A Study of Polish Family with Scoliosis and Limb Contractures Expands the MYH3 Disease Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Proband
2.2. The Proband’s Family
2.3. Genetic Testing
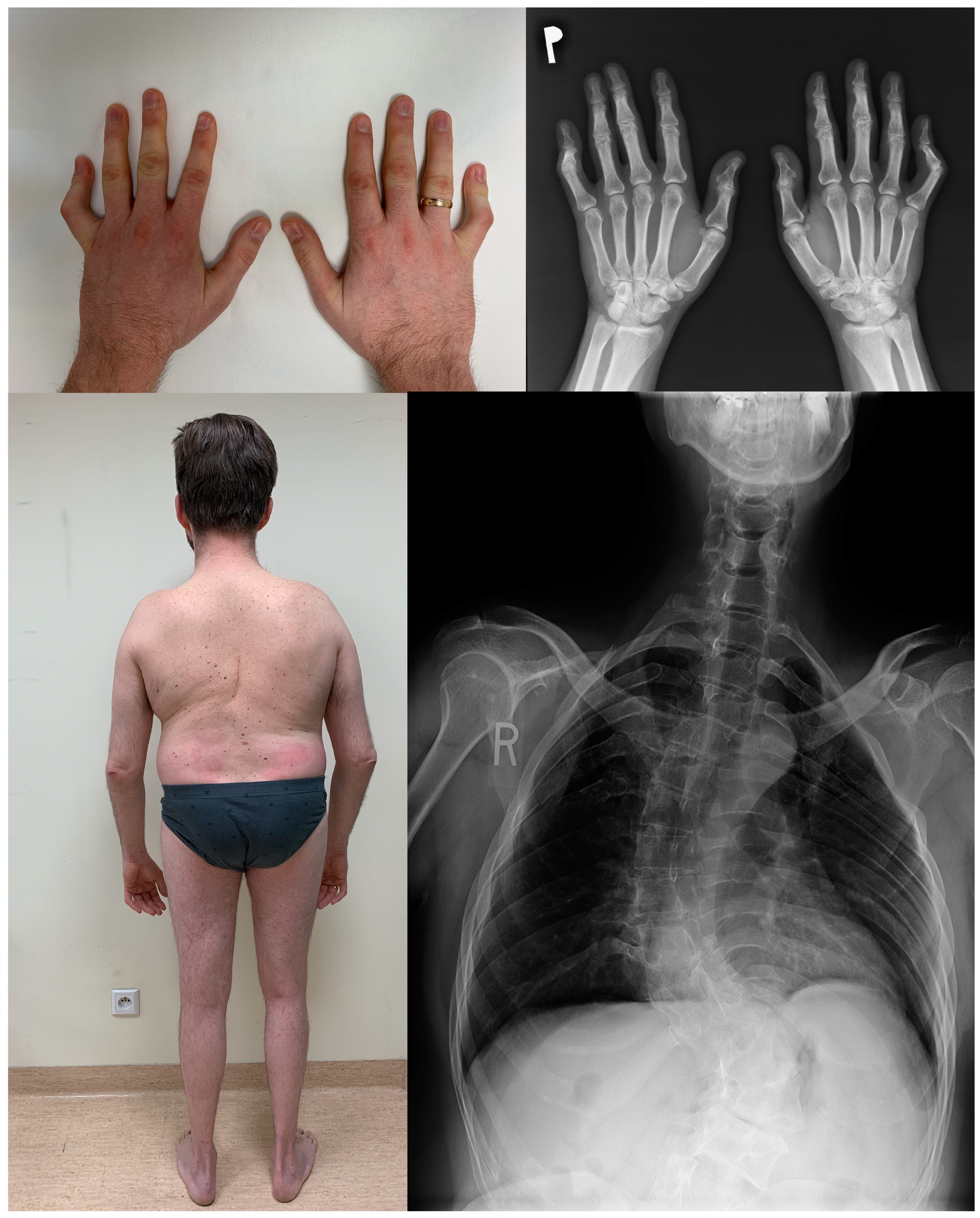
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
- -
- Bony blocks or partial bony blocks between the occipitocervical junctions; the C1 vertebra and C2 vertebra; the L4 vertebra; the L5 vertebra; and the lumcosacral junctions (all subjects);
- -
- Unconjoined/hypoplasia of the posterior arch of the C1 vertebra (subjects II.4 and II.7);
- -
- Spina bifida of the L5 and S1 vertebra (subject II.4);
- -
- Narrow vertebra canal (subjects I.1. and II.2);
- -
- Lumbar vertebrae with atypical morphology (all subjects);
- -
- Congenital lower hypoplastic intervertebral discs (all subjects).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Yu, X.; Shen, J. Environmental aspects of congenital scoliosis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 5751–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passias, P.G.; Poorman, G.W.; Jalai, C.M.; Diebo, B.G.; Vira, S.; Horn, S.R.; Baker, J.F.; Shenoy, K.; Hasan, S.; Buza, J.; et al. Incidence of Congenital Spinal Abnormalities Among Pediatric Patients and Their Association with Scoliosis and Systemic Anomalies. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, e608–e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toydemir, R.M.; Rutherford, A.; Whitby, F.G.; Jorde, L.B.; Carey, J.C.; Bamshad, M.J. Mutations in embryonic myosin heavy chain (MYH3) cause Freeman-Sheldon syndrome and Sheldon-Hall syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieba, J.; Zhang, W.; Chong, J.X.; Forlenza, K.N.; Martin, J.H.; Heard, K.; Grange, D.K.; Butler, M.G.; Kleefstra, T.; Lachman, R.S.; et al. A postnatal role for embryonic myosin revealed by MYH3 mutations that alter TGFbeta signaling and cause autosomal dominant spondylocarpotarsal synostosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, M.; Stedman, H.H.; Sylvester, J.E.; Fertels, S.H.; Wu, Q.L.; Raychowdhury, M.K.; Rubinstein, N.A.; Kelly, A.M.; Sarkar, S. Human embryonic myosin heavy chain cDNA. Interspecies sequence conservation of the myosin rod, chromosomal locus and isoform specific transcription of the gene. FEBS Lett. 1989, 256, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Travis, M.; Blau, H.; Leinwand, L.A. Expression and DNA sequence analysis of a human embryonic skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain gene. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1989, 17, 6167–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzanicz, M.; Wachowska, M.; Cook, E.C.; Lisowski, P.; Kuzniewska, B.; Szymanska, K.; Diecke, S.; Prigione, A.; Szczaluba, K.; Szybinska, A.; et al. Novel calcineurin A (PPP3CA) variant associated with epilepsy, constitutive enzyme activation and downregulation of protein expression. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plon, S.E.; Eccles, D.M.; Easton, D.; Foulkes, W.D.; Genuardi, M.; Greenblatt, M.S.; Hogervorst, F.B.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Spurdle, A.B.; Tavtigian, S.V.; et al. Sequence variant classification and reporting: Recommendations for improving the interpretation of cancer susceptibility genetic test results. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerschaut, I.; De Coninck, S.; Steyaert, W.; Barnicoat, A.; Bayat, A.; Benedicenti, F.; Berland, S.; Blair, E.M.; Breckpot, J.; de Burca, A.; et al. A clinical scoring system for congenital contractural arachnodactyly. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrtovec, T.; Pernus, F.; Likar, B. A review of methods for quantitative evaluation of spinal curvature. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamshad, M.; Van Heest, A.E.; Pleasure, D. Arthrogryposis: A review and update. J. Bone Joint. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron-Christie, S.R.; Wells, C.F.; Simon, M.; Wessels, M.; Tang, C.Z.N.; Wei, W.; Takei, R.; Aarts-Tesselaar, C.; Sandaradura, S.; Sillence, D.O.; et al. Recessive Spondylocarpotarsal Synostosis Syndrome Due to Compound Heterozygosity for Variants in MYH3. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapito, R.; Goldenberg, A.; Paul, N.; Pichot, A.; David, A.; Hamel, A.; Dumant-Forest, C.; Leroux, J.; Ory, B.; Isidor, B.; et al. Protein-altering MYH3 variants are associated with a spectrum of phenotypes extending to spondylocarpotarsal synostosis syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajsharghi, H.; Kimber, E.; Kroksmark, A.K.; Jerre, R.; Tulinius, M.; Oldfors, A. Embryonic myosin heavy-chain mutations cause distal arthrogryposis and developmental myosin myopathy that persists postnatally. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Kang, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.L. A MYH3 mutation identified for the first time in a Chinese family with Sheldon-Hall syndrome (DA2B). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncbilek, E.; Alanay, Y. Congenital contractural arachnodactyly (Beals syndrome). Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2006, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, M.; Ye, Y.; Lin, J.; et al. Diagnostic yield and clinical impact of exome sequencing in early-onset scoliosis (EOS). J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivante, A.; Ityel, H.; Pode-Shakked, B.; Chen, J.; Shril, S.; van der Ven, A.T.; Mann, N.; Schmidt, J.M.; Segel, R.; Aran, A.; et al. Exome sequencing in Jewish and Arab patients with rhabdomyolysis reveals single-gene etiology in 43% of cases. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, M.; Accogli, A.; De Grandis, E.; Allegri, A.; Bagowski, C.P.; Shoukier, M.; Maghnie, M.; Capra, V. A novel pathogenic MYH3 mutation in a child with Sheldon-Hall syndrome and vertebral fusions. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subject | I.1 | II.2 | II.4 | II.6 | II.7 | III.4 | III.5 | III.7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological attributes | sex | Male | Male | Female | Female | Female | Female | Male | Female | |
| age (years) | 69 | 41 | 38 | 31 | 31 | 13 | 6 | 2 | ||
| Stature and trunk | Physical finding | short stature | + | + | + | + | + | −25c | 25c | 75c |
| short neck | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | ||
| Radiological finding | scoliosis | + | + | + | + | + | − | mild | mild | |
| vertebral fusion | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | ? | ||
| Face | Physical finding | downslating palpebral fissures | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Upper limb | Physical finding | joint contractures | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| camptodactyly | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | ||
| elongation of the proximal and middle phalanges of the hands | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||
| Radiological finding | carpal fusion | + | − | − | + | − | ? | ? | ? | |
| Lower limb | Physical finding | dysplasia of the calf muscles | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| joint contractures | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | mild | ||
| hallux vagus | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | ||
| partial syndactyly of the II and III toes | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||
| Elongation of the proximal phalanges and metatarsal bones | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | ||
