The Genome Survey Analysis of Female and Male Sepiella japonica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection and Genome Sequencing
2.3. K-mer Analysis and Genome Assembly
2.4. Microsatellite Identification
2.5. Mitochondrial Genome Assembly and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Effective Population Size Inferrence
3. Results
3.1. Size, Heterozygosity Ratio, and Repeat Sequence Ratio
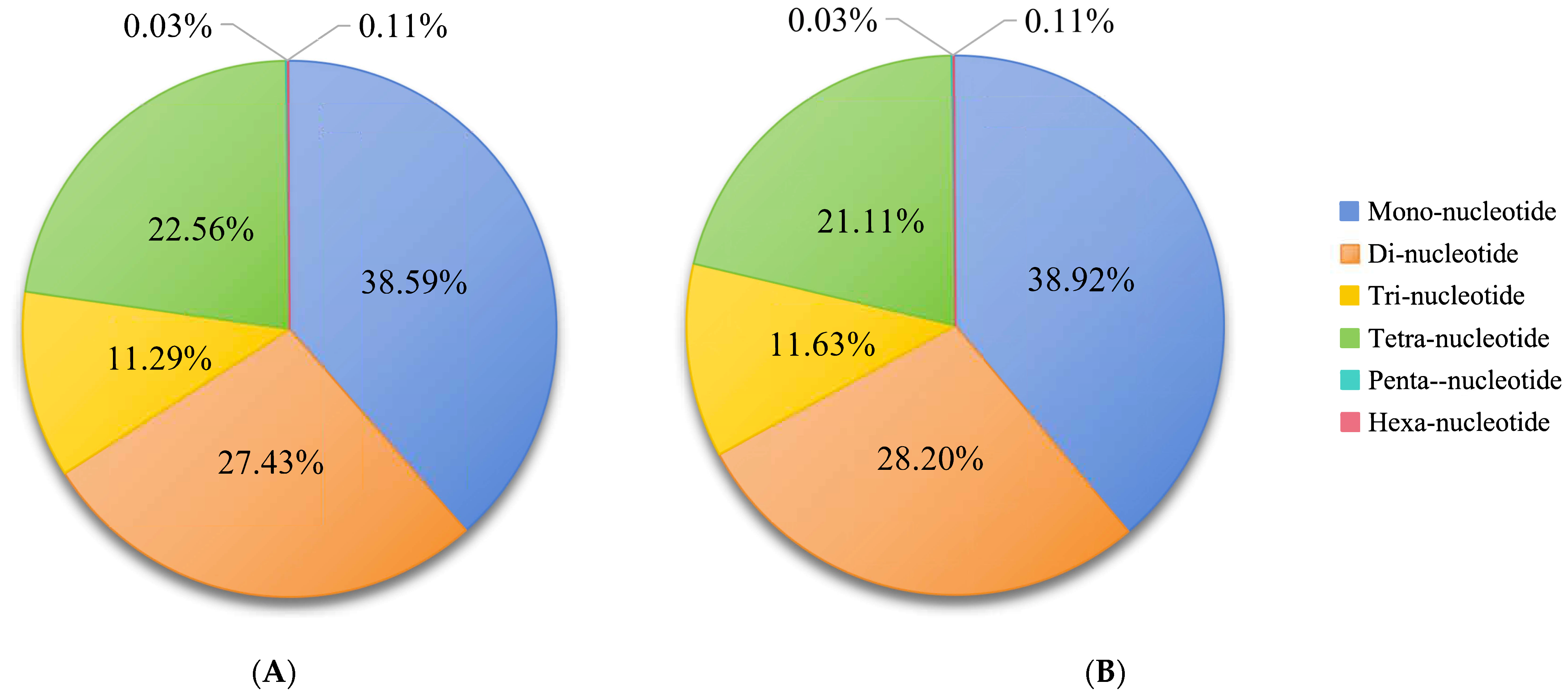
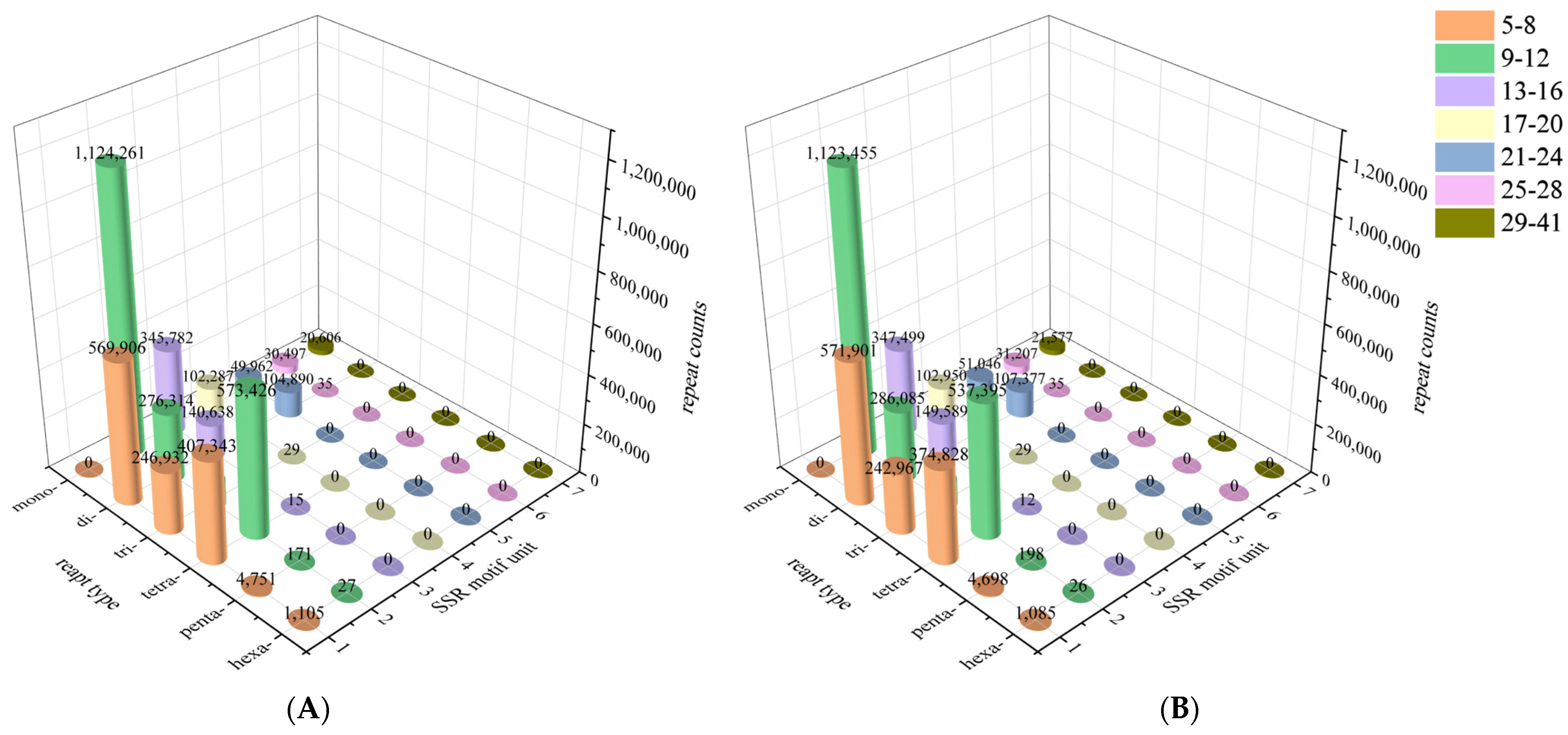
3.2. Identification of Microsatellite Motifs
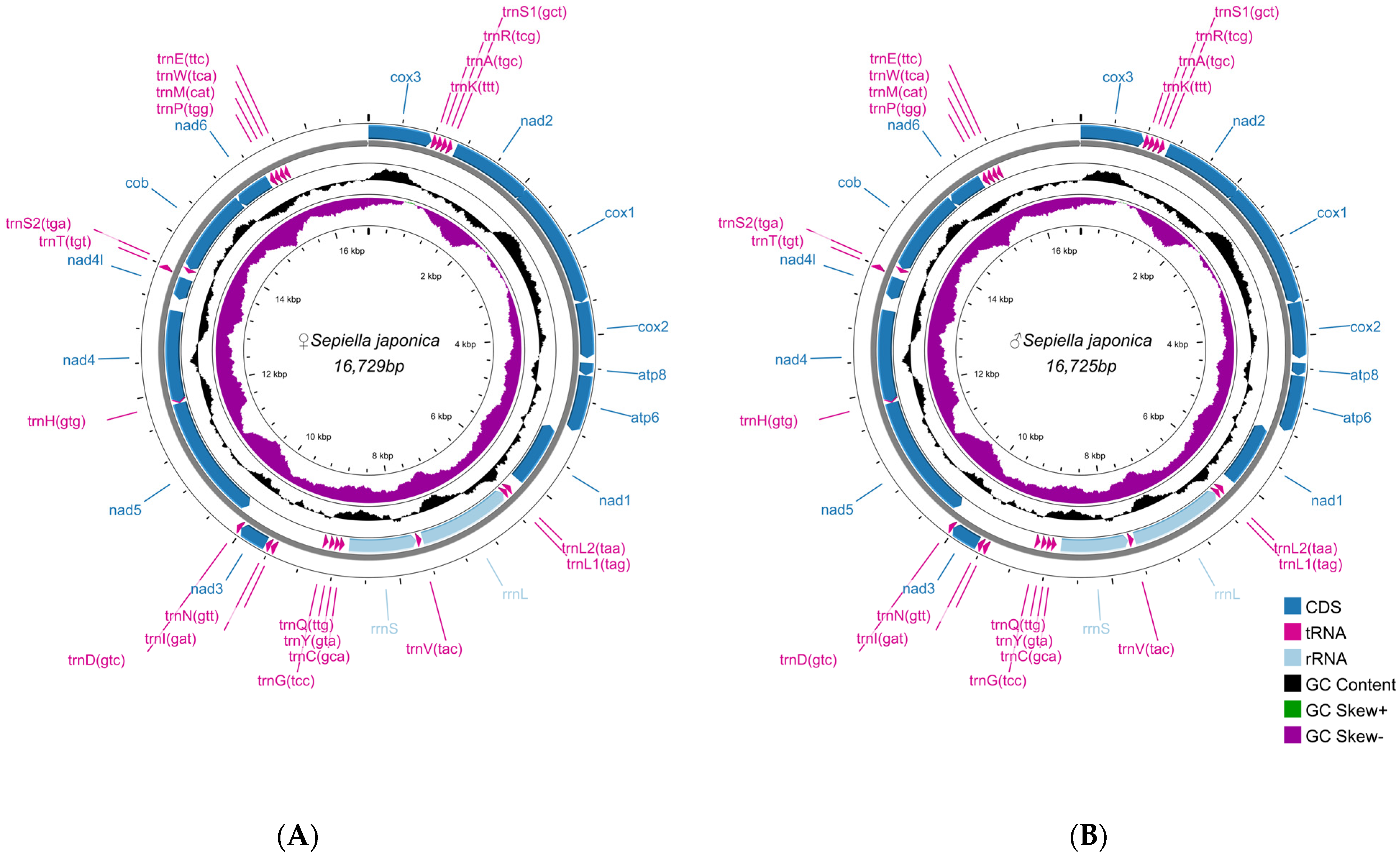
3.3. Characterization of S. japonica Mitochondrial Genome
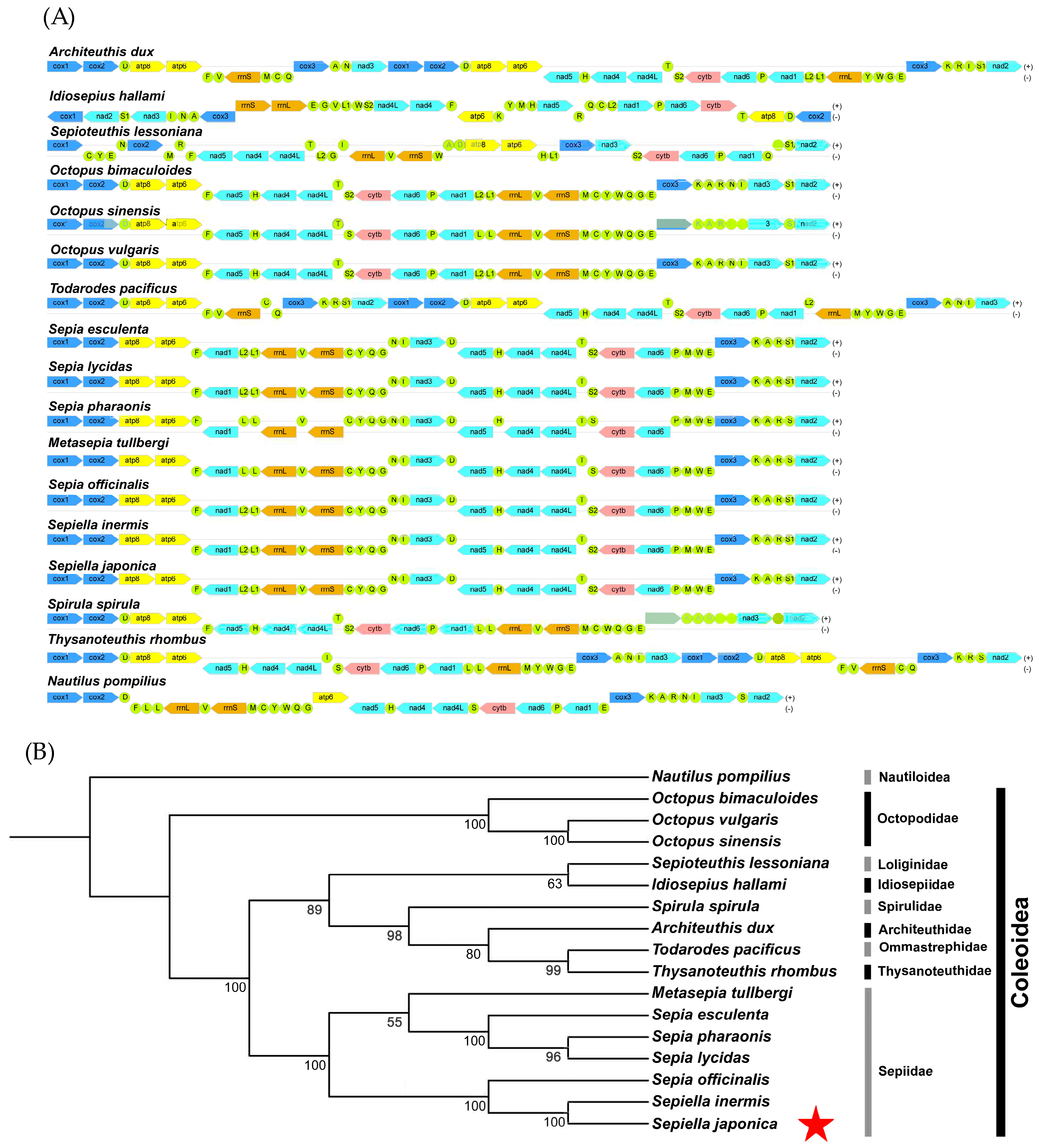
3.4. Phylogenetic Relationships of S. japonica Based on Mitochondrial Genome
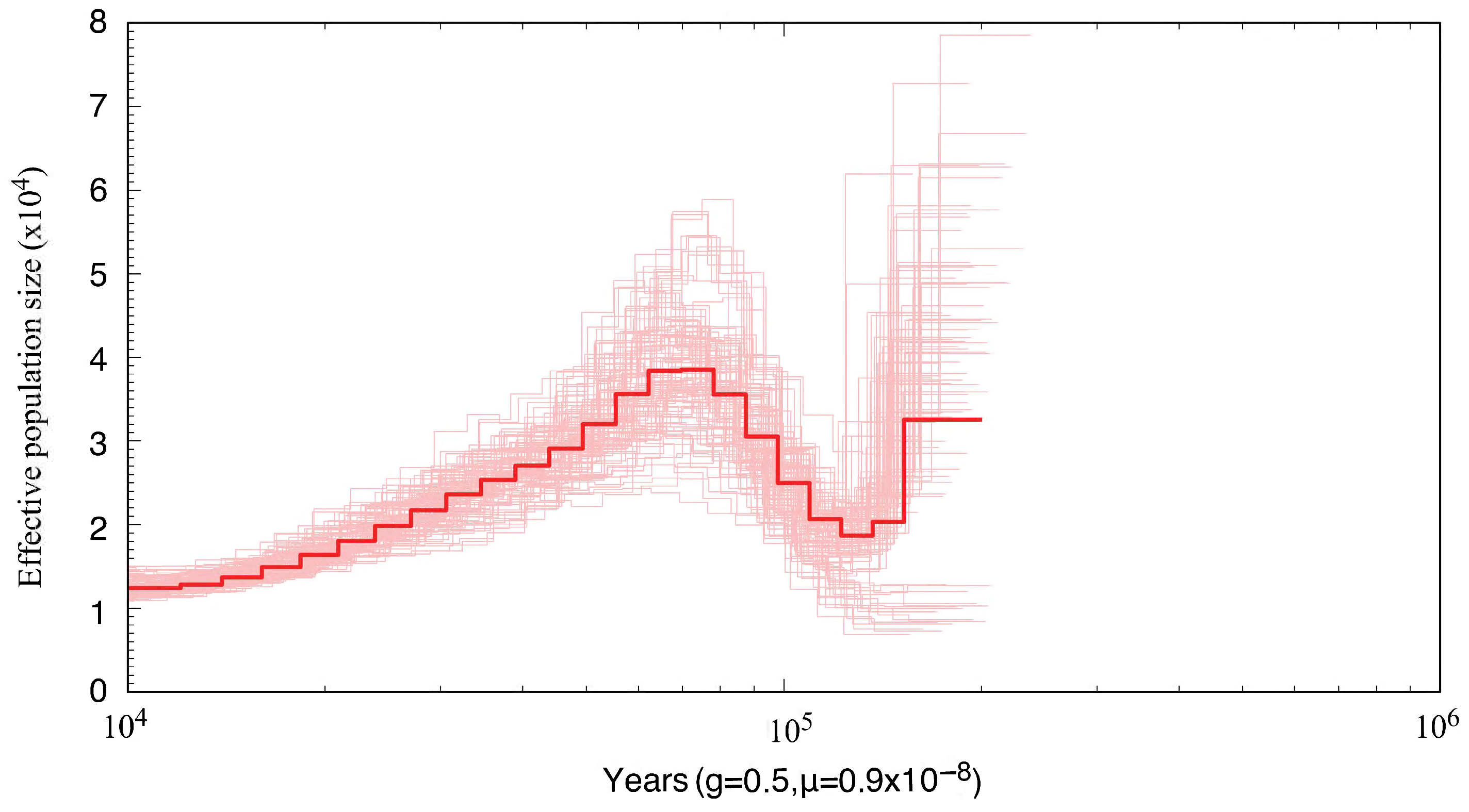
3.5. Population Size Dynamics of S. japonica
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsueh, M.M. Morphology and Possible Function of Sepiella japonica Sasaki, 1929 (Sepiidae: Cephalopoda: Mollusca); AGRIS; NSYSU: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2002; Available online: https://agris.fao.org (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Wu, T.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Y.D.; Xuan, W.D.; Fang, G.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, F. The factors driving the spatial variation in the selection of spawning grounds for Sepiella japonica in offshore Zhejiang Province, China. Fishes 2023, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rencken, S.; Tushev, G.; Hain, D.; Ciirdaeva, E.; Simakov, O.; Laurent, G. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the European common cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destanović, D.; Schultz, D.T.; Styfhals, R.; Cruz, F.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Gut, M.; Gut, I.; Fiorito, G.; Simakov, O.; Alioto, T.S.; et al. A chromosome-level reference genome for the common octopus, Octopus vulgaris (Cuvier, 1797). G3 Genes Genomes Genet 2023, 13, jkad220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Migaud, H.; Wang, C.; Bekaert, M. Pharaoh cuttlefish, Sepia pharaonis, genome reveals unique reflectin camouflage gene set. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 639670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcaid, M.; Casaburi, G.; McAnulty, S.J.; Schmidbaur, H.; Suria, A.M.; Moriano-Gutierrez, S.; Pankey, M.S.; Oakley, T.H.; Kremer, N.; Koch, E.J.; et al. Symbiotic organs shaped by distinct modes of genome evolution in cephalopods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3030–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mao, F.; Mu, H.W.; Huang, M.W.; Bao, Y.B.; Wang, L.L.; Wong, N.K.; Xiao, S.; Dai, H.; Xiang, Z.M.; et al. The genome of Nautilus pompilius illuminates eye evolution and biomineralization. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritschard, E.A.; Whitelaw, B.; Albertin, C.B.; Cooke, I.R.; Strugnell, J.M.; Simakov, O. Coupled genomic evolutionary histories as signatures of organismal innovations in cephalopods: Co-evolutionary signatures across levels of genome organization may shed light on functional linkage and origin of cephalopod novelties. BioEssays 2019, 41, 1900073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, C.B.; Simakov, O.; Mitros, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Pungor, J.R.; Edsinger-Gonzales, E.; Brenner, S.; Ragsdale, C.W.; Rokhsar, D.S. The octopus genome and the evolution of cephalopod neural and morphological novelties. Nature 2015, 524, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidbaur, H.; Kawaguchi, A.; Clarence, T.; Fu, X.; Hoang, O.P.; Zimmermann, B.; Ritschard, E.A.; Weissenbacher, A.; Foster, J.S.; Nyholm, S.V.; et al. Emergence of novel cephalopod gene regulation and expression through large-scale genome reorganization. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.X.; Shan, X.X.; Shi, Q. Research advances in the genomics and applications for molecular breeding of aquaculture animals. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedringhaus, T.P.; Milanova, D.; Kerby, M.B.; Snyder, M.P.; Barron, A.E. Landscape of next-generation sequencing technologies. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4327–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Q.X.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Y.F.; Wang, L.B. B. Genome survey sequencing and genetic background characterization of yellow horn based on next-generation sequencing. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4303–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.P.; Zhuang, H.B.; Yu, J.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, H.H.; Zhu, M.Y.; Tong, Z.K. Genome survey of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata): Identification of genomic SSRs and demonstration of their utility in genetic diversity analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.L.; Yi, S.K.; Li, Y.H. Genome survey sequencing of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yang, C.P.; Qu, G.Z. Genome survey sequencing of Betula platyphylla. Forests 2019, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M. A first insight into the genomic background of Ilex pubescens (Aquifoliaceae) by flow cytometry and genome survey sequencing. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liu, M.X.; Lu, X.Y.; Sun, S.S.; Cheng, Y.W.; Ya, H.Y. Genome survey sequencing and identification of genomic SSR markers for Rhododendron micranthum. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmira Ziya, M.; Salih, K.; Mortaza, K.; Nergiz, Ç.; Hatice, G. Genome survey of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) by next generation sequencing: Development of novel SSR markers and genetic diversity in Pistacia species. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.J.; Sun, Z.C.; Lou, F.R.; Gao, T.X.; Song, N. Genomic characteristics and profile of microsatellite primers for Acanthogobius ommaturus by genome survey sequencing. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, E.T.; Charles, M.; Féménia, M.; Rebours, E.; Vaiman, A.; Rocha, D. Survey of mitochondrial sequences integrated into the bovine nuclear genome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.H.; Xu, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, N.; Liu, L.; Ren, B.Y.; Gao, T.X.; Liu, C. A whole-genome survey and the mitochondrial genome of Acanthocepola indica provide insights into its phylogenetic relationships in Priacanthiformes. Animals 2024, 14, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yang, M.J.; Sun, J.C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.Y. Genome survey on invasive veined rapa whelk (Rapana venosa) and development of microsatellite loci on large scale. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Lei, X.; Bai, S.Q.; Xiong, Y.L.; Liu, W.H.; Wu, W.D.; Yu, Q.Q.; Dong, Z.X.; Yang, J.; Ma, X. Genomic survey sequencing, development and characterization of single- and multi-locus genomic SSR markers of Elymus sibiricus L. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.X.; Du, X.Q.; Ma, S.Y.; Song, N.; Zhao, L.L. Whole-genome survey analyses provide a new perspective for the evolutionary biology of shimofuri goby, Tridentiger bifasciatus. Animals 2022, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.F.; Fu, Y.T.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W. Genome-wide identification and expression profiles of sex-related gene families in the Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2024, 50, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Luo, X.; You, W.W.; Shen, M.H.; Fu, J.Q.; Ke, C.H. Development of a sex-specific molecular marker reveals the ZW/ZZ sex-determination system in Babylonia areolata. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 742044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aflitos, S.A.; Severing, E.; Sanchez-Perez, G.; Peters, S.; De Jong, H.; De Ridder, D. Cnidaria: Fast, reference-free clustering of raw and assembled genome and transcriptome NGS data. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranallo-Benavidez, T.R.; Jaron, K.S.; Schatz, M.C. GenomeScope 2.0 and Smudgeplot for reference-free profiling of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Shi, Y.J.; Yuan, J.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Mu, D.S.; Fan, W. Estimation of genomic characteristics by analyzing k-mer frequency in de novo genome projects. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1308.2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikhi, R.; Rizk, G. Space-efficient and exact de Bruijn graph representation based on a Bloom filter. Algor. Mol. Biol. 2013, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Bui, Q.M. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Inference of human population history from individual whole-genome sequences. Nature 2011, 475, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooldridge, T.B.; Ford, S.M.; Conwell, H.C.; Hyde, J.; Harris, K.; Shapiro, B. Direct measurement of the mutation rate and its evolutionary consequences in a critically endangered mollusk. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2025, 42, msae266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.H.; Yang, T.Y.; Yanagimoto, T.; Gao, T.X. Comprehensive draft genome analyses of three rockfishes (Scorpaeniformes, Sebastiscus) via genome survey sequencing. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Tanizawa, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Tanifuji, G.; Kamikawa, R.; Nakamura, Y. A practical assembly guideline for genomes with various levels of heterozygosity. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupše, N.; Reid, A.; Taite, M.; Kubodera, T.; Allcock, A.L. Cuttlefishes (Cephalopoda, Sepiidae): The bare bones—An hypothesis of relationships. Mar. Biol. 2023, 170, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.L.; Strugnell, J.M. A new pygmy squid, Idiosepius hallami n. sp. (Cephalopoda: Idiosepiidae) from eastern Australia and elevation of the southern endemic ‘notoides’ clade to a new genus, Xipholeptos n. gen. Zootaxa 2018, 4369, 451–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.H.; Bian, L.; Ge, J.L.; Han, F.M.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, X.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Lin, Z.S.; Shi, H.L.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the East Asian common octopus (Octopus sinensis) using PacBio sequencing and Hi-C technology. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Kang, S.; Ahn, D.H.; Jung, S.H.; Rhee, H.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.J.; Han, Y.H.; Ryu, K.B.; et al. The genome of common long-arm octopus Octopus minor. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffing, G.C.; Tittes, S.; Small, S.T.; Songco-Casey, J.O.; Piscopo, D.M.; Pungor, J.R.; Miller, A.C.; Niell, C.M.; Kern, A.D. Cephalopod sex determination and its ancient evolutionary origin. Curr. Biol. 2025, 35, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccoy, M.J.; Fire, A.Z. Intron and gene size expansion during nervous system evolution. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, C.; Song, W.; Migaud, H.; Wang, C.; Bekaert, M. The whole-genome sequencing and hybrid assembly of Mytilus coruscus. Front. Genet 2020, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qu, Y.Q.; Shi, H.L.; Ping, H.L.; Gao, T.X. The genome survey of male and female Hapalogenys analis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1492138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Effects of different temperatures on the embryos of Sepiella japonica and analysis of its chromosomal karyotype. China Fish. 2024, 583, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, X.M.; Li, J.T.; Liu, G.M.; Kuang, Y.Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, X.H.; Ren, L.F.; Wang, G.L.; et al. Genome sequence and genetic diversity of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoulek, D.; Borůvková, V.; Ocalewicz, K.; Symonová, R. GC and repeats profiling along chromosomes-the future of fish compositional cytogenomics. Genes 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Korol, A.B.; Fahima, T.F.; Beiles, A.; Nevo, E. Microsatellites: Genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: A review. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, K.; Yamashita, M. Characterization of Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Sepiella japonica (Cephalopoda: Sepiidae). NCBI; 2011. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NC_017749.1 (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Guo, B.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Z.M.; Xu, K.D.; Ping, H.L.; Shi, H.L. Characterization of complete mitochondrial genome and phylogeny of Sepia lycidas (Sepioidea, Sepiidae). Pak. J. Zool. 2018, 50, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeck, K.; Rouby, H.; Purcell, A.; Sun, Y.; Sambridge, M. Sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15296–15303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratt, R.M.; Lisiecki, L.E. A late pleistocene sea level stack. Clim. Past 2016, 12, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yu, K.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N. Significant sea-level fluctuations in the western tropical Pacific during the mid-Holocene. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2024, 39, e2023PA004783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.N.; Jamandre, B.W.; Hsu, C.C.; Tzeng, W.N.; Durand, J.D. Plio-Pleistocene sea-level and temperature fluctuations in the northwestern Pacific promoted speciation in the globally distributed flathead mullet Mugil cephalus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Accession | Length (bp) | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nautilus pompilius | NC_035715.1 | 15,693 | Nautilidae |
| Octopus bimaculoides | NC_029723.1 | 15,733 | Octopodidae |
| Octopus vulgaris | NC_006353.1 | 15,744 | Octopodidae |
| Sepioteuthis lessoniana | NC_007894.1 | 16,631 | Loliginidae |
| Idiosepius hallami | KF647895.1 | 16,183 | Idiosepiidae |
| Spirula spirula | NC_034682.1 | 15,472 | Spirulidae |
| Architeuthis dux | NC_011581.1 | 20,331 | Architeuthidae |
| Todarodes pacificus | NC_006354.1 | 20,254 | Ommastrephidae |
| Thysanoteuthis rhombus | NC_058301.1 | 20,545 | Thysanoteuthidae |
| Metasepia tullbergi | MT974497.1 | 16,182 | Sepiidae |
| Sepia esculenta | NC_009690.1 | 16,199 | Sepiidae |
| Sepia pharaonis | NC_021146.1 | 16,208 | Sepiidae |
| Sepia lycidas | NC_022468.1 | 16,244 | Sepiidae |
| Sepia officinalis | NC_007895.1 | 16,163 | Sepiidae |
| Sepiella inermis | NC_022693.1 | 16,191 | Sepiidae |
| Octopus sinensis | NC_052881.1 | 15,737 | Octopodidae |
| Sepiella japonica | PX243620 | 16,729 | Sepiidae |
| Library Name | Type | Read Number | Base Count (Gb) | Read Length (bp) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1M-J-1 | raw | 392,466,944 | 58.87 | 150 | 99.45 | 97.99 | 35.30 |
| dedup | 386,993,714 | 57.30 | 148 | 99.45 | 97.99 | 35.12 | |
| C1M-J-2 | raw | 1,533,736,568 | 230.06 | 150 | 99.45 | 98.01 | 35.38 |
| dedup | 1,459,025,604 | 216.77 | 148 | 99.45 | 98.01 | 35.24 | |
| C1M-J-3 | raw | 1,519,472,688 | 227.92 | 150 | 99.43 | 97.92 | 35.26 |
| dedup | 1,446,429,734 | 214.51 | 148 | 99.43 | 97.92 | 35.10 | |
| Total | raw | 3,445,676,200 | 516.85 | 150 | 99.44 | 97.97 | 35.32 |
| dedup | 3,292,449,052 | 488.58 | 148 | 99.44 | 97.97 | 35.16 | |
| X1M-J-1 | raw | 351,953,724 | 52.79 | 150 | 99.50 | 98.17 | 35.57 |
| dedup | 347,458,202 | 51.34 | 147 | 99.50 | 98.17 | 35.35 | |
| X1M-J-2 | raw | 1,457,509,058 | 218.63 | 150 | 99.44 | 97.96 | 35.46 |
| dedup | 1,388,606,834 | 205.78 | 148 | 99.44 | 97.96 | 35.27 | |
| X1M-J-3 | raw | 1,648,035,630 | 247.21 | 150 | 99.40 | 97.83 | 35.45 |
| dedup | 1,562,234,556 | 231.34 | 148 | 99.40 | 97.83 | 35.26 | |
| Total | raw | 3,457,498,412 | 518.63 | 150 | 99.43 | 97.92 | 35.47 |
| dedup | 3,298,299,592 | 488.46 | 148 | 99.43 | 97.92 | 35.27 |
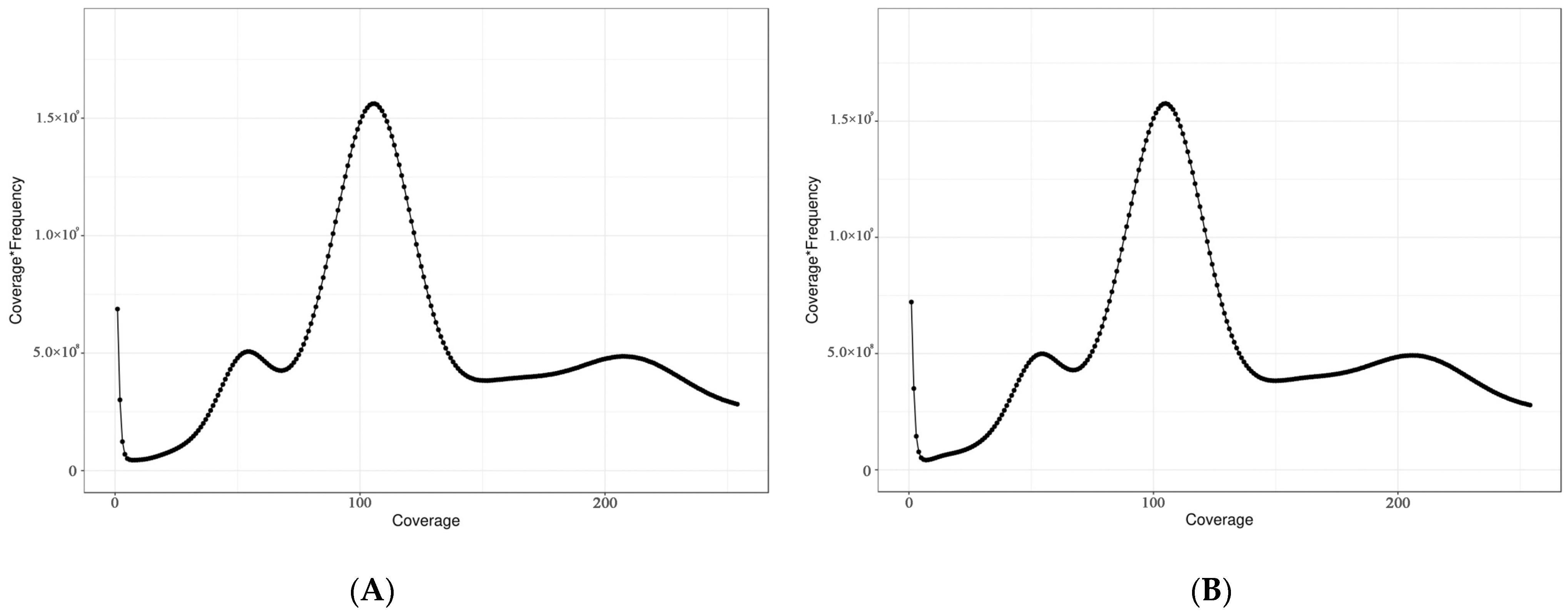
| Sample | K-mer Number | K-mer Depth | Genome Size (bp) | Revised Genome Size (bp) | Heterozygous Ratio (%) | Repeat (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 435,897,116,926 | 102 | 4,317,320,000 | 4,310,509,074 | 0.85 | 76.05 |
