Integrative In Silico Analysis to Identify Functional and Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) Protein and UTRs: Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Susceptibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval of PD-1 nsSNPs from the Database
2.2. Determining the Most Deleterious SNPs
2.3. The Identification of nsSNPs Within the Domains of the PD-1 Protein
2.4. Analyzing the Effects of the nsSNPs on PD-1 Protein Stability
2.5. Investigating the Impact of nsSNPs on the 3D Structure of the PD-1 Protein
2.6. Evaluation of Molecular Pathogenicity of nsSNPs
2.7. Oncogenic and Phenotypic Analysis
2.8. Identification of Cancer and Association with nsSNPs
2.9. In Silico Analysis of PDCD1Gene Expression Profiles and Their Correlation with Survival Prognosis
2.10. Protein–Protein Interactions Analysis Using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING)
2.11. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analysis Using STRING
2.12. Analysis of the Functional Relevance of Non-Coding SNPs (ncSNPs) in the PDCD1 Gene Regulatory Function Analysis Through RegulomeDB
2.13. Analysis of the Effect of 3UTR SNPs on microRNA (miRNA)-Binding Sites
3. Results
3.1. Prediction of Functionally Important nsSNPs in the PDCD1 Gene
3.2. Identification of Structural and Functional Domains of the PD-1 Protein Using InterPro
3.3. Prediction of Impact of nsSNPs on PD-1 Protein Stability
3.4. Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on PD-1 Protein According to Project HOPE
3.5. Predicting the Molecular Mechanisms of PD-1 nsSNP Pathogenicity Using MutPred2
3.6. Oncogenic Potential of nsSNPs Using Cscape and Cscape- Somatic
3.7. Association of the Damaging nsSNPs with Cancer
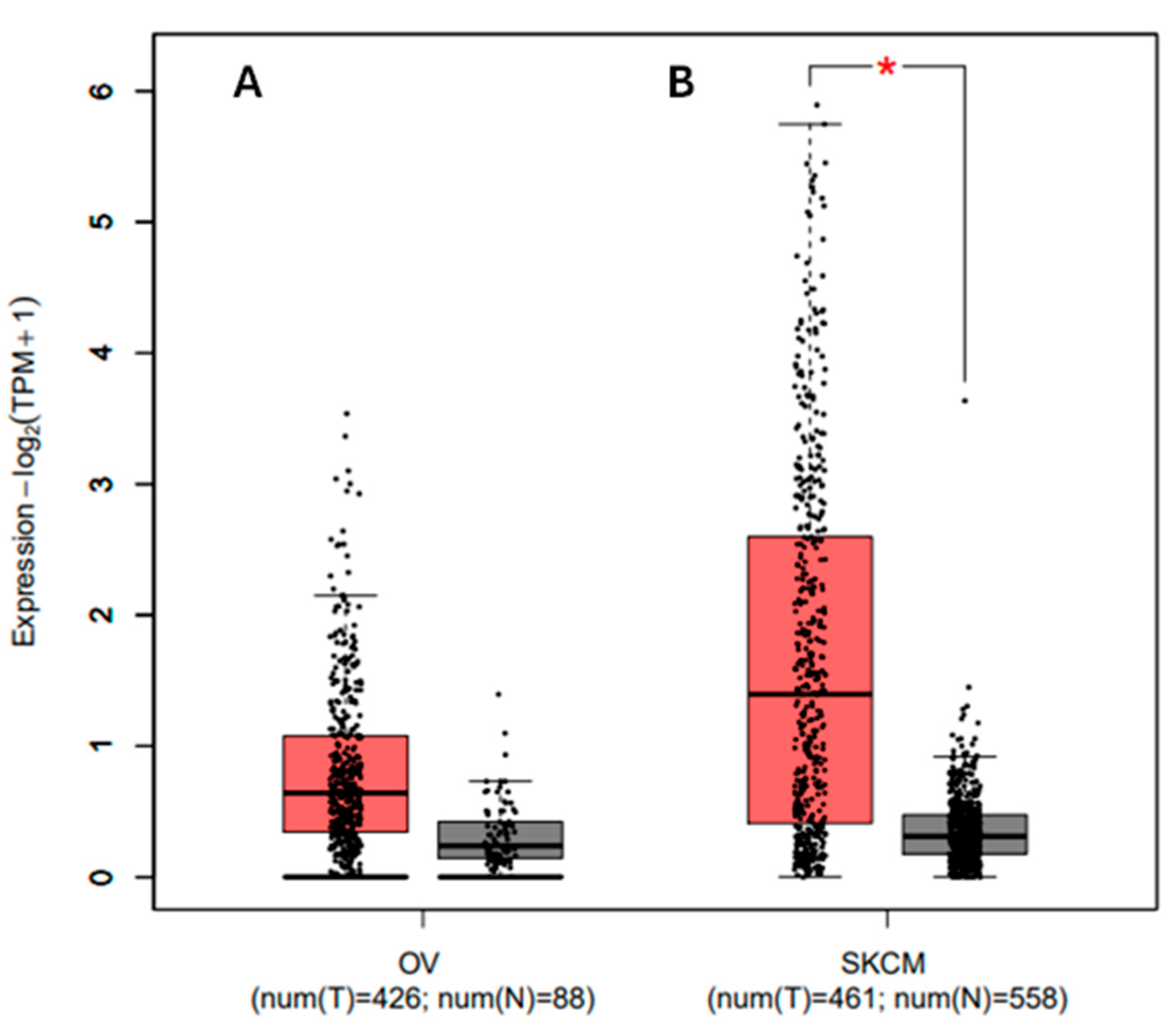
3.8. Analyzing the Gene Expression Profile for the PDCD1 Gene in Association with Cancer and Prognosis
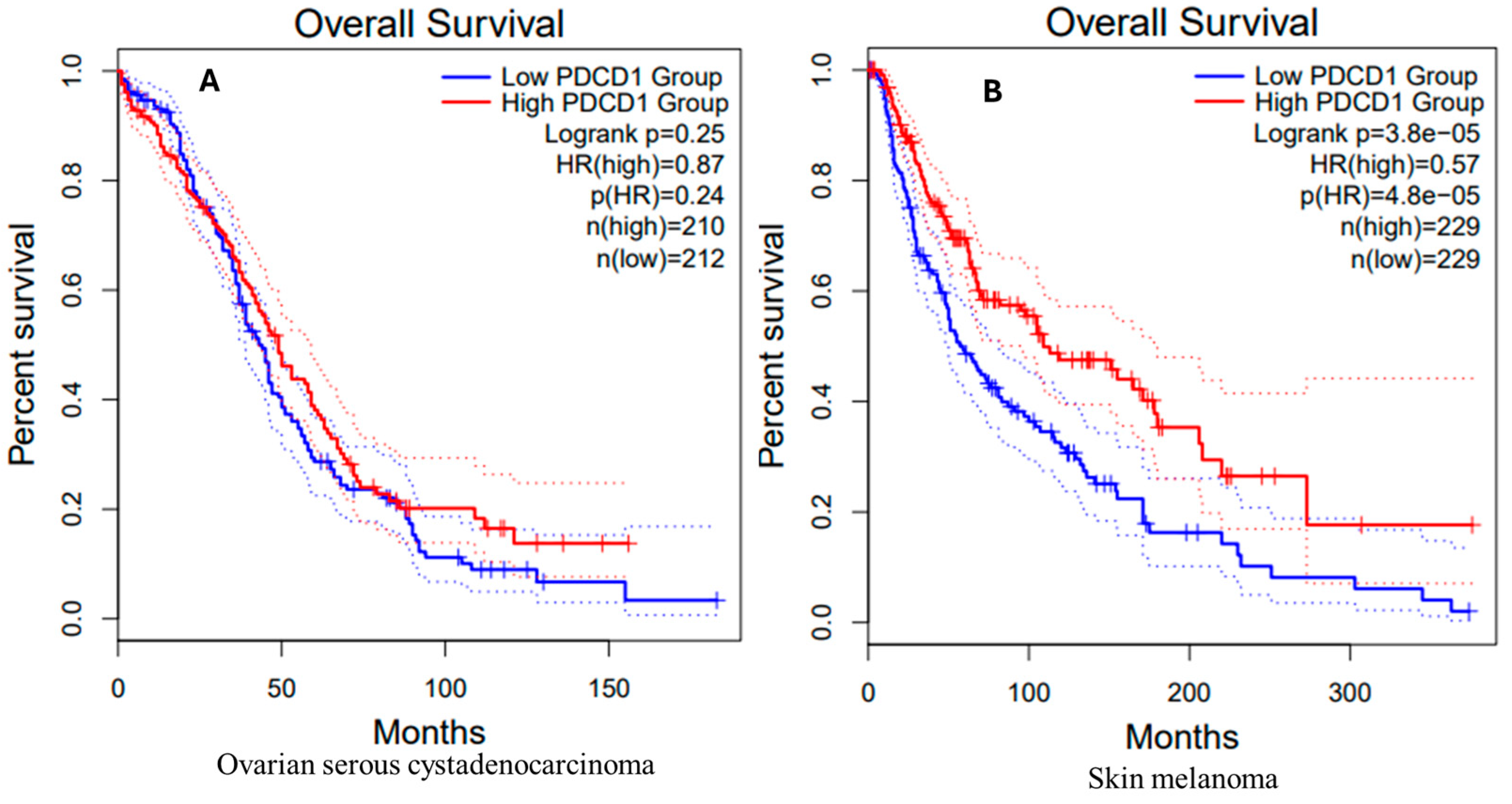
3.9. Survival Analysis in OV and SKCM Patients
OV Patients
SKCM Patients
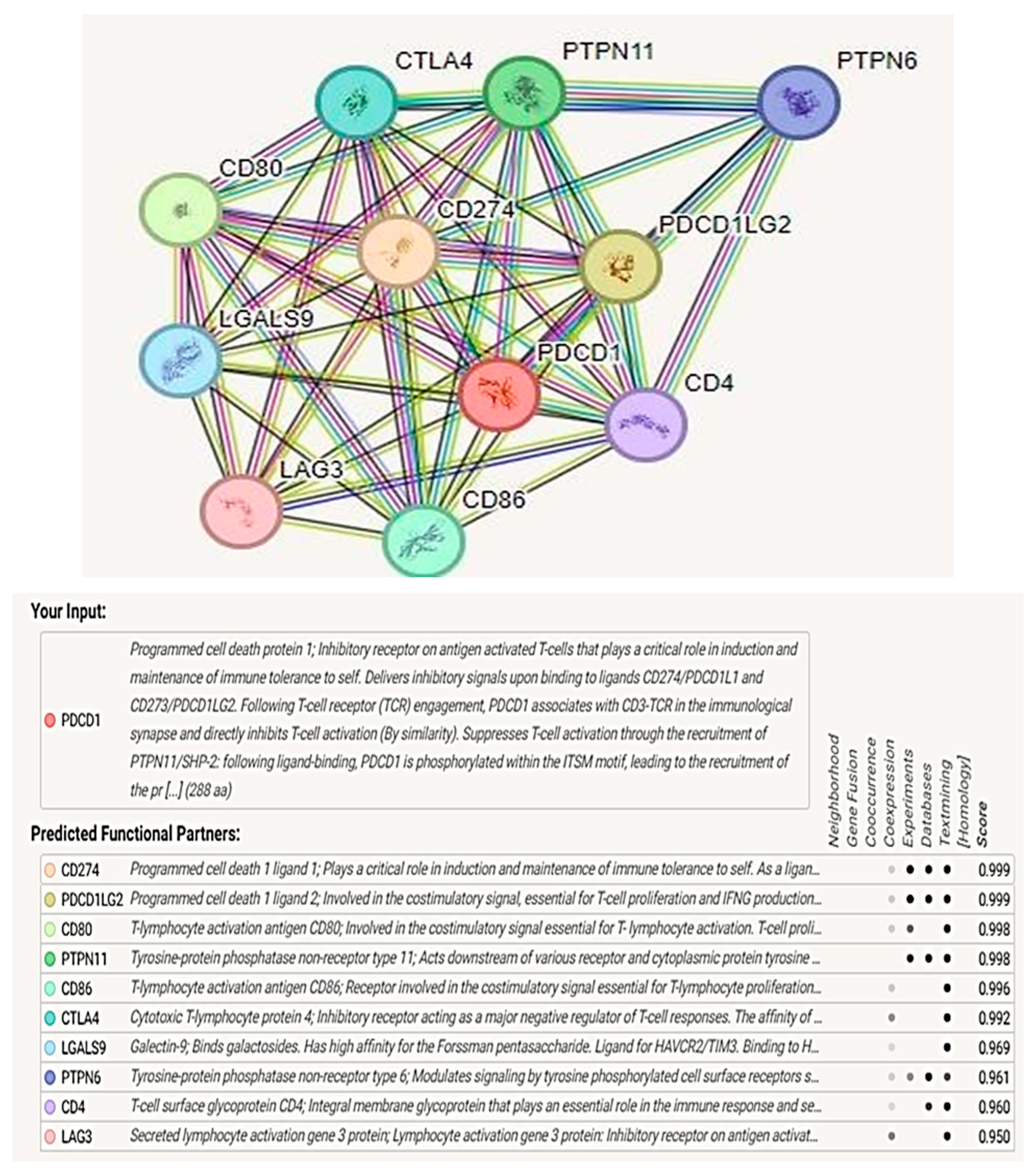
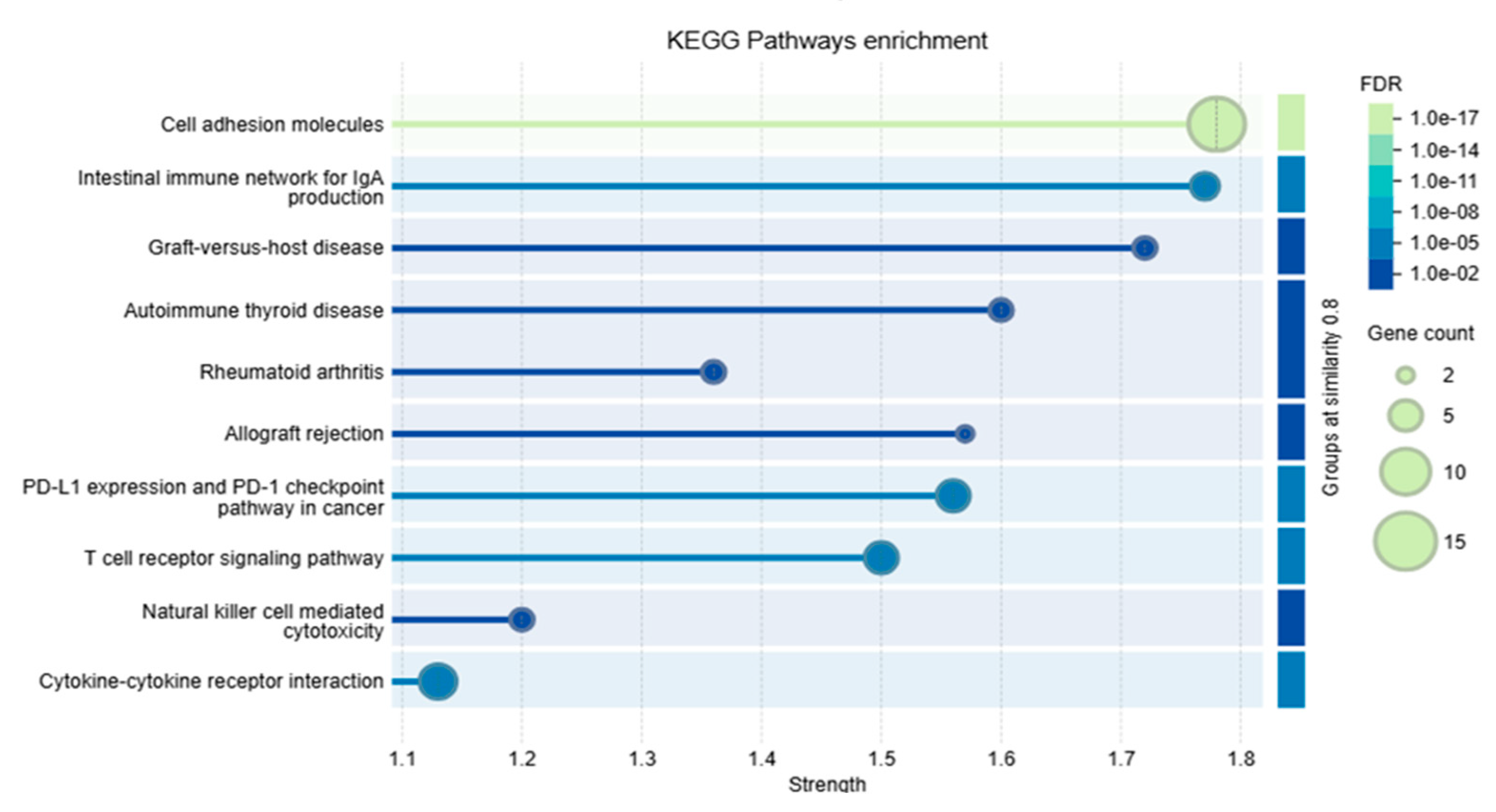
3.10. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.11. Evaluation of the Functional Consequences of Non-Coding SNPs Using RegulomeDB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.C.; Latchman, Y.E.; Buhlmann, J.E.; Tomczak, M.F.; Horwitz, B.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. Regulation of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression during normal and autoimmune responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 2706–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Akiba, H.; Iwai, H.; Matsuda, H.; Aoki, M.; Tanno, Y.; Shin, T.; Tsuchiya, H.; Pardoll, D.M.; Okumura, K.; et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5538–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Ishida, Y.; Kawaichi, M.; Honjo, T. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human PD-1 gene (PDCD1). Genomics 1994, 23, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, K.M.; Kitel, R.; Przetocka, S.; Golik, P.; Guzik, K.; Musielak, B.; Dömling, A.; Dubin, G.; Holak, T.A. Structure of the Complex of Human Programmed Death 1, PD-1, and Its Ligand PD-L1. Structure 2015, 23, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolutti, R.; Sun, X.; Kao, J.; Maute, R.L.; Ring, A.M.; Bowman, G.R.; Kruse, A.C. Structure and Dynamics of PD-L1 and an Ultra-High-Affinity PD-1 Receptor Mutant. Structure 2016, 24, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Bardhan, K.; Boussiotis, V.A.; Patsoukis, N. The PD-1 Interactome. Adv. Biol. 2021, 5, 2100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Assal, A.; Lazar-Molnar, E.; Yao, Y.; Zang, X. Human cancer immunotherapy with antibodies to the PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.-H.; Chan, L.-C.; Li, C.-W.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.-C. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Castejon, M.; Marin, F.; Soler-Rivas, C.; Reglero, G.; Visioli, F.; Rodriguez-Casado, A. Functional non-synonymous polymorphisms prediction methods: Current approaches and future developments. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 5095–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Fan, B.; Mao, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Kuai, L.; Ding, X.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; Miao, X. Association between PDCD1 gene polymorphisms and psoriasis susceptibility in the Chinese population. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Z.; Pang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Fang, T.; Ma, Q.; et al. Association of programmed cell death 1 (PDCD1) gene polymorphisms with colorectal cancer among Han Chinese population. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi = Zhonghua Yixue Yichuanxue Zazhi = Chin. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 35, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Karami, S.; Sarabandi, S.; Moazeni-Roodi, A.; Małecki, A.; Ghavami, S.; Wiechec, E. Association between PD-1 and PD-L1 Polymorphisms and the Risk of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Cancers 2019, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, U.; Arkinjan, M. Association of programmed death-1 gene polymorphism rs2227981 with tumor: Evidence from a meta analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 13282–13288. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Hu, E.; Li, W.; Lv, J.; He, Y.; Deng, G.