetrate spheroids and large tumor xenografts that are inherently resistant to trastuzumab mediated ADCC. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1365172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velcheti, V.; Schalper, K.A.; Carvajal, D.E.; Anagnostou, V.K.; Syrigos, K.N.; Sznol, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Gettinger, S.N.; Chen, L.; Rimm, D.L. Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixido, C.; Vilarino, N.; Reyes, R.; Reguart, N. PD-L1 expression testing in non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918763493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Yu, X.; Flores-Villanueva, P.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Young, K.H.; Ma, X.; et al. Targeting PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer using CAR T cells. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Mao, Y.; He, H.; Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. PD-L1 chimeric costimulatory receptor improves the efficacy of CAR-T cells for PD-L1-positive solid tumors and reduces toxicity in vivo. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Mei, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Current status and future perspectives. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ding, H.; Chen, S.; Jiang, G.; Huang, X. Inhalable nanovesicles loaded with a STING agonist enhance CAR-T cell activity against solid tumors in the lung. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Gadd, M.E.; Qie, Y.; Otamendi-Lopez, A.; Sanchez-Garavito, J.E.; Brooks, M.M.; Ulloa Navas, M.J.; Hundal, T.; Li, S.; Jones, V.K.; et al. Solid cancer-directed CAR T cell therapy that attacks both tumor and immunosuppressive cells via targeting PD-L1. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2024, 32, 200891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, C.; Xia, S.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, H.; Fang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, B.; et al. Severe delayed pulmonary toxicity following PD-L1-specific CAR-T cell therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarstrom, S. The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: Structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1999, 9, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, J.H.; Hong, S.H.; Jeon, E.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Yoo Ie, R.; Park, J.G.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, H.C.; et al. Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen Levels and the Risk of Whole-body Metastatic Potential in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, N.; Okamoto, S.; Amaishi, Y.; Sato, E.; Seo, N.; Mineno, J.; Takesako, K.; Kato, T.; Shiku, H. Efficient tumor regression by adoptively transferred CEA-specific CAR-T cells associated with symptoms of mild cytokine release syndrome. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1211218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Shan, J.; Hong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Shen, J.; et al. Hypoxia-Responsive CAR-T Cells Exhibit Reduced Exhaustion and Enhanced Efficacy in Solid Tumors. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.I.; Bae, J.Y.; Hong, J.T.; Jo, S.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, T.D. Developing CAR-T/NK cells that target EphA2 for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1448438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D. Revolutionizing Lung Cancer Treatment: Innovative CRISPR-Cas9 Delivery Strategies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Potter, J.; Kumar, S.; Zou, Y.; Quintanilla, R.; Sridharan, M.; Carte, J.; Chen, W.; Roark, N.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Rapid and highly efficient mammalian cell engineering via Cas9 protein transfection. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 208, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodzka, A.; Knopik-Skrocka, A.; Kowalska, K.; Kurzawa, P.; Krzyzaniak, M.; Stencel, K.; Bryl, M. Molecular alterations of driver genes in non-small cell lung cancer: From diagnostics to targeted therapy. EXCLI J. 2023, 22, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guernet, A.; Mungamuri, S.K.; Cartier, D.; Sachidanandam, R.; Jayaprakash, A.; Adriouch, S.; Vezain, M.; Charbonnier, F.; Rohkin, G.; Coutant, S.; et al. CRISPR-Barcoding for Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity Modeling and Functional Analysis of Oncogenic Driver Mutations. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Alteration | Frequency | Targeted Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | Exon 19 del, L858R, T790M | ~15–35% (Asian > Caucasian) | Osimertinib, gefitinib, erlotinib |
| KRAS | G12C and others | ~25–30% | Sotorasib (for G12C) |
| ALK | EML4-ALK fusion | ~3–7% | Alectinib, lorlatinib, crizotinib |
| ROS1 | Fusion | ~1–2% | Crizotinib, entrectinib |
| BRAF | V600E mutation | ~1–3% | Dabrafenib + trametinib |
| MET | Exon 14 skipping, amplification | ~3% | Capmatinib, tepotinib |
| HER2 | Exon 20 insertion | ~1–3% | Trastuzumab deruxtecan |
| RET | Fusions | ~1–2% | Selpercatinib, pralsetinib |
| NTRK | Gene fusions | Rare (<1%) | Larotrectinib, entrectin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziółkowska-Suchanek, I.; Rozwadowska, N. Advancements in Gene Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Prospects. Genes 2025, 16, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050569
Ziółkowska-Suchanek I, Rozwadowska N. Advancements in Gene Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Prospects. Genes. 2025; 16(5):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050569
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiółkowska-Suchanek, Iwona, and Natalia Rozwadowska. 2025. "Advancements in Gene Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Prospects" Genes 16, no. 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050569
APA StyleZiółkowska-Suchanek, I., & Rozwadowska, N. (2025). Advancements in Gene Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Prospects. Genes, 16(5), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050569





