MAPT Locus in Parkinson’s Disease Patients of Ashkenazi Origin: A Stratified Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Standard Protocol Approvals, Registrations, and Patient Consents
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Quality Filters
2.4. Variant Annotations
2.5. Genotyping
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
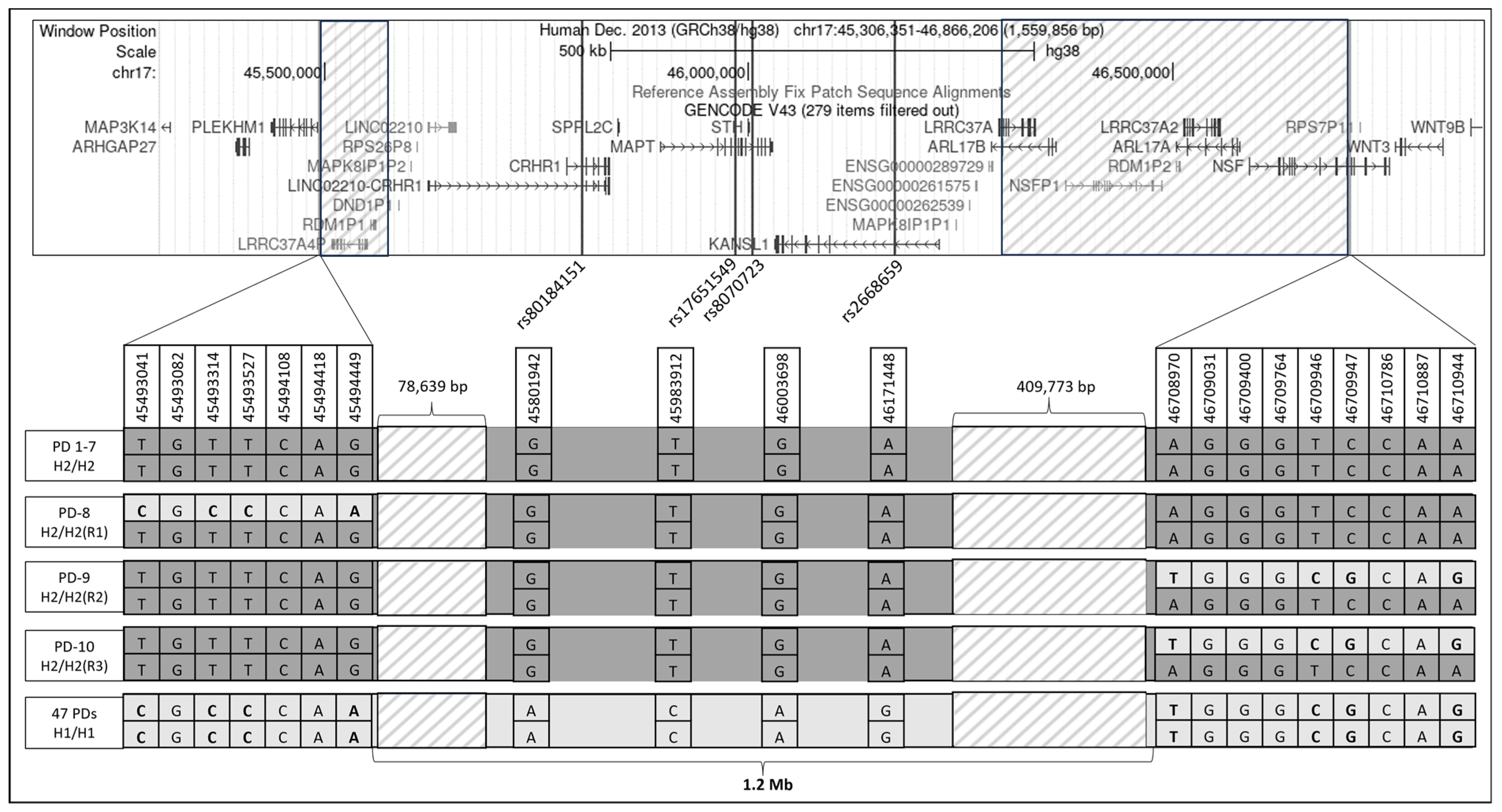
3.1. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
3.2. H2 Haplotype Analysis
3.3. H2 Is Associated with All Subgroups of PD
3.4. H2 Is Not Associated with Age at Motor Symptom Onset
3.5. Structural Variations in H2 Haplotype
3.6. The Effect of H2 Haplotype on RNA Expression and Splice Variant Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.A.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefansson, H.; Helgason, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Masson, G.; Barnard, J.; Baker, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; Ingason, A.; Gudnadottir, V.G.; et al. A common inversion under selection in Europeans. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skipper, L.; Wilkes, K.; Toft, M.; Baker, M.; Lincoln, S.; Hulihan, M.; Ross, O.A.; Hutton, M.; Aasly, J.; Farrer, M. Linkage disequilibrium and association of MAPT H1 in Parkinson disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, P.; Ezquerra, M.; Perez, J.C.; Chakraverty, S.; Norton, J.; Racette, B.A.; McKeel, D.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Tolosa, E.; Goate, A.M. Novel haplotypes in 17q21 are associated with progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, G.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Vronskaya, M.; Lambert, J.-C.; Chung, J.; Naj, A.C.; Kunkle, B.W.; Wang, L.-S.; Bis, J.C.; Bellenguez, C.; et al. A novel Alzheimer disease locus located near the gene encoding tau protein. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargini, R.; Segura-Collar, B.; Sánchez-Gómez, P. Novel Functions of the Neurodegenerative-Related Gene Tau in Cancer. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andorfer, C.; Kress, Y.; Espinoza, M.; de Silva, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Barde, Y.-A.; Duff, K.; Davies, P. Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettger, L.M.; Handsaker, R.E.; Zody, M.C.; McCarroll, S.A. Structural haplotypes and recent evolution of the human 17q21.31 region. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, O.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Cohen-Avinoam, D.; Shiner, T.; Thaler, A.; Cedarbaum, J.M.; John, S.; Lalioti, M.; Gurevich, T.; Bar-Shira, A.; et al. Revisiting the non-Gaucher-GBA-E326K carrier state: Is it sufficient to increase Parkinson’s disease risk? Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, K.; Rudakou, U.; Gan-Or, Z. New therapeutic approaches to Parkinson’s disease targeting GBA, LRRK2 and Parkin. Neuropharmacology 2022, 202, 108822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacic, V.; Ozelius, L.J.; Clark, L.N.; Bar-Shira, A.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Gurevich, T.; Gusev, A.; Kedmi, M.; Kenny, E.E.; Liu, X.; et al. Genome-wide mapping of IBD segments in an Ashkenazi PD cohort identifies associated haplotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4693–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, O.