Suppression of Nodule Formation by RNAi Knock-Down of Bax inhibitor-1a in Lotus japonicus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the LjBI-1 Gene Family
2.2. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis and Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
2.3. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.4. Generation of Transgenic Hairy Roots
2.5. LjBI-1-Specific RNAi
2.6. qPCR Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Rhizobial Infection Assay
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of LjBI-1 Genes in L. japonicus
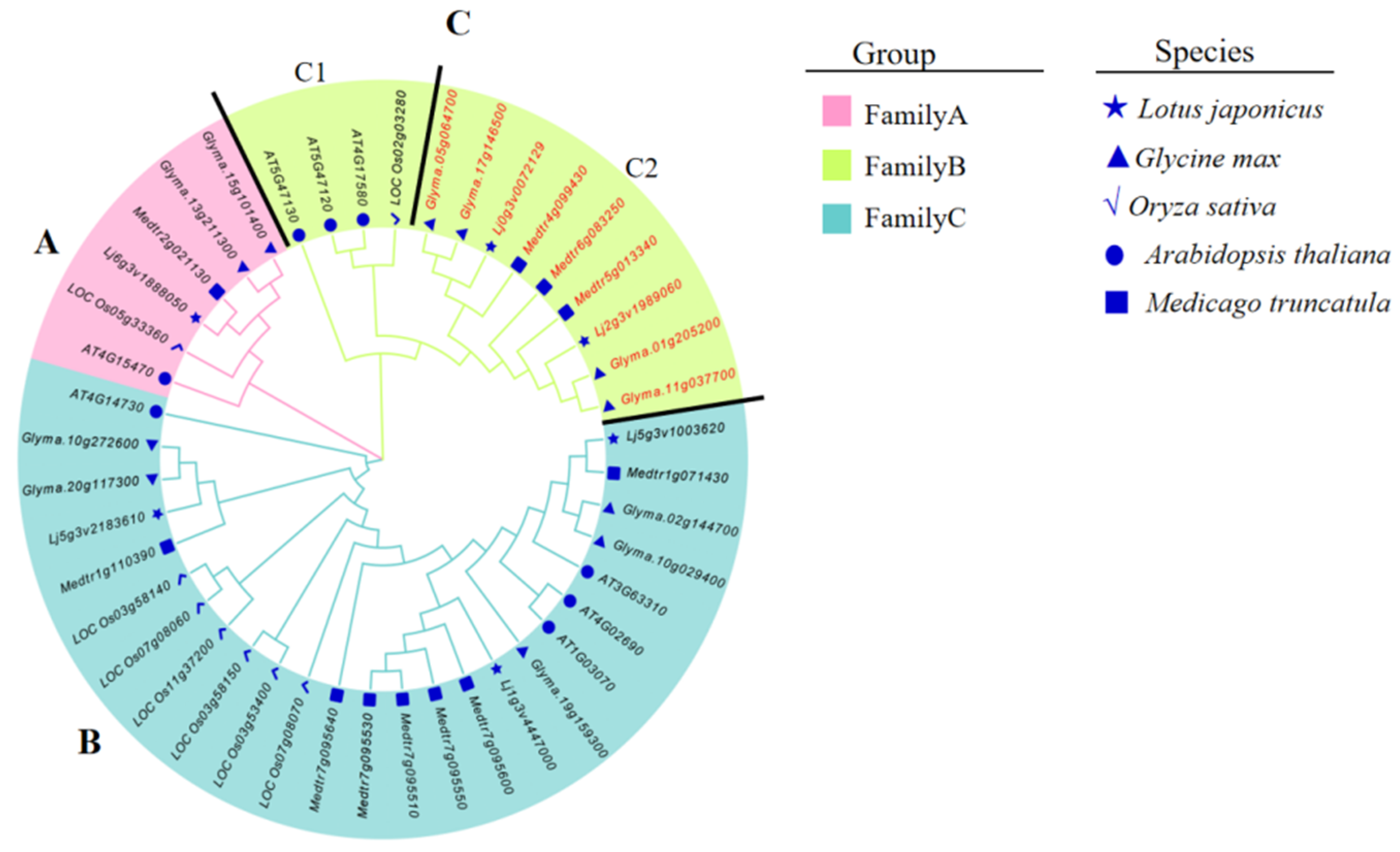
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of BI-1 Genes from L. japonicus, M. truncatula, G. max, A. thaliana, and O. sativa
3.3. Expression Profile of LjBI-1 Genes in L. japonicus Roots with and Without Inoculation of MAFF303099
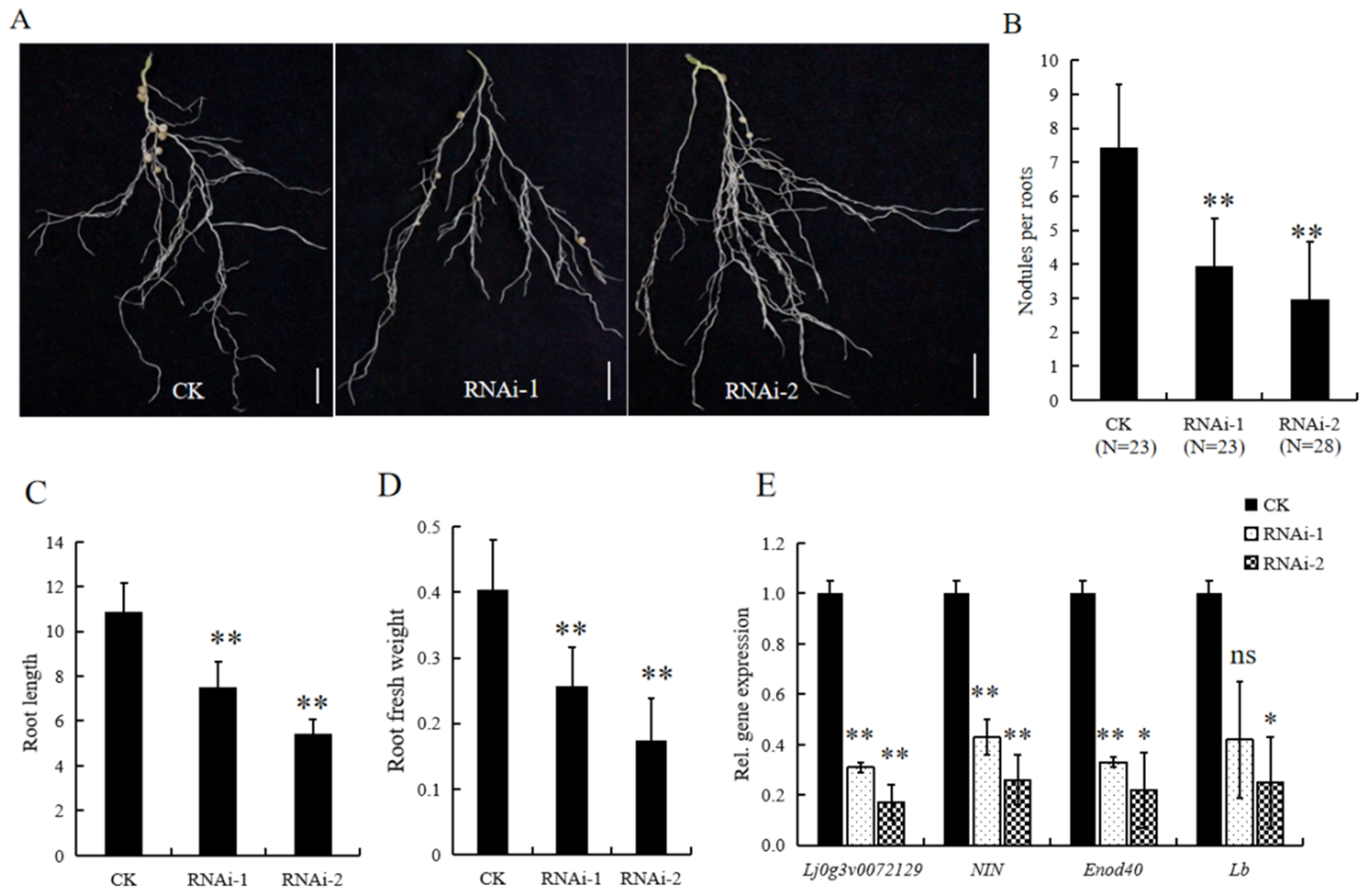
3.4. Suppression of Nodulation by LjBI-1a RNAi
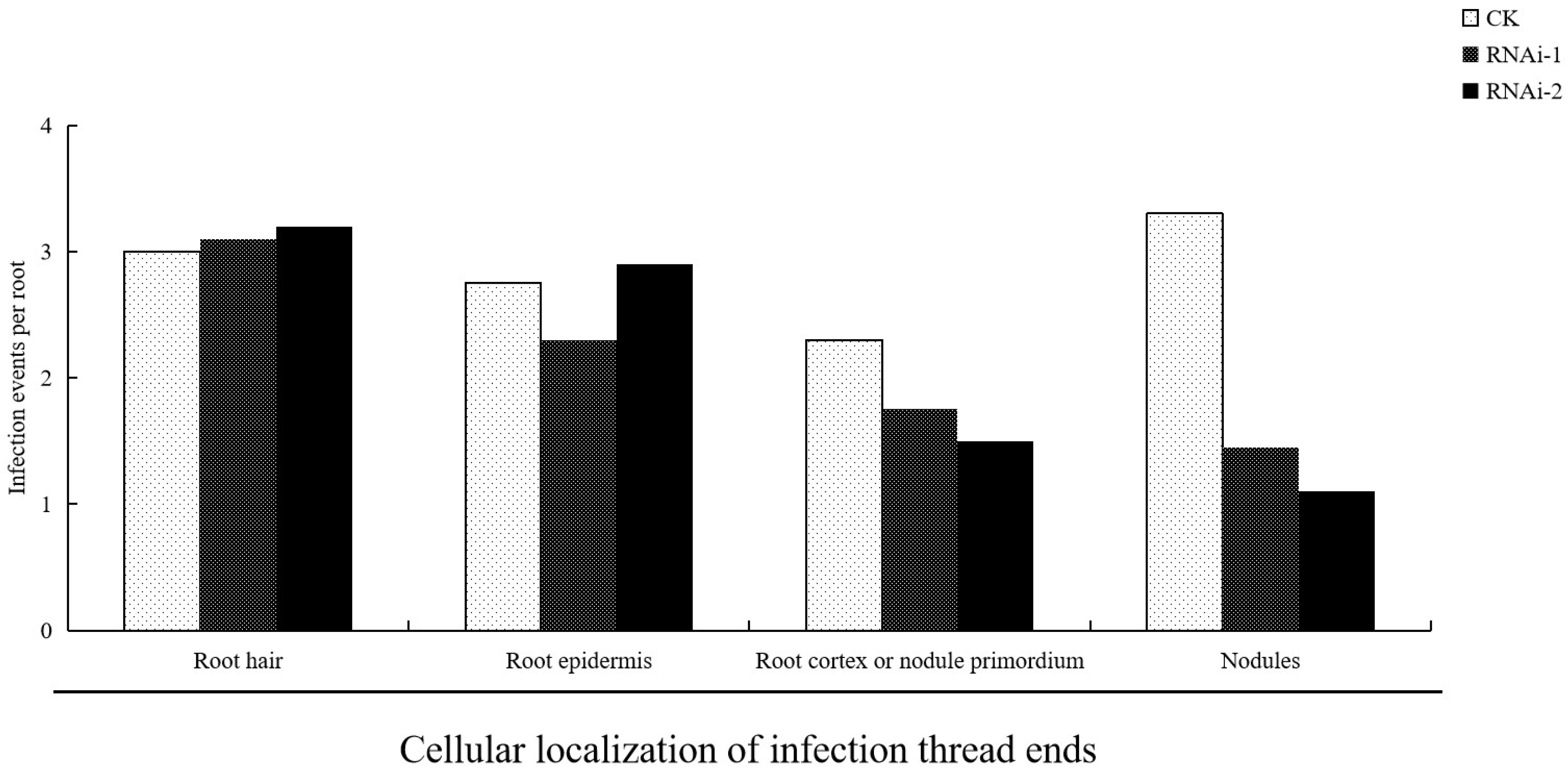
3.5. Suppression of Rhizobial Infection by LjBI-1a RNAi
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopittke, P.M.; Dalal, R.C.; Finn, D.; Menzies, N.W. Global changes in soil stocks of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulphur as influenced by long-term agricultural production. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 23, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zou, J.; Han, Z.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Niu, S.; Horwath, W.R.; Zhu-Barker, X. Global soil-derived ammonia emissions from agricultural nitrogen fertilizer application: A refinement based on regional and crop-specific emission factors. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 27, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, J.; Ahmad, S.; Malik, M. Nitrogenous fertilizers: Impact on environment sustainability, mitigation strategies, and challenges. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, E. Diversity and regulation of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in plants. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, R543–R559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, S.; Praharaj, S.; Brestic, M.; Sahoo, R.K.; Sagar, L.; Shankar, T.; Palai, J.B.; Sahoo, U.; Sairam, M.; Pramanick, B.; et al. Rhizobium as Biotechnological Tools for Green Solutions: An Environment-Friendly Approach for Sustainable Crop Production in the Modern Era of Climate Change. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.F.; Wang, E.T.; Ji, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J. Recent development and new insight of diversification and symbiosis specificity of legume rhizobia: Mechanism and application. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udvardi, M.; Poole, P.S. Transport and Metabolism in Legume-Rhizobia Symbioses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 781–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaharada, Y.; Nielsen, M.W.; Kelly, S.; James, E.K.; Andersen, K.R.; Rasmussen, S.R.; Füchtbauer, W.; Madsen, L.H.; Heckmann, A.B.; Radutoiu, S.; et al. Differential regulation of the Epr3 receptor coordinates membrane-restricted rhizobial colonization of root nodule primordia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, W.J.; Broughton, W.J. Symbiotic use of pathogenic strategies: Rhizobial protein secretion systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broghammer, A.; Krusell, L.; Blaise, M.; Sauer, J.; Sullivan, J.T.; Maolanon, N.; Vinther, M.; Lorentzen, A.; Madsen, E.B.; Jensen, K.J.; et al. Legume receptors perceive the rhizobial lipochitin oligosaccharide signal molecules by direct binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13859–13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, R.; Galera, C.; de Billy, F.; Penmetsa, R.V.; Journet, E.P.; Maillet, F.; Rosenberg, C.; Cook, D.; Gough, C.; Dénarié, J. Four genes of controlling components of a nod factor transduction pathway. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1647–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Halane, M.K.; Gassmann, W.; Stacey, G. The Role of Plant Innate Immunity in the Legume-Rhizobium Symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 535–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-P.; Liang, W.; Liu, C.-W.; Xie, F.; Murray, J.D.; Chiurazzi, M. Unraveling the rhizobial infection thread. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilbé, J.; Montiel, J.; Arrighi, J.-F.; Stougaard, J. Molecular Mechanisms of Intercellular Rhizobial Infection: Novel Findings of an Ancient Process. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 922982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganova, A.V.; Brewin, N.J.; Tsyganov, V.E. Structure and Development of the Legume-Rhizobial Symbiotic Interface in Infection Threads. Cells 2021, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montiel, J.; Reid, D.; Grønbæk, T.H.; Benfeldt, C.M.; James, E.K.; Ott, T.; Ditengou, F.A.; Nadzieja, M.; Kelly, S.; Stougaard, J. Distinct signaling routes mediate intercellular and intracellular rhizobial infection in Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Jurado, S.; Rodríguez-Navarro, D.N.; Kawaharada, Y.; Perea, J.F.; Gil-Serrano, A.; Jin, H.; An, Q.; Rodríguez-Carvajal, M.A.; Andersen, S.U.; Sandal, N.; et al. Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 Invades Lotus burttii by Crack Entry in a Nod Factor–and Surface Polysaccharide–Dependent Manner. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, E.B.; Gresshoff, P.M.; Su, H.; Ferguson, B.J. Legumes Regulate Symbiosis with Rhizobia via Their Innate Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Berendsen, R.L. Beneficial microbes going underground of root immunity. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2860–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Asamizu, E.; Kato, T.; Nakao, M.; Sasamoto, S.; Watanabe, A.; Ono, A.; Kawashima, K.; et al. Genome Structure of the Legume, Lotus japonicus. DNA Res. 2008, 15, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guether, M.; Neuhauser, B.; Balestrini, R.; Dynowski, M.; Ludewig, U.; Bonfante, P. A Mycorrhizal-Specific Ammonium Transporter from Lotus japonicus Acquires Nitrogen Released by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorite, M.J.; Videira e Castro, I.; Muñoz, S.; Sanjuán, J. Phylogenetic relationship of Lotus uliginosus symbionts with bradyrhizobia nodulating genistoid legumes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. Bax inhibitor-1, a mammalian apoptosis suppressor identified by functional screening in yeast. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Watanabe, N.; Nagano, M.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Lam, E. Bax inhibitor-1: A highly conserved endoplasmic reticulum-resident cell death suppressor. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Lam, E. BAX Inhibitor-1 Modulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-mediated Programmed Cell Death in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3200–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Lam, E. Bax Inhibitor-1, a Conserved Cell Death Suppressor, Is a Key Molecular Switch Downstream from a Variety of Biotic and Abiotic Stress Signals in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3149–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbat, M.; Zeba, N.; Kim, S.R.; Hong, C.B. A BAX inhibitor-1 gene in Capsicum annuum is induced under various abiotic stresses and endows multi-tolerance in transgenic tobacco. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Guo, N.; Li, S.; Duan, M.; Wang, G.; Zong, M.; Han, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J. Characterization of the Bax Inhibitor-1 Family in Cauliflower and Functional Analysis of BobBIL4. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Huang, X.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Han, D.; Kang, Z. Wheat BAX inhibitor-1 contributes to wheat resistance to Puccinia striiformis. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4571–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Iwabuchi, M.; Nakasone, A.; Shimamoto, K.; Uchimiya, H.; Kawai-Yamada, M. Arabidopsis Bax inhibitor-1 promotes sphingolipid synthesis during cold stress by interacting with ceramide-modifying enzymes. Planta 2014, 240, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, M.; Kakuta, C.; Fukao, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Kawai-Yamada, M. Arabidopsis Bax inhibitor-1 interacts with enzymes related to very-long-chain fatty acid synthesis. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-López, A.; Díaz, M.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Guillén, G.; Sánchez, F.; Díaz-Camino, C. Uncovering Bax inhibitor-1 dual role in the legume–rhizobia symbiosis in common bean roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Ke, D.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Sun, S.; Shen, J.; et al. The Bax inhibitor GmBI-1α interacts with a Nod factor receptor and plays a dual role in the legume–rhizobia symbiosis. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5820–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, H.; Kouchi, H. Gene Silencing by Expression of Hairpin RNA in Roots and Root Nodules. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, H.; Ke, D.X.; Cai, K.; Wang, C.; Gou, H.L.; Hong, Z.L.; Zhang, Z.M. A MAP Kinase Kinase Interacts with SymRK and Regulates Nodule Organogenesis in. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilworth, B. Control of Leghaemoglobin Synthesis in Snake Beans. Biochem. J. 1971, 125, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Tansengco, M.L.; Hayashi, M.; Kawaguchi, M.; Imaizumi-Anraku, H.; Murooka, Y. crinkle, a novel symbiotic mutant that affects the infection thread growth and alters the root hair, trichome, and seed development in. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Zhu, H.; Gou, H.; Fu, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, T.; Ke, D.; Kang, H.; Xie, Q.; Hong, Z.; et al. A Ubiquitin Ligase of Symbiosis Receptor Kinase Involved in Nodule Organogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunton, J.E.; Gilmour, M.W.; Baptista, K.P.; Lawley, T.D.; Taylor, D.E. Interaction between the co-inherited TraG coupling protein and the TraJ membrane-associated protein of the H-plasmid conjugative DNA transfer system resembles chromosomal DNA translocases. Microbiology 2007, 153, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charon, C.; Johansson, C.; Kondorosi, E.; Kondorosi, A.; Crespi, M. enod40 induces dedifferentiation and division of root cortical cells in legumes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8901–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauser, L.; Roussis, A.; Stiller, J.; Stougaard, J. A plant regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules. Nature 1999, 402, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Bisseling, T. Evolution of NIN and NIN-like Genes in Relation to Nodule Symbiosis. Genes 2020, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Hargrove, M.S. Distal heme pocket regulation of ligand binding and stability in soybean leghemoglobin. Proteins 2003, 50, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, W.J.; Zhang, F.; Perret, X.; Staehelin, C. Signals exchanged between legumes and agricultural uses and perspectives. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.J.; Mavengere, N.R.; Ellis, A.G. The structure of legume-rhizobium interaction networks and their response to tree invasions. Aob Plants 2016, 8, plw038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Leng, P.; Feng, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Shan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Hao, Q.; et al. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses provide new insight into symbiotic host specificity. iScience 2024, 27, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaeizad, V.; Imani, J.; Kogel, K.