Multi-Omics Analysis of Survival-Related Splicing Factors and Identifies CRNKL1 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. RNA-Sequencing
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. siRNA Synthesis
2.5. Cell Transfection
2.6. RNA Isolation, RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.9. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.10. Cell Proliferation Assays (CCK-8)
2.11. Colony Formation Experiment
2.12. Sphere Formation Experiment
2.13. In Vitro Migration and Invasion Assays
2.14. Wound Healing Assays
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
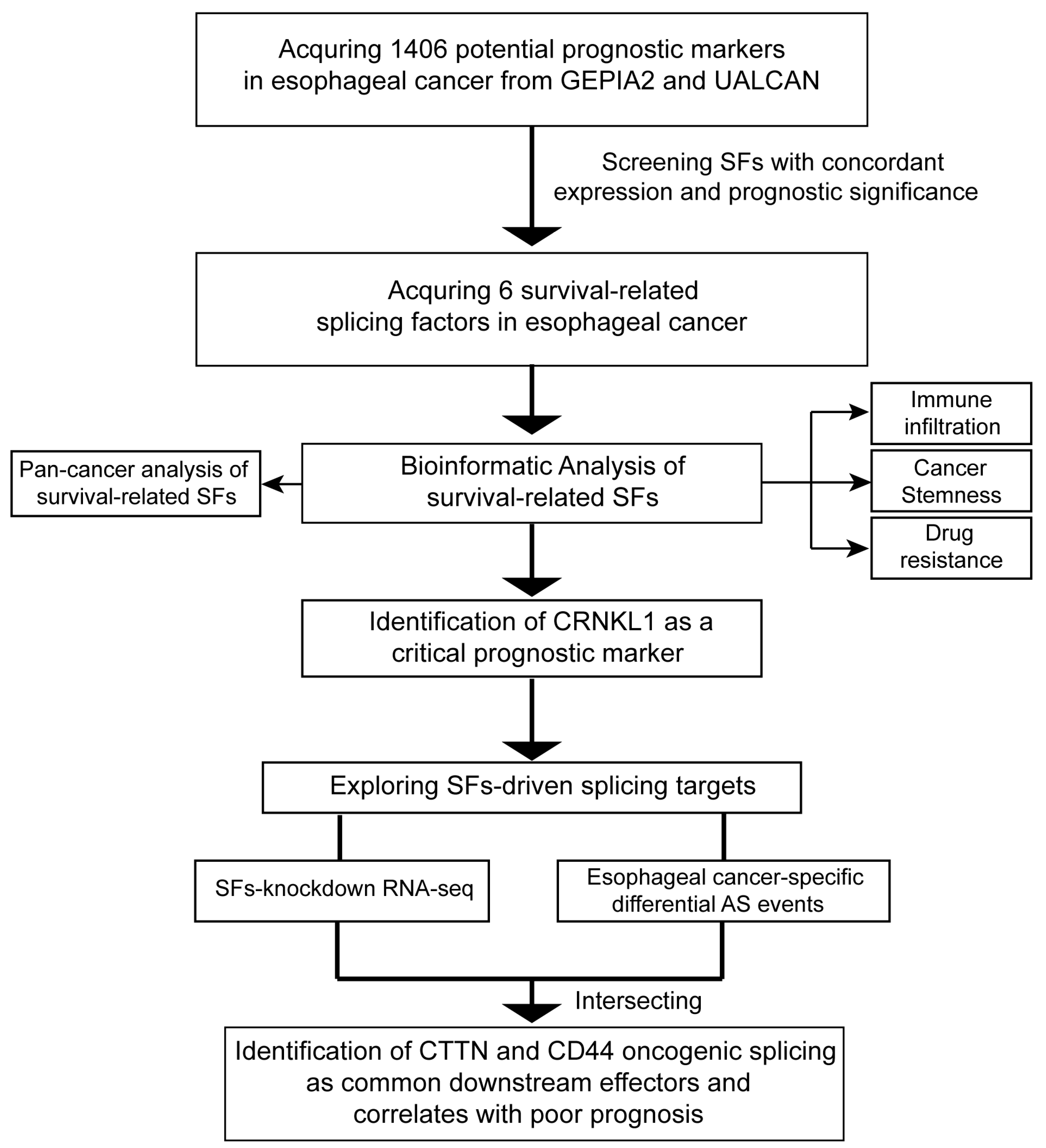
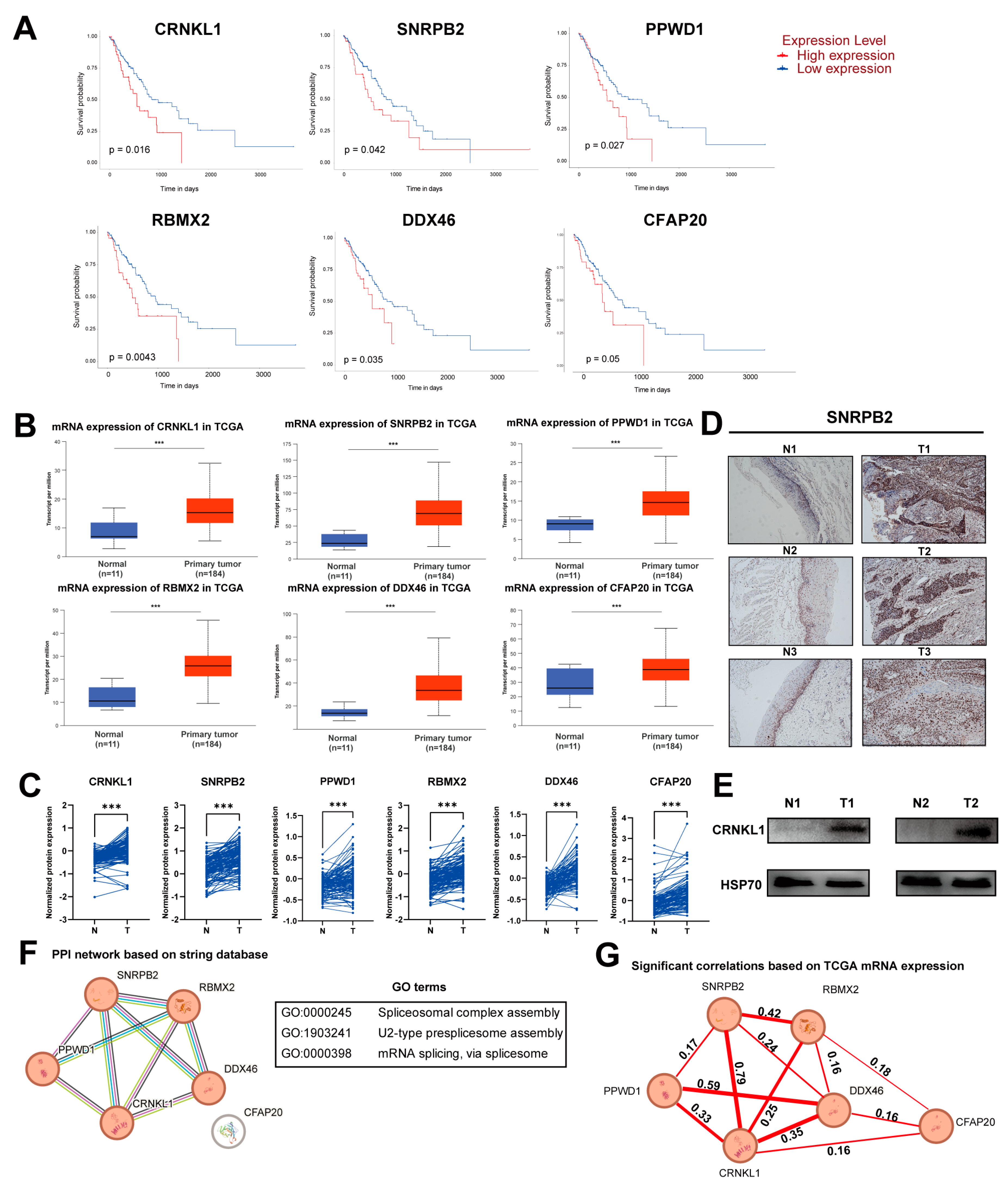
3.1. Identification of Survival-Related SFs in Esophageal Cancer
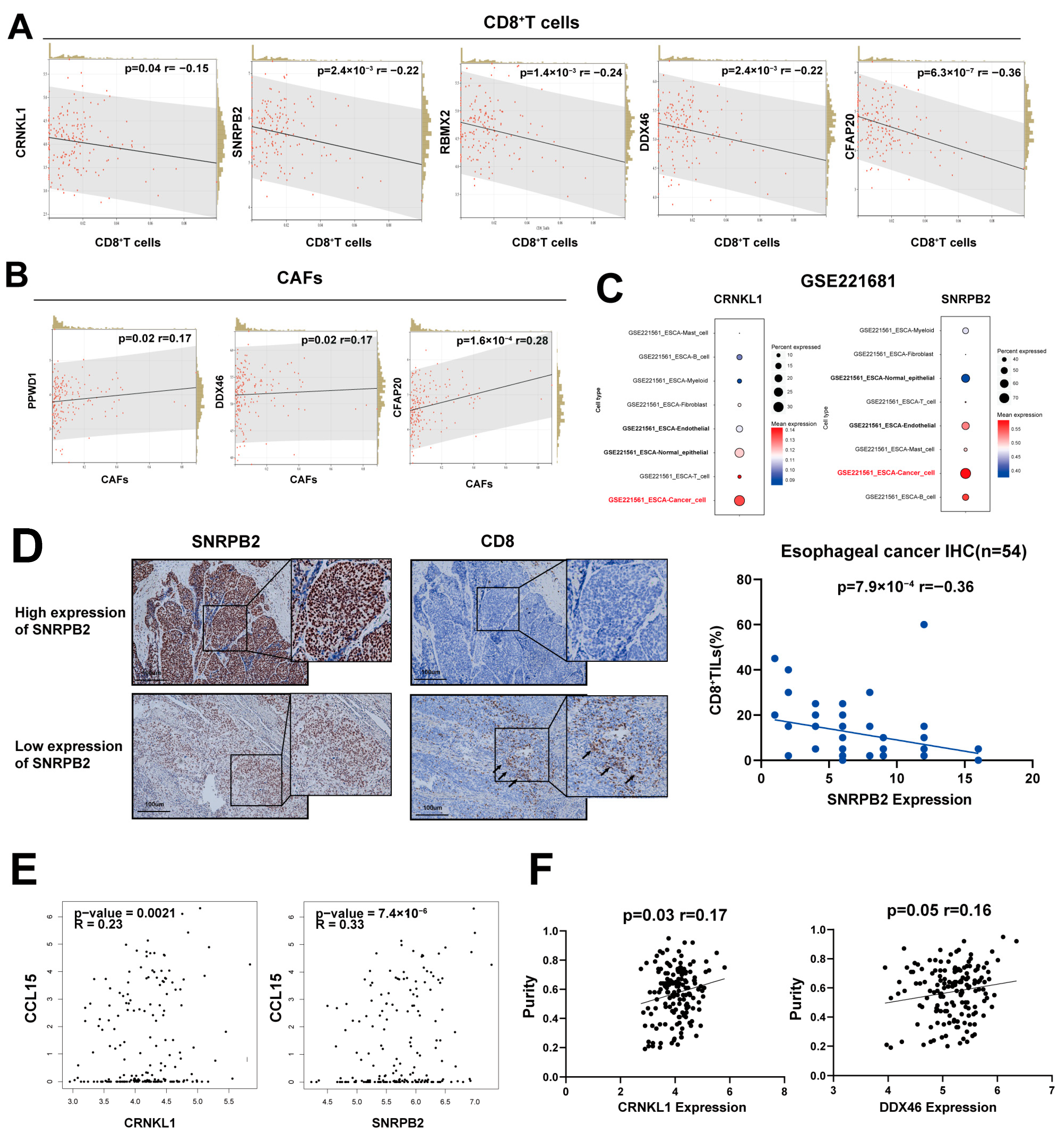
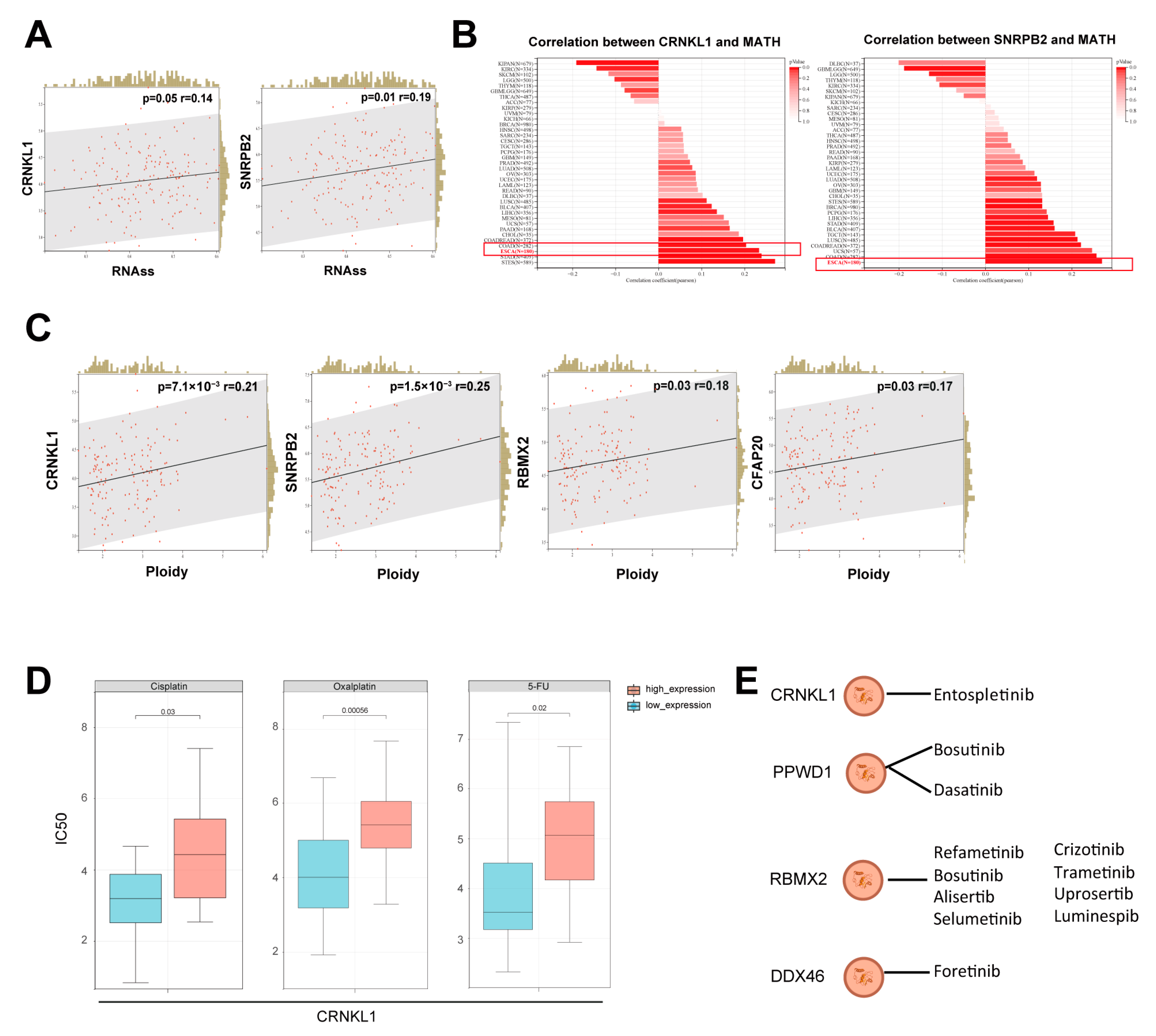
3.2. Survival-Related SFs Correlate with Immune Infiltration, Cancer Stemness, and Drug Resistance in Esophageal Cancer
3.3. Identification of CRNKL1 as a Prognostic Marker for Esophageal Cancer
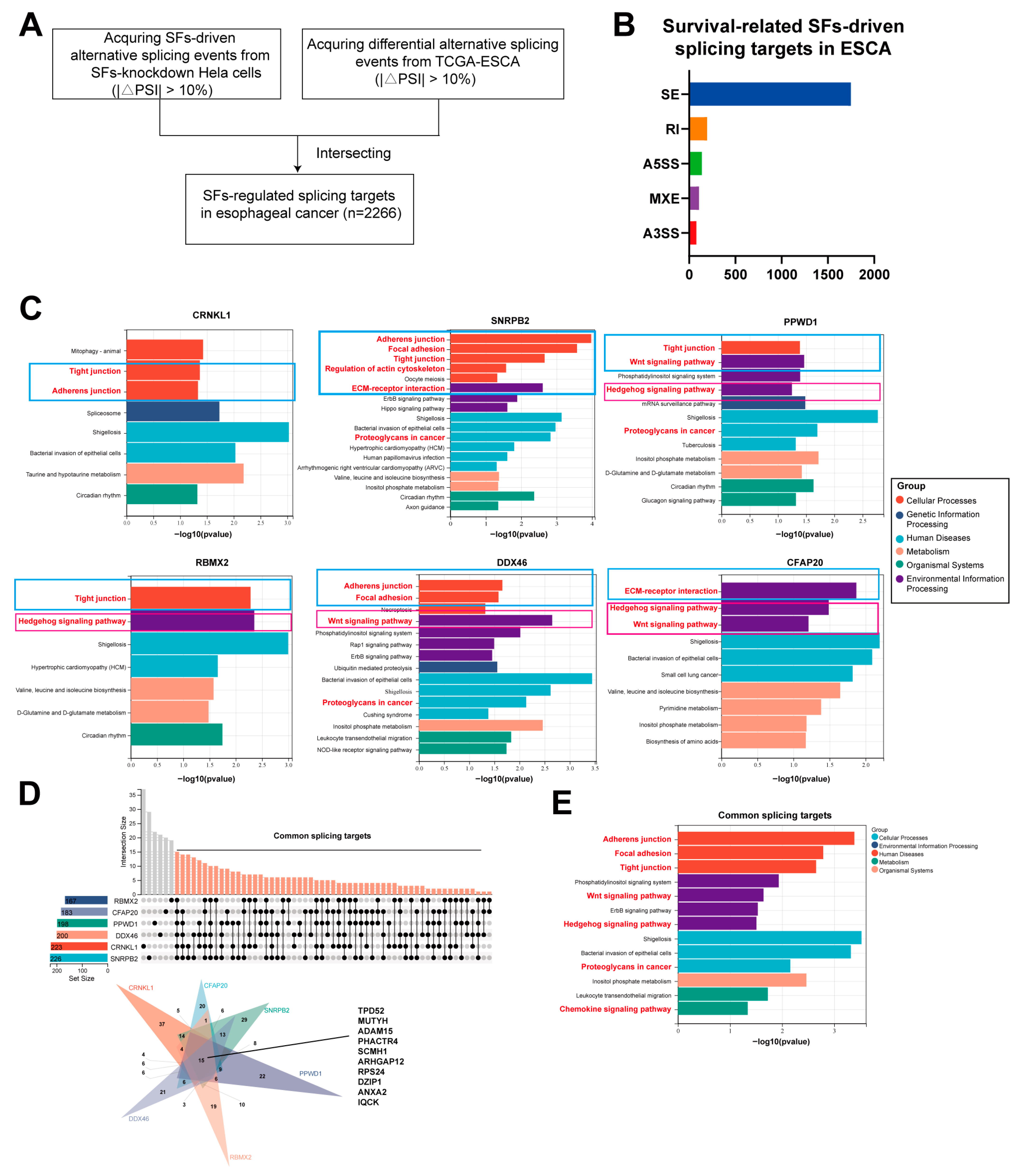
3.4. The Downstream Splicing Targets Regulated by Survival-Related SFs Are Highly Similar
3.5. Oncogenic AS Events, Including Cortactin and CD44, Act as Common Downstream Effectors of Survival-Related SFs
3.6. The Expression of Survival-Related Splicing Factors in Pan-Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESCA | Esophageal Cancer |
| SF | Splicing Factor |
| CRNKL1 | Crooked Neck Like 1 |
| CTTN | Cortactin |
| AS | Alternative Splicing |
| TME | The tumor microenvironment |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| CAF | Cancer-Associated Fibroblast |
| PSI | Percent spliced in |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| ONT | Oxford Nanopore Technologies |
