The GNAS Gene: Fibrous Dysplasia, McCune–Albright Syndrome, and Skeletal Structure and Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The GNAS Gene
Gsα and Stromal Stem Cell Differentiation
3. Skeletal Manifestations of FD/MAS
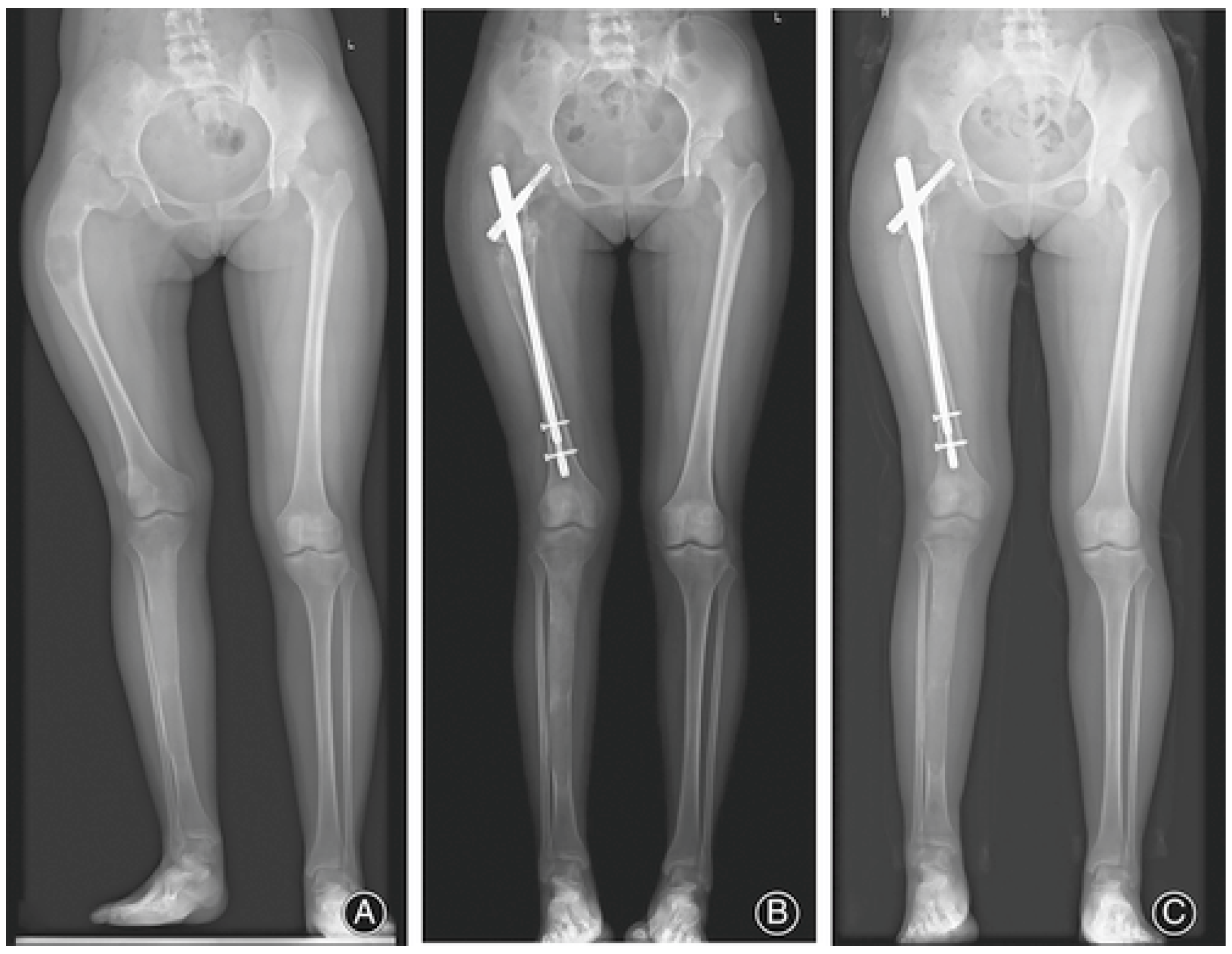
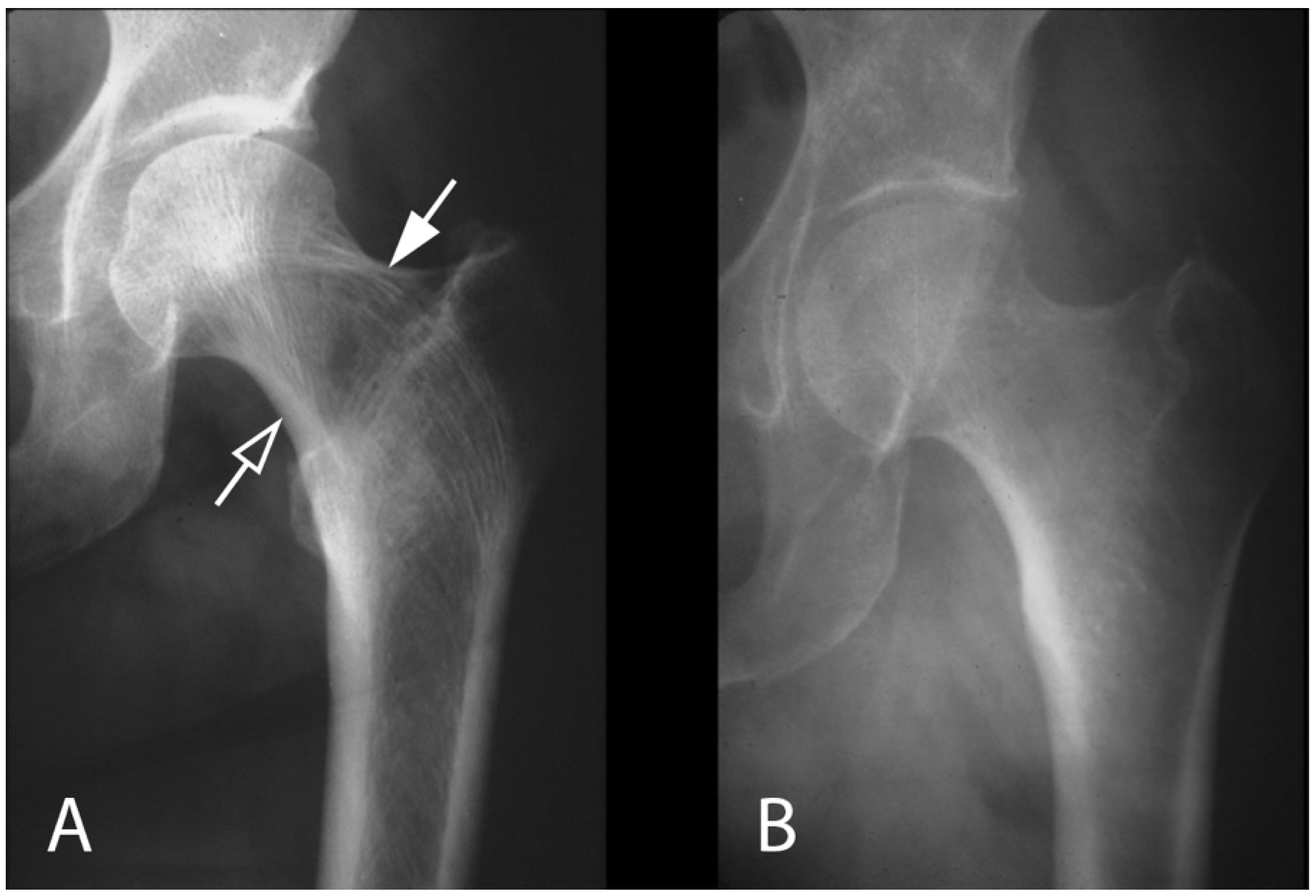
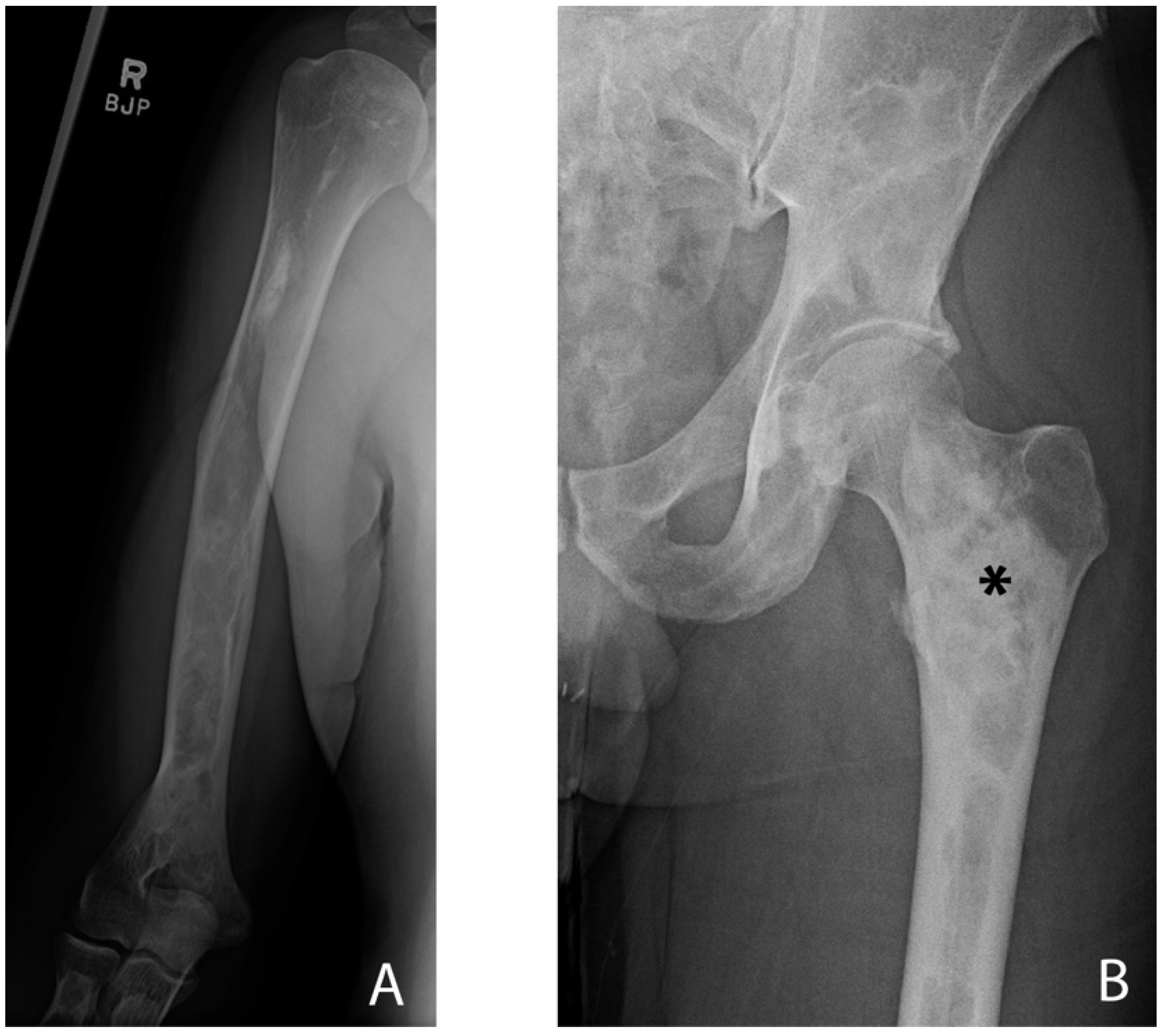
3.1. Appendicular Manifestations of FD/MAS
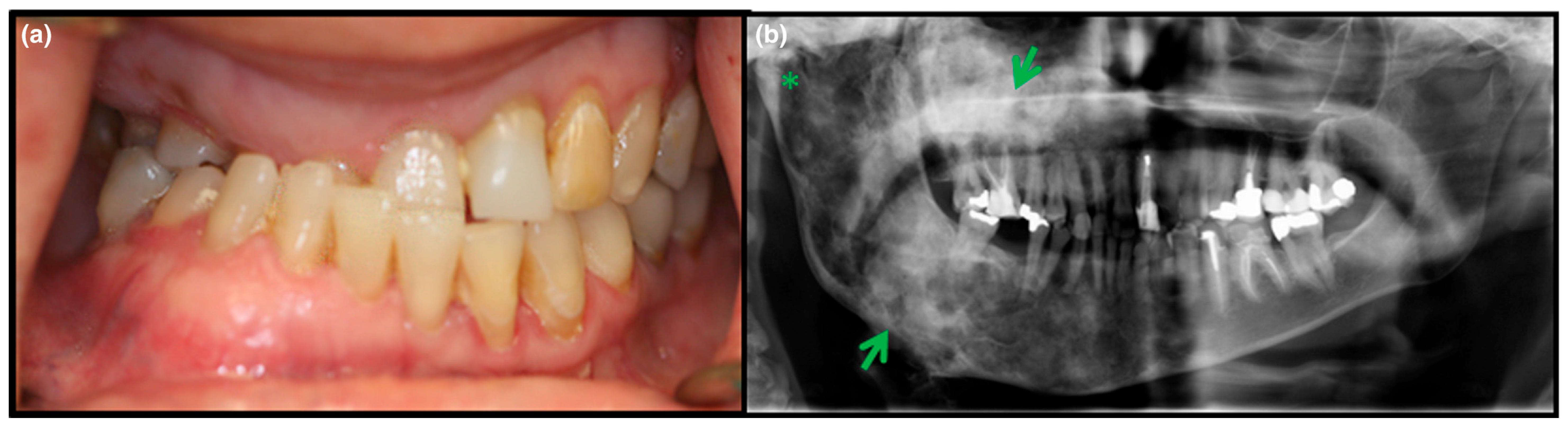
3.2. Axial/Craniofacial Manifestations of FD/MAS
4. Bone Biomechanics and Fibrous Dysplasia
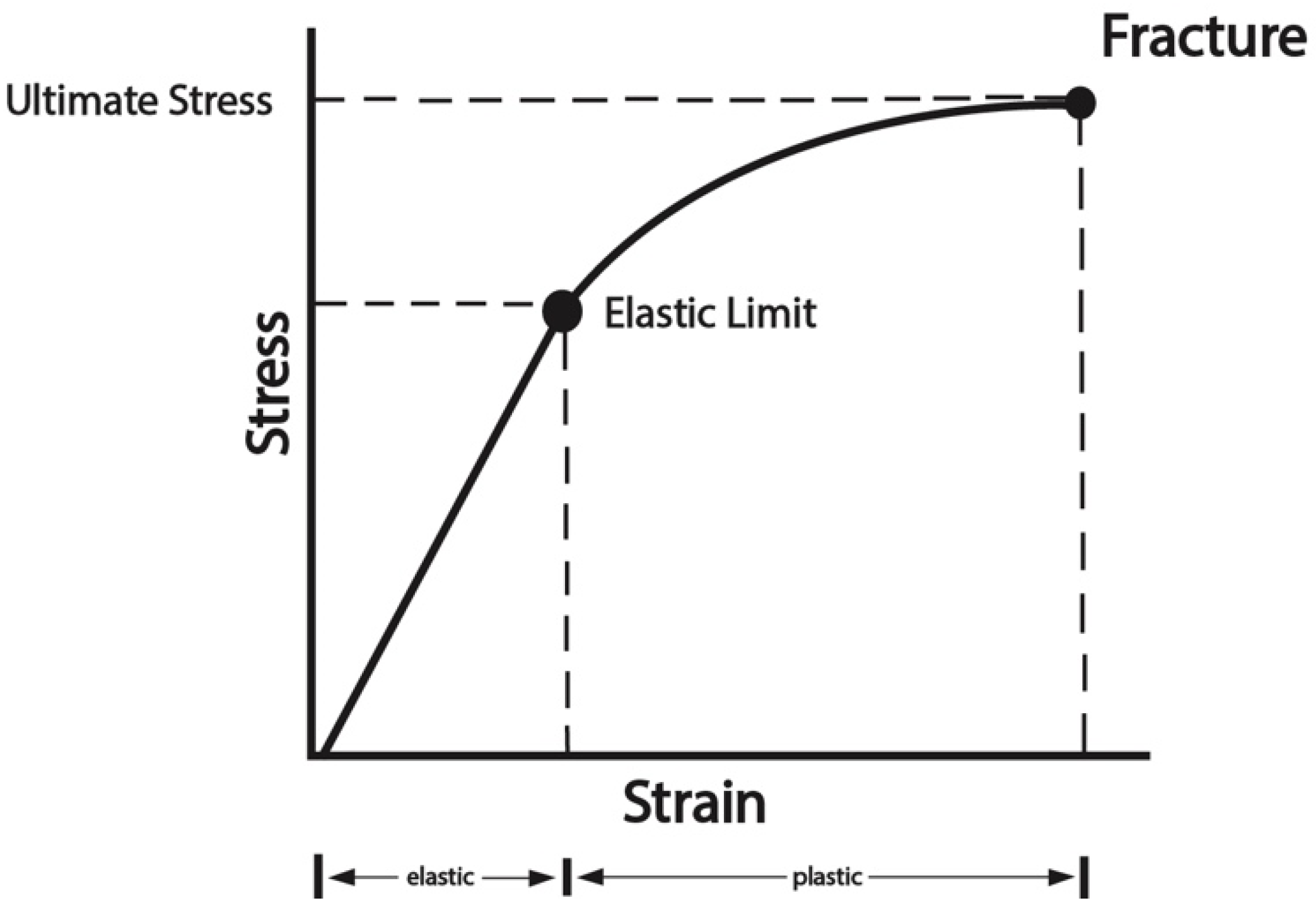
4.1. Biomechanics of Bone
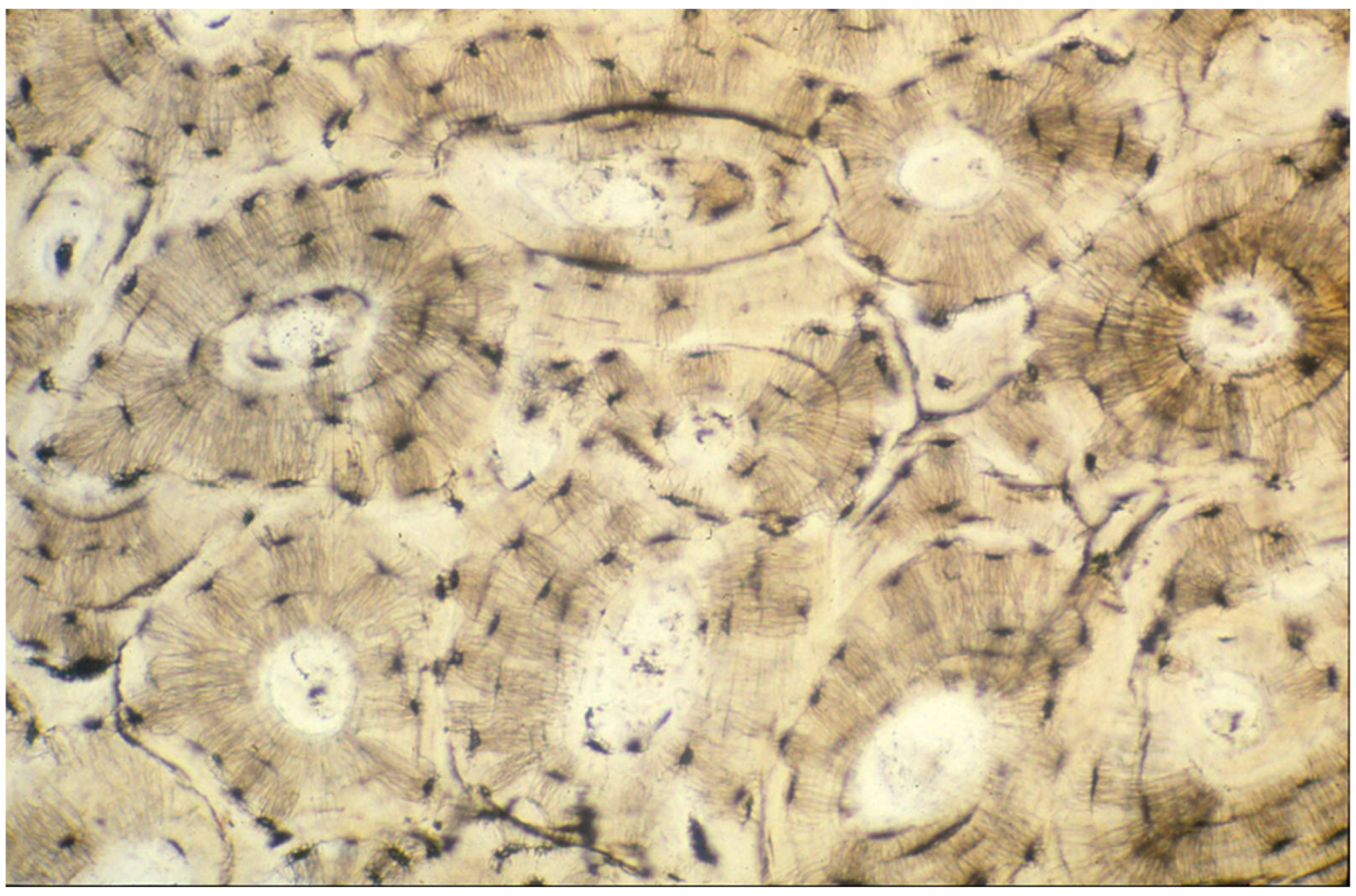
4.1.1. Levels of Bone Organization—Matrix-Level Organization
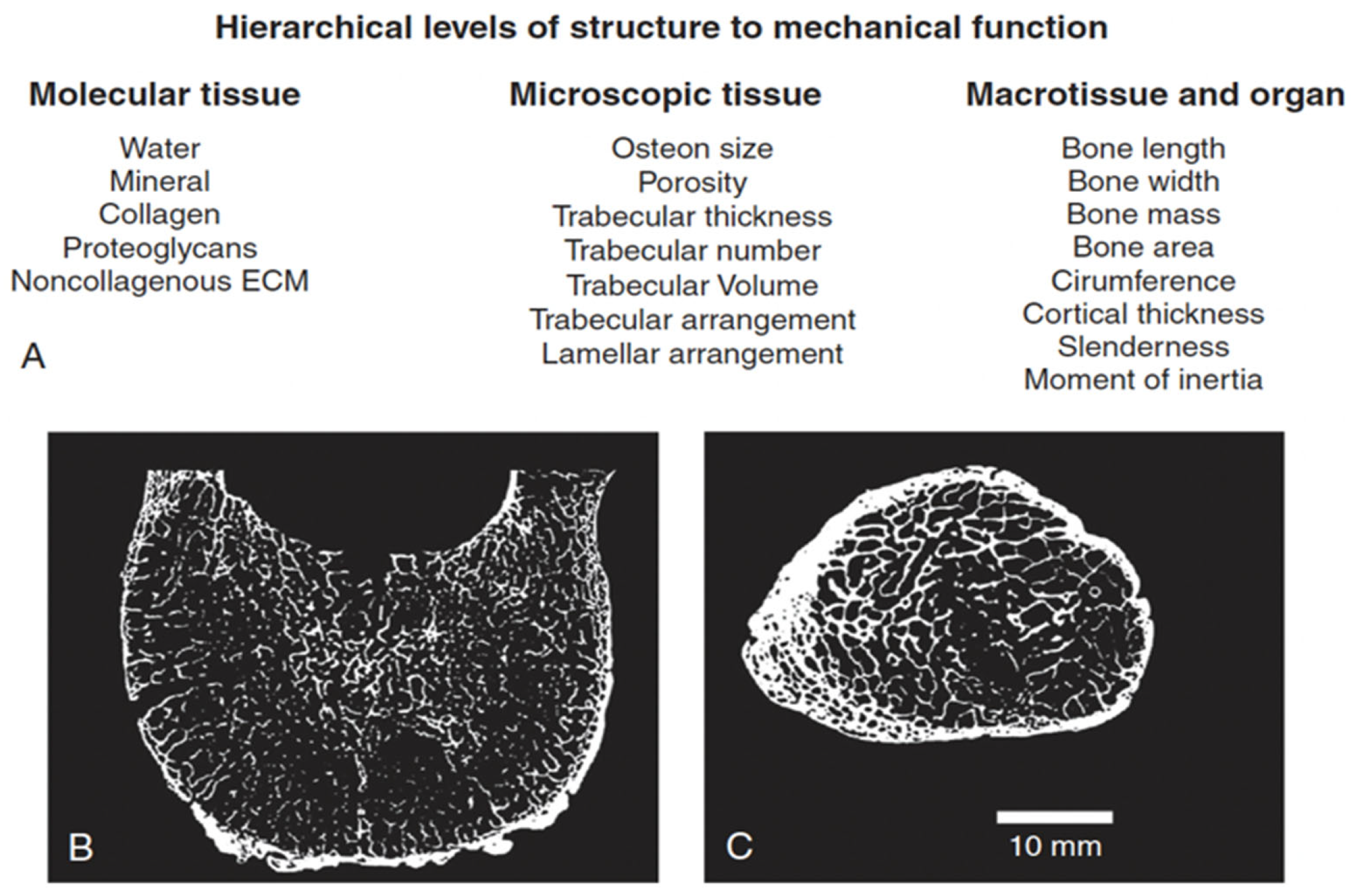
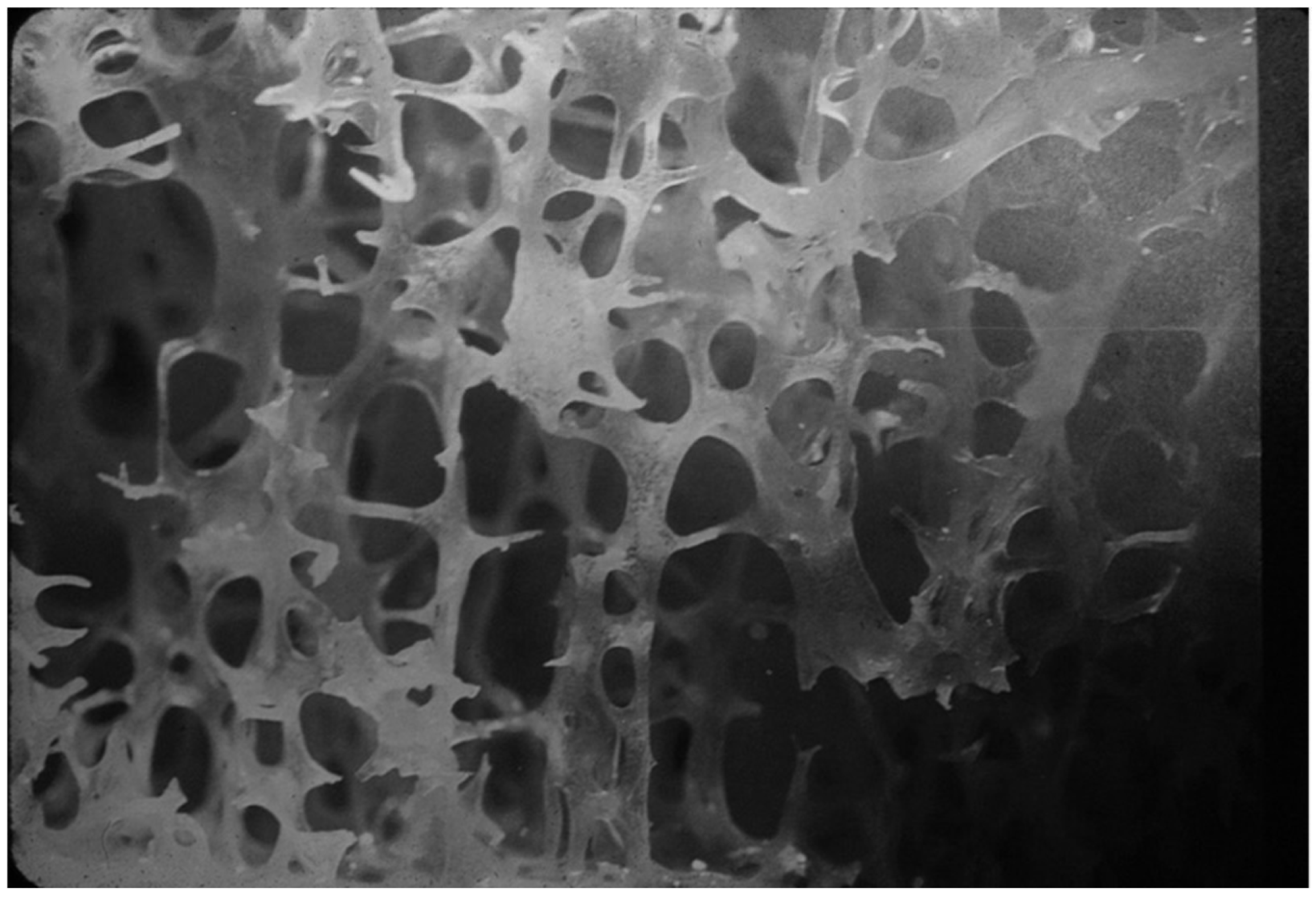
4.1.2. Levels of Bone Organization—Microarchitecture
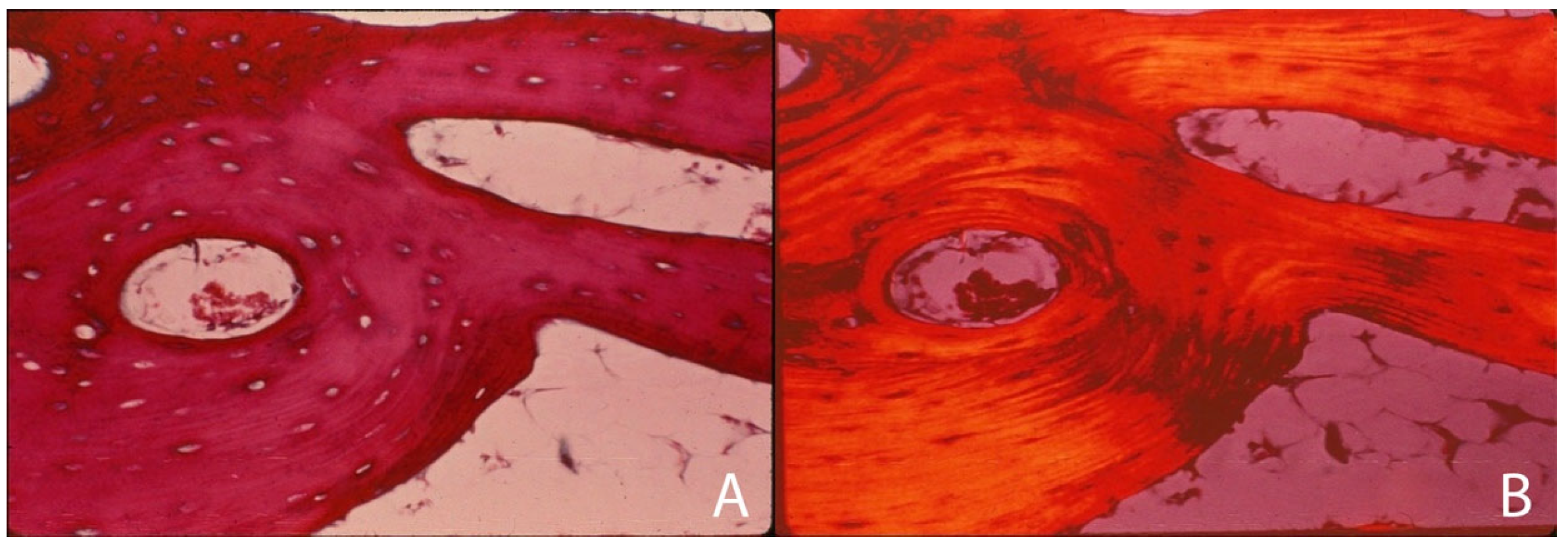
4.1.3. Levels of Bone Organization—Cortex
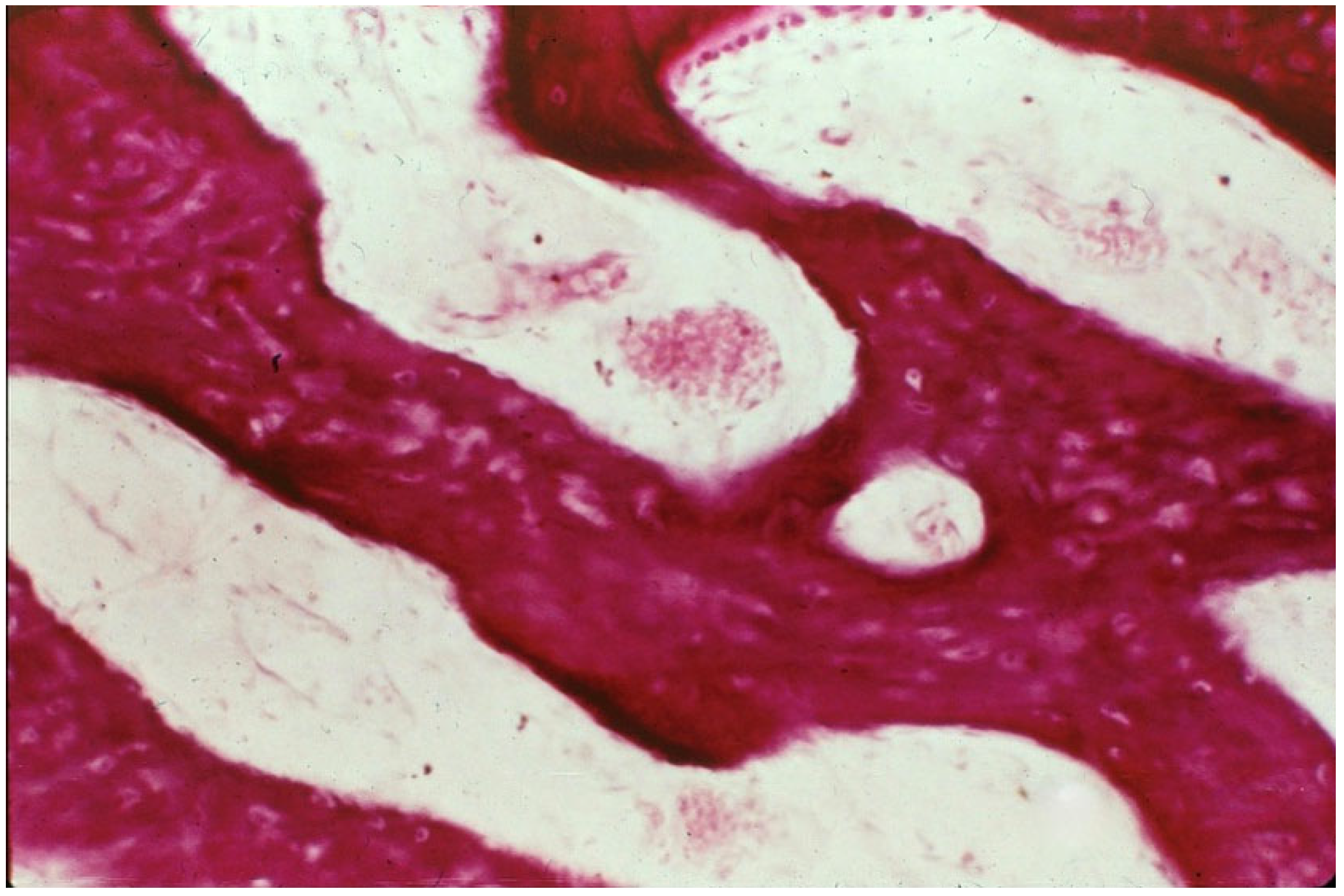
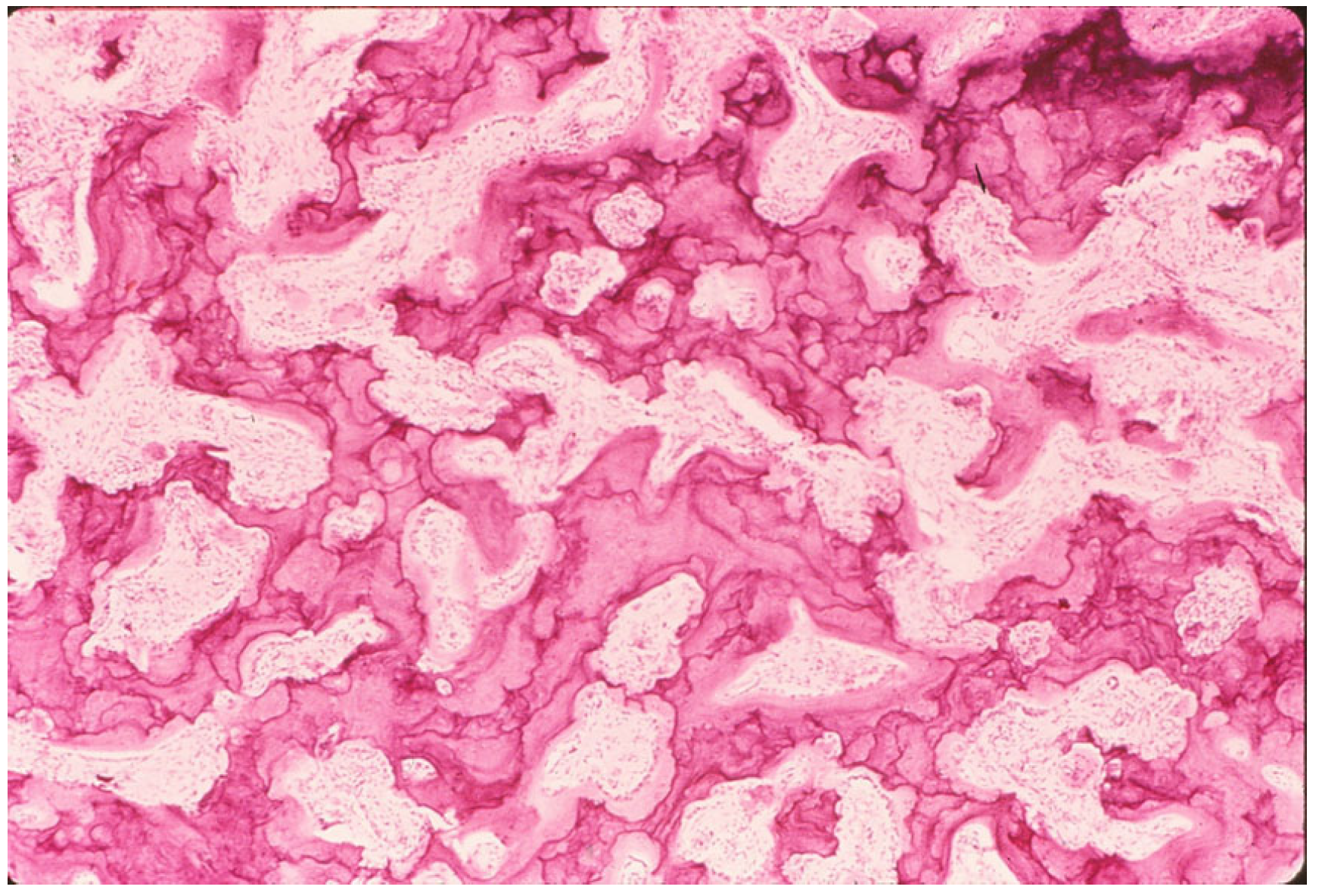
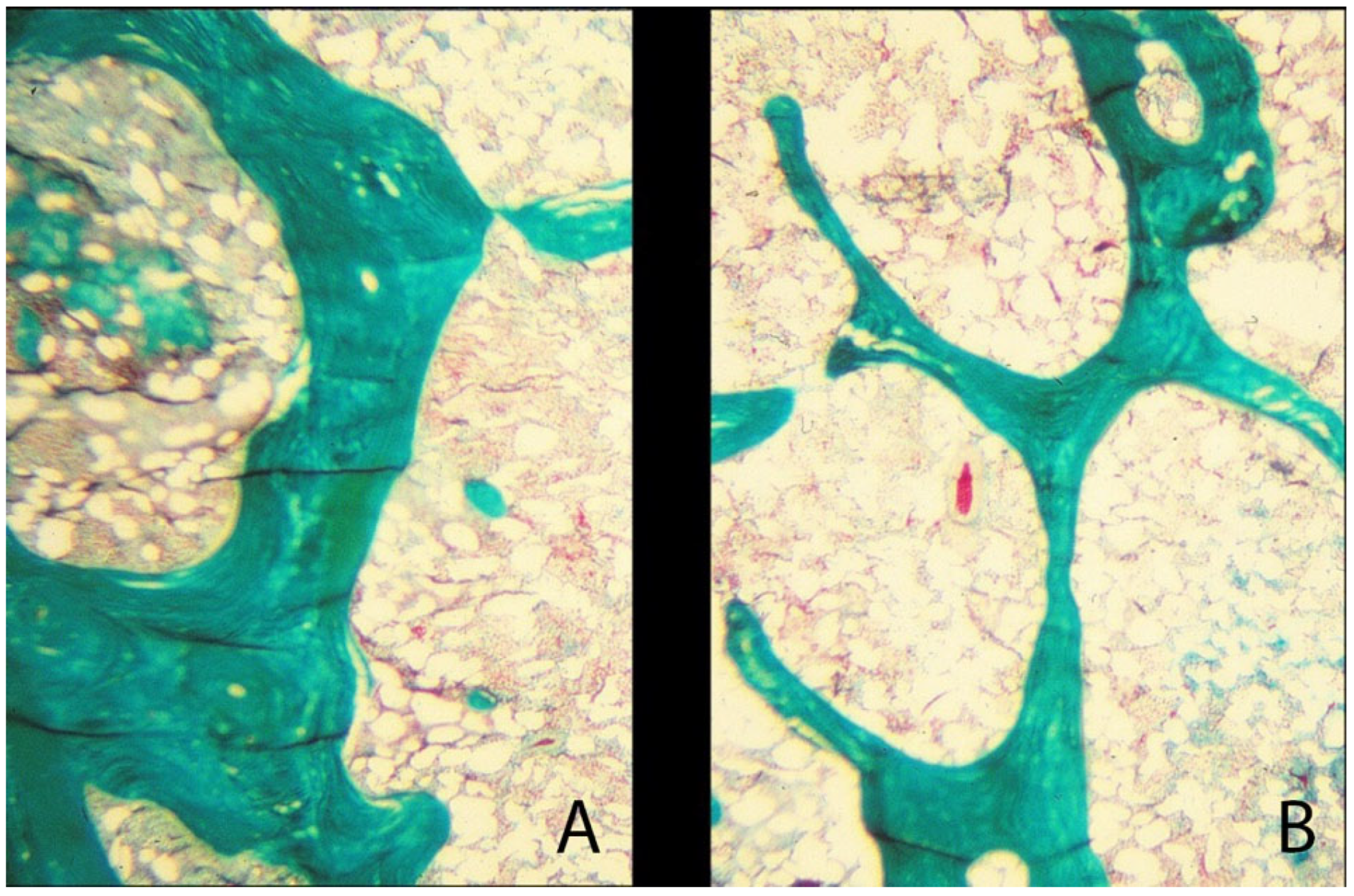
4.2. Bone Pathology of Fibrous Dysplasia
5. Current and Future Therapeutics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAS | McCune–Albright syndrome |
| FD | fibrous dysplasia |
| Gsα | alpha subunit of a stimulatory G protein |
| NESP55 | neuroendocrine secretory protein 55 |
| XLαs | extra-large variant of Gsα |
| PHP1A | pseudohypoparathyroidism 1A |
| PPHP | pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| FGF23 | fibroblast growth factor 23 |
References
- McCune, D.J.; Bruch, H. Osteodystrophia Fibrosa: Report of a Case in Which the Condition Was Combined with Precocious Puberty, Pathologic Pigmentation of the Skin and Hyperthyroidism, with a Review of the Literature. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1937, 54, 806–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, F.; Butler, A.M.; Hampton, A.O.; Smith, P. Syndrome Characterized by Osteitis Fibrosa Disseminata, Areas of Pigmentation and Endocrine Dysfunction, with Precocious Puberty in Females. N. Engl. J. Med. 1937, 216, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, L. Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia. Arch. Surg. 1938, 36, 874–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, L.S.; Shenker, A.; Gejman, P.V.; Merino, M.J.; Friedman, E.; Spiegel, A.M. Activating Mutations of the Stimulatory G Protein in the McCune–Albright Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.K.; Boyce, A.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.; Ong, J.; Defabianis, P.; Offiah, A.; Arunde, P.; Shaw, N.; Pos, V.D.; Underhil, A.; et al. Best practice management guidelines for fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome: A consensus statement from the FD/MAS international consortium. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Symbol Report|HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:4392 (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Pai, B.; Ferdinand, D. Fibrous dysplasia causing safeguarding concerns. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orphanet: Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone. Available online: http://www.orpha.net/en/disease/detail/249 (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Orphanet: McCune-Albright Syndrome. Available online: http://www.orpha.net/en/disease/detail/562?mode=name&name=mccune%20albright (accessed on 6 October 2025).
- Riddle, N.D.; Bui, M.M. Fibrous dysplasia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.E.; Vágó, E.; Abrahamsen, B.; Dekkers, O.M.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Rejnmark, L.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M. Incidence and Prevalence of Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome: A Nationwide Registry-Based Study in Denmark. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, A.M.; Collins, M.T. Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome: A Rare, Mosaic Disease of Gαs Activation. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, I.; Zhadina, M.; Collins, M.T.; Boyce, A.M. Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone and McCune-Albright Syndrome: A Bench to Bedside Review. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 104, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, K.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; He, Q. GNAS locus: Bone related diseases and mouse models. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1255864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastepe, M. The GNAS Locus: Quintessential Complex Gene Encoding Gsalpha, XLalphas, and other Imprinted Transcripts. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, P.; Carter, A.; Simons, C.; Guo, V.; Puckett, C.; Kamholz, J.; Spiegel, A.; Nirenberg, M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8893–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, S.; Werner, R.; Ahrens, W.; Hoppe, U.; Marschke, C.; Staedt, P.; Hiort, O. A disruptive mutation in exon 3 of the GNAS gene with albright hereditary osteodystrophy, normocalcemic pseudohypoparathyroidism, and selective long transcript variant Gsalpha-L deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüppner, H. Molecular Definition of Pseudohypoparathyroidism Variants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullan, P.; Germain-Lee, E.L. Aberrant Bone Regulation in Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy dueto Gnas Inactivation: Mechanisms and Translational Implications. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2022, 20, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L. McCune-Albright Syndrome. In Medical Genetics Summaries; Pratt, V.M., Scott, S.A., Pirmohamed, M., Esquivel, B., Kattman, B.L., Malheiro, A.J., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Riminucci, M.; Fisher, L.W.; Shenker, A.; Spiegel, A.M.; Bianco, P.; Gehron Robey, P. Fibrous dysplasia of bone in the McCune-Albright syndrome: Abnormalities in bone formation. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Y.; Aarnisalo, P.; Bastepe, M.; Sinha, P.; Fulzele, K.; Selig, M.K.; Chen, M.; Poulton, I.J.; Purton, L.E.; Sims, N.A.; et al. Gsα enhances commitment of mesenchymal progenitors to the osteoblast lineage but restrains osteoblast differentiation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3492–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, S.; Bastepe, M. GNAS Spectrum of Disorders. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2015, 13, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, P.J.; de Pollak, C.; Chanson, P.; Lomri, A. Increased proliferation of osteoblastic cells expressing the activating Gs alpha mutation in monostotic and polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara, S.; Ikeda, M.; Ozawa, H.; Akiyama, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakahama, K.-I. Role of cAMP in phenotypic changes of osteoblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, B.; Labella, R.; Donsante, S.; Remoli, C.; Spica, E.; Coletta, I.; Farinacci, G.; Dello Spedale Venti, M.; Saggio, I.; Serafini, M.; et al. GsαR201C and estrogen reveal different subsets of bone marrow adiponectin expressing osteogenic cells. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, B.; Berry, C.; Boyce, A.; Charles, J.F.; Collins, M.T.; Corsi, A.; Fierro, F.A.; Heegaard, A.-M.; van der Heijden, H.; Hoffman, C.S.; et al. Fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome: State-of-the-art advances, pathogenesis, and basic/translational research. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2025, 20, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, B.; Tavanti, C.; Farinacci, G.; Gosti, G.; Leonetti, M.; Donsante, S.; Giannicola, G.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.; Corsi, A.; Ippolito, E.; et al. Bone pain in fibrous dysplasia does not rely on aberrant sensory nerve sprouting or neuroma formation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2025, 40, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, D.W. Augmented Reality-Assisted Surgery for Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthetic Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, D.J.; Garcia, R.; Haselhuhn, J.J.; Zhou, Y.; Murugan, P.; Sembrano, J.N. Minimally invasive fixation and management of sacral fibrous dysplasia with impending pathological fracture: Illustrative case. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2025, 9, CASE25159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Xing, L.; Huang, W.; Ji, N.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Q.; Han, X.; Bai, D.; Zhao, X. Protein kinase A is a dependent factor and therapeutic target in mouse models of fibrous dysplasia. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, K.L.; Park, J.; Yu, X.; Hsiao, E.C. Update on the medical management of fibrous dysplasia of the bone. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 16, 20420188251347350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, E.S.; Kelly, M.H.; Brillante, B.; Chen, C.C.; Ziran, N.; Lee, J.S.; Feuillan, P.; Leet, A.I.; Kushner, H.; Robey, P.G.; et al. Onset, progression, and plateau of skeletal lesions in fibrous dysplasia and the relationship to functional outcome. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Min, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Duan, H.; Tu, C. The West China Hospital radiographic classification for fibrous dysplasia in femur and adjacent bones: A retrospective analysis of 205 patients. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Duan, H.; Tu, C. Radiographic classification and treatment of fibrous dysplasia of the proximal femur: 227 femurs with a mean follow-up of 6 years. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, E.; Farsetti, P.; Boyce, A.M.; Corsi, A.; De Maio, F.; Collins, M.T. Radiographic classification of coronal plane femoral deformities in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, J.A.; Tella, S.H.; Tuthill, K.F.; Kim, L.; Guthrie, L.C.; Paul, S.M.; Stanton, R.; Collins, M.T.; Boyce, A.M. Scoliosis in Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome: Factors Associated with Curve Progression and Effects of Bisphosphonates. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricalde, P.; Magliocca, K.R.; Lee, J.S. Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 24, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; FitzGibbon, E.; Butman, J.A.; Dufresne, C.R.; Kushner, H.; Wientroub, S.; Robey, P.G.; Collins, M.T. Normal vision despite narrowing of the optic canal in fibrous dysplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintoye, S.O.; Lee, J.S.; Feimster, T.; Booher, S.; Brahim, J.; Kingman, A.; Riminucci, M.; Robey, P.G.; Collins, M.T. Dental characteristics of fibrous dysplasia and McCune-Albright syndrome. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2003, 96, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, A.B.; Collins, M.T.; Boyce, A.M. Fibrous dysplasia of bone: Craniofacial and dental implications. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, C.; Boyce, A.M.; Kaban, L.B.; Peacock, Z.S.; Mannstadt, M.; Upadhyay, J.; Craniofacial Fibrous Dysplasia Research Team. Identifying Pain Subtypes in Patients with Craniofacial Lesions of Fibrous Dysplasia/McCune-Albright Syndrome. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2025, 83, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Wasserman, G.; Meir, T.; Silver, J.; Naveh-Many, T. PTH increases FGF23 gene expression and mediates the high-FGF23 levels of experimental kidney failure: A bone parathyroid feedback loop. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2010, 299, F882–F889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeska, R.J.; Kennedy, O.D.; Schaffler, M.B.; Morgan, E.F.; Gerstenfeld, L.C. Chapter 10: Biology of Bone. In Orthopaedic Basic Science: Foundations of Clinical Practice; Aaron, R.K., Ed.; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: Rosemont, IL, USA; Ovid Technologies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frassica, F.J.; Inoue, N.; Virolainen, P.; Chao, E.Y. Skeletal system: Biomechanical concepts and relationships to normal and abnormal conditions. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1997, 27, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, D.B.; Wallace, J.M. Chapter 11: Bone Biomechanics. In Orthopaedic Basic Science: Foundations of Clinical Practice; Aaron, R.K., Ed.; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: Rosemont, IL, USA; Ovid Technologies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.M.; Castellani, C.M.; Popp, K.L.; Guerriere, K.I.; Matheny, R.W.; Nindl, B.C.; Bouxsein, M.L. The Central Role of Osteocytes in the Four Adaptive Pathways of Bone’s Mechanostat. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2020, 48, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, P.; Rizzoli, R. Bone strength and its determinants. Osteoporos. Int. 2003, 14 (Suppl. 3), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L. Bone quality: Where do we go from here? Osteoporos. Int. 2003, 14 (Suppl. 5), S118–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, F.; Hayes, W.; Keaveny, T.; Boskey, A.; Einhorn, T.; Iannoti, J. Form and function of bone. In Orthopaedic Basic Science; Simon, S.R., Ed.; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: Rosemont, IL, USA, 1994; pp. 127–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ingvar, D.H.; Nordfeldt, S.; Pettersson, R. Behold Man: A Photographic Journey of Discovery Inside the Body; Little, Brown and Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, S.A.; Goulet, R.; McCubbrey, D. Measurement and significance of three-dimensional architecture to the mechanical integrity of trabecular bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1993, 53 (Suppl. 1), S127–S132; discussion S132–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, P.; Laib, A.; Bonjour, J.P.; Meyer, J.M.; Rüegsegger, P.; Rizzoli, R. Dietary essential amino acid supplements increase bone strength by influencing bone mass and bone microarchitecture in ovariectomized adult rats fed an isocaloric low-protein diet. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, P.; Bourrin, S.; Bonjour, J.P.; Meyer, J.M.; Rizzoli, R. Protein undernutrition-induced bone loss is associated with decreased IGF-I levels and estrogen deficiency. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augat, P.; Schorlemmer, S. The role of cortical bone and its microstructure in bone strength. Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. 