Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Morocco: Identification of Causative Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Biochemical Analyses
2.3. Genetic Techniques
2.4. Assessment of Pathogenicity of DNA Variants
2.5. Assay for Effects on Splicing of ARSA Variant c.854+1dup
3. Results
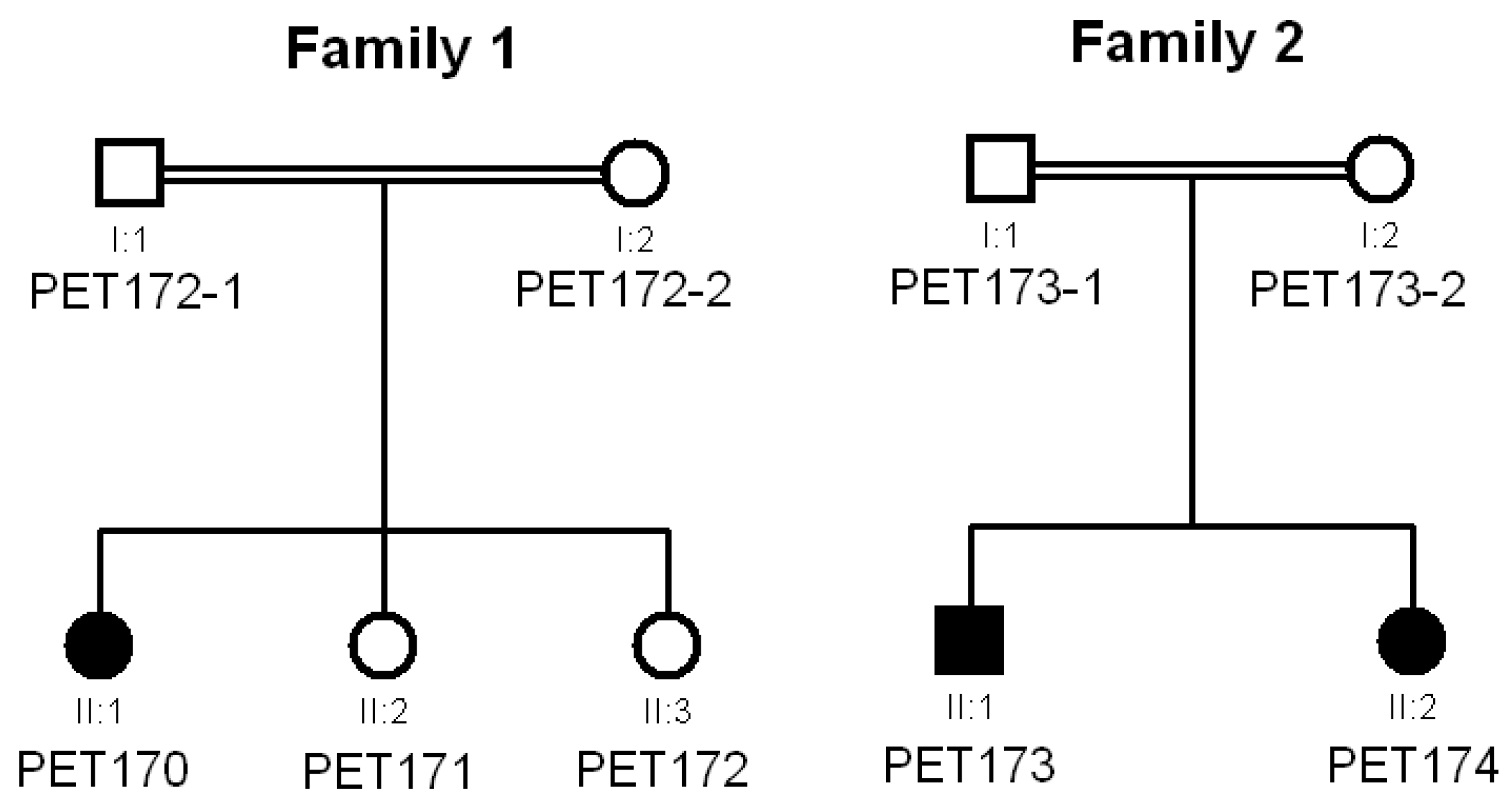
3.1. Clinical Data
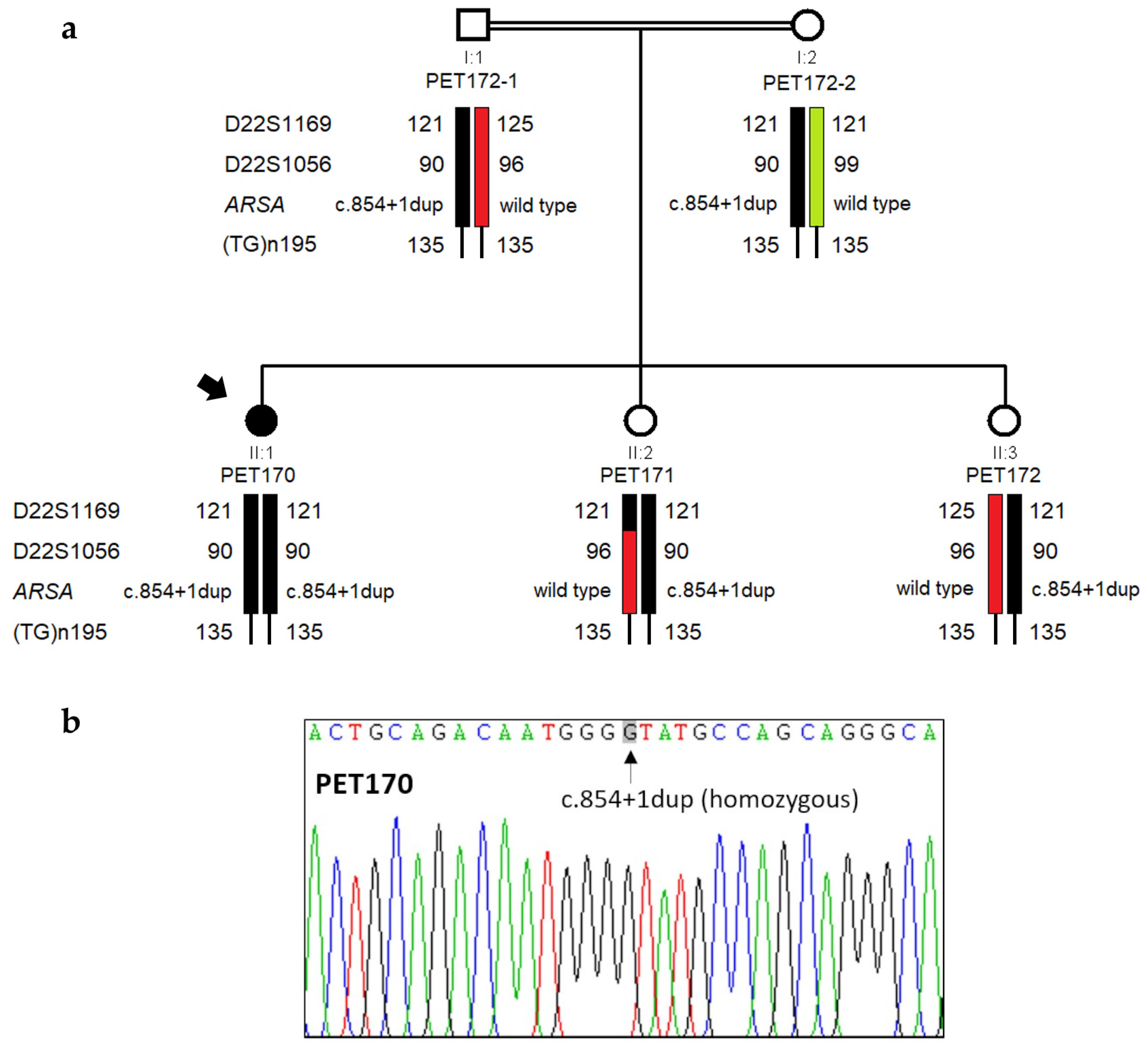
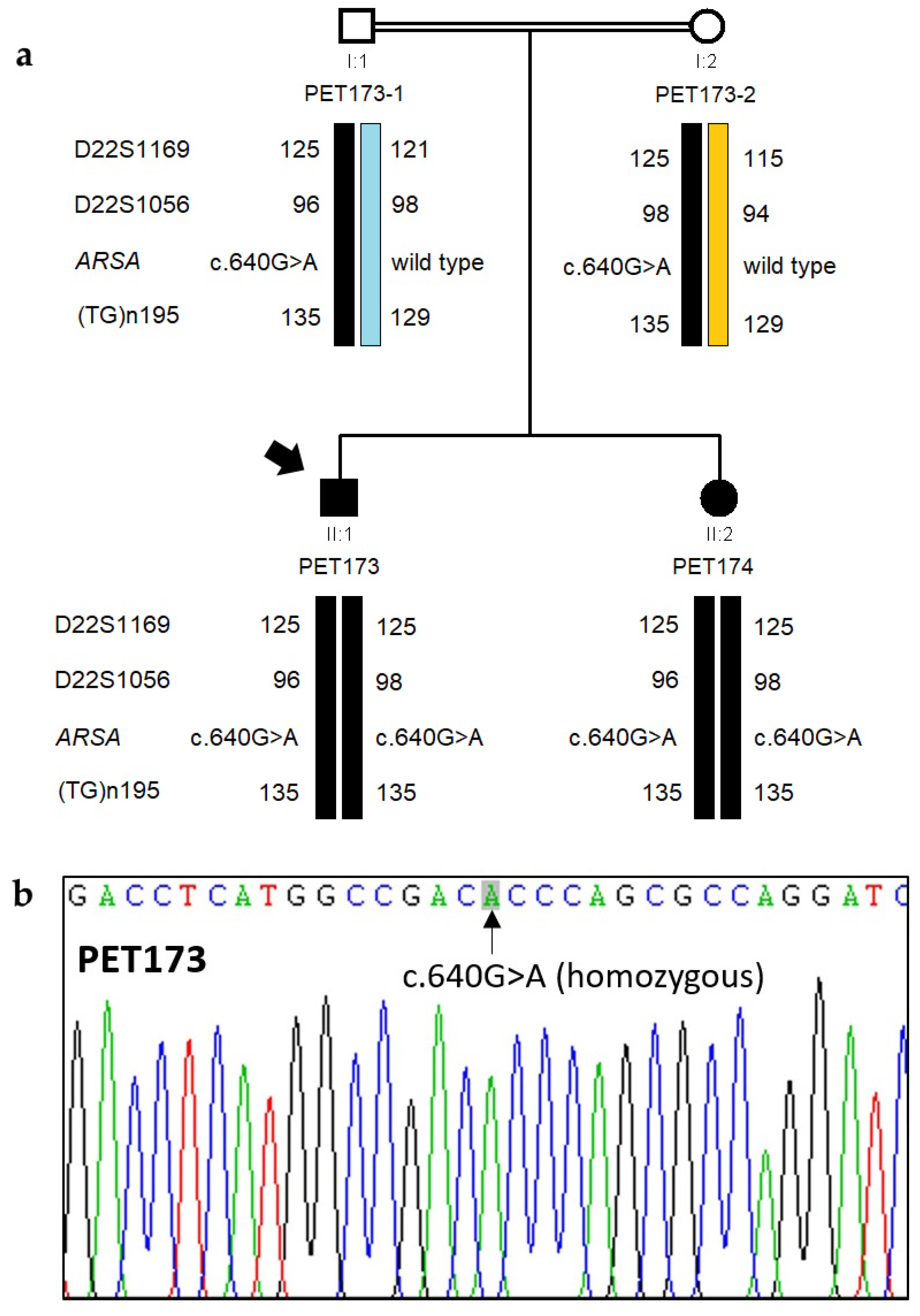
3.2. Genetic Analysis by NGS
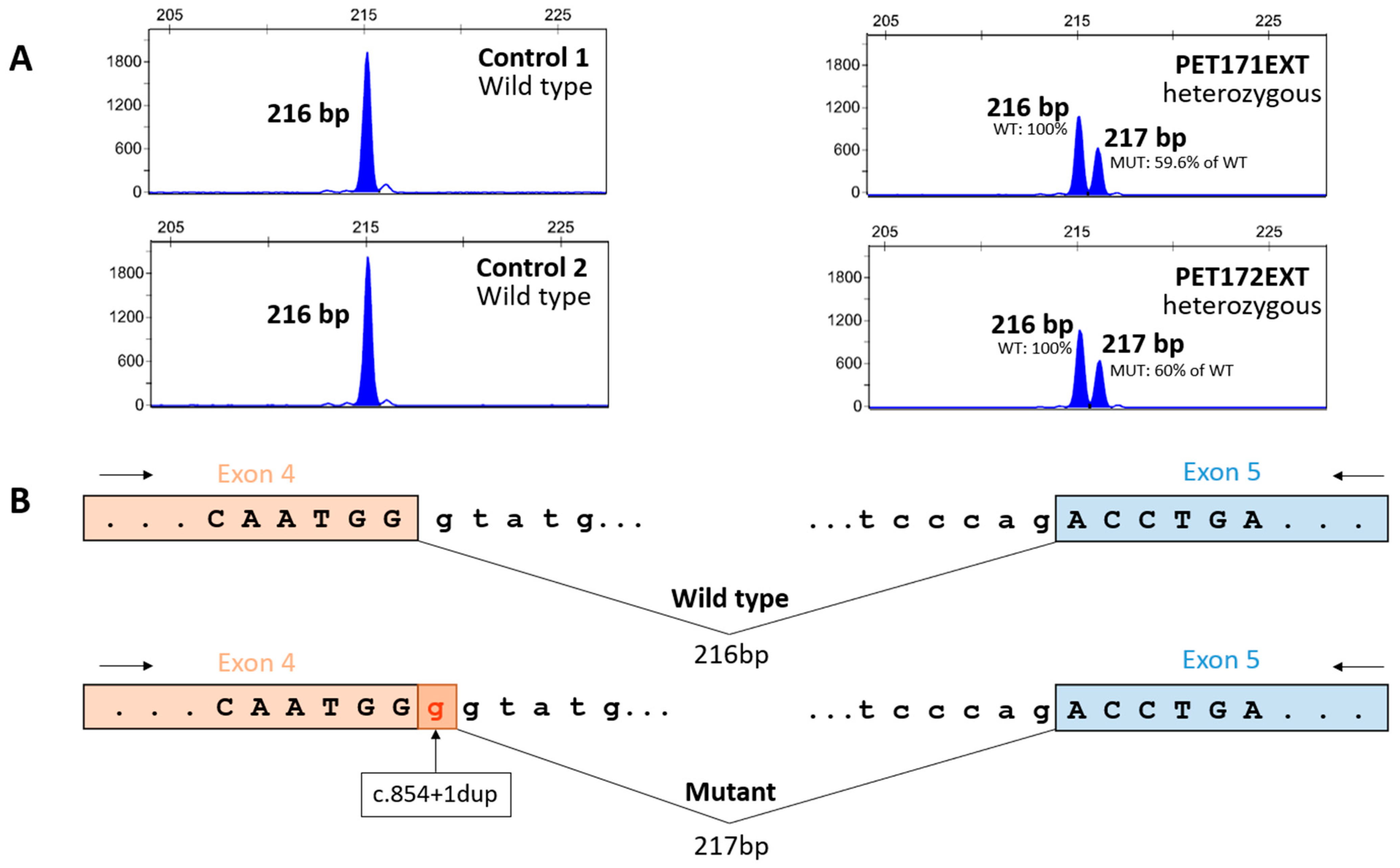
3.3. Functional Analysis of ARSA Variant c.854+1dup
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mistry, P.K.; Sadan, S.; Yang, R.; Yee, J.; Yang, M. Consequences of diagnostic delays in type 1 Gaucher disease: The need for greater awareness among hematologists-oncologists and an opportunity for early diagnosis and intervention. Am. J. Hematol. 2007, 82, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani-Montez, S.C.; Bomberger, J.; Zhang, C.; Cohen, J.; McKay, L.; Evans, W.R.H. Educational needs in diagnosing rare diseases: A multinational, multispecialty clinician survey. Genet. Med. Open 2023, 1, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, A.; Larson, S.; Carek, P.; Peabody, M.R.; Peterson, L.E.; Mainous, A.G. Prevalence and practice for rare diseases in primary care: A national cross-sectional study in the USA. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baynam, G.; Hartman, A.L.; Letinturier, M.C.V.; Bolz-Johnson, M.; Carrion, P.; Grady, A.C.; Dong, X.; Dooms, M.; Dreyer, L.; Graessner, H.; et al. Global health for rare diseases through primary care. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e1192–e1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Commision to End the Diagnostic Odyssey for Children with a Rare Disease. Ending the Diagnostic Odyssey for Children with a Rare Disease: Year One Report. 