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Casey, F.; Meltzer-Fridrich, H.; Yaacov, O.; Waldman, Y.Y.; Lin, D.; Mordechai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cullen, P.F.; et al. PARK16 locus: Differential effects of the non-coding rs823114 on Parkinson’s disease risk, RNA expression, and DNA methylation. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr-Urtreger, A.; Shifrin, C.; Rozovski, U.; Rosner, S.; Bercovich, D.; Gurevich, T.; Yagev-More, H.; Bar-Shira, A.; Giladi, N. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation in Ashkenazi Jews with Parkinson disease: Is there a gender effect? Neurology 2007, 69, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, O.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Shiner, T.; Attar, R.; Mordechai, Y.; Waldman, Y.Y.; Bar-Shira, A.; Thaler, A.; Gurevich, T.; Mirelman, A.; et al. R869C mutation in molecular motor KIF17 gene is involved in dementia with Lewy bodies. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 13, e12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Schubach, M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD-Splice-improving genome-wide variant effect prediction using deep learning-derived splice scores. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.A.; Hitz, B.C.; Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Jain, K.; Baymuradov, U.K.; Narayanan, A.K.; et al. The Encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): Data portal update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D794–D801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.T.; Guo, J.; di Ronza, A.; Sardiello, M. Aminode: Identification of Evolutionary Constraints in the Human Proteome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maunakea, A.K.; Nagarajan, R.P.; Bilenky, M.; Ballinger, T.J.; D’Souza, C.; Fouse, S.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Hong, C.; Nielsen, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature 2010, 466, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan-Or, Z.; Bar-Shira, A.; Mirelman, A.; Gurevich, T.; Giladi, N.; Orr-Urtreger, A. The age at motor symptoms onset in LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease is affected by a variation in the MAPT locus: A possible interaction. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 46, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.A.; Müller, S.A.; Mentrup, T.; Shmueli, M.D.; Niemeyer, J.; Haug-Kröper, M.; von Blume, J.; Mayerhofer, A.; Feederle, R.; Schröder, B.; et al. Signal peptide peptidase-like 2c impairs vesicular transport and cleaves SNARE proteins. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e46451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunn, B.H.M.; Cragg, S.J.; Bolam, J.P.; Spillantini, M.-G.; Wade-Martins, R. Impaired intracellular trafficking defines early Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, O.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Banfi, S.; Nigro, V.; Bar-Shira, A.; Thaler, A.; Gurevich, T.; Mirelman, A.; Giladi, N.; Alcalay, R.N.; et al. Novel variants in genes related to vesicle-mediated-transport modify Parkinson’s disease risk. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 139, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.; Van Nguyen, N.; Georgiev, P.; Gaub, A.; Brettschneider, J.; Cusack, S.; Kadlec, J.; Akhtar, A. Structural analysis of the KANSL1/WDR5/KANSL2 complex reveals that WDR5 is required for efficient assembly and chromatin targeting of the NSL complex. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Wang, S.; Li, K. Identification of Parkinson’s disease-associated chromatin regulators. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutar, M.P.M.; Melandri, D.; O’Callaghan, B.; Annuario, E.; Monaghan, A.E.; Welsh, N.J.; D’Sa, K.; Guelfi, S.; Zhang, D.; Pittman, A.; et al. Regulation of mitophagy by the NSL complex underlies genetic risk for Parkinson’s disease at 16q11.2 and MAPT H1 loci. Brain 2022, 145, 4349–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Yang, H. Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cells 2019, 8, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganley, I.G. Strengthening the link between mitophagy and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2022, 145, 4154–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koks, S.; Pfaff, A.L.; Bubb, V.J.; Quinn, J.P. Transcript Variants of Genes Involved in Neurodegeneration Are Differentially Regulated by the APOE and MAPT Haplotypes. Genes 2021, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, R.; Wang, Y.; Vandrovcova, J.; Guelfi, S.; Witeolar, A.; Karch, C.M.; Schork, A.J.; Fan, C.C.; Brewer, J.B.; International FTD-Genomics Consortium (IFGC); et al. Genetic architecture of sporadic frontotemporal dementia and overlap with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Makowski, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, A.; Kaufmann, T.; Smeland, O.B.; Fiecas, M.; Yang, J.; Visscher, P.M.; Chen, C.-H. Chromosomal inversion polymorphisms shape human brain morphology. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falola, M.I.; Wiener, H.W.; Wineinger, N.E.; Cutter, G.R.; Kimberly, R.P.; Edberg, J.C.; Arnett, D.K.; Kaslow, R.A.; Tang, J.; Shrestha, S. Genomic copy number variants: Evidence for association with antibody response to anthrax vaccine adsorbed. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannuzzi, G.; Siswara, P.; Malig, M.; Marques-Bonet, T.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Mullikin, J.C.; Ventura, M.; Eichler, E.E. Evolutionary dynamism of the primate LRRC37 gene family. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, K.R.; Pugh, D.A.; Liu, Y.; Patel, T.; Renton, A.E.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Gan-Or, Z.; Heutink, P.; Siitonen, A.; Bertelsen, S.; et al. 17q21.31 sub-haplotypes underlying H1-associated risk for Parkinson’s disease are associated with LRRC37A/2 expression in astrocytes. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Meng, L.; He, M.; Zhang, Z. Tau in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Cisterna-García, A.; Yu, E.; Bustos, B.I.; Krohn, L.; Lubbe, S.J.; Botía, J.A.; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC); Gan-Or, Z. Genome-wide association study stratified by MAPT haplotypes identifies potential novel loci in Parkinson’s disease. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genotype | Number of PD Patients (%) | Number of Females (%) | Average Age at Onset (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carriers of GBA1 mutations a | 235 (20%) | 94 (40%) | 58.7 (10.5) |
