Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CrRLK1-like Gene Family in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Its Role in PAMP-Triggered Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Identification of CrRLK1Ls in S. tuberosum
2.3. Sequence Analysis and Chromosomal Localization in S. tuberosum
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of StCrRLK1Ls
2.5. Analysis of Structural Characterization in S. tuberosum
2.6. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter of StCrRLK1L Genes
2.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of StCrRLK1L Genes
2.8. ROS Production Assay
3. Results
3.1. The Identification of CrRLK1L Subfamily Genes in the S. tuberosum Genome
3.2. StCrRLK1L Gene Distribution on S. tuberosum Chromosome
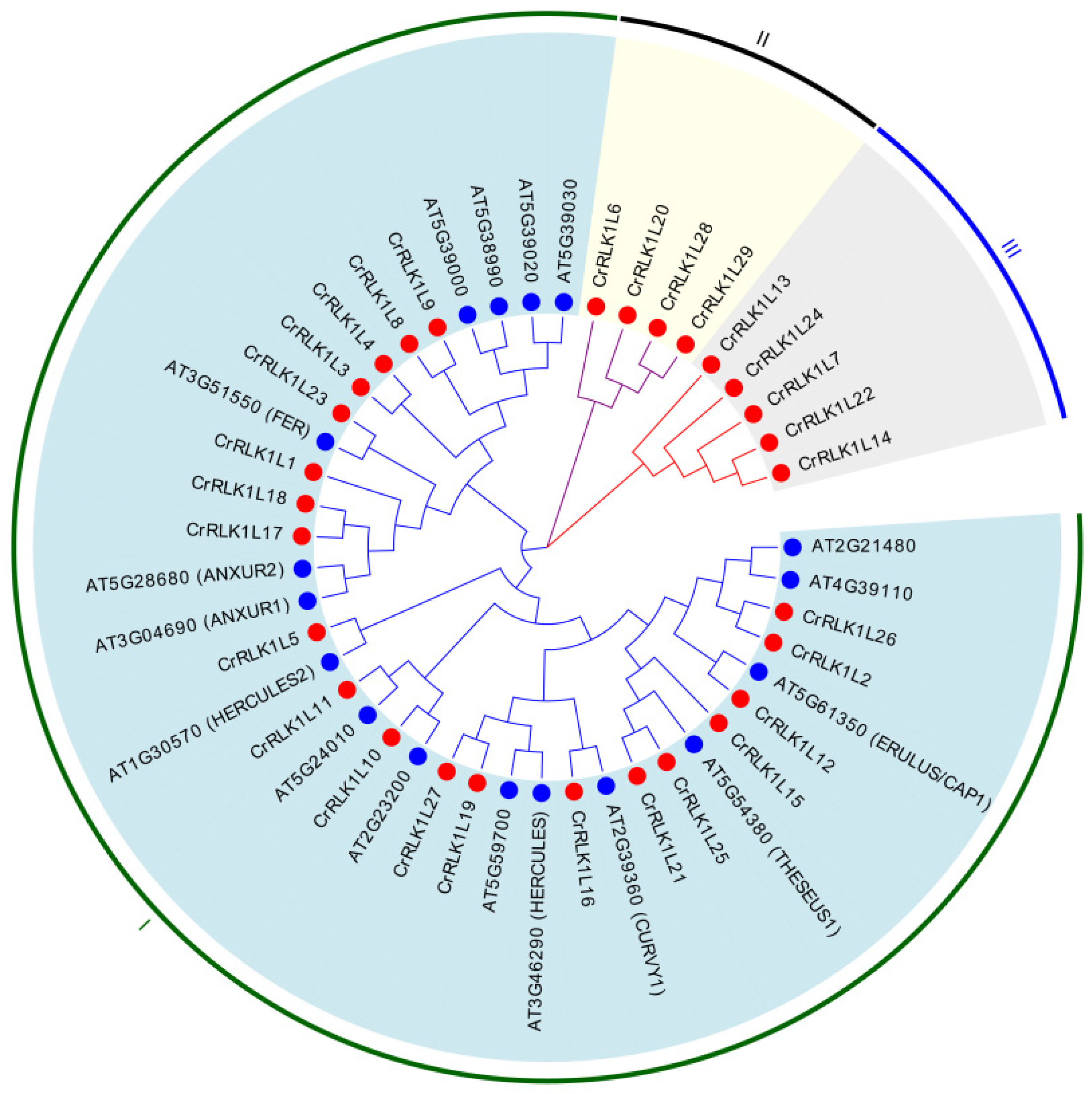
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the CrRLK1L Family in A. thaliana and S. tuberosum
3.4. Gene Structure and Conserved Protein Motif Composition of StCrRLK1L Genes
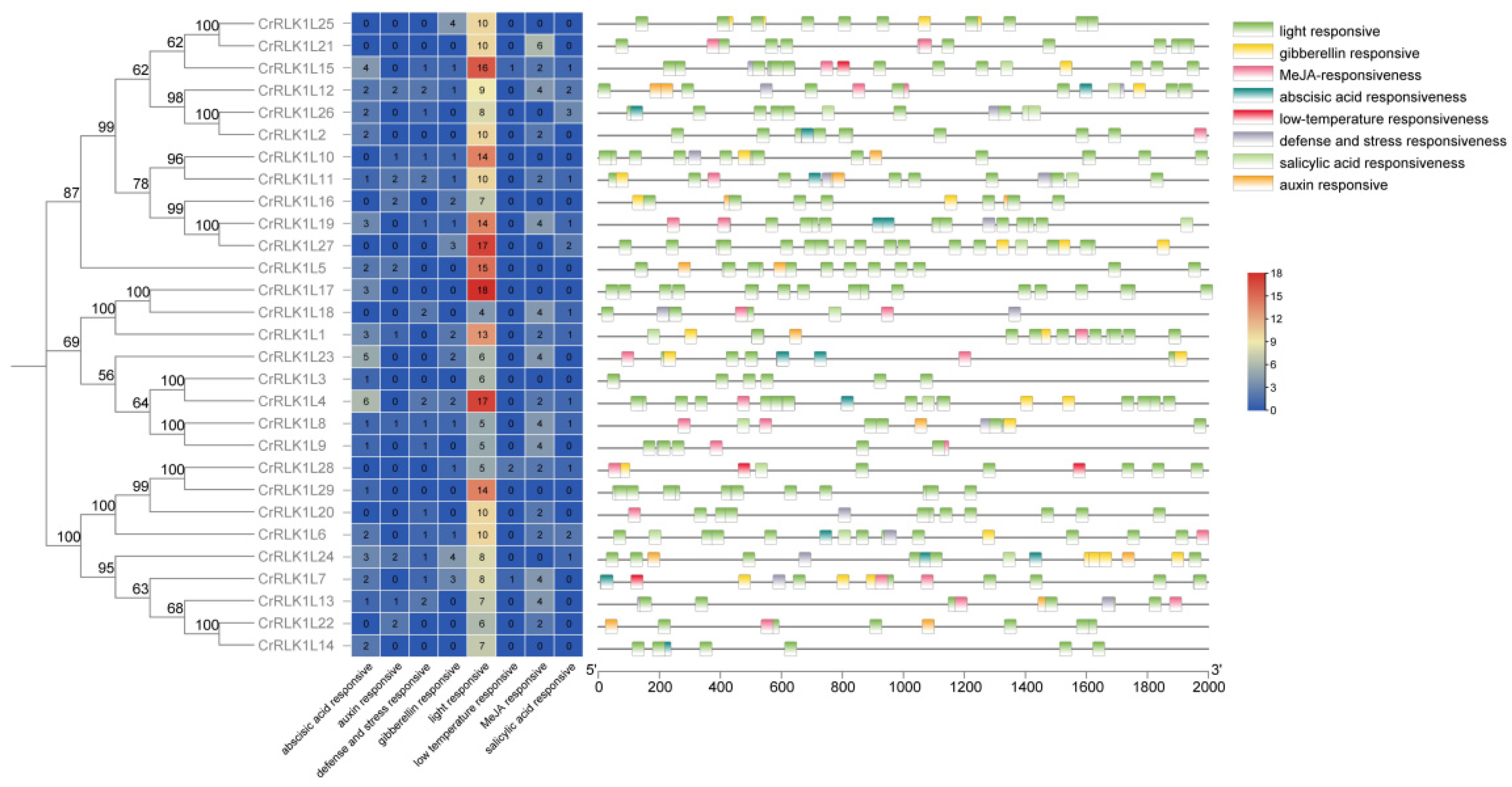
3.5. Stress-Related Cis-Elements in the Promoter of StCrRLK1L Genes
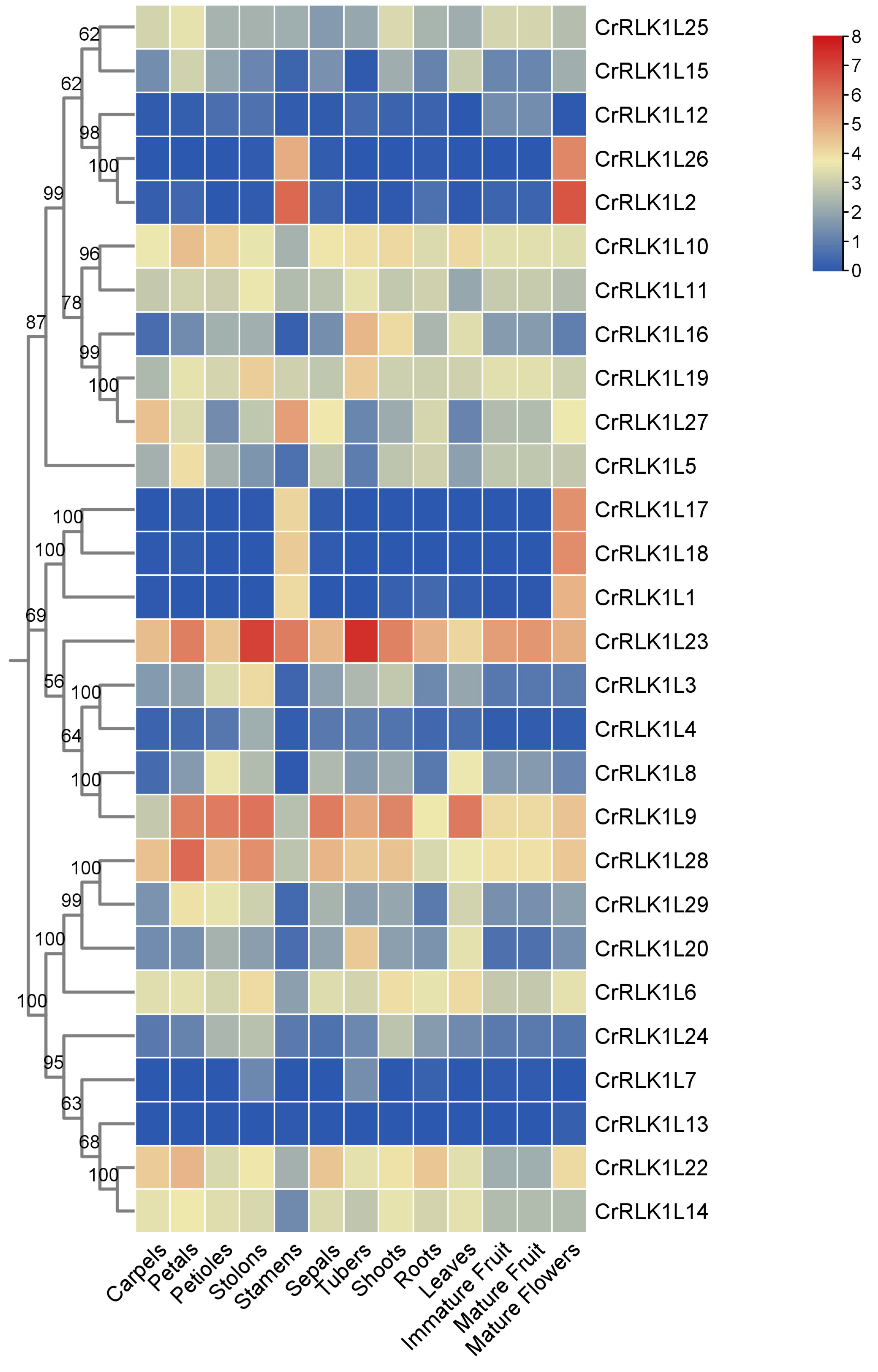
3.6. Expression Pattern Analysis of StCrRLK1L Genes in Different Tissues
3.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of StCrRLK1L Genes Under Phytohormonal- and Abiotic- Stress Treatments
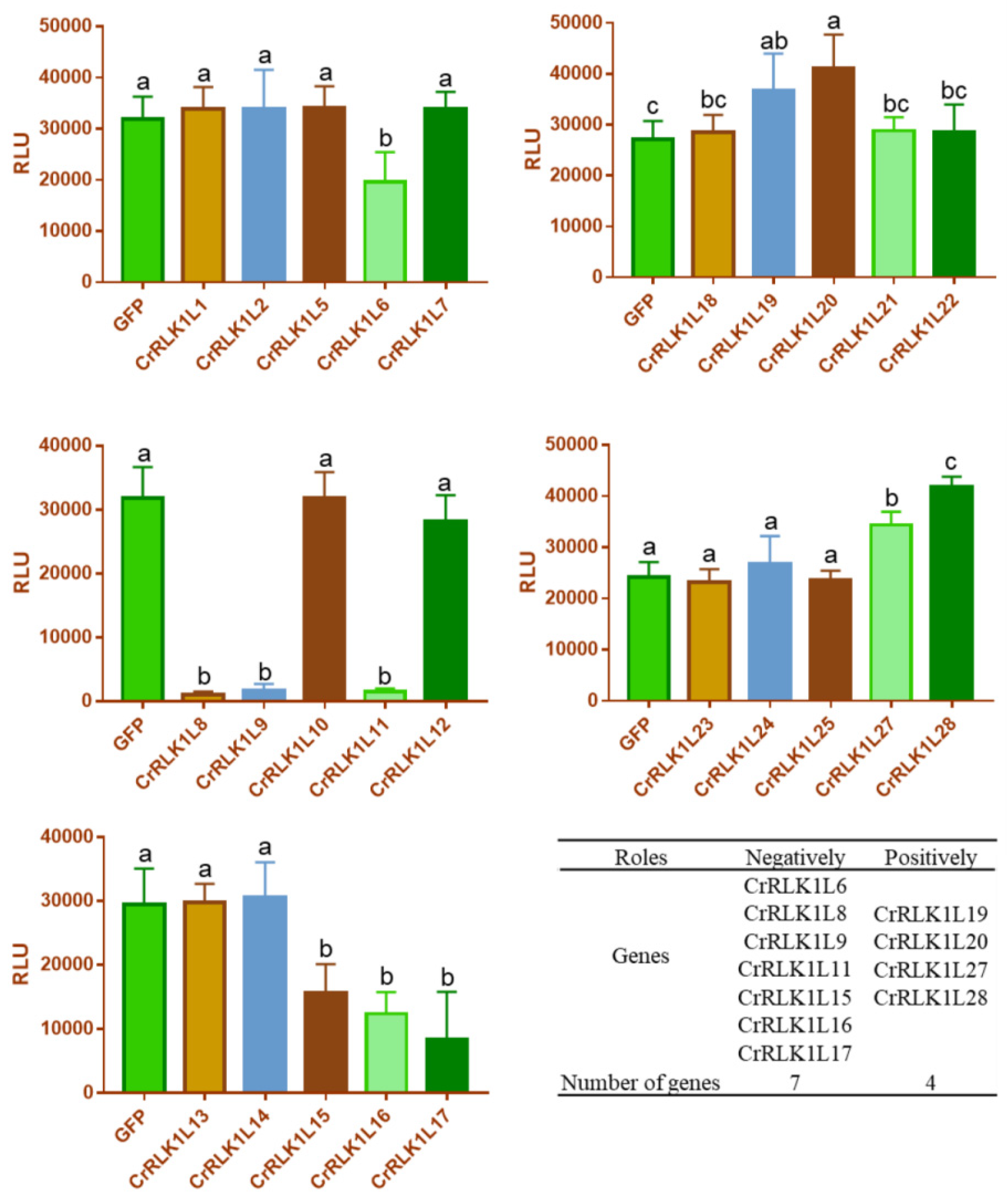
3.8. Analysis of the Role of StCrRLK1L Genes in flg22-Induced ROS in N. benthamiana
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, E.R.; Walker, J.C. Receptor-like protein kinases: The keys to response. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Deguchi, M.; Brustolini, O.J.; Santos, A.A.; Silva, F.F.; Fontes, E.P. The tomato RLK superfamily: Phylogeny and functional predictions about the role of the LRRII-RLK subfamily in antiviral defense. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Muth, P.; Irmler, S.; Schröder, G.; Schröder, J. Novel type of receptor-like protein kinase from a higher plant (Catharanthus roseus). cDNA, gene, intramolecular autophosphorylation, and identification of a threonine important for auto- and substrate phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26684–26689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Kessler, S.A.; Grossniklaus, U. The walls have ears: The role of plant CrRLK1Ls in sensing and transducing extracellular signals. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, H.; Müller, L.M.