Epidermal Differentiation Genes of the Common Wall Lizard Encode Proteins with Extremely Biased Amino Acid Contents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of EDC Genes in Genome Sequences
2.2. Proteomics
3. Results
3.1. The Organization of the EDC of the Common Wall Lizard Differs from the Canonical EDC Structure
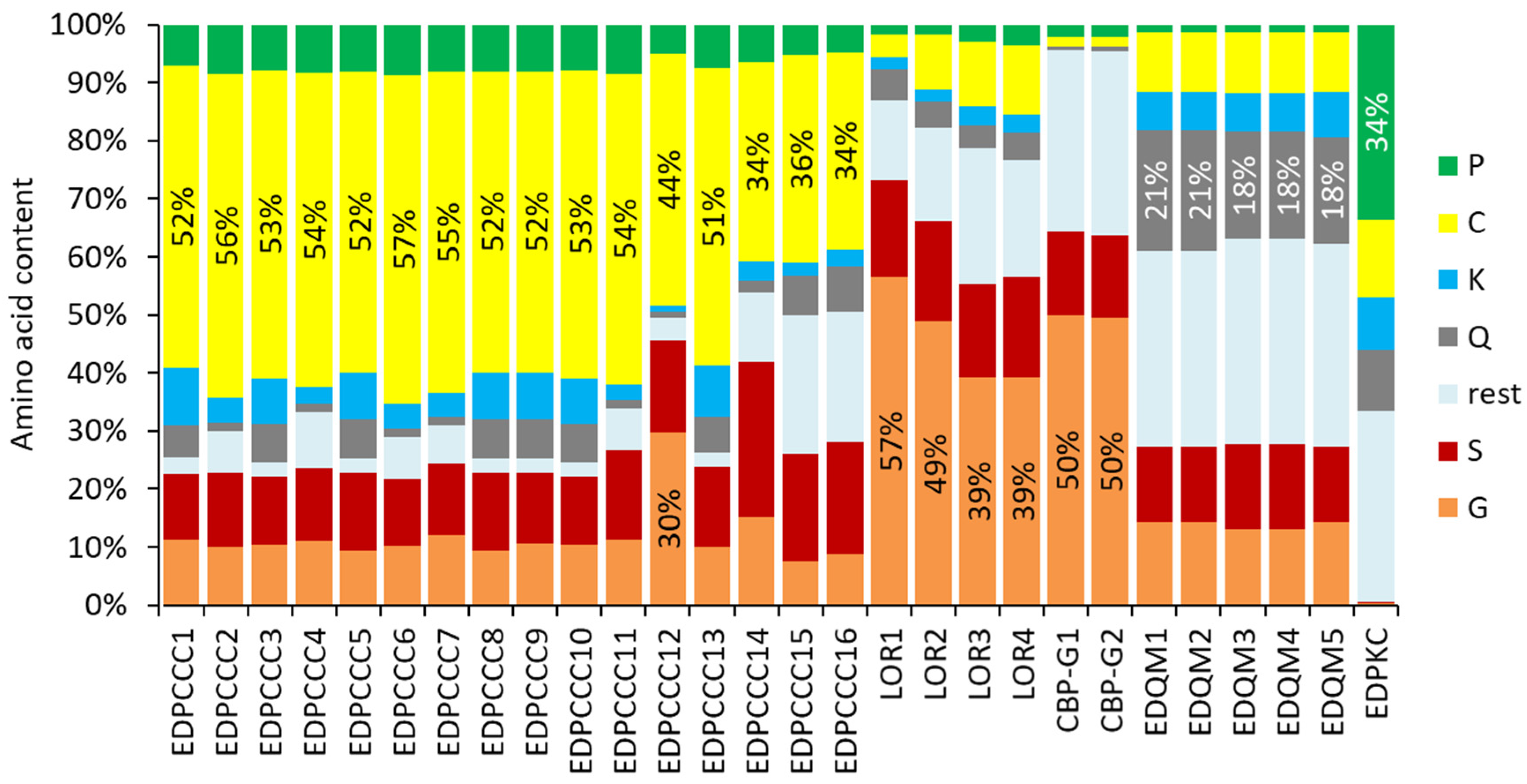
3.2. The EDPCCCs of the Common Wall Lizard Have Uniquely High Cysteine Contents
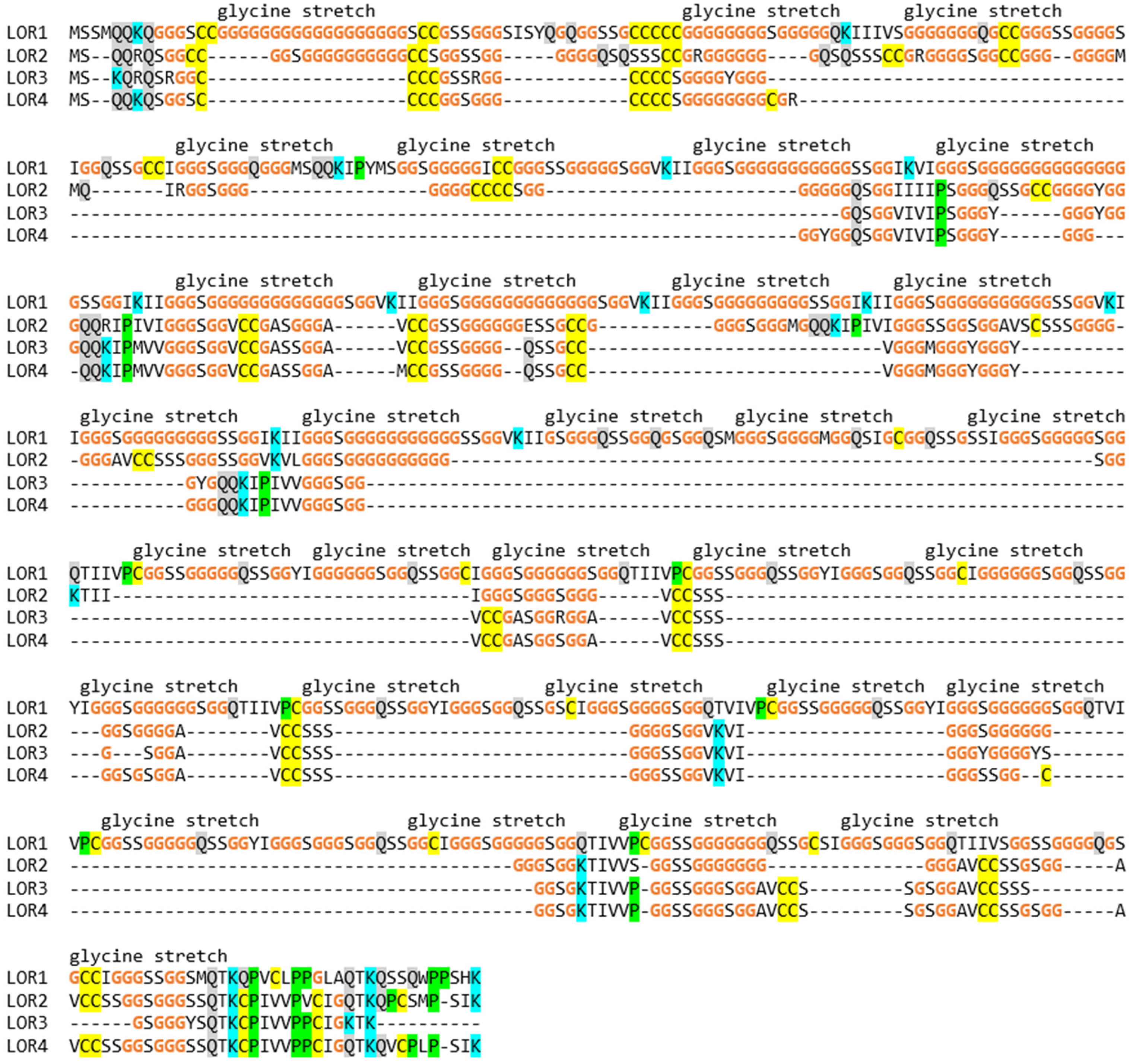
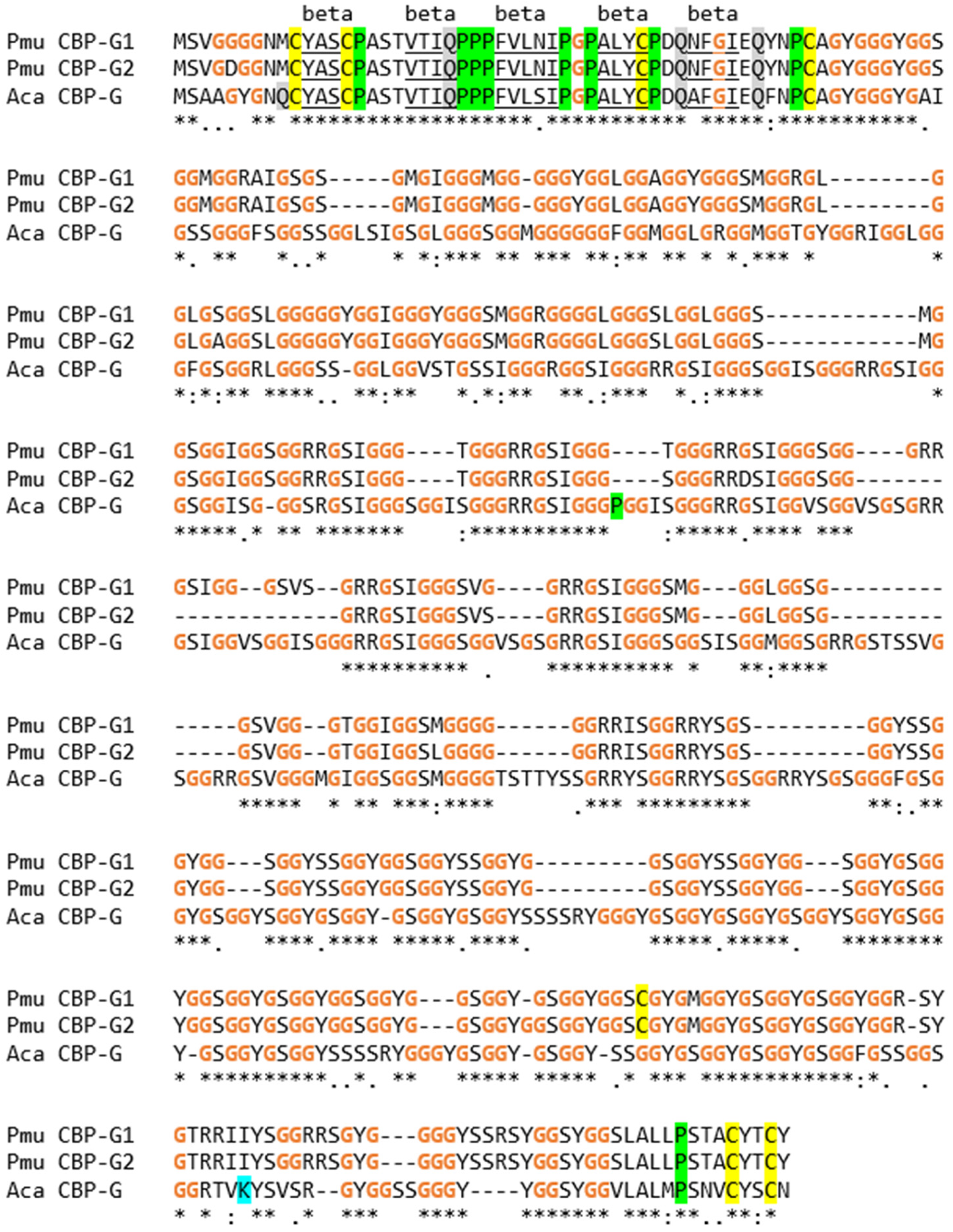
3.3. The EDC of the Wall Lizard Comprises Genes That Encode Loricrin and Corneous Beta-Proteins with Extremely High Glycine Contents
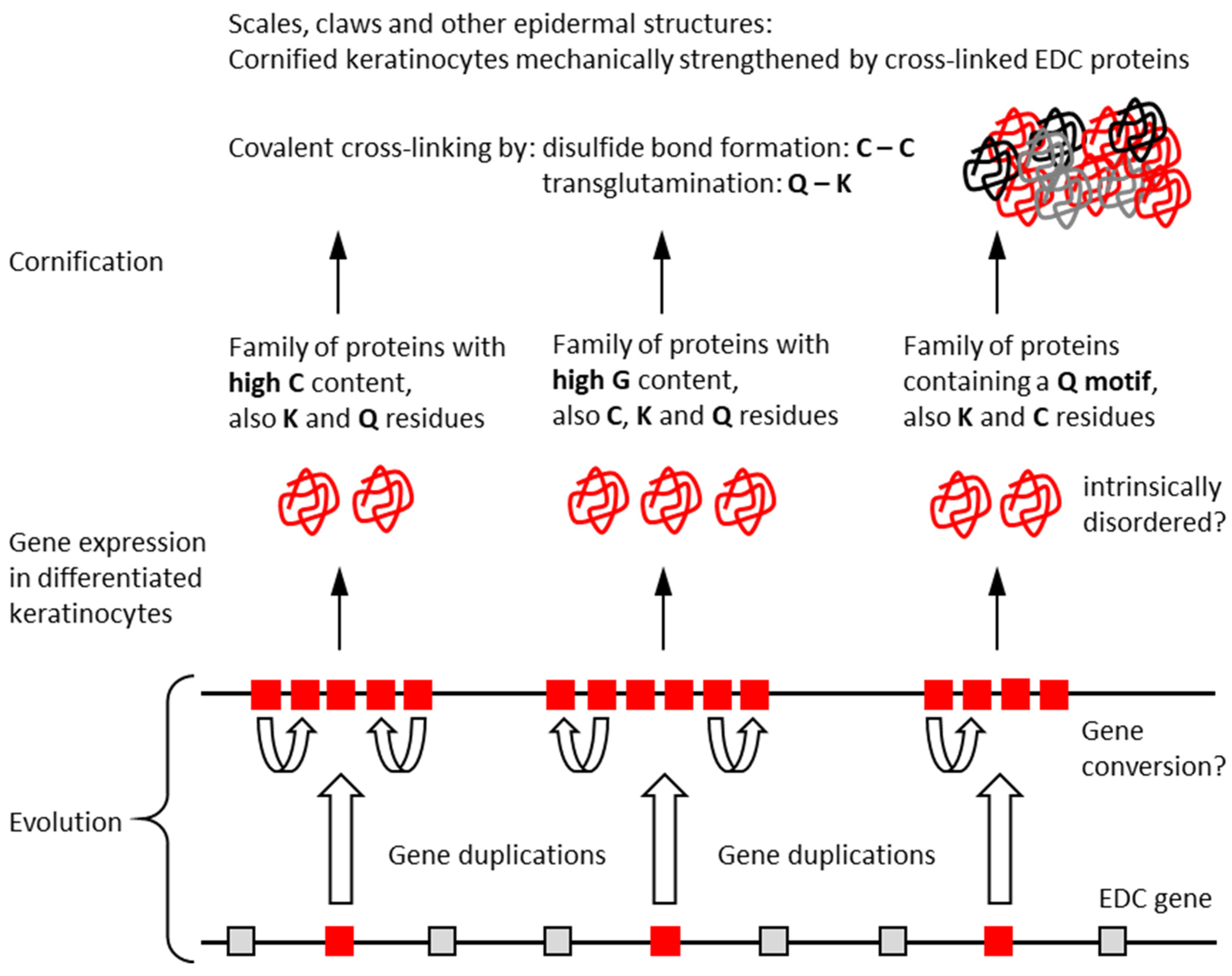
3.4. Gene Duplications Have Led to High Numbers of EDC Protein Paralogs in the Common Wall Lizard
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhart, L.; Lippens, S.; Tschachler, E.; Declercq, W. Cell death by cornification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T. Epidermal barrier development via corneoptosis: A unique form of cell death in stratum granulosum cells. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Adaptation to the land: The skin of reptiles in comparison to that of amphibians and endotherm amniotes. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2003, 298, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhouailly, D. Evo devo of the vertebrates integument. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, E.; Yenmiş, M.; Pombal, M.A.; Molist, P.; Megías, M.; Arman, S.; Veselỳ, M.; Anderson, R.; Ayaz, D. Comparison of vertebrate skin structure at class level: A review. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 3543–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.; Toulza, E.; Hsu, C.Y.; Pellerin, L.; Balica, S.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Paul, C.; Serre, G.; Jonca, N.; Simon, M. Update on the epidermal differentiation complex. Front. Biosci. (Landmark ed.) 2012, 17, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kypriotou, M.; Huber, M.; Hohl, D. The human epidermal differentiation complex: Cornified envelope precursors, S100 proteins and the ‘fused genes’ family. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, A.; Korge, B.P.; Compton, J.G.; Ziegler, A.; Steinert, P.M.; Mischke, D. Physical mapping of a functional cluster of epidermal differentiation genes on chromosome 1q21. Genomics 1993, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutteghem, A.; Djian, P.; Green, H. Ancient origin of the gene encoding involucrin, a precursor of the cross-linked envelope of epidermis and related epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15481–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guzman Strong, C.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Cheng, J.; Sears, K.E.; Segre, J.A. A milieu of regulatory elements in the epidermal differentiation complex syntenic block: Implications for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Valle, L.; Nardi, A.; Bonazza, G.; Zucal, C.; Emera, D.; Alibardi, L. Forty keratin-associated beta-proteins (beta-keratins) form the hard layers of scales, claws, and adhesive pads in the green anole lizard, Anolis carolinensis. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, B.; Mlitz, V.; Hermann, M.; Rice, R.H.; Eigenheer, R.A.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Evolutionary origin and diversification of epidermal barrier proteins in amniotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3194–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Strasser, B.; Sipos, W.; Schmidt, H.A.; Mlitz, V.; Sukseree, S.; Weissenbacher, A.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Comparative genomics identifies epidermal proteins associated with the evolution of the turtle shell. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Mlitz, V.; Strasser, B.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Identification and comparative analysis of the epidermal differentiation complex in snakes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Strasser, B.; Lachner, J.; Sukseree, S.; Sipos, W.; Weissenbacher, A.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Comparative analysis of epidermal differentiation genes of crocodilians suggests new models for the evolutionary origin of avian feather proteins. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Identification of epidermal differentiation genes of the tuatara provides insights into the early evolution of lepidosaurian skin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbinder, J.; Sachslehner, A.P.; Holthaus, K.B.; Eckhart, L. Comparative genomics of monotremes provides insights into the early evolution of mammalian epidermal differentiation genes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlitz, V.; Strasser, B.; Jaeger, K.; Hermann, M.; Ghannadan, M.; Buchberger, M.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Trichohyalin-like proteins have evolutionarily conserved roles in the morphogenesis of skin appendages. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.N.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandilands, A.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Hull, P.R.; O’Regan, G.M.; Clayton, T.H.; Watson, R.M.; Carrick, T.; Evans, A.T.; Liao, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the gene encoding filaggrin uncovers prevalent and rare mutations in ichthyosis vulgaris and atopic eczema. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, R.D.; Parry, D.A. Filamentous structure of hard β-keratins in the epidermal appendages of birds and reptiles. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 82, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Eckhart, L.; Dalla Valle, L.; Alibardi, L. Review: Evolution and diversification of corneous beta-proteins, the characteristic epidermal proteins of reptiles and birds. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2018, 330, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamilov, R.; Robinson, V.L.; Aneskievich, B.J. Seeing keratinocyte proteins through the looking glass of intrinsic disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachslehner, A.P.; Surbek, M.; Golabi, B.; Geiselhofer, M.; Jäger, K.; Hess, C.; Kuchler, U.; Gruber, R.; Eckhart, L. Transglutaminase activity is conserved in stratified epithelia and skin appendages of mammals and birds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Roop, D.R. The epidermis: Redox governor of health and diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Aguilar, R.; Reyes, F.; Kudera, J.; Hošek, J. (Eds.) The Reptile Database. Available online: http://www.reptile-database.org (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Pincheira-Donoso, D.; Bauer, A.M.; Meiri, S.; Uetz, P. Global taxonomic diversity of living reptiles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, L. The skin of Reptiles: Epidermis and dermis. In Biology of the Integument, Volume 2 Vertebrates; Bereiter-Hahn, J., Matoltsy, A.G., Sylvia-Richards, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 150–187. [Google Scholar]
