Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Sorghum CNGC Gene Families
2.2. Analysis of SbCNGC Chromosome Localization and Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of CNGC in Sorghum
2.4. SbCNGC Gene Characteristics
2.5. Predictive Analysis of Cis-Elements of the SbCNGC Promoter
2.6. Duplication Analyses of SbCNGCs
2.7. Prediction of miRNAs Targeting SbCNGC
2.8. GO and KEGG Annotation Analysis
2.9. Analysis of SbCNGC Gene Expression Pattern in Different Tissues and Different Abiotic Stresses
2.10. Plant Material and Abiotic Stress Treatments
2.11. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis of SbCNGC Gene Expression Under Cold and Heat Stresses
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of the SbCNGC Gene in Sorghum
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the SbCNGC Gene Family
3.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs of SbCNGC Genes
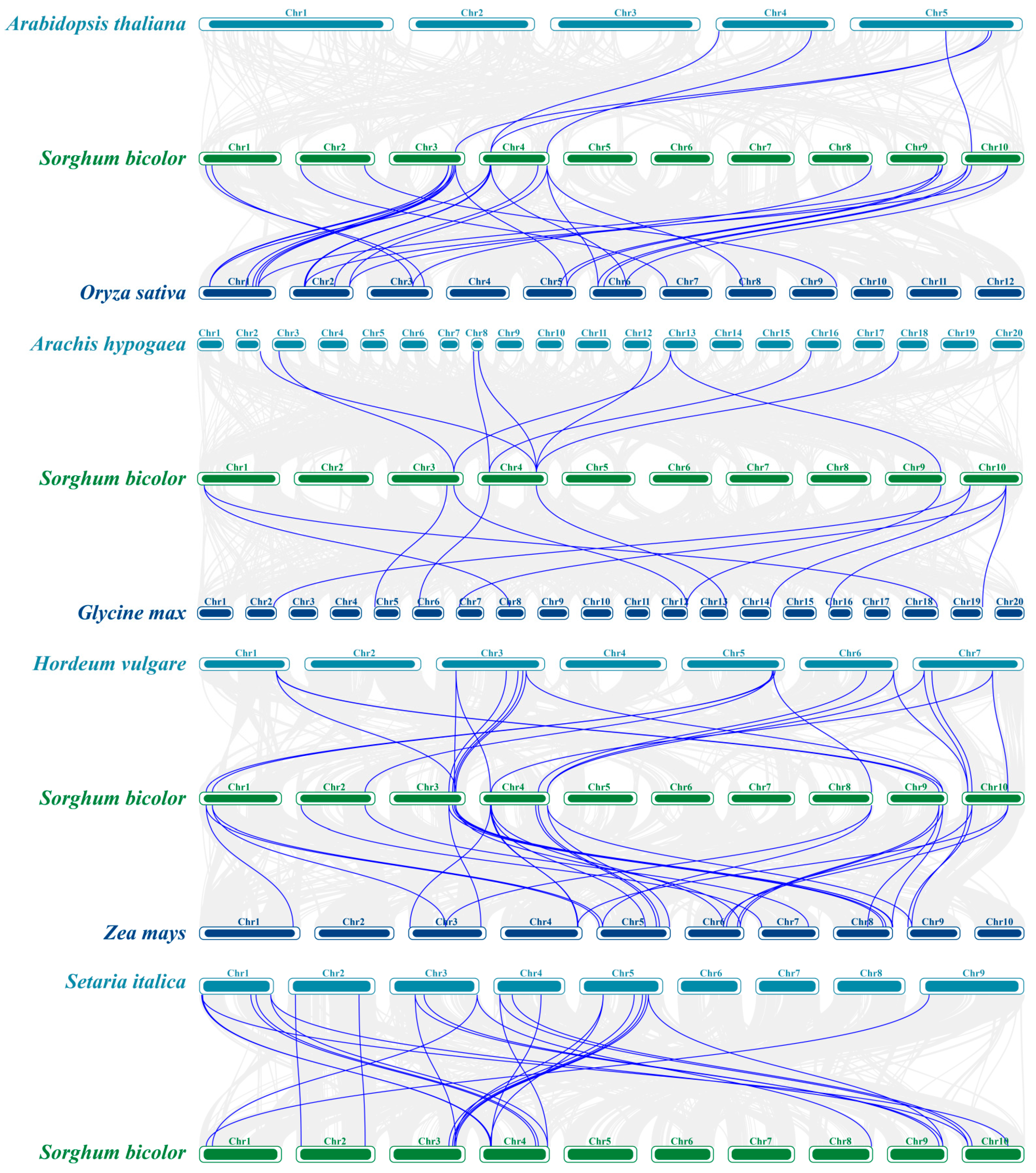
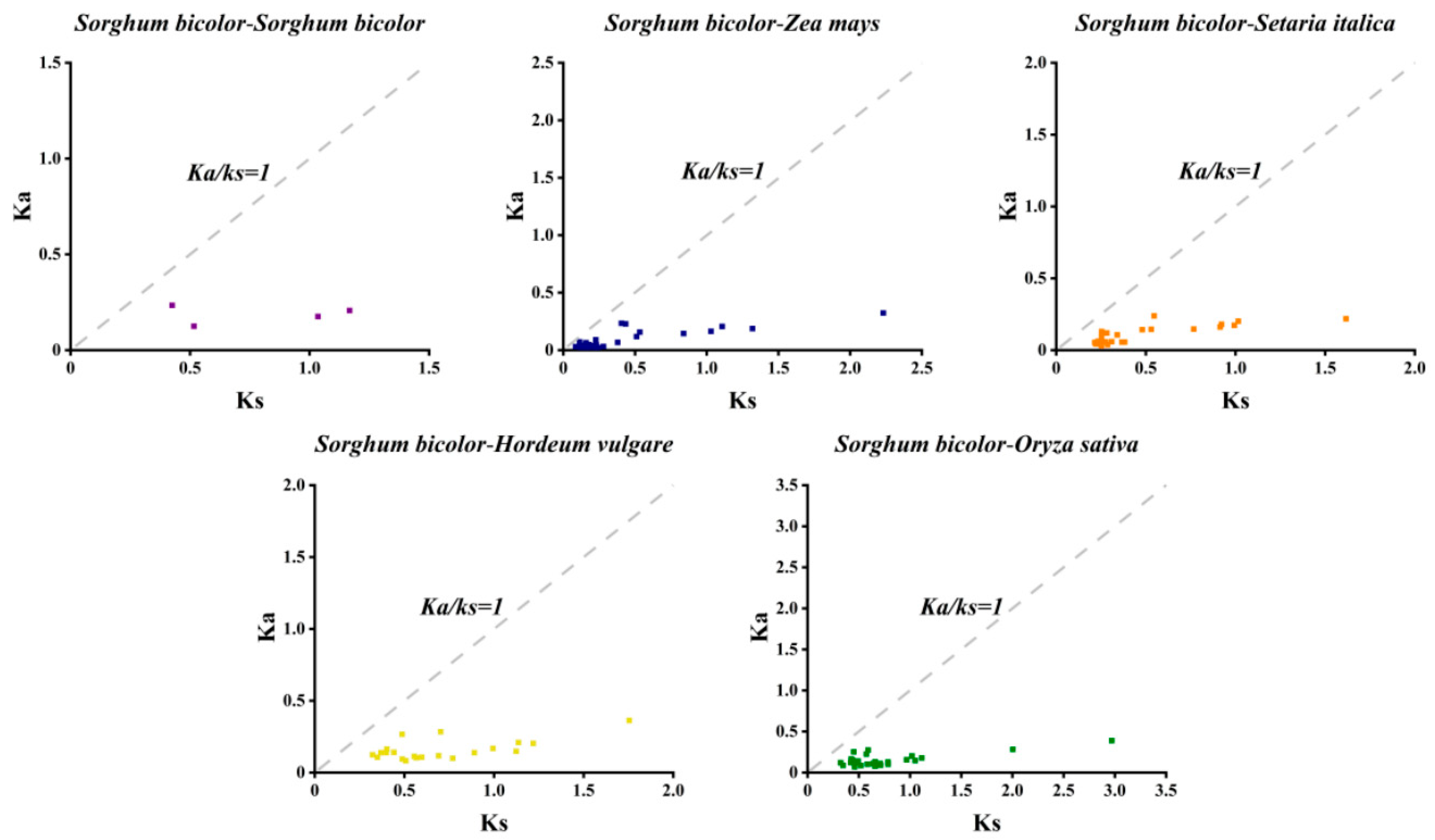
3.4. Comparative Analysis of SbCNGC Gene Duplication Events with Other Species
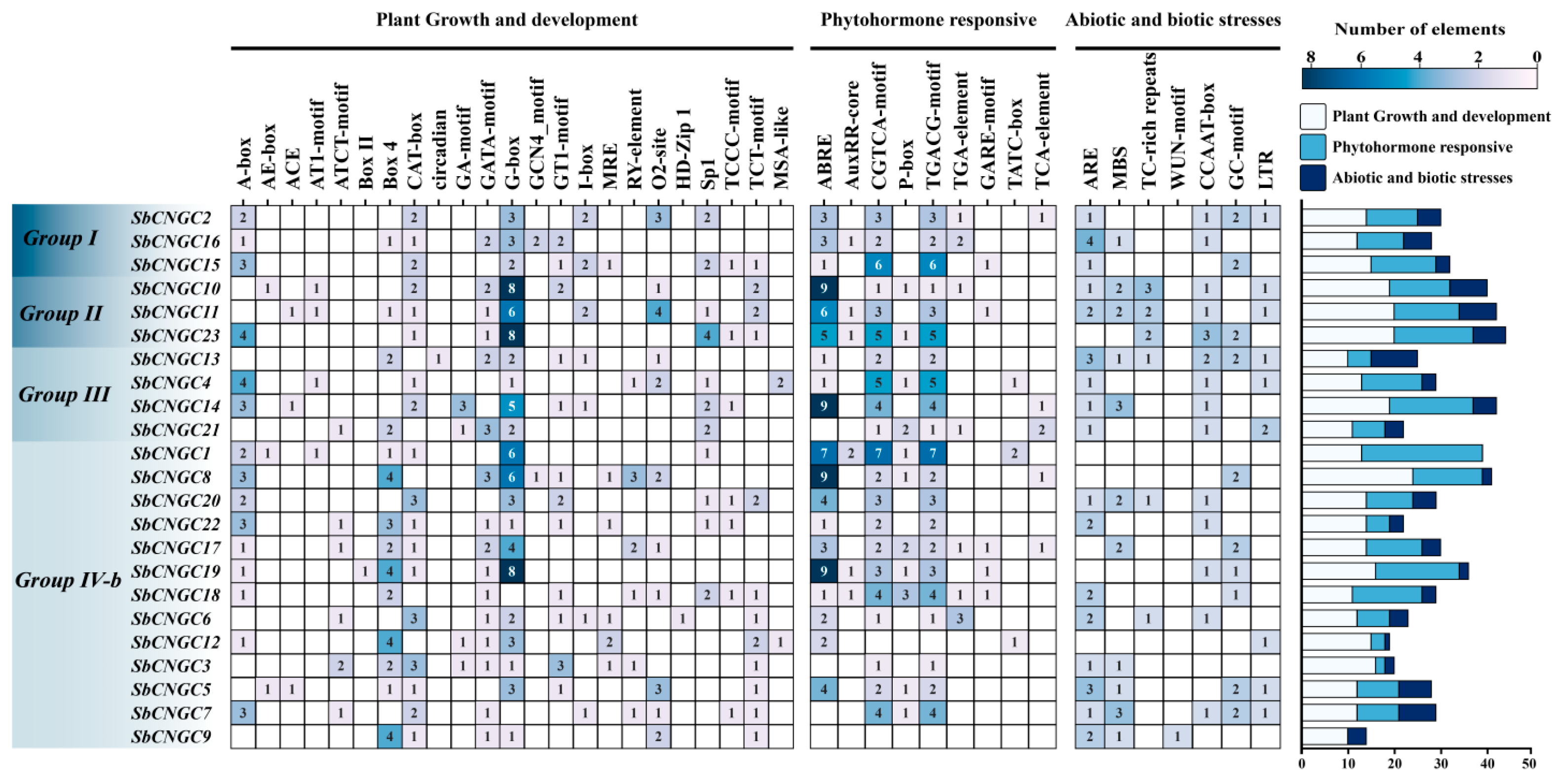
3.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of SbCNGC Genes
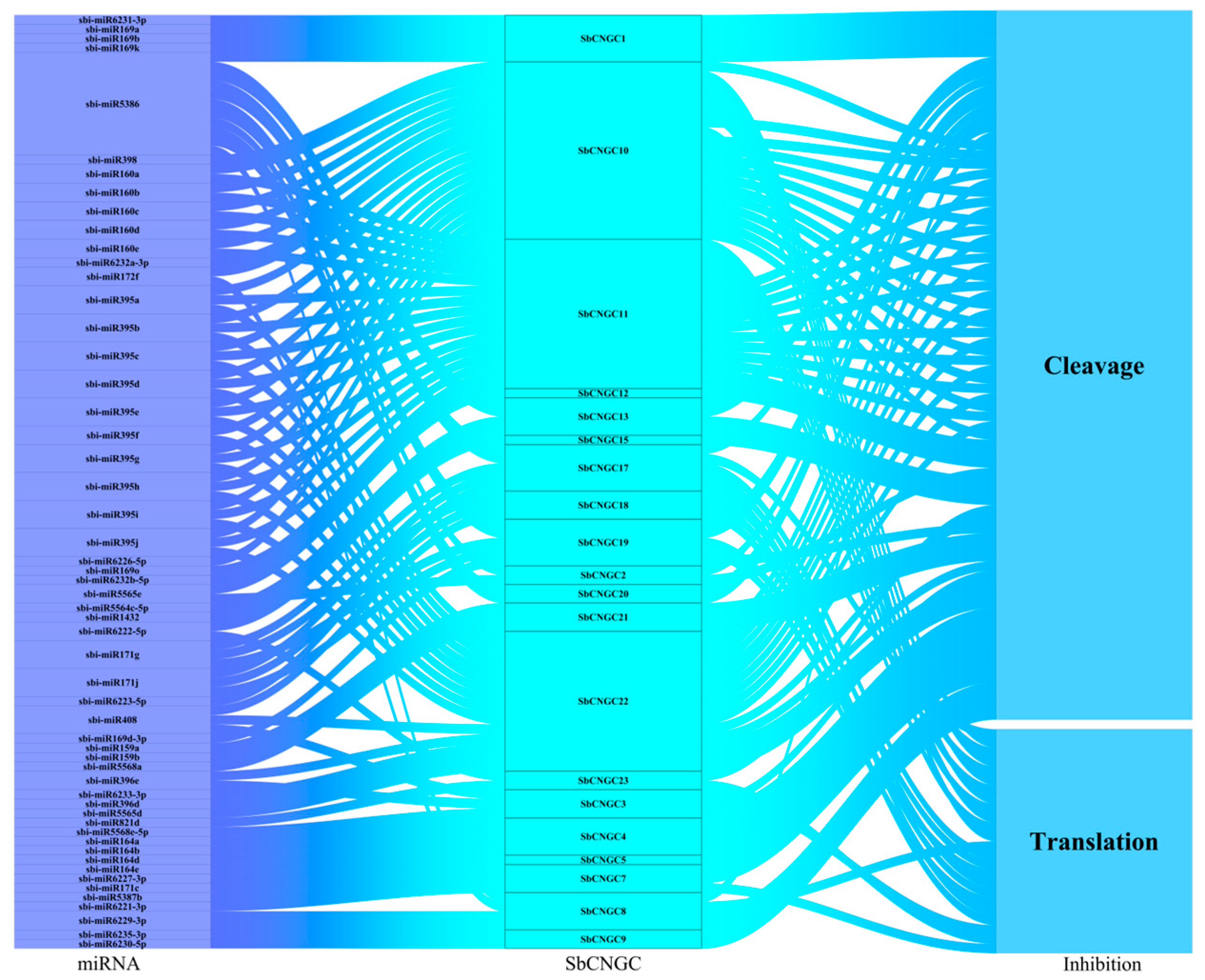
3.6. miRNA-Mediated Post-Transcriptional Regulation of SbCNGC Genes
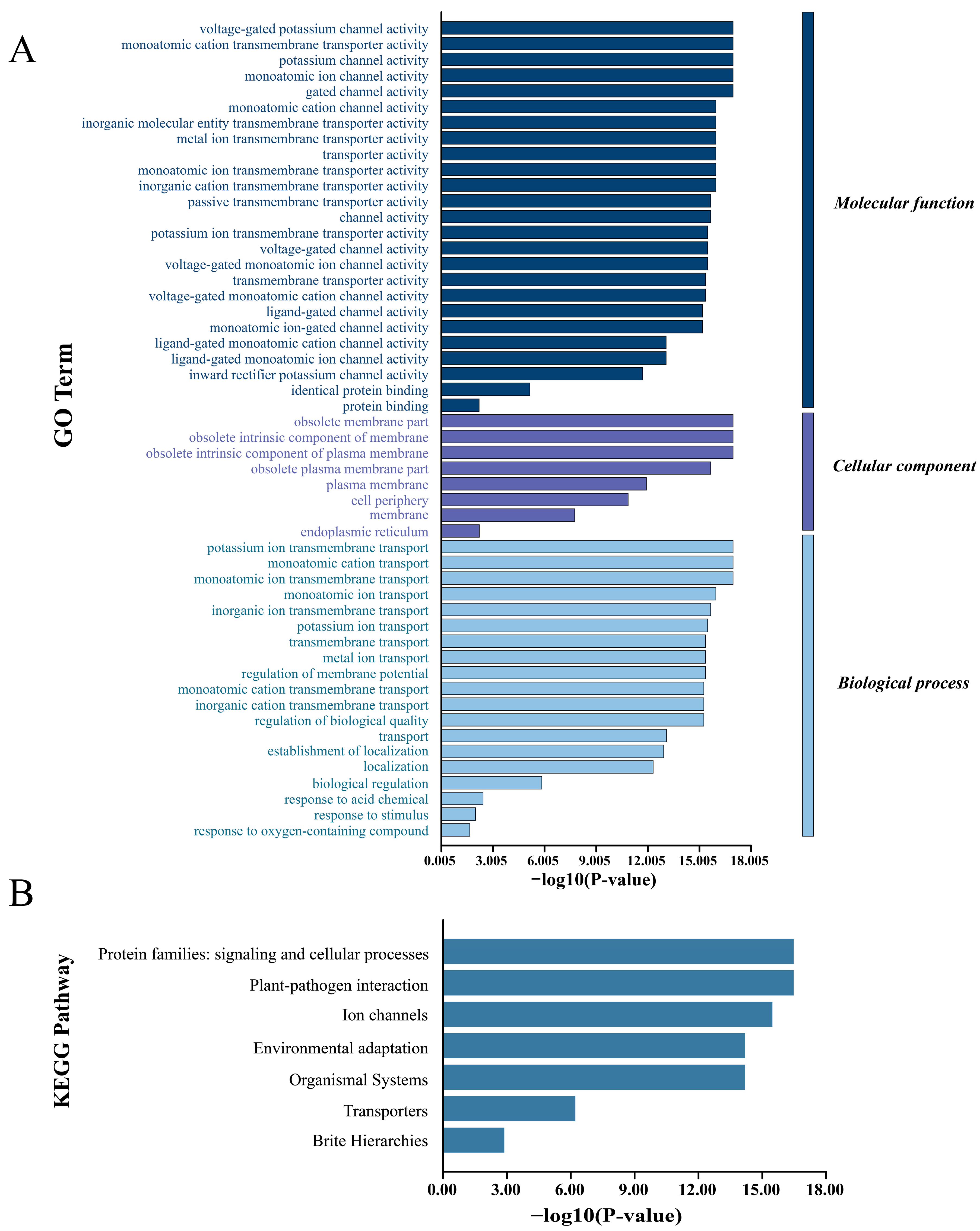
3.7. GO Enrichment and KEGG Pathway Analysis of SbCNGC Gene Family Members
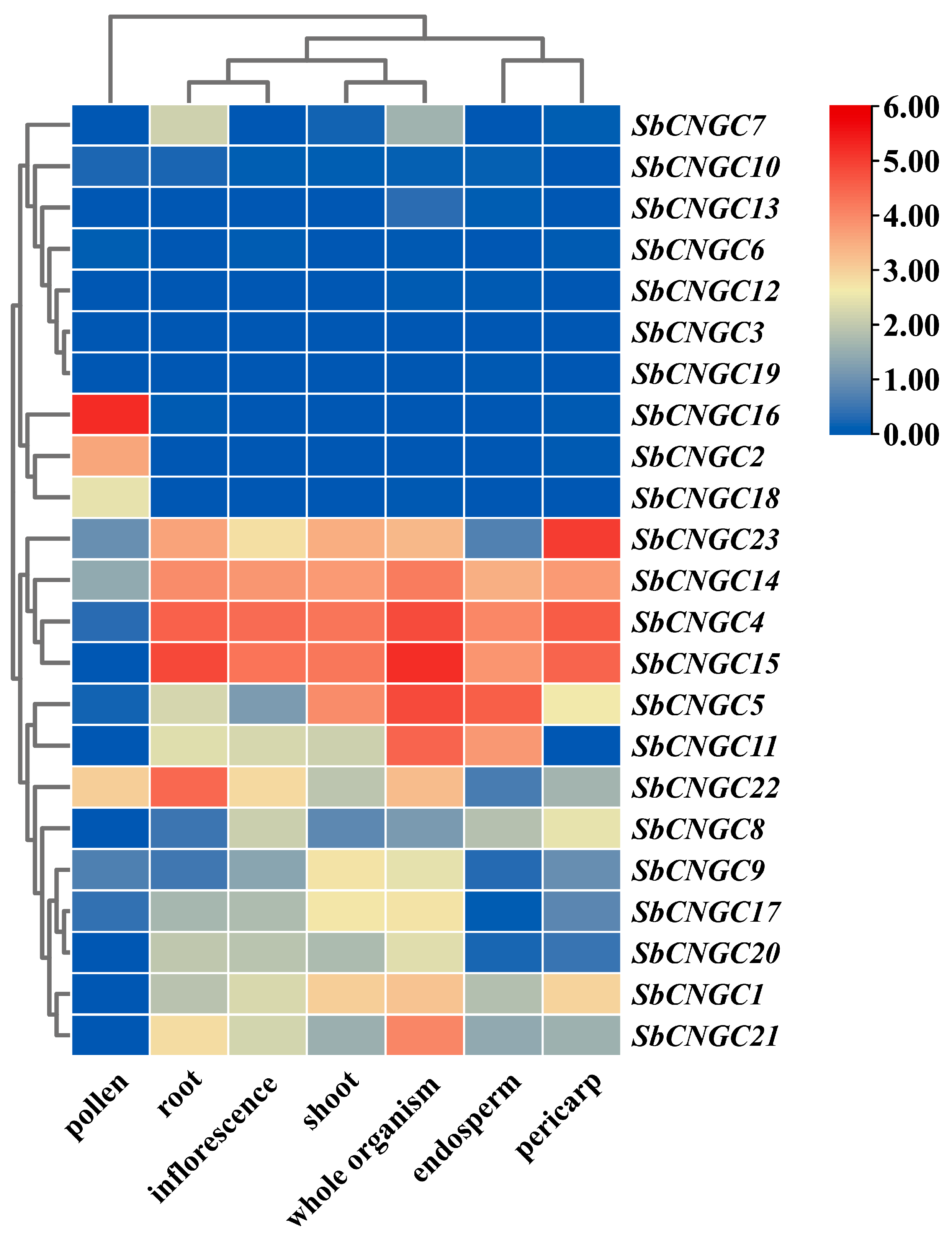
3.8. Expression Profiles of SbCNGC Genes in Different Tissues
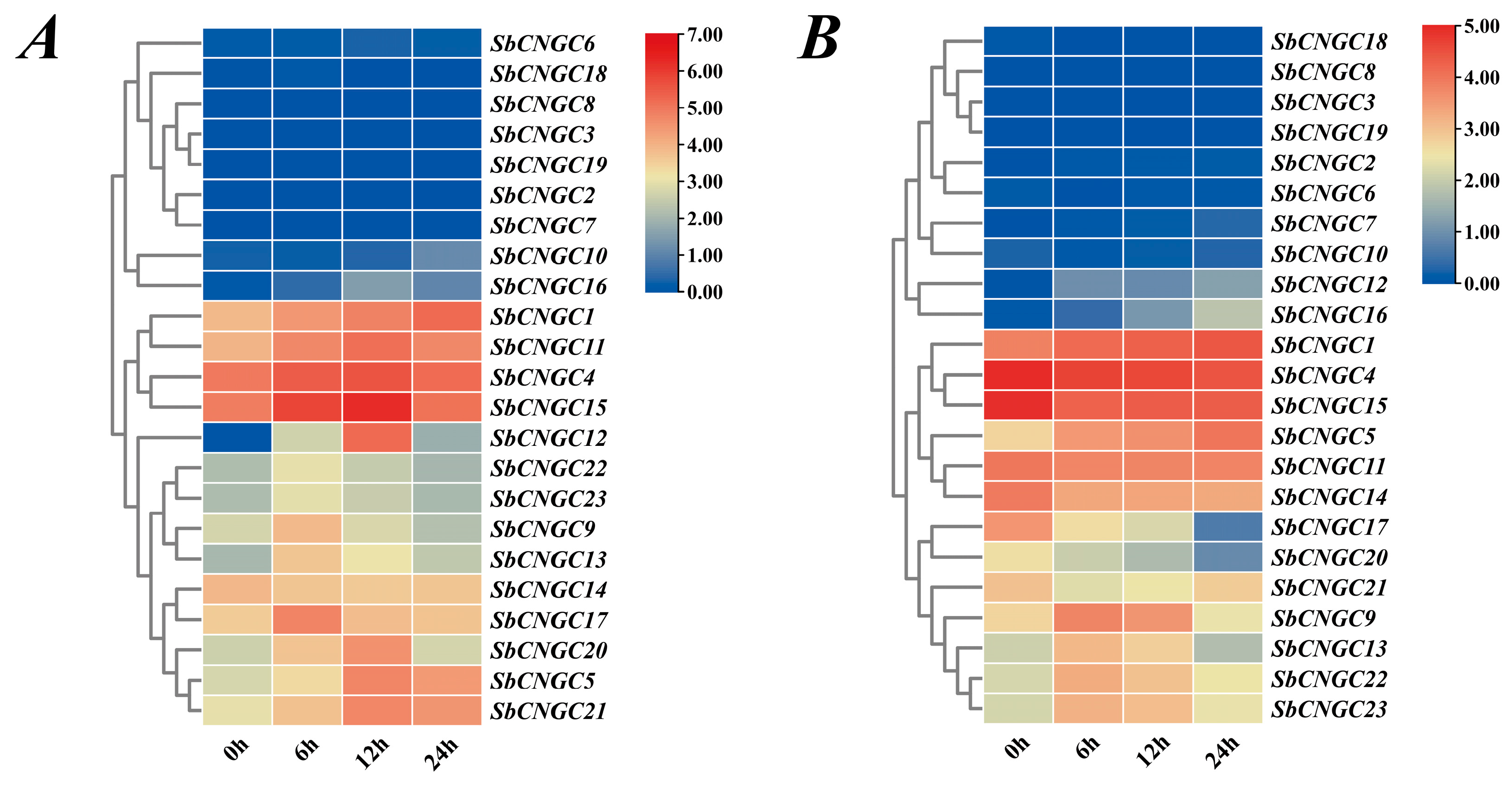
3.9. Expression Analysis of SbCNGC Genes Under Abiotic Stresses
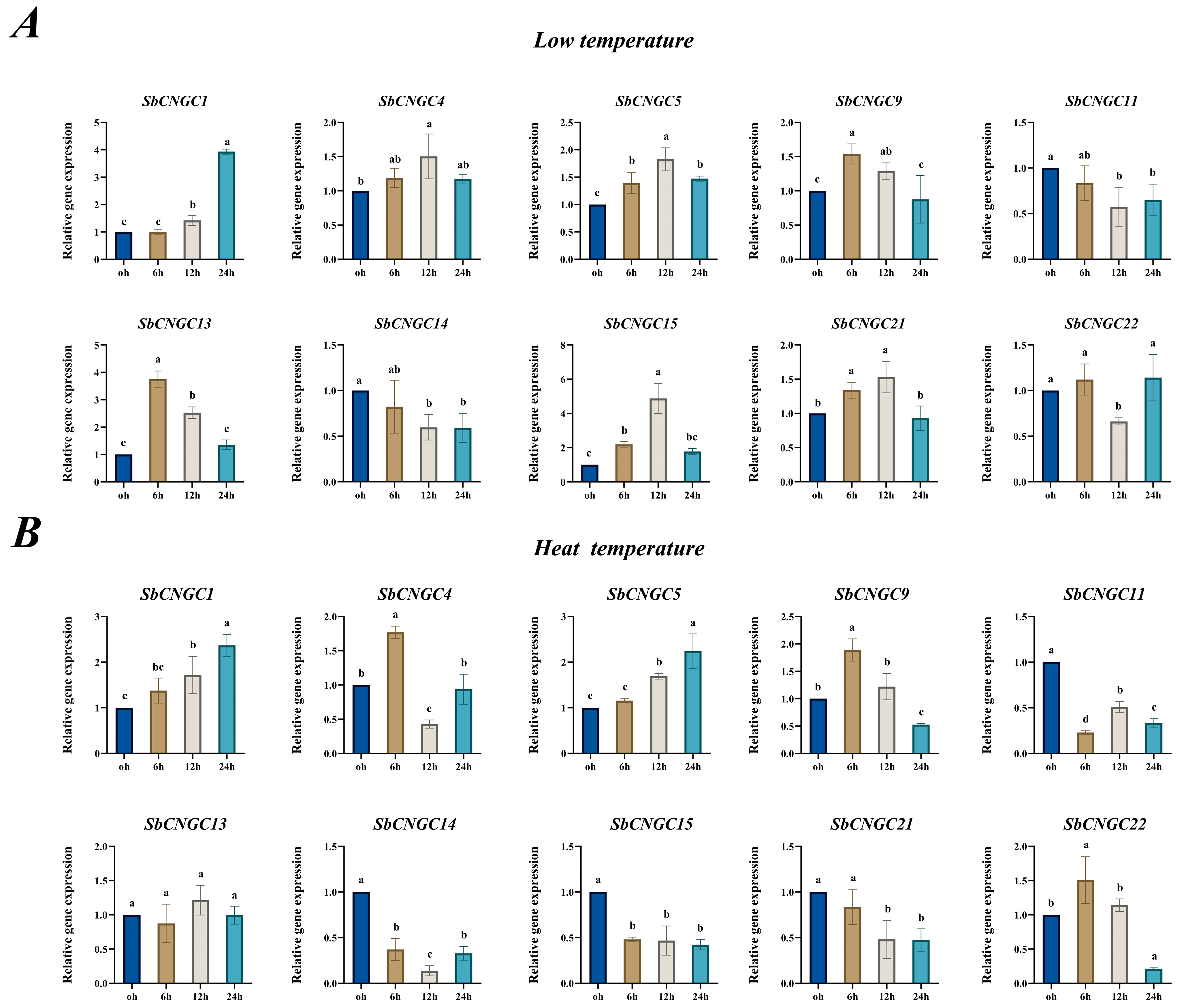
