Systematic Analysis of miR-506-3p Target Genes Identified Key Mediators of Its Differentiation-Inducing Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
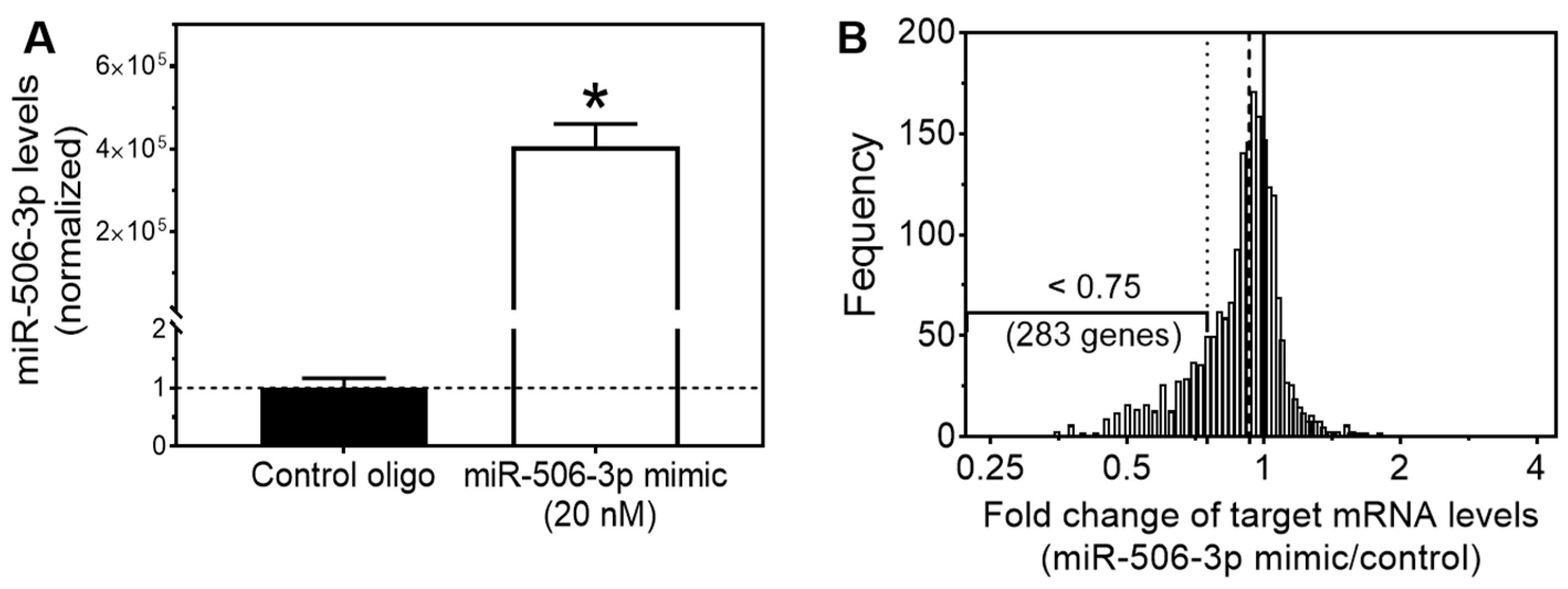
3.1. Expression Array Analysis Identified miR-506-3p Target Genes with Their mRNA Levels Down-Regulated by miR-506-3p Mimic
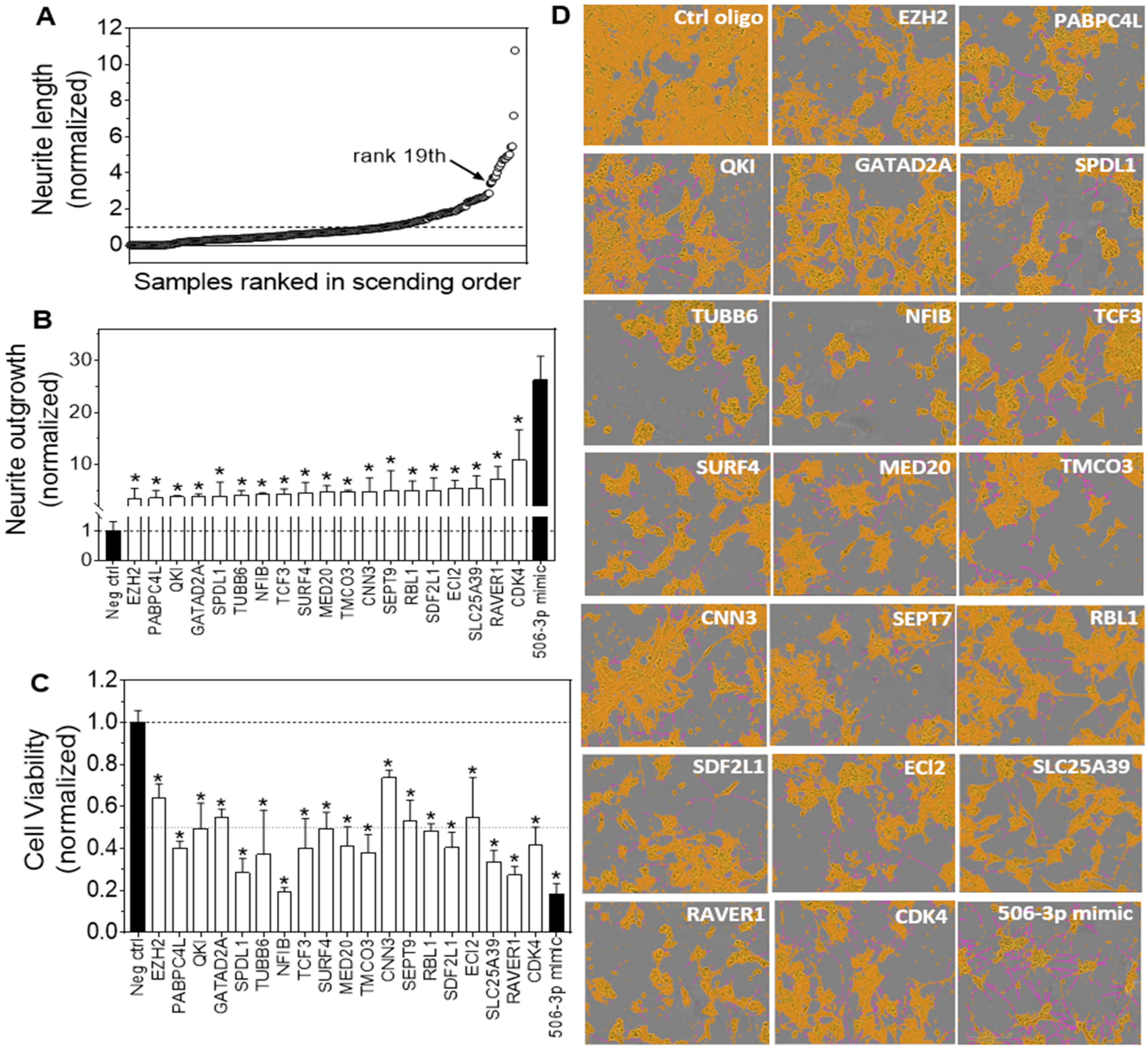
3.2. HCS Identified Target Genes of miR-506-3p with Their Knockdown by siRNAs Significantly Inducing Neurite Outgrowth in Neuroblastoma Cells
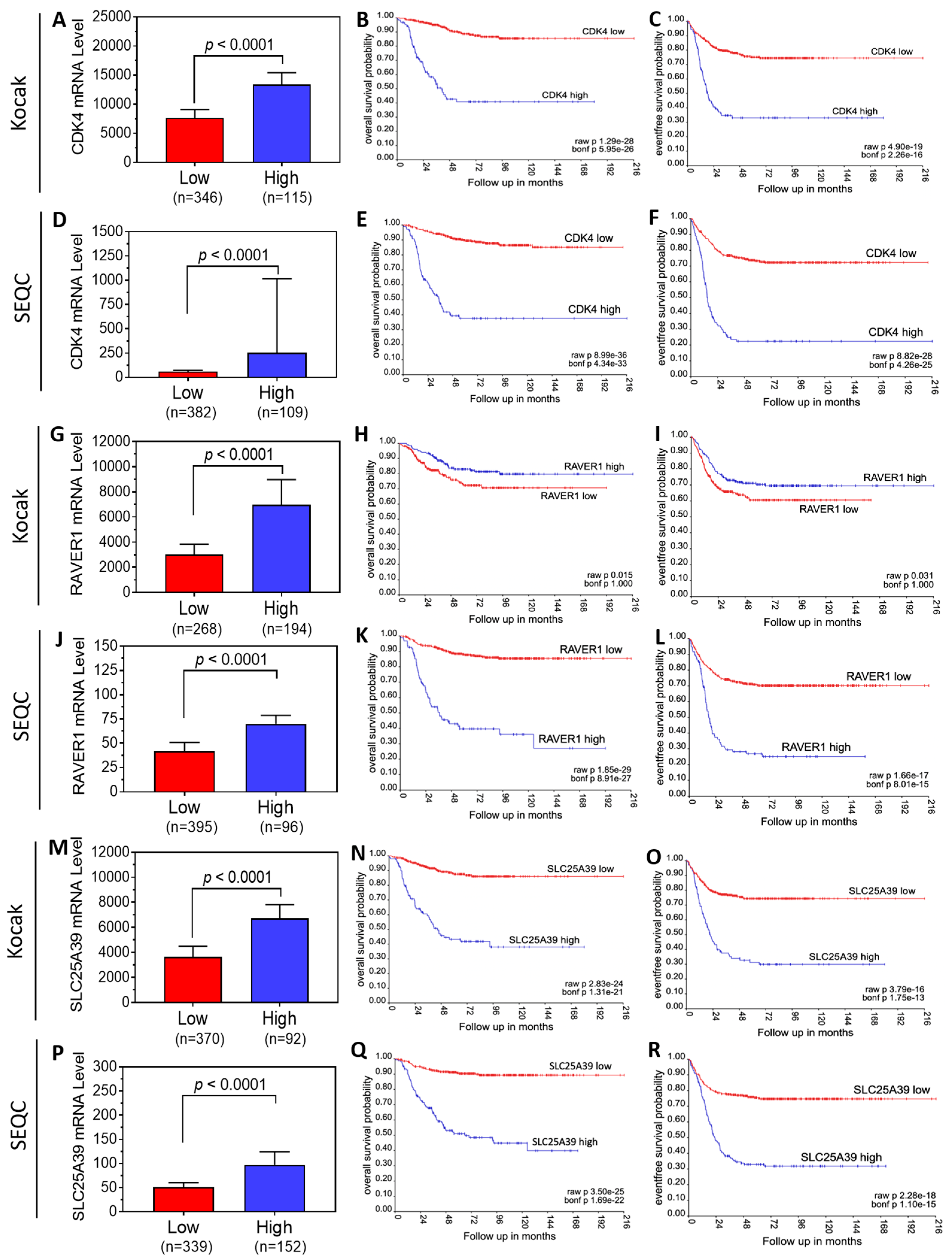
3.3. Neuroblastoma Patient Survival Analysis Shows That 13 of the 19 Target Genes Exhibit Oncogenic Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chung, C.; Boterberg, T.; Lucas, J.; Panoff, J.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Hero, B.; Bagatell, R.; Hill-Kayser, C.E. Neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68 (Suppl. S2), e28473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.U.; Shohet, J.M. Neuroblastoma: Molecular pathogenesis and therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, J.I.; Dyberg, C.; Wickstrom, M. Neuroblastoma-A Neural Crest Derived Embryonal Malignancy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marayati, R.; Williams, A.P.; Bownes, L.V.; Quinn, C.H.; Stewart, J.E.; Mroczek-Musulman, E.; Atigadda, V.R.; Beierle, E.A. Novel retinoic acid derivative induces differentiation and growth arrest in neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodenko, I.V.; Kalinovsky, D.V.; Doronin, I.I.; Deyev, S.M.; Kholodenko, R.V. Neuroblastoma Origin and Therapeutic Targets for Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7394268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, N.C.; Chung, D.H. Neuroblastoma. Adv. Pediatr. 2011, 58, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Reynolds, C.P.; Seeger, R.C.; Shimada, H.; Adkins, E.S.; Haas-Kogan, D.; Gerbing, R.B.; London, W.B.; Villablanca, J.G. Long-term results for children with high-risk neuroblastoma treated on a randomized trial of myeloablative therapy followed by 13-cis-retinoic acid: A children’s oncology group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravindan, N.; Subramanian, K.; Somasundaram, D.B.; Herman, T.S.; Aravindan, S. MicroRNAs in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis, therapy resistance, and disease evolution. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 1086–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.-W.; Chang, T.-C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, P.; Wiggins, J.F.; Daige, C.L.; Cho, C.; Omotola, M.; Brown, D.; Weidhaas, J.B.; Bader, A.G.; Slack, F.J. Systemic delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Hsiao, T.-H.; Lin, G.; Kosti, A.; Yu, X.; Suresh, U.; Chen, Y.; Tomlinson, G.E.; Pertsemlidis, A.; et al. A high-content morphological screen identifies novel microRNAs that regulate neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Takenobu, H.; Setyawati, A.N.; Akita, N.; Haruta, M.; Satoh, S.; Shinno, Y.; Chikaraishi, K.; Mukae, K.; Akter, J. EZH2 regulates neuroblastoma cell differentiation via NTRK1 promoter epigenetic modifications. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2714–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernaza, A.; Cardus, D.F.; Smith, J.L.; Partridge, V.; Baker, A.L.; Lewis, E.G.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, Z.; Du, L. Identification of CDKN3 as a Key Gene that Regulates Neuroblastoma Cell Differentiation. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Schageman, J.J.; Subauste, M.C.; Saber, B.; Hammond, S.M.; Prudkin, L.; Wistuba, I.I.; Ji, L.; Roth, J.A.; Minna, J.D.; et al. miR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor gene FUS1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Shelton, S.D.; Sung, D.C.; Li, M.; Hernandez, D.; Zhang, M.; Losiewicz, M.D.; Chen, Y.; Pertsemlidis, A.; et al. A combined gene expression and functional study reveals the crosstalk between N-Myc and differentiation-inducing microRNAs in neuroblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79372–79387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Partridge, V.; Sousares, M.; Shelton, S.D.; Holland, C.L.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Du, L. microRNA-2110 functions as an onco-suppressor in neuroblastoma by directly targeting Tsukushi. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan Koster, R.V.; Zwijnenburg, D.; Molenaar, P.; Prins, R.W.; Hoyng, L.; Versteeg, R.; Molenaar, J.; Kool, M.; Valentijn, L. R2: Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform. Available online: https://r2.amc.nl (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Zhao, Z.; Ma, X.; Sung, D.; Li, M.; Kosti, A.; Lin, G.; Chen, Y.