Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 in Russian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
| Population/ Country Conducting the Study | Number of Samples Analyzed | Number of Variants Found, Method of Analysis | Probands with PTPN11 (% of Variants Detected)/Number of Probands for Which a Clinic Was Available | P (Fischer) | Most Common Variant (%/Absolute Number of Person) | Delayed Growth (%/Absolute Number of Person) | P (Fischer) | Heart Defects (%/Absolute Number of Person) | P (Fischer) | Developmental Delay (%/Absolute Number of Person) | P (Fischer) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russia (this publication) | 308 (panel 23 genes) | 206 (NGS) | 105 (51%)/102 | p.Asn308Asp (21.9%/23) | 61.7%/63 | 77.4%/79 | 34.3%/35 | ||||
| China [26] | NR Inherited Disease Panel (containing 2742 genes) sequencing | 103 (NGS) | 50 (48.5%)/50 | 0.688 | p.Asn308Asp (28.0%/14) | 74%/37 | 0.302 | 82%/41 | 0.181 | 78%/39 | 0.009 |
| Italy [27] | 80 (panel 11 genes) | 37 (NGS) | 22 (59.5%)/22 | 0.457 | p.Asn308Asp (18.2%/4) | NR | NR | NR | |||
| USA [22] | 1254 (845 prenatal diagnostic + 409 postnatal) (panel 9 genes) | 145 (NGS) | 96 (66.2%) Postnatal: 63 PTPN11 (72.4%), other 24: SOS1 (8.0%), RAF1 (5.7%), BRAF (4.6%), SHOC2 (3.4%), MAP2K1 (2.3%), KRAS (2.3%), and HRAS (1.1%). Prenatal: PTPN11 37.8% (28) SOS1 27% (20) 9.5% (7) for MAP2K2, 8.1% (6) for RAF1, 6.8% (5) for BRAF, 4.1% (3) for HRAS, 2.7% (2) for KRAS and SHOC2 each, and only 1.4% (1) for MAP2K1 | 0.024 | p.Tyr63Cys (13.5%/13) | NR | NR | NR | |||
| Central European (Slovakia, Slovenia, Austria, Hungary, Czech Republic) [28] | 51 (panel 13 genes) | 35 (NGS) | 22 (62.8%)/22 | 0.336 | p.Tyr63Cys (18.2%/4) Asn308Asp (13.6%/3) | 77.2%/17 | 0.296 | 63.6%/14 | 0.79 | 40.9%/9 | 0.332 |
| Korea [29] | 59 (Sanger, 4 genes (PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, and RAF1)) | 30 | 16 (53.3%)/16 | 1 | p. Ala72Gly (2/-), p.Gln79Arg (2/-), p.Ala461Thr (2/-) | 56.2%/9 | 0.577 | 68.75%/11 | 1 | 25%/4 | 0.052 |
| Türkiye [30] | 31 (Sanger, 6 genes (PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, RAF1, SHOC2, NRAS and CBL)) | 11 | 7 (63.6%)/7 | 0.54 | p.Phe285Ser (2/-) | 71.4%/5 | 1 | 71.4%/5 | 1 | 57.1%/4 | 1 |
| Italy [31] | 40 (Sanger, 3 genes (PTPN11, KRAS, SOS1)) | 15 | 14 (93.3%)/14 | 0.044 | - | 100%/14 | 0.007 | 100%/14 | 0.015 | NR | |
| Spain [21] | 643 (Sanger, 6 genes (PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, BRAF, KRAS and HRAS)) | 230 | 172 (74.8%) 172 PTPN11+, 14 SOS1+, 9 RAF1+, 5 BRAF+ | <0.001 | p.Asn308Asp (27.3%/47) | NR | 69.7%/120 | 1 | NR | ||
| India [25] | 363 (PTPN11) | 107 (Sanger) | 107/107 | - | p.Asn308Asp (11.2%/12) | 43/40.2% | 0.005 | 62.6%/7 | 0.495 | 0 | <0.001 |
| Germany [23] | 57 (PTPN11) | 34 (Sanger) | 34/34 | - | p.Asn308Asp (17.6%/6 | 28/82.3% | 0.096 | 41.2%/14 | 0.015 | 53%/18 | 1 |
| Japan [32] | 45 (PTPN11) | 18 (Sanger) | 18/18 | - | p.Gln79Arg (16.7%/3) | 0 | <0.001 | 83.3%/15 | 0.366 | NR | |
| Italy [33] | 425 (PTPN11) | 204 (Sanger) | 204/116 | - | p.Asn308Asp (19.6%/40) | NR | - | NR | NR | ||
| Italy [34] | 84 (PTPN11) | 34 (Sanger) | 34/34 | - | p.Asn308Asp (17.6%/6) | 64.7%/22 | 1 | 58.8%/20 | 0.369 | 14.7%/5 | <0.001 |
| Germany [24] | 96 (PTPN11) | 32 (Sanger) | 32/32 | - | p.Tyr63Cys (28.1%/9) | 43.75%/14 | 0.079 | 65.6%/21 | 0.815 | 43.75%/14 | 0.39 |
| Netherlands [35] | 170 (PTPN11) | 76 (Sanger) | 76/76 | - | p.Asn308Asp (21.1%/16) | 54%/41 | 0.291 | 81.6%/62 | 0.104 | 36.8%/28 | 0.079 |
