SNP Genotype Imputation in Forensics—A Performance Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Samples
2.2. Imputation
2.3. Performance Tests and Statistics
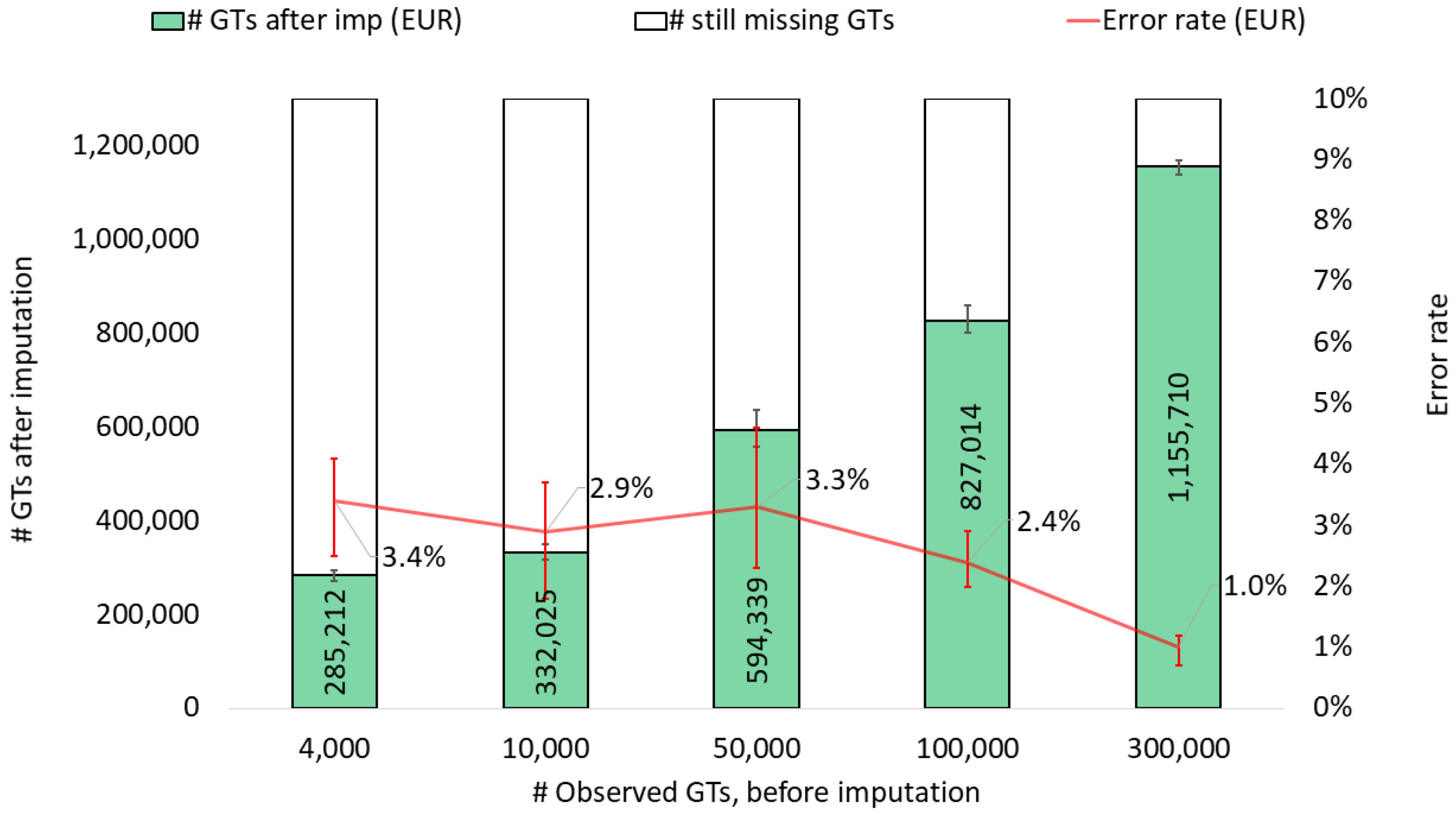
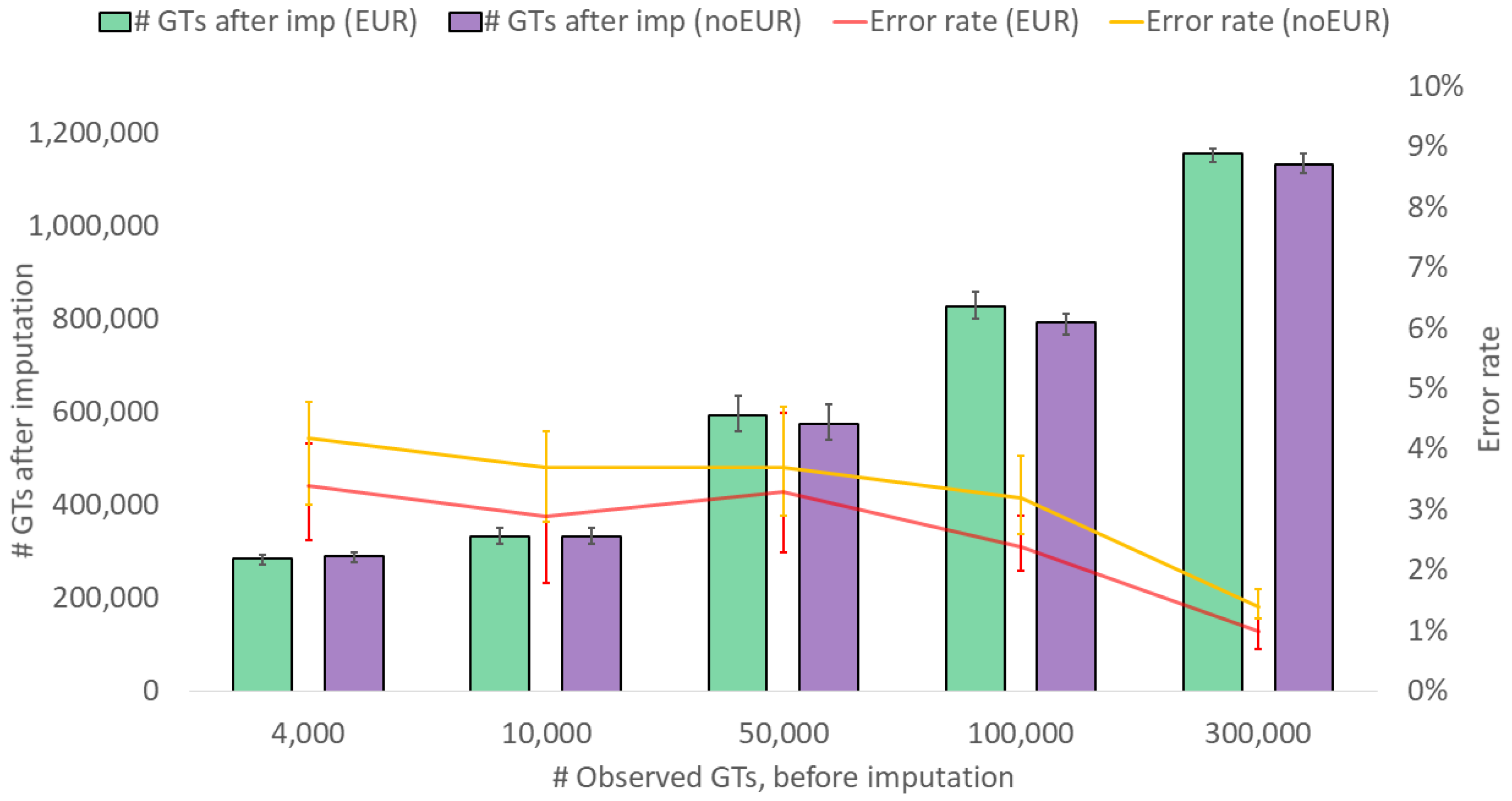
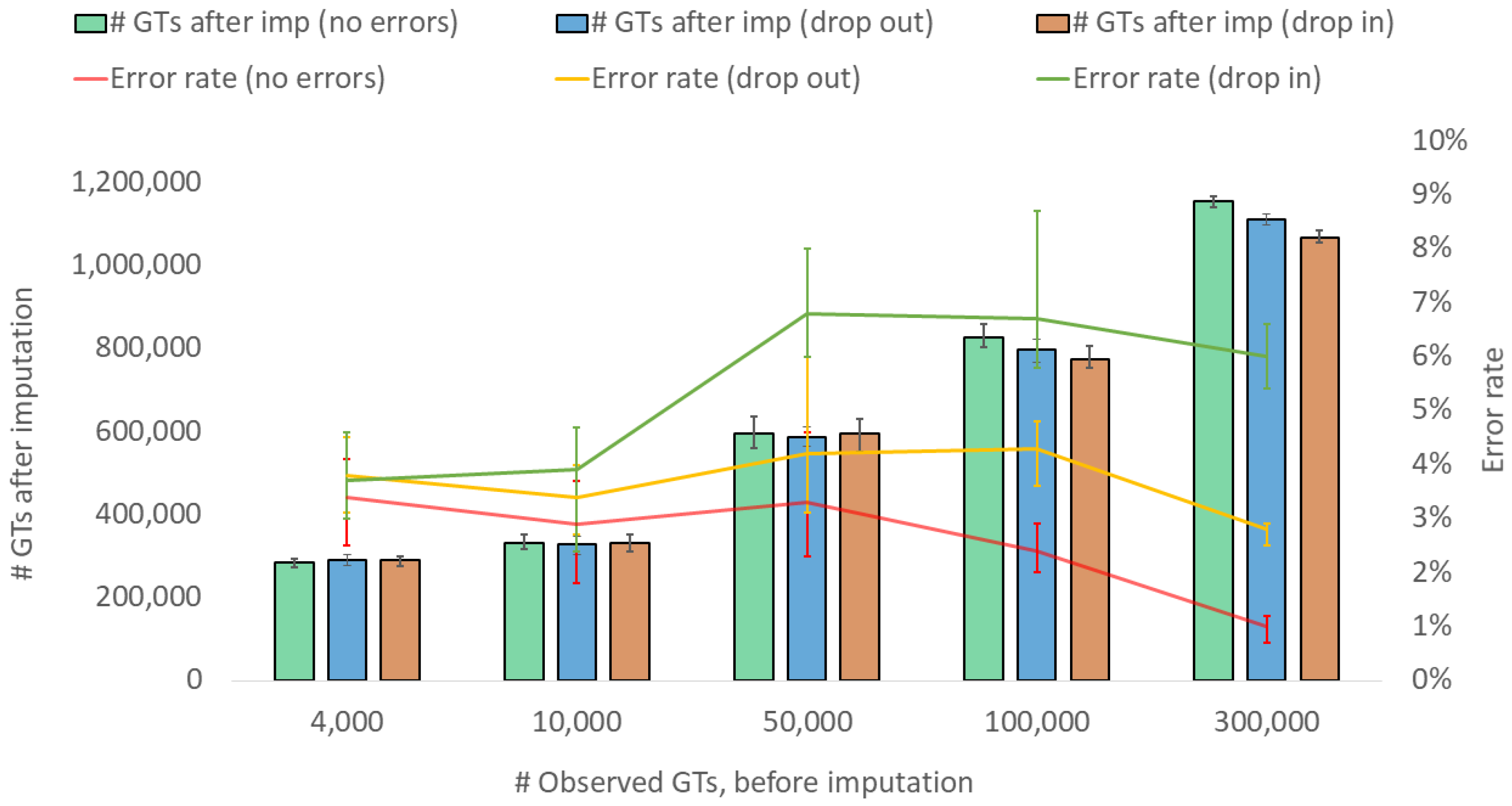
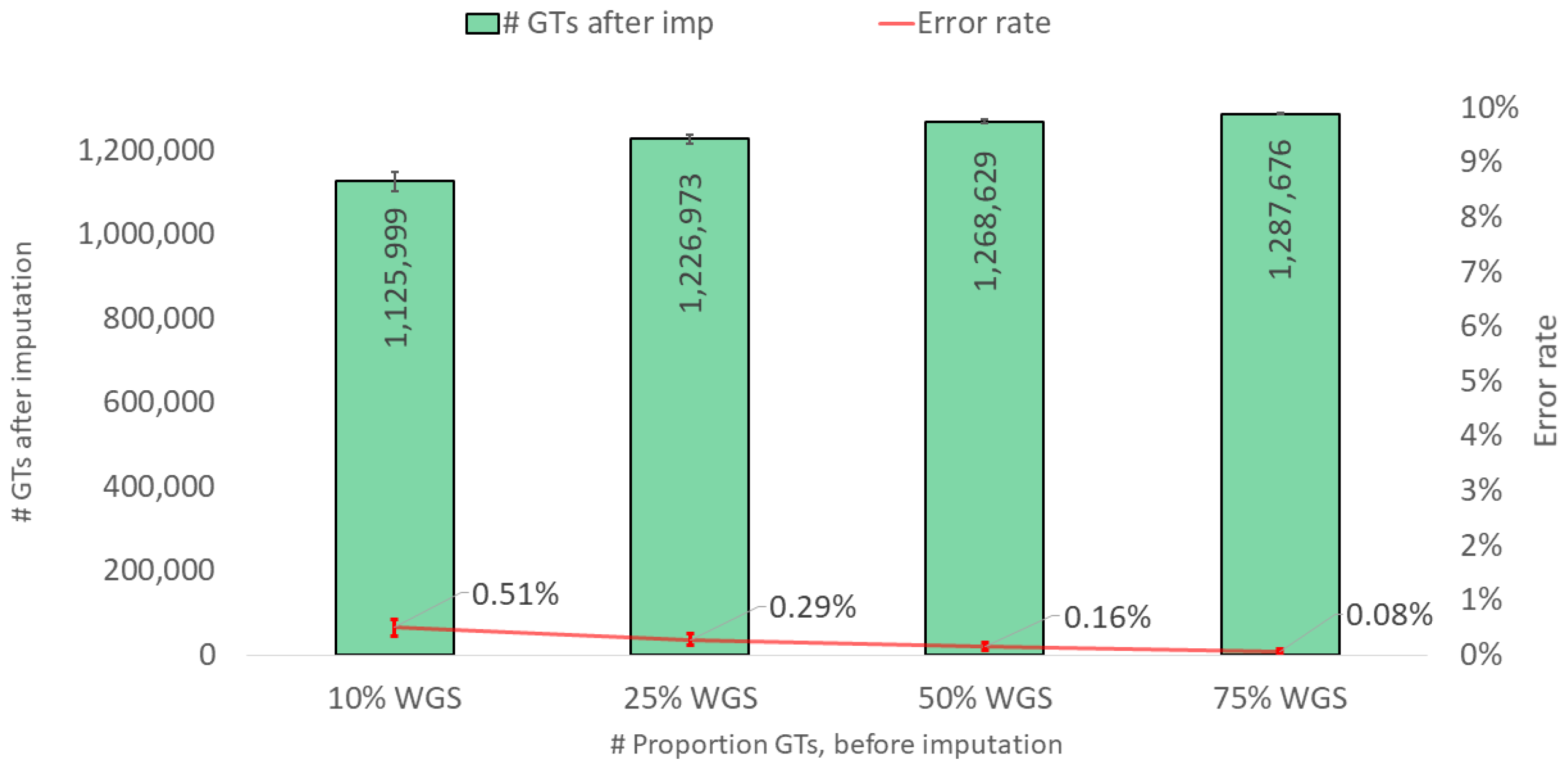
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treccanil, M.; Locatelli, E.; Patuzzo, C.; Malerba, G. A broad overview of genotype imputation: Standard guidelines, approaches, and future investigations in genomic association studies. Biocell 2023, 47, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. A One-Penny Imputed Genome from Next-Generation Reference Panels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Browning, B.L. Genotype Imputation from Large Reference Panels. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2018, 19, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bakker, P.I.; Ferreira, M.A.; Jia, X.; Neale, B.M.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Voight, B.F. Practical aspects of imputation-driven meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, R122–R128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C.C.; Su, Z.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. Designing genome-wide association studies: Sample size, power, imputation, and the choice of genotyping chip. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Edge, M.D.; Algee-Hewitt, B.F.B.; Li, J.Z.; Rosenberg, N.A. Statistical Detection of Relatives Typed with Disjoint Forensic and Biomedical Loci. Cell 2018, 175, 848–858.