3.10. Time-Specific Analysis of SbCNGC Gene Expression Under Cold and Heat Stress Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pantoja, O. Recent advances in the physiology of ion channels in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 463–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.N.; Cho, S.H.; Wang, L.; Pham, A.Q.; Davies, J.M.; Stacey, G. Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 6 is involved in extracellular ATP signaling and plant immunity. Plant J. 2022, 109, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, L.; Singh, A.; Wang, H.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, B. Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant responses to abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, R. Glutamate receptors in plants. Ann. Bot. 2002, 90, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, F.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Pei, Z.M. Evolution of osmosensing OSCA1 Ca2+ channel family coincident with plant transition from water to land. Plant Genome 2022, 15, e20198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chai, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Luan, S. Dynamic interactions of plant CNGC subunits and calmodulins drive oscillatory Ca2+ channel activities. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 710–725.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.K.; Vadassery, J. Channels hold the key: Cyclic nucleotide gated channels (CNGC) in plant biotic stress signaling. J. Endocytob. Cell Res. 2015, 581, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Schuurink, R.C.; Shartzer, S.F.; Fath, A.; Jones, R.L. Characterization of a calmodulin-binding transporter from the plasma membrane of barley aleurone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.; Neuhaus, G. Characterisation of calmodulin binding to cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels from Arabidopsis thaliana. Febs Lett. 2000, 471, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, N.; Dou, G.; Meng, D.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, Y. Identification of the CNGC Gene Family in Rice and Mining of Alleles for Application in Rice Improvement. Plants 2023, 12, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Yin, G.; Chai, M.; Sun, L.; Wei, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Fu, X.; Li, S. Systematic analysis of CNGCs in cotton and the positive role of GhCNGC32 and GhCNGC35 in salt tolerance. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Bai, Y.X.; Ban, L.P.; Ren, J.D.; Shang, Q.X.; Li, W.Y. Identification of soybean CNGC gene family and screening of root rot resistance genes. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saand, M.A.; Xu, Y.-P.; Li, W.; Wang, J.-P.; Cai, X.-Z. Cyclic nucleotide gated channel gene family in tomato: Genome-wide identification and functional analyses in disease resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Z.; Kakar, K.U.; Ullah, R.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Shu, Q.-Y.; Ren, X.-l. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Genomics 2019, 111, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Kang, Y.; Ren, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, P.; Liao, L.; Wang, W.; Qian, L.; Guan, M. Identification and expression analysis of BnaCNGC family gene in the response to phytohormones, abiotic and biotic stresses in Brassica napus. J. Plant Interact. 2021, 16, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Qiao, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the CNGC gene family in maize. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Islam, M.A.; Lin, H.; Ji, C.; Duan, Y.; Liu, P.; Zeng, Q.; Day, B.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. Genome-wide identification of cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel gene family in wheat and functional analyses of TaCNGC14 and TaCNGC16. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirungu, J.N.; Magwanga, R.O.; Shiraku, M.L.; Okuto, E.; Cai, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Agong’, S.G.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the CNGC gene family in upland cotton under multiple stress conditions. J. Cotton Res. 2023, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xuan, X.; Su, S.; Guo, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression analysis of CNGC Genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Fei, C.-F.; Gu, L.-L.; Sun, S.-J.; Xu, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.-F. Three CNGC family members, CNGC5, CNGC6, and CNGC9, are required for constitutive growth of Arabidopsis root hairs as Ca2+-permeable channels. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Tian, W.; Dong, M.; Zhu, H.; Luan, S.; Li, L. Arabidopsis CNGC14 mediates calcium influx required for tip growth in root hairs. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeder, W.; Yoshioka, K. CNGCs break through—A rice cyclic nucleotide-gated channel paves the way for pollen tube growth. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J. OsCNGC13 promotes seed-setting rate by facilitating pollen tube growth in stylar tissues. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, A.; Köhler, B.; Palme, K.; Wolff, P.; Dietrich, P. Salt-dependent regulation of a CNG channel subfamily in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wan, H.; Yang, Y. Transcriptional activation and phosphorylation of OsCNGC9 confer enhanced chilling tolerance in rice. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saand, M.A.; Xu, Y.-P.; Munyampundu, J.-P.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.-R.; Cai, X.-Z. Phylogeny and evolution of plant cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel (CNGC) gene family and functional analyses of tomato CNGCs. DNA Res. 2015, 22, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yang, S.; Lai, D.; Weng, W.; Fan, Y.; Wu, W.; Ma, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, M.; Ruan, J. Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression level analysis of the TALE gene family in Sorghum bicolor. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszyn, M.; Świeżawska, B.; Szmidt-Jaworska, A.; Jaworski, K. Cyclic nucleotide gated channels (CNGCs) in plant signalling—Current knowledge and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 241, 153035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, Z.; Kakar, K.U.; Saand, M.A.; Shu, Q.-Y. Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel gene family in rice, identification, characterization and experimental analysis of expression response to plant hormones, biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; An, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Wu, K. Genome-wide identification of the CNGC gene family and negative regulation of drought tolerance by HvCNGC3 and HvCNGC16 in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 210, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; DeFalco, T.A.; Moeder, W.; Yoshioka, K. The Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels AtCNGC2 and AtCNGC4 work in the same signaling pathway to regulate pathogen defense and floral transition. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Ming, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X.; Fu, D.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gong, Z. Differential phosphorylation of Ca2+-permeable channel CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE–GATED CHANNEL20 modulates calcium-mediated freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 4356–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Hu, P.; Zhu, T.; Wang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L. CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED ION CHANNELs 14 and 16 promote tolerance to heat and chilling in rice. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1794–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaratiello, G.; Risoli, S.; Antichi, D.; Pellegrini, E.; Nali, C.; Lorenzini, G.; Pampana, S.; Pisuttu, C.; Tonelli, M.; Cotrozzi, L. Exogenous melatonin application helps late-sown durum wheat to cope with waterlogging under Mediterranean environmental conditions. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
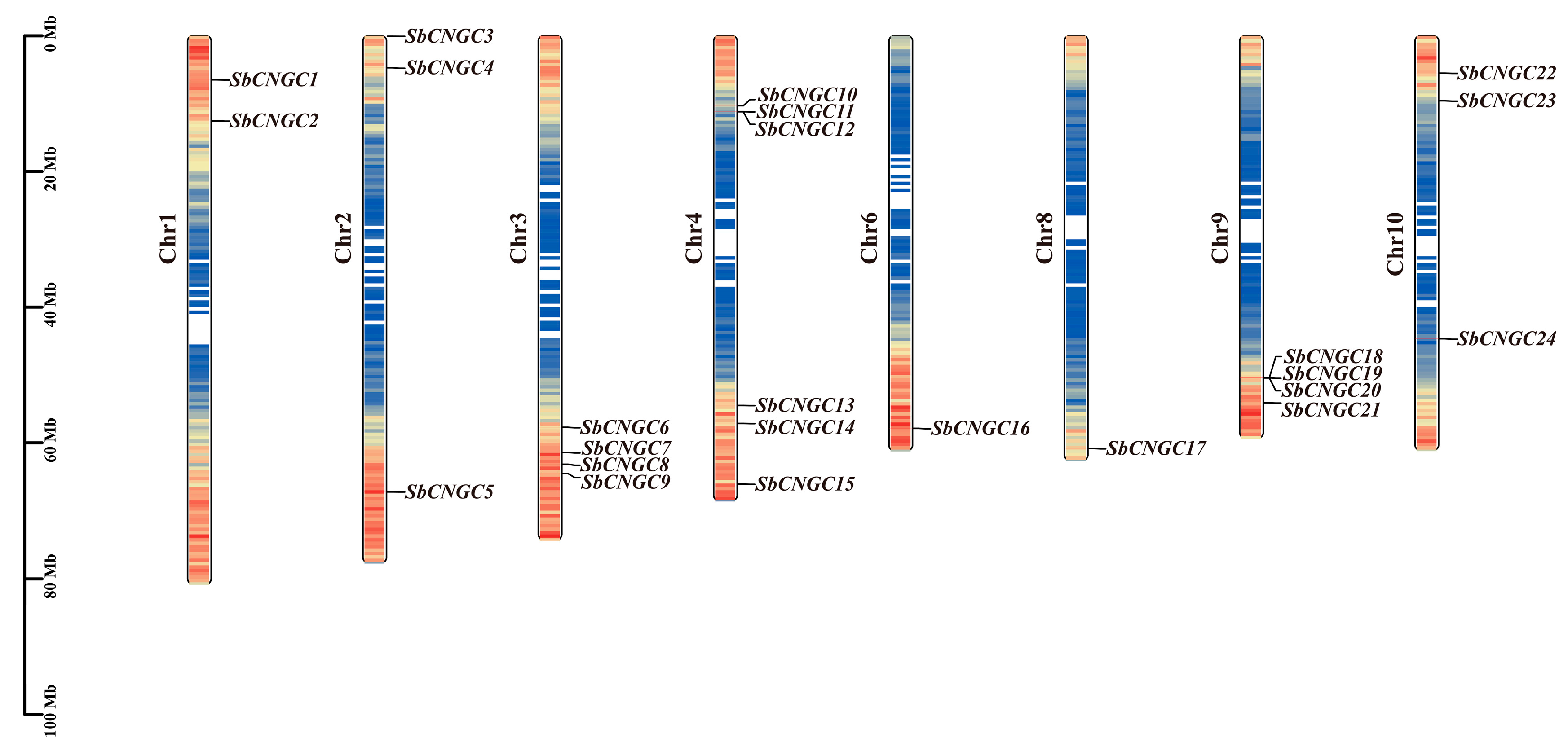
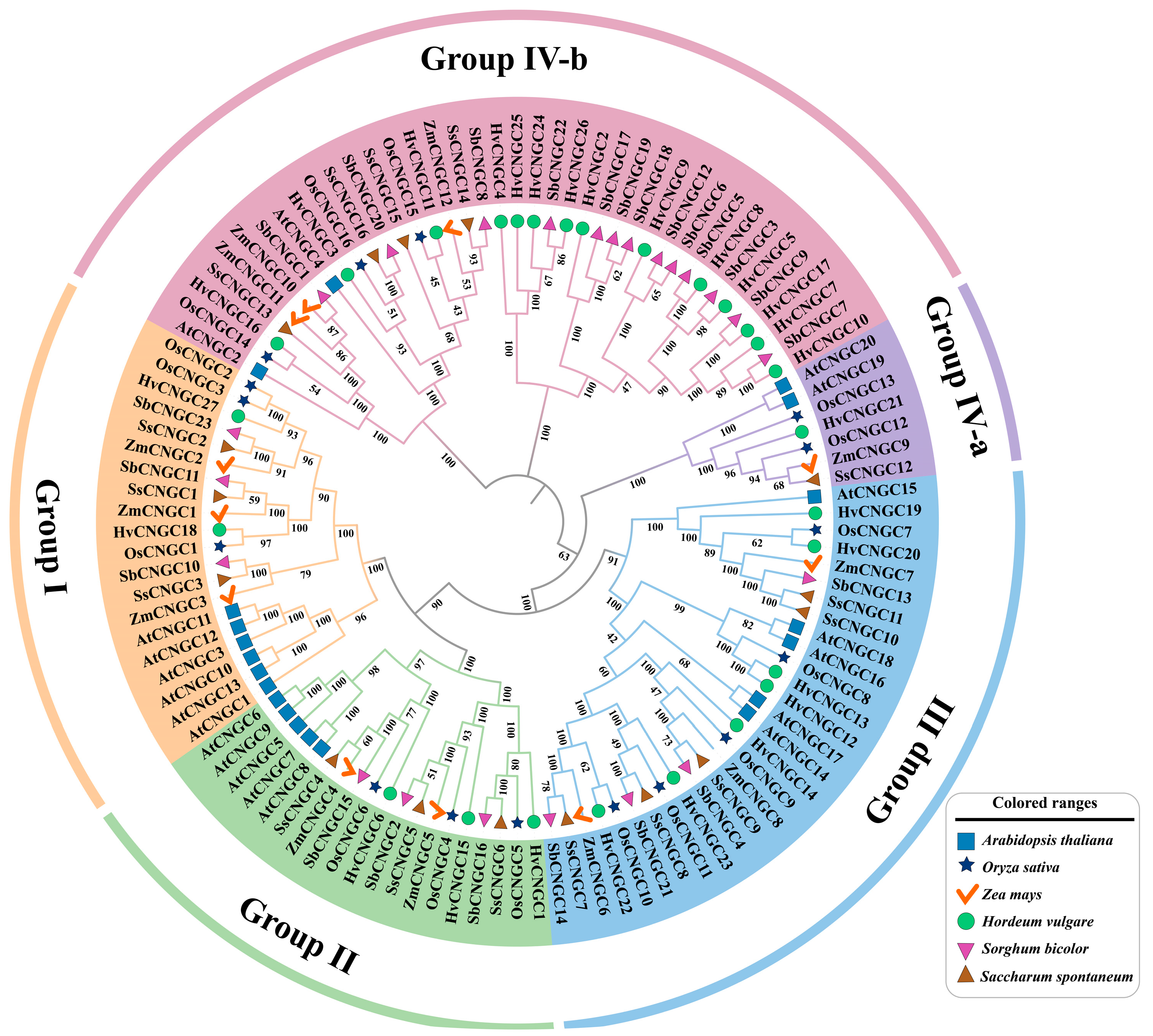
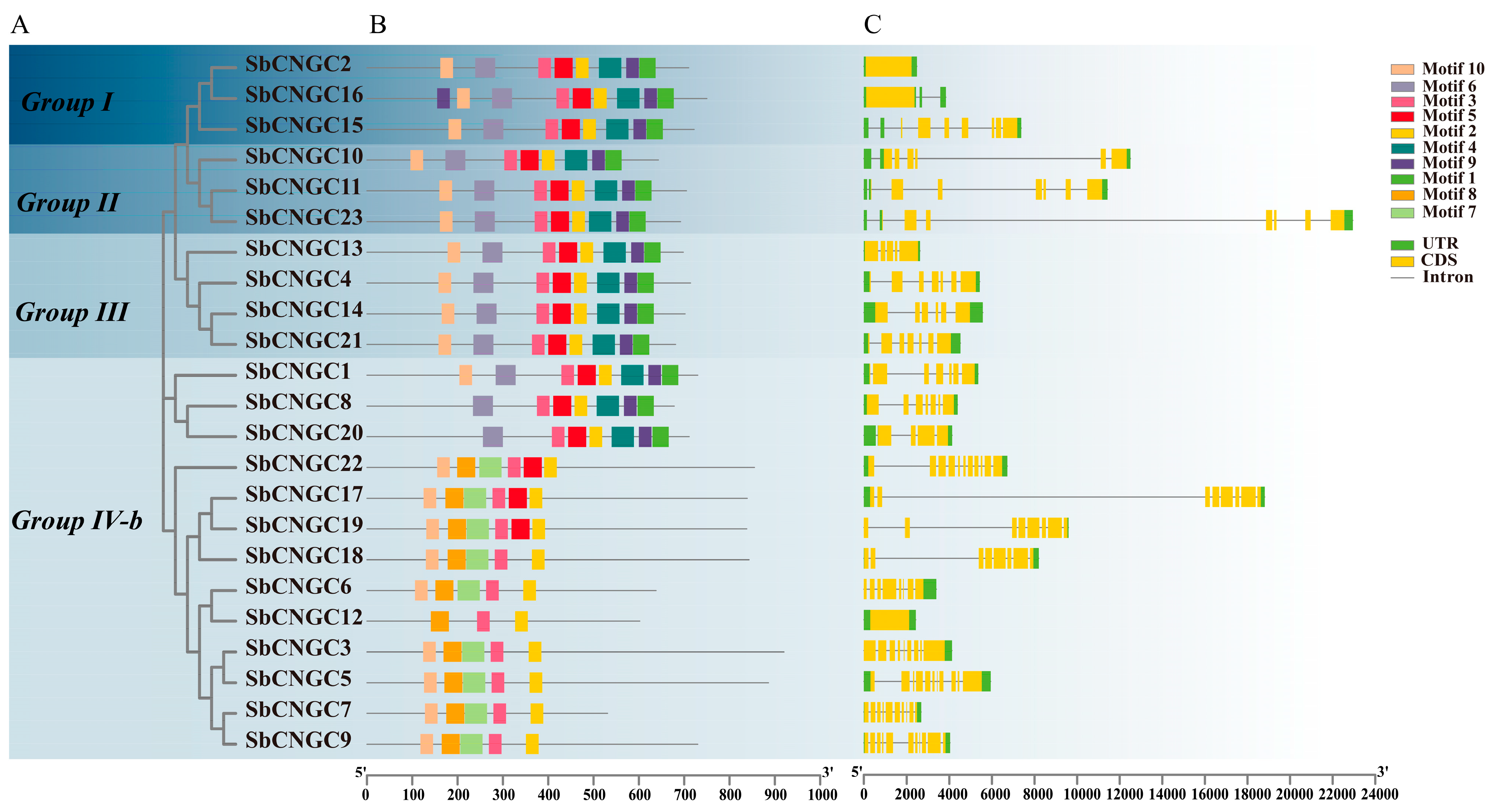

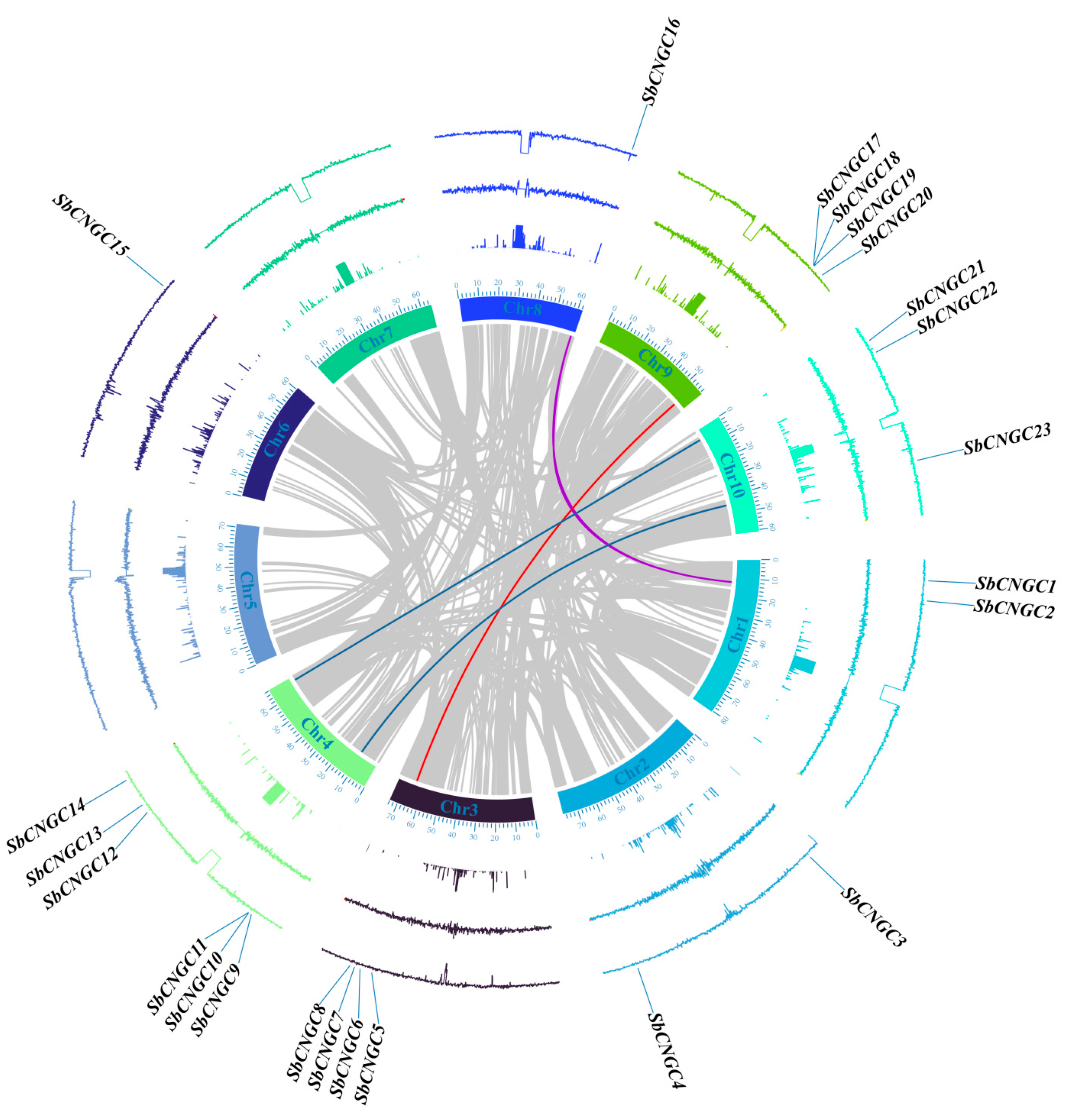
| Name | Gene ID | Chrom | Number of Amino Acid (aa) | Molecular Weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SbCNGC1 | XM_002466378.2 | Chr1 | 729 | 81,533.04 | 9.34 | 57.47 | 94.92 | 0.102 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC2 | XM_002466707.2 | Chr1 | 709 | 80,987.67 | 9.4 | 54.9 | 90.94 | −0.121 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC3 | XM_021453318.1 | Chr2 | 919 | 100,649.17 | 8.18 | 43.78 | 86.54 | −0.141 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC4 | XM_002460609.2 | Chr2 | 713 | 82,328.6 | 9.19 | 49.21 | 91.67 | −0.208 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC5 | XM_002458189.2 | Chr3 | 885 | 99,321.75 | 7.04 | 39.84 | 94.42 | −0.13 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC6 | XM_021456300.1 | Chr3 | 637 | 71,042.55 | 8.29 | 40.97 | 94.74 | 0.035 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC7 | XM_002456331.2 | Chr3 | 530 | 61,024.6 | 8.64 | 46.83 | 93.62 | −0.055 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC8 | XM_002458555.2 | Chr3 | 677 | 75,481.41 | 9.69 | 53.39 | 90.96 | −0.073 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC9 | XM_002453555.2 | Chr4 | 729 | 83,534.61 | 6.3 | 38.1 | 88.55 | −0.19 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC10 | XM_002453582.2 | Chr4 | 642 | 73,383.79 | 8.4 | 51.93 | 94.95 | 0.008 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC11 | XM_021459169.1 | Chr4 | 704 | 80,327.93 | 9.09 | 44.54 | 91.72 | −0.079 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC12 | XM_002454023.2 | Chr4 | 601 | 65,801.8 | 7.23 | 40.12 | 96.96 | 0.136 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC13 | XM_021458611.1 | Chr4 | 697 | 80,905.02 | 9.69 | 55.42 | 90.98 | −0.112 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC14 | XM_002454637.2 | Chr4 | 701 | 80,045.61 | 9.08 | 41.34 | 92.54 | −0.05 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC15 | XM_002447160.2 | Chr6 | 721 | 82,522.16 | 9.15 | 47.07 | 86.16 | −0.111 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC16 | XM_002442510.2 | Chr8 | 749 | 85,154.09 | 9.54 | 49.73 | 84.15 | −0.18 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC17 | XM_002441096.2 | Chr9 | 838 | 92,793.4 | 7.09 | 34.04 | 95.76 | −0.058 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC18 | XM_021447292.1 | Chr9 | 842 | 93,389.95 | 6.31 | 35.84 | 97.49 | −0.031 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC19 | XM_002441100.2 | Chr9 | 837 | 93,301.97 | 6.06 | 32.3 | 96.43 | −0.029 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC20 | XM_021447943.1 | Chr9 | 710 | 78,637.37 | 9.74 | 50.05 | 86.04 | −0.1 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC21 | XM_002436576.2 | Chr10 | 680 | 78,657.88 | 9.03 | 42.17 | 93.6 | −0.125 | Cell membrane |
| SbCNGC22 | XM_021449564.1 | Chr10 | 854 | 97,265.64 | 5.95 | 42.89 | 94.56 | −0.15 | Nucleus |
| SbCNGC23 | XM_021449645.1 | Chr10 | 691 | 80,003.45 | 9.47 | 51.91 | 89.77 | −0.166 | Cell membrane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Jiao, W.; Huang, K.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Cao, X. Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses. Genes 2025, 16, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121405
Luo Y, Jiao W, Huang K, Li X, Li J, Wang M, Zhang R, Cao X. Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses. Genes. 2025; 16(12):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121405
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yu, Wenda Jiao, Kun Huang, Xiang Li, Jiaqi Li, Minli Wang, Ruidong Zhang, and Xiong Cao. 2025. "Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses" Genes 16, no. 12: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121405
APA StyleLuo, Y., Jiao, W., Huang, K., Li, X., Li, J., Wang, M., Zhang, R., & Cao, X. (2025). Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses. Genes, 16(12), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121405




