mRNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism of Pinellia ternata Bulbil Initiation Induced by Phytohormones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
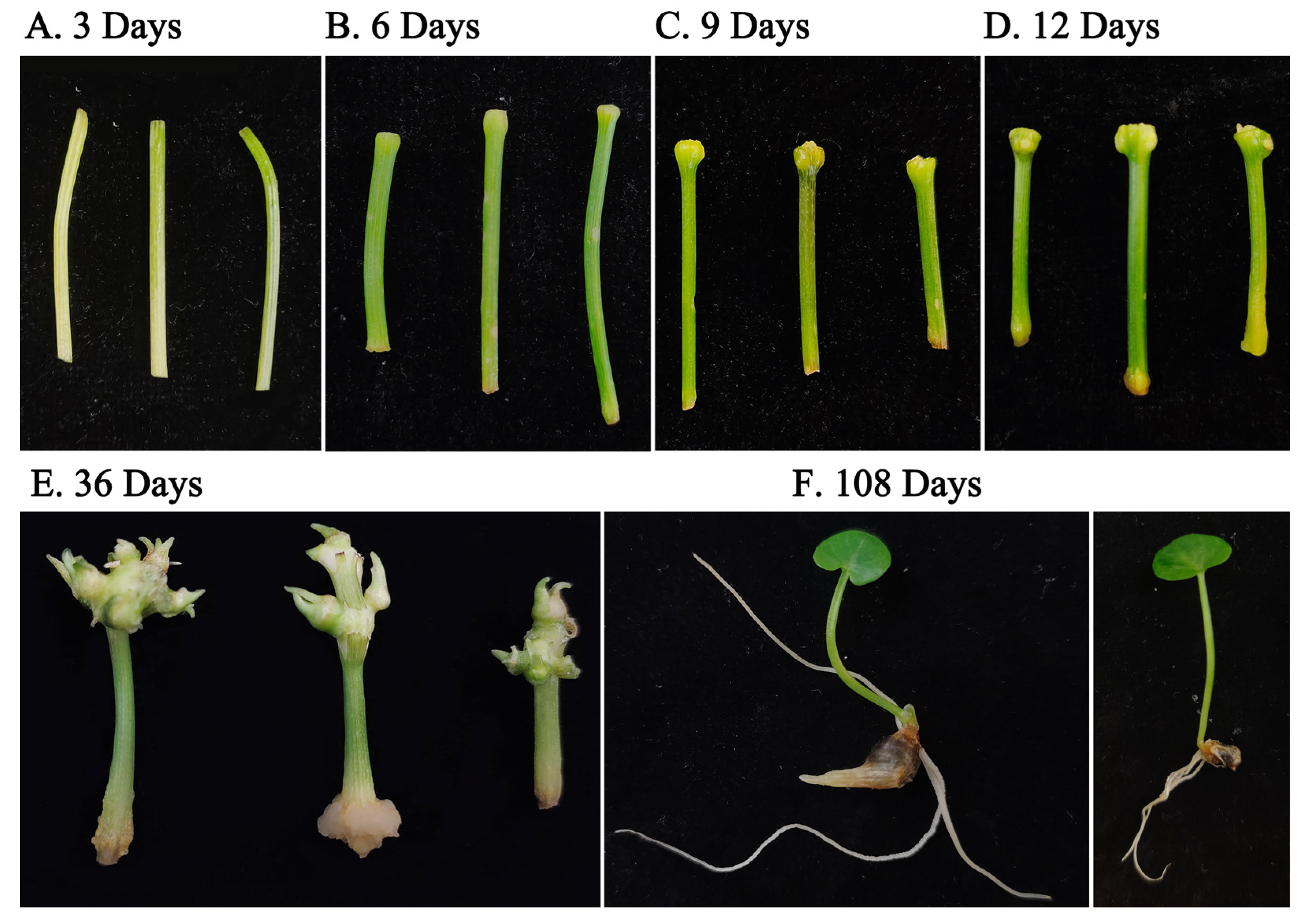
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. RNA Extraction, RNA Sequencing, and Small RNA Sequencing
2.3. Analysis of mRNA-Seq
2.4. Analysis of miRNA-Seq
2.5. qRT-PCR Validation
3. Results
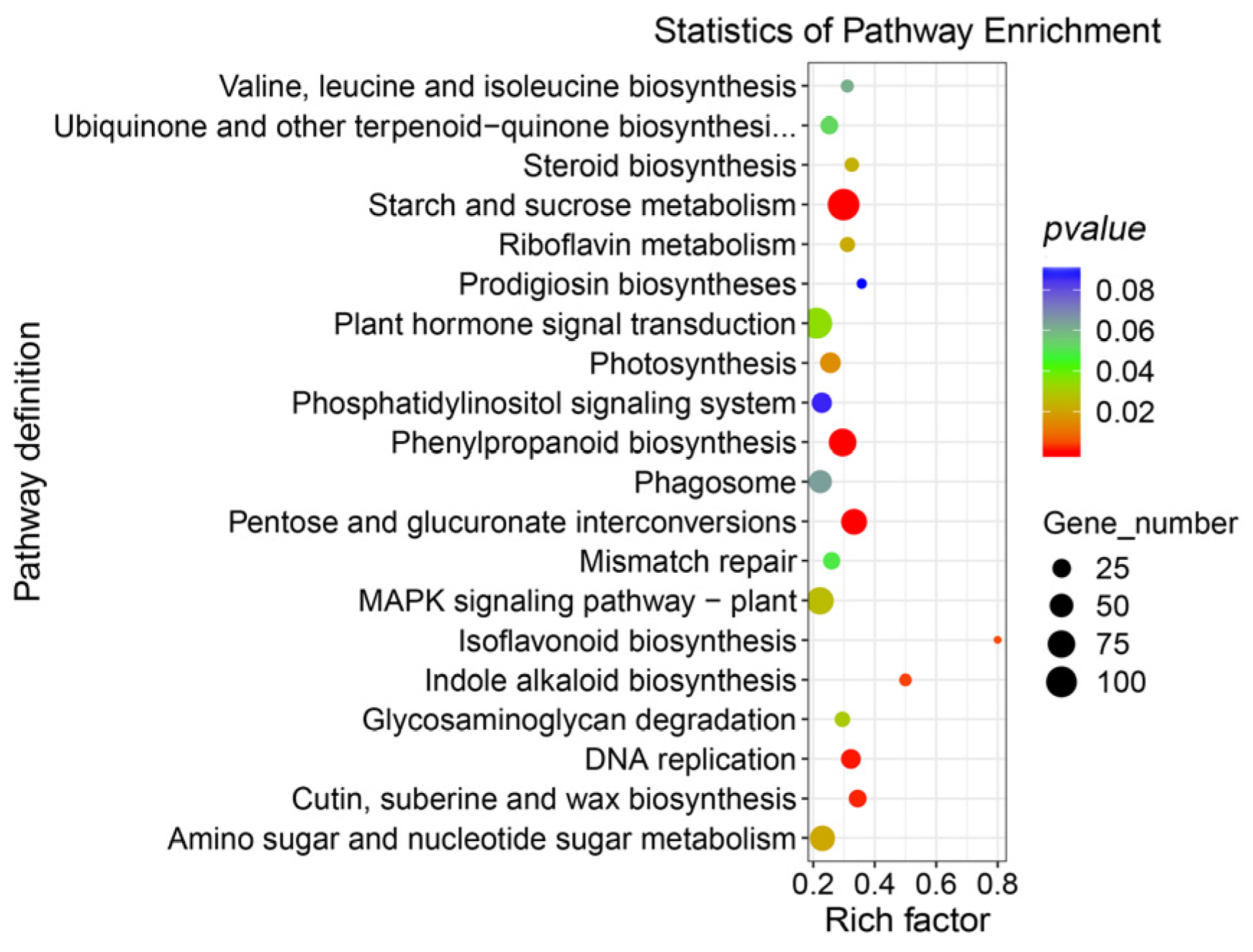
3.1. Differentially Expressed Genes and Gene Function Enrichment Analysis of RNA-Seq
3.2. miRNAs Differentially Expressed in TCp and TCb Samples
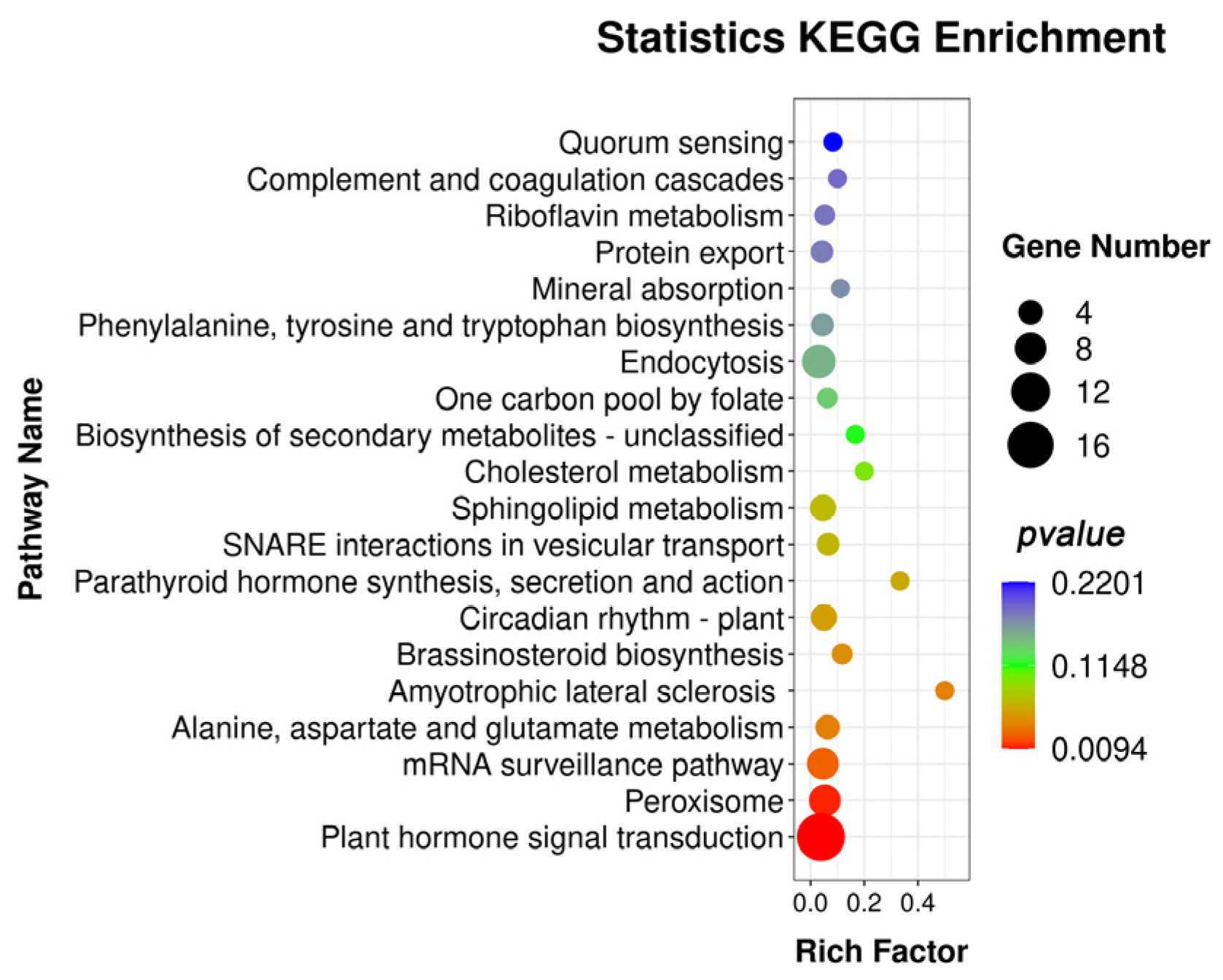
3.3. miRNA Target Gene Prediction and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Validation of Differential Gene and miRNA Expression by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C. The ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological profile of the genus Pinellia. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Qi, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y. A comprehensive review on ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation, and quality control of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; He, Z. Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit: A review of its germplasm resources, genetic diversity and active components. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, M.; Bi, M.; Tang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ming, J.; Yang, P. WUSCHEL-related homeobox genes cooperate with cytokinin to promote bulbil formation in Lilium lancifolium. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Jiang, W.; Tao, Z.M.; Pan, X.J.; Yu, W.H.; Huang, H.L. Morphological and stage-specific transcriptome analyses reveal distinct regulatory programs underlying yam (Dioscorea alata L.) bulbil growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chu, J.; Yao, X. Regulation Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinolide on Bulbil Formation and Development in Pinellia ternata. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 809769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Hu, F.; Yang, P.P. Research Progress on Plant Bulbil Formation. In Molecular Plant Breeding; GenBreed Publisher: Richmond, BC, Canada, 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Ye, D.; Xu, T. Transcriptome analysis of Pinellia ternata mutant based on high throughput sequencing. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2018, 59, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Du, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Z. Morphological Observation and Anatomical Study on Bulbil Development of Pinellia ternata. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2014, 34, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, X. Study on the Rapid-Propagation Technical System with the Petioles of Pinellia ternate Breit as Explants. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 6, 2247–2248+2284. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L. Position Effect of the Leaf Stalks from Pinellia ternate (Thunb.) Berit. and Its Influencing Factors. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham Juarez, M.J.; Hernandez Cardenas, R.; Santoyo Villa, J.N.; O’Connor, D.; Sluis, A.; Hake, S.; Ordaz-Ortiz, J.; Terry, L.; Simpson, J. Functionally different PIN proteins control auxin flux during bulbil development in Agave tequilana. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3893–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xu, Y.; Xue, J. Formation of Microtubers from the Petiole of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Berit. in vitro and Change of Endogenous Hormones Content. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2007, 26, 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Zhan, L.; Mohr, T.; Cheng, P.; Huo, N.; Gu, R.; Pei, D.; Sun, J.; et al. Deep sequencing and transcriptome analyses to identify genes involved in secoiridoid biosynthesis in the Tibetan medicinal plant Swertia mussotii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponniah, S.K.; Thimmapuram, J.; Bhide, K.; Kalavacharla, V.K.; Manoharan, M. Comparative analysis of the root transcriptomes of cultivated sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam) and its wild ancestor (Ipomoea trifida [Kunth] G. Don). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Tian, C.; Xia, L.; Chen, H.; Du, S.; Luo, X. Cloning and Expressional Analysis of PteAUX1 Gene Related to Bulbil Development of Pinellia ternata. In Molecular Plant Breeding; GenBreed Publisher: Richmond, BC, Canada, 2021; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; He, Q.; Dong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lou, Y.; Hua, X.; Xu, T. Selection of suitable candidate genes for mRNA expression normalization in bulbil development of Pinellia ternata. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-P.; Xu, L.-F.; Xu, H.; He, G.-R.; Feng, Y.-Y.; Cao, Y.-W.; Tang, Y.-C.; Yuan, S.-X.; Ming, J. Morphological and anatomical observation during the formation of bulbils in Lilium lancifolium. Caryologia 2018, 71, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xu, L.; Xu, H.; Tang, Y.; He, G.; Cao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, S.; Ming, J. Histological and Transcriptomic Analysis during Bulbil Formation in Lilium lancifolium. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-N.; Cronk, Q.C.B. Meristem fate and bulbil formation in Titanotrichum (Gesneriaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, Y.S.; Purnima. Morphology, anatomy and development of bulbil in some dioscoreas. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. 1983, 92, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Yang, P.; Tang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qi, X.; Xu, L.; Ming, J. Mechanism of exogenous cytokinins inducing bulbil formation in Lilium lancifolium in vitro. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Kim, C.; Zhang, D.-G.; Zhang, J.-W.; Li, Z.-M.; Nie, Z.-L.; Sun, H. Zhengyia shennongensis: A new bulbiliferous genus and species of the nettle family (Urticaceae) from central China exhibiting parallel evolution of the bulbil trait. Taxon 2013, 62, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.-M.; Chen, L.-Q.; Li, Y.H.; Xin, Z.-Y.; Xie, H. Research Progress of Vegetative Vivipary in Plants. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2020, 28, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, M.; Li, H.; Ling, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L. Full-length transcriptome-referenced analysis reveals crucial roles of hormone and wounding during induction of aerial bulbils in lily. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y. Anatomical Study on the Generation of the Buibil of the Chinese Yam. Acta Agric. Univ. Pekin. 1994, 20, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, D. Bulbil development of Pinellia cordata. Guihaia 2018, 38, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, S.-Q.; Luo, R. Morphological Observation and Anatomical Study on Bulbil Development of Lilium sulphureum. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2012, 32, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Chao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, J.; Zhang, A.; Sheng, W.; Duan, Y.; et al. Full-length transcriptome analysis of shade-induced promotion of tuber production in Pinellia ternata. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y. The Mechanism of Auxin Involving in Bulbil Formation of Lilium lancifolium. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Yan, R.; Yin, J.; Zhang, P.; Guo, W.; Li, C. Research on Tissue Culture for Rapid Propagation and in vitro Bulbils Regeneration System of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2013, 33, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Yang, P.; Cao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Ming, J. Cytokinin Type-B Response Regulators Promote Bulbil Initiation in Lilium lancifolium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, T. Microtubule organization and microtubule-associated proteins in plant cells. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 312, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P. Study on Sucrose Metabolism during Bulbil Formation of Lilium lancifolium and LlSUS2 Gene Cloning. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goren, S.; Lugassi, N.; Stein, O.; Yeselson, Y.; Schaffer, A.A.; David-Schwartz, R.; Granot, D. Suppression of sucrose synthase affects auxin signaling and leaf morphology in tomato. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.M.; Brill, E.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Furbank, R.T.; Ruan, Y.L. Overexpression of a potato sucrose synthase gene in cotton accelerates leaf expansion, reduces seed abortion, and enhances fiber production. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, H.D.; Ellis, D.D.; Gilbert, M.; Mansfield, S.D. Up-regulation of sucrose synthase and UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase impacts plant growth and metabolism. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curaba, J.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. miRNAs in the crosstalk between phytohormone signalling pathways. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, D.; Nemhauser, J.; Yang, Z. Auxin: Small molecule, big impact. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.; Mongelard, G.; Floková, K.; Păcurar, D.I.; Novák, O.; Staswick, P.; Kowalczyk, M.; Păcurar, M.; Demailly, H.; Geiss, G.; et al. Auxin Controls Arabidopsis Adventitious Root Initiation by Regulating Jasmonic Acid Homeostasis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, P.; Xu, L.; Ma, H.; Huang, H. Plant fertility defects induced by the enhanced expression of microRNA167. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Poethig, R.S. Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thalianaby miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 2006, 133, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curaba, J.; Spriggs, A.; Taylor, J.; Li, Z.; Helliwell, C. miRNA regulation in the early development of barley seed. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yarra, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, H. miRNAs as key regulators via targeting the phytohormone signaling pathways during somatic embryogenesis of plants. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Yuan, D.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X. Small RNA and degradome sequencing reveal complex miRNA regulation during cotton somatic embryogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1521–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabana, A.A.; Rajesh, M.K.; Antony, G. Dynamic changes in the expression pattern of miRNAs and associated target genes during coconut somatic embryogenesis. Planta 2020, 251, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, S.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Qi, L. Genome-wide identification of microRNAs in larch and stage-specific modulation of 11 conserved microRNAs and their targets during somatic embryogenesis. Planta 2012, 236, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lai, Z. Comparative analysis reveals dynamic changes in miRNAs and their targets and expression during somatic embryogenesis in longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Singh, A.K.; Chaudhary, B. Target-mimicry based miRNA167-diminution ameliorates cotton somatic embryogenesis via transcriptional biases of auxin signaling associated miRNAs and genes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. PCTOC 2020, 141, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, C.L.; O’Neill, S.D.; Zhang, X.S. Auxin-inducedWUSexpression is essential for embryonic stem cell renewal during somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 59, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xue, X.