The Role of Fc-like Receptor 3 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
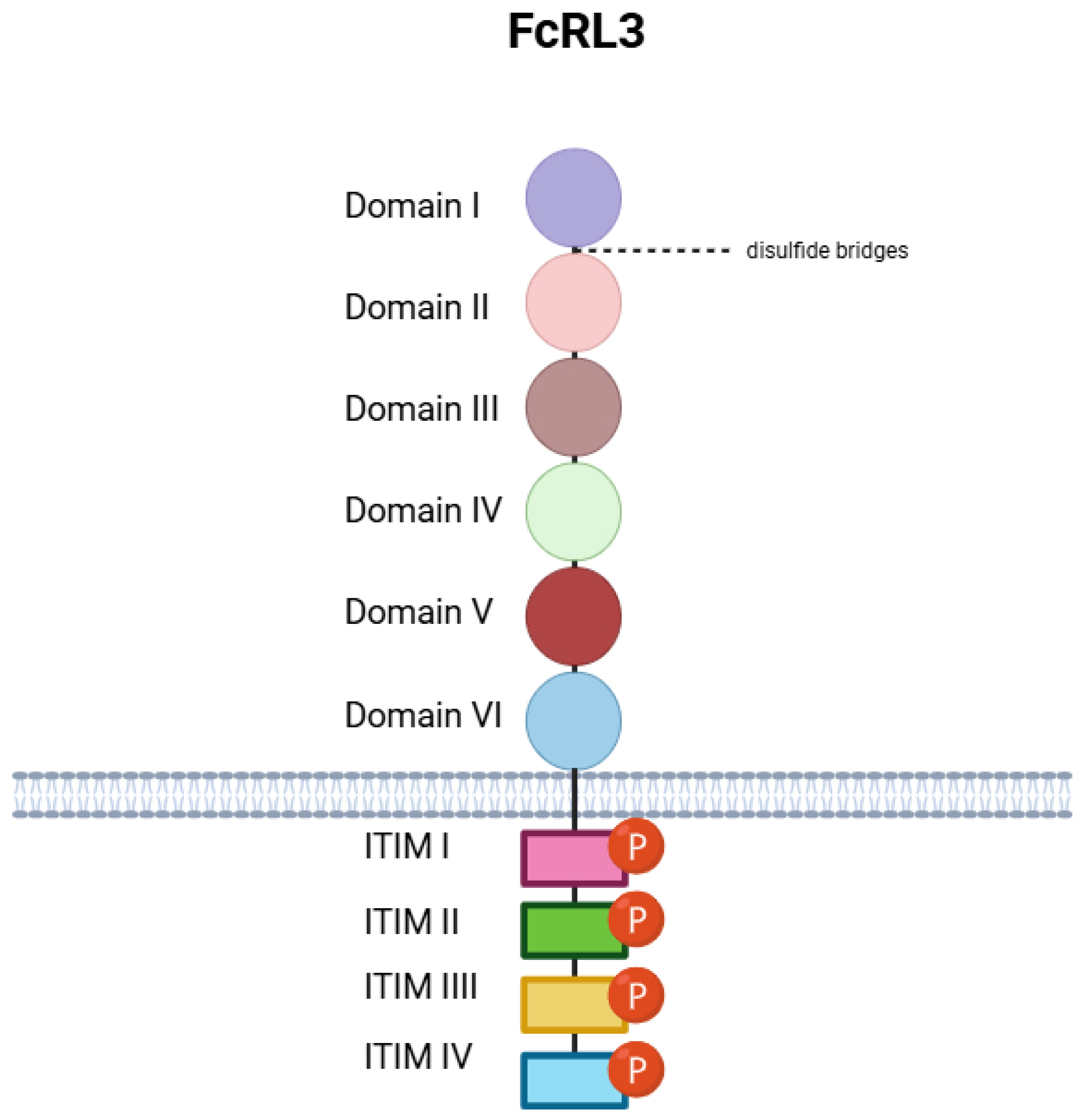
3. Biology of FcRL3: Classification, Functions, and Structure
- Domain I (21–98);
- Domain II (99–182);
- Domain III (192–270);
- Domain IV (284–369);
- Domain V (383–470);
- Domain VI (476–563).
