Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Gene–Environment Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample and Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OFC | Orofacial cleft |
| CL/P | Cleft lip with or without cleft palate |
| CPO | Cleft palate only |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| PoO | Parent of origin |
References
- Jiang, R.; Bush, J.O.; Lidral, A.C. Development of the upper lip: Morphogenetic and molecular mechanisms. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panamonta, V.; Pradubwong, S.; Panamonta, M.; Chowchuen, B. Global Birth Prevalence of Orofacial Clefts: A Systematic Review. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2015, 98 (Suppl. 7), S11–S21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christensen, K.; Juel, K.; Herskind, A.M.; Murray, J.C. Long term follow up study of survival associated with cleft lip and palate at birth. BMJ 2004, 328, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngai, C.W.; Martin, W.L.; Tonks, A.; Wyldes, M.P.; Kilby, M.D. Are isolated facial cleft lip and palate associated with increased perinatal mortality? A cohort study from the West Midlands Region, 1995–1997. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2005, 17, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivertsen, A.; Wilcox, A.J.; Skjaerven, R.; Vindenes, H.A.; Abyholm, F.; Harville, E.; Lie, R.T. Familial risk of oral clefts by morphological type and severity: Population based cohort study of first degree relatives. BMJ 2008, 336, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.B.; Wade, M.J. What are maternal effects (and what are they not)? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, H.A.; Cheverud, J.M.; Wolf, J.B. Genomic imprinting and parent-of-origin effects on complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Murray, J.C.; Marazita, M.L.; Munger, R.G.; Ruczinski, I.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Wu, T.; Murray, T.; Redett, R.J.; Wilcox, A.J.; et al. Genome wide study of maternal and parent-of-origin effects on the etiology of orofacial clefts. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jugessur, A.; Shi, M.; Gjessing, H.K.; Lie, R.T.; Wilcox, A.J.; Weinberg, C.R.; Christensen, K.; Boyles, A.L.; Daack-Hirsch, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; et al. Maternal genes and facial clefts in offspring: A comprehensive search for genetic associations in two population-based cleft studies from Scandinavia. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Ludwig, K.U.; Böhmer, A.C.; Rubini, M.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.; Mossey, P.A.; Mangold, E.; Sharp, A.J. Genome-wide analysis of parent-of-origin effects in non-syndromic orofacial clefts. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sinnathamby, V.; Yu, Y.; Sikora, L.; Johnson, C.Y.; Mossey, P.; Little, J. Folate intake, markers of folate status and oral clefts: An updated set of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1699–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lie, R.T.; Wilcox, A.J.; Taylor, J.; Gjessing, H.K.; Saugstad, O.D.; Aabyholm, F.; Vindenes, H. Maternal smoking and oral clefts: The role of detoxification pathway genes. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, H.J.; Hassan, M.H.; Innes, N.P.; Elkodary, H.M.; Little, J.; Mossey, P.A. Passive smoking in the etiology of non-syndromic orofacial clefts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossey, P.A.; Little, J.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.; Molloy, A.; Peterlin, B.; Shaw, W.C.; Johnson, C.; FitzPatrick, D.R.; Franceschelli, P.; Rubini, M. Genetic Interactions in Nonsyndromic Orofacial Clefts in Europe-EUROCRAN Study. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2017, 54, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjessing, H.K.; Lie, R.T. Case-parent triads: Estimating single- and double-dose effects of fetal and maternal disease gene haplotypes. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2006, 70, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Gaynor, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, R.; Dey, R.; Arnett, D.K.; Aslibekyan, S.; et al. Dynamic incorporation of multiple in silico functional annotations empowers rare variant association analysis of large whole-genome sequencing studies at scale. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GTEx Consortium. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, J.; Bowler, E.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Hall, P.; Hastings, E.; Junkins, H.; McMahon, A.; Milano, A.; Morales, J.; et al. The new NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies (GWAS Catalog). Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D896–D901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Du, Y.; Niu, G.; Xia, S.; Liu, J. Folate deficiency may increase the risk for elevated TSH in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium; Aleksander, S.A.; Balhoff, J.; Carbon, S.; Cherry, J.M.; Drabkin, H.J.; Ebert, D.; Feuermann, M.; Gaudet, P.; Harris, N.L.; et al. The Gene Ontology knowledgebase in 2023. Genetics 2023, 224, iyad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugessur, A.; Murray, J.C. Orofacial clefting: Recent insights into a complex trait. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, T.C. Taking it to the max: The genetic and developmental mechanisms coordinating midfacial morphogenesis and dysmorphology. Clin. Genet. 2004, 65, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzotti, A.; Balansky, R.M.; Cartiglia, C.; Camoirano, A.; Longobardi, M.; De Flora, S. Genomic and transcriptional alterations in mouse fetus liver after transplacental exposure to cigarette smoke. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivorra, C.; Fraga, M.F.; Bayon, G.F.; Fernandez, A.F.; Garcia-Vicent, C.; Chaves, F.J.; Redon, J.; Lurbe, E. DNA methylation patterns in newborns exposed to tobacco in utero. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Garland, M.A.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Reynolds, K.; McMahon, M.; Rajakumar, R.; Islam, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Cellular and developmental basis of orofacial clefts. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1558–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerdevik, M.; Haaland, O.A.; Romanowska, J.; Lie, R.T.; Jugessur, A.; Gjessing, H.K. Parent-of-origin-environment interactions in case-parent triads with or without independent controls. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2018, 82, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaland, O.A.; Jugessur, A.; Gjerdevik, M.; Romanowska, J.; Shi, M.; Beaty, T.H.; Marazita, M.L.; Murray, J.C.; Wilcox, A.J.; Lie, R.T.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of parent-of-origin interaction effects with environmental exposure (PoOxE): An application to European and Asian cleft palate trios. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaland, O.A.; Lie, R.T.; Romanowska, J.; Gjerdevik, M.; Gjessing, H.K.; Jugessur, A. A Genome-Wide Search for Gene-Environment Effects in Isolated Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate Triads Points to an Interaction between Maternal Periconceptional Vitamin Use and Variants in ESRRG. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Venkataraghavan, S.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Leslie, E.J.; Marazita, M.L.; Feingold, E.; Weinberg, S.M.; Ruczinski, I.; Taub, M.A.; Scott, A.F.; et al. Detecting Gene-Environment Interaction for Maternal Exposures Using Case-Parent Trios Ascertained Through a Case with Non-Syndromic Orofacial Cleft. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 621018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Fallin, M.D.; Shi, M.; Ruczinski, I.; Liang, K.Y.; Hetmanski, J.B.; Wang, H.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Huang, S.; Ye, X.; et al. Evidence of gene-environment interaction for the RUNX2 gene and environmental tobacco smoke in controlling the risk of cleft lip with/without cleft palate. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, D.; Vergara, C.; Taub, M.A.; Wojcik, G.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Beaty, T.H.; Duggal, P. Benchmarking statistical methods for analyzing parent-child dyads in genetic association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2022, 46, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, J.; Higgins, J.P.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Moher, D.; Gagnon, F.; von Elm, E.; Khoury, M.J.; Cohen, B.; Davey-Smith, G.; Grimshaw, J.; et al. STrengthening the REporting of Genetic Association Studies (STREGA): An extension of the STROBE statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasevic, N. Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting. Master’s Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Number of Triads/Dyads (%) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 444) | Cleft Lip with or Without Palate (n = 317) | Cleft Palate Only (n = 125) | |