-Y.; Zhao, B.; Chao, L.-M.; Chen, D.-Y.; Cui, W.-R.; Mao, Y.-B.; Wang, L.-J.; Chen, X.-Y. Interaction between Two Timing MicroRNAs Controls Trichome Distribution in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Cai, W.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.J. Arabidopsis miR171-Targeted Scarecrow-Like Proteins Bind to GT cis-Elements and Mediate Gibberellin-Regulated Chlorophyll Biosynthesis under Light Conditions. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Mai, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Luo, Q.; Yang, H.-Q. MicroRNA171c-Targeted SCL6-II, SCL6-III, and SCL6-IV Genes Regulate Shoot Branching in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llave, C.; Kasschau, K.D.; Rector, M.A.; Carrington, J.C. Endogenous and Silencing-Associated Small RNAs in Plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, H.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Mogi, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Tsutsumi, N. miRNAs control HAM1 functions at the single-cell-layer level and are essential for normal embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 96, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yan, A.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, B.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y. A signal cascade originated from epidermis defines apical-basal patterning of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizotto, E.A.; Dunoyer, P.; Rahm, N.; Himber, C.; Voinnet, O. In vivo investigation of the transcription, processing, endonucleolytic activity, and functional relevance of the spatial distribution of a plant miRNA. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-M.; Kou, S.-J.; Liu, Y.-L.; Fang, Y.-N.; Xu, Q.; Guo, W.-W. Genomewide analysis of small RNAs in nonembryogenic and embryogenic tissues of citrus: microRNA-and siRNA-mediated transcript cleavage involved in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.F.; Long, J.M.; Yin, Z.P.; Jiang, N.; Feng, M.Q.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W.W.; Wu, X.M. miR171 modulates induction of somatic embryogenesis in citrus callus. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Yu, R.; Limera, C.; Gong, Y.; Liu, L. Genome-Wide Identification of Embryogenesis-Associated microRNAs in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) by High-Throughput Sequencing. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.-M.; Liu, C.-Y.; Feng, M.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.-M.; Guo, W.-W. miR156-SPL modules regulate induction of somatic embryogenesis in citrus callus. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2979–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.