Integrating Transcriptomics and Machine Learning to Uncover the FLI1-PARP14-Immune Axis in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
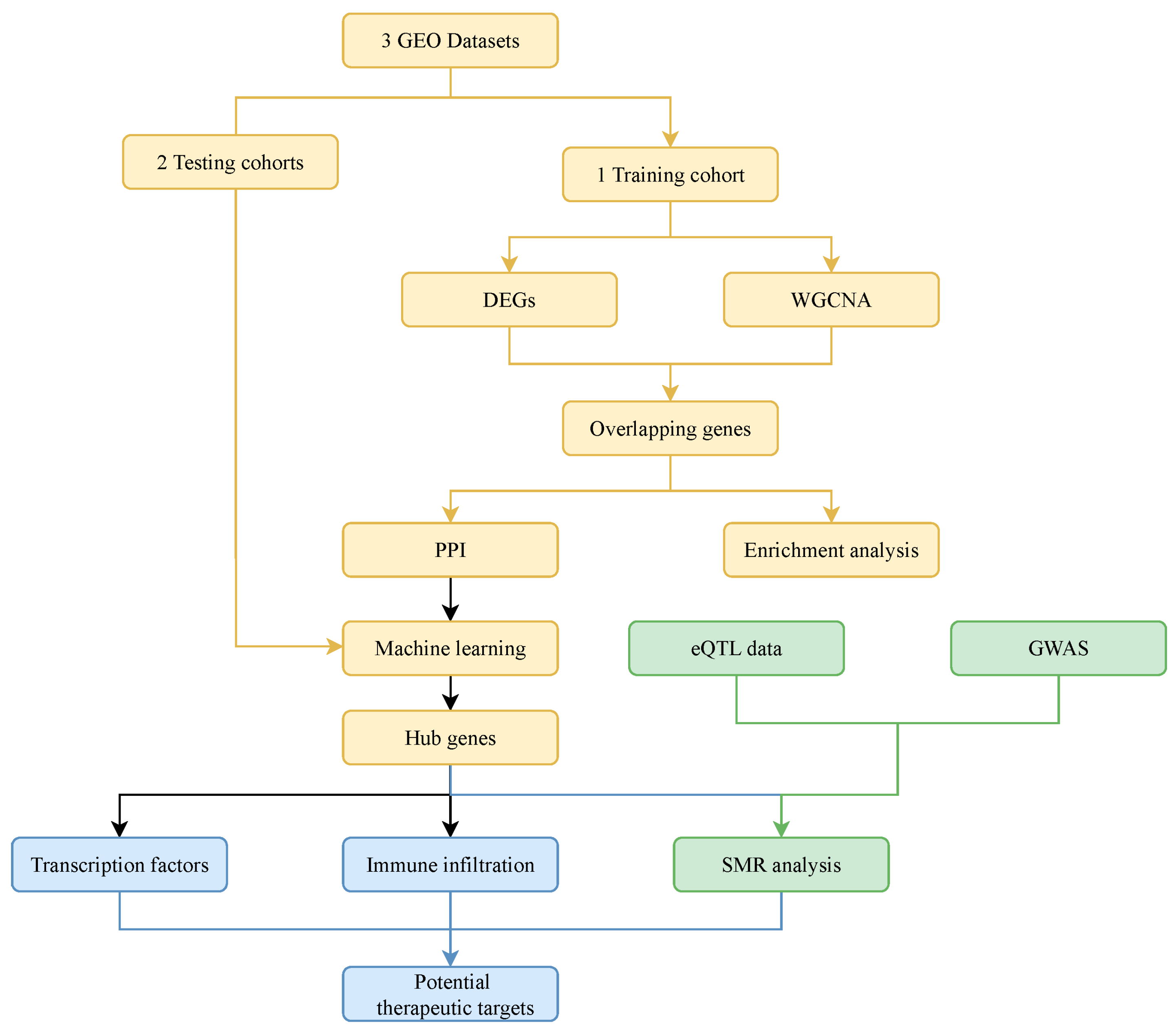
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
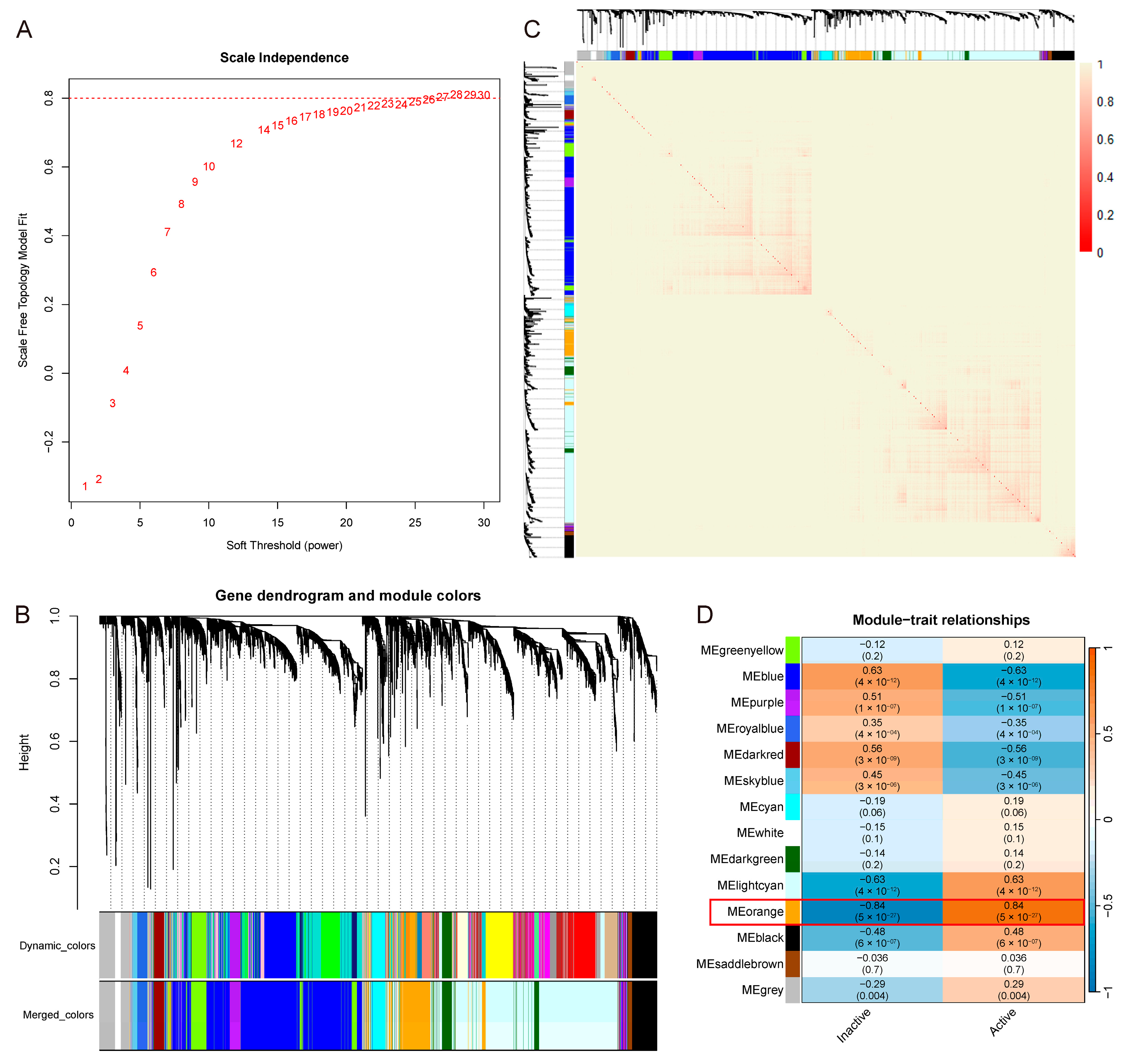
2.3. WGCNA
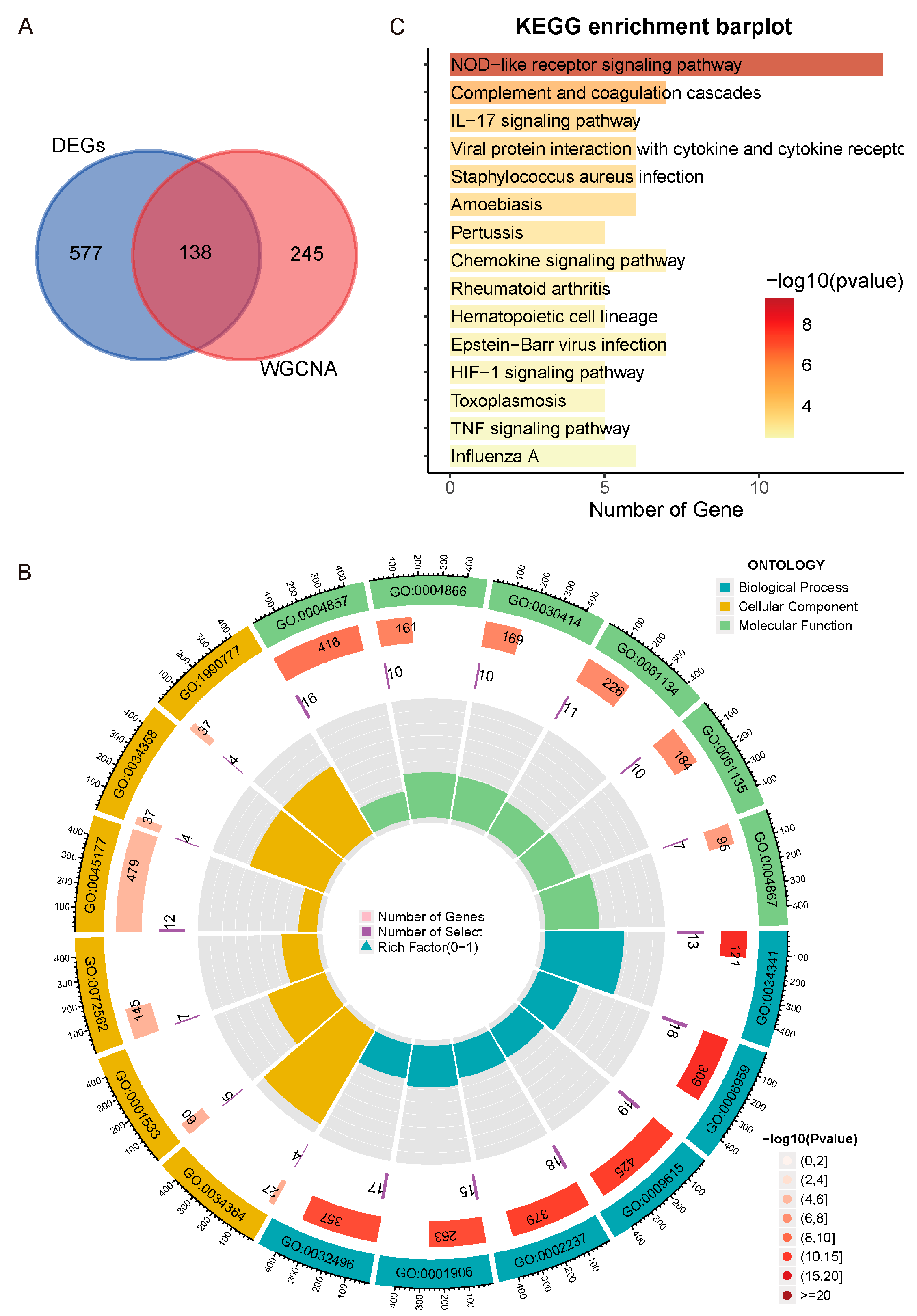
2.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis
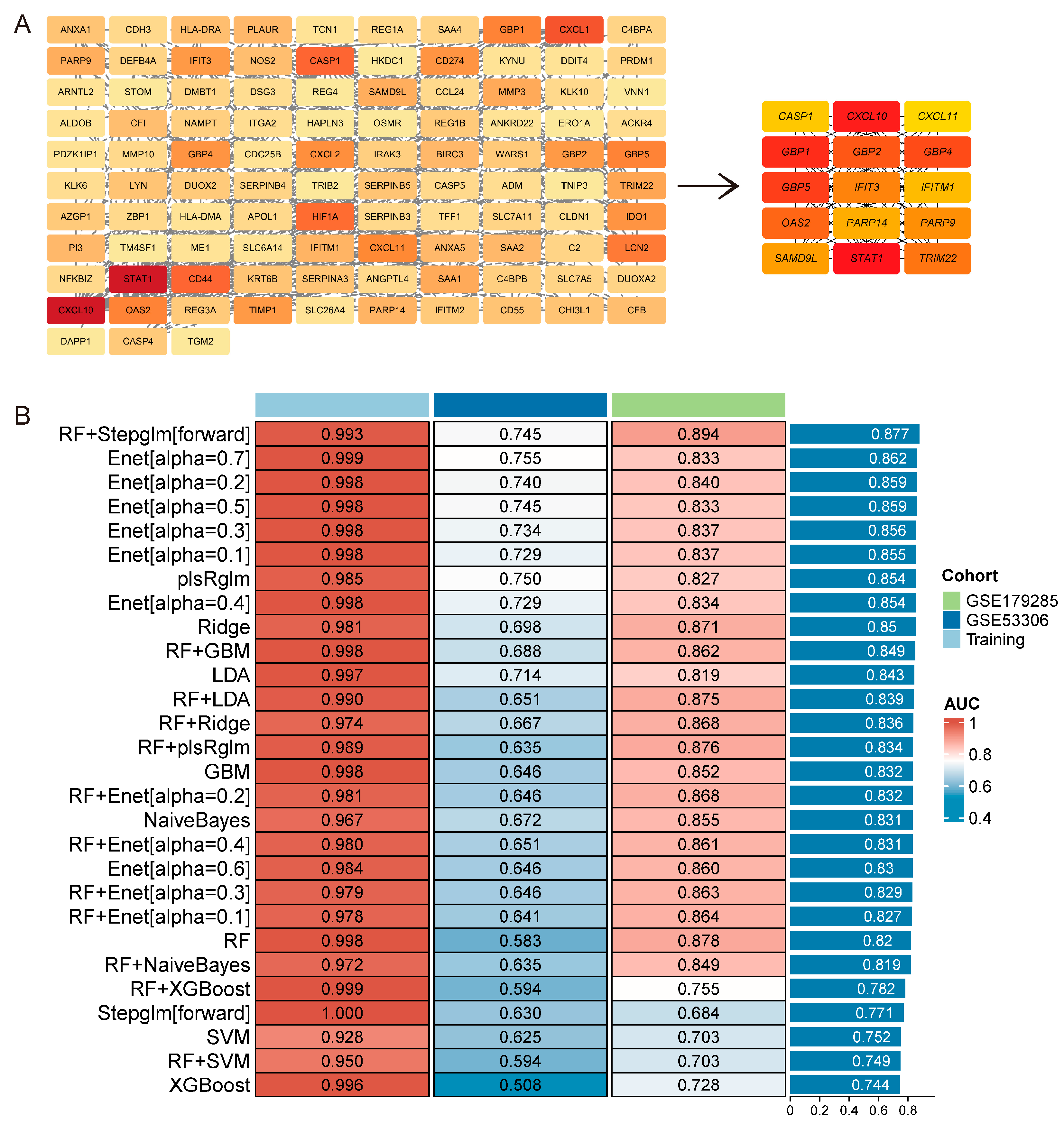
2.6. Machine Learning Algorithm Analysis
2.7. Diagnostic Value and Expression Patterns of Hub Genes
2.8. Prediction of Transcription Factors
2.9. Summary-Data–Based Mendelian Randomization (SMR) Analysis
2.10. Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DEGs Correlated with UC Activity
3.2. Meorange Module Strongest Correlated with UC Activity
3.3. Immune System and Cytokine-Driven Inflammation Closely Associated with UC Activity
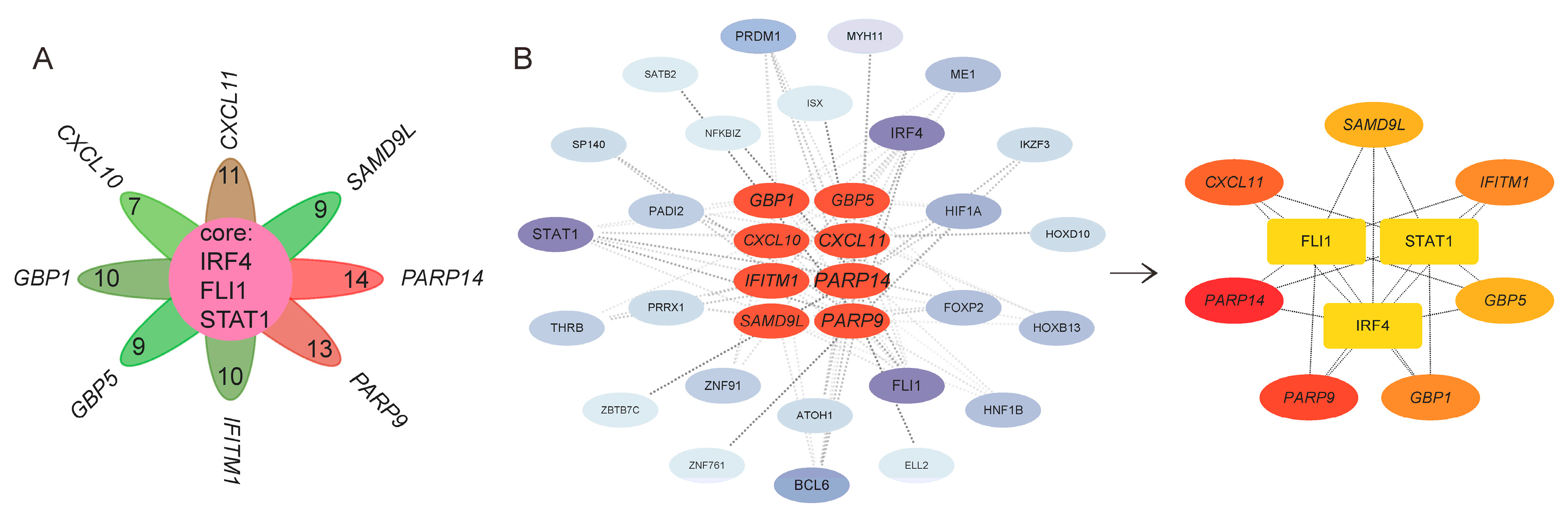
3.4. Characteristic Genes Associated with UC Activity
3.5. Hub Genes and Diagnostic Capability in UC Activity
3.6. TFs of Characteristic Genes in UC Activity
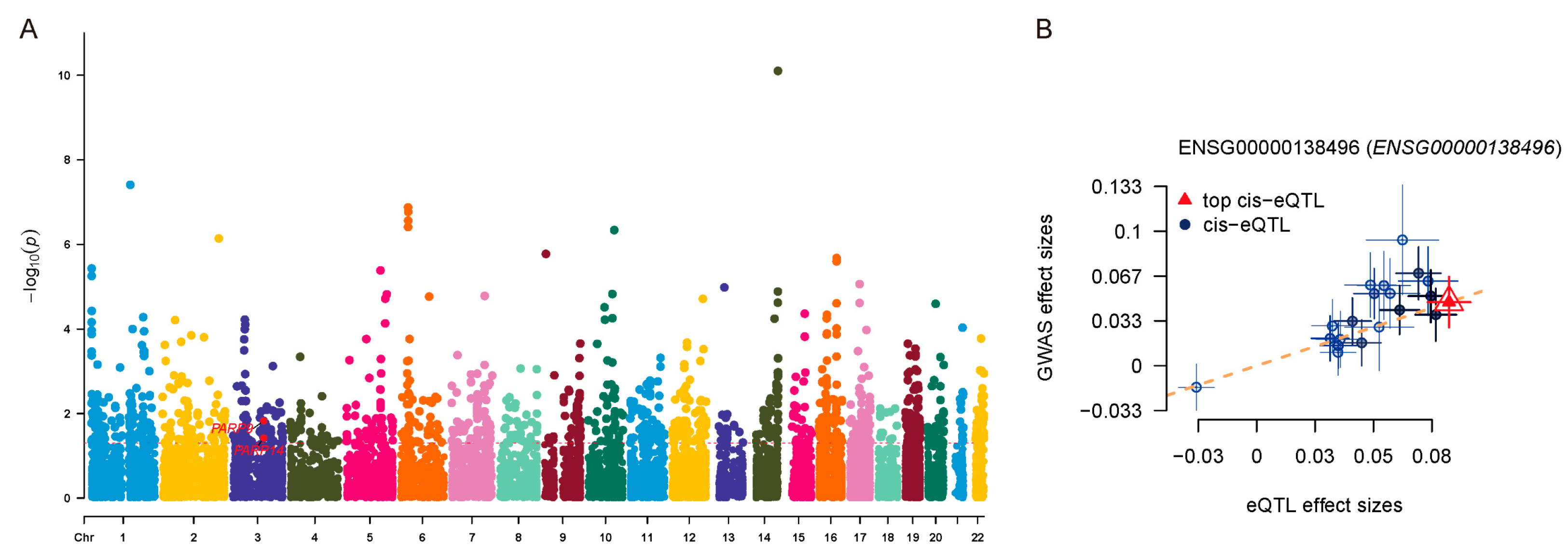
3.7. Causal Association Between PARP14 Expression and UC Risk Identified by SMR Analysis
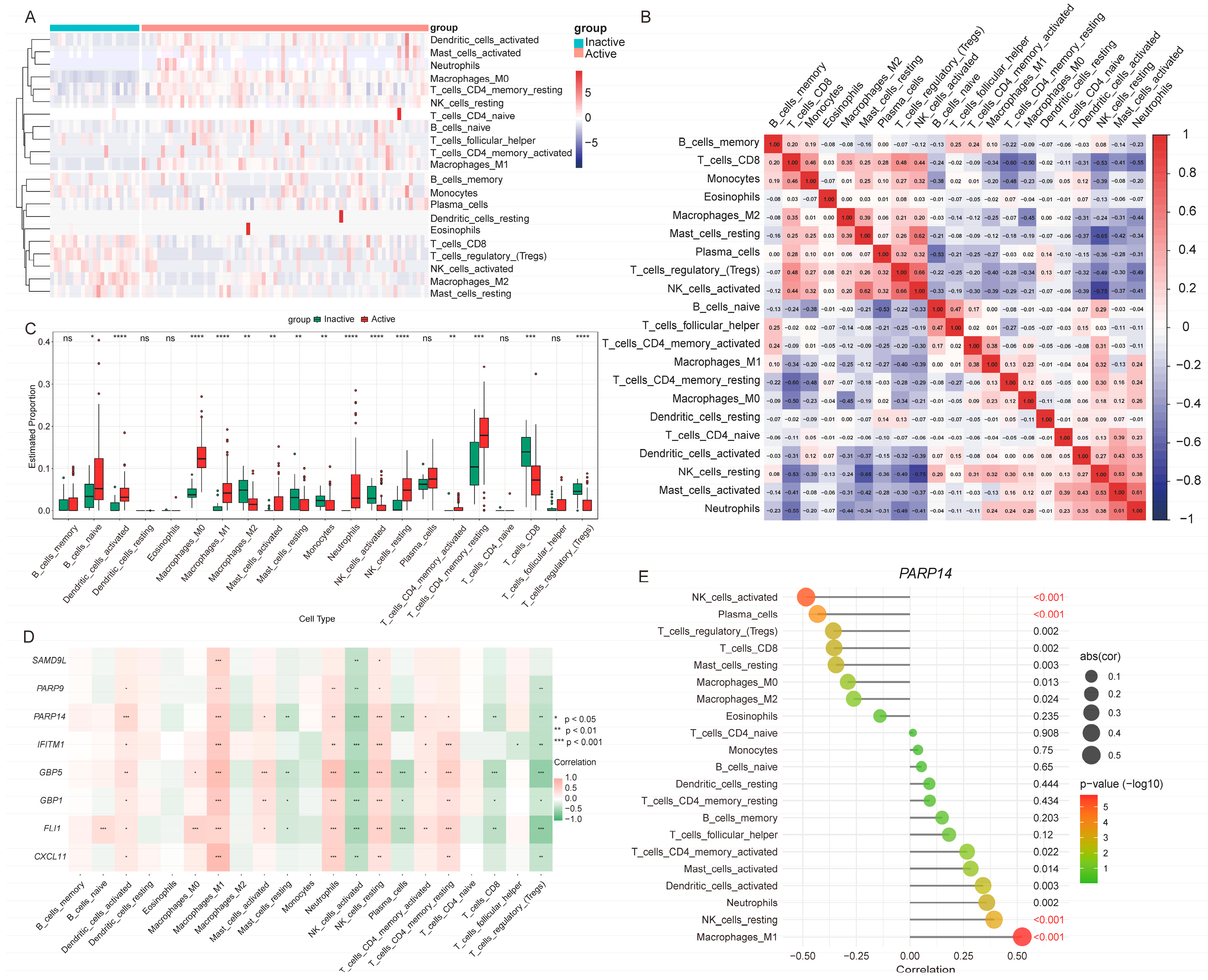
3.8. Immune Cell Infiltration Patterns Associated with UC Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| eQTL | Expression quantitative trait locus |
| GBM | Gradient boosting machine |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LM22 | Leukocyte signature matrix |
| Lasso | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| MCC | Maximal clique centrality |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| plsR-glm | Partial least squares regression with generalized linear model |
