Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Polish Cohort with Most Cases Due to Novel CREBBP and EP300 Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Genetic Analysis
3. Results
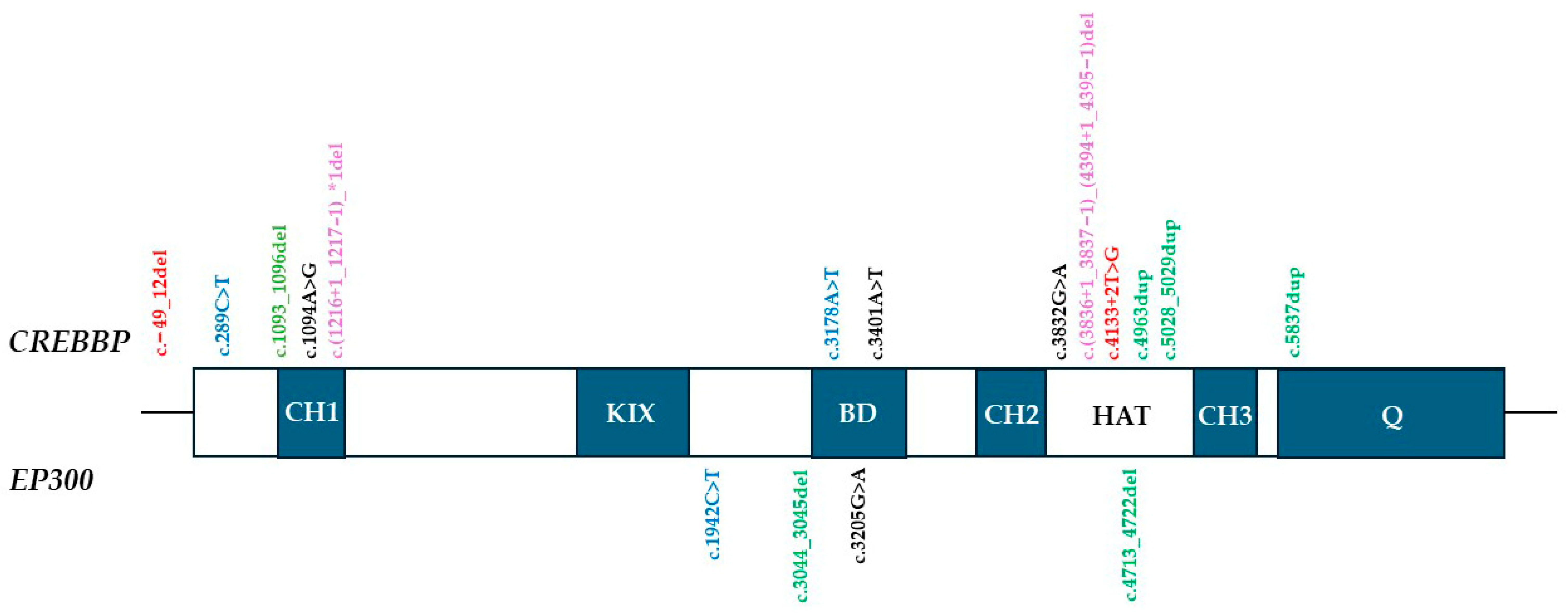
3.1. Molecular Findings
| Patient ID | Gender | Genotype (cDNA) | Protein Effect | Typical Facial Dysmorphism # | Short Stature | Microcephaly | Broad Thumbs/Halluces | Cardiac Anomalies | Skeletal and/or Dental Anomalies | Hypotonia | NDD/ID | Hypertrichosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREBBP NM_004380.3, NP_004371.2, chr16(GRCh38):g.3725054–3880713 | ||||||||||||
| P01 | F | c.[4963dup];[=] | p.(Leu1655Profs*5) | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P02 | M | c.[3178A>T];[=] | p.(Lys1060*) | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y |
| P03 | F | c.[5028_5029dup];[=] | p.(Glu1677Glyfs*68) | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P04 | M | c.[(1216+1_1217−1)_*1del];[=] | p.? | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y |
| P05 | M | c.[(3836+1_3837−1)_(4394+1_4395−1)del];[=] | p.? | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P06 | M | c.[4133+2T>G];[=] | p.? | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P07 | M | c.[289C>T];[=] | p.(Gln97)* | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P08 | M | c.[−49_12del];[=] | p.? start loss | Y | Y | Y | N/Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P09 | M | c.[1093_1096del];[=] | p.(His365Serfs*23) | Y | Y | Y | N/N | N | Y | Y | Y | N |
| P10 | F | c.[5837dup];[=] | p.(Pro1947Thrfs*19) | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | NA | Y | Y | Y |
| P11 | F | c.[3832G>A];[=] | p.(Glu1278Lys) | Y | Y | Y | Y/Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P12 | F | c.[3401A>T];[=] | p.(Asp1134Val) | Y | Y | N | Y/Y | N | N | N | Y | Y |
| P13 | F | c.[1094A>G];[=] | p.(His365Arg) | N | Y | Y | N/Y | N | N | Y | Y | N |
| EP300 NM_001429.4, NP_001420.2, chr22(GRCh38):g41092510–41180077 | ||||||||||||
| P14 | F | c.[1942C>T];[=] | p.(Arg648*) | Y | Y | Y | N/N | N | Y | Y | Y | N |
| P15 | F | c.[4713_4722del];[=] | p.(Gly1572Metfs*23) | Y | Y | Y | N/Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| P16 | F | c.[3044_3045del];[=] | p.(Arg1015Lysfs*3) | Y | N | Y | Y/Y | Y | N | N | Y | N |
| P17 | F | c.[3205G>A];[=] | p.(Asp1069Asn) | N | N | N | N/Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N |
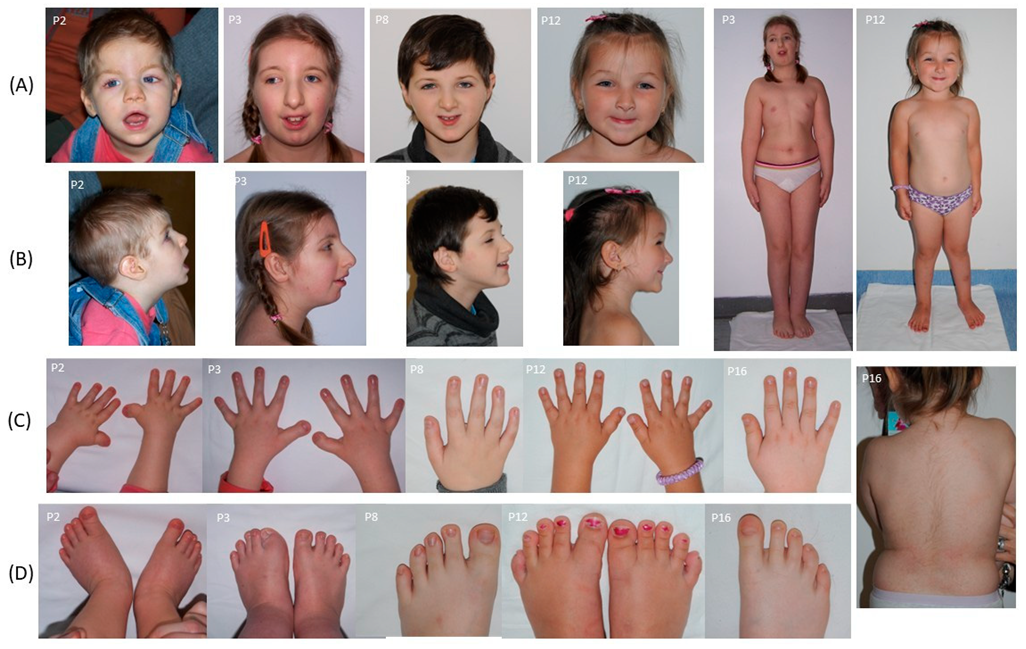
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACGS | Association for Clinical Genomic Science |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| aCGH | array comparative genomic hybridization |
| AMP | Association for Molecular Pathology |
| ASD | atrial septal defect |
| BD | bromodomain |
| CBP | CREB-binding protein |
| CH | cysteine-histidine-rich domain |
| CMHI | Children’s Memorial Health Institute |
| CNV | copy number variant |
| CREB | cyclic AMP response element-binding protein |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
| EP300 | E1A binding protein p300 |
| HAT | histone acetyltransferase |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| HGVS | Human Genome Variation Society |
| ID | intellectual disability |
| KIX | CREB-binding domain |
| LP | likely pathogenic |
| LOVD | Leiden Open Variation Database |
| MLPA | multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification |
| MKHK | Menke–Hennekam syndrome |
| N | absent |
| NA | not applicable |
| NCBD/IBiD | nuclear coactivator binding domain/interferon-binding domain |
| NDD | neurodevelopmental delay |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| P | pathogenic |
