Forensic STR Loci and Schizophrenia: An Exploration of Implications for Forensic Applications and Genetic Privacy
Highlights
- We found no statistically significant associations between 19 forensic STR loci and schizophrenia, even after comprehensive multiple-testing corrections.
- Among these loci, TH01 emerged as a locus of interest due to its established regulatory relationship with the dopamine-related TH gene, underscoring its relevance to neuropsychiatric research.
- The results of our study highlight potential ethical concerns related to the unintended disclosure of sensitive health information through forensic STR profiles, emphasizing the dual-use dilemma in forensic genetics.
- Through our study, we confirm that forensic STR loci remain robust tools for identification but lack evidence regarding their application in predicting psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia.
- These findings reinforce the need for updated legal and ethical frameworks in forensic DNA database management, ensuring privacy and data security as genetic technologies evolve.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection and Quality Control
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.3. PCR Amplification and Fragment Analysis
2.4. Gender Influence Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium and Comparison of 19 STR Loci
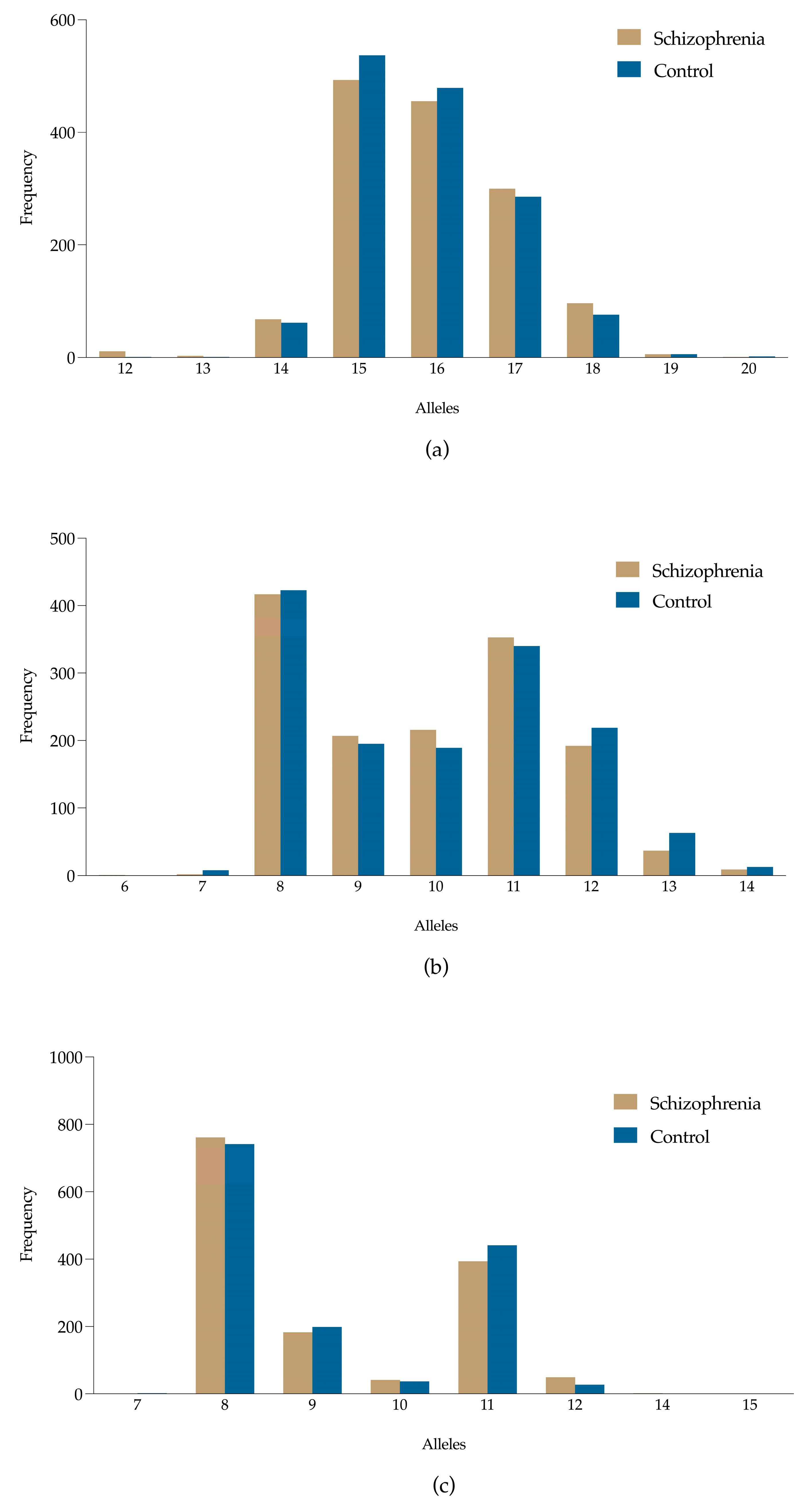
3.2. Allele Frequency Distributions of D3S1358, D13S317, and TPOX Loci
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butler, J.M. Genetics and Genomics of Core Short Tandem Repeat Loci Used in Human Identity Testing. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hares, D.R. Expanding the CODIS Core Loci in the United States. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2012, 6, e52–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanis, S.H.; Wagner, J.K. Characterization of the Standard and Recommended CODIS Markers. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, S169–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.C. Functional Implications of Genetic Variation in Non-Coding DNA for Disease Susceptibility and Gene Regulation. Clin. Sci. 2003, 104, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkin, S.M. Expandable DNA Repeats and Human Disease. Nature 2007, 447, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.E.; Todd, P.K. Native Functions of Short Tandem Repeats. eLife 2023, 12, e84043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos, M.M.; Zavaleta, Y.J.A.; Roldan, A.; Reyes, R.-J.; Guardado, M.; Chavez Rojas, B.; Nyein, T.; Rodriguez Vega, A.; Santos, M.; Huerta-Sanchez, E.; et al. Associations between Forensic Loci and Expression Levels of Neighboring Genes May Compromise Medical Privacy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121024119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyner, N.; Barash, M.; McNevin, D. Forensic Autosomal Short Tandem Repeats and Their Potential Association with Phenotype. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacewicz, R.; Babol-Pokora, K.; Berent, J.; Pepinski; Szram, S. Are Tetranucleotide Microsatellites Implicated in Neuropsychiatric Diseases? Int. Congr. Ser. 2006, 1288, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacewicz, R.; Szram, S.; Gałecki, P.; Berent, J. Will Genetic Polymorphism of Tetranucleotide Sequences Help in the Diagnostics of Major Psychiatric Disorders? Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 162, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumaji, A.; Kuroda, T.; Yamada, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Toru, M. An Association of the Polymorphic Repeat of Tetranucleotide (TCAT) in the First Intron of the Human Tyrosine Hydroxylase Gene with Schizophrenia in a Japanese Sample. J. Neural Transm. 