| Carriers of LRRK2-G2019S mutation | 145 (12.1%) | 65 (44.8%) | 58.5 (10.5) |
| Carriers of dual mutations | 25 (2.1%) | 17 (68%) | 58.5 (9.9) |
| Carriers of SMPD1-L302P mutation | 8 (0.7%) | 3 (37.5%) | 55.5 (12.7) |
| Non-Carriers (NC) | 787 (65.6%) | 297 (37.7%) | 61.5 (11.4) |
| Total | 1200 | 476 (39.6%) | 60.5 (11.2) |
| Chromosome: Position (hg38) | Reference > Alternates | Identifier | CADD Phred Score | Gene Names | Sequence Ontology | Amino Acid Change | Gene Region | In Evolutionarily Constrained Region (Aminode) | ENCODE- (ENCODE Accession- cCREs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17:46225515 | C>T | rs2532404 | 20.70 | KANSL1 | Upstream variant | N.A | Upstream | N.A | EH38E1866648—promoter-like signature |
| 17:45983912 | C>T | rs17651549 | 24.90 | MAPT | Missense variant | NP_001364194.1: p.Arg445Trp | Exon 5 | Yes | None |
| 17:45846707 | T>C | rs12373123 | 24.80 | SPPL2C | Missense variant | NP_787078.2: p.Ser601Pro | Exon 1 | Yes | None |
| 17:45846288 | G>C | rs12185233 | 23.50 | SPPL2C | Missense variant | NP_787078.2: p.Arg461Pro | Exon 1 | Yes | None |
| 17:45825139 | C>T | rs4341787 | 21.70 | CRHR1, LINC02210-CRHR1 | Intron variant, Intron variant | N.A | Intron 4, Intron 6 | N.A | EH38E1866300—distal enhancer-like signature |
| Group | Number of Alternate Alleles (AFs) | Number of Alternate Alleles/Total Alleles in AJ Controls (AF) a | Allelic Odds Ratio b (95% Confidential Interval, p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AJ-PD patients (n = 1200) | 515 (0.214) | 1259/4912 (0.256) | 0.793 (0.705–0.891, 0.0001) | |
| Stratified analysis | GBA1-PD (n = 235) | 99 (0.211) | 0.774 (0.615–0.975, 0.030) | |
| LRRK2-PD (n = 145) | 56 (0.193) | 0.694 (0.515–0.936, 0.017) | ||
| NC-PD (n = 787) | 345 (0.219) | 0.815 (0.712–0.933, 0.003) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shani, S.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Bar-Shira, A.; Thaler, A.; Gurevich, T.; Mirelman, A.; Giladi, N.; Alcalay, R.N.; Goldstein, O.; Orr-Urtreger, A. MAPT Locus in Parkinson’s Disease Patients of Ashkenazi Origin: A Stratified Analysis. Genes 2024, 15, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010046
Shani S, Gana-Weisz M, Bar-Shira A, Thaler A, Gurevich T, Mirelman A, Giladi N, Alcalay RN, Goldstein O, Orr-Urtreger A. MAPT Locus in Parkinson’s Disease Patients of Ashkenazi Origin: A Stratified Analysis. Genes. 2024; 15(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleShani, Shachar, Mali Gana-Weisz, Anat Bar-Shira, Avner Thaler, Tanya Gurevich, Anat Mirelman, Nir Giladi, Roy N. Alcalay, Orly Goldstein, and Avi Orr-Urtreger. 2024. "MAPT Locus in Parkinson’s Disease Patients of Ashkenazi Origin: A Stratified Analysis" Genes 15, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010046
APA StyleShani, S., Gana-Weisz, M., Bar-Shira, A., Thaler, A., Gurevich, T., Mirelman, A., Giladi, N., Alcalay, R. N., Goldstein, O., & Orr-Urtreger, A. (2024). MAPT Locus in Parkinson’s Disease Patients of Ashkenazi Origin: A Stratified Analysis. Genes, 15(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010046





