Plastome Sequences Uncover the Korean Endemic Species Polygonatum grandicaule (Asparagaceae) as Part of the P. odoratum Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling, DNA Extraction, and Plastome Assembly
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3. Nucleotide Diversity (Pi), Repeat Analyses, and Molecular Diagnostic Characteristics
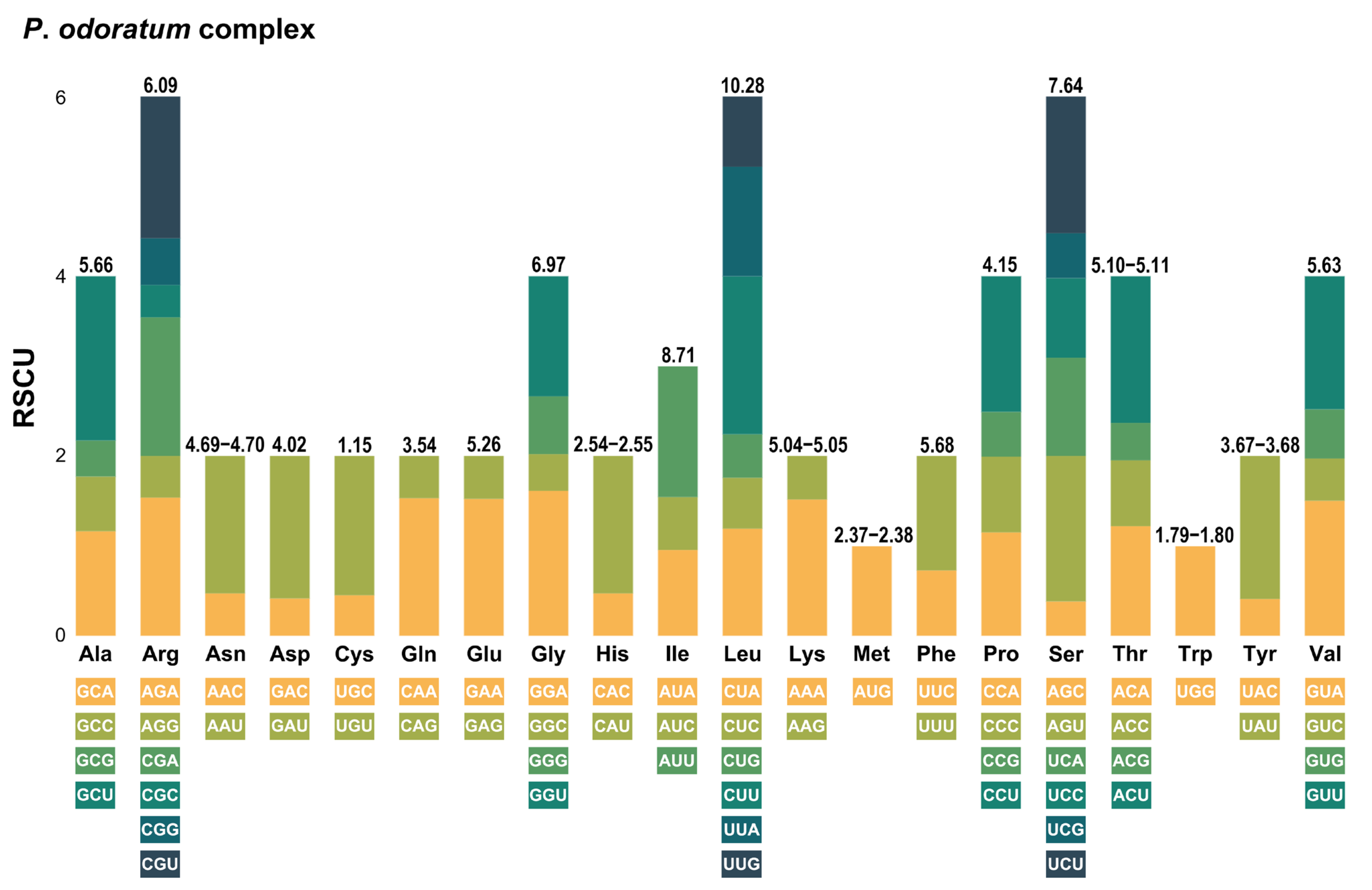
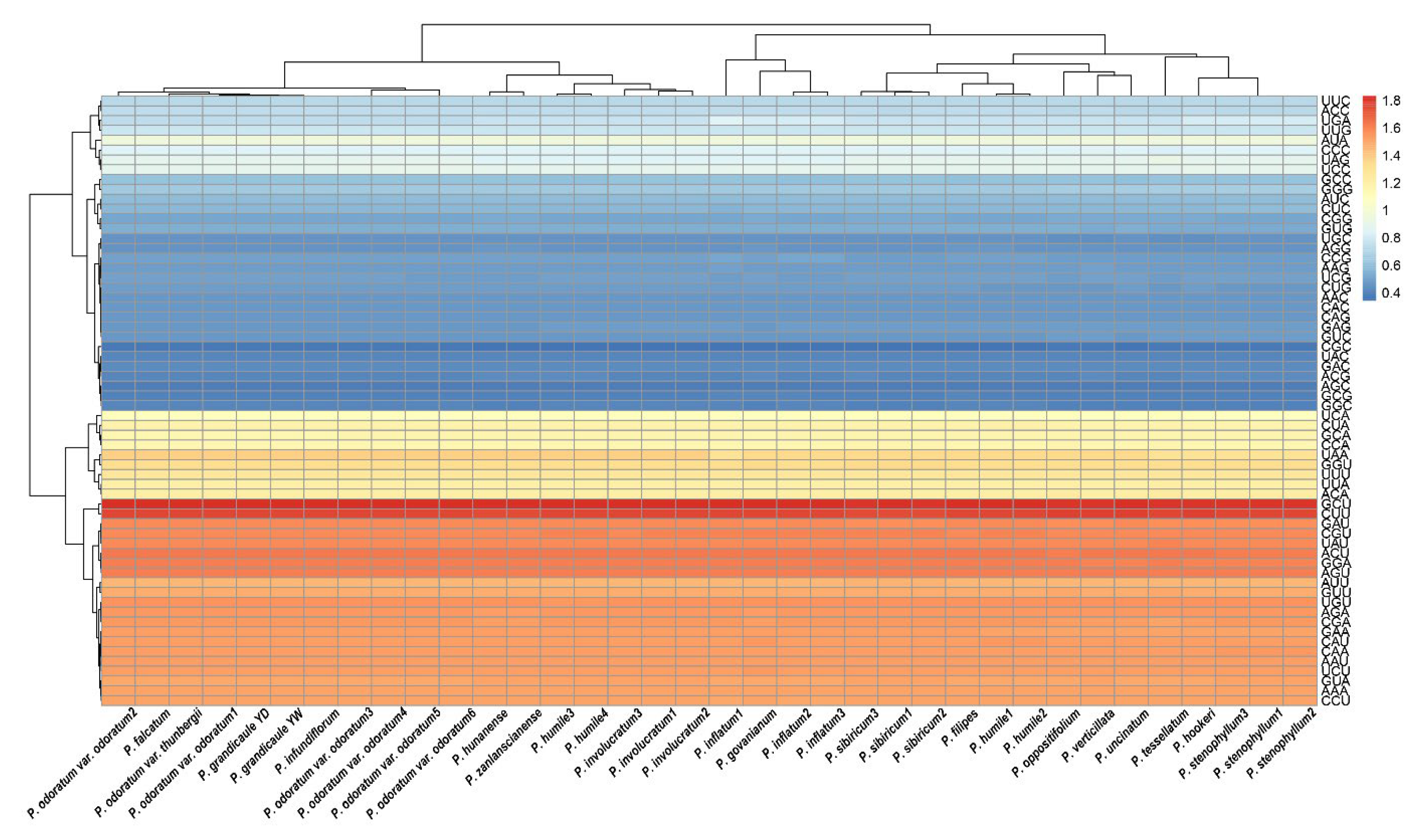
2.4. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage (RSCU) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plastome Characteristics
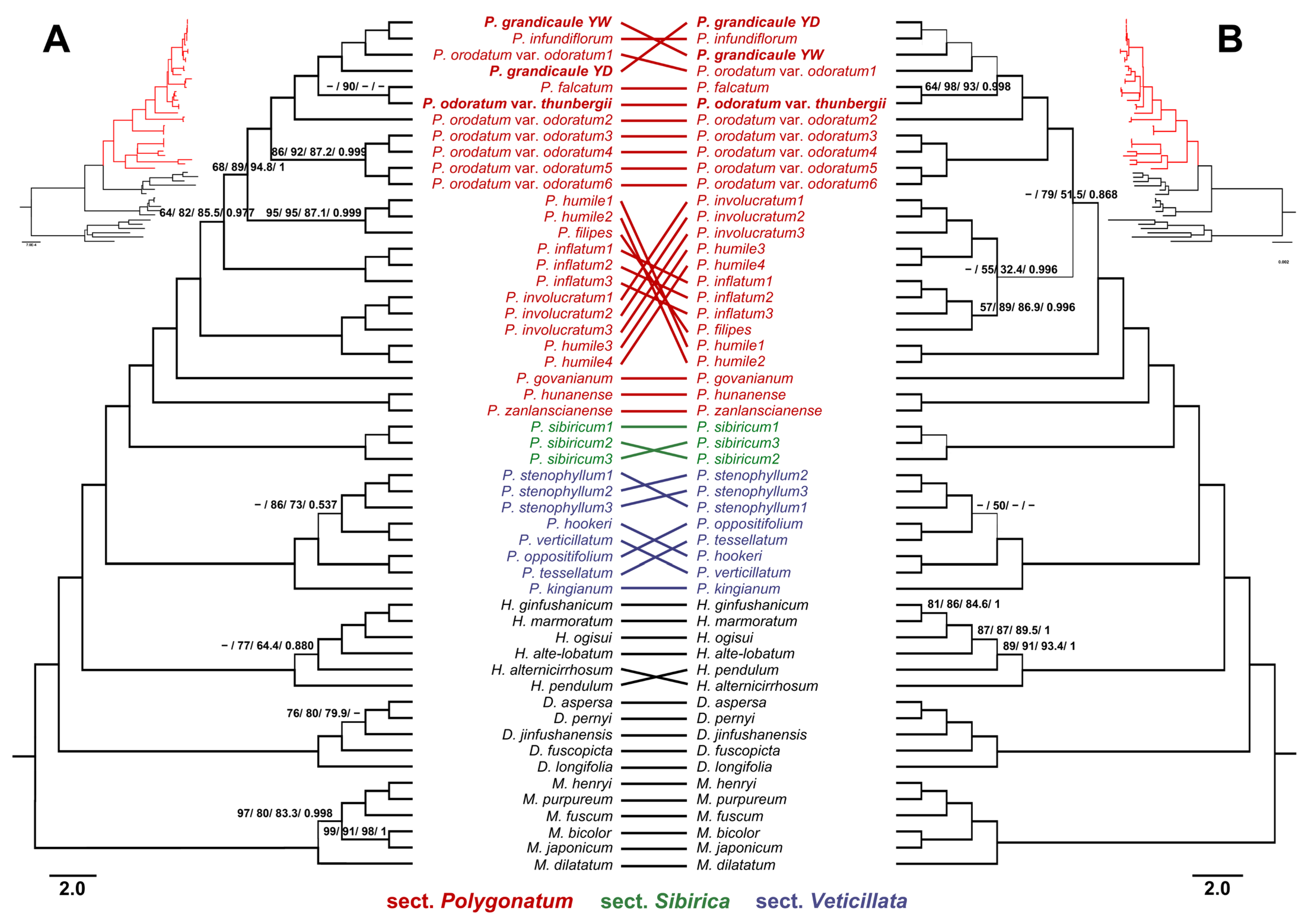
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships
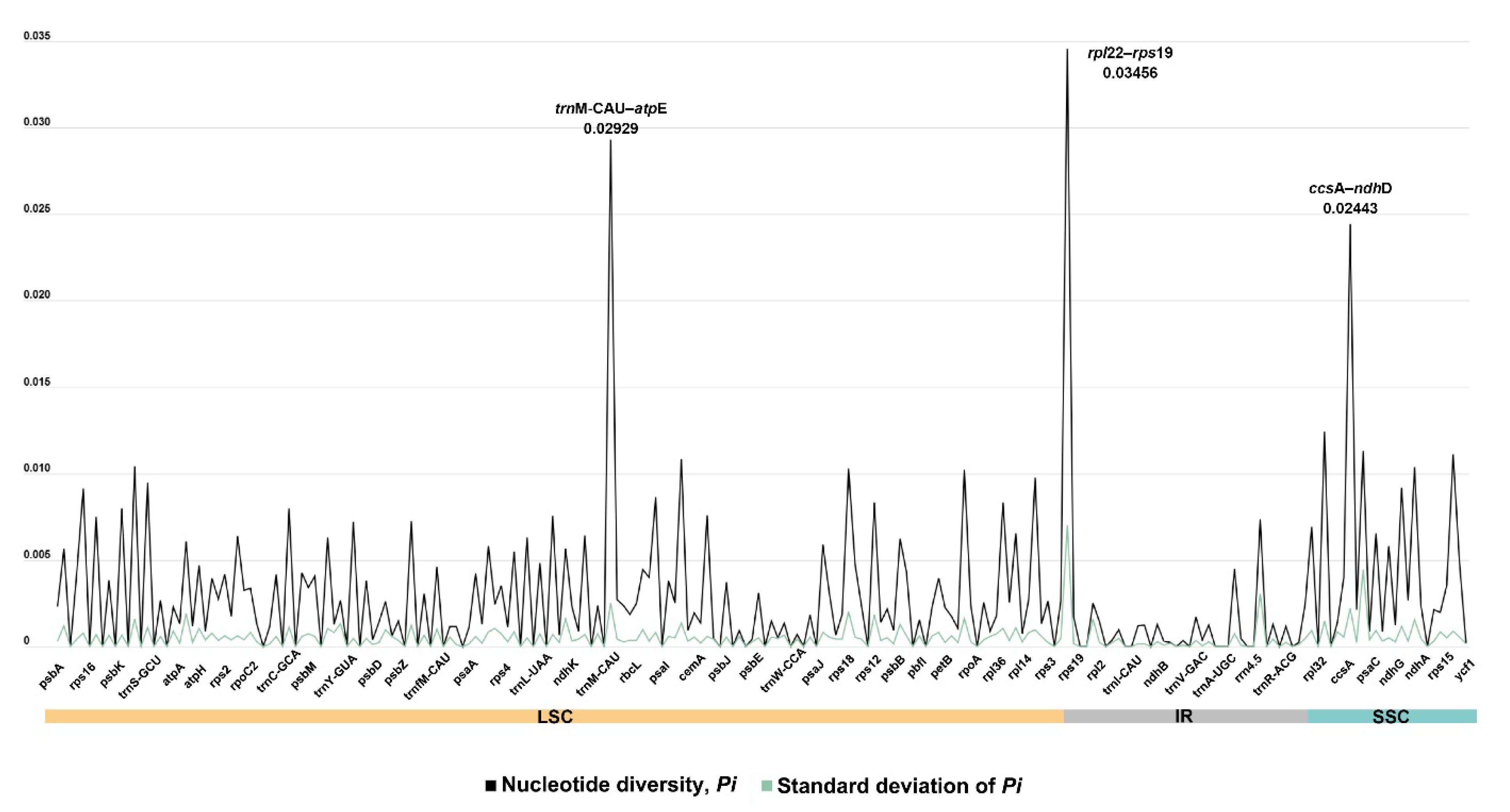
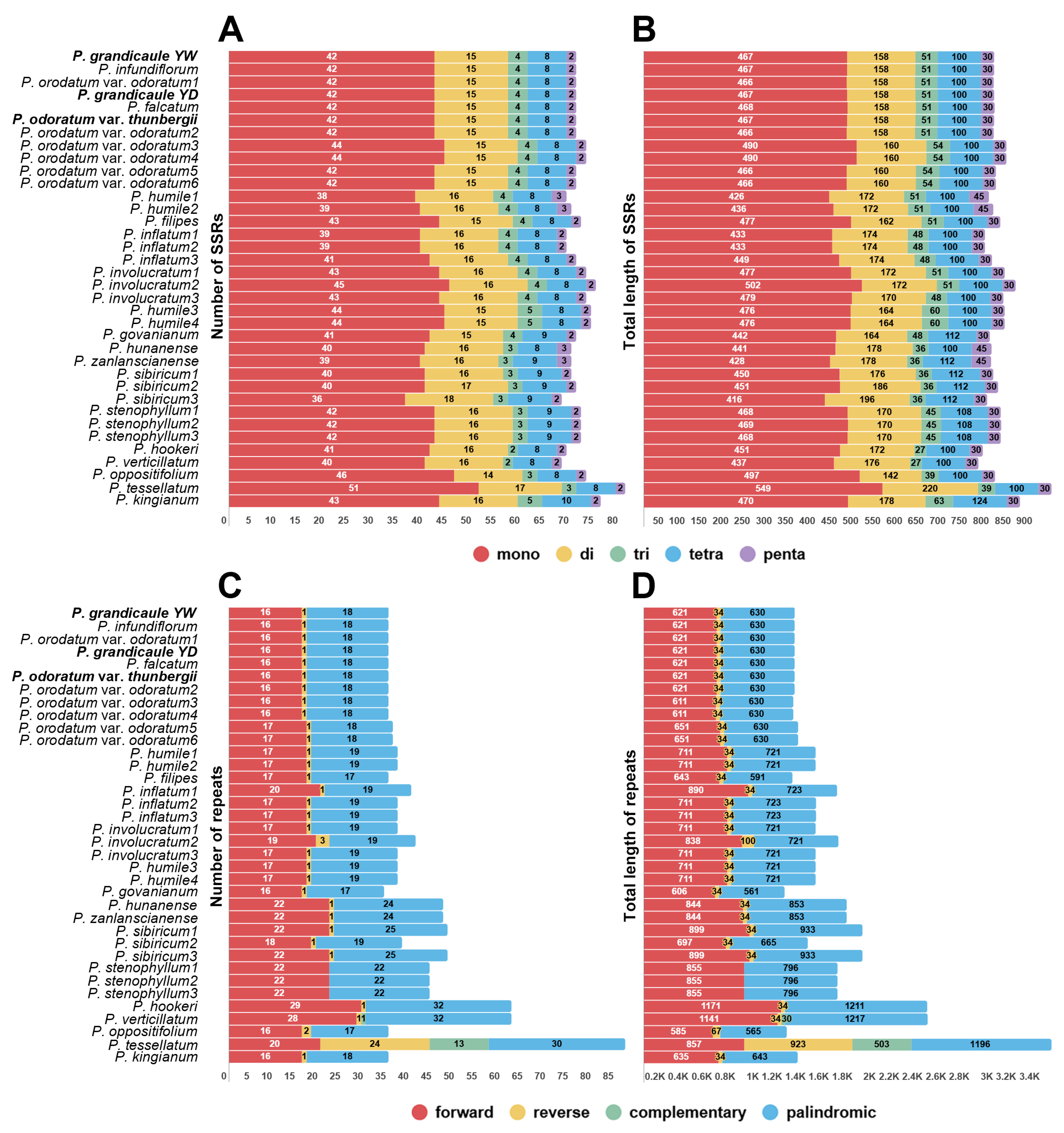
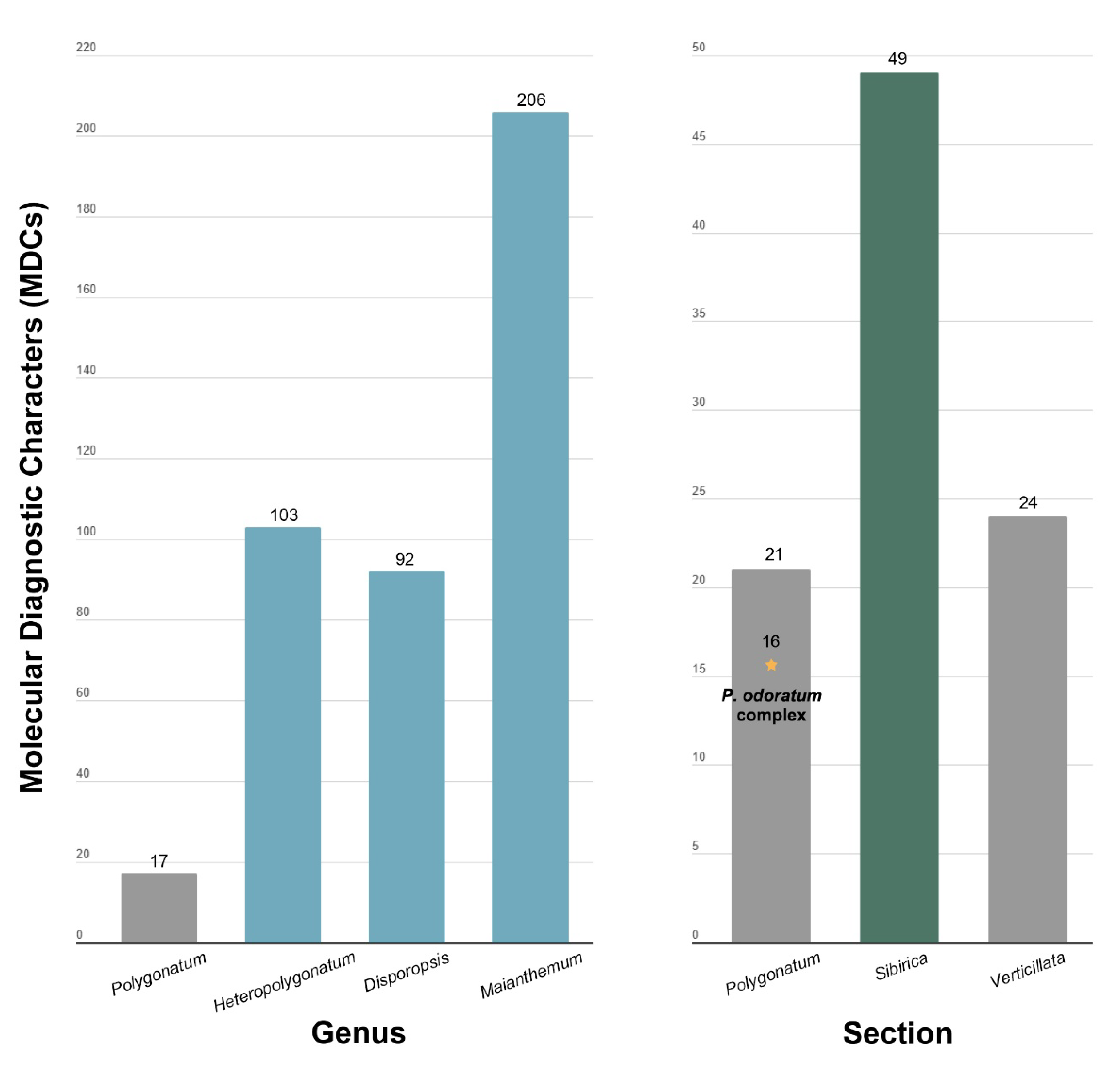
3.3. Comparative Plastome Sequences Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. The Characteristics of Plastomes in Polygonatum
4.2. Taxonomic Ambiguity of Korean Endemic Polygonatum: A Phylogenetic Reassessment
4.3. Comparative Analyses and Putative Markers for Polygonatum
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duminil, J.; Di Michele, M. Plant species delimitation: A comparison of morphological and molecular markers. Plant Biosyst. 2009, 143, 528–542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Guo, X.; Niu, J.; Duojie, D.; Li, X.; Opgenoorth, L.; Zou, J. Molecular phylogeography and evolutionary history of the endemic species Corydalis hendersonii (Papaveraceae) on the Tibetan Plateau inferred from chloroplast DNA and ITS sequence variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 436. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, M.; Jaén-Molina, R.; Marrero, Á.; Mesa, R.; Díaz-Pérez, A.; Caujapé-Castells, J. New molecular evidence for Canarian endemic Ruta (Rutaceae: Ruteae) reveals a complex evolutionary history and overlooked diversification processes. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 201, 80–99. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Da Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Fu, C.-N.; Mo, Z.-Q.; Möller, M.; Yang, J.-B.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Li, D.-Z.; Gao, L.-M. Testing the complete plastome for species discrimination, cryptic species discovery and phylogenetic resolution in Cephalotaxus (Cephalotaxaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 768810. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Qin, K.; Li, T.; Qu, T.; Luo, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Li, P.; Fu, Z. A new species, Aster yaoshanensis (Asteracae, Astereae), from Guangxi (China), based on morphology and molecular phylogenetic data. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1367917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.Y.; Hyun-Do, J.; Chang, K.S.; Choi, H.J.; Son, D.C. A checklist of endemic plants on the Korean Peninsula II. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2023, 53, 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, C.G.; Oh, B.U.; Kim, Y.S. A new species of Polygonatum (Liliaceae) from Korea: P. infundiflorum. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 1998, 28, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, C.G.; Oh, B.U.; Kim, Y.S. A new species of Polygonatum from Korea; P. grandicaule. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 1998, 28, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Tamura, M.; Wu, Z.; Raven, P. Polygonatum mill. Flora China 2000, 24, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, W.S. The genera of Ruscaceae in the southeastern United States. Harv. Pap. Bot. 2003, 7, 93–149. [Google Scholar]