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Grossniklaus, U. CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases: Not just another brick in the wall. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. THESEUS, FERONIA and relatives: A family of cell wall-sensing receptor kinases? Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.N.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, L.H.; Jeong, H.J.; An, G.; Jung, K.H. Genome-wide identification and analysis of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinases in rice. Planta 2015, 241, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Miranda, J.; Fonseca-García, C.; Nava, N.; Pacheco, R.; Quinto, C. Genome-Wide Identification of the CrRLK1L Subfamily and Comparative Analysis of Its Role in the Legume-Rhizobia Symbiosis. Genes 2020, 11, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, E.; Cai, C.; Zheng, Y.; Shang, X.; Fang, L.; Guo, W. Genome-wide analysis of CrRLK1L gene family in Gossypium and identification of candidate CrRLK1L genes related to fiber development. Mol. Genet. Genom. MGG 2016, 291, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, T.F.; Sun, G.Z.; Zheng, J.C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.Z.; Wei, W.L.; Xu, Z.S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Catharanthus roseus RLK1-Like in Soybean and GmCrRLK1L20 Responds to Drought and Salt Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 614909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, L.; Ye, H.; Yu, X.; Algreen, A.; Yin, Y. Three related receptor-like kinases are required for optimal cell elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7648–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Li, C.; Cheung, A.Y.; Wu, H.M. FERONIA receptor-like kinase regulates RHO GTPase signaling of root hair development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17821–17826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslauriers, S.D.; Larsen, P.B. FERONIA is a key modulator of brassinosteroid and ethylene responsiveness in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Yu, F.; Li, J.; Van de Poel, B.; Tan, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, M.; Chen, L.; et al. FERONIA receptor kinase interacts with S-adenosylmethionine synthetase and suppresses S-adenosylmethionine production and ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Lan, W.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Liu, X.; et al. FERONIA interacts with ABI2-type phosphatases to facilitate signaling cross-talk between abscisic acid and RALF peptide in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5519–E5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Lituiev, D.S.; Nestorova, A.; Franck, C.M.; Thirugnanarajah, S.; Grossniklaus, U. ANXUR receptor-like kinases coordinate cell wall integrity with growth at the pollen tube tip via NADPH oxidases. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Roy, S.; Kritsas, K.; Grobei, M.A.; Jaciubek, M.; Schroeder, J.I.; Grossniklaus, U. Disruption of the pollen-expressed FERONIA homologs ANXUR1 and ANXUR2 triggers pollen tube discharge. Development 2009, 136, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, H.; Feng, B.; Hu, Z.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Franck, C.M.; Meng, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, T.; et al. Differential Regulation of Two-Tiered Plant Immunity and Sexual Reproduction by ANXUR Receptor-Like Kinases. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 3140–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, M.; Monaghan, J.; Smakowska-Luzan, E.; Rovenich, H.; Lehner, A.; Holton, N.; Belkhadir, Y.; Zipfel, C. The receptor kinase FER is a RALF-regulated scaffold controlling plant immune signaling. Science 2017, 355, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liang, X.; Bao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G.; Feng, X.; Dou, D. A malectin-like receptor kinase regulates cell death and pattern-triggered immunity in soybean. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e50442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, D.M.; McLean, K.; Ramsay, G.; Waugh, R.; Bryan, G.J. A single domestication for potato based on multilocus amplified fragment length polymorphism genotyping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14694–14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camire, M.E.; Kubow, S.; Donnelly, D.J. Potatoes and human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, W. Phytophthora infestans: The plant (and R gene) destroyer. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D427–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.S.; Eddy, S.R.; Portugaly, E. Hidden Markov model speed heuristic and iterative HMM search procedure. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38 (Suppl. S2), W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, B.; Mu, D.; Ni, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanaoka, M.M.; Torii, K.U. FERONIA as an upstream receptor kinase for polar cell growth in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17461–17462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Restrepo, J.M.; Huck, N.; Kessler, S.; Gagliardini, V.; Gheyselinck, J.; Yang, W.C.; Grossniklaus, U. The FERONIA receptor-like kinase mediates male-female interactions during pollen tube reception. Science 2007, 317, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Ploderer, M.; Mongelard, G.; Gutierrez, L.; Hauser, M.T. Role of CrRLK1L Cell Wall Sensors HERCULES1 and 2, THESEUS1, and FERONIA in Growth Adaptation Triggered by Heavy Metals and Trace Elements. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.A.; Lindner, H.; Jones, D.S.; Grossniklaus, U. Functional analysis of related CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases in pollen tube reception. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chu, L.C.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, L.Q.; Ye, D. The Arabidopsis CrRLK1L protein kinases BUPS1 and BUPS2 are required for normal growth of pollen tubes in the pistil. Plant J. 2018, 95, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenaers, S.; Balcerowicz, D.; Costa, A.; Vissenberg, K. The Kinase ERULUS Controls Pollen Tube Targeting and Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenaers, S.; Balcerowicz, D.; Breen, G.; Hill, K.; Zdanio, M.; Mouille, G.; Holman, T.J.; Oh, J.; Wilson, M.H.; Nikonorova, N.; et al. The Auxin-Regulated CrRLK1L Kinase ERULUS Controls Cell Wall Composition during Root Hair Tip Growth. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 722–732.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachomo, E.W.; Baptiste, L.J.; Kefela, T.; Saidel, W.M.; Kotchoni, S.O. The Arabidopsis CURVY1 (CVY1) gene encoding a novel receptor-like protein kinase regulates cell morphogenesis, flowering time and seed production. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Watson, J.M.; Stasnik, P.; Borowska, M.; Neuhold, J.; Berger, M.; Stolt-Bergner, P.; Schoft, V.; Hauser, M.T. Multiplex mutagenesis of four clustered CrRLK1L with CRISPR/Cas9 exposes their growth regulatory roles in response to metal ions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, A.; Gelani, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Heat tolerance in plants: An overview. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Suzuki, N.