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Hsiao, T.-H.; Du, L. microRNA-449a functions as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma through inducing cell differentiation and cell cycle arrest. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, R.; Du, L.; Zhao, Z.; McMillan, E.; Kosti, A.; Yang, C.-R.; Suraokar, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Genetic mutation of p53 and suppression of the miR-17 approximately 92 cluster are synthetic lethal in non-small cell lung cancer due to upregulation of vitamin D Signaling. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yue, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Zhao, L.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, X. CNN3 acts as a potential oncogene in cervical cancer by affecting RPLP1 mRNA expression. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Deng, X.; Guo, B.; Wu, B.; Fan, Y. Knockdown of GATAD2A suppresses cell proliferation in thyroid cancer in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y. NFIB promotes the progression of gastric cancer by upregulating circMAP7D1 to stabilize HER2 mRNA. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker-Santos, D.D.; Lonergan, K.M.; Gronostajski, R.M.; Lam, W.L. Nuclear Factor I/B: A Master Regulator of Cell Differentiation with Paradoxical Roles in Cancer. EBio. Med. 2017, 22, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanoh, S.; Kadiwala, J.; Pinte, L.; Morell, C.M.; Lenaerts, A.-S.; Vallier, L. Simultaneous depletion of RB, RBL1 and RBL2 affects endoderm differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Yan, B.; Ma, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Ji, F.; Yao, Z. Expression of TCF3 in Wilms’ tumor and its regulatory role in kidney tumor cell viability, migration and apoptosis in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, K. WNT signaling in stem cell differentiation and tumor formation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1422–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Haseeb, M.; Pirzada, R.H.; Ain, Q.U.; Choi, S. Wnt