| Ridge | Ridge regression |
| RF | Random forest |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SMR | Summary-data–based mendelian randomization |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| Stepglm | Stepwise generalized linear model |
| glmBoost | Boosted generalized linear model |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| WGCNA | Weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| XGBoost | Extreme gradient boosting |
References
- Seyedian, S.S.; Nokhostin, F.; Malamir, M.D. A Review of the Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment Methods of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.-F. Ulcerative Colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Berre, C.; Honap, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Ulcerative Colitis. Lancet 2023, 402, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Ha, C. Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.J.; Kalla, R.; Ho, G.-T. Ulcerative Colitis: Recent Advances in the Understanding of Disease Pathogenesis. F1000Researchs 2020, 9, F1000 Faculty Rev-294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-H.; Zhu, C.-X.; Quan, Y.-S.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, W.-W.; Tan, B.; Wang, X.-Y. Relationship between Intestinal Microbiota and Ulcerative Colitis: Mechanisms and Clinical Application of Probiotics and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauduit, A.; Mas, E.; Solà-Tapias, N.; Ménard, S.; Barreau, F. Main Genetic Factors Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Their Consequences on Intestinal Permeability: Involvement in Gut Inflammation. J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 60, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Dai, W.; Dong, M.; Dai, C.; Wu, S. MUC2 and Related Bacterial Factors: Therapeutic Targets for Ulcerative Colitis. EBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Jiang, X.