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Association of PD-1 polymorphisms with the risk and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma in the northeastern Chinese Han population. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y. Association of the programmed cell death-1 PD1.5 C>T polymorphism with cervical cancer risk in a Chinese population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 10–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savabkar, S.; Azimzadeh, P.; Chaleshi, V.; Mojarad, E.N.; Aghdaei, H.A. Programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas, M.R.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H.; Miri, A.; Ghaderi, A.; Erfani, N. Association of PDCD1 gene markers with susceptibility to thyroid cancer. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.S. Genetic polymorphism and immunological evaluation of PD-1 in Iraqi patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2024, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, S.; Sattarifard, H.; Kiumarsi, M.; Sarabandi, S.; Taheri, M.; Hashemi, M.; Bahari, G.; Ghavami, S. Evaluating the Possible Association between PD-1 (Rs11568821, Rs2227981, Rs2227982) and PD-L1 (Rs4143815, Rs2890658) Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Breast Cancer in a Sample of Southeast Iranian Women. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Sheng, L.; Yi, Q.-H. Correlation of PD-1/PD-L1 polymorphisms and expressions with clinicopathologic features and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cancer Biomarkers Sect. A Dis. Markers 2018, 21, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, K.; Gong, P.; Qiao, F.; Wang, L.; Cui, H.; Sui, X.; Gao, J.; Fan, H. A novel functional TagSNP Rs7560488 in the DNMT3A1 promoter is associated with susceptibility to gastric cancer by modulating promoter activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Liu, D.; Qiu, X.; Qiao, F.; Wu, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, W. A functional polymorphism in the DNA methyltransferase-3A promoter modifies the susceptibility in gastric cancer but not in esophageal carcinoma. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, F.; Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Hou, S.; Tian, Y.; Fu, W.; Xie, D.; et al. The rs391957 variant cis-regulating oncogene GRP78 expression contributes to the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, L.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, B. Functional promoter rs2295080 T>G variant in MTOR gene is associated with risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 70, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunna, N.R.; Naushad, S.M.; Vuree, S.; Anuradha, C.; Sailaja, K.; Surekha, D.; Rao, D.R.; Vishnupriya, S. Association of thymidylate synthase 5’-UTR 28bp tandem repeat and serine hydroxymethyltransfarase C1420T polymorphisms with susceptibility to acute leukemia. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vooght, K.M.K.; van Wijk, R.; van Solinge, W.W. Management of gene promoter mutations in molecular diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Mashima, H.; Miki, D.; Kuroda, S.; Hamaoka, M.; Aikata, H.; Chayama, K.; Ohdan, H. PD1 gene polymorphism is associated with a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma following liver resection, cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Tatemaysu, T.; Okuda, K.; Moriyama, S.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. PD-1 gene promoter polymorphisms correlate with a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhang, N.; Ning, W.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.-A. Variant SNPs at the microRNA complementary site in the B7-H1 3’-untranslated region increase the risk of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. microRNA-4717 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the PD1 3’ untranslated region: A mechanism for regulating PD-1 expression and function in HBV-associated liver diseases. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18933–18944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Zhang, P.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. PD-1 mRNA expression is associated with clinical and viral profile and PD1 3’-untranslated region polymorphism in patients with chronic HBV infection. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihab, H.; Jadid, F.; Foka, P.; Zaidane, I.; El Fihry, R.; Georgopoulou, U.; Marchio, A.; Elhabazi, A.; Chair, M.; Pineau, P.; et al. Programmed cell death-1 3’-untranslated region polymorphism is associated with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-A.; Tsai, E.-Y.; Liu, S.-H.; Hung, S.-D.H.; Chang, S.-J.; Chao, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Li, C.-W. Post-translational Modification of PD-1: Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Kim, A.M.J.; Lim, S.-O. Glycosylation of Immune Receptors in Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosu, M. Inhibition of N-Glycosylation towards Novel Anti-Cancer Chemotherapeutics. J. Mol. Pharm. Org. Process Res. 2018, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, C.-W.; Chung, E.M.; Yang, R.