- Alibardi, L. The process of cornification evolved from the initial keratinization in the epidermis and epidermal derivatives of vertebrates: A new synthesis and the case of sauropsids. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 327, 263–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnes-Mason, M.D.; Ortega, J.; Beaupre, S.J. The metabolic effort and duration of ecdysis in timber rattlesnakes: Implications for time-energy budgets of reptiles. Ecol. Evol. Physiol. 2024, 97, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, F.; Lachner, J.; Hermann, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Convergent evolution of cysteine-rich keratins in hard skin appendages of terrestrial vertebrates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A.D.; Winter, D.J. Keratin intermediate filament chains in the European common wall lizard (Podarcis muralis) and a potential keratin filament crosslinker. J. Struct. Biol. 2021, 213, 107793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, T. Duplications in corneous beta protein genes and the evolution of gecko adhesion. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2019, 59, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.; Pinho, C.; Pérez I de Lanuza, G.; Afonso, S.; Brejcha, J.; Rubin, C.J.; Wallerman, O.; Pereira, P.; Sabatino, S.J.; Bellati, A.; et al. Regulatory changes in pterin and carotenoid genes underlie balanced color polymorphisms in the wall lizard. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5633–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, P.; Pérez I de Lanuza, G.; Carneiro, M.; Andrade, P.; Pinho, C. The role of historical biogeography in shaping colour morph diversity in the common wall lizard. Mol. Ecol. 2024, 33, e17338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Miñano, M.; Uller, T.; Pettersen, A.K.; Nord, A.; Fitzpatrick, L.J.; While, G.M. Sexual color ornamentation, microhabitat choice, and thermal physiology in the common wall lizard (Podarcis muralis). J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Ultrastructural localization of alpha-keratins in the regenerating epidermis of the lizard Podarcis muralis during formation of the shedding layer. Tissue Cell 2000, 32, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Maurizii, M.G.; Taddei, C. Immunocytochemical and electrophoretic distribution of cytokeratins in the regenerating epidermis of the lizard Podarcis muralis. J. Morphol. 2000, 246, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Loricrin-like immunoreactivity during keratinization in lizard epidermis. J. Morphol. 2002, 254, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Immunolocalization of nestin in the lizard Podarcis muralis indicates up-regulation during the process of tail regeneration and epidermal differentiation. Ann. Anat. 2014, 196, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Immunolocalization of tumor suppressors arhgap28 and retinoblastoma in the lizard Podarcis muralis suggests that they contribute to the regulated regeneration of the tail. J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alföldi, J.; Di Palma, F.; Grabherr, M.; Williams, C.; Kong, L.; Mauceli, E.; Russell, P.; Lowe, C.B.; Glor, R.E.; Jaffe, J.D.; et al. The genome of the green anole lizard and a comparative analysis with birds and mammals. Nature 2011, 477, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel-Fischer, L.; Sobieszek, I.J.; Wagner, A.; Sacnun, J.M.; Watschinger, B.; Aufricht, C.; Kratochwill, K.; Herzog, R. In-depth analysis of the extracorporeal proteome adsorbed to dialysis membranes during hemodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Strasser, B.; Eckhart, L. Immunolocalization of loricrin in the maturing α-layer of normal and regenerating epidermis of the lizard Anolis carolinensis. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2015, 324, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohl, D.; Mehrel, T.; Lichti, U.; Turner, M.L.; Roop, D.R.; Steinert, P.M. Characterization of human loricrin. Structure and function of a new class of epidermal cell envelope proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6626–6636. [Google Scholar]