2), ii27–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Giannini, S. Bone microarchitecture as an important determinant of bone strength. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2004, 27, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L. Determinants of skeletal fragility. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, B.; Spica, E.; Remoli, C.; Labella, R.; Di Filippo, A.; Donsante, S.; Bini, F.; Raimondo, D.; Marinozzi, F.; Boyde, A.; et al. RANKL Inhibition in Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone: A Preclinical Study in a Mouse Model of the Human Disease. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 2171–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, M.; Hamdy, N.A.T.; Appelman-Dijkstra, N.M. Clinical and translational pharmacological aspects of the management of fibrous dysplasia of bone. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.; Pan, K.S.; Collins, M.T.; Boyce, A.M. The Clinical Spectrum of McCune-Albright Syndrome and Its Management. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 92, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Littman, J.L.; Yang, W.; Feder, N.; Kaadan, A.; Amin, A.; Aaron, R.K. The GNAS Gene: Fibrous Dysplasia, McCune–Albright Syndrome, and Skeletal Structure and Function. Genes 2025, 16, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111360
Littman JL, Yang W, Feder N, Kaadan A, Amin A, Aaron RK. The GNAS Gene: Fibrous Dysplasia, McCune–Albright Syndrome, and Skeletal Structure and Function. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLittman, Jake Louis, Wentian Yang, Noah Feder, Amr Kaadan, Ali Amin, and Roy K. Aaron. 2025. "The GNAS Gene: Fibrous Dysplasia, McCune–Albright Syndrome, and Skeletal Structure and Function" Genes 16, no. 11: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111360
APA StyleLittman, J. L., Yang, W., Feder, N., Kaadan, A., Amin, A., & Aaron, R. K. (2025). The GNAS Gene: Fibrous Dysplasia, McCune–Albright Syndrome, and Skeletal Structure and Function. Genes, 16(11), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111360