| Maternal periconceptual exposure | |||
| Smoking | 99 (22.3) | 73 (23.0) | 26 (20.8) |
| Supplements containing folic acid | 218 (49.1) | 152 (47.9) | 66 (52.8) |
| Child sex | |||
| Male | 272 (61.3) | 213 (67.2) | 57 (45.6) |
| Female | 172 (38.7) | 104 (32.8) | 68 (54.4) |
| Country of origin | |||
| Italy | 233 (52.5) | 182 (57.4) | 49 (39.2) |
| UK | 33 (7.4) | 18 (5.7) | 15 (12.0) |
| Spain | 8 (1.8) | 8 (2.5) | 0 (0) |
| Hungary | 84 (18.9) | 56 (17.7) | 28 (22.4) |
| Bulgaria | 31 (7.0) | 25 (7.9) | 6 (4.8) |
| Estonia | 24 (5.4) | 10 (3.2) | 14 (11.2) |
| Slovakia | 31 (7.0) | 18 (5.7) | 13 (10.4) |
| SNP | Chromosome (chr) | Minor/Other Allele (Minor Allele Frequency) | Gene | p-value 1 | Pooled Region p-Value 2 | Relative Risk or Relative Risk Ratio 3 (No Environment/Environment) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal—Folic acid supplementation | ||||||
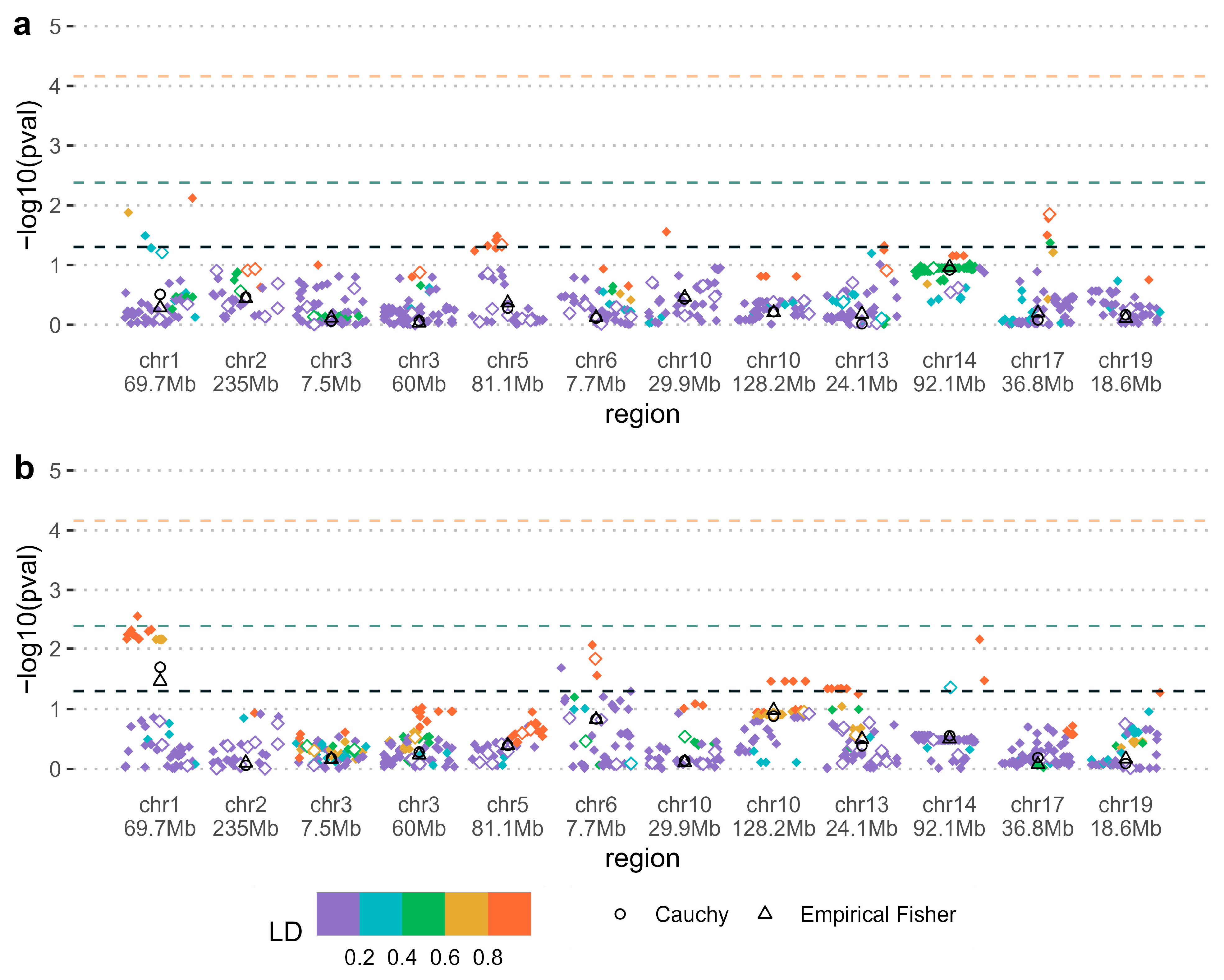
| rs12729671 | chr1 69.7Mb | C/T (0.22) | LRRC7 | 0.0029 | 0.020 | 1.48 [1.07, 2.08]/0.73 [0.52, 1.02] |
| Parent of origin—Smoking | ||||||
| rs1437897 | chr2 133Mb | A/G (0.26) | NCKAP5 | 0.0033 | 0.041 | 0.60 [0.33, 1.07]/3.97 [1.27, 12.03] |
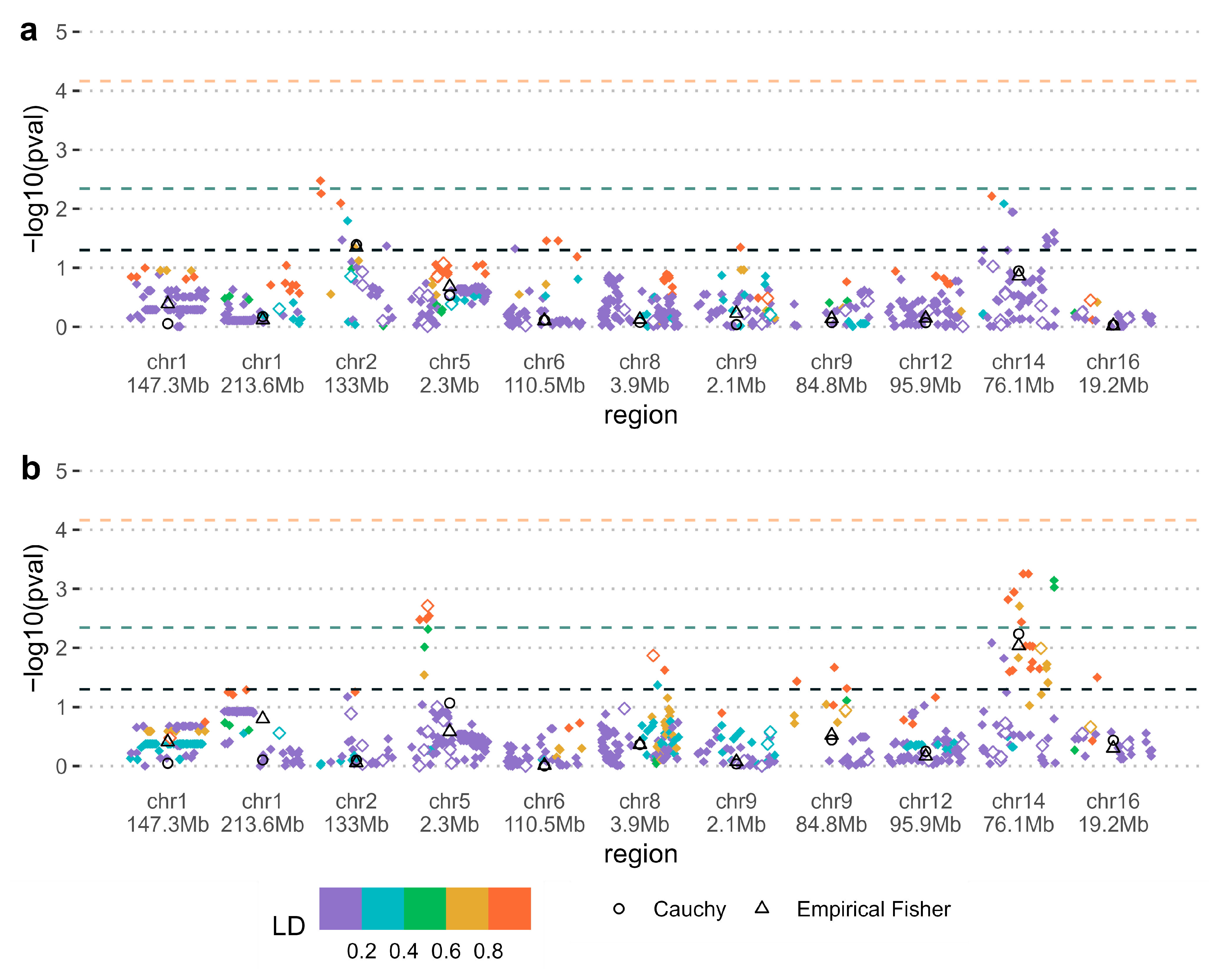
| Parent of origin—Folic acid supplementation | ||||||
| rs139115930 | chr14 76.1Mb | C/T (0.15) | Intergenic | 0.00056 | 0.0058 | 2.89 [1.22, 7.01]/0.29 [0.11, 0.75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasevic, N.; Bastasic, J.; Rubini, M.; Rakesh, M.R.; Burkett, K.M.; Ray, D.; Mossey, P.A.; Peterlin, B.; Khan, M.F.J.; Ravaei, A.; et al. Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Gene–Environment Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting. Genes 2025, 16, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020195
Rasevic N, Bastasic J, Rubini M, Rakesh MR, Burkett KM, Ray D, Mossey PA, Peterlin B, Khan MFJ, Ravaei A, et al. Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Gene–Environment Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting. Genes. 2025; 16(2):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020195
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasevic, Nikola, Joseph Bastasic, Michele Rubini, Mohan R. Rakesh, Kelly M. Burkett, Debashree Ray, Peter A. Mossey, Borut Peterlin, Mohammad Faisal J. Khan, Amin Ravaei, and et al. 2025. "Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Gene–Environment Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting" Genes 16, no. 2: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020195
APA StyleRasevic, N., Bastasic, J., Rubini, M., Rakesh, M. R., Burkett, K. M., Ray, D., Mossey, P. A., Peterlin, B., Khan, M. F. J., Ravaei, A., Autelitano, L., Meazzini, M. C., Little, J., & Roy-Gagnon, M.-H. (2025). Maternal and Parent-of-Origin Gene–Environment Effects on the Etiology of Orofacial Clefting. Genes, 16(2), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020195