2019. Available online: https://globalrarediseasecommission.com/our-work/ (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Platt, F.M.; d’Azzo, A.; Davidson, B.L.; Neufeld, E.F.; Tifft, C.J. Lysosomal storage diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, F.M. Emptying the stores: Lysosomal diseases and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, T.; Lemire, G.; Kernohan, K.D.; Howley, H.E.; Adams, D.R.; Boycott, K.M. New diagnostic approaches for undiagnosed rare genetic diseases. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2020, 21, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, G.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Ciubotariu, C.; Piris-Villaespesa, M.; Gandía, M.; Martín-Moro, F.; Gutiérrez-Solana, L.G.; Morado, M.; López-Jiménez, J.; Sánchez-Herranz, A.; et al. Early detection of lysosomal diseases by screening of cases of idiopathic splenomegaly and/or thrombocytopenia with a next-generation sequencing gene panel. JIMD Rep. 2019, 51, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimardanova, A.A.; Chulpanova, D.S.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Mullagulova, A.I.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Allegrucci, C.; Rizvanov, A.A. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: Diagnosis, modeling, and treatment approaches. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 576221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, M.; Rodrigues, A.M.S.; Assiri, I.; Sabir, E.; Lafhal, K.; Najeh, S.; Jakani, M.; Imad, N.; Bourrahouat, A.; Ait Sab, I.; et al. Sphingolipidoses in Morocco: Chemical profiling for an affordable and rapid diagnosis strategy. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023, 168, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, R.; Narayanan, C.P.; Arunodaya, G.R.; Taranath Shetty, K. Serum arylsulfatase A assay in metachromatic leukodystrophy: An experience in a neuropsychiatric set-up. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 1995, 10, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beratis, N.G.; Aaron, A.M.; Hirschhorn, K. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: Detection in serum. J. Pediatr. 1973, 83, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacil, Z.; Babu Kumar, A.; Liao, H.C.; Auray-Blais, C.; Stark, S.; Suhr, T.R.; Scott, C.R.; Turecek, F.; Gelb, M.H. Sulfatide analysis by mass spectrometry for screening of metachromatic leukodystrophy in dried blood and urine samples. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Daiker, J.; Sadilek, M.; Ruiz-Schultz, N.; Kumar, A.B.; Norcross, S.; Dansithong, W.; Suhr, T.; Escolar, M.L.; Scott, C.R.; et al. Toward newborn screening of metachromatic leukodystrophy: Results from analysis of over 27,000 newborn dried blood spots. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Kumar, A.B.; Daiker, J.; Yi, F.; Sadilek, M.; De Mattia, F.; Fumagalli, F.; Calbi, V.; Damiano, R.; Della Bona, M.; et al. Leukocyte and dried blood spot arylsulfatase A assay by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6341–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Castillo, F.J.; Muñoz, G.; Gandía, M.; Ciubotariu, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Piris-Villaespesa, M.; Domínguez-Ruiz, M.; Calderón, E.; González-Meneses, A.; López-Jiménez, J.; et al. Genetic screening of lysosomal disorders: An account of five years’ experience with NGS-based resequencing panels. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 135, S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, H.L.; Bale, S.J.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; Berg, J.S.; Brown, K.K.; Deignan, J.L.; Friez, M.J.; Funke, B.H.; Hegde, M.R.; Lyon, E.; et al. ACMG clinical laboratory standards for next-generation sequencing. Genet. Med. 2013, 15, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VarSome: The Human Genomic Variant Search Engine. Available online: https://varsome.com/ (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Laugwitz, L.; Schoenmakers, D.H.; Adang, L.A.; Beck-Woedl, S.; Bergner, C.; Bernard, G.; Bley, A.; Boyer, A.; Calbi, V.; Dekker, H.; et al. Newborn screening in metachromatic leukodystrophy—European consensus-based recommendations on clinical management. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2024, 49, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinVar. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). Available online: https://omim.org/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Reese, M.G.; Eeckman, F.H.; Kulp, D.; Haussler, D. Improved splice site detection in Genie. J. Comput. Biol. 1997, 4, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.; Burge, C.B. Maximum entropy modeling of short sequence motifs with applications to RNA splicing signals. J. Comput. Biol. 2004, 11, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhaus, R.; Proft, S.; Schuelke, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schwarz, J.M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2021. Nucl. Acids Res. 2021, 49, W446–W451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; et al. A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes. Nature 2024, 625, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IGSR: The International Genome Sample Resource and the 1000 Genomes Project. Available online: https://www.internationalgenome.org (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Chen, L.; Yan, H.; Cao, B.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Shi, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Identification of Novel ARSA Mutations in Chinese Patients with Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Int. J. Genomics 2018, 2018, 2361068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velho, R.V.; De Pace, R.; Klünder, S.; Sperb-Ludwig, F.; Lourenço, C.M.; Schwartz, I.V.; Braulke, T.; Pohl, S. Analyses of disease-related GNPTAB mutations define a novel GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase interaction domain and an alternative site-1 protease cleavage site. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labauge, P.; Renard, D.; Castelnovo, G.; Sabourdy, F.; de Champfleur, N.; Levade, T. β-mannosidosis: A new cause of spinocerebellar ataxia. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieselmann, V.; Polten, A.; Kreysing, J.; von Figura, K. Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency: Loss of a polyadenylylation signal and N-glycosylation site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9436–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugwitz, L.; Santhanakumaran, V.; Spieker, M.; Boehringer, J.; Bender, B.; Gieselmann, V.; Beck-Woedl, S.; Bruchelt, G.; Harzer, K.; Kraegeloh-Mann, I.; et al. Extremely low arylsulfatase a enzyme activity does not necessarily cause symptoms: A long-term follow-up and review of the literature. JIMD Rep. 2022, 63, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanakumaran, V.; Groeschel, S.; Harzer, K.; Kehrer, C.; Elgün, S.; Beck-Wödl, S.; Hengel, H.; Schöls, L.; Haack, T.B.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; et al. Predicting clinical phenotypes of metachromatic leukodystrophy based on the arylsulfatase A activity and the ARSA genotype?—Chances and challenges. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 137, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Tomatsu, S.C. Mucolipidoses overview: Past, present, and future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straniero, L.; Rimoldi, V.; Monfrini, E.; Bonvegna, S.; Melistaccio, G.; Lake, J.; Soldà, G.; Aureli, M.; Shankaracharya; Keagle, P.; et al. Role of lysosomal gene variants in modulating GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease risk. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Ye, H.; De-Paula, R.B.; Mangleburg, C.G.; Wu, T.; Lee, T.V.; Li, Y.; Duong, D.; Phillips, B.; Cruchaga, C.; et al. Functional screening of lysosomal storage disorder genes identifies modifiers of α-synuclein neurotoxicity. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ham, A.; Ma, T.C.; Kuo, S.H.; Kanter, E.; Kim, D.; Ko, H.S.; Quan, Y.; Sardi, S.P.; Li, A.