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappo, E.; Rosenberg, N.A. Solving the Arizona search problem by imputation. iScience 2024, 27, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmar, A.; Fagerholm, S.A.; Staaf, J.; Sjolund, P.; Ansell, R. Getting the conclusive lead with investigative genetic genealogy—A successful case study of a 16 year old double murder in Sweden. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2021, 53, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerner, A.E.; Novroski, N.M.; Mandape, S.; King, J.L.; Crysup, B.; Coble, M.D. Identifying distant relatives using benchtop-scale sequencing. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2024, 69, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Haplotype phasing: Existing methods and new developments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, S.C.; Forer, L.; Schonherr, S.; LeFaive, J.; Martins, T.; Welch, R.; Gagliano Taliun, S.A.; Braff, D.; Johnsen, J.M.; Kenny, E.E.; et al. Extent to which array genotyping and imputation with large reference panels approximate deep whole-genome sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yuan, N.; Yang, M.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Sheng, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, J. Comprehensive Assessment of Genotype Imputation Performance. Hum. Hered. 2018, 83, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahoon, J.L.; Rui, X.; Tang, E.; Simons, C.; Langie, J.; Chen, M.; Lo, Y.C.; Chiang, C.W.K. Imputation accuracy across global human populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G. Rare and common variants: Twenty arguments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; D’Atanasio, E.; Cassidy, L.M.; Scheib, C.L.; Kivisild, T. Evaluating genotype imputation pipeline for ultra-low coverage ancient genomes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M. Genetics and genomics of core short tandem repeat loci used in human identity testing. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, M.D.; Algee-Hewitt, B.F.B.; Pemberton, T.J.; Li, J.Z.; Rosenberg, N.A. Linkage disequilibrium matches forensic genetic records to disjoint genomic marker sets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5671–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomes Project, C.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Browning, S.R. Genotype Imputation with Millions of Reference Samples. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmar, A.; Sjolund, P.; Lundqvist, B.; Klippmark, T.; Algenas, C.; Green, H. Whole-genome sequencing of human remains to enable genealogy DNA database searches—A case report. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2020, 46, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.; Walichiewicz, P.; Forouzmand, E.; Barta, R.; Didier, M.; Han, Y.; Perez, J.C.; Snedecor, J.; Zlatkov, C.; Padmabandu, G.; et al. Developmental validation of the ForenSeq(R) Kintelligence kit, MiSeq FGx(R) sequencing system and ForenSeq Universal Analysis Software. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2024, 71, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorden, E.M.; Greytak, E.M.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Cady, J.; McMahon, T.P.; Armentrout, S.; Marshall, C. Extended kinship analysis of historical remains using SNP capture. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2022, 57, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmar, A.; Sturk-Andreaggi, K.; Daniels-Higginbotham, J.; Thomas, J.T.; Marshall, C. The FORCE Panel: An All-in-One SNP Marker Set for Confirming Investigative Genetic Genealogy Leads and for General Forensic Applications. Genes 2021, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howie, B.N.