| scRNA-seq | single-cell RNA sequencing analysis |
| RNAss | RNA based Stemness Scores |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit 8 |
| FAHSYSU | The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University |
| SYSUCC | Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Bai, M.; Dai, L.; Guo, X.; Leng, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, Z.; Mao, T.; Pang, Q.; Shen, L.; et al. CACA guidelines for holistic integrative management of esophageal carcinoma. Holist. Integr. Oncol. 2023, 2, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.-H.; Huang, R.-Q.; Liu, Y.-L.; Cao, S.-M.; Qian, C.-N. An increase in early cancer detection rates at a single cancer center: Experiences from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. Vis. Cancer Med. 2022, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Deboever, N.; Jones, C.M.; Yamashita, K.; Ajani, J.A.; Hofstetter, W.L. Advances in diagnosis and management of cancer of the esophagus. BMJ 2024, 385, e074962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ule, J.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing Regulatory Networks: Functions, Mechanisms, and Evolution. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 329–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnal, S.C.; Lopez-Oreja, I.; Valcarcel, J. Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer-implications for care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar]
- Frankiw, L.; Baltimore, D.; Li, G. Alternative mRNA splicing in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 675–687. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, R.F.; Abdel-Wahab, O. Dysregulation and therapeutic targeting of RNA splicing in cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 536–546. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.; Aifantis, I. RNA Splicing and Cancer. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 631–644. [Google Scholar]
- Malcovati, L.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Bowen, D.T.; Boultwood, J.; Della Porta, M.G.; Pascutto, C.; Travaglino, E.; Groves, M.J.; Godfrey, A.L.; Ambaglio, I.; et al. Clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2011, 118, 6239–6246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jbara, A.; Lin, K.T.; Stossel, C.; Siegfried, Z.; Shqerat, H.; Amar-Schwartz, A.; Elyada, E.; Mogilevsky, M.; Raitses-Gurevich, M.; Johnson, J.L.; et al. RBFOX2 modulates a metastatic signature of alternative splicing in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 617, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogalska, M.E.; Mancini, E.; Bonnal, S.; Gohr, A.; Dunyak, B.M.; Arecco, N.; Smith, P.G.; Vaillancourt, F.H.; Valcarcel, J. Transcriptome-wide splicing network reveals specialized regulatory functions of the core spliceosome. Science 2024, 386, 551–560. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Kutschera, E.; Adams, J.I.; Kadash-Edmondson, K.E.; Xing, Y. rMATS-turbo: An efficient and flexible computational tool for alternative splicing analysis of large-scale RNA-seq data. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 1083–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Wu, X.; Fan, R.; Yao, X.; Wu, H.; Duan, C.; Gong, Y.; et al. OncoSplicing 3.0: An updated database for identifying RBPs regulating alternative splicing events in cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1460–D1466. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.T.; Krainer, A.R. PSI-Sigma: A comprehensive splicing-detection method for short-read and long-read RNA-seq analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 5048–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Song, Z.; Zhong, X.; Huang, M.; Shen, D.; Gao, P.; Qian, X.; Wang, M.; He, X.; Wang, T.; et al. Sangerbox: A comprehensive, interaction-friendly clinical bioinformatics analysis platform. iMeta 2022, 1, e36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z.; Guan, Y.; Pan, D.; Hu, Z.; Sun, L.; Fu, Z.; et al. scCancerExplorer: A comprehensive database for interactively exploring single-cell multi-omics data of human pan-cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1526–D1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Epigenetically upregulated oncoprotein PLCE1 drives esophageal carcinoma angiogenesis and proliferation via activating the PI-PLCepsilon-NF-kappaB signaling pathway and VEGF-C/Bcl-2 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xie, L.; He, Y.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.X.; Bai, X.F.; Deng, D.X.; Xu, X.E.; Liao, L.D.; Lin, W.; et al. Large-scale and high-resolution mass spectrometry-based proteomics profiling defines molecular subtypes of esophageal cancer for therapeutic targeting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4961. [Google Scholar]
- Racle, J.; de Jonge, K.; Baumgaertner, P.; Speiser, D.E.; Gfeller, D. Simultaneous enumeration of cancer and immune cell types from bulk tumor gene expression data. Elife 2017, 