| Radiological finding | peripheral instability with plantar deviation of the toes at the IP I joints with predominance of the right foot | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | |
| tarsal fusion | − | − | − | − | − | ? | ? | ? | ||
| Phenotype | Arthrogryposis, Distal, Type 2A (Freeman–Sheldon) [4] | Arthrogryposis, Distal, Type 2B3 (Sheldon–Hall) [5,6] | Contractures, Pterygia and Spondylocarpotarsal Fusion Syndrome 1A [7,8,9] | Contractures, Pterygia and Spondylocarpotarsal Fusion Syndrome 1B [9] | Family Described within the Presented Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inheritance | AD | AD | AD | AR | AD |
| face | very small mouth, pinched lips, H-shaped dimpling of the chin | Triangular face Facial contractures that result in deep nasolabial folds Attached earlobes Downslating palpebral fissures Broad bridge of nose Small mouth | Microcephaly (in some patients) Ptosis cleft palate Downslating palpebral fissures Low-set posteriorly rotted ears Hearing loss (in some patients) | Dysmorphic features Cleft palate (rare) | Downslating palpebral fissures |
| neck | Short neck | n.d. | Short neck Webbed neck | Short neck Webbed neck | Short neck |
| contractures | Multiple (shoulders, elbows, thumbs, hips, knees, toes) | Multiple (shoulders, elbows, fingers, hips, knees, feet) | Elbows, knees, hips (in same patients) | Variable (neck, shoulders, elbows, fingers, hips and/or knees) | Multiple (elbows, hands, fingers, hips, knees, feet) |
| spine | Kyphoscoliosis (frequently develops) Spina bifida occulta | Scoliosis (rare) | Scoliosis Vertebral fusion Hemivertebrae Spondylolisthesis (rare) | Scoliosis Vertebral fusion | Scoliosis |
| hands | Cortical thumbs Camptodactyly Ulnar deviation | Camptodactyly Ulnar deviation Palmar position of the thumb Overlapping finger | Carpal fusion Camptodactyly V finger clinodactyly | Carpal fusion | Camptodactyly and isolated defects, e.g., elongation of the phalanges |
| feet | Talipes equinovarus Contracted toes | Hallux vagus Talipes equinovarus | Tarsal fusion | Tarsal fusion Club foot (rare) | Isolated defects, e.g., hallux vagus, partial syndactyly, peripheral instability with plantar deviation of the toes |
| skin | Skin thickening on fingers | Hypoplastic or absent flexion creases of palms | Variable pterygia (neck, elbows and/or fingers) | Variable pterygia (neck, elbows, fingers and/ or knees) | Abnormal pigmentation Skin dryness |
| hight | Short stature | Short stature | Short stature | n.d. | Short stature |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frasuńska, J.; Pollak, A.; Turczyn, P.; Kutkowska-Kaźmierczak, A.; Pepłowski, J.; Płoski, R.; Tarnacka, B. A Study of Polish Family with Scoliosis and Limb Contractures Expands the MYH3 Disease Spectrum. Genes 2024, 15, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010125
Frasuńska J, Pollak A, Turczyn P, Kutkowska-Kaźmierczak A, Pepłowski J, Płoski R, Tarnacka B. A Study of Polish Family with Scoliosis and Limb Contractures Expands the MYH3 Disease Spectrum. Genes. 2024; 15(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrasuńska, Justyna, Agnieszka Pollak, Paweł Turczyn, Anna Kutkowska-Kaźmierczak, Jakub Pepłowski, Rafał Płoski, and Beata Tarnacka. 2024. "A Study of Polish Family with Scoliosis and Limb Contractures Expands the MYH3 Disease Spectrum" Genes 15, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010125
APA StyleFrasuńska, J., Pollak, A., Turczyn, P., Kutkowska-Kaźmierczak, A., Pepłowski, J., Płoski, R., & Tarnacka, B. (2024). A Study of Polish Family with Scoliosis and Limb Contractures Expands the MYH3 Disease Spectrum. Genes, 15(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010125