| PDA | patent ductus arteriosus |
| PFO | patent foramen ovale |
| POLdb | Polish rare disease database |
| RSTS | Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome |
| Q | glutamine-rich domain |
| SNV | single nucleotide variant |
| TAZ | transcriptional adapter zinc-binding domain |
| VEP | Variant Effect Predictor |
| VSD | ventricular septal defect |
| VUS | variant of uncertain significance |
| Y | present |
References
- Rubinstein, J.H.; Taybi, H. Broad Thumbs and Toes and Facial Abnormalities. A Possible Mental Retardation Syndrome. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1963, 105, 588–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekam, R.C.; Van Den Boogaard, M.J.; Sibbles, B.J.; Van Spijker, H.G. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in The Netherlands. Am. J. Med. Genet. Suppl. 1990, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, M.; Launspach, M.; Holdhof, D.; Nguyen, L.; Engel, V.; Filser, S.; Peters, F.; Immenschuh, J.; Hellwig, M.; Niesen, J.; et al. The Transcriptional Coactivator and Histone Acetyltransferase CBP Regulates Neural Precursor Cell Development and Migration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.H.; Smolik, S. CBP/P300 in Cell Growth, Transformation, and Development. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.A. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Menke, L.A.; DDD Study; Gardeitchik, T.; Hammond, P.; Heimdal, K.R.; Houge, G.; Hufnagel, S.B.; Ji, J.; Johansson, S.; Kant, S.G.; et al. Further Delineation of an Entity Caused by CREBBP and EP300 Mutations but Not Resembling Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2018, 176, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banka, S.; Sayer, R.; Breen, C.; Barton, S.; Pavaine, J.; Sheppard, S.E.; Bedoukian, E.; Skraban, C.; Cuddapah, V.A.; Clayton-Smith, J. Genotype–Phenotype Specificity in Menke–Hennekam Syndrome Caused by Missense Variants in Exon 30 or 31 of CREBBP. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2019, 179, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghshenas, S.; Bout, H.J.; Schijns, J.M.; Levy, M.A.; Kerkhof, J.; Bhai, P.; McConkey, H.; Jenkins, Z.A.; Williams, E.M.; Halliday, B.J.; et al. Menke-Hennekam Syndrome; Delineation of Domain-Specific Subtypes with Distinct Clinical and DNA Methylation Profiles. HGG Adv. 2024, 5, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Byun, C.K.; Kim, H.; Lim, B.C.; Hwang, H.; Choi, J.E.; Hwang, Y.S.; Seong, M.-W.; Park, S.S.; Kim, K.J.; et al. Clinical and Mutational Spectrum in Korean Patients with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: The Spectrum of Brain MRI Abnormalities. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halat-Wolska, P.; Ciara, E.; Pac, M.; Obrycki, Ł.; Wicher, D.; Iwanicka-Pronicka, K.; Bielska, E.; Chałupczyńska, B.; Siestrzykowska, D.; Kostrzewa, G.; et al. Molecular Review of Suspected Alport Syndrome Patients—A Single-Centre Experience. Genes 2025, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.S.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkie, M.; Cassidy, E.-J.; Berry, I.; Owens, M.; Turnbull, C.; Scott, R.H.; Taylor, R.W.; Deans, Z.C.; Ellard, S.; Baple, E.L.; et al. ACGS Best Practice Guidelines for Variant Classification in Rare Disease 2024; ACGS: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, E.R.; Andersen, E.F.; Cherry, A.M.; Kantarci, S.; Kearney, H.; Patel, A.; Raca, G.; Ritter, D.I.; South, S.T.; Thorland, E.C.; et al. Technical Standards for the Interpretation and Reporting of Constitutional Copy-Number Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen). Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekam, R.C.M. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2006, 14, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fergelot, P.; Van Belzen, M.; Van Gils, J.; Afenjar, A.; Armour, C.M.; Arveiler, B.; Beets, L.; Burglen, L.; Busa, T.; Collet, M.; et al. Phenotype and Genotype in 52 Patients with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome Caused by EP300 Mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2016, 170, 3069–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaka, T.; Kurosawa, K.; Izumi, K.; Yoshida, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Okamoto, N.; Torii, C.; Kosaki, R.; Masuno, M.; Hosokai, N.; et al. Screening for Partial Deletions in the CREBBP Gene in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome Patients Using Multiplex PCR/Liquid Chromatography. Genet. Test. 2006, 10, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spena, S.; Milani, D.; Rusconi, D.; Negri, G.; Colapietro, P.; Elcioglu, N.; Bedeschi, F.; Pilotta, A.; Spaccini, L.; Ficcadenti, A.; et al. Insights into Genotype-Phenotype Correlations from CREBBP Point Mutation Screening in a Cohort of 46 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome Patients. Clin. Genet. 2015, 88, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokunohe, D.; Nakano, H.; Akasaka, E.; Toyomaki, Y.; Sawamura, D. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome with Multiple Pilomatricomas: The First Case Diagnosed by CREBBP Mutation Analysis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, E.; Duncan-Flavell, P.J.; Howarth, R.J.; Hobbs, J.I.; Thomas, N.S.; Bunyan, D.J. Screening of a Large Rubinstein-Taybi Cohort Identified Many Novel Variants and Emphasizes the Importance of the CREBBP Histone Acetyltransferase Domain. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 2508–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ye, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Case Report: A Preterm Infant with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome and Marmorata Telangiectatica Harboring a Frameshift Mutation in the CREBBP Gene. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1059658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VCV000009433.37—ClinVar—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/9433/ (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- VCV001331276.3—ClinVar—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/1331276/?oq=%22ep300%22[GENE]+%22c.3205G%3EA%22[VARNAME]&m=NM_001429.4(EP300):c.3205G%3EA%20(p.Asp1069Asn)%3Fterm=ep300%20c.3205G%3EA (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Mujtaba, S.; He, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yan, S.; Plotnikova, O.; Sachchidanand; Sanchez, R.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J.; Ronai, Z.; Zhou, M.-M. Structural Mechanism of the Bromodomain of the Coactivator CBP in P53 Transcriptional Activation. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Ferreon, J.C.; Ferreon, A.C.M.; Arai, M.; Wright, P.E. Graded Enhancement of P53 Binding to CREB-Binding Protein (CBP) by Multisite Phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19290–19295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacombe, D.; Bloch-Zupan, A.; Bredrup, C.; Cooper, E.B.; Houge, S.D.; García-Miñaúr, S.; Kayserili, H.; Larizza, L.; Lopez Gonzalez, V.; Menke, L.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Management in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: First International Consensus Statement. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, D.; Manzoni, F.M.P.; Pezzani, L.; Ajmone, P.; Gervasini, C.; Menni, F.; Esposito, S. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Clinical Features, Genetic Basis, Diagnosis, and Management. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2015, 41, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekendo-Ngongang, C.; Owosela, B.; Fleischer, N.; Addissie, Y.A.; Malonga, B.; Badoe, E.; Gupta, N.; Moresco, A.; Huckstadt, V.; Ashaat, E.A.; et al. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in Diverse Populations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorry, E.K.; Keddache, M.; Lanphear, N.; Rubinstein, J.H.; Srodulski, S.; Fletcher, D.; Blough-Pfau, R.I.; Grabowski, G.A. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2008, 146A, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gils, J.; Magdinier, F.; Fergelot, P.; Lacombe, D. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Model of Epigenetic Disorder. Genes 2021, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Kar, A.L.; Houge, G.; Shaw, A.C.; De Jong, D.; Van Belzen, M.J.; Peters, D.J.M.; Hennekam, R.C.M. Keloids in Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Clinical Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galéra, C.; Taupiac, E.; Fraisse, S.; Naudion, S.; Toussaint, E.; Rooryck-Thambo, C.; Delrue, M.-A.; Arveiler, B.; Lacombe, D.; Bouvard, M.-P. Socio-Behavioral Characteristics of Children with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2009, 39, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, N.; Pearson, E.; Shelley, L.; Greenhill, C.; Tarver, J.; Waite, J. The Behavioral Phenotype of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2022, 188, 2536–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cieślikowska, A.; Madej-Pilarczyk, A.; Iwanowski, P.; Iwanicka-Pronicka, K.; Wicher, D.; Jędrzejowska, M.; Jurkiewicz, D.; Gawlik, M.; Piekutowska-Abramczuk, D.; Halat-Wolska, P.; et al. Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Polish Cohort with Most Cases Due to Novel CREBBP and EP300 Variants. Genes 2025, 16, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101206
Cieślikowska A, Madej-Pilarczyk A, Iwanowski P, Iwanicka-Pronicka K, Wicher D, Jędrzejowska M, Jurkiewicz D, Gawlik M, Piekutowska-Abramczuk D, Halat-Wolska P, et al. Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Polish Cohort with Most Cases Due to Novel CREBBP and EP300 Variants. Genes. 2025; 16(10):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101206
Chicago/Turabian StyleCieślikowska, Agata, Agnieszka Madej-Pilarczyk, Piotr Iwanowski, Katarzyna Iwanicka-Pronicka, Dorota Wicher, Maria Jędrzejowska, Dorota Jurkiewicz, Marzena Gawlik, Dorota Piekutowska-Abramczuk, Paulina Halat-Wolska, and et al. 2025. "Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Polish Cohort with Most Cases Due to Novel CREBBP and EP300 Variants" Genes 16, no. 10: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101206
APA StyleCieślikowska, A., Madej-Pilarczyk, A., Iwanowski, P., Iwanicka-Pronicka, K., Wicher, D., Jędrzejowska, M., Jurkiewicz, D., Gawlik, M., Piekutowska-Abramczuk, D., Halat-Wolska, P., Błaszkiewicz, J., Mendrek, I., Chrzanowska, K., Młynek, M., Stawiński, P., Kosińska, J., Krajewska-Walasek, M., & Ciara, E. (2025). Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Comprehensive Analysis of a Polish Cohort with Most Cases Due to Novel CREBBP and EP300 Variants. Genes, 16(10), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101206





