SAMBA: Structure-Learning of Aquaculture Microbiomes Using a Bayesian Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
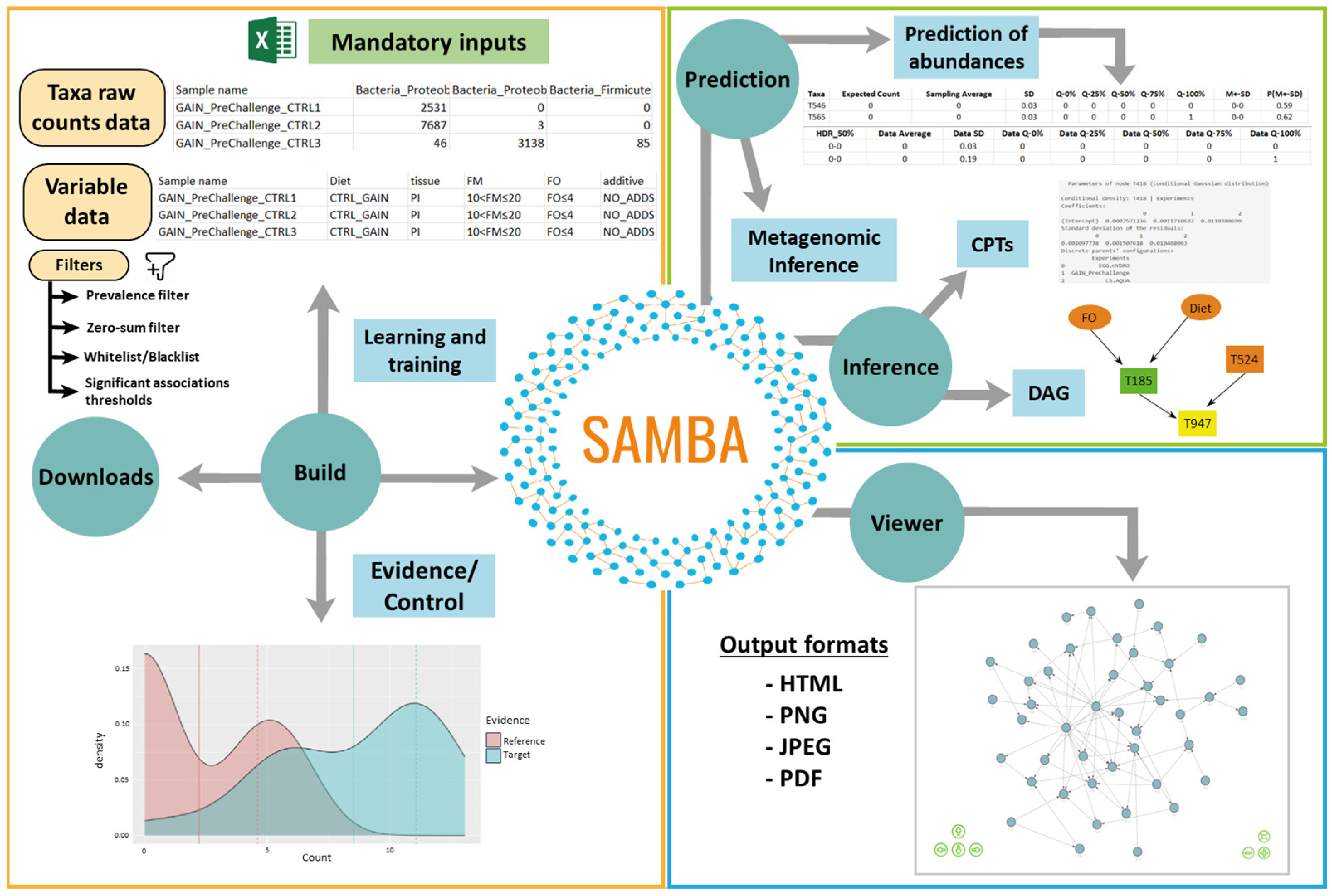
2.1. SAMBA Modules
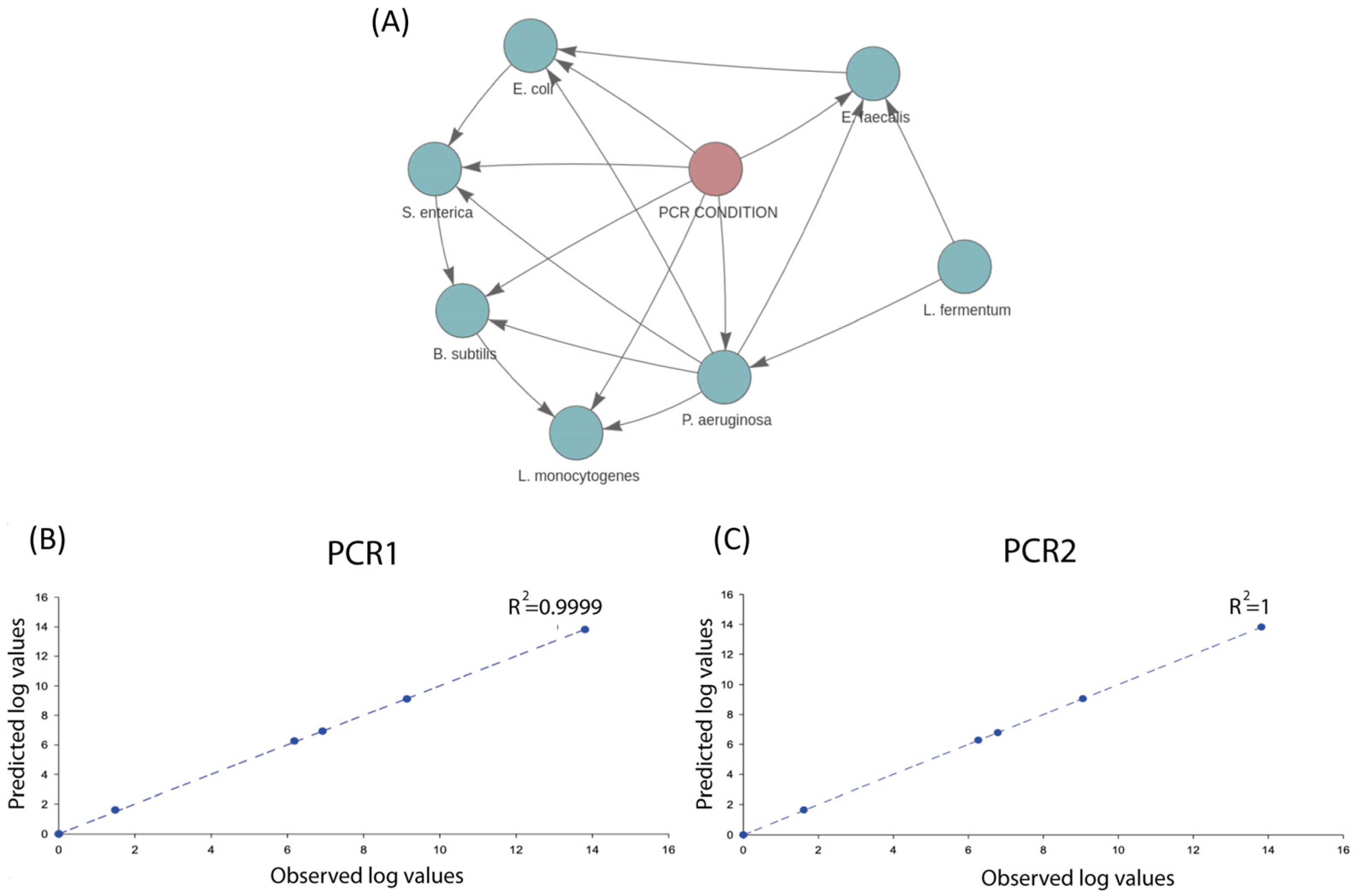
2.2. Artificial Testing Dataset (Sequencing and Dataset Definition)
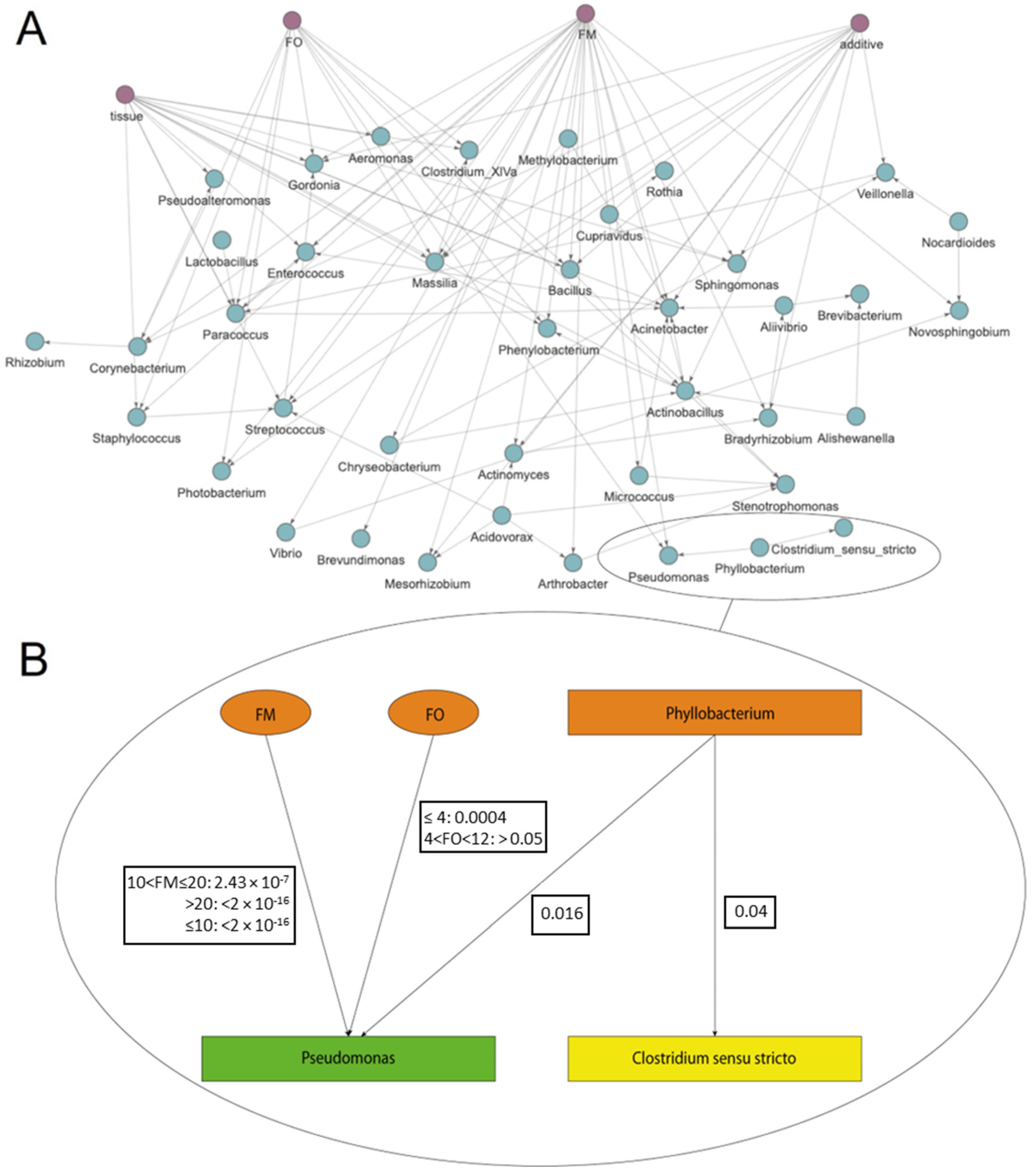
2.3. Empirically Testing S. aurata Dataset (Sequencing, Experimental Design, Rearing Conditions, and Dataset Definition)
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Naya-Català, F.; Rimoldi, S.; Piazzon, M.C.; Torrecillas, S.; Toxqui, M.S.; Fontanillas, R.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Hostins, B.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; et al. Highlights from gut microbiota survey in farmed fish—European sea bass and gilthead sea bream case studies. Aquac. Eur. 2022, 47, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Abberton, M.; Batley, J.; Bentley, A.; Bryant, J.; Cai, H.; Cockram, J.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Cseke, L.J.; Dempewolf, H.; De Pace, C.; et al. Global agricultural intensification during climate change: A role for genomics. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Naya-Català, F.; Perera, E.; Palenzuela, O.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Genetic selection for growth drives differences in intestinal microbiota composition and parasite disease resistance in gilthead sea bream. Microbiome 2020, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Diet and Host Genetics Drive the Bacterial and Fungal Intestinal Metatranscriptome of Gilthead Sea Bream. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 883738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Torrecillas, S.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Fontanillas, R.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Montero, D.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Genetics and Nutrition Drive the Gut Microbiota Succession and Host-Transcriptome Interactions through the Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Production Cycle. Biology 2022, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K. Open challenges for microbial network construction and analysis. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, A.; Mathé, E.; Merling, M.; Ma, Q.; Liu, B. Network analyses in microbiome based on high-throughput multi-omics data. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1639–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M. Structure variability in Bayesian networks. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0909.1685. [Google Scholar]
