A Case Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Microdeletion at Chromosome 21q21.3q22.13 Using Whole-Exome Sequencing and CNV Analysis in a Moroccan Child with Global Developmental Delay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
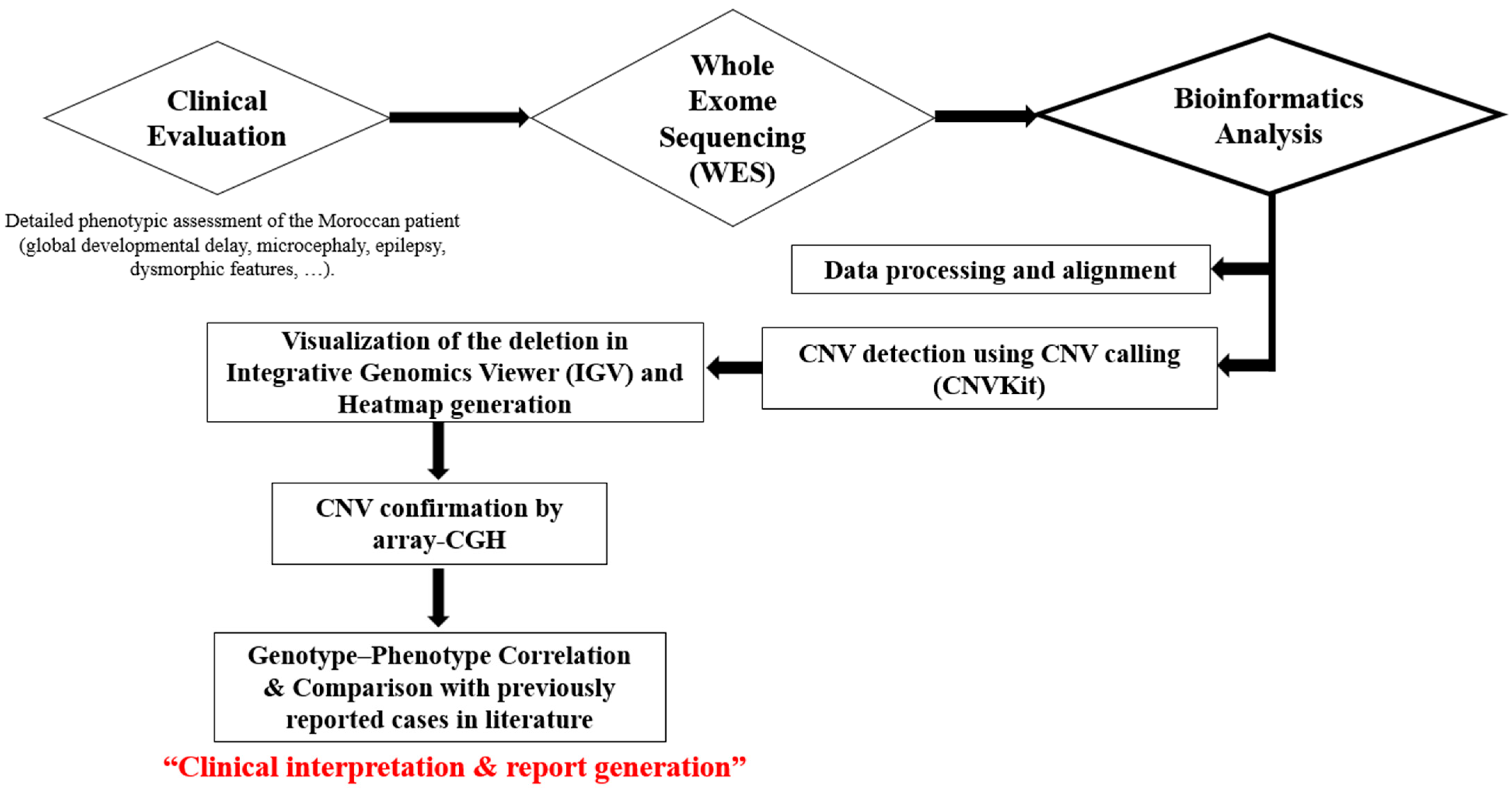
2.1. Clinical Features of the Patient
2.2. Genomic Analysis
2.2.1. DNA Extraction
2.2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2.3. CNV Detection and Visualization
2.2.4. SNP-CGH Array
2.2.5. Gene–Phenotype Prioritization and Heatmap Generation
2.3. Workflow Overview
3. Results
Phenotype–Genotype Correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNV | Copy Number Variant |
| WES | Whole Exome Sequencing |
| GDD | Global Developmental Delay |
| SNP-CGH | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism—Comparative Genomic Hybridization |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| IGV | Integrative Genomics Viewer |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| ORF | Open Reading Frame |
| LOC | Locus |
| ZTTK | Zhu–Tokita–Takenouchi–Kim |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| SNV | Single-Nucleotide Variant |
References
- Carvill, G.L.; Mefford, H.C. Microdeletion Syndromes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013, 23, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modha, B. Global Developmental Delay and Its Considerations in Paediatric Dental Care—A Case Report. Oral 2021, 1, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M.J.; Braxton, A.A.; Shao, Y.; Lewis, A.M.; Vincent, M.; Küry, S.; Besnard, T.; Isidor, B.; Latypova, X.; Bézieau, S.; et al. De Novo Truncating Variants in SON Cause Intellectual Disability, Congenital Malformations, and Failure to Thrive. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemans, A.J.M.; Truijen, K.M.G.; Kim, J.-H.; Alaçam, Z.; Faivre, L.; Collins, K.M.; Gerkes, E.H.; van Haelst, M.; van de Laar, I.M.B.H.; Lindstrom, K.; et al. Establishing the Phenotypic Spectrum of ZTTK Syndrome by Analysis of 52 Individuals with Variants in SON. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Shinde, D.N.; Reijnders, M.R.F.; Hauser, N.S.; Belmonte, R.L.; Wilson, G.R.; Bosch, D.G.M.; Bubulya, P.A.; Shashi, V.; Petrovski, S.; et al. De Novo Mutations in SON Disrupt RNA Splicing of Genes Essential for Brain Development and Metabolism, Causing an Intellectual-Disability Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slezak, R.; Smigiel, R.; Rydzanicz, M.; Pollak, A.; Kosinska, J.; Stawinski, P.; Malgorzata Sasiadek, M.; Ploski, R. Phenotypic Expansion in Zhu-Tokita-Takenouchi-Kim Syndrome Caused by de Novo Variants in the SON Gene. Mol. Genet. Genomic. Med. 2020, 8, e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilik, İ.A.; Malszycki, M.; Lübke, A.K.; Schade, C.; Meierhofer, D.; Aktaş, T. SON and SRRM2 Are Essential for Nuclear Speckle Formation. eLife 2020, 9, e60579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lai, S.-K.; Sim, D.Y.; Ang, W.S.L.; Li, H.Y.; Roca, X. SRRM2 Organizes Splicing Condensates to Regulate Alternative Splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 8599–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Matsuki, T.; Fukada, M.; Eda, S.; Toya, A.; Iio, A.; Tabata, H.; Nakayama, A. Knockdown of Son, a Mouse Homologue of the ZTTK Syndrome Gene, Causes Neuronal Migration Defects and Dendritic Spine Abnormalities. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.-Y.; DeKelver, R.C.; Lo, M.-C.; Nguyen, T.A.; Matsuura, S.; Boyapati, A.; Pandit, S.; Fu, X.-D.; Zhang, D.-E. SON Controls Cell Cycle Progression by Coordinated Regulation of RNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushary, S.T.; Revah-Politi, A.; Barua, S.; Ganapathi, M.; Accogli, A.; Aggarwal, V.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Cappuccio, G.; Capra, V.; Fagerberg, C.R.; et al. ZTTK Syndrome: Clinical and Molecular Findings of 15 Cases and a Review of the Literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2021, 185, 3740–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, F. A de Novo Heterozygous Variant in the SON Gene Is Associated with Zhu-Tokita-Takenouchi-Kim Syndrome. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Petrovski, S.; Xie, P.; Ruzzo, E.K.; Lu, Y.-F.; McSweeney, K.M.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Nissenkorn, A.; Anikster, Y.; Oz-Levi, D.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing in Undiagnosed Genetic Diseases: Interpreting 119 Trios. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Huang, H.; Yang, L. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of ZTTK Syndrome Caused by SON Heterozygous Mutation c.394C>T. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, K.; Miyake, N.; Mizuguchi, T.; Miyatake, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Tsuchida, N.; Sekiguchi, F.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Nakashima, M.; et al. Large-Scale Discovery of Novel Neurodevelopmental Disorder-Related Genes through a Unified Analysis of Single-Nucleotide and Copy Number Variants. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilemis, F.-N.; Marinakis, N.M.; Veltra, D.; Svingou, M.; Kekou, K.; Mitrakos, A.; Tzetis, M.; Kosma, K.; Makrythanasis, P.; Traeger-Synodinos, J.; et al. Germline CNV Detection through Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES) Data Analysis Enhances Resolution of Rare Genetic Diseases. Genes 2023, 14, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braddock, S.R.; South, S.T.; Schiffman, J.D.; Longhurst, M.; Rowe, L.R.; Carey, J.C. Braddock-Carey Syndrome: A 21q22 Contiguous Gene Syndrome Encompassing RUNX1. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170, 2580–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinawi, M.; Erez, A.; Shardy, D.L.; Lee, B.; Naeem, R.; Weissenberger, G.; Chinault, A.C.; Cheung, S.W.; Plon, S.E. Syndromic Thrombocytopenia and Predisposition to Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Caused by Constitutional Microdeletions on Chromosome 21q. Blood 2008, 112, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Investigation of Copy Number Variations on Chromosome 21 Detected by Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) Microarray in Patients with Congenital Anomalies. Mol. Cytogenet. 2018, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; You, J.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, N.; Duan, J.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, M.; et al. Expanding the Mutational Spectrum of ZTTK Syndrome: A de Novo Variant with Global Developmental Delay and Malnutrition in a Chinese Patient. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2023, 11, e2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Expanding Phenotype of ZTTK Syndrome Due to the Heterozygous Variant of SON Gene Focusing on Liver Involvement: Patient Report and Literature Review. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/14/3/739 (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- de Smith, A.J.; Trewick, A.L.; Blakemore, A.I.F. Implications of Copy Number Variation in People with Chromosomal Abnormalities: Potential for Greater Variation in Copy Number State May Contribute to Variability of Phenotype. HUGO J. 2010, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranger, B.E.; Forrest, M.S.; Dunning, M.; Ingle, C.E.; Beazley, C.; Thorne, N.; Redon, R.; Bird, C.P.; de Grassi, A.; Lee, C.; et al. Relative Impact of Nucleotide and Copy Number Variation on Gene Expression Phenotypes. Science 2007, 315, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briegel, W.; Hoyer, J. Psychiatric Disorders and Distal 21q Deletion—A Case Report. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errichiello, E.; Novara, F.; Cremante, A.; Verri, A.; Galli, J.; Fazzi, E.; Bellotti, D.; Losa, L.; Cisternino, M.; Zuffardi, O. Dissection of Partial 21q Monosomy in Different Phenotypes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Five Cases and Review of the Literature. Mol. Cytogenet. 2016, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzaki, E.; Morin, G.; Pollazzon, M.; Papa, F.T.; Buoni, S.; Hayek, J.; Andrieux, J.; Lecerf, L.; Popovici, C.; Receveur, A.; et al. Syndromic Mental Retardation with Thrombocytopenia Due to 21q22.11q22.12 Deletion: Report of Three Patients. Am. J. Med. Genet A 2010, 152A, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Crabben, S.; van Binsbergen, E.; Ausems, M.; Poot, M.; Bierings, M.; Buijs, A. Constitutional RUNX1 Deletion Presenting as Non-Syndromic Thrombocytopenia with Myelodysplasia: 21q22 ITSN1 as a Candidate Gene in Mental Retardation. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, e8–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.D.; Wiedmeier, S.E.; Yaish, H.M. A Neonate with Congenital Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Chromosomal Microdeletion at 21q22.11 Including the Gene RUNX1. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béri-Dexheimer, M.; Latger-Cannard, V.; Philippe, C.; Bonnet, C.; Chambon, P.; Roth, V.; Grégoire, M.-J.; Bordigoni, P.; Lecompte, T.; Leheup, B.; et al. Clinical Phenotype of Germline RUNX1 Haploinsufficiency: From Point Mutations to Large Genomic Deletions. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukadin, L.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, E.Y.; Stone, J.K.; Ungerleider, N.; Baddoo, M.C.; Kong, H.K.; Richard, A.; Tran, J.; Giannini, H.; et al. SON Inhibits Megakaryocytic Differentiation via Repressing RUNX1 and the Megakaryocytic Gene Expression Program in Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukadin, L.; Park, E.y.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, E.E.Y. Abstract 1482: SON Represses RUNX1 Expression and Impairs Megakaryocytic Differentiation in Down Syndrome Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (DS-AMKL). Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, T.E.; de Bruijn, M.F.T.R.; Stacy, T.; Talebian, L.; Lind, E.; Robin, C.; Binder, M.; Dzierzak, E.; Speck, N.A. Runx1 Expression Marks Long-Term Repopulating Hematopoietic Stem Cells in the Midgestation Mouse Embryo. Immunity 2002, 16, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genomic Coordinates | CNV Size (kb) | Number of Genes | Classification | Disorder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| arr[GRCh37] 21q21.3q22.13 (30093156_38340656)x1 | 8248 | 124 | Pathogenic | 21q22.11q22.12 Microdeletion syndrome |
| List of Genes Spanning the 21q21.3–q22.13 Deleted Region |
|---|
| N6AMT1, LTN1, RWDD2B, USP16, CCT8, MAP3K7CL, LINC00189, BACH1, BACH1-IT2, BACH1- IT3, GRIK1-AS2, GRIK1, GRIK1-AS1, CLDN17, LINC00307, CLDN8, KRTAP24-1, KRTAP25-1, KRTAP26-1, KRTAP27-1, KRTAP23-1, KRTAP13-2, MIR4327, KRTAP13-1, KRTAP13-3, KRTAP13-4, KRTAP15-1, KRTAP19-1, KRTAP19-2, KRTAP19-3, KRTAP19-4, KRTAP19-5, KRTAP19-6, KRTAP19- 7, KRTAP22-2, KRTAP6-3, KRTAP6-2, KRTAP22-1, KRTAP6-1, KRTAP20-1, KRTAP20-4, KRTAP20-2, KRTAP20-3, KRTAP21-3, KRTAP21-2, KRTAP21-1, KRTAP8-1, KRTAP7-1, KRTAP11-1, KRTAP19-8, TIAM1, LOC150051, SOD1, SCAF4, HUNK, LINC00159, MIS18A, MIS18A-AS1, MRAP, URB1, SNORA80A, URB1-AS1, EVA1C, TCP10L, CFAP298-TCP10L, CFAP298, SYNJ1, PAXBP1-AS1, PAXBP1, C21orf62-AS1, C21orf62, LINC01690, OLIG2, LINC00945, OLIG1,LOC101928107, LINC01548, IFNAR2, IL10RB-DT, IL10RB, IFNAR1,IFNGR2, TMEM50B, DNAJC28, GART, MIR6501, SON, DONSON, CRYZL1, ITSN1, ATP5PO, LINC00649, LOC101928126, SLC5A3, MRPS6, LINC00310, KCNE2, SMIM11A, FAM243A, SMIM34A, KCNE1, RCAN1, CLIC6, LINC00160, LINC01426, RUNX1, RUNX1-IT1, LOC100506403, MIR802, PPP1R2P2, LOC101928269, LINC01436, SETD4, CBR1, LOC100133286, LOC105369306, CBR3, CBR3-AS1, DOP1B, MORC3, CHAF1B, CLDN14, SIM2, HLCS. |
| Study (Year)— Reference | Genomic Coordinates/CNV Size (hg19) | Key Genes Included (RUNX1/SON) | Main Clinical Features Reported | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our study (2025) | arr[GRCh37] 21q21.3–q22.13 (30093156–38340656)—~8.2 Mb | 124 genes; includes SON and RUNX1 | Global developmental delay, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, epilepsy, cortical atrophy, growth delay | WES with CNV calling: confirmed by SNP-CGH array |
| Braddock–Carey et al., 2016 (AJMG A) [17] | chr21:31391467–39118687 (hg19)—~7.7 Mb | Includes RUNX1 and multiple neighboring genes | Severe developmental delay, dysmorphism, thrombocytopenia, behavioral problems | aCGH/microarray |
| Shinawi et al., 2008 (Blood) [18] | reported constitutional deletions involving 21q22 (various sizes) | RUNX1 included in several patients | Hereditary thrombocytopenia, predisposition to myeloid malignancies; some neuro features | aCGH/cytogenetics |
| Li et al., 2018 (BMC Gnomiques) [19] | various microdeletions on chr21 (reviewed cases) | variable (some include the SON region) | Developmental delay, microcephaly, seizures, congenital anomalies | aCGH/CNV studies |
| Tang et al., 2023 (Molecular Genetics and Genomic Medicine) [20] | Single-gene SON loss-of-function (frameshift/nonsense), not large deletion | SON (variants e.g., c.1845_1870del26) | Developmental delay, seizures, brain anomalies | Exome/targeted sequencing |
| Pietrobattista et al., 2023 (Genes) [21] | (review) | SON (discussed) | Broad ZTTK phenotype spectrum, hypotonia, seizures, multisystemic features | Review/database analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jouali, F.; El Haddoumi, G.; Antra, I.; Benhida, R.; Ben Itto, A.; Fekkak, J. A Case Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Microdeletion at Chromosome 21q21.3q22.13 Using Whole-Exome Sequencing and CNV Analysis in a Moroccan Child with Global Developmental Delay. Genes 2025, 16, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111280
Jouali F, El Haddoumi G, Antra I, Benhida R, Ben Itto A, Fekkak J. A Case Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Microdeletion at Chromosome 21q21.3q22.13 Using Whole-Exome Sequencing and CNV Analysis in a Moroccan Child with Global Developmental Delay. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111280
Chicago/Turabian StyleJouali, Farah, Ghyzlane El Haddoumi, Imane Antra, Rachid Benhida, Afaf Ben Itto, and Jamal Fekkak. 2025. "A Case Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Microdeletion at Chromosome 21q21.3q22.13 Using Whole-Exome Sequencing and CNV Analysis in a Moroccan Child with Global Developmental Delay" Genes 16, no. 11: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111280
APA StyleJouali, F., El Haddoumi, G., Antra, I., Benhida, R., Ben Itto, A., & Fekkak, J. (2025). A Case Report: Identification of a Pathogenic Microdeletion at Chromosome 21q21.3q22.13 Using Whole-Exome Sequencing and CNV Analysis in a Moroccan Child with Global Developmental Delay. Genes, 16(11), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111280