6, e26476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malta, T.M.; Sokolov, A.; Gentles, A.J.; Burzykowski, T.; Poisson, L.; Weinstein, J.N.; Kaminska, B.; Huelsken, J.; Omberg, L.; Gevaert, O.; et al. Machine Learning Identifies Stemness Features Associated with Oncogenic Dedifferentiation. Cell 2018, 173, 338–354.e315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mroz, E.A.; Rocco, J.W. MATH, a novel measure of intratumor genetic heterogeneity, is high in poor-outcome classes of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral. Oncol. 2013, 49, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David, U.; Amon, A. Context is everything: Aneuploidy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yang, H.; Lin, A.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Carr, S.R.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. CPADS: A web tool for comprehensive pancancer analysis of drug sensitivity. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae237. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Schnoor, M.; Stradal, T.E.; Rottner, K. Cortactin: Cell Functions of A Multifaceted Actin-Binding Protein. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; You, B.; You, Y.; Gu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Lei, W.; et al. Stiffness promotes cell migration, invasion, and invadopodia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the WT-CTTN level. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 836–846. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Wyler, E.; Milek, M.; Grewe, B.; Kirchner, P.; Ekici, A.; Silva, A.B.O.V.; Jungnickl, D.; Full, F.; Thomas, M.; et al. CRNKL1 Is a Highly Selective Regulator of Intron-Retaining HIV-1 and Cellular mRNAs. mBio 2021, 12, e02520–e02525. [Google Scholar]