- ITIM I (648–653, sequence: LTYSSL);
- ITIM II (660–665, SYNSIV);
- ITIM III (690–695, LEYSSL);
- ITIM IV (720–725, LHYQSV).
- Cys44–Cys82 (Domain I);
- Cys120–Cys163 (Domain II);
- Cys211–Cys260 (Domain III);
- Cys309–Cys358 (Domain IV);
- Cys404–Cys451 (Domain V);
- Cys497–Cys544 (Domain VI).
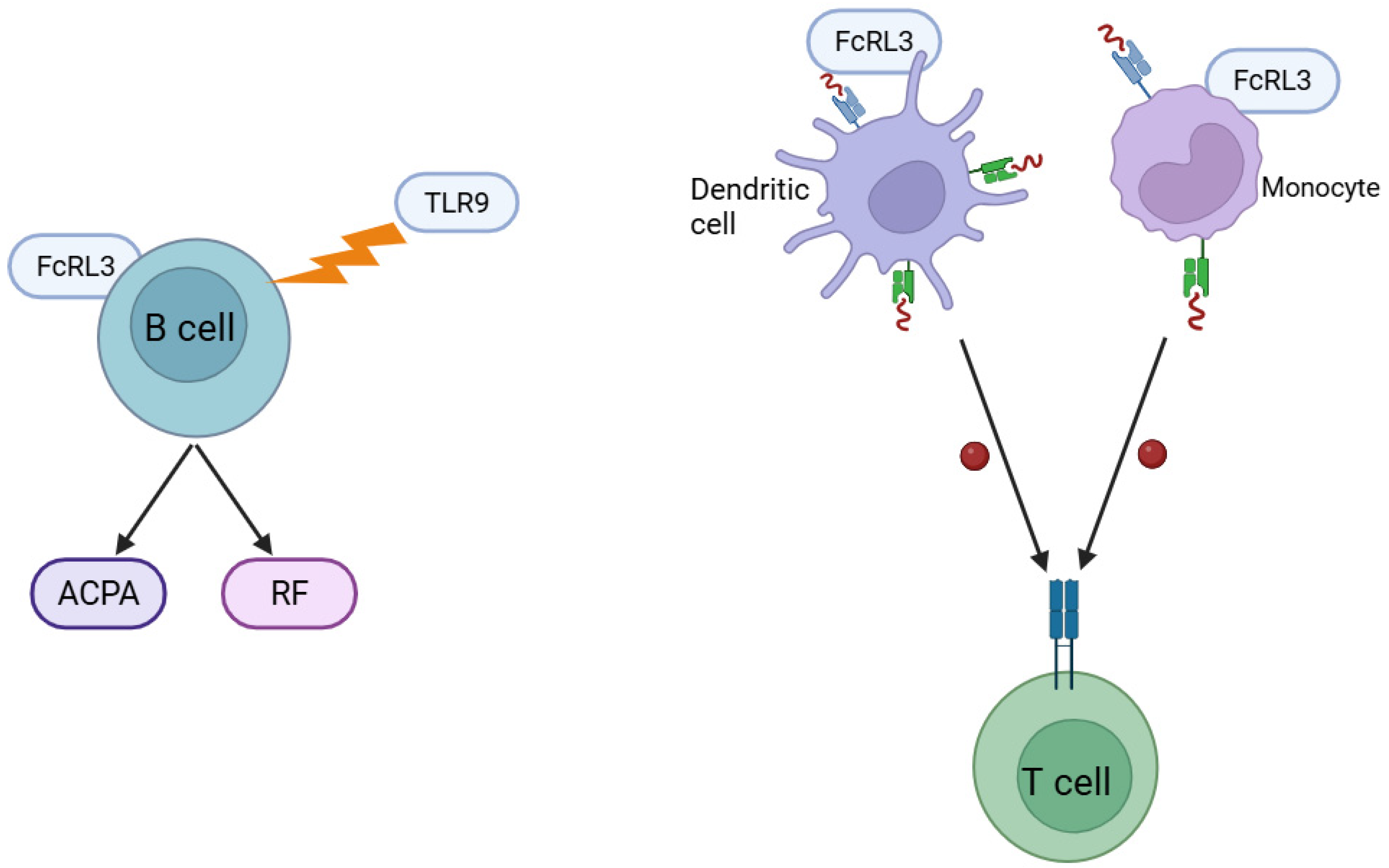
4. Molecular Mechanisms of FcRL3 Action in the Pathogenesis of RA: Involvement in Autoantibody Production and Antigen Presentation
5. Association of FcRL3 Polymorphism with RA in Different Populations
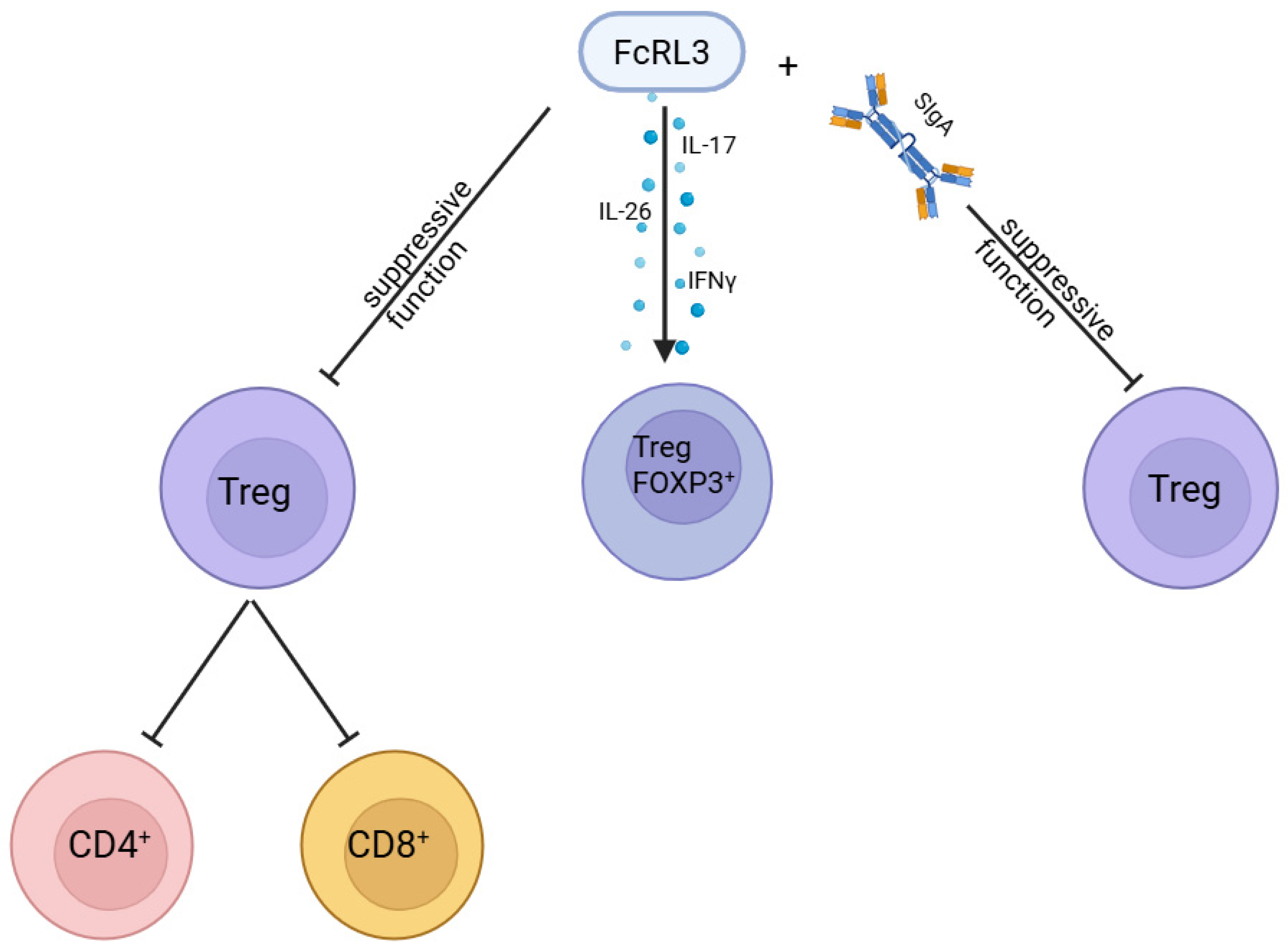
6. FCRL3 as a Negative Regulator of Treg Function and Receptor for sIgA
7. FcRL3 Expression in the Immune System: Regulation Under Physiological and Inflammatory Conditions
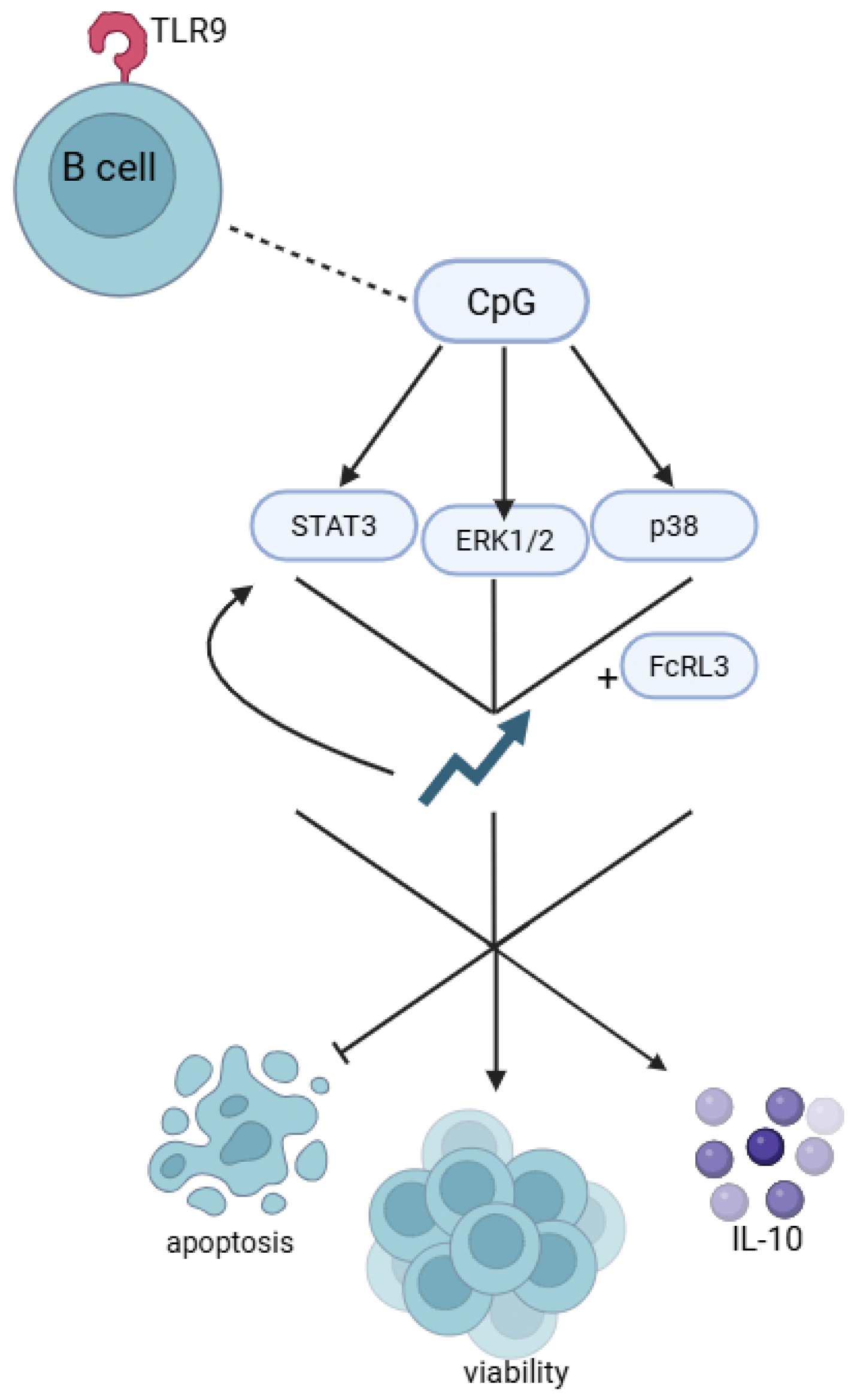
8. The Role of FCRL3 in Regulating B-Cell Responses to TLR9 Stimulation by CpG Sequences
9. FCRL3 Polymorphisms and Anti-ApoA-1 IgG Antibody Response
10. The FCRL Gene Family in the Pathophysiology of Diseases
11. Challenges and Prospects for the Development of New FcRL3-Targeted Drugs for the Treatment of RA
12. Therapeutic Potential Targeting FcRL3 and Previous Attempts at Modulation Using Anti-FcRL3 Antibodies and Signalling Pathway Inhibitors
13. Perspective for the Future
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACPAs | Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies |
| FCRH | Fc receptor homologue |
| FcRL3 | Fc-like receptor 3 |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IRTA | Immunoglobulin superfamily receptor translocation associated |
| ITAM | Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif |
| ITIM | Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-α |
| Treg | Regulatory T-cell |
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviña-Zubieta, J.A.; Choi, H.K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Etminan, M.; Esdaile, J.M.; Lacaille, D. Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, M.F.; Crowson, C.S.; Pond, G.R.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Frequency of Infection in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared with Controls: A Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilicki, M. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th ed.; Longo, D., Fauci, A., Kasper, D., Hauser, S., Jameson, J., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw Hill Professional: Columbus, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor, A.J.; Snieder, H.; Rigby, A.S.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kaprio, J.; Aho, K.; Silman, A.J. Characterizing the Quantitative Genetic Contribution to Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Data from Twins. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genetics & Rheumatic Diseases. Available online: https://rheumatology.org/genetics-rheumatic-diseases (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Akhtar, M.; Ali, Y.; Islam, Z.-U.; Arshad, M.; Rauf, M.; Ali, M.; Maodaa, S.N.