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.J.; Cho, H. Reconstruction of private genomes through reference-based genotype imputation. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. Fast two-stage phasing of large-scale sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Bose, M.; Bircan, K.O.; Terpolovsky, A.; Bamunusinghe, V.; Bohn, S.; Khan, U.; Novkovic, B.; Yazdi, P.G. A comparative analysis of current phasing and imputation software. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Gola, D.; Konig, I.R. Assessment of Imputation Quality: Comparison of Phasing and Imputation Algorithms in Real Data. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 724037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B. Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, D.; Tillmar, A. Forensic genealogy-A comparison of methods to infer distant relationships based on dense SNP data. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2019, 42, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Singleton, A.B.; Hardy, J.A.; Abecasis, G.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Scheet, P. Genotype-imputation accuracy across worldwide human populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kling, D.; Phillips, C.; Kennett, D.; Tillmar, A. Investigative genetic genealogy: Current methods, knowledge and practice. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2021, 52, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshyara, N.R.; Scholz, M. Impact of genetic similarity on imputation accuracy. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcu, E.; Sanna, S.; Fuchsberger, C.; Fritsche, L.G. Genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 78, 1.25.1–1.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C. Forensic genetic analysis of bio-geographical ancestry. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 18, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.D.; Nagraj, V.P.; Scholz, M.; Jessa, S.; Acevedo, C.; Ge, J.; Woerner, A.E.; Budowle, B. Evaluating the Impact of Dropout and Genotyping Error on SNP-Based Kinship Analysis With Forensic Samples. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 882268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaeddini, R.; Walsh, S.J.; Abbas, A. Forensic implications of genetic analyses from degraded DNA—A review. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2010, 4, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Willer, C.; Sanna, S.; Abecasis, G. Genotype imputation. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinacci, S.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Hofmeister, R.J.; Delaneau, O. Efficient phasing and imputation of low-coverage sequencing data using large reference panels. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tillmar, A.; Kling, D. SNP Genotype Imputation in Forensics—A Performance Study. Genes 2024, 15, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111386
Tillmar A, Kling D. SNP Genotype Imputation in Forensics—A Performance Study. Genes. 2024; 15(11):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111386
Chicago/Turabian StyleTillmar, Andreas, and Daniel Kling. 2024. "SNP Genotype Imputation in Forensics—A Performance Study" Genes 15, no. 11: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111386
APA StyleTillmar, A., & Kling, D. (2024). SNP Genotype Imputation in Forensics—A Performance Study. Genes, 15(11), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111386