Signaling in the Regulation of Immune Cell and Cancer Therapeutics. Cells 2019, 8, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (1) Rank | (2) Name | (3) Target Site:miRNA Sequence | (4) Seed Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CDK4 3′ UTR | 5′ AGAGAUUACUUUGCUGCCUUA 3′ | 355–362 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 2 | RAVER1 3′ UTR | 5′ CCCUCCCCUUCUGAUGCCUUA 3′ | 648–655 |
| 5′ CGCUGAAACCCUGCAGCCUUA 3′ | 226–232 | ||
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 3 | SLC25A39 3′ UTR | 5′ GAGACCCAGCCAAGUGCCUUU 3′ | 69–75 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 4 | ECI2 3′ UTR | 5′ AAUAAGCUUCAUUGUGCCUUU 3′ | 87–93 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 5 | SDF2L1 3′ UTR | 5′ UAGGGGUCCUCAAGUGCCUUU 3′ | 92–98 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 6 | RBL1 3′ UTR | 5′ AGGAAUAUUUUAAGUGCCUUU 3′ | 210–216 |
| 5′ CUCACCCCUUCUCGUGCCUUU 3′ | 838–844 | ||
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 7 | SEPT9 3′ UTR | 5′ CCUGGAGCAGAAAGUGCCUUU 3′ | 626–632 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 8 | CNN3 3′ UTR | 5′ CUUUUAAGAAAAAUUGCCUUA 3′ | 127–133 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 9 | TMCO3 3′ UTR | 5′ UGUGGUGCCUGGAUGUGCCUU 3′ | 707–713 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 10 | MED20 3′ UTR | 5′ GCUGUUUUACUCCGUGCCUUA 3′ | 213–220 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 11 | SURF4 3′ UTR | 5′ UUUACAAUUUGUGAUGCCUUA 3′ | 1344–1350 |
| 5′ AAGUUUUCUAACACUGCCUUA 3′ | 1391–1397 | ||
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 12 | TCF3 3′ UTR | 5′ AGAGAAGAAAAAAAUGCCUUA 3′ | 394–401 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 13 | NFIB 3′ UTR | 5′ ACUGACUUUCUAGAUGCCUUA 3′ | 312–319 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 14 | TUBB6 3′ UTR | 5′ UUCUUGAACCCUGGUGCCUGU 3′ | 61–65 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 15 | SPDL1 3′ UTR | 5′ CUGGCAUUUUCAUGUGCCUUU3′ | 586–592 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 16 | GATAD2A 3′ UTR | 5′ GCAAAAGUGUGAGAUGCCUUA 3′ | 2316–2323 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 17 | QKI 3′ UTR | 5′ UAAAGAAAAGAAAGUGCCUUA 3′ | 8119–8125 |
| 5′ UUGUAGUUUUAAAAUGCCUUA 3′ | 6081–6087 | ||