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Mizoguchi, T.; Yoshida, R.; Ichimura, K.; Shinozaki, K. Calmodulin-dependent activation of MAP kinase for ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2011, 41, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chakravorty, D.; Assmann, S.M. The G Protein β-Subunit, AGB1, Interacts with FERONIA in RALF1-Regulated Stomatal Movement. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 2426–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zayed, O.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, P.; Hsu, C.C.; Zhang, L.; Tao, W.A.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Zhu, J.K. Leucine-rich repeat extensin proteins regulate plant salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13123–13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finka, A.; Cuendet, A.F.; Maathuis, F.J.; Saidi, Y.; Goloubinoff, P. Plasma membrane cyclic nucleotide gated calcium channels control land plant thermal sensing and acquired thermotolerance. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3333–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, W.F.; Delauré, S.L.; De Bolle, M.F.; Cammue, B.P. The role of ethylene in host-pathogen interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, S.D. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: From receptor kinase activation to transcriptional networks regulating plant development. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yeh, F.L.; Cheung, A.Y.; Duan, Q.; Kita, D.; Liu, M.C.; Maman, J.; Luu, E.J.; Wu, B.W.; Gates, L.; et al. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins as chaperones and co-receptors for FERONIA receptor kinase signaling in Arabidopsis. Elife 2015, 4, e06587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, L.; Sudat, S.; Dudoit, S.; Zhu, T.; Luan, S. Diverse transcriptional programs associated with environmental stress and hormones in the Arabidopsis receptor-like kinase gene family. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Nolan, T.M.; Song, G.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Schnable, P.S.; Walley, J.W.; Yin, Y. FERONIA Receptor Kinase Contributes to Plant Immunity by Suppressing Jasmonic Acid Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3316–3324.