- Motohashi, N.; Zhang, G.-W.; Shirataki, Y. Functional bioactivity of Polygonatum species. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2003, 3, 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P.; Gao, W. The genus Polygonatum: A review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Rauf, A. Phytochemistry of genus Polygonatum: A review. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 3, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J. Chemical constituents of the genus Polygonatum and their role in medicinal treatment. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1934578X1501000439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Nie, Z.-L.; Deng, T.; Wen, J.; Yang, Y.-P. Phylogenetics and evolution of phyllotaxy in the Solomon’s seal genus Polygonatum (Asparagaceae: Polygonateae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 176, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.-G. A taxonomic review of Korean Polygonatum (Ruscaceae). Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2002, 32, 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubna; Asaf, S.; Khan, I.; Jan, R.; Asif, S.; Bilal, S.; Kim, K.-M.; AL-Harrasi, A. Genetic characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the Nigella sativa (black seed) plastome. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Zhang, J.Q. Plastomic data shed new light on the phylogeny, biogeography, and character evolution of the family Crassulaceae. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, J. Phylogenomic analysis and development of molecular markers for the determination of twelve plum cultivars (Prunus, Rosaceae). BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.-L.; Mo, Z.-Q.; Xiang, X.-G.; Milne, R.I.; Jacquemyn, H.; Burgess, K.S.; Sun, Y.-N.; Yan, H.; Qiu, L.; Yang, B.-Y. Plastome phylogenomics and morphological traits analyses provide new insights into the phylogenetic position, species delimitation and speciation of Triplostegia (Caprifoliaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Hao, G.; Zhou, R.; Luo, D.; Cao, K.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X. Insights into the phylogenetic relationships and species boundaries of the Myricaria squamosa complex (Tamaricaceae) based on the complete chloroplast genome. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruhlman, T.A.; Jansen, R.K. The plastid genomes of flowering plants. In Chloroplast Biotechnology: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Floden, A.; Schilling, E. Using phylogenomics to reconstruct phylogenetic relationships within tribe Polygonateae (Asparagaceae), with a special focus on Polygonatum. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 129, 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Fan, Q.; Liao, W. Plastid genome sequencing, identification of nuclear SNP markers, and quality assessment of medicinal rhizomatous herb Polygonatum odoratum (Asparagaceae) cultivars. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 7660–7676. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Qian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, B.; Chen, S.; Yang, F.; Xu, Z.; Duan, B. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome and new insights into phylogenetic relationships of Polygonatum and tribe Polygonateae. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 882189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Jin, R.; Chen, H.; Comes, H.P. Out of the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains: Phylogenomics, biogeography and diversification of Polygonatum Mill. (Asparagaceae) in the Northern Hemisphere. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2022, 169, 107431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Jiang, H.; Wanga, V.O.; Dong, X.; Hu, G. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of six Polygonatum species (Asparagaceae). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Landis, J.B.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, N.; Luo, Y.; Liu, H. Phylogeny and evolution of Asparagaceae subfamily Nolinoideae: New insights from plastid phylogenomics. Ann. Bot. 2023, 131, 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Dong, S.; Gong, Q.; Xu, Q.; Ge, Y. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of four polygonatum species insights into DNA barcoding, evolution, and phylogeny. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Ha, Y.-H.; Son, D.C.; Kim, S.-C. First record of the complete chloroplast genome of Polygonatum infundiflorum (Asparagaceae), a Korean endemic species. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2023, 8, 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J. DNA protocols for plants. In Molecular Techniques in Taxonomy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq–versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA Genes in Genomic Sequences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Poczai, P.; Hyvönen, J.; Tang, J.; Amiryousefi, A. Chloroplot: An online program for the versatile plotting of organelle genomes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 576124. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.-Q.; Zhang, M.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Nie, Z.-L.; Wen, J.; Meng, Y. Phylogenomics and divergence pattern of Polygonatum (Asparagaceae: Polygonateae) in the north temperate region. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2024, 190, 107962. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D. PAUP* 4.0 b. 4a. In Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony* (and Other Methods); Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; FigTree. Tree Figure Drawing Tool. 2009. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merckelbach, L.M.; Borges, L.M. Make every species count: Fastachar software for rapid determination of molecular diagnostic characters to describe species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. DAMBE7: New and improved tools for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.-X.; Chang, X.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Qi, Z.-C.; Wang, R.-H.; Yan, X.-L.; Li, P. Evolutionary comparison of the complete chloroplast genomes in Convallaria species and phylogenetic study of asparagaceae. Genes 2022, 13, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Choi, M.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, S.-C. Plastome characterization and phylogenomic analysis yield new insights into the evolutionary relationships among the species of the subgenus Bryocles (Hosta; Asparagaceae) in East Asia. Plants 2021, 10, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnett, G.J.; Könyves, K.; Bilsborrow, J.; David, J.; Culham, A. The complete plastome of Hyacinthoides non-scripta (L.) Chouard ex Rothm.(Asparagaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, R.S.; Olmstead, R.G.; Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Lao, N.T.; Heggie, L.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C.; Morden, C.W. Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, E.; Skuza, L. Horizontal gene transfer involving chloroplasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. A phylogenetic study of Chinese Polygonatum (Polygonateae, Asparagaceae). Nord. J. Bot. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Yuan, H.; Xiang-Yun, Z. Report on karyotypes of 6 species in 4 genera of Polygonateae from China. J. Syst. Evol. 1990, 28, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, M.N. Biosystematic studies on the genus Polygonatum (Asparagaceae) V. Taxonomic revision of species in Japan. Acta Phytotaxon. Et Geobot. 2008, 59, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.K.; Jang, C.G.; Oh, B.U.; Kim, Y.S. A cytotaxonomic study of genus Polygonatum in Korea. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 1998, 28, 187–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, A.; Glick, L.; Abadi, S.; Einhorn, M.; Kopelman, N.M.; Salman-Minkov, A.; Mayzel, J.; Chay, O.; Mayrose, I. The Chromosome Counts Database (CCDB)—A community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.G.; Kim, Y.S. The palynological study on the Korean Polygonatum (Liliaceae). Korean J. Plant Taxon. 1999, 29, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Liu, Y.J.; Xia, Q.P.; Bahadur, S.; Hussain, A.; Shao, J.W.; Shuaib, M. Pollen micromorphology of eastern Chinese Polygonatum and its role in taxonomy by using scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, W.; Su, H.; Chen, Q. Pollen Morphological Characteristics of 46 Germplasm Resources of Polygonatum and Its Taxonomic Implications. Plants 2024, 13, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Seo, J.W.; Byeon, J.H.; Ahn, Y.S.; Cha, S.W.; Cho, J.H. Morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Polygonatum species based on chloroplast DNA sequences. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2014, 22, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.Y.; Won, H.S.; Lee, S.R. Species delimitation in the Polygonatum odoratum complex (Asparagaceae) based on phylogenomic and morphometric data. Taxon 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Wang, T.; Tan, J.; Liu, C.; Yan, H. Plastid genome comparison and phylogenetic analyses of the Chinese group of medicinal species and related taxa within Asparagus genus. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1508898. [Google Scholar]
- Celiński, K.; Kijak, H.; Wiland-Szymańska, J. Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic inference of the Canary Islands Dragon Tree (Dracaena draco L.). Forests 2020, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, L.; Qu, X. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of Asparagus meioclados Levl. and Asparagus munitus Wang et SC Chen plastomes and utility of plastomes mutational hotspots. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15622. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kim, S.-C. Hosta clausa (Asparagaceae) in East Asia: Intraspecific chloroplast genome variation and its phylogenomic implications. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317884. [Google Scholar]