- Sciarrillo, R.; Wojtuszkiewicz, A.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Jansen, G.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Giovannetti, E.; Cloos, J. The role of alternative splicing in cancer: From oncogenesis to drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 53, 100728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Zhou, Z.; Huddleston, K.A.; Harrison, D.A.; Reed, R.; Coleman, T.A.; Rymond, B.C. Crooked neck is a component of the human spliceosome and implicated in the splicing process. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1576, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ji, Z.; Gao, F.; Wu, J.; Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zheng, R.; Wang, M. Cigarette smoking combined with genetic variation regulates the m6A methylation of CRNKL1 and is associated with bladder cancer risk. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar]
- van Rossum, A.G.S.H.; de Graaf, J.H.; Schuuring-Scholtes, E.; Kluin, P.M.; Fan, Y.-X.; Zhan, X.; Moolenaar, W.H.; Schuuring, E. Alternative Splicing of the Actin Binding Domain of Human Cortactin Affects Cell Migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45672–45679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Gu, M.; Cai, Z.K.; Zhao, H.; Sun, S.C.; Liu, C.; Zhan, M.; Chen, Y.B.; Wang, Z. TGF-beta1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness of prostate cancer cells by inducing PCBP1 degradation and alternative splicing of CD44. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 949–962. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.S.; Liu, Z.; Sweef, O.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Zeidler-Erdely, P.C.