- Michiels, M.; Larrañaga, P.; Bielza, C. BayeSuites: An open web framework for massive Bayesian networks focused on neuroscience. Neurocomputing 2021, 428, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, E.T.; Pereira, T.; O’Neill, P.K.; Erill, I. A Bayesian inference method for the analysis of transcriptional regulatory networks in metagenomic data. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2016, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazal, M.; Mathee, K.; Ruiz-Perez, D.; Cickovski, T.; Narasimhan, G. Inferring directional relationships in microbial communities using signed Bayesian networks. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazal, M.; Stebliankin, V.; Mathee, K.; Yoo, C.; Narasimhan, G. Causal effects in microbiomes using interventional calculus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Mathematical foundations. In Introduction to Algorithms for Data Mining and Machine Learning; Yang, X.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yuniarti, I.; Glenk, K.; McVittie, A.; Nomosatryo, S.; Triwisesa, E.; Suryono, T.; Santoso, A.B.; Ridwansyah, I. An application of Bayesian Belief Networks to assess management scenarios for aquaculture in a complex tropical lake system in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M. Learning Bayesian Networks with the bnlearn R Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Dong, X.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, J.; Christiani, D.C.; Wei, Y.; Chen, F. shinyBN: An online application for interactive Bayesian network inference and visualization. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrady, S.; Jouffe, L. Bayesian Networks and BayesiaLab: A Practical Introduction for Researchers; Bayesia: Franklin, TN, USA, 2015; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Cheng, J.; Allaire, J.; Stievert, C.; Schloerke, B.; Xie, Y.; Allen, J.; McPherson, J.; Dipert, A.; Borges, B. shiny: Web Application Framework for r. R package Version 1.7.4. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/shiny/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Hartemink, A.J. Principled Computational Methods for the Validation Discovery of Genetic Regulatory Networks; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.B. Zero-inflated Poisson and binomial regression with random effects: A case study. Biometrics 2000, 56, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutari, M.; Graafland, C.E.