-H.; Zou, R.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Fan, Z.-N. Unveiling the Key Genes, Environmental Toxins, and Drug Exposures in Modulating the Severity of Ulcerative Colitis: A Comprehensive Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1162458. [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Moss, A.C.; Farraye, F.A. Ulcerative Colitis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, N.K.; Torres, J.; Rubin, D.T. What Does Disease Progression Look Like in Ulcerative Colitis, and How Might It Be Prevented? Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzik, T.; Koletzko, S.; Kannengiesser, K.; Dignass, A. Ulcerative Colitis-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithms. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Isaacs, K.L.; Schneider, Y.; Siddique, S.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Singh, S.; AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salice, M.; Rizzello, F.; Calabrese, C.; Calandrini, L.; Gionchetti, P. A Current Overview of Corticosteroid Use in Active Ulcerative Colitis. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.-T.; Teichert, C.; Pruijt, M.; De Voogd, F.; D’Haens, G.; Gecse, K. Transmural Healing in Ulcerative Colitis Patients Improves Long-Term Outcomes Compared to Endoscopic Healing Alone. J. Crohns Colitis 2025, 19, jjaf149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, P.-L.; Lakatos, L. Risk for Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis: Changes, Causes and Management Strategies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakov, R. New Markers in Ulcerative Colitis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 497, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Ye, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Identification of Inflammation-Related Diagnostic Biomarker and Molecular Subtypes in Ulcerative Colitis Based on Machine Learning. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qi, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S. Integrating Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Machine Learning to Dissect Tryptophan Metabolism in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Võsa, U.; Claringbould, A.; Westra, H.-J.; Bonder, M.J.; Deelen, P.; Zeng, B.; Kirsten, H.; Saha, A.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Yazar, S.; et al. Large-Scale Cis- and Trans-eQTL Analyses Identify Thousands of Genetic Loci and Polygenic Scores That Regulate Blood Gene Expression. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. “Mendelian Randomization”: Can Genetic Epidemiology Contribute to Understanding Environmental Determinants of Disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, D. Comprehensive Analysis Reveals Key Genes and Environmental Toxin Exposures Underlying Treatment Response in Ulcerative Colitis Based on In-Silico Analysis and Mendelian Randomization. Aging 2023, 15, 14141–14171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Chung, F.R.; Delau, O.; Dane, B.; Levine, I.; Meng, X.; Chodosh, J.; da Luz Moreira, A.; Simon, J.N.; Axelrad, J.E.; et al. Risk of Malnutrition Increases in the Year Prior to Surgery among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2025, 18, 17562848251365036. [Google Scholar]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Farré, R.; Verstockt, S.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Schuit, F.; Vermeire, S.; Arijs, I.; et al. Genetic and Transcriptomic Bases of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Zhi, F.; Li, A.; Li, C.; Berger, A.E.; Boorgula, M.P.; Barkataki, S.; Courneya, J.-P.; Chen, Y.; et al. Mobilization of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Genes Distinguishes Active from Inactive Lesional Tissue in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4615–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Fuh, F.; Ichikawa, R.; Acres, M.; Hackney, J.A.; Hulme, G.; Carey, C.D.; Palmer, J.; Jones, C.J.; Long, A.K.; et al. Regulation and Role of αE Integrin and Gut Homing Integrins in Migration and Retention of Intestinal Lymphocytes during Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Weng, S.; Guo, C.; Dang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Integration Develops an Immune-Derived lncRNA Signature for Improving Outcomes in Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. TFTF: An R-Based Integrative Tool for Decoding Human Transcription Factor-Target Interactions. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of Summary Data from GWAS and eQTL Studies Predicts Complex Trait Gene Targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust Enumeration of Cell Subsets from Tissue Expression Profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Shang, S.; Yu, S.; Cui, L.; Li, S.; He, N. Identification and Exploration of Pharmacological Pyroptosis-Related Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 998470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Xu, B.; Kang, H.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Pang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z. The Role of Macrophage Polarization in Ulcerative Colitis and Its Treatment. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 199, 107227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.; Mao, C.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Ferroptosis in Ulcerative Colitis: Potential Mechanisms and Promising Therapeutic Targets. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Song, Q.; Tan, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Liao, S.; Yu, K.; Mei, Z.; Lv, L. Seliciclib Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis by Inhibiting Ferroptosis and Improving Intestinal Inflammation. Life Sci. 2024, 351, 122794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.-C.; Zheng, J.-H.; Cheng, Y.-Z.; Weng, W.-P.; Zhong, R.-L.; Sun, S.-L.; Shi, Y.-S.; Pan, X.-D. Pterosin B Improves Cognitive Dysfunction by Promoting Microglia M1/M2 Polarization through Inhibiting Klf5/Parp14 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Cong, K.; Lou, S.; Li, Z.; Wei, P.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, L.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Potent and Highly Selective PARP14 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 9755–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, L.; Mou, C.; Zhao, J.; Go, Y.Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Z. African Swine Fever Virus A179L Inhibits Interferon Induced Transmembrane Protein 1 Activation of NF-κB Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhong, S.-L.; Chen, T.; Liu, S.-Z.; Zhang, S.-L.; Xie, X.-X.; Liu, T.; Yang, W. Rhoifolin Attenuates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Restoring Th17/Treg Balance. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 11109–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruland, T.; Østvik, A.E.; Sandvik, A.K.; Hansen, M.D. Host-Viral Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhama, A.R.; Kapadia, M.R. Management of Dysplasia in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2021, 31, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Li, L.; Sun, C.; Li, L.; Tang, F.; Huang, D.; Li, Z.; Tan, Y.; et al. Benzoylpaeoniflorin Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis by Inhibiting Ferroptosis through Targeting Phosphogluconic Dehydrogenase. Phytomedicine 2025, 147, 157111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Datasets | Samples from UC Patients | Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inactive Phase | Active Phase | ||
| GSE75214 | 23 | 74 | Training cohort |
| GSE53306 | 12 | 16 | Testing cohorts |
| GSE179285 | 32 | 23 | |
| Gene | Training | Testing | Average AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE75214 | GSE53306 | GSE179285 | ||
| CXCL11 | 0.9 | 0.771 | 0.894 | 0.855 |
| PARP14 | 0.952 | 0.703 | 0.864 | 0.840 |
| IFITM1 | 0.973 | 0.729 | 0.789 | 0.830 |
| SAMD9L | 0.975 | 0.562 | 0.874 | 0.804 |
| GBP1 | 0.949 | 0.646 | 0.792 | 0.796 |
| GBP5 | 0.961 | 0.609 | 0.803 | 0.791 |
| PARP9 | 0.936 | 0.604 | 0.818 | 0.786 |
| CXCL10 | 0.907 | 0.609 | 0.764 | 0.760 |
| Key TF | Description | Training | GSE53306 | GSE179285 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p Value | log2FC | p Value | log2FC | p Value | log2FC | ||