| Taxa | Length and G+C Content | GenBank Accession No. | Voucher (Accession) | |||
| LSC bp (G+C%) | SSC bp (G+C%) | IR bp (G+C%) | Total bp (G+C%) | |||
| P. grandicaule Y.S.Kim, B.U.Oh & C.G.Jang (Yeongdong, Chungcheongbuk-do) | 83,527 (35.8) | 18,457 (31.6) | 26,297 (43.0) | 154,578 (37.7) | PV199344 | JH220610014 |
| P. grandicaule Y.S.Kim, B.U.Oh & C.G.Jang (Yeongwol, Gangwon-do) | 83,528 (35.8) | 18,457 (31.6) | 26,297 (43.0) | 154,579 (37.7) | PV199345 | JH220617027 |
| Polygonatum odoratum var. thunbergii (C.Morren & Decne.) H.Hara (Danyang, Chungcheongbuk-do) | 83,527 (35.8) | 18,457 (31.6) | 26,297 (43.0) | 154,578 (37.7) | PV199346 | JH220617013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Plastome Sequences Uncover the Korean Endemic Species Polygonatum grandicaule (Asparagaceae) as Part of the P. odoratum Complex. Genes 2025, 16, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040398
Jung J, Kim H-J, Kim J-H. Plastome Sequences Uncover the Korean Endemic Species Polygonatum grandicaule (Asparagaceae) as Part of the P. odoratum Complex. Genes. 2025; 16(4):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040398
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Joonhyung, Hyuk-Jin Kim, and Joo-Hwan Kim. 2025. "Plastome Sequences Uncover the Korean Endemic Species Polygonatum grandicaule (Asparagaceae) as Part of the P. odoratum Complex" Genes 16, no. 4: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040398
APA StyleJung, J., Kim, H.-J., & Kim, J.-H. (2025). Plastome Sequences Uncover the Korean Endemic Species Polygonatum grandicaule (Asparagaceae) as Part of the P. odoratum Complex. Genes, 16(4), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040398