| Taiwan [36] | 34 (PTPN11) | 13 (Sanger) | 13/13 | - | p. Tyr63Cys (2/-), p.Glu139Asp (2/-), p.Met504Val (2/-) | 84.6%/11 | 0.199 | 69.2%/9 | 1 | 84.6%/11 | 0.06 |
| Greece [37] | 80 (PTPN11) | 17 (Sanger) | 17/17 | - | p.Ala188Gly (29.4%/5) | 76.5%/13 | 0.393 | 64.7%/11 | 0.773 | 64.7%/11 | 0.58 |
| Egypt [38] | NR (PTPN11) | 21 (Sanger) | 21/21 | - | NR | 71.4%/15 | 0.6 | 71.4%/15 | 1 | 52.4%/11 | 1 |
| Brazil [39] | 50 (PTPN11) | 21 (Sanger) | 21/21 | - | p.Gln79Arg (3/14.2%) | 95.2%/20 | 0.005 | 90.5%/19 | 0.078 | NR | |
| Türkiye [40] | NR (PTPN11) | 20 (Sanger) | 20 | - | p.Asn308Asp (25%/5) | 80%/16 | 0.267 | 80%/16 | 0.402 | 30%/6 | 0.118 |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aoki, Y.; Niihori, T.; Kawame, H.; Kurosawa, K.; Ohashi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Filocamo, M.; Kato, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kure, S.; et al. Germline Mutations in HRAS Proto-Oncogene Cause Costello Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brems, H.; Chmara, M.; Sahbatou, M.; Denayer, E.; Taniguchi, K.; Kato, R.; Somers, R.; Messiaen, L.; De Schepper, S.; Fryns, J.-P.; et al. Germline Loss-of-Function Mutations in SPRED1 Cause a Neurofibromatosis 1-like Phenotype. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirstea, I.C.; Kutsche, K.; Dvorsky, R.; Gremer, L.; Carta, C.; Horn, D.; Roberts, A.E.; Lepri, F.; Merbitz-Zahradnik, T.; Konig, R.; et al. A Restricted Spectrum of NRAS Mutations Causes Noonan Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeddu, V.; Di Schiavi, E.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Ma’ayan, A.; Sarkozy, A.; Fodale, V.; Cecchetti, S.; Cardinale, A.; Martin, J.; Schackwitz, W.; et al. Mutation of SHOC2 Promotes Aberrant Protein N-Myristoylation and Causes Noonan-like Syndrome with Loose Anagen Hair. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, S.; De Luca, A.; Stellacci, E.; Rossi, C.; Checquolo, S.; Lepri, F.; Caputo, V.; Silvano, M.; Buscherini, F.; Consoli, F.; et al. Heterozygous Germline Mutations in the CBL Tumor-Suppressor Gene Cause a Noonan Syndrome-like Phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niihori, T.; Aoki, Y.; Narumi, Y.; Neri, G.; Cavé, H.; Verloes, A.; Okamoto, N.; Hennekam, R.C.M.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Wieczorek, D.; et al. Germline KRAS and BRAF Mutations in Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, B.; Sarkozy, A.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Carta, C.; Oishi, K.; Martinelli, S.; Pogna, E.A.; Schackwitz, W.; Ustaszewska, A.; Landstrom, A.; et al. Gain-of-Function RAF1 Mutations Cause Noonan and LEOPARD Syndromes with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaque, M.A.; Nishizawa, T.; Komoike, Y.; Yagi, H.; Furutani, M.; Amo, R.; Kamisago, M.; Momma, K.; Katayama, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Germline Gain-of-Function Mutations in RAF1 Cause Noonan Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.E.; Araki, T.; Swanson, K.D.; Montgomery, K.T.; Schiripo, T.A.; Joshi, V.A.; Li, L.; Yassin, Y.; Tamburino, A.M.; Neel, B.G.; et al. Germline Gain-of-Function Mutations in SOS1 Cause Noonan Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubbert, S.; Zenker, M.; Rowe, S.L.; Böll, S.; Klein, C.; Bollag, G.; van der Burgt, I.; Musante, L.; Kalscheuer, V.; Wehner, L.-E.; et al. Germline KRAS Mutations Cause Noonan Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, M.; Kalidas, K.; Shaw, A.; Song, X.; Musat, D.L.; van der Burgt, I.; Brunner, H.G.; Bertola, D.R.; Crosby, A.; Ion, A.; et al. PTPN11 Mutations in Noonan Syndrome: Molecular Spectrum, Genotype-Phenotype Correlation, and Phenotypic Heterogeneity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, M.; Mehler, E.L.; Goldberg, R.; Zampino, G.; Brunner, H.G.; Kremer, H.; van der Burgt, I.; Crosby, A.H.; Ion, A.; Jeffery, S.; et al. Mutations in PTPN11, Encoding the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2, Cause Noonan Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawson, T.; Saxton, T.M. Signaling Networks—Do All Roads Lead to the Same Genes? Cell 1999, 97, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajan, M.; de Rocca Serra, A.; Valet, P.; Edouard, T.; Yart, A. SHP2 Sails from Physiology to Pathology. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natalia, B.; Gos Monika, O.E. The Rasopathies As an Example of Ras/Mapk Pathway Disturbances—Clinical Presentation and Molecular Pathogenesis of Selected Syndromes. Dev. Period Med. 2014, 18, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Schubbert, S.; Shannon, K.; Bollag, G. Hyperactive Ras in Developmental Disorders and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rocca Serra-Nédélec, A.; Edouard, T.; Tréguer, K.; Tajan, M.; Araki, T.; Dance, M.; Mus, M.; Montagner, A.; Tauber, M.; Salles, J.-P.; et al. Noonan Syndrome-Causing SHP2 Mutants Inhibit Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Release via Growth Hormone-Induced ERK Hyperactivation, Which Contributes to Short Stature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4257–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, B.D.; Tartaglia, M. Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Lentigines; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews®: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Digilio, M.C.; Conti, E.; Sarkozy, A.; Mingarelli, R.; Dottorini, T.; Marino, B.; Pizzuti, A.; Dallapiccola, B. Grouping of Multiple-Lentigines/LEOPARD and Noonan Syndromes on the PTPN11 Gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziats, M.N.; Ahmad, A.; Bernat, J.A.; Fisher, R.; Glassford, M.; Hannibal, M.C.; Jacher, J.E.; Weiser, N.; Keegan, C.E.; Lee, K.N.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Analysis of 523 Patients by Genetics Evaluation and Clinical Exome Sequencing. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquieta, B.; Santomé, J.L.; Carcavilla, A.; Guillén-Navarro, E.; Pérez-Aytés, A.; Sánchez del Pozo, J.; García-Miñaur, S.; Castillo, E.; Alonso, M.; Vendrell, T.; et al. Alterations in RAS-MAPK Genes in 200 Spanish Patients with Noonan and Other Neuro-Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous Syndromes. Genotype and Cardiopathy. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2012, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, N.T.; Wilson Mathews, D.R.; Rosenblum, L.S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, H.; Heim, R.A. Comparative Assessment of Gene-Specific Variant Distribution in Prenatal and Postnatal Cohorts Tested for Noonan Syndrome and Related Conditions. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, M.; Buheitel, G.; Rauch, R.; Koenig, R.; Bosse, K.; Kress, W.; Tietze, H.-U.; Doerr, H.-G.; Hofbeck, M.; Singer, H.