Development and Application of an SNP Marker for High-Throughput Detection and Utilization of the badh2 Gene in Rice Breeding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Isolation and Marker Development
2.3. Experiment Design and Measuring 2-AP Content
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Mutation Type in Aromatic Lines
3.2. Multiplex-Ready PCR Assay
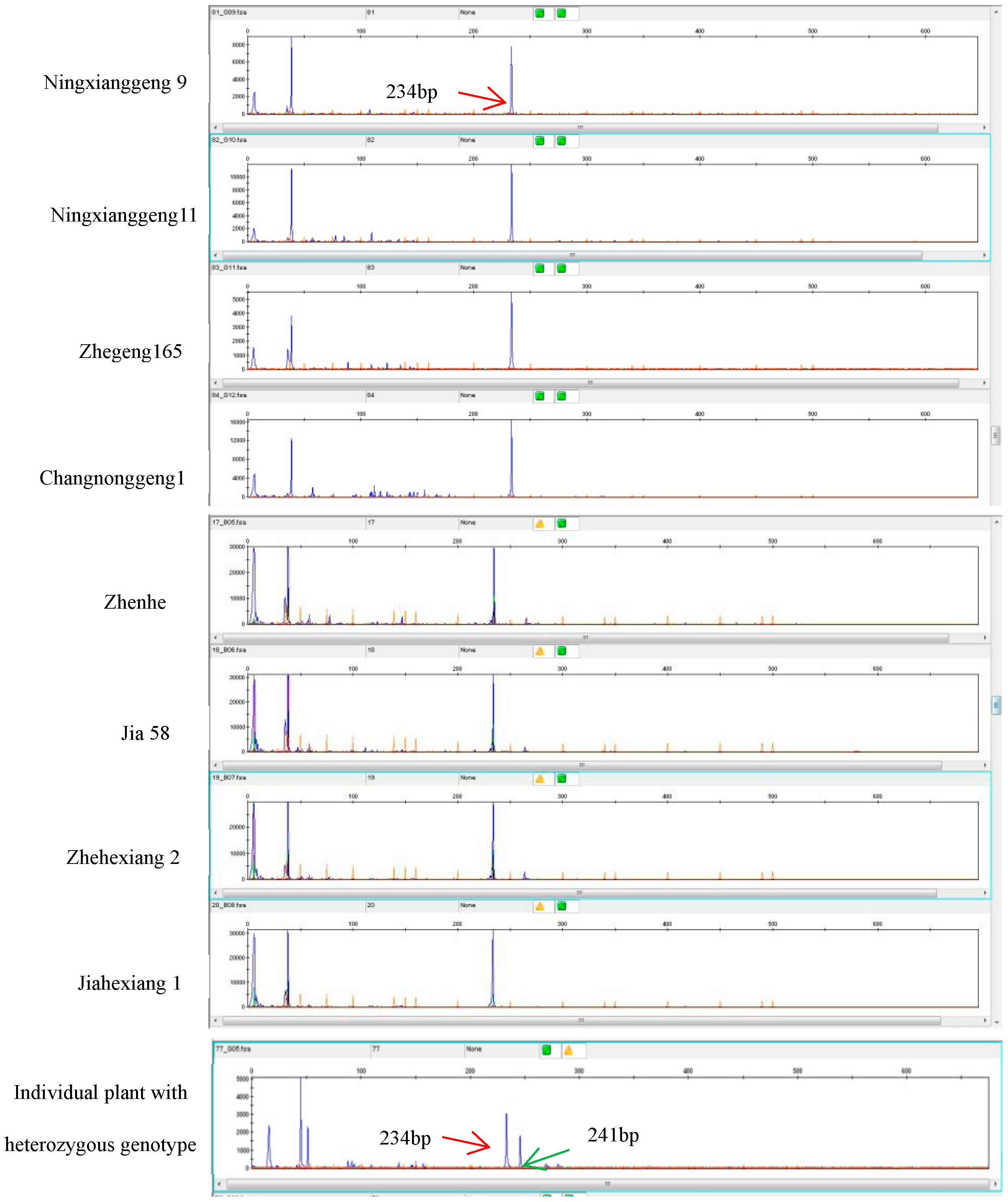
3.3. KASP Assay for the badh2 Gene
3.4. Measurement of 2-AP Content and Agronomic Characteristic
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-AP | 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline |
| CAPS | Cleaved amplified polymorphism sequence |
| dCAPS | Derived CAPS |
| HRM | High-resolution melting |
| TS-PCR | Temperature switch PCR |
| KASP | Kompetitive allele-specific PCR |
| badh2-E2 | The second exon of badh2 |
| badh2-E7 | The seventh exon of badh2 |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| RILs | Recombinant inbred lines |
| PH | Plant height |
| PL | Panicle length |
| EP | Effective panicles 104/ha |
| TNGP | Total number of grains per panicle |
| NFGP | Number of filled grains per panicle |
| SSR | Seed sating rat |
| TGW | Thousand-grain weight (g) |
References
- Yajima, I.; Yanai, T.; Nakamura, M.; Sakakibar, H.; Habu, T. Volatile flavor components of cooked rice kaorimai (scented rice, O. sativa japonica). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1979, 43, 2425–2429. [Google Scholar]
- Buttery, R.G.; Ling, L.C.; Juliano, B.O.; Turnbaugh, J.G. Cooked rice aroma and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1983, 31, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, L.M.T.; Fitzgerald, T.L.; Henry, R.J.; Jin, Q.; Waters, D.L.E. The gene for fragrance in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2005, 3, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, L.M.T.; Gillies, S.A.; Brushett, D.J.; Waters, D.L.; Henry, R.J. Inactivation of an aminoaldehyde dehydrogenase is responsible for fragrance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Flavor of cereal products—A review. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, K.; Wootton, M.; Paton, J.E. Sensory testing of Australian fragrant, imported fragrant, and non-fragrant rice aroma. Int. J. Food Prop. 2004, 7, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, B.C.; Sidiq, E.A. A rapid technique for scent determination in rice. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 1978, 38, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Widjaja, R.; Craske, J.; Wotton, D. Comparative studies on volatile components of non-fragrant and fragrant rices. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 70, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriseadka, T.; Wongpornchai, S.; Kitsawatpaiboon, P. Rapid method for quantitative analysis of the aroma impact compound, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, in fragrant rice using automated headspace gas chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8183–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prabhu, K.V.; Mohapatra, T.; Singh, S.N.; Sharma, T.R.; Nagarajan, M.; Vinod, K.K.; Singh, U.D.; et al. Marker assisted selection: A paradigm shift in Basmati breeding. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2011, 71, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani, G. Marker aided selection for aroma in F2 populations of rice. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 10, 15845–15848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, B.; Jahufer, M.; Brouwer, J.; Pang, E. An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: The basic concepts. Euphytica 2005, 142, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Ji, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, M. Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, K.; Shobha Rani, N.; Pandey, M.K.; Sivaranjani, A.K.; Neeraja, C.N.; Balachandran, S.M.; Sheshu Madhav, M.; Viraktamath, B.C.; Prasad, G.S.V.; Sundaram, R.M. Development of a simple functional marker for fragrance in rice and its validation in Indian basmati and non-basmati fragrant rice varieties. Mol. Breed. 2009, 24, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Tang, S.; Chen, M.; Wei, X.; He, J.; Luo, J.; Jiao, G.; Hu, Y.; Xie, L.; Hu, P. Haplotype variation at Badh2, the gene determining fragrance in rice. Genomics 2013, 101, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Discovery of a new fragrance allele and development of functional markers for identifying diverse fragrant genotypes in rice. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Jiang, H.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hu, P.; Tang, S. Genetic diversity of global aromatic rice varieties. Plant Divers. Resour. 2015, 37, 871–880. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Waters, D.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Henry, R.J.; Reinke, R.F. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker linked to the fragrance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 2003, 165, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarawathi, Y.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Mohapatra, T.; Sharma, T.R.; Singh, N.K. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for basmati quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Breed. 2008, 21, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, M. Discovery of a new fragrance allele and the development of functional markers for the breeding of fragrant rice varieties. Mol. Breed. 