-H.; Eichmann, R.; Hückelhoven, R. Over-expression of the cell death regulator BAX inhibitor-1 in barley confers reduced or enhanced susceptibility to distinct fungal pathogens. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 118, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, N.; Lisak, D.A.; Schneider, L.; Habicht, J.; Pergande, M.; Methner, A. The ancient cell death suppressor BAX inhibitor-1. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Name | Gene ID | Chromosome Location | Transcript Numbers | Protein Size (aa) | MW (kDa) | PI | Signal Peptide | Exon | Intron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LjBI-1a | Lj0g3v0072129 | chr4:34395727-34398462 | 1 | 249 | 27651.19 | 8.85 | 0.0210% | 4 | 3 |
| LjBI-1b | Lj1g3v4447000 | chr1:10917466-10919589 | 1 | 240 | 26873.15 | 8.90 | 0.1240% | 4 | 3 |
| LjBI-1c | Lj2g3v1989060 | chr2:1184961-1187596 | 2 | 246 | 27291.95 | 9.26 | 0.0390% | 6 | 5 |
| LjBI-1d | Lj5g3v1003620 | chr5:24312170-24315258 | 1 | 242 | 27075.23 | 6.55 | 0.1410% | 4 | 3 |
| LjBI-1e | Lj5g3v2183610 | chr5:2502444-2504025 | 1 | 240 | 27101.31 | 7.65 | 0.0210% | 4 | 3 |
| LjBI-1f | Lj6g3v1888050 | chr6:52345422-52347607 | 1 | 255 | 28373.34 | 6.41 | 0.2280% | 4 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, F.; Ke, D.; Lu, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Liang, W.; Yuan, S.; Chen, H. Suppression of Nodule Formation by RNAi Knock-Down of Bax inhibitor-1a in Lotus japonicus. Genes 2025, 16, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010058
Jin F, Ke D, Lu L, Hu Q, Zhang C, Li C, Liang W, Yuan S, Chen H. Suppression of Nodule Formation by RNAi Knock-Down of Bax inhibitor-1a in Lotus japonicus. Genes. 2025; 16(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Fuxiao, Danxia Ke, Lu Lu, Qianqian Hu, Chanjuan Zhang, Chao Li, Wanwan Liang, Songli Yuan, and Haifeng Chen. 2025. "Suppression of Nodule Formation by RNAi Knock-Down of Bax inhibitor-1a in Lotus japonicus" Genes 16, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010058
APA StyleJin, F., Ke, D., Lu, L., Hu, Q., Zhang, C., Li, C., Liang, W., Yuan, S., & Chen, H. (2025). Suppression of Nodule Formation by RNAi Knock-Down of Bax inhibitor-1a in Lotus japonicus. Genes, 16(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010058