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Jalil, F. Characterization of Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk-Associated SNPs and Identification of Novel Therapeutic Sites Using an In-Silico Approach. Biology 2021, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Sandor, C.; Stahl, E.A.; Freudenberg, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Jia, X.; Alfredsson, L.; Padyukov, L.; Klareskog, L.; Worthington, J.; et al. Five Amino Acids in Three HLA Proteins Explain Most of the Association between MHC and Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, U.D.; Swainson, L.A.; Mold, J.E.; Graf, J.D.; Imboden, J.B.; McCune, J.M. A Functional Variant in FCRL3 Is Associated with Higher Fc Receptor-like 3 Expression on T Cell Subsets and Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowcock, A.M.; Cookson, W.O.C.M. The Genetics of Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Atopic Dermatitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, R43–R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J.; Kotzin, B.L. Autoimmune Disease: Why and Where It Occurs. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic Insights from the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Venrooij, W.J.; van Beers, J.J.B.C.; Pruijn, G.J.M. Anti-CCP Antibodies: The Past, the Present and the Future. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving Concepts of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, S.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Matsuzaki, K.; Itoh, K.; Ishiyama, S.; Saito, S.; Inoue, K.; Kamatani, N.; Gillespie, M.T.; et al. IL-17 in Synovial Fluids from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Is a Potent Stimulator of Osteoclastogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The Immunology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Guo, T.B.; He, D.; Fang, L.; Liu, X.; Xiao, L.; Chen, X.; Wan, B.; et al. Phosphorylation of FOXP3 Controls Regulatory T Cell Function and Is Inhibited by TNF-α in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Kraus, Z.; Dement-Brown, J.; Alabi, O.; Starost, K.; Tolnay, M. Human Fc Receptor-like 3 Inhibits Regulatory T Cell Function and Binds Secretory IgA. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1292–1299.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, D.; Di Matteo, A.; Emery, P. Biomarkers in the diagnosis, prognosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2025, 62, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.S.; Dennis, G.; Odom, M.R.; Gibson, A.W.; Kimberly, R.P.; Burrows, P.D.; Cooper, M.D. Fc Receptor Homologs: Newest Members of a Remarkably Diverse Fc Receptor Gene Family. Immunol. Rev. 2002, 190, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, L.A.; Mold, J.E.; Bajpai, U.D.; McCune, J.M. Expression of the Autoimmune Susceptibility Gene FcRL3 on Human Regulatory T Cells Is Associated with Dysfunction and High Levels of PD-1. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3639–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamzadeh, D.; Kazemi, T.; Amirghofran, Z.; Shabani, M. Update on Fc Receptor-like (FCRL) Family: New Immunoregulatory Players in Health and Diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.S. Fc Receptor-like Molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 525–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Schreeder, D.M.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Davis, R.S. FCRL3 Promotes TLR9-Induced B-Cell Activation and Suppresses Plasma Cell Differentiation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2980–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt. Q96P31 · FCRL3_HUMAN. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/Uniprotkb/Q96P31/Entry (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Rapoport, T.A. Protein Translocation across the Eukaryotic Endoplasmic Reticulum and Bacterial Plasma Membranes. Nature 2007, 450, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaci, A.M.; Förster, F. Take Me Home, Protein Roads: Structural Insights into Signal Peptide Interactions during ER Translocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. FCRL3. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000160856-FCRL3/Summary/Gene (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Halaby, D.M.; Mornon, J.P. The Immunoglobulin Superfamily: An Insight on Its Tissular, Species, and Functional Diversity. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. Fc Receptor-Like Protein 3. Available online: https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/entry/Q96P31 (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Vondrakova, J.; Frolikova, M.; Ded, L.; Cerny, J.; Postlerova, P.; Palenikova, V.; Simonik, O.; Nahacka, Z.; Basus, K.; Valaskova, E.; et al. MAIA, Fc Receptor-like 3, Supersedes JUNO as IZUMO1 Receptor during Human Fertilization. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn0047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Jiménez-Movilla, M.; Cots-Rodríguez, P.; Viola, C.; Wright, G.J. No Evidence for a Direct Extracellular Interaction between Human Fc Receptor–like 3 (MAIA) and the Sperm Ligand IZUMO1. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadk6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, Y.; Myouzen, K.; Yamada, R.; Suzuki, A.; Kurosaki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, K. FCRL3, an Autoimmune Susceptibility Gene, Has Inhibitory Potential on B-Cell Receptor-Mediated Signaling. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5502–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Wu, D.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Terao, C.; Ikari, K.; Kochi, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Contributes to Biology and Drug Discovery. Nature 2014, 506, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasishta, A. Diagnosing Early-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Anti-CCP Antibodies. Am. Clin. Lab. 2002, 21, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, G.C.; Scheinberg, M.A.; Aparecida da Silva, M.; Maciel, S. Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies in Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, G.R.A.; Cooper, M.D. Immunoregulatory Roles for Fc Receptor-like Molecules. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 350, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, K. Genetic Basis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Current Review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Jiang, Y. High Frequencies of Activated B Cells and T Follicular Helper Cells Are Correlated with Disease Activity in Patients with New-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S.; Ise, T.; Pastan, I. Fc Receptor-like 3 Protein Expressed on IL-2 Non-Responsive Subset of Human Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 7518–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro-Iglesias, A.; Montes, A.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Cañete, J.D.; Raya, E.; Magro-Checa, C.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Caliz, R.; Ferrer, M.A.; Joven, B.; et al. Evaluation of 12 GWAS-Drawn SNPs as Biomarkers of Rheumatoid Arthritis Response to TNF Inhibitors. A Potential SNP Association with Response to Etanercept. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkó, J.; Besenyei, T.; Laki, J.; Glant, T.T.; Mikecz, K.; Szekanecz, Z. Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis—A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Matsubara, T. A Genome-wide Association Study Identifying the SNPs Predictive of Rapid Joint Destruction in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issilbayeva, A.; Ainabekova, B.; Zhetkenev, S.; Meiramova, A.; Akhmetova, Z.; Karina, K.; Kozhakhmetov, S.; Nurgaziyev, M.; Chulenbayeva, L.; Poddighe, D.; et al. Association Study of Anticitrullinated Peptide Antibody Status with Clinical Manifestations and SNPs in Patients Affected with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study. Dis. Markers 2024, 2022, 2744762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, V.F.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; van der Woude, D. The Role of Autoantibodies in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, D.A.; Avdeeva, A.S.; Rybakova, V.V.; Demidova, N.V.; Nasonov, E.L. Clinical Features of ACPA-Negative and ACPA-Positive Variants of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 517, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, Y.; Yamada, R.; Suzuki, A.; Harley, J.B.; Shirasawa, S.; Sawada, T.; Bae, S.-C.; Tokuhiro, S.; Chang, X.; Sekine, A.; et al. A Functional Variant in FCRL3, Encoding Fc Receptor-like 3, Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Several Autoimmunities. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamada, R.; Kochi, Y.; Sawada, T.; Okada, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Kamatani, Y.; Mori, M.; Shimane, K.; Hirabayashi, Y.; et al. Functional SNPs in CD244 Increase the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Japanese Population. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, M.M.; Wesoly, J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. FCRL3 Promoter 169 CC Homozygosity Is Associated with Susceptibility to Rheumatoid Arthritis in Dutch Caucasians. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eike, M.C.; Nordang, G.B.N.; Karlsen, T.H.; Boberg, K.M.; Vatn, M.H.; IBSEN study group; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Rønningen, K.S.; Joner, G.; Flatø, B.; et al. The FCRL3 −169T>C Polymorphism Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Shows Suggestive Evidence of Involvement with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in a Scandinavian Panel of Autoimmune Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Associations between eNOS Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Yang, Z. FCRL3 Polymorphisms and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Maehlen, M.T.; Olsen, I.C.; Andreassen, B.K.; Viken, M.K.; Jiang, X.; Alfredsson, L.; Källberg, H.; Brynedal, B.; Kurreeman, F.; Daha, N.; et al. Genetic Risk Scores and Number of Autoantibodies in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, S.; Bowes, J.; Potter, C.; Worthington, J.; Barton, A. Association of the FCRL3 Gene with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Further Example of Population Specificity? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.C. Association between Functional Fc Receptor-like 3 (FCRL3) −169 C/T Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 35, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.; Eyre, S. Investigation of Polymorphisms in the FCRL3 Gene in UK Caucasians with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 336–338. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; He, C.; Peng, L.; Xing, S.; Bai, M.; Rong, H.; Yuan, D.; He, Y.; He, X.; et al. Fc Receptor-like 1, 3, and 6 Variants Are Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk in the Chinese Han Population. Genes Environ. 2021, 43, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinewietfeld, M.; Hafler, D.A. The Plasticity of Human Treg and Th17 Cells and Its Role in Autoimmunity. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.J.; Fuchs, A.; Colonna, M. Cutting Edge: Human FcRL4 and FcRL5 Are Receptors for IgA and IgG. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4741–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.M.; Shevach, E.M. CD4+CD25+ Immunoregulatory T Cells Suppress Polyclonal T Cell Activation In Vitro by Inhibiting Interleukin 2 Production. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Kuniyasu, Y.; Toda, M.; Sakaguchi, N.; Itoh, M.; Iwata, M.; Shimizu, J.; Sakaguchi, S. Immunologic Self-Tolerance Maintained by CD25+CD4+ Naturally Anergic and Suppressive T Cells: Induction of Autoimmune Disease by Breaking Their Anergic/Suppressive State. Int. Immunol. 