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Who learns better Bayesian network structures: Accuracy and speed of structure learning algorithms. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2019, 115, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, B.; Gomes, C.P. Hill-climbing Search. In Encyclopedia of Cognitive Science; Nadel, L., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 333–336. ISBN 9780470018866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Kleiber, C.; Jackman, S. Regression Models for Count Data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, L.M. A Scoring Function for Learning Bayesian Networks Based on Mutual Information and Conditional Independence Tests. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 2149–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, H. A Unifying Framework for Parallel and Distributes Processing in R using Futures. R J. 2021, 13, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, J.; van der Zander, B.; Gilthorpe, M.S.; Liskiewicz, M.; Ellison, G.T. Robust causal inference using directed acyclic graphs: The R package ‘dagitty’. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.; Altman, T.; Billington, R.; Dreher, K.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Holland, T.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Kubo, A.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of Pathway/Genome Databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D459–D471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.A.; Chu, K.; Palaniappan, K.; Pillay, M.; Ratner, A.; Huang, J.; Huntemann, M.; Varghese, N.; White, J.R.; Seshadri, R.; et al. IMG/M v.5.0: An integrated data management and comparative analysis system for microbial genomes and microbiomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D666–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W200–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, P.; Kozlov, A.M.; Czech, L.; Morel, B.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. EPA-ng: Massively Parallel Evolutionary Placement of Genetic Sequences. Syst. Biol. 2018, 68, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Winker, K.; Kado, D.M.; Orwoll, E.; Manary, M.; et al. Phylogenetic Placement of Exact Amplicon Sequences Improves Associations with Clinical Information. mSystems 2018, 3, e00021-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, L.; Barbera, P.; Stamatakis, A. Genesis and Gappa: Processing, analyzing and visualizing phylogenetic (placement) data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3263–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almende, B.; Thieurmel, B.; Robert, T. visNetwork: Network Visualization Using’vis. js’ Library. R Package Version 2.0.9. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/visNetwork/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Fernandes, R. bnviewer: Bayesian Networks Interactive Visualization and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. R Package Version 0.1.6. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/bnviewer/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJournal Complex. Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, J.; Tan, X. DT: A Wrapper of the JavaScript Library ‘DataTables’. R Package Version 0.26. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/DT/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Attali, D. shinyjs: Easily Improve the User Experience of Your Shiny Apps in Seconds. R Package Version 2.1.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/shinyjs/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Vaidyanathan, R.; Xie, Y.; Allaire, J.J.; Cheng, J.; Sievert, C.; Russell, K. htmlwidgets: HTML Widgets for R. R Package Version 1.6.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/htmlwidgets/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Attali, D.; von Hertzen, N.; Grey, E. shinyscreenshot: Capture Screenshots of Entire Pages or Parts of Pages in ‘Shiny’. R Package Version 0.2.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/shinyscreenshot/index.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Toxqui-Rodriguez, S.; Naya-Català, F.; Sitja-Bobadilla, A.; Piazzon, M.C.; Perez-Sanchez, J. Fish microbiomics: Strengths and limitations of MinION sequencing of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) intestinal microbiota. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Completing bacterial genome assemblies with multiplex MinION sequencing. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, W.; D’Hert, S.; Schultz, D.T.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C. NanoPack: Visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijon, P.; Chikhi, R.; Varré, J.S. yacrd and fpa: Upstream tools for long-read genome assembly. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3894–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Jiménez, P.; Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Estensoro, I.; Calduch-Giner, J.