| Male | 435,678,168,857 | 102 | 4,222,250,000 | 4,215,254,265 | 0.77 | 75.91 |
| Total Length (bp) | Total Number | Max Length (bp) | N50 Length (bp) | N90 Length (bp) | GC Content (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | contig | 4,197,030,785 | 21,378,004 | 23,523 | 508 | 57 | 34.15 |
| Male | contig | 4,206,358,660 | 21,355,316 | 23,780 | 511 | 57 | 34.15 |
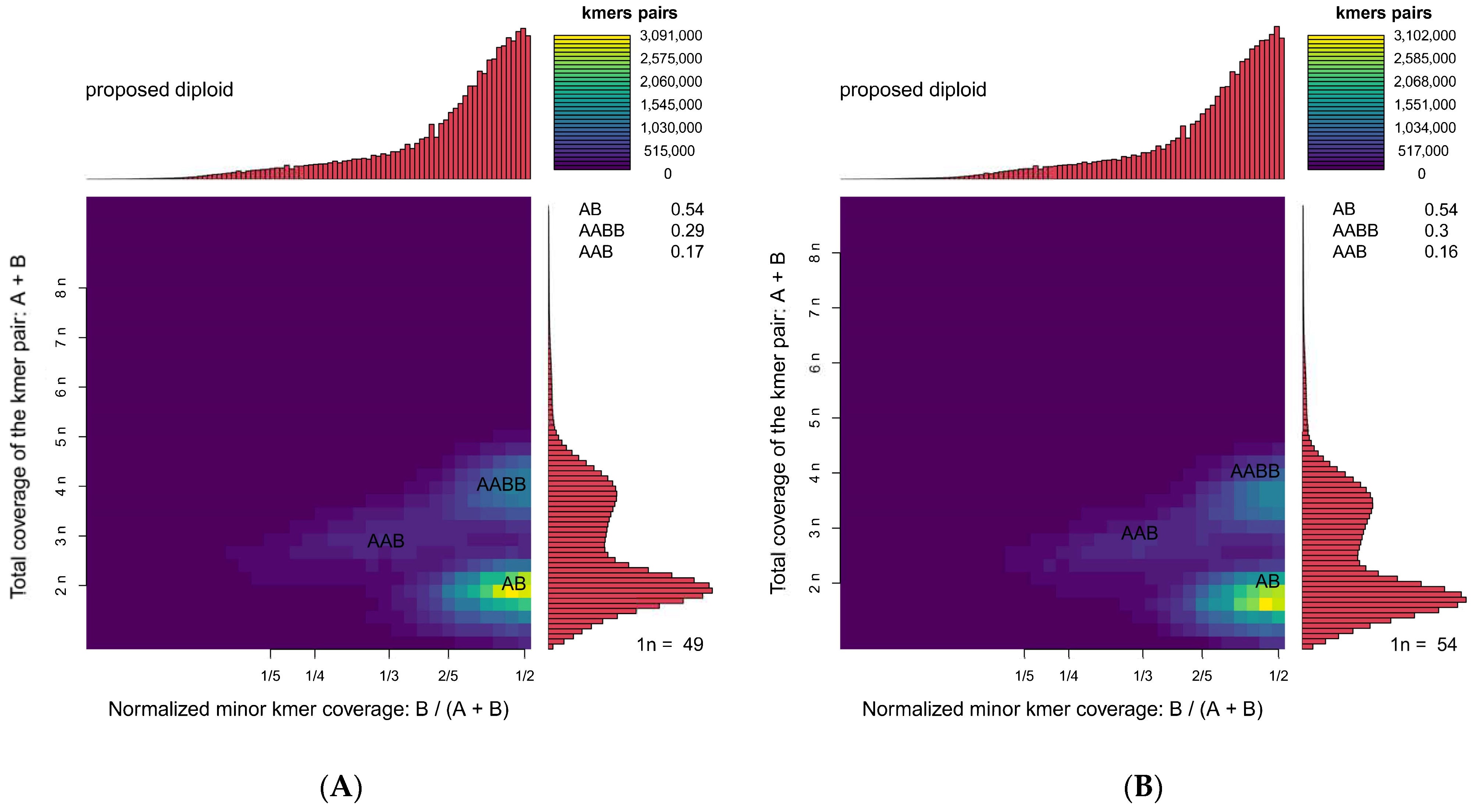
| Peak | K-mers | K-mers [Proportion] | Summit B/(A + B) | Summit A + B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | AB | 63,723,397 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 98.06 |
| AABB | 34,490,621 | 0.29 | 0.48 | 199.5 | |
| AAB | 20,076,357 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 148.78 | |
| Male | AB | 62,713,232 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 92.96 |
| AABB | 34,793,915 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 205.99 | |
| AAB | 18,889,638 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 143.19 |
| Female | Male | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of sequences examined | 21,378,004 | 21,355,316 |
| Total size of examined sequences (bp) | 4,197,030,785 | 4,206,358,660 |
| Total number of identified SSRs | 4,347,973 | 4,322,277 |
| Number of SSR containing sequences | 3,175,080 | 3,152,792 |
| Number of sequences containing more than 1 SSR | 789,477 | 785,798 |
| Number of SSRs present in compound formation | 666,189 | 658,486 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, T.; Zhang, X. The Genome Survey Analysis of Female and Male Sepiella japonica. Genes 2025, 16, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101215
Ren Y, Qu Y, Wang F, Gao T, Zhang X. The Genome Survey Analysis of Female and Male Sepiella japonica. Genes. 2025; 16(10):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101215
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Yuting, Yinquan Qu, Fenglin Wang, Tianxiang Gao, and Xiumei Zhang. 2025. "The Genome Survey Analysis of Female and Male Sepiella japonica" Genes 16, no. 10: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101215
APA StyleRen, Y., Qu, Y., Wang, F., Gao, T., & Zhang, X. (2025). The Genome Survey Analysis of Female and Male Sepiella japonica. Genes, 16(10), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101215