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Noonan Syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2004, 144, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musante, L.; Kehl, H.G.; Majewski, F.; Meinecke, P.; Schweiger, S.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Wieczorek, D.; Hinkel, G.K.; Tinschert, S.; Hoeltzenbein, M.; et al. Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in 96 Patients with Noonan Syndrome and Five Patients with Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous Syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 11, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athota, J.P.; Bhat, M.; Nampoothiri, S.; Gowrishankar, K.; Narayanachar, S.G.; Puttamallesh, V.; Farooque, M.O.; Shetty, S. Molecular and Clinical Studies in 107 Noonan Syndrome Affected Individuals with PTPN11 Mutations. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, R.; Tan, X.; Li, N.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Molecular and Phenotypic Spectrum of Noonan Syndrome in Chinese Patients. Clin. Genet. 2019, 96, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, F.R.; Scavelli, R.; Digilio, M.C.; Gnazzo, M.; Grotta, S.; Dentici, M.L.; Pisaneschi, E.; Sirleto, P.; Capolino, R.; Baban, A.; et al. Diagnosis of Noonan Syndrome and Related Disorders Using Target next Generation Sequencing. BMC Med. Genet. 2014, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čizmárová, M.; Hlinková, K.; Bertok, S.; Kotnik, P.; Duba, H.C.; Bertalan, R.; Poločková, K.; Košťálová, Ľ.; Pribilincová, Z.; Hlavatá, A.; et al. New Mutations Associated with Rasopathies in a Central European Population and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2016, 80, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.M.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, G.-H.; Yoo, H.-W. PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, and RAF1 Gene Analysis, and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Korean Patients with Noonan Syndrome. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şimşek-Kiper, P.; Alanay, Y.; Gülhan, B.; Lissewski, C.; Türkyılmaz, D.; Alehan, D.; Çetin, M.; Utine, G.; Zenker, M.; Boduroğlu, K. Clinical and Molecular Analysis of RASopathies in a Group of Turkish Patients. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, G.B.; Baldassarre, G.; Delmonaco, A.G.; Biamino, E.; Banaudi, E.; Carta, C.; Rossi, C.; Silengo, M.C. Clinical and Molecular Characterization of 40 Patients with Noonan Syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 51, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Hasegawa, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Nagai, T.; Kinoshita, E.; Tanaka, Y.; Kanegane, H.; Ohyama, K.; Onishi, T.; Hanew, K.; et al. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 11 mutation analysis and clinical assessment in 45 patients with Noonan syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3359–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, M.; Martinelli, S.; Stella, L.; Bocchinfuso, G.; Flex, E.; Cordeddu, V.; Zampino, G.; van der Burgt, I.; Palleschi, A.; Petrucci, T.C.; et al. Diversity and Functional Consequences of Germline and Somatic PTPN11 Mutations in Human Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, A. Correlation between PTPN11 Gene Mutations and Congenital Heart Defects in Noonan and LEOPARD Syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongmans, M.; Sistermans, E.A.; Rikken, A.; Nillesen, W.M.; Tamminga, R.; Patton, M.; Maier, E.M.; Tartaglia, M.; Noordam, K.; van der Burgt, I. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Noonan Syndrome: New Data and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2005, 134A, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-S.; Lin, J.-L.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lin, S.-P.; Chao, M.-C.; Lo, F.-S. Mutational Analysis of PTPN11 Gene in Taiwanese Children with Noonan Syndrome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2007, 106, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Issakidis, M.; Gole, E.; Kosma, K.; Fryssira, H.; Fretzayas, A.; Nicolaidou, P.; Kitsiou-Tzeli, S. Phenotypic Spectrum of 80 Greek Patients Referred as Noonan Syndrome and PTPN11 Mutation Analysis: The Value of Initial Clinical Assessment. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essawi, M.L.; Ismail, M.F.; Afifi, H.H.; Kobesiy, M.M.; El Kotoury, A.; Barakat, M.M. Mutational Analysis of the PTPN11 Gene in Egyptian Patients with Noonan Syndrome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bertola, D.R.; Pereira, A.C.; Albano, L.M.J.; De Oliveira, P.S.L.; Kim, C.A.; Krieger, J.E. PTPN11 Gene Analysis in 74 Brazilian Patients with Noonan Syndrome or Noonan-like Phenotype. Genet. Test. 2006, 10, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atik, T.; Aykut, A.; Hazan, F.; Onay, H.; Goksen, D.; Darcan, S.; Tukun, A.; Ozkinay, F. Mutation Spectrum and Phenotypic Features in Noonan Syndrome with PTPN11 Mutations: Definition of Two Novel Mutations. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpont, E.I.; Pierpont, M.E.; Mendelsohn, N.J.; Roberts, A.E.; Tworog-Dube, E.; Seidenberg, M.S. Genotype Differences in Cognitive Functioning in Noonan Syndrome. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszka, P.; Porras, A.R.; Addissie, Y.A.; Moresco, A.; Medrano, S.; Mok, G.T.K.; Leung, G.K.C.; Tekendo-Ngongang, C.; Uwineza, A.; Thong, M.-K.; et al. Noonan Syndrome in Diverse Populations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertola, D.R.; Pereira, A.C.; de Oliveira, P.S.L.; Kim, C.A.; Krieger, J.E. Clinical Variability in a Noonan Syndrome Family with a New PTPN11 Gene Mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2004, 130A, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, M.; Edouard, T.; Blair, J.C.; Cappa, M. Noonan syndrome: Improving recognition and diagnosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
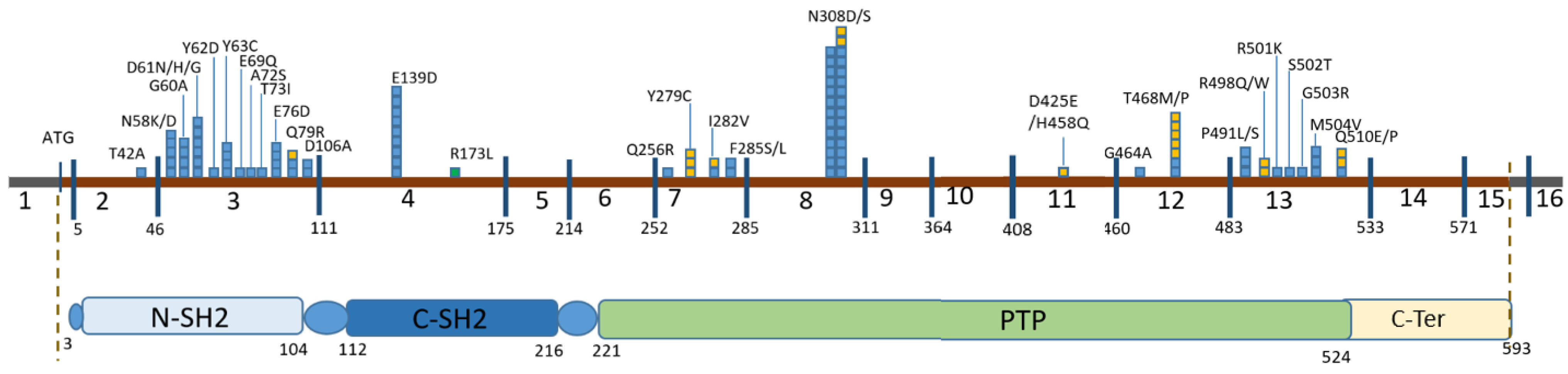

| Position in cDNA | Exon | Position in the Protein | Domain | Number of Chromosomes | Variant Pathogenicity (ACMG Criteria for Previously Undescribed Variants) | HGMD ID | Frequency by GnomAD v.2.1.1 | Frequency in RF (2600 Chromosomes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.124A>G | 2 | p.Thr42Ala | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM021125 | - | - |
| c.172A>G | 3 | p.Asn58Asp | N-SH2 | 3 | P | CM044250 | - | - |
| c.174C>A | 3 | p.Asn58Lys | N-SH2 | 2 | P | CM1619079 | - | - |
| c.179G>C | 3 | p.Gly60Ala | N-SH2 | 4 | P | CM021126 | - | - |
| c.181G>A | 3 | p.Asp61Asn | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM021127 | - | - |
| c.181G>C | 3 | p.Asp61His | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM101143 | - | - |
| c.182A>G | 3 | p.Asp61Gly | N-SH2 | 5 | P | CM013415 | - | - |
| c.184T>G | 3 | p.Tyr62Asp | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM21128 | - | - |