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, A.H.; Lai, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, J.; et al. Targeting Glycosylated PD-1 Induces Potent Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Chikuma, S.; Kondo, T.; Hibino, S.; Machiyama, H.; Yokosuka, T.; Nakano, M.; Yoshimura, A. Blockage of Core Fucosylation Reduces Cell-Surface Expression of PD-1 and Promotes Anti-tumor Immune Responses of T Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, M.; Liu, K.; He, J.; Ma, D.; Ma, X.; Tan, S.; Gao, G.F.; et al. PD-1 N58-Glycosylation-Dependent Binding of Monoclonal Antibody Cemiplimab for Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, K.; Aksoylar, H.-I.; Le Bourgeois, T.; Strauss, L.; Weaver, J.D.; Delcuze, B.; Charest, A.; Patsoukis, N.; Boussiotis, V.A. Phosphorylation of PD-1-Y248 is a marker of PD-1-mediated inhibitory function in human T cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-W.; Lim, S.-O.; Xia, W.; Lee, H.-H.; Chan, L.-C.; Kuo, C.-W.; Khoo, K.-H.; Chang, S.-S.; Cha, J.-H.; Kim, T.; et al. Glycosylation and stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, E.; Cheung, J.; Zhu, J.; Su, X.; Taylor, M.J.; Wallweber, H.A.; Sasmal, D.K.; Huang, J.; Kim, J.M.; Mellman, I.; et al. T cell costimulatory receptor CD28 is a primary target for PD-1-mediated inhibition. Science 2017, 355, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celis-Gutierrez, J.; Blattmann, P.; Zhai, Y.; Jarmuzynski, N.; Ruminski, K.; Grégoire, C.; Ounoughene, Y.; Fiore, F.; Aebersold, R.; Roncagalli, R.; et al. Quantitative Interactomics in Primary T Cells Provides a Rationale for Concomitant PD-1 and BTLA Coinhibitor Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3315–3330.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Shi, R.; Gao, B.; Cai, J. N-linked glycosylation of PD-L1/PD-1: An emerging target for cancer diagnosis and treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Tokheim, C.; Bailey, M.H.; Yaron, T.M.; Stathias, V.; Geffen, Y.; Imbach, K.J.; Cao, S.; Anand, S.; et al. Pan-cancer proteogenomics connects oncogenic drivers to functional states. Cell 2023, 186, 3921–3944.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroverkhova, D.; Przytycka, T.M.; Panchenko, A.R. Panchenko. Cancer driver mutations: Predictions and reality. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-Pardo, E.; Valencia, A.; Godzik, A. Understanding oncogenicity of cancer driver genes and mutations in the cancer genomics era. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 4233–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, M.; Shen, B. Deciphering oncogenic drivers: From single genes to integrated pathways. Briefings Bioinform. 2014, 16, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.E.; McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Thormann, A.; Schuilenburg, H.; Sheppard, D.; Parton, A.; Armean, I.M.; Trevanion, S.J.; Flicek, P.; et al. Ensembl variation resources. Database 2018, 2018, bay119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendl, J.; Stourac, J.; Salanda, O.; Pavelka, A.; Wieben, E.D.; Zendulka, J.; Brezovsky, J.; Damborsky, J. PredictSNP: Robust and Accurate Consensus Classifier for Prediction of Disease-Related Mutations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P.; Casadio, R. I-Mutant2.0: Predicting stability changes upon mutation from the protein sequence or structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W306–W310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Randall, A.; Baldi, P. Prediction of protein stability changes for single-site mutations using support vector machines. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 62, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venselaar, H.; Beek, T.A.T.; Kuipers, R.K.; Hekkelman, M.L.; Vriend, G. Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Urresti, J.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Pagel, K.A.; Lin, G.N.; Nam, H.-J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Sebat, J.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; et al. MutPred2: Inferring the molecular and phenotypic impact of amino acid variants. bioRxiv 2017, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Urresti, J.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Pagel, K.A.; Lin, G.N.; Nam, H.-J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Sebat, J.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; et al. Inferring the molecular and phenotypic impact of amino acid variants with MutPred2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.F.; Shihab, H.A.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. CScape: A tool for predicting oncogenic single-point mutations in the cancer genome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.F.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. CScape-somatic: Distinguishing driver and passenger point mutations in the cancer genome. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3637–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Ziebarth, J.D.; Cui, Y. PolymiRTS Database 3.0: Linking polymorphisms in microRNAs and their target sites with human diseases and biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D86–D91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngnak, P.; Kozono, Y.; Kozono, H.; Iwai, H.; Otsuki, N.; Jin, H.; Omura, K.; Yagita, H.; Pardoll, D.M.; Chen, L.; et al. Differential binding properties of B7-H1 and B7-DC to programmed death-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Xu, A.; Xu, J. Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Signaling, Cancer, and Beyond. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhnovich, E.; Abkevich, V.; Ptitsyn, O. Conserved residues and the mechanism of protein folding. Nature 1996, 379, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenberg, O.; Gong, L.I.; Bloom, J.D. Mutational effects on stability are largely conserved during protein evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 21071–21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Teng, F.; Kong, L. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 5023–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| SNP ID | AA Change | PredictSNP | MAPP, PhD-SNP, PolyPhan-1, PolyPhan-2, SIFT, SNAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs2124872179 | L17P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1192883440 | L25V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861799 | D26G | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861799 | D26V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs756045758 | S27F | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs756045758 | S27Y | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700939528 | D29H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1017421889 | D29V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1380273970 | R30C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1044516789 | R30H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1412459900 | R30M | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1412459900 | R30T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs751727384 | P31L | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs757336262 | P31T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861485 | L42H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700937498 | G47R | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861379 | G47V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861330 | N49H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861330 | N49Y | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861291 | A50D | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861238 | C54R | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861138 | N58I | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861011 | L65P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124861011 | L65Q | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700935524 | W67C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860994 | W67R | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860964 | Y68D | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860846 | N74T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860823 | Q75E | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860779 | D77H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860762 | K78Q | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs987449655 | L79V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860722 | A80G | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860734 | A80P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860734 | A80S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860734 | A80T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1358028393 | A81P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1358028393 | A81T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1380350073 | A81V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860682 | F82S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1380273970 | R86C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1044516789 | R86P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1214961588 | P89R | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700932618 | D92G | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700932618 | D92V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1427055411 | R94C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs757156727 | R94H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs757156727 | R94P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs757156727 | R94L | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs758277335 | R96C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs773349951 | R96P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs533395656 | V97F | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860396 | N102I | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1256572186 | N116K | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs772130993 | D117V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860218 | G119D | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1230474759 | G119S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860176 | G124V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124860004 | V144E | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs1700919273 | W186G | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856625 | D222Y | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856605 | Y223C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856613 | Y223H | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856613 | Y223N | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856605 | Y223S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856588 | G224V | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856554 | L226P | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856554 | L226Q | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856517 | F228C | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856528 | F228I | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856528 | F228L | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856517 | F228S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856517 | F228Y | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856503 | Q229K | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856279 | C241W | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856283 | C241R | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856201 | Y248S | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856181 | A249D | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856190 | A249T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856153 | I251T | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856153 | I251N | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856129 | V252D | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs2124856114 | F253I | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| rs775100301 | W286G | Deleterious | Deleterious |
| SNP ID | AA Change | I-Mutant | RI | DDG-Free Energy Change Value (kcal/mol) | MUpro | DDG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2124872179 | L17P | Decrease | 4 | −0.72 | Decrease | −1.31 |
| rs1192883440 | L25V | Decrease | 6 | −0.05 | Decrease | −0.85 |
| rs2124861799 | D26G | Decrease | 2 | −0.24 | Decrease | −1.53 |
| rs2124861799 | D26V | Decrease | 0 | −0.17 | Decrease | −0.43 |
| rs756045758 | S27F | Increase | 1 | −0.12 | Decrease | −0.06 |
| rs756045758 | S27Y | Increase | 3 | −0.3 | Decrease | −0.37 |
| rs1700939528 | D29H | Decrease | 5 | −0.79 | Decrease | −0.89 |
| rs1017421889 | D29V | Decrease | 1 | −0.26 | Decrease | −0.33 |
| rs1380273970 | R30C | Decrease | 4 | −0.94 | Decrease | −0.77 |
| rs1044516789 | R30H | Decrease | 7 | −1.18 | Decrease | −1.13 |
| rs1412459900 | R30M | Decrease | 7 | −2.11 | Decrease | −0.49 |
| rs1412459900 | R30T | Decrease | 8 | −1.91 | Decrease | −1.02 |
| rs751727384 | P31L | Decrease | 5 | −0.21 | Decrease | −0.37 |
| rs757336262 | P31T | Decrease | 9 | −1.89 | Decrease | −1.44 |
| rs2124861485 | L42H | Decrease | 8 | −2.2 | Decrease | −1.79 |
| rs1700937498 | G47R | Decrease | 8 | −2.06 | Decrease | −0.79 |
| rs2124861379 | G47V | Decrease | 1 | −0.88 | Decrease | −0.52 |
| rs2124861330 | N49H | Decrease | 8 | −1.45 | Decrease | −0.56 |
| rs2124861330 | N49Y | Decrease | 1 | 0.1 | Decrease | −0.34 |
| rs2124861291 | A50D | Decrease | 0 | −0.28 | Decrease | −0.82 |
| rs2124861238 | C54R | Decrease | 6 | −1.15 | Decrease | −1.05 |
| rs2124861138 | N58I | Increase | 2 | 1.25 | Decrease | −0.32 |
| rs2124861011 | L65P | Decrease | 7 | −0.34 | Decrease | −2.04 |
| rs2124861011 | L65Q | Decrease | 9 | −1.34 | Decrease | −1.63 |
| rs1700935524 | W67C | Decrease | 7 | −1.4 | Decrease | −0.88 |
| rs2124860994 | W67R | Decrease | 9 | −1.65 | Decrease | −0.82 |
| rs2124860964 | Y68D | Decrease | 4 | −0.29 | Decrease | −1.66 |
| rs2124860846 | N74T | Decrease | 0 | −1.35 | Decrease | −1.55 |
| rs2124860823 | Q75E | Increase | 4 | 0.48 | Decrease | −0.79 |
| rs2124860779 | D77H | Decrease | 6 | −0.57 | Decrease | −1.21 |
| rs2124860762 | K78Q | Decrease | 4 | −0.76 | Decrease | −0.23 |
| rs987449655 | L79V | Decrease | 8 | −0.54 | Decrease | −0.94 |
| rs2124860722 | A80G | Decrease | 8 | −1.15 | Decrease | −1.13 |
| rs2124860734 | A80P | Decrease | 0 | −1.52 | Decrease | −0.89 |
| rs2124860734 | A80S | Decrease | 9 | −0.58 | Decrease | −0.6 |
| rs2124860734 | A80T | Decrease | 8 | −1.08 | Decrease | −0.73 |
| rs1358028393 | A81P | Decrease | 1 | −1.83 | Decrease | −1.94 |
| rs1358028393 | A81T | Decrease | 8 | −1.2 | Decrease | −1.55 |
| rs1380350073 | A81V | Decrease | 2 | −0.27 | Decrease | −1.27 |
| rs2124860682 | F82S | Decrease | 9 | −2.07 | Decrease | −2.37 |
| rs1380273970 | R86C | Decrease | 5 | −0.36 | Decrease | −0.22 |
| rs1044516789 | R86P | Decrease | 7 | −1.89 | Decrease | −0.74 |
| rs1214961588 | P89R | Decrease | 7 | −0.41 | Decrease | −0.79 |
| rs1700932618 | D92G | Decrease | 2 | −0.93 | Decrease | −0.78 |
| rs1700932618 | D92V | Increase | 0 | −0.2 | Increase | 0.07 |
| rs1427055411 | R94C | Decrease | 5 | −0.41 | Decrease | −1.31 |
| rs757156727 | R94H | Decrease | 8 | −0.73 | Decrease | −1.59 |
| rs757156727 | R94L | Decrease | 8 | −0.3 | Decrease | −0.72 |
| rs757156727 | R94P | Decrease | 5 | −1.19 | Decrease | −1.79 |
| rs758277335 | R96C | Decrease | 5 | −0.41 | Decrease | −0.78 |
| rs773349951 | R96P | Decrease | 5 | −1.19 | Decrease | −1.19 |
| rs533395656 | V97F | Decrease | 8 | −1.21 | Decrease | −0.92 |
| rs2124860396 | N102I | Decrease | 2 | −0.01 | Decrease | −0.02 |
| rs1256572186 | N116K | Decrease | 7 | −2.14 | Decrease | −1.81 |
| rs772130993 | D117V | Decrease | 5 | −1.59 | Decrease | −0.73 |
| rs2124860218 | G119D | Decrease | 9 | −1.22 | Decrease | −0.43 |
| rs1230474759 | G119S | Decrease | 9 | −1.49 | Decrease | −0.72 |
| rs2124860176 | G124V | Decrease | 4 | −1 | Decrease | −0.28 |
| rs2124860004 | V144E | Decrease | 4 | −1.15 | Decrease | −0.94 |
| rs1700919273 | W186G | Decrease | 9 | −2.7 | Decrease | −1.54 |
| rs2124856625 | D222Y | Decrease | 3 | −0.77 | Decrease | −0.89 |
| rs2124856605 | Y223C | Decrease | 3 | 0.53 | Decrease | −1.23 |
| rs2124856613 | Y223H | Decrease | 8 | −1.56 | Decrease | −1.64 |
| rs2124856613 | Y223N | Decrease | 6 | −1.41 | Decrease | −1.37 |