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy defect triggered by heterozygous GBA mutations. Autophagy 2019, 15, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.; Schapira, A.H.V. GBA variants and Parkinson disease: Mechanisms and treatments. Cells 2022, 11, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, J.; Merino, P.; Nuckols, A.; Johnson, M.; Kukar, T. Lysosome dysfunction as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases: Lessons from frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 154, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linscott, K.B.; Cassady, J.A.; Robin, N.H. Occam’s razor dulled: The occurrence of multiple genetic diagnoses. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2021, 33, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target 1 | Exons | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Annealing T (°C) | Amplicon (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gDNA, ARSA | 3–4 | Upper: CCATCGATTTCTAGGCATCCC | 64 | 708 |
| Lower: TCACCCACTATGTTCTTGGCAA | ||||
| cDNA, ARSA | 4–5 | Upper: FAM- CAGAGCTTTGCAGAGCGTTCA | 64 | 216 |
| Lower: CTCGTAGGTCGTTCCCTTTCCA | ||||
| gDNA, GNPTAB | 13 (part) | Upper: CTCAGACTCAAAGAATTAAAGGAA | 55 | 536 |
| Lower: GGGCTCTCCTTGTTGAGTTA | ||||
| gDNA, MANBA | 14 | Upper: CTTCTCTCATGCTAAGGGGCTAGT | 58 | 498 |
| Lower: GAGTTGGGTGGCTGTAGTTCC |
| Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Annealing T (°C) | Amplicon (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D22S1169 | Upper: FAM- GCACACACATGCACATAATC | 56 | 118–138 |
| Lower: AACAACTTCCAGCAGACG | |||
| D22S1056 | Upper: HEX- CACCCCCCCAAAAAAGTGT | 56 | 90–100 |
| Lower: ATGCTGTTTCTCACCCCAGT | |||
| (TG)n195 | Upper: HEX- AAACGTTTGACTGAGCCAAGCA | 56 | ~135 |
| Lower: GTCCACTCACCCACGCACAGA |
| Gene 1 | Variant | Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) 2 | ACMG Criteria | Classification | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA | Protein | |||||
| ARSA | c.640G>A | p.(Ala214Thr) | 4 × 10−6 (global) 1 × 10−5 (African) | PM1, PM2, PM5 | Likely pathogenic | [29] |
| ARSA | c.854+1dup | p.(Pro286Thr*fs2) | 0 (global) | PVS1, PM2, PP3 | Pathogenic | This work |
| GNPTAB | c.1931_1932inv | p.(Thr644Met) | 0 (global) | PS3, PS4, PM2, PM3 | Pathogenic | [30] |
| MANBA | c.1922G>A | p.(Arg641His) | 7 × 10−5 (global) 4 × 10−5 (African) | PS3, PS4, PM2, PP3 | Pathogenic | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammoud, M.; Domínguez-Ruiz, M.; Assiri, I.; Rodrigues, D.; Aboussair, N.; Lanza, V.F.; Villarrubia, J.; Colón, C.; Fdil, N.; del Castillo, F.J. Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Morocco: Identification of Causative Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS). Genes 2024, 15, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121515
Hammoud M, Domínguez-Ruiz M, Assiri I, Rodrigues D, Aboussair N, Lanza VF, Villarrubia J, Colón C, Fdil N, del Castillo FJ. Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Morocco: Identification of Causative Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS). Genes. 2024; 15(12):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121515
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammoud, Miloud, María Domínguez-Ruiz, Imane Assiri, Daniel Rodrigues, Nisrine Aboussair, Val F. Lanza, Jesús Villarrubia, Cristóbal Colón, Naima Fdil, and Francisco J. del Castillo. 2024. "Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Morocco: Identification of Causative Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)" Genes 15, no. 12: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121515
APA StyleHammoud, M., Domínguez-Ruiz, M., Assiri, I., Rodrigues, D., Aboussair, N., Lanza, V. F., Villarrubia, J., Colón, C., Fdil, N., & del Castillo, F. J. (2024). Metachromatic Leukodystrophy in Morocco: Identification of Causative Variants by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS). Genes, 15(12), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121515