2001, 108, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, W. Genetic polymorphism of 8 STR loci in schizophrenic patients. J. Dalian Med. Univ. 2014, 36, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coon, H.; Myles-Worsley, M.; Tiobech, J.; Hoff, M.; Rosenthal, J.; Bennett, P.; Reimherr, F.; Wender, P.; Dale, P.; Polloi, A.; et al. Evidence for a Chromosome 2p13–14 Schizophrenia Susceptibility Locus in Families from Palau, Micronesia. Mol. Psychiatry 1998, 3, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yu, W.; Fang, F. Correlation of Microsatellite DNA FGA Gene Polymorphism with Occurrence and Rehabilitation of Schizophrenia. Chin. J. Clin. Rehabil. 2004, 8, 2286–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yu, W.; Fang, F.; Wang, X. Polymorphism of Microsatellite DNA vWA in Random Population and Schizophrenic Patients. Chin. J. Clin. Rehabil. 2005, 53, 252–254. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, X. Number of STR Repeats as a Potential New Quantitative Genetic Marker for Complex Diseases, Illustrated by Schizophrenia. Biochem. Genet. 2007, 45, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Luo, H.; Sun, W.; Liu, H. Relationship between Polymorphism of Gene D8S1179, D21S11, D18S51 and Schizophrenia. J. Dalian Med. Univ. 2009, 31, 510–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ba, H.; Tan, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Yu, H. Association of Aggressive Behaviors of Schizophrenia with Short Tandem Repeats Loci. Chin. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 34, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ba, H.; Zou, H.; Zhou, X. The Association of 20 Short Tandem Repeat Loci of Autosomal Chromosome with Male Schizophrenia. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Yang, C.; Lu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, H. Review of Alternative Approaches to Calculation of a Confidence Interval for the Odds Ratio of a 2 × 2 Con-tingency Table. J. Psychiatry 2022, 35, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Amorim, D.; Rivera-Baltanás, T.; López, M.; Spuch, C.; Olivares, J.M.; Agís-Balboa, R.C. Schizophrenia: A Review of Potential Biomarkers. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 93, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modai, S.; Shomron, N. Molecular Risk Factors for Schizophrenia. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, L. Beyond Discrimination: Generative AI Applications and Ethical Challenges in Forensic Psychiatry. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1346059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanèse, V.; Biguet, N.F.; Kiefer, H.; Bayard, E.; Mallet, J.; Meloni, R. Quantitative Effects on Gene Silencing by Allelic Variation at a Tetranucleotide Microsatellite. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anney, R.J.; Olsson, C.A.; Lotfi-Miri, M.; Patton, G.C.; Williamson, R. Nicotine Dependence in a Prospective Population-Based Study of Adolescents: The Protective Role of a Functional Tyrosine Hydroxylase Polymorphism. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2004, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serretti, A.; Macciardi, F.; Verga, M.; Cusin, C.; Pedrini, S.; Smeraldi, E. Tyrosine Hydroxylase Gene Associated with Depressive Symptomatology in Mood Disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 81, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, M.; Suzuki, S.; Hinokio, Y.; Hirai, M.; Satoh, Y.; Tashiro, A.; Utsumi, A.; Awata, T.; Hongo, M.; Toyota, T. Tyrosine Hydroxylase Gene Microsatellite Polymorphism Associated with Insulin Resistance in Depressive Disorder. Metab.—Clin. Exp. 2000, 49, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, K.; Miyatake, R.