| c.188A>G | 3 | p.Tyr63Cys | N-SH2 | 4 | P | CM013416 | 0.00001195 | - |
| c.205G>C | 3 | p.Glu69Gln | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM030493 | - | - |
| c.214G>T | 3 | p.Ala72Ser | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM013418 | - | - |
| c.218C>T | 3 | p.Thr73Ile | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM021129 | - | - |
| c.228G>C | 3 | p.Glu76Asp | N-SH2 | 1 | P | CM013419 | - | - |
| c.228G>T | 3 | p.Glu76Asp | N-SH2 | 3 | P | CM060442 | - | - |
| c.236A>G | 3 | p.Gln79Arg | N-SH2 | 3 | P | CM013420 | - | - |
| c.317A>C | 3 | p. Asp106Ala | C-SH2 | 2 | P | CM021130 | - | - |
| c.417G>C | 4 | p.Glu139Asp | C-SH2 | 11 | P | CM021132 | - | - |
| c.417G>T | 4 | p.Glu139Asp | C-SH2 | 1 | P | CM021131 | - | - |
| c.767A>G | 7 | p.Gln256Arg | PTP | 1 | P | CM030495 | - | - |
| c.836A>G | 7 | p.Tyr279Cys | PTP | 3 | P | CM021133 | - | - |
| c.844A>G | 7 | p.Ile282Val | PTP | 2 | P | CM013421 | - | - |
| c.854T>C | 7 | p.Phe285Ser | PTP | 1 | P | CM021134 | - | - |
| c.855T>G | 7 | p.Phe285Leu | PTP | 1 | P | CM073286 | - | - |
| c.922A>G | 8 | p.Asn308Asp | PTP | 23 | P | CM013422 | 0.00001193 | - |
| c.923A>G | 8 | p.Asn308Ser | PTP | 5 | P | CM021135 | - | - |
| c.1391G>C | 12 | p.Gly464Ala | PTP | 1 | P | CM041070 | - | - |
| c.1402A>C | 12 | p.Thr468Pro | PTP | 1 | P | CM074987 | - | - |
| c.1403C>T | 12 | p.Thr468Met | PTP | 6 | P | CM021672 | 0.000003981 | - |
| c.1471C>T | 13 | p.Pro491Ser | PTP | 2 | P | CM1711582 | 0.000003976 | - |
| c.1472C>T | 13 | p.Pro491Leu | PTP | 1 | P | CM053389 | - | - |
| c.1492C>T | 13 | p.Arg498Trp | PTP | 1 | P | CM041072 | 0.000003976 | - |
| c.1493G>A | 13 | p.Arg498Gln | PTP | 1 | P (PM1, PM2, PM5, PP3, PP5) | RCV002471444.1 | - | - |
| c.1502G>A | 13 | p.Arg501Lys | PTP | 1 | P | CM021137 | - | - |
| c.1504T>A | 13 | p.Ser502Thr | PTP | 1 | P | CM022450 | - | - |
| c.1507G>A | 13 | p.Gly503Arg | PTP | 1 | P | CM060440 | - | - |
| c.1510A>G | 13 | p.Met504Val | PTP | 3 | P | CM013423 | 0.000003976 | - |
| c.1528C>G | 13 | p.Gln510Glu | PTP | 2 | P | CM055503 | - | - |
| c.1529A>C | 13 | p.Gln510Pro | PTP | 1 | P | CM043070 | - | - |
| c.518G>T | 4 | p.Arg173Leu | C-SH2 | 1 | VOUS (PM2, PP2, PP3) | - | 0.00001591 | - |
| c.1275C>G | 11 | p.Asp425Glu | PTP | 1 | VOUS (PM2, PP2, PP3) re-classified as LP (de novo) | - | - | - |
| c.1374C>G | 11 | p.His458Gln | PTP | 1 | VOUS (PM2, PP2, PP3) re-classified as LP (de novo) | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlova, A.; Guseva, D.; Demina, N.; Polyakov, A.; Ryzhkova, O. Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 in Russian Cohort. Genes 2024, 15, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030345
Orlova A, Guseva D, Demina N, Polyakov A, Ryzhkova O. Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 in Russian Cohort. Genes. 2024; 15(3):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030345
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlova, Anna, Daria Guseva, Nina Demina, Aleksander Polyakov, and Oksana Ryzhkova. 2024. "Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 in Russian Cohort" Genes 15, no. 3: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030345
APA StyleOrlova, A., Guseva, D., Demina, N., Polyakov, A., & Ryzhkova, O. (2024). Spectrum of Mutations in PTPN11 in Russian Cohort. Genes, 15(3), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030345