| FLI1 | Fli-1 proto-oncogene, ETS transcription factor | 1.07 × 10−10 | 1.078 | 0.0305 | 0.560 | 9.47 × 10−4 | 0.702 |
| STAT1 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 | 3.87 × 10−14 | 1.035 | 0.404 | −0.194 | 1.96 × 10−4 | 0.833 |
| IRF4 | interferon regulatory factor 4 | 4.67 × 10−16 | 1.665 | 0.162 | 0.453 | 7.27 × 10−5 | 0.739 |
| Gene | b_SMR | se_SMR | p_SMR | p_HEIDI | nsnp_HEIDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARP14 | 0.0722 | 0.0348 | 0.0378 | 0.240 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Song, G. Integrating Transcriptomics and Machine Learning to Uncover the FLI1-PARP14-Immune Axis in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Pathogenesis. Genes 2025, 16, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111342
Zheng Z, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Chen H, Song G. Integrating Transcriptomics and Machine Learning to Uncover the FLI1-PARP14-Immune Axis in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Pathogenesis. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zhizhong, Yayu Zhang, Zhixing Gao, Houyu Chen, and Gang Song. 2025. "Integrating Transcriptomics and Machine Learning to Uncover the FLI1-PARP14-Immune Axis in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Pathogenesis" Genes 16, no. 11: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111342
APA StyleZheng, Z., Zhang, Y., Gao, Z., Chen, H., & Song, G. (2025). Integrating Transcriptomics and Machine Learning to Uncover the FLI1-PARP14-Immune Axis in Ulcerative Colitis Activity and Pathogenesis. Genes, 16(11), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111342