| rs2124856605 | Y223S | Decrease | 8 | −1.71 | Decrease | −1.47 |
| rs2124856588 | G224V | Decrease | 4 | −0.82 | Decrease | −0.67 |
| rs2124856554 | L226P | Decrease | 7 | −1.83 | Decrease | −1.77 |
| rs2124856554 | L226Q | Decrease | 9 | −2.31 | Decrease | −1.51 |
| rs2124856517 | F228C | Decrease | 7 | −2.06 | Decrease | −1.1 |
| rs2124856528 | F228I | Decrease | 7 | −1.19 | Decrease | −0.54 |
| rs2124856528 | F228L | Decrease | 8 | −2.08 | Decrease | −0.58 |
| rs2124856517 | F228S | Decrease | 9 | −2.99 | Decrease | −1.32 |
| rs2124856517 | F228Y | Decrease | 4 | −0.28 | Decrease | −0.87 |
| rs2124856503 | Q229K | Increase | 3 | −0.02 | Decrease | −1.74 |
| rs2124856279 | C241W | Decrease | 3 | −0.43 | Decrease | −0.68 |
| rs2124856283 | C241R | Decrease | 3 | −0.87 | Decrease | −0.62 |
| rs2124856201 | Y248S | Decrease | 6 | −1.33 | Decrease | −1.41 |
| rs2124856181 | A249D | Decrease | 2 | −0.22 | Decrease | −0.64 |
| rs2124856190 | A249T | Decrease | 6 | −0.74 | Decrease | −0.85 |
| rs2124856153 | I251T | Decrease | 8 | −2.46 | Decrease | −1.54 |
| rs2124856153 | I251N | Decrease | 4 | −0.95 | Decrease | −1.38 |
| rs2124856129 | V252D | Decrease | 8 | −1.38 | Decrease | −1.57 |
| rs2124856114 | F253I | Decrease | 6 | −0.71 | Decrease | −0.55 |
| rs775100301 | W286G | Decrease | 9 | −2.5 | Decrease | −2.03 |
| AA Variation | MutPred2 Score | Molecular Mechanisms with p-Values Less than 0.05 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| L17P | 0.739 | - Gain of loop | 0.02 |
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 0.02 | ||
| C54R | 0.962 | - Altered metal binding | 2.60 × 10−3 |
| - Loss of disulfide linkage at C54 | 5.50 × 10−4 | ||
| - Altered ordered interface | 0.02 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 5.60 × 10−4 | ||
| - Gain of strand | 0.05 | ||
| - Loss of N-linked glycosylation at N58 | 5.6 × 10−3 | ||
| - Gain of catalytic site at C54 | 0.02 | ||
| - Gain of GPI-anchor amidation at N49 | 0.01 | ||
| L65P | 0.905 | - Altered transmembrane protein | 1.00 × 10−4 |
| - Altered stability | 0.01 | ||
| L65Q | 0.827 | - Altered transmembrane protein | 7.80 × 10−5 |
| - Altered stability protein | 0.05 | ||
| W67C | 0.844 | - Altered transmembrane protein | 1.20 × 10−4 |
| - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 0.04 | ||
| - Loss of strand | 1.70 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered ordered interface | 5.50 × 10−3 | ||
| - Loss of loop | 0.04 | ||
| - Gain of disulfide linkage at W67 | 0.04 | ||
| W67R | 0.853 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 3.90 × 10−3 |
| - Altered ordered interface | 0.04 | ||
| - Loss of strand | 4.40 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 3.90 × 10−4 | ||
| - Loss of loop | 0.05 | ||
| Y68D | 0.925 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 7.90 × 10−3 |
| - Altered ordered interface | 6.60 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 6.50 × 10−4 | ||
| - Loss of strand | 0.01 | ||
| - Altered stability | 0.01 | ||
| A80P | 0.794 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 9.20 × 10−3 |
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 1.50 × 10−4 | ||
| - Gain of strand | 0.01 | ||
| A81P | 0.633 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 8.50 × 10−3 |
| - Altered stability | 4.10 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 1.50 × 10−4 | ||
| - Gain of strand | 0.01 | ||
| D117V | 0.805 | - Gain of ADP-ribosylation at R112 | 0.02 |
| - Altered disordered interface | 0.04 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 0.02 | ||
| - Gain of N-linked glycosylation at N116 | 0.02 | ||
| W186G | 0.627 | - Loss of helix | 2.90 × 10−3 |
| - Altered ordered interface | 3.70 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered signal peptide | 2.10 × 10−3 | ||
| Y223N | 0.631 | - Altered disordered interface | 7.40 × 10−3 |
| - Altered ordered interface | 8.80 × 10−3 | ||
| - Loss of strand | 0.01 | ||
| - Loss of phosphorylation at Y223 | 0.03 | ||
| - Loss of proteolytic cleavage at D222 | 0.02 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 0.02 | ||
| - Loss of sulfation at Y223 | 3.60 × 10−3 | ||
| Y223S | 0.529 | - Altered disordered interface | 8.30 × 10−3 |
| - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 0.02 | ||
| - Altered ordered interface | 6.20 × 10−3 | ||
| - Loss of strand | 0.03 | ||
| - Gain of proteolytic cleavage at D222 | 1.90 × 10−3 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 0.02 | ||
| - Loss of sulfation at Y223 | 3.60 × 10−3 | ||
| L226P | 0.533 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 3.40 × 10−3 |
| - Altered disordered interface | 0.04 | ||
| - Altered stability | 0.01 | ||
| - Gain of proteolytic cleavage at D222 | 0.02 | ||
| - Altered transmembrane protein | 0.02 | ||
| - Gain of sulfation at Y223 | 2.30 × 10−3 | ||
| Y248S | 0.52 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 1.00 × 10−3 |
| - Altered ordered interface | 0.02 | ||
| - Gain of O-linked glycosylation at T250 | 0.02 | ||
| - Altered stability | 0.04 | ||
| - Altered metal binding | 0.01 | ||
| - Loss of pyrrolidone carboxylic acid at Q245 | 0.04 | ||
| I251N | 0.634 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 7.70 × 10−3 |
| - Altered stability | 0.01 | ||
| - Altered metal binding | 0.01 | ||
| - Gain of sulfation at Y248 | 0.03 | ||
| V252D | 0.503 | - Gain of intrinsic disorder | 0.01 |
| - Altered stability | 0.01 | ||
| - Altered metal binding | 0.01 |
| AA | Cscape | CScape Somatic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP ID | Change | Input | Coding Score | Message | Coding Score | Warning |
| rs2124872179 | L17P | 2,242800941,A,G | 0.6021 | Oncogenic | 0.839552 | Driver |
| rs1192883440 | L25V | 2,242800918,A,C | 0.581048 | Oncogenic | 0.661509 | Driver |
| rs2124861238 | C54R | 2,242795049,A,G | 0.627091 | Oncogenic | 0.50485 | Driver |
| rs2124861011 | L65P | 2,242795015,A,G | 0.561139 | Oncogenic | 0.407533 | Passenger |
| rs2124861011 | L65Q | 2,242795015,A,T | 0.503205 | Oncogenic | 0.270022 | Passenger |
| rs1700935524 | W67C | 2,242795008,C,A | 0.68252 | Oncogenic | 0.341358 | Passenger |
| rs2124860994 | W67R | 2,242795010,A,T | 0.697808 | Oncogenic | 0.292476 | Passenger |
| rs2124860964 | Y68D | 2,242795007,A,C | 0.682908 | Oncogenic | 0.450469 | Passenger |
| rs987449655 | L79V | 2,242794974,G,C | 0.668644 | Oncogenic | 0.419805 | Passenger |
| rs2124860722 | A80G | 2,242794970,G,C | 0.626369 | Oncogenic | 0.606956 | Driver |
| rs2124860734 | A80S | 2,242794971,C,A | 0.626567 | Oncogenic | 0.312374 | Passenger |
| rs2124860734 | A80P | 2,242794971,C,G | 0.76545 | Oncogenic | 0.679769 | Driver |
| rs2124860734 | A80T | 2,242794971,C,T | 0.613367 | Oncogenic | 0.30405 | Passenger |
| rs1358028393 | A81P | 2,242794968,C,G | 0.75435 | Oncogenic | 0.781253 | Driver |
| rs772130993 | D117V | 2,242794859, T,A | 0.5334 | Oncogenic | 0.376371 | Passenger |
| rs1700919273 | W186G | 2,242794386, A,C | 0.568592 | Oncogenic | 0.386691 | Passenger |
| rs2124856625 | D222Y | 2,242793413, C,A | 0.633163 | Oncogenic | 0.250538 | Passenger |
| rs2124856605 | Y223C | 2,242793409, T,C | 0.632424 | Oncogenic | 0.488143 | Passenger |
| rs2124856605 | Y223S | 2,242793409,T,G | 0.613155 | Oncogenic | 0.497009 | Passenger |
| rs2124856613 | Y223H | 2,242793410,A,G | 0.71215 | Oncogenic | 0.539332 | Driver |
| rs2124856613 | Y223N | 2,242793410,A,T | 0.647973 | Oncogenic | 0.396041 | Passenger |
| rs2124856588 | G224V | 2,242793406,C,A | 0.57769 | Oncogenic | 0.297241 | Passenger |
| rs2124856554 | L226P | 2,242793400,A,G | 0.80086 | Oncogenic | 0.631527 | Driver |
| rs2124856554 | L226Q | 2,242793400,A,T | 0.685336 | Oncogenic | 0.376093 | Passenger |
| rs2124856517 | F228C | 2,242793394,A,C | 0.719549 | Oncogenic | 0.486534 | Passenger |
| rs2124856517 | F228S | 2,242793394,A,G | 0.730018 | Oncogenic | 0.656042 | Driver |
| rs2124856517 | F228Y | 2,242793394,A,T | 0.675506 | Oncogenic | 0.326339 | Passenger |
| rs2124856528 | F228L | 2,242793395,A,G | 0.675661 | Oncogenic | 0.436829 | Passenger |
| rs2124856528 | F228I | 2,242793395,A,T | 0.661021 | Oncogenic | 0.295953 | Passenger |
| rs2124856279 | C241W | 2,242793354,A,C | 0.662798 | Oncogenic | 0.823574 | Driver |
| 3UTR | |||
| Chromosome Location | dbSNP IDs | Rank | Score |
| chr2:241850262..241850263 | rs543306494 | 2a | 1 |
| chr2:241850175..241850176 | rs560497981 | 2b | 0.82852 |
| chr2:241850400..241850401 | rs550396273 | 2b | 1 |
| chr2:241850045..241850046 | rs554459879 | 4 | 0.70497 |
| chr2:241850245..241850246 | rs55676463 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850249..241850250 | rs1559446557 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850531..241850532 | rs186922590 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850656..241850657 | rs569664740 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850657..241850658 | rs536846778 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850661..241850662 | rs558753231 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850699..241850700 | rs554320171 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850787..241850788 | rs543637140 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850802..241850803 | rs565450127 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241850832..241850833 | rs532613262 | 4 | 0.74401 |
| chr2:241850953..241850954 | rs565440440 | 4 | 0.70497 |
| chr2:241850993..241850994 | rs1400745867 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| 5UTR | |||
| Chromosome Location | dbSNP IDs | Rank | Score |
| chr2:241858839..241858840 | rs55970948 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241858858..241858859 | rs544843762 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241858863..241858864 | rs199970743 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| chr2:241858873..241858874 | rs374271577 | 4 | 0.60906 |
| Location | dbSNP ID | Variant Type | Wobble Base Pair | Ancestral Allele | Allele | miR ID | Conservation | miRSite | Function Class | Context+ Score Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 242792211 | rs142909968 | INDEL | N | - | C | hsa-miR-1296-5p | 2 | ggGGCCCTAgtacc | O | −0.135 |
| hsa-miR-4512 | 2 | ggGGCCCTAgtacc | O | −0.148 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6895-5p | 2 | ggGGCCCTAgtacc | O | −0.146 | ||||||
| 242792225 | rs41379345 | SNP | Y | G | A | hsa-miR-214-5p | 2 | ACAGGCAttcccc | C | −0.101 |
| hsa-miR-6514-3p | 2 | ACAGGCAttcccc | C | −0.171 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6811-3p | 2 | ACAGGCAttcccc | C | −0.105 | ||||||
| 242792254 | rs55942126 | SNP | N | C | C | hsa-miR-1233-5p | 2 | ggCTCCCACcagg | D | −0.105 |
| hsa-miR-4300 | 2 | gGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.132 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-4456 | 2 | ggctcCCACCAGg | D | −0.078 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-541-3p | 2 | ggctCCCACCAgg | D | −0.092 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-5591-5p | 2 | gGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.125 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6090 | 2 | gGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.149 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-654-5p | 2 | ggctCCCACCAgg | D | −0.102 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6726-5p | 2 | gGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.125 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6769a-5p | 2 | ggctCCCACCAgg | D | −0.102 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6769b-5p | 2 | ggctCCCACCAgg | D | −0.102 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6778-5p | 2 | ggCTCCCACcagg | D | −0.086 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6827-5p | 2 | GGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.348 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-920 | 2 | gGCTCCCAccagg | D | −0.132 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-92a-2-5p | 2 | ggctCCCACCAgg | D | −0.08 | ||||||
| A | hsa-miR-505-5p | 2 | GGCTCCAaccagg | C | −0.144 | |||||
| hsa-miR-6874-5p | 2 | gGCTCCAAccagg | C | −0.115 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-92a-1-5p | 2 | ggctCCAACCAgg | C | −0.071 | ||||||
| 242792292 | rs56015708 | SNP | N | C | C | hsa-miR-4506 | 2 | tggaACCCATTcc | D | −0.154 |
| 242792398 | rs55676463 | SNP | Y | G | A | hsa-miR-6512-3p | 2 | GGCTGGAgttgac | C | −0.099 |
| hsa-miR-6720-5p | 2 | GGCTGGAgttgac | C | −0.099 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6849-3p | 2 | GGCTGGAgttgac | C | −0.102 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-766-3p | 2 | gGCTGGAGttgac | C | −0.099 | ||||||
| 242792447 | rs41428445 | SNP | N | C | T | hsa-miR-4790-3p | 2 | acACCATTCggga | C | 0.007 |
| 242792748 | rs6605260 | SNP | N | C | C | hsa-miR-7113-5p | 2 | gaaacgCCCTGGA | D | −0.078 |
| T | hsa-miR-665 | 2 | gaaacgTCCTGGA | C | −0.043 | |||||
| 242792754 | rs55869797 | SNP | Y | G | A | hsa-miR-450b-3p | 2 | cATCCCAAaacgc | C | −0.067 |
| hsa-miR-5089-5p | 2 | cATCCCAAaacgc | C | −0.028 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-5187-5p | 2 | CATCCCAaaacgc | C | −0.084 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6728-5p | 2 | CATCCCAAaacgc | C | −0.213 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-769-3p | 2 | cATCCCAAaacgc | C | −0.057 | ||||||
| 242792772 | rs55721013 | SNP | N | C | T | hsa-miR-3663-3p | 2 | aGGTGCTCctggc | C | −0.175 |
| 242792831 | rs41492945 | SNP | Y | G | A | hsa-miR-760 | 2 | cgcccCAGAGCCt | C | −0.059 |
| 242792851 | rs6605259 | SNP | Y | G | A | hsa-miR-6508-3p | 2 | ggcgccATGGCCC | C | −0.092 |
| 242792926 | rs111422100 | SNP | Y | G | G | hsa-miR-4514 | 2 | CTGCCTGcgtcca | D | −0.076 |
| hsa-miR-4692 | 2 | CTGCCTGcgtcca | D | −0.085 | ||||||
| A | hsa-miR-1910-3p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.084 | |||||
| hsa-miR-2682-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.114 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-34b-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.11 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-449c-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.121 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6511a-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.094 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6808-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.078 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-6893-5p | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.075 | ||||||
| hsa-miR-940 | 2 | CTGCCTAcgtcca | C | −0.078 | ||||||
| 242793011 | rs6749527 | SNP | Y | G | G | hsa-miR-1304-3p | 2 | caCAGTGAGccca | D | −0.062 |
| hsa-miR-4284 | 3 | cacaGTGAGCCca | D | −0.158 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Nakhle, H.; Al-Shahrani, R.; Al-Ahmadi, J.; Al-Madani, W.; Al-Juhani, R. Integrative In Silico Analysis to Identify Functional and Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) Protein and UTRs: Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Susceptibility. Genes 2025, 16, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030307
Al-Nakhle H, Al-Shahrani R, Al-Ahmadi J, Al-Madani W, Al-Juhani R. Integrative In Silico Analysis to Identify Functional and Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) Protein and UTRs: Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Susceptibility. Genes. 2025; 16(3):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030307
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Nakhle, Hakeemah, Retaj Al-Shahrani, Jawanah Al-Ahmadi, Wesal Al-Madani, and Rufayda Al-Juhani. 2025. "Integrative In Silico Analysis to Identify Functional and Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) Protein and UTRs: Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Susceptibility" Genes 16, no. 3: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030307
APA StyleAl-Nakhle, H., Al-Shahrani, R., Al-Ahmadi, J., Al-Madani, W., & Al-Juhani, R. (2025). Integrative In Silico Analysis to Identify Functional and Structural Impacts of nsSNPs on Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) Protein and UTRs: Potential Biomarkers for Cancer Susceptibility. Genes, 16(3), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030307