- Steinert, P.M.; Mack, J.W.; Korge, B.P.; Gan, S.Q.; Haynes, S.R.; Steven, A.C. Glycine loops in proteins: Their occurrence in certain intermediate filament chains, loricrins and single-stranded RNA binding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1991, 13, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, C.; Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Zhou, K.; Li, P. Expression analysis of alpha keratins and corneous beta-protein genes during embryonic development of Gekko japonicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poterlowicz, K.; Yarker, J.L.; Malashchuk, I.; Lajoie, B.R.; Mardaryev, A.N.; Gdula, M.R.; Sharov, A.A.; Kohwi-Shigematsu, T.; Botchkarev, V.A.; Fessing, M.Y. 5C analysis of the Epidermal Differentiation Complex locus reveals distinct chromatin interaction networks between gene-rich and gene-poor TADs in skin epithelial cells. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leśniak, W. Dynamics and epigenetics of the epidermal differentiation complex. Epigenomes 2024, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowman, J.E. Diversity of trichocyte keratins and keratin associated proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1054, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziller, A.; Fraissinet-Tachet, L. Metallothionein diversity and distribution in the tree of life: A multifunctional protein. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holthaus, K.B.; Sachslehner, A.P.; Steinbinder, J.; Eckhart, L. Epidermal Differentiation Genes of the Common Wall Lizard Encode Proteins with Extremely Biased Amino Acid Contents. Genes 2024, 15, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091136
Holthaus KB, Sachslehner AP, Steinbinder J, Eckhart L. Epidermal Differentiation Genes of the Common Wall Lizard Encode Proteins with Extremely Biased Amino Acid Contents. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091136
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolthaus, Karin Brigit, Attila Placido Sachslehner, Julia Steinbinder, and Leopold Eckhart. 2024. "Epidermal Differentiation Genes of the Common Wall Lizard Encode Proteins with Extremely Biased Amino Acid Contents" Genes 15, no. 9: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091136
APA StyleHolthaus, K. B., Sachslehner, A. P., Steinbinder, J., & Eckhart, L. (2024). Epidermal Differentiation Genes of the Common Wall Lizard Encode Proteins with Extremely Biased Amino Acid Contents. Genes, 15(9), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091136





