Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
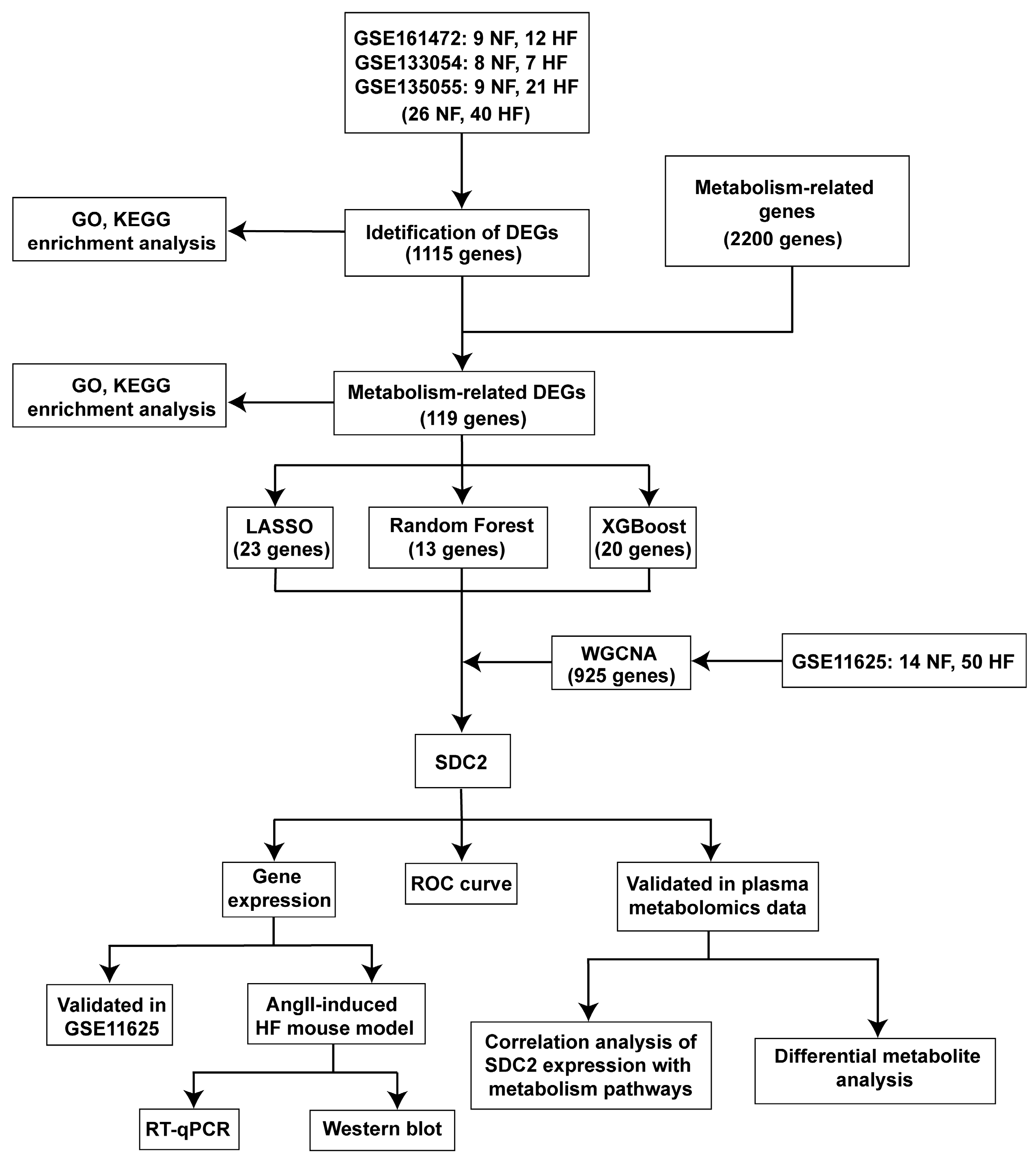
2.1. Data Preprocessing and Integration
2.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in HF and Related Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Machine Learning
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.5. Single-Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA)
2.6. Mouse Model of Heart Failure
2.7. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Receiver Operating Characteristic Analysis
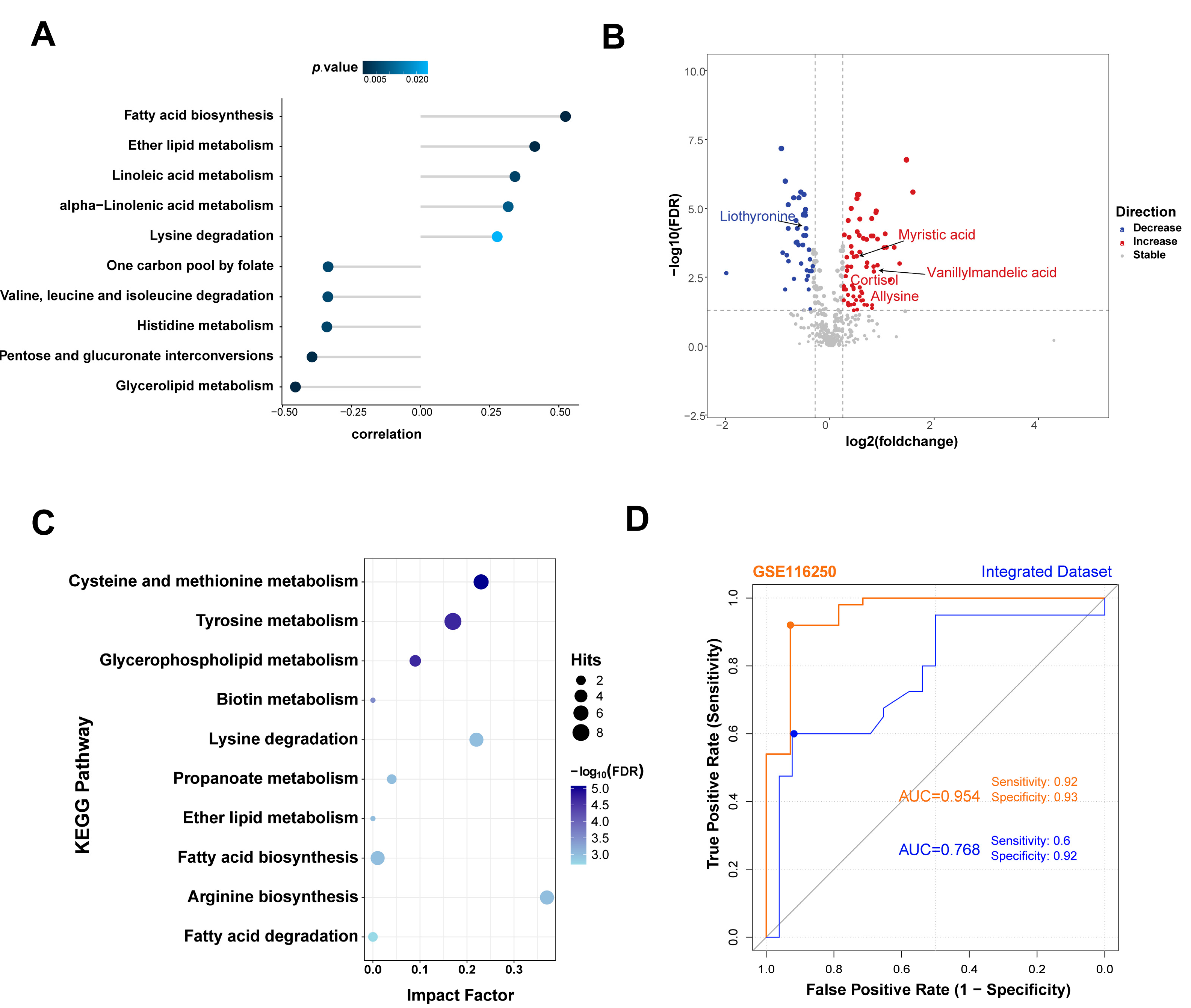
2.10. Identification of Differential Metabolites in Plasma Metabolomics
2.11. Drug Identification via DrugBank Database
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
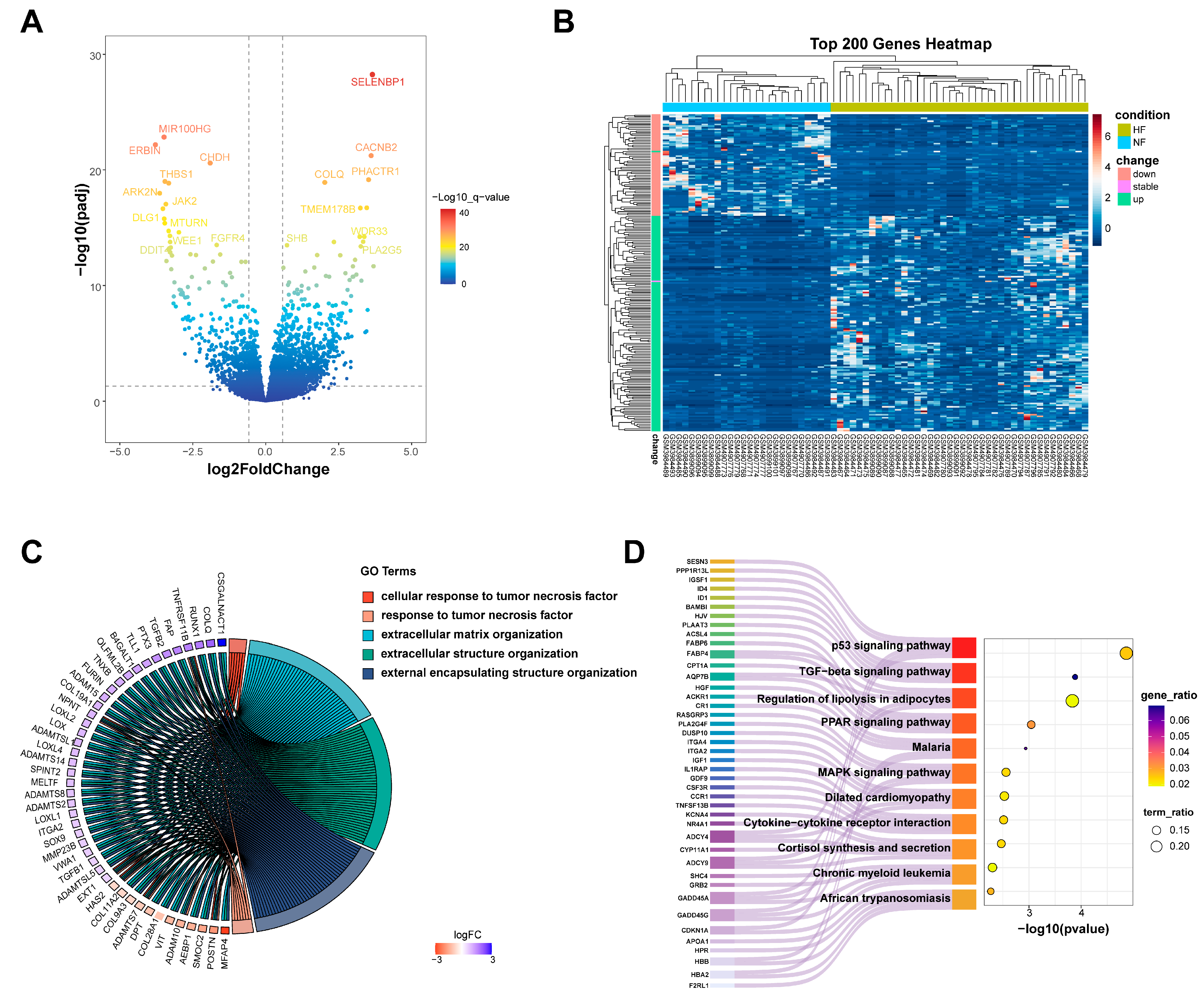
3.1. Identification of DEGs in HF
3.2. Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in HF
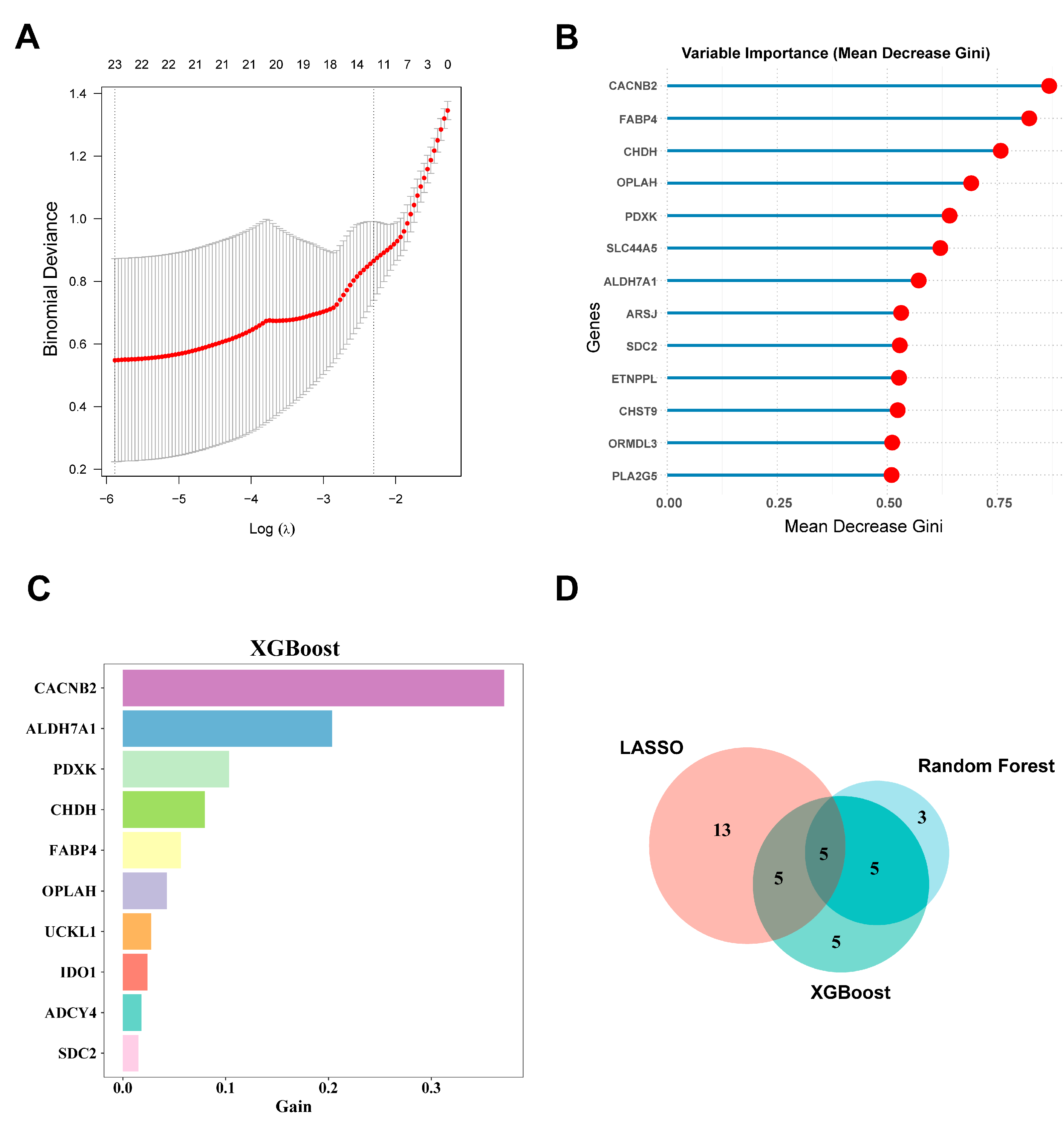
3.3. Screening of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes Associated with HF via Machine Learning
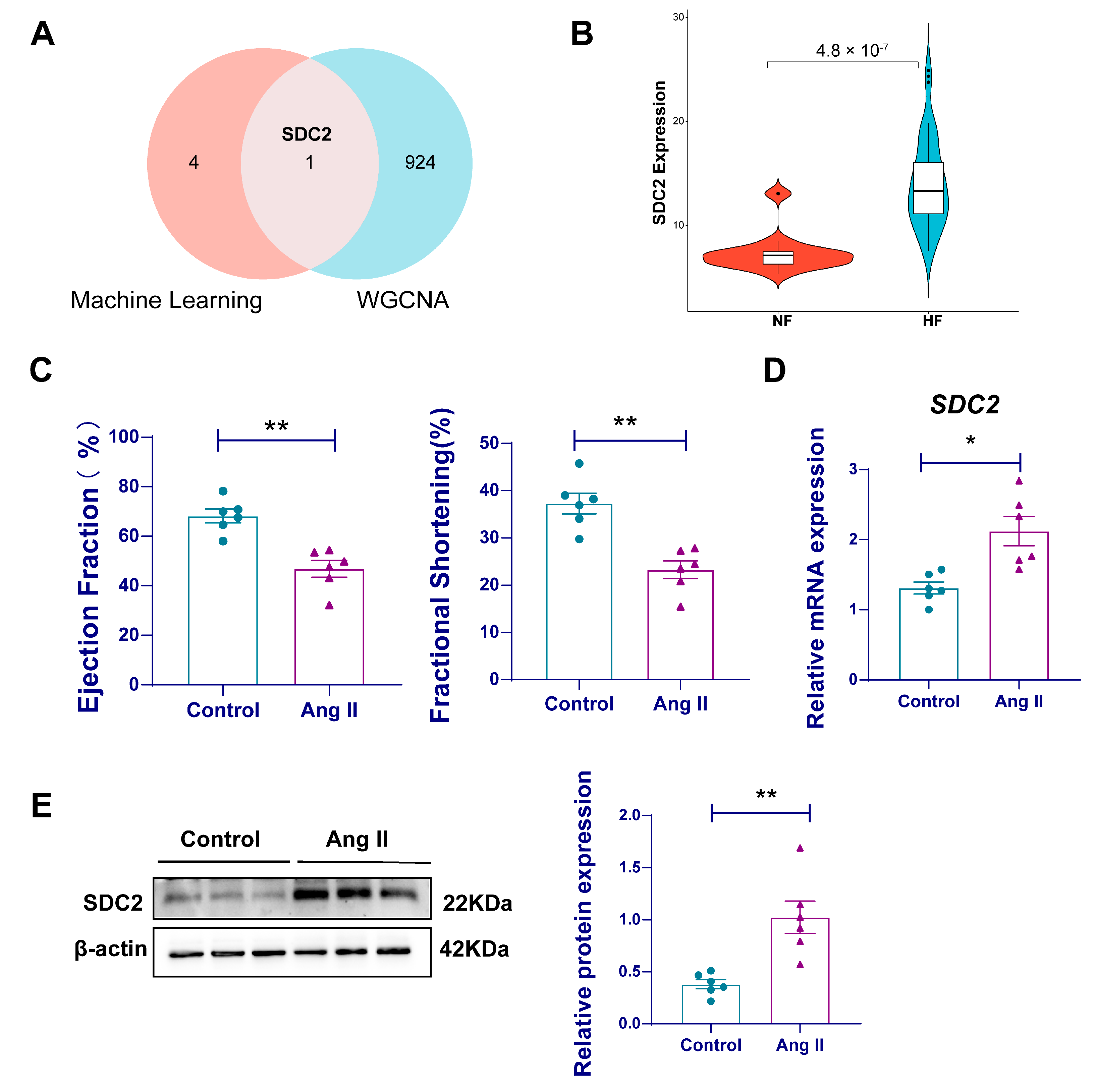
3.4. Identification of Gene Modules in HF Using WGCNA
3.5. SDC2 Is a Key Gene Associated with HF
3.6. SDC2 Expression Is Associated with Metabolic Changes in HF
3.7. Potential Clinical Applications of SDC2 in the Diagnosis and Treatment of HF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cellular component |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GS | Gene significance |
| HF | Heart failure |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LASSO | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| MF | Molecular function |
| MM | Module membership |
| NF | Non-failing |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription quantitative PCR |
| SDC2 | Syndecan 2 |
| WGCNA | Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Tanai, E.; Frantz, S. Pathophysiology of Heart Failure. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 6, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Sha, X.; Huang, C.; Hu, L.; Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Mitochondrial GSNOR Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction via ANT1 Denitrosylation. Circ. Res. 2023, 133, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.E.; Cowie, M.R.; Chow, A.W. Prediction and prevention of sudden cardiac death in heart failure. Heart 2005, 91, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, N.; Judge, A.; Tran, J.; Mohseni, H.; Hedgecott, D.; Crespillo, A.P.; Allison, M.; Hemingway, H.; Cleland, J.G.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Temporal trends and patterns in heart failure incidence: A population-based study of 4 million individuals. Lancet 2018, 391, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, N.L.; Zhong, W.; Shu, J.; Abu Much, A.; Lotan, D.; Grupper, A.; Younis, A.; Dai, H. Burden of heart failure and underlying causes in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, P.; Gao, B.; Li, D.; Wu, C.; Zhu, X.; He, Y.; Mo, F.; Qi, Y.; Jin, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. The transcriptional repressor HEY2 regulates mitochondrial oxidative respiration to maintain cardiac homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Tian, R.; Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1487–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Paltzer, W.G.; Mahmoud, A.I. The Role of Metabolism in Heart Failure and Regeneration. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 702920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Dalt, L.; Cabodevilla, A.G.; Goldberg, I.J.; Norata, G.D. Cardiac lipid metabolism, mitochondrial function, and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritterhoff, J.; Tian, R. Metabolic mechanisms in physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: New paradigms and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 812–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yin, J.; Dwyer, D.; Yamawaki, T.; Zhou, H.; Ge, H.; Han, C.Y.; Shkumatov, A.; Snyder, K.; Ason, B.; et al. Chamber-enriched gene expression profiles in failing human hearts with reduced ejection fraction. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Yu, P.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, L. Single-Cell Reconstruction of Progression Trajectory Reveals Intervention Principles in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circulation 2020, 141, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jia, P.; Xiong, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lai, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, J. Multi-level transcriptome sequencing identifies COL1A1 as a candidate marker in human heart failure progression. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, M.E.; Cocciolo, A.; Slavov, D.; Jones, K.L.; Sweet, J.R.; Graw, S.L.; Reece, T.B.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Bristow, M.R.; Mestroni, L.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of human heart failure reveals dysregulated cell adhesion in dilated cardiomyopathy and activated immune pathways in ischemic heart failure. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sillanpää, M.J. Overview of LASSO-related penalized regression methods for quantitative trait mapping and genomic selection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, L.; Vitale, R.; van Vorstenbosch, R.; Stavropoulos, G.; Pender, J.; Jonkers, D.; Schooten, F.V.; Smolinska, A. Constructing bi-plots for random forest: Tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1131, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, G.; Rao, D.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Immune Landscape of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis at Single-Cell Level. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Klinger, C.M.; Franklin, M.; Oler, E.; Wilson, A.; Pon, A.; Cox, J.; Chin, N.E.L.; Strawbridge, S.A.; et al. DrugBank 6.0: The DrugBank Knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1265–D1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Pan, C.; Cai, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Pang, J.; Xu, F.; Wu, S.; Kou, T.; et al. Plasma metabolomics reveals the shared and distinct metabolic disturbances associated with cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essner, J.J.; Chen, E.; Ekker, S.C. Syndecan-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonova, E.I.; Galzitskaia, O.V. Role of syndecan-2 in amyloid plaque formation. Mol. Biol. 2015, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.W. Chapter 18—Isolation and functional analysis of syndecans. In Methods in Cell Biology; Mecham, R.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 143, pp. 317–333. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, J.J.; Zhang, F.; Beaudet, J.M.; Linhardt, R.J.; Colón, W. Divergent effect of glycosaminoglycans on the in vitro aggregation of serum amyloid A. Biochimie 2014, 104, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Lei, Y.T.; Hong, C.J.; Hsueh, Y.P. Syndecan-2 induces filopodia and dendritic spine formation via the neurofibromin-PKA-Ena/VASP pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 177, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.M.; Li, J.P. Towards understanding the roles of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 516028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, C.M.; da Silva, D.A.; Sartorio, P.V.; Silva, T.D.; Saad, S.S.; Nader, H.B.; Forones, N.M.; Toma, L. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Human Colorectal Cancer. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2018, 2018, 8389595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.D.; Oh, T.J.; Chung, T.H.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, Y.N.; An, S.; Kim, N.K. Early detection of colorectal cancer based on presence of methylated syndecan-2 (SDC2) in stool DNA. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Lu, F.; Ding, Z.; Huang, L.; Hu, K.; Chen, J.; Wei, L. Identification of Heparan Sulfate in Dilated Cardiomyopathy by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 900428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchnowski, P.; Śmigielski, W. Usefulness of myocardial damage biomarkers in predicting cardiogenic shock in patients undergoing heart valve surgery. Kardiol. Pol. 2024, 82, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krittayaphong, R.; Boonyasirinant, T.; Saiviroonporn, P.; Thanapiboonpol, P.; Nakyen, S.; Udompunturak, S. Correlation Between NT-Pro BNP Levels and Left Ventricular Wall Stress, Sphericity Index and Extent of Myocardial Damage: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, I.C.; Mîrșu-Păun, A.; Bejan, C.G.; Stănescu, A.-M.A. NT-proBNP for Heart Failure Screening in Primary Care in an Eastern European Country: What We Know and Proposed Steps. Epidemiologia 2025, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Mueller, C.; Mirò, O.; Pascual Figal, D.A.; Jacob, J.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Llorens, P.; Wussler, D.; Kozhuharov, N.; et al. Admission high-sensitivity troponin T and NT-proBNP for outcome prediction in acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 293, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L.; Vergaro, G.; Ripoli, A.; Latini, R.; Masson, S.; Magnoli, M.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Tavazzi, L.; et al. Prognostic Value of High-Sensitivity Troponin T in Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation 2018, 137, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Datasets | Year | Sample Size | Platform | Read Length | Layout | Sequencing Technology | Instrument Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE161472 [12] | 2020 | 9 NF; 12 HF | GPL11154 | 150 bp | Paired | Illumina | HiSeq 2000 |
| GSE133054 [13] | 2019 | 8 NF; 7 HF | GPL18537 | 70 bp | Paired | Illumina | NextSeq 500 |
| GSE135055 [14] | 2020 | 9 NF; 21 HF | GPL16791 | 150 bp | Paired | Illumina | Hiseq 2500 |
| GSE116250 [15] | 2018 | 14 NF; 50 HF | GPL16791 | 50 bp | Single | Illumina | Hiseq 2500 |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| SDC2-Forward | ACAGAAGTTCTAGCAGCCGTC |
| SDC2-Reverse | TGGATGGTTTGCGTTCTCCA |
| β-actin-Forward | CACTGTCGAGTCGCGTCC |
| β-actin-Reverse | TCATCCATGGCGAACTGGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.; Lv, B.; Du, J.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Cui, C.; Jin, H. Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis. Genes 2025, 16, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030305
Peng H, Lv B, Du J, Huang Y, Cui Q, Cui C, Jin H. Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis. Genes. 2025; 16(3):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030305
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Hanlin, Boyang Lv, Junbao Du, Yaqian Huang, Qinghua Cui, Chunmei Cui, and Hongfang Jin. 2025. "Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis" Genes 16, no. 3: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030305
APA StylePeng, H., Lv, B., Du, J., Huang, Y., Cui, Q., Cui, C., & Jin, H. (2025). Identification of Metabolism-Related Hub Genes in Heart Failure via Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis. Genes, 16(3), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030305