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, T.; Hirao, T.; Suwaki, H. Delusional Disorder: Molecular Genetic Evidence for Dopamine Psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 26, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.-L.; Wasserman, D.; Geijer, T.; Jönsson, E.G.; Terenius, L. Tyrosine Hydroxylase Allelic Distribution in Suicide Attempters. Psychiatry Res. 1997, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ba, H.; Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, J.; Zhu, A. Association study between the genetic polymorphism of 15 STR loci and the crime of rape. Chin. J. Behav. Med. Brain Sci. 2010, 12, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Ba, H.; Gao, Z. Association Study of the Genetic Polymorphism of Fifteen Short Tandem Repeats Loci and Aggressive Violent Behavior. Chin. J. Psychiatry 2012, 45, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ba, H.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H.; Guo, W. Case-Control Study of Allele Frequencies of 15 Short Tandem Repeat Loci in Males with Impulsive Violent Behavior. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2013, 25, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chun, H.; Yu, H.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J. Association of 15 short tandem repeats loci with aggressive behavior. Chin. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 31, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guloksuz, S.; Pries, L.-K.; Delespaul, P.; Kenis, G.; Luykx, J.J.; Lin, B.D.; Richards, A.L.; Akdede, B.; Binbay, T.; Altınyazar, V.; et al. Examining the Independent and Joint Effects of Molecular Genetic Liability and Environmental Exposures in Schizophrenia: Results from the EUGEI Study. World Psychiatry 2019, 18, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekroud, A.M.; Bondar, J.; Delgadillo, J.; Doherty, G.; Wasil, A.; Fokkema, M.; Cohen, Z.; Belgrave, D.; DeRubeis, R.; Iniesta, R.; et al. The Promise of Machine Learning in Predicting Treatment Outcomes in Psychiatry. World Psychiatry 2021, 20, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F. Efficiency Evaluation and Strategy Research of National DNA Database Construction. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uberoi, D.; Palmour, N.; Joly, Y. The Advent of Forensic DNA Databases: It’s Time to Agree on Some International Governance Principles! Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2024, 72, 103095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders | Psychiatry Online. Available online: https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/book/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425787 (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- QIAamp DNA Mini and Blood Mini Handbook—EN—QIAGEN. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/gb/resources/resourcedetail?id=62a200d6-faf4-469b-b50f-2b59cf738962&lang=en (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- QubitTM dsDNA HS Assay Kit User Guide. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.cn/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/Qubit_dsDNA_HS_Assay_UG.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- QubitTM 4 Fluorometer User Guide. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.cn/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/MAN0017209_Qubit_4_Fluorometer_UG.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Graffelman, J.; Weir, B.S. Testing for Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium at Biallelic Genetic Markers on the X Chromosome. Heredity 2016, 116, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacewicz, R.; Gałecki, P. Association of the Tyrosine Hydroxylase Gene Polymorphism with Schizophrenia in the Population of Central Poland. Psychiatr. Pol. 2008, 42, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaus, S.; Mamlins, E.; Hautzel, H.; Müller, H.-W. Acute Anxiety Disorder, Major Depressive Disorder, Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia Are Related to Different Patterns of Nigrostriatal and Mesolimbic Dopamine Dysfunction. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 381–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, M.; Gabriel, L.; Daniella, N. Microdeletion of 16q24.1–Q24.2—A Unique Etiology of Lymphedema–Distichiasis Syndrome and Neurodevelopmental Disorder—Michelson—2022—American Journal of Medical Genetics Part a—Wiley Online Library. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 188, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| STR | Schizophrenia HWE-p | Control HWE-p | Allele Fisher-p 1 | Genotype Fisher-p 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D3S1358 | 0.6673 | 0.6623 | 0.0365 | 0.4579 |
| D6S1043 | 0.2895 | 0.4032 | 0.9639 | 0.5520 |
| D13S317 | 0.2897 | 0.5134 | 0.0332 | 0.0825 |
| Penta E | 0.8561 | 0.1464 | 0.5316 | 0.0381 |
| TH01 | 0.1719 | 0.2792 | 0.4401 | 0.7627 |
| D18S51 | 0.7118 | 0.2055 | 0.3929 | 0.1826 |
| D2S1338 | 0.4025 | 0.1177 | 0.8525 | 0.9520 |
| CSF1PO | 0.8570 | 0.7528 | 0.3880 | 0.7514 |
| Penta D | 0.2666 | 0.4112 | 0.9979 | 0.9789 |
| D16S539 | 0.7509 | 0.2885 | 0.4223 | 0.2831 |
| vWA | 0.4424 | 0.9972 | 0.4633 | 0.7761 |
| D21S11 | 0.4602 | 0.5158 | 0.7409 | 0.5459 |
| D7S820 | 0.6633 | 0.9355 | 0.5852 | 0.9348 |
| D5S818 | 0.1876 | 0.5141 | 0.7231 | 0.4079 |
| TPOX | 0.9957 | 0.9282 | 0.0237 | 0.3918 |
| D8S1179 | 0.6169 | 0.1156 | 0.2312 | 0.0636 |
| D12S391 | 0.2351 | 0.4518 | 0.2533 | 0.1182 |
| D19S433 | 0.8145 | 0.3474 | 0.2986 | 0.3373 |
| FGA | 0.1229 | 0.7229 | 0.7133 | 0.3778 |
| Allele | D3S1358 | D13S317 | TPOX | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia | Control | Schizophrenia | Control | Schizophrenia | Control | |
| N = 717 (%) | N = 725 (%) | N = 717 (%) | N = 725 (%) | N = 717 (%) | N = 725 (%) | |
| 6 | 1 (0.07%) | #N/A | ||||
| 7 | 2 (0.14%) | 8 (0.55%) | 2 (0.14%) | |||
| 8 | 417 (29.08%) | 423 (29.17%) | 762 (53.14%) | 741 (51.10%) | ||
| 9 | 207 (14.44%) | 195 (13.45%) | 183 (12.76%) | 199 (13.72%) | ||
| 10 | 216 (15.06%) | 189 (13.03%) | 42 (2.93%) | 38 (2.62%) | ||
| 11 | 353 (24.62%) | 340 (23.45%) | 394 (27.48%) | 442 (30.48%) | ||
| 12 | 11 (0.77%) | 1 (0.07%) | 192 (13.39%) | 219 (15.10%) | 50 (3.49%) | 28 (1.93%) |
| 13 | 3 (0.21%) | 1 (0.07%) | 37 (2.58%) | 63 (4.34%) | ||
| 14 | 68 (4.74%) | 62 (4.28%) | 9 (0.63%) | 13 (0.90%) | 2 (0.14%) | |
| 15 | 493 (34.38%) | 537 (37.03%) | 1 (0.07%) | |||
| 16 | 455 (31.73%) | 479 (33.03%) | ||||
| 17 | 300 (20.92%) | 286 (19.72%) | ||||
| 18 | 97 (6.76%) | 76 (5.24%) | ||||
| 19 | 6 (0.42%) | 6 (0.41%) | ||||
| 20 | 1 (0.07%) | 2 (0.14%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Yang, C.; Hua, Z.; Shen, Q.; Chen, A.; Ba, H.; Zhang, S. Forensic STR Loci and Schizophrenia: An Exploration of Implications for Forensic Applications and Genetic Privacy. Genes 2024, 15, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121525
Yang Q, Yang C, Hua Z, Shen Q, Chen A, Ba H, Zhang S. Forensic STR Loci and Schizophrenia: An Exploration of Implications for Forensic Applications and Genetic Privacy. Genes. 2024; 15(12):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121525
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qi, Chun Yang, Zhiqi Hua, Qi Shen, Anqi Chen, Huajie Ba, and Suhua Zhang. 2024. "Forensic STR Loci and Schizophrenia: An Exploration of Implications for Forensic Applications and Genetic Privacy" Genes 15, no. 12: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121525
APA StyleYang, Q., Yang, C., Hua, Z., Shen, Q., Chen, A., Ba, H., & Zhang, S. (2024). Forensic STR Loci and Schizophrenia: An Exploration of Implications for Forensic Applications and Genetic Privacy. Genes, 15(12), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121525