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z. Long noncoding RNA ABHD11-AS1 interacts with SART3 and regulates CD44 RNA alternative splicing to promote lung carcinogenesis. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ke, H.; Zhang, H.; Zou, L.; Yang, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiao, B. TDP43 promotes stemness of breast cancer stem cells through CD44 variant splicing isoforms. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 428. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, T.; Fan, M.; Zeng, Z.; Peng, L.; Qian, C.-N.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B. Multi-Omics Analysis of Survival-Related Splicing Factors and Identifies CRNKL1 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer. Genes 2025, 16, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040379
Gao T, Fan M, Zeng Z, Peng L, Qian C-N, Zhao X, Huang B. Multi-Omics Analysis of Survival-Related Splicing Factors and Identifies CRNKL1 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer. Genes. 2025; 16(4):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040379
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Tianrui, Meiling Fan, Zhongyuan Zeng, Lixia Peng, Chao-Nan Qian, Xia Zhao, and Bijun Huang. 2025. "Multi-Omics Analysis of Survival-Related Splicing Factors and Identifies CRNKL1 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer" Genes 16, no. 4: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040379
APA StyleGao, T., Fan, M., Zeng, Z., Peng, L., Qian, C.-N., Zhao, X., & Huang, B. (2025). Multi-Omics Analysis of Survival-Related Splicing Factors and Identifies CRNKL1 as a Therapeutic Target in Esophageal Cancer. Genes, 16(4), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040379





