SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Period, and Sample Collection
2.2. Quality Assurance
2.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.4. Complementary DNA (cDNA) Synthesis, DNA Library Preparation, and Whole Genome Sequencing
2.5. Sequence and Metadata Analysis
2.6. Computation of SNP Distances in Samples to the SARS-CoV-2 Reference Genome
2.7. Evolutionary Divergence Between Sequences and Overall Sequence Pairs
2.8. Phylogenetic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Genome Sequences
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Subjects
3.2. Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
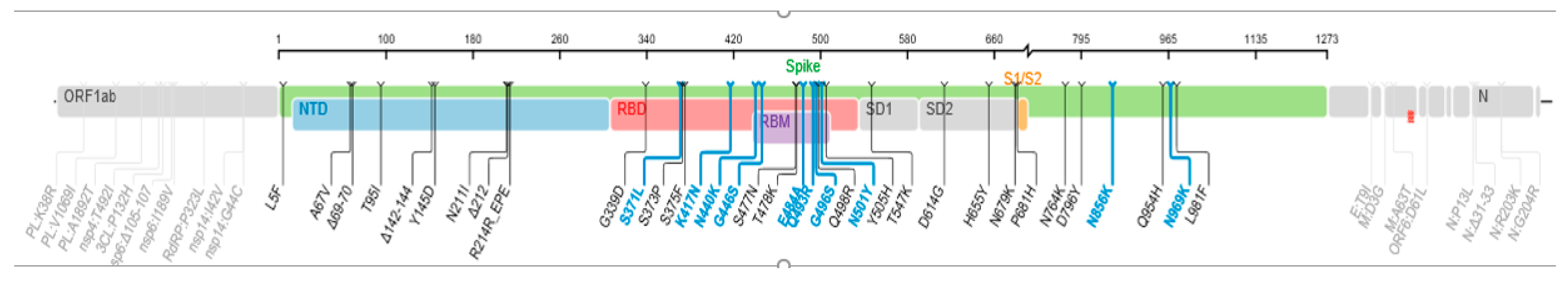
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Variants Identified
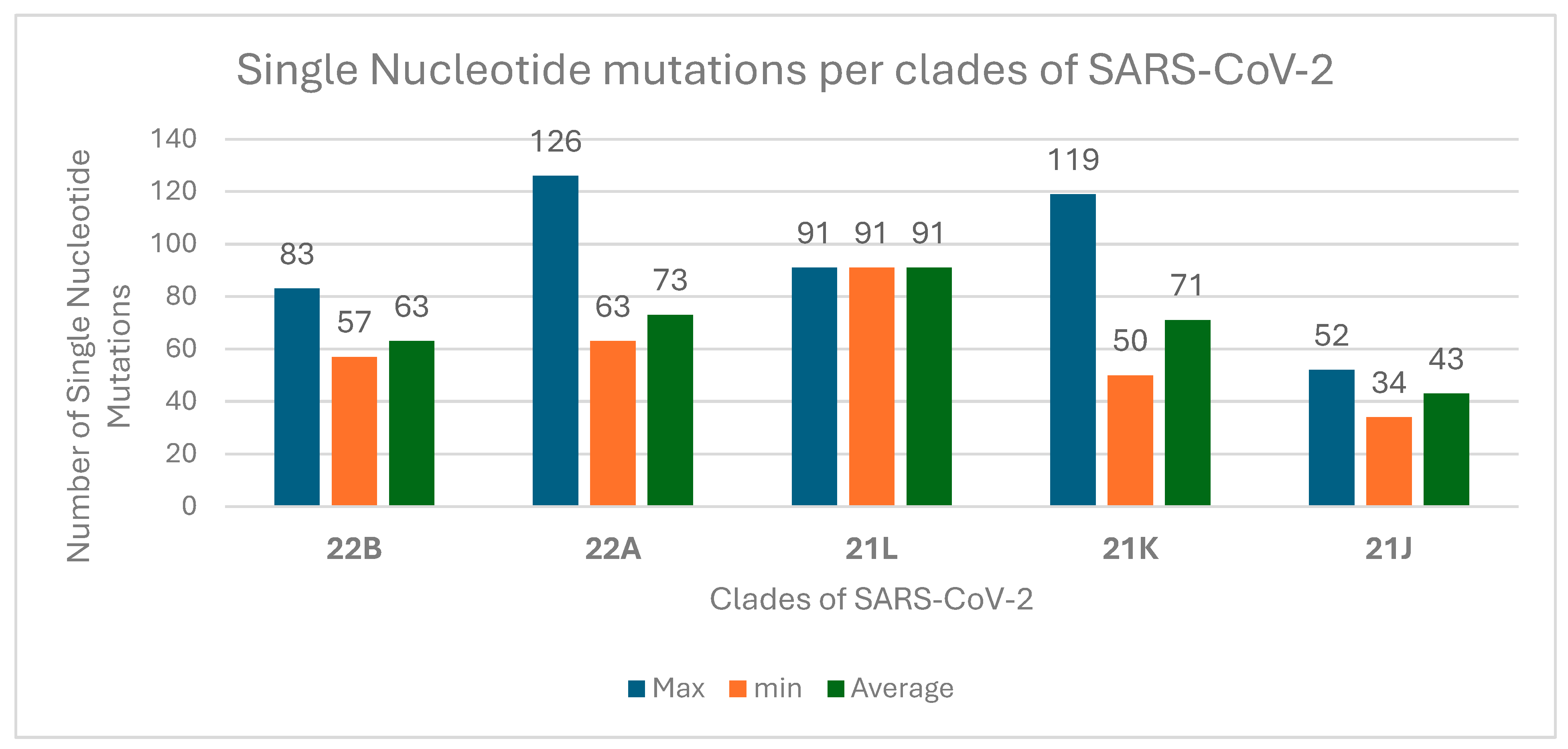
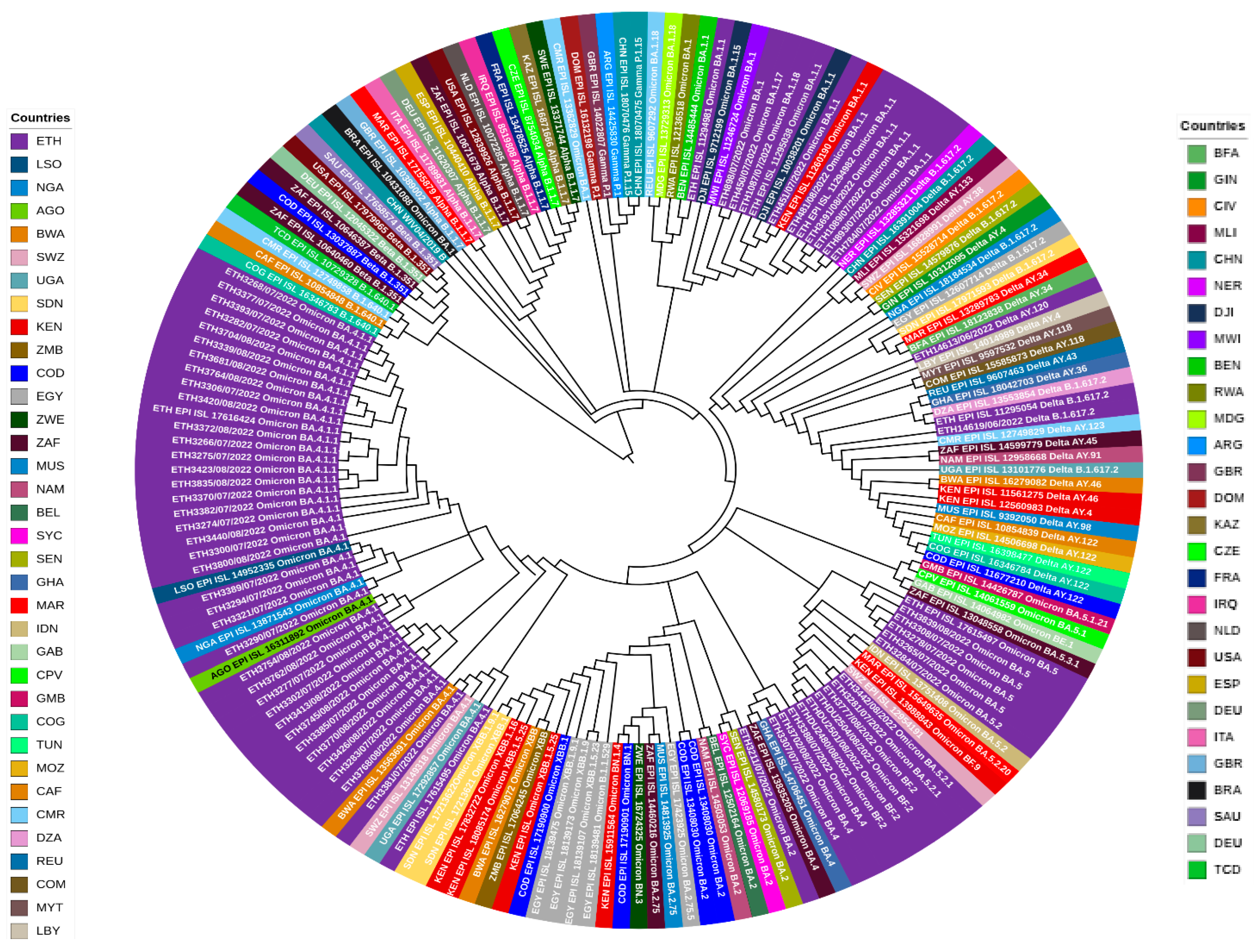
3.4. Evolutionary Divergence and Phylogenetic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Tao, Q.; Weaver, S.; Sanderford, M.; Caraballo-Ortiz, M.A.; Sharma, S.; Pond, S.L.K.; Miura, S. An Evolutionary Portrait of the Progenitor SARS-CoV-2 and Its Dominant Offshoots in COVID-19 Pandemic. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3046–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Infection Prevention Precautions. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/transmission-of-sars-cov-2-implications-for-infection-prevention-precautions (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Farhud, D.D.; Mojahed, N. SARS-CoV-2 Notable Mutations and Variants: A Review Article. Iran. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome Composition and Divergence of the Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.-F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.-W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryo-EM Structure of the SARS-Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein in Complex with Its Host Cell Receptor ACE2|PLOS Pathogens. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1007236 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Malone, B.; Urakova, N.; Snijder, E.J.; Campbell, E.A. Structures and functions of coronavirus replication–transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Africa CDC. Africa Identifies First Case of Coronavirus Disease: Statement by the Director of Africa CDC. Available online: https://africacdc.org/news-item/africa-identifies-first-case-of-coronavirus-disease-statement-by-the-director-of-africa-cdc/ (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethiopia Confirms First Coronavirus Case. Available online: https://www.aa.com.tr/en/africa/ethiopia-confirms-first-coronavirus-case/1765130 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Ethiopia COVID—Coronavirus Statistics—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/ethiopia/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Gudina, E.K.; Ali, S.; Girma, E.; Gize, A.; Tegene, B.; Hundie, G.B.; Sime, W.T.; Ambachew, R.; Gebreyohanns, A.; Bekele, M.; et al. Seroepidemiology and model-based prediction of SARS-CoV-2 in Ethiopia: Longitudinal cohort study among front-line hospital workers and communities. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkt, S.; Ali, S.; Gudina, E.K.; Adissu, W.; Gize, A.; Muenchhoff, M.; Graf, A.; Krebs, S.; Elsbernd, K.; Kisch, R.; et al. Long-term monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and variants in Ethiopia provides prediction for immunity and cross-immunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, R.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Tegally, H.; Scheepers, C.; Althaus, C.L.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Bester, P.A.; Boni, M.F.; Chand, M.; et al. Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in southern Africa. Nature 2022, 603, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, A.; Tshiabuila, D.; Van Wyk, S.; Tesfaye, A.; Mboowa, G.; Oyola, S.O.; Tesema, S.K.; Baxter, C.; Martin, D.; Lessells, R.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in Ethiopia, 2020–2022. Genes 2023, 14, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisay, A.; Abera, A.; Dufera, B.; Endrias, T.; Tasew, G.; Tesfaye, A.; Hartnack, S.; Beyene, D.; Desta, A.F. Diagnostic accuracy of three commercially available one step RT-PCR assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in resource limited settings. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioer Technology Introduction. Available online: https://conference.medgenetics.ru/upload/Bioer%20Technology%20Product%20Intro-711_%D0%A0%D0%9C%D0%A2.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- QIAGEN QIAamp® Viral RNA Mini Handbook, July 2020—Google Search. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=QIAGEN+QIAamp%C2%AE+Viral+RNA+Mini+Handbook%2C+July+2020.&rlz=1C1GCEU_enET1014ET1014&oq=QIAGEN+QIAamp%C2%AE+Viral+RNA+Mini+Handbook%2C+July+2020.&aqs=chrome.69i57.1026j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Burrows-Wheeler Alignment (BWA)—Research Computing Documentation. Available online: https://wiki.rc.usf.edu/index.php/Burrows-Wheeler_Alignment_(BWA) (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows-Wheeler Aligner. Available online: https://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- O’Toole, Á.; Scher, E.; Underwood, A.; Jackson, B.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Colquhoun, R.; Ruis, C.; Abu-Dahab, K.; Taylor, B.; et al. Assignment of epidemiological lineages in an emerging pandemic using the pangolin tool. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksamentov, I.; Roemer, C.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Neher, R.A. Nextclade: Clade assignment, mutation calling and quality control for viral genomes. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GISAID Initiative. Available online: https://www.epicov.org/epi3/frontend#28d967 (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- NCBI Virus. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/virus/vssi/#/virus?SeqType_s=Nucleotide&VirusLineage_ss=Severe%20acute%20respiratory%20syndrome%20coronavirus%202,%20taxid:2697049&utm_source=nuccore&utm_medium=referral&Authors_idx%20q.op%3DAND=Hailu&SubmitterAffil_idx%20q.op%3DOR=Ethiopian%20Public%20Health%20Institute&SubmitterCountry_idx%20q.op%3DOR=Ethiopia (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- GitHub—Tseemann/Snp-Dists: Pairwise SNP Distance Matrix from a FASTA Sequence Alignment. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snp-dists (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation|Nucleic Acids Research|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/49/W1/W293/6246398?login=true (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Matson, M.J.; Yinda, C.K.; Seifert, S.N.; Bushmaker, T.; Fischer, R.J.; Doremalen, N.V.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Munster, V.J. Effect of Environmental Conditions on SARS-CoV-2 Stability in Human Nasal Mucus and Sputum. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirakov, I.; Stankova, P.; Bakalov, D.; Mirani, Y.; Bardarska, L.; Paraskova, G.; Popov, I.; Alexandrova, A.; Dimitrov, G.; Mizgova, G.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of the Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Mediterranean Part of Bulgaria, During the First Wave of the Pandemic. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 18, 438–450. Available online: https://microbiologyjournal.org/retrospective-analysis-of-the-spread-of-sars-cov-2-in-the-mediterranean-part-of-bulgaria-during-the-first-wave-of-the-pandemic/ (accessed on 19 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Saki, M.; Sirakov, I.; Akrami, S. Pathogenesis of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. J. Commun. Dis. 2022, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Improving Response as Ethiopia Marks Two Years Since First COVID-19 Case|WHO|Regional Office for Africa. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/countries/ethiopia/news/improving-response-ethiopia-marks-two-years-first-covid-19-case (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Anteneh, A.; Getachew, A.; Kenera, M.; Salim, A.; Kedir, F.; Belayihun, B.; Felker-Kantor, E. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in Ethiopia: A latent class analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwangani, B.; Munodawafa, D.; Chadambuka, A. COVID-19 Infections and Deaths between Rural and Urban Provinces of Zimbabwe, 2020: A Spatial Variations Analysis. Texila Int. J. Public Health 2023, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Khavarian-Garmsir, A.R. The COVID-19 pandemic: Impacts on cities and major lessons for urban planning, design, and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavia, N.; Sharma, N.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Milekic, B. An Atypical Presentation of Acute Pulmonary Embolism With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Pneumonia. Cureus 2020, 12, e8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.-Y.; Filler, R.; Mathew, S.; Buley, J.; Iliaki, E.; Bruno-Murtha, L.A.; Osgood, R.; Christophi, C.A.; Fernandez-Montero, A.; Kales, S.N. COVID-19 symptoms predictive of healthcare workers’ SARS-CoV-2 PCR results. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarris, G.; de Rougemont, A.; Estienney, M.-A.; Journet, J.; Lariotte, A.-C.; Aubignat, D.; Rebibou, J.-M.; De La Vega, M.F.; Legendre, M.; Belliot, G.; et al. Chronic kidney disease linked to SARS-CoV-2 infection: A case report. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucirka, L.M.; Lauer, S.A.; Laeyendecker, O.; Boon, D.; Lessler, J. Variation in False-Negative Rate of Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction–Based SARS-CoV-2 Tests by Time Since Exposure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maio, N.; Walker, C.R.; Turakhia, Y.; Lanfear, R.; Corbett-Detig, R.; Goldman, N. Mutation Rates and Selection on Synonymous Mutations in SARS-CoV-2. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldivar-Espinoza, B.; Garcia-Segura, P.; Novau-Ferré, N.; Macip, G.; Martínez, R.; Puigbò, P.; Cereto-Massagué, A.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallve, S. The Mutational Landscape of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, S.; Ma, K. A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E.; Bozdayi, G.; Yigit, S.; Muftah, H.; Dizbay, M.; Tunccan, O.G.; Fidan, I.; Caglar, K. Genomic characterization of SARS-CoV-2 isolates from patients in Turkey reveals the presence of novel mutations in spike and nsp12 proteins. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6016–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, W.H.; Kandeil, A.; El-Shesheny, R.; Khalifa, M.K.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Showky, S.; Naguib, A.; Elguindy, N.; Fahim, M.; Abu Elsood, H.; et al. Insight into Genetic Characteristics of Identified SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Egypt from March 2020 to May 2021. Pathogens 2022, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Qin, B.; Chen, P.; Zhu, K.; Hou, P.; Wojdyla, J.A.; Wang, M.; Cui, S. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, G.; Abdelghaffar, H.; Seadawy, M.G.; El-Hosseny, M.F.; Gad, A.F.; Ageez, A.; ElShafei, A.; Mohammed, S.S.; Ali, M.S.; El-Ashry, M. abd E.-R. Genome sequencing reveals existence of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 variant in Egypt. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.-Y.; Wang, W.-B.; Gao, R.-D.; Zhou, A.-M. Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutation, infectivity, transmission, and vaccine resistance. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Omicron Variant (COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2) by BNO News. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/d/viewer?mid=1lKX8ikHpKAkWCvuXn2g-CVW3OmHbN-k- (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Zaman, K.; Shete, A.M.; Mishra, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Reddy, M.M.; Sahay, R.R.; Yadav, S.; Majumdar, T.; Pandey, A.K.; Dwivedi, G.R.; et al. Omicron BA.2 lineage predominance in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-positive cases during the third wave in North India. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 955930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-T.; Polotan, F.G.M.; Sotelo, G.I.S.; Dolor, A.Y.M.; Tujan, M.A.A.; Gomez, M.R.R.; Onza, J.T.; Chang, A.K.T.; Bautista, C.T.; Carandang, J.C.; et al. Lineage BA.2 dominated the Omicron SARS-CoV-2 epidemic wave in the Philippines. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Rauseo, A.M.; O’Halloran, J.A. What Are the Clinical Implications of the SARS-CoV-2 Variants. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemayehu, D.H.; Adnew, B.; Alemu, F.; Tefera, D.A.; Seyoum, T.; Beyene, G.T.; Gelanew, T.; Negash, A.A.; Abebe, M.; Mihret, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequences of SARS-CoV-2 Isolates from Ethiopian Patients. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e0072121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, P.V.; Ghafari, M.; Beer, M.; Lythgoe, K.; Simmonds, P.; Stilianakis, N.I.; Katzourakis, A. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.W.; Capoferri, A.A.; Katusiime, M.G.; Patro, S.C.; Kearney, M.F. Low genetic diversity may be an Achilles heel of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24614–24616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Classifications | Variants | Name | First Reported Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| VOC | alpha | GRY (B.1.1.7 + Q.*) | United Kingdom |
| VOC | Beta | GH/501Y.V2 (B.1.351 + B.1.351.2 + B.1.351 + 3) | South Africa |
| VOC | Gamma | GR/501Y.V3 (P.1 + P.1*) | Brazil and Japan |
| VOC | Omicron | GRA (B.1.1.529 + BA.*) | Botswana, South Africa, and Hong Kong |
| Variant of interest (VOI) | Lambda | GR/452Q.V1 (C.37 + C.37.1) | Peru |
| VOI | Mu | GH (B.1.621 + B.1.621.1) | Colombia |
| VOI | GRA (XBB.1.5 + XBB.1.5.*) | Australia, India, and Bangladesh | |
| VOC | GRA (XBB.1.16 + XBB.1.1.16.*) | India | |
| Variant under monitoring (VUM) | GRA (XBB + XBB.*, excluding XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.2, XBB.2.3) | India | |
| VUM | GRA (XBB.1.9.1 + XBB.19.1.*) | Indonesia, Singapore, and Israel | |
| VUM | GH/490R (B.1.640 + B.1.640.*) | Congo and France. Except for the Gamma VOC |
| Characteristics | Number (n) | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 19 | 30 |
| Male | 44 | 70 | |
| Age Group | ≤20 | 8 | 13 |
| 21–30 | 20 | 32 | |
| 31–40 | 13 | 21 | |
| 41–50 | 10 | 16 | |
| 51–60 | 4 | 6 | |
| >60 | 8 | 13 | |
| Testing Sites | Oromia | 15 | 24 |
| Amhara | 3 | 5 | |
| Addis Ababa | 44 | 70 | |
| SNNPR | 1 | 1 | |
| Signs and Symptoms | No | 19 | 30 |
| Yes | 44 | 70 | |
| Co-morbidity | No | 36 | 57 |
| Yes | 27 | 43 | |
| Travel History | No | 55 | 87 |
| Yes | 8 | 13 | |
| Vaccination Status | Not vaccinated | 38 | 60 |
| Vaccinated | 25 | 40 | |
| Reason for Testing | Contact with cases | 10 | 16 |
| Follow-up | 2 | 3 | |
| Suspect | 43 | 68 | |
| Travel purpose | 8 | 13 | |
| Variants of SARS-CoV-2 Virus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | Omicron | |||
| Sex | Female | Number | 1 | 18 |
| % | 5.3 | 94.7 | ||
| Male | Number | 1 | 43 | |
| % | 2.3 | 97.7 | ||
| Vaccination | No | Number | 2 | 36 |
| % | 5.3 | 94.7 | ||
| Yes | Number | 0 | 25 | |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Signs and Symptoms | No | Number | 0 | 19 |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Yes | Number | 2 | 42 | |
| % | 4.5 | 95.5 | ||
| Travel History | No | Number | 2 | 53 |
| % | 3.6 | 96.4 | ||
| Yes | Number | 0 | 8 | |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Ethiopian Nationality | No | Number | 0 | 1 |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Yes | Number | 2 | 60 | |
| % | 3.2 | 96.8 | ||
| Age Group | ≤20 | Number | 0 | 8 |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 21–30 | Number | 1 | 19 | |
| % | 5.0 | 95.0 | ||
| 31–40 | Number | 0 | 13 | |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 41–50 | Number | 1 | 9 | |
| % | 10.0 | 90.0 | ||
| 51–60 | Number | 0 | 4 | |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| >60 | Number | 0 | 8 | |
| % | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hailu, G.; Legesse, M.; Mulu, A.; Medhin, G.; Tsegaye, M.M.; Alemayehu, D.H.; Ayele, A.; Gebreegziabxier, A.; Tayachew, A.; Aguine, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19. Genes 2025, 16, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030351
Hailu G, Legesse M, Mulu A, Medhin G, Tsegaye MM, Alemayehu DH, Ayele A, Gebreegziabxier A, Tayachew A, Aguine A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19. Genes. 2025; 16(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleHailu, Getnet, Mengistu Legesse, Andargachew Mulu, Girmay Medhin, Mesfin Mengesha Tsegaye, Dawit Hailu Alemayehu, Abaysew Ayele, Atsbeha Gebreegziabxier, Adamu Tayachew, Adimkewu Aguine, and et al. 2025. "SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19" Genes 16, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030351
APA StyleHailu, G., Legesse, M., Mulu, A., Medhin, G., Tsegaye, M. M., Alemayehu, D. H., Ayele, A., Gebreegziabxier, A., Tayachew, A., Aguine, A., Dejene, H., Tessema, S. K., Onywera, H., Stanislas, A. E., Abate, E., Marcello, A., & Bitew, M. (2025). SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19. Genes, 16(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030351