2008, 22, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Zhao, G.C.; Li, J.Y. Development of molecular markers used to identify two types of fragrant rice and analysis of mutation sites od Badh2 gene in 24 varieties of fragrant rice. Plant Divers. Resour. 2011, 33, 667–673. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, F.S.G.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Mohamed, M.T.; Rahim, H.A.; Latif, M.A.; Aslani, F. The genetic and molecular origin of natural variation for the fragrance trait in an elite Malaysian aromatic rice through quantitative trait loci mapping using SSR and gene-based markers. Gene 2015, 555, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Ma, G.; Wang, J. Development and utilization of the functional co-dominant KASP marker for thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2022, 69, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke, M. An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.J.; Nguyen, T.M.; Waterman, A.; Chalmers, K.J. Multiplex-ready PCR: A new method for multiplexed SSR and SNP genotyping. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Ka, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Bak, W.C.; Jeong, S.J.; Seong, J.Y.; Suh, D.S. Microsatellite markers for population-genetic studies of shiitake (Lentinula edodes) strains. Genes Genom. 2009, 31, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, J.; Hayden, M. Multiplex-Ready Technology for mid-throughput genotyping of molecular markers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1145, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, C.C.; Bergman, C.; Delgado, J.T.; Bryant, R. Screening for 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in the headspace of rice using SPME/GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.N.; Tang, A.; Tang, S.Q.; Luo, J.; Jiao, G.A.; Wu, J.L.; Hu, P.S. A new deletion mutation of fragrant gene and the development of three molecular markers for fragrance in rice. Plant Breed. 2011, 130, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, K.M.; Arikit, S.; Wanchana, S.; Yoshihashi, T.; Choowongkomon, K.; Vanavichit, A. A PCR-based marker for a locus conferring the aroma in Myanmar rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Jia, Q.; Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Mao, Y. Advances in cloning functional genes for rice yield traits and molecular design breeding in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1206165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, M.A.; Sackville Hamilton, N.R.; Calingacion, M.N.; Verhoeven, H.A.; Butardo, V.M. Is there a second fragrance gene in rice? Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
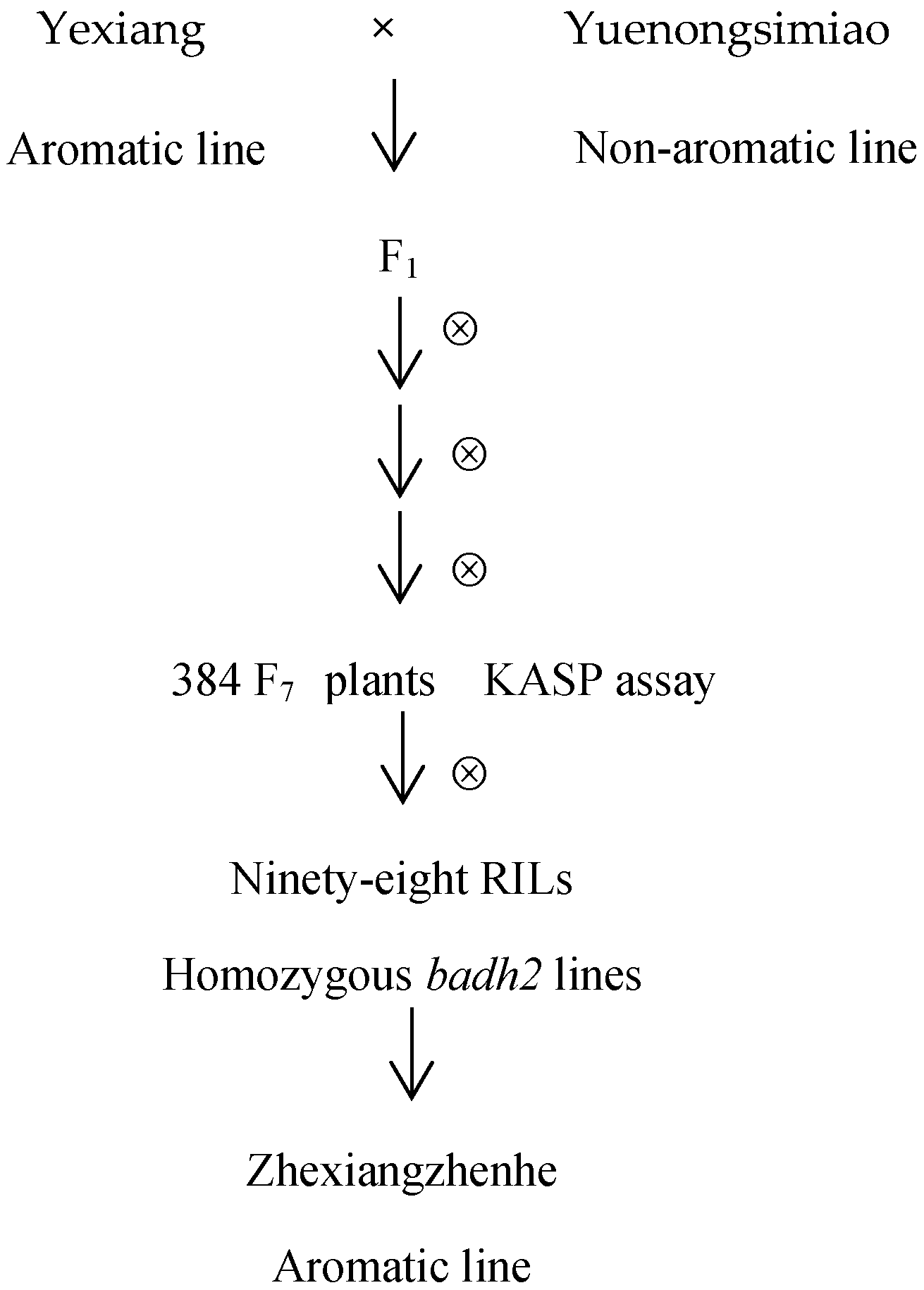



| Subspecies | Line Name | Aromatic Type |