1998, 10, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoguchi, R.; Hori, S.; Takahashi, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Homeostatic Maintenance of Natural Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ Regulatory T Cells by Interleukin (IL)-2 and Induction of Autoimmune Disease by IL-2 Neutralization. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-B.; Zhou, R.-H.; Liu, C.-M. TLR9/FCRL3 Regulates B Cell Viability, Apoptosis, and Antibody and IL-10 Production through ERK1/2, P38, and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2022, 58, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farh, K.K.-H.; Marson, A.; Zhu, J.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Housley, W.J.; Beik, S.; Shoresh, N.; Whitton, H.; Ryan, R.J.H.; Shishkin, A.A.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Fine Mapping of Causal Autoimmune Disease Variants. Nature 2015, 518, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, A.; Housley, W.J.; Hafler, D.A. Genetic Basis of Autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Feldman, M. Heterogeneity of Autoimmune Diseases: Pathophysiologic Insights from Genetics and Implications for New Therapies. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, E.B.; Vongpatanasin, W.; Skaug, B.; Karp, D.R.; Ayers, C.; de Lemos, J.A. Antinuclear Antibodies Are Associated with All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the General Population. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2669–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaarala, O.; Mänttäri, M.; Manninen, V.; Tenkanen, L.; Puurunen, M.; Aho, K.; Palosuo, T. Anti-Cardiolipin Antibodies and Risk of Myocardial Infarction in a Prospective Cohort of Middle-Aged Men. Circulation 1995, 91, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajeganova, S.; Humphreys, J.H.; Verheul, M.K.; van Steenbergen, H.W.; van Nies, J.A.B.; Hafström, I.; Svensson, B.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Trouw, L.A.; Verstappen, S.M.M.; et al. Anticitrullinated Protein Antibodies and Rheumatoid Factor Are Associated with Increased Mortality but with Different Causes of Death in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Study in Three European Cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.L.; Zidovetzki, R.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Tsao, B.P.; Criswell, L.A.; Kimberly, R.P.; Harley, J.B.; Sivils, K.L.; Vyse, T.J.; Gaffney, P.M.; et al. GWAS Identifies Novel SLE Susceptibility Genes and Explains the Association of the HLA Region. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, E.A.