| 5′ AUUCACAUCUCCUCUGCCUUA 3′ | 5685–5691 | ||
| 5′ UUUUAAAACUACUGUGCCUUA 3′ | 2844–2851 | ||
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 18 | PABPC4L 3′ UTR | 5′ CUUUUGUGCCCAAGUGCCUUA 3′ | 3244–3251 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ | ||
| 19 | EZH2 3′ UTR | 5′ UCCUCUGAAACAGCUGCCUUA 3′ | 36–42 |
| hsa-miR-506-3p | 3′ AGAUGAGUCUUCCCACGGAAU 5′ |
| (1) Rank | (2) Gene | (3) Dataset | (4) OS Probability | (5) EFS Probability | (6) Oncogenic Potential | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Expression Group | High Expression Group | Raw p Value | Bonf p Value | Low Expresion Group | High Expression Group | Raw p Value | Bonf p Value | ||||
| 1 | CDK4 | aKocak | 0.85 | 0.41 | 1.29 × 10−28 | 5.95 × 10−26 | 0.75 | 0.33 | 4.90 × 10−19 | 2.26 × 10−16 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.85 | 0.38 | 8.99 × 10−36 | 4.34 × 10−33 | 0.72 | 0.22 | 8.82 × 10−28 | 4.26 × 10−25 | |||
| 2 | RAVER1 | aKocak | 0.71 | 0.80 | 1.50 × 10−2 | 1 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 3.10 × 10−2 | 1 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.85 | 0.27 | 1.85 × 10−29 | 8.91 × 10−27 | 0.70 | 0.25 | 1.66 × 10−17 | 8.01 × 10−15 | |||
| 3 | SLC25A39 | aKocak | 0.86 | 0.38 | 2.83 × 10−24 | 1.31 × 10−21 | 0.74 | 0.30 | 3.79 × 10−16 | 1.75 × 10−13 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.89 | 0.40 | 3.50 × 10−25 | 1.69 × 10−22 | 0.75 | 0.32 | 2.28 × 10−18 | 1.10 × 10−15 | |||
| 4 | ECI2 | aKocak | 0.19 | 0.76 | 9.75 × 10−11 | 4.49 × 10−8 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 7.4 × 10−2 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.47 | 0.76 | 6.95 × 10−5 | 3.40 × 10−2 | 0.40 | 0.63 | 5.10 × 10−2 | 1 | |||
| 5 | SDF2L1 | aKocak | 0.80 | 0.58 | 1.69 × 10−5 | 7.81 × 10−3 | 0.71 | 0.44 | 3.45 × 10−7 | 1.59 × 10−4 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.79 | 0.45 | 9.27 × 10−8 | 4.48 × 10−5 | 0.66 | 0.30 | 2.72 × 10−9 | 1.32 × 10−6 | |||
| 6 | RBL1 | aKocak | 0.76 | 0.21 | 3.00 × 10−11 | 1.38 × 10−8 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 2.62 × 10−4 | 1.21 × 10−1 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.78 | 0.21 | 4.52 × 10−9 | 2.18 × 10−6 | 0.64 | 0.27 | 8.19 × 10−5 | 4.00 × 10−2 | |||
| 7 | SEPT9 | aKocak | 0.26 | 0.76 | 8.96 × 10−4 | 4.13 × 10−1 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 3.40 × 10−2 | 1 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.78 | 0.55 | 2.23 × 10−6 | 1.07 × 10−3 | 0.65 | 0.39 | 1.13 × 10−4 | 5.55 × 10−2 | |||
| 8 | CNN3 | aKocak | 0.80 | 0.59 | 1.68 × 10−4 | 7.7 × 10−2 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 7.45 × 10−4 | 3.43 × 10−1 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.78 | 0.54 | 1.42 × 10−5 | 6.48 × 10−3 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 5.12 × 10−1 | |||
| 9 | TMCO3 | aKocak | 0.45 | 0.87 | 6.38 × 10−16 | 2.94 × 10−13 | 0.35 | 0.77 | 8.97 × 10−15 | 4.14 × 10−12 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.48 | 0.87 | 5.30 × 10−15 | 2.56 × 10−12 | 0.42 | 0.71 | 1.32 × 10−8 | 6.37 × 10−6 | |||
| 10 | MED20 | aKocak | 0.76 | 0.63 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 1 | 0.66 | 0.47 | 2.37 × 10−3 | 1 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.79 | 0.34 | 1.56 × 10−9 | 7.55 × 10−7 | 0.66 | 0.20 | 9.70 × 10−13 | 4.68 × 10−10 | |||
| 11 | SURF4 | aKocak | 0.81 | 0.55 | 1.36 × 10−5 | 6.27 × 10−3 | 0.71 | 0.44 | 3.29 × 10−5 | 1.5 × 10−2 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.81 | 0.36 | 4.21 × 10−20 | 2.03 × 10−17 | 0.67 | 0.27 | 2.84 × 10−14 | 1.37 × 10−11 | |||
| 12 | TCF3 | aKocak | 0.79 | 0 | 9.85 × 10−32 | 4.54 × 10−29 | 0.68 | 0 | 1.75 × 10−15 | 8.09 × 10−13 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.82 | 0.22 | 2.25 × 10−34 | 1.09 × 10−31 | 0.68 | 0.16 | 1.76 × 10−19 | 8.49 × 10−17 | |||
| 13 | NFIB | aKocak | 0.83 | 0.52 | 2.02 × 10−10 | 9.29 × 10−8 | 0.69 | 0.49 | 1.18 × 10−4 | 5.4 × 10−2 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.82 | 0.45 | 9.16 × 10−14 | 4.42 × 10−11 | 0.67 | 0.37 | 1.69 × 10−8 | 8.16 × 10−6 | |||
| 14 | TUBB6 | aKocak | 0.55 | 0.87 | 2.91 × 10−15 | 1.34 × 10−12 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 1.30 × 10−8 | 6.00 × 10−6 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.80 | 0.53 | 1.41 × 10−6 | 6.80 × 10−4 | 0.67 | 0.34 | 6.41 × 10−8 | 3.10 × 10−5 | |||
| 15 | SPDL1 | aKocak | 0.77 | 0.40 | 1.25 × 10−7 | 5.75 × 10−5 | 0.67 | 0.28 | 6.92 × 10−7 | 3.19 × 10−4 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.87 | 0.47 | 5.38 × 10−17 | 2.60 × 10−14 | 0.71 | 0.40 | 5.31 × 10−13 | 2.57 × 10−10 | |||
| 16 | GATAD2A | aKocak | 0.81 | 0.39 | 2.75 × 10−20 | 1.27 × 10−17 | 0.70 | 0.34 | 4.08 × 10−10 | 1.88 × 10−7 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.81 | 0.29 | 4.50 × 10−27 | 2.17 × 10−24 | 0.67 | 0.16 | 4.74 × 10−18 | 2.29 × 10−15 | |||
| 17 | QKI | aKocak | 0.54 | 0.79 | 2.02 × 10−4 | 9.3 × 10−2 | 0.45 | 0.68 | 2.14 × 10−3 | 9.87 × 10−1 | No |
| sSEQC | 0.81 | 0.64 | 2.09 × 10−3 | 1 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 1.70 × 10−2 | 1 | |||
| 18 | PABP4CL | aKocak | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.77 | 0.25 | 6.58 × 10−7 | 3.18 × 10−4 | 0.63 | 0.27 | 5.30 × 10−4 | 2.56 × 10−1 | |||
| 19 | EZH2 | aKocak | 0.78 | 0.43 | 2.28 × 10−4 | 1.05 × 10−1 | 0.68 | 0.33 | 6.76 × 10−7 | 3.12 × 10−4 | Yes |
| sSEQC | 0.80 | 0.46 | 1.48 × 10−5 | 7.15 × 10−3 | 0.65 | 0.43 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 6.43 × 10−3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardus, D.F.; Smith, M.T.; Vernaza, A.; Smith, J.L.; Del Buono, B.; Parajuli, A.; Lewis, E.G.; Mesa-Diaz, N.; Du, L. Systematic Analysis of miR-506-3p Target Genes Identified Key Mediators of Its Differentiation-Inducing Function. Genes 2024, 15, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101268
Cardus DF, Smith MT, Vernaza A, Smith JL, Del Buono B, Parajuli A, Lewis EG, Mesa-Diaz N, Du L. Systematic Analysis of miR-506-3p Target Genes Identified Key Mediators of Its Differentiation-Inducing Function. Genes. 2024; 15(10):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101268
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardus, Daniela F., Mitchell T. Smith, Alexandra Vernaza, Jadyn L. Smith, Brynn Del Buono, Anupa Parajuli, Emma G. Lewis, Nakya Mesa-Diaz, and Liqin Du. 2024. "Systematic Analysis of miR-506-3p Target Genes Identified Key Mediators of Its Differentiation-Inducing Function" Genes 15, no. 10: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101268
APA StyleCardus, D. F., Smith, M. T., Vernaza, A., Smith, J. L., Del Buono, B., Parajuli, A., Lewis, E. G., Mesa-Diaz, N., & Du, L. (2024). Systematic Analysis of miR-506-3p Target Genes Identified Key Mediators of Its Differentiation-Inducing Function. Genes, 15(10), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101268