|---|---|---|
| japonica | Ningxianggeng 9, Ningxianggeng 11, Zhegeng 165, Changnonggeng 1, Zhenhe, Jia 58, Jiahexiang 1 | aromatic |
| indica | Zhuxianglisi, Meixiangxinzhan, Junhexiangzhan, Guangliangxiang 3, Nongxiang 18, Nongxiang 42, Yuzhenxiang, Chuangxiang 5, Meixiangzhan 2, Xiangyaxiangzhan, Yexiang, Zhexiangsimiao, 99 xiang, Taixiang 8, 19 xiang, Yingxiangsimiao | aromatic |
| japonica | Nippornbare | Non-aromatic |
| indica | Yuenongsimiao | Non-aromatic |
| Target Area | Primer | Primer Sequence | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exon2 | exon2-F1 | CACCCTCTGCTTCTGCCTCT | Sanger sequencing |
| exon2-R1 | CAGCCATGCTTCCAACTTATTC | ||
| Exon7 | exon7-F1 | TGGTCTTCCTTCAGGTGTGC | Sanger sequencing |
| exon7-R1 | TCCAGTGAAACAGGCTGTCA | ||
| Exon2 | M13-Bh2-1F | TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTCATCGGTACCCTCCTCTTCA | Multiplex-Ready PCR |
| FAM-M13-Bh2-1F | FAM-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTCATCGGTACCCTCCTCTTCA | ||
| Bh2-1R | ATTGCGCGGAGGTACTTG | ||
| Exon7 | Kexon7-F1 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAAGGTAGGGTGGTGACTA | KASP assay |
| Kexon7-F2 | GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTAAGGTAGGGTGGTGACTC | ||
| Kexon7-R | CCTGTACGGAACACACGCA |
| Lines | PH | PL | EP | TNGP | NFGP | SSR | TGW (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhexiangzhenhe | 115.7 ± 2.3 | 20.5 ± 3.1 | 305.8 ± 25.4 | 185.3 ± 5.6 | 165.7 ± 11.6 | 89.4 ± 3.8 | 24.2 ± 0.6 |
| Yuenongsimiao | 116.5 ± 3.5 | 20.3 ± 3.5 | 308.4 ± 28.8 | 183.8 ± 4.5 | 166.8 ± 12.5 | 90.75 ± 4.5 | 23.9 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, H.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Lou, J.; Qi, Y. Development and Application of an SNP Marker for High-Throughput Detection and Utilization of the badh2 Gene in Rice Breeding. Genes 2025, 16, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101132
Fang H, Huang H, Yu L, Wang L, Lou J, Qi Y. Development and Application of an SNP Marker for High-Throughput Detection and Utilization of the badh2 Gene in Rice Breeding. Genes. 2025; 16(10):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101132
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Hao, Huifang Huang, Lan Yu, Linyou Wang, Jue Lou, and Yongbin Qi. 2025. "Development and Application of an SNP Marker for High-Throughput Detection and Utilization of the badh2 Gene in Rice Breeding" Genes 16, no. 10: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101132
APA StyleFang, H., Huang, H., Yu, L., Wang, L., Lou, J., & Qi, Y. (2025). Development and Application of an SNP Marker for High-Throughput Detection and Utilization of the badh2 Gene in Rice Breeding. Genes, 16(10), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101132