-Q.; Lu, M.-D.; Long, J.-M.; Yin, Z.-P.; Jiang, N.; Wang, P.-B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.-W.; Wu, X.-M.; Cubas, P. miR156 regulates somatic embryogenesis by modulating starch accumulation in citrus. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 6170–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene ID | miRNA Sequences | Reverse Transcription Primer | Primer Sequences (Forward/Reverse, 5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| aly-miR167a-5p | TGAAGCTGCCAGCATGATCTGA | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCAGAT | CGTGAAGCTGCCAGCATG AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| mes-miR171a | TTGAGCCGCGTCAATATCTCC | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGAGAT | CGTTGAGCCGCGTCAAT AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| sbi-miR156a_L 1 | TGACAGAAGAGAGTGAGCAC | GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTC | GCGCGCTGACAGAAGAGAGT AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| Gene | Annotation | Homolog Locus | Primer Sequences (Forward/Reverse, 5′–3′) | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARF6 | Auxin response factor 6-like isoform x1 | XM_026023239.1 | AGGGCGATGTTCTTCTCGTC GGGTCTTGATGGCTCGCATA | 187 bp |
| IAA4 | Auxin-responsive protein iaa4 isoform x3 | XM_015774120 | ATCTGAGGCTGGGGTTTAGC TCACGAAGAAGGTTGCTTGC | 192 bp |
| SCL6 | Scarecrow-like protein 6 | XM_015771585 | GTTCCAGTAGCACACCTCCC CCACCAAACCCGATGTCGAA | 184 bp |
| SPL16 | Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 16 | XM_015793891.2 | TGATCGAGGAAATGAGGCCG CGAACTTGAGGTAGGGGCAG | 189 bp |
| SUS2 | Sucrose synthase 2 | XM_039929826.1 | GCGGAGATCATAGTGGACGG ACAGCGTCATCAACCTCTCTG | 199 bp |
| AMY2 | α amylase | XM_015779949.2 | AAGGAGAGCTATGGCGACTG GTGGGTATTCCTGGGTGTGT | 187 bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Fan, H.; Pei, X.; Hua, X.; Xu, T.; He, Q. mRNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism of Pinellia ternata Bulbil Initiation Induced by Phytohormones. Genes 2023, 14, 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091727
Xu W, Fan H, Pei X, Hua X, Xu T, He Q. mRNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism of Pinellia ternata Bulbil Initiation Induced by Phytohormones. Genes. 2023; 14(9):1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091727
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wenxin, Haoyu Fan, Xiaomin Pei, Xuejun Hua, Tao Xu, and Qiuling He. 2023. "mRNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism of Pinellia ternata Bulbil Initiation Induced by Phytohormones" Genes 14, no. 9: 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091727
APA StyleXu, W., Fan, H., Pei, X., Hua, X., Xu, T., & He, Q. (2023). mRNA-Seq and miRNA-Seq Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism of Pinellia ternata Bulbil Initiation Induced by Phytohormones. Genes, 14(9), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091727