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Gene ID | Chromosome | Gene Location | Protein Length (aa) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | pI | Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrRLK1L1 | PGSC0003DMG400021842 | Chr.1 | 45253663-45256227 | 854 | 95.05 | 6.39 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L2 | PGSC0003DMG400043836 | Chr.1 | 86334523-86337144 | 873 | 96.03 | 5.67 | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L3 | PGSC0003DMG400041071 | Chr.2 | 8613635-8617042 | 1135 | 127.21 | 7.35 | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L4 | PGSC0003DMG400010577 | Chr.2 | 8619185-8623457 | 1188 | 132.56 | 8.35 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L5 | PGSC0003DMG400021186 | Chr.2 | 29091367-29093973 | 868 | 96.30 | 5.57 | Cytoplasm |
| CrRLK1L6 | PGSC0003DMG400028454 | Chr.2 | 31321077-31328397 | 772 | 86.05 | 6.22 | Cell membrane |
| CrRLK1L7 | PGSC0003DMG400030658 | Chr.2 | 41983221-41988281 | 729 | 82.42 | 8.22 | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L8 | PGSC0003DMG400001369 | Chr.2 | 45448141-45451011 | 856 | 95.43 | 6.13 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Mitochondrion, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L9 | PGSC0003DMG400001368 | Chr.2 | 45458609-45461396 | 873 | 97.31 | 6.25 | Cell membrane, Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L10 | PGSC0003DMG400014875 | Chr.3 | 7287447-7289903 | 818 | 91.57 | 5.80 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L11 | PGSC0003DMG400026325 | Chr.3 | 17666491-17668947 | 818 | 91.27 | 7.56 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L12 | PGSC0003DMG400024665 | Chr.3 | 55546289-55548550 | 753 | 83.34 | 6.11 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L13 | PGSC0003DMG400002602 | Chr.3 | 60521274-60526772 | 789 | 87.97 | 5.94 | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L14 | PGSC0003DMG400010746 | Chr.5 | 11413805-11419243 | 875 | 97.96 | 6.14 | Cell membrane |
| CrRLK1L15 | PGSC0003DMG400023419 | Chr.5 | 50431633-50434161 | 842 | 92.84 | 6.59 | Chloroplast, Cytoplasm |
| CrRLK1L16 | PGSC0003DMG400023508 | Chr.5 | 50582425-50584881 | 818 | 91.31 | 5.55 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L17 | PGSC0003DMG400007299 | Chr.6 | 214455-217448 | 997 | 108.69 | 7.10 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L18 | PGSC0003DMG400007307 | Chr.6 | 219466-222135 | 889 | 97.92 | 5.51 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L19 | PGSC0003DMG400009689 | Chr.6 | 6421767-6424256 | 829 | 90.65 | 5.77 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L20 | PGSC0003DMG400017291 | Chr.7 | 50903025-50912626 | 1027 | 113.29 | 8.40 | Cell membrane |
| CrRLK1L21 | PGSC0003DMG402019252 | Chr.7 | 53653922-53656429 | 835 | 91.64 | 5.31 | Cell membrane, Chloroplast, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L22 | PGSC0003DMG400001732 | Chr.9 | 6573941-6582660 | 928 | 102.67 | 5.76 | Cell membrane |
| CrRLK1L23 | PGSC0003DMG400029885 | Chr.9 | 19231605-19234274 | 889 | 97.15 | 5.93 | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L24 | PGSC0003DMG401017656 | Chr.9 | 43843516-43847797 | 904 | 101.13 | 5.78 | Cell membrane |
| CrRLK1L25 | PGSC0003DMG400025030 | Chr.10 | 1778266-1780770 | 834 | 91.29 | 5.30 | Cytoplasm, Extracell, Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L26 | PGSC0003DMG400003406 | Chr.10 | 45284880-45287498 | 872 | 96.70 | 5.96 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L27 | PGSC0003DMG400015547 | Chr.11 | 45084629-45087133 | 834 | 91.51 | 5.73 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L28 | PGSC0003DMG400015391 | Chr.12 | 180926-184123 | 627 | 69.16 | 6.54 | Nucleus |
| CrRLK1L29 | PGSC0003DMG400028617 | Chr.12 | 50035429-50041955 | 924 | 102.81 | 6.06 | Cell membrane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Ji, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CrRLK1-like Gene Family in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Its Role in PAMP-Triggered Immunity. Genes 2025, 16, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030308
Bao Y, Zhao R, Hu S, Li X, Wang L, Wang J, Ji J, Wang W, Zhu C, Chen J, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CrRLK1-like Gene Family in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Its Role in PAMP-Triggered Immunity. Genes. 2025; 16(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Yazhou, Ru Zhao, Sixian Hu, Xiaoli Li, Like Wang, Ji Wang, Junbin Ji, Weiduo Wang, Changqing Zhu, Jiajia Chen, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CrRLK1-like Gene Family in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Its Role in PAMP-Triggered Immunity" Genes 16, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030308
APA StyleBao, Y., Zhao, R., Hu, S., Li, X., Wang, L., Wang, J., Ji, J., Wang, W., Zhu, C., Chen, J., Ben, A., Peng, J., & Liu, T. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CrRLK1-like Gene Family in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and Its Role in PAMP-Triggered Immunity. Genes, 16(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030308