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Remmers, E.F.; Xie, G.; Eyre, S.; Thomson, B.P.; Li, Y.; Kurreeman, F.A.S.; Zhernakova, A.; Hinks, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Meta-Analysis Identifies Seven New Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plagnol, V.; Howson, J.M.M.; Smyth, D.J.; Walker, N.; Hafler, J.P.; Wallace, C.; Stevens, H.; Jackson, L.; Simmonds, M.J.; Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Autoantibody Positivity in Type 1 Diabetes Cases. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.A.; Taylor, K.E.; Graham, R.R.; Nititham, J.; Lee, A.T.; Ortmann, W.A.; Jacob, C.O.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Tsao, B.P.; Harley, J.B.; et al. Differential Genetic Associations for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Anti–dsDNA Autoantibody Production. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium (TASC); Burton, P.R.; Clayton, D.G.; Cardon, L.R.; Craddock, N.; Deloukas, P.; Duncanson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; McCarthy, M.I.; et al. Association Scan of 14,500 Nonsynonymous SNPs in Four Diseases Identifies Autoimmunity Variants. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.S.; Shedlock, A.M.; Langefeld, C.D. Genetics of Autoimmune Diseases: Insights from Population Genetics. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochos, P.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Virzi, J.; Pagano, S.; Satta, N.; Hartley, O.; Montecucco, F.; Mach, F.; Kutalik, Z.; Waeber, G.; et al. Anti-Apolipoprotein A-1 IgG Predict All-Cause Mortality and Are Associated with Fc Receptor-Like 3 Polymorphisms. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotsapas, C.; Hafler, D.A. Immune-Mediated Disease Genetics: The Shared Basis of Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, T.; Asgarian-Omran, H.; Memarian, A.; Shabani, M.; Sharifian, R.A.; Vossough, P.; Ansaripour, B.; Rabbani, H.; Shokri, F. Low Representation of Fc Receptor-like 1-5 Molecules in Leukemic Cells from Iranian Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Mei, Y.; Gao, J.; Ge, R.; Ye, D.; Zou, Y.; et al. Association of FCRL4 Polymorphisms on Disease Susceptibility and Severity of Ankylosing Spondylitis in Chinese Han Population. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dec, P.; Plewa, P.; Kubisa, A.; Pawlik, A. The Role of Fc-like Receptor 3 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genes 2025, 16, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111318
Dec P, Plewa P, Kubisa A, Pawlik A. The Role of Fc-like Receptor 3 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111318
Chicago/Turabian StyleDec, Paweł, Paulina Plewa, Adam Kubisa, and Andrzej Pawlik. 2025. "The Role of Fc-like Receptor 3 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis" Genes 16, no. 11: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111318
APA StyleDec, P., Plewa, P., Kubisa, A., & Pawlik, A. (2025). The Role of Fc-like Receptor 3 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genes, 16(11), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111318