À.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Van Mullem, D.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Reshaping of Gut Microbiota in Gilthead Sea Bream Fed Microbial and Processed Animal Proteins as the Main Dietary Protein Source. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 705041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Wiggers, G.A.; Piazzon, M.C.; López-Martínez, M.I.; Estensoro, I.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Martínez-Cuesta, M.C.; Requena, T.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Miguel, M.; et al. Modulation of Gilthead Sea Bream Gut Microbiota by a Bioactive Egg White Hydrolysate: Interactions Between Bacteria and Host Lipid Metabolism. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 698484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Naya-Català, F.; Pereira, G.V.; Estensoro, I.; Del Pozo, R.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Nuez-Ortín, W.G.; Palenzuela, O.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Dias, J.; et al. A novel fish meal-free diet formulation supports proper growth and does not impair intestinal parasite susceptibility in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) with a reshape of gut microbiota and tissue-specific gene expression patterns. Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Cheng, F.; Wei, Q.; Ji, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhong, X.; Tao, R.; Wen, Z.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; et al. A Bayesian framework that integrates multi-omics data and gene networks predicts risk genes from schizophrenia GWAS data. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Perez, D.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Bourguignon, N.; Mathee, K.; Lerner, B.; Bar-Joseph, Z.; Narasimhan, G. Dynamic Bayesian Networks for Integrating Multi-omics Time Series Microbiome Data. mSystems 2021, 6, e01105-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenere, A.; Rundquist, O.; Gustafsson, M.; Altafini, C. Multi-omics protein-coding units as massively parallel Bayesian networks: Empirical validation of causality structure. iScience 2022, 25, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderburn, R.W.M. Generalized Linear Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, J. A comprehensive evaluation of microbial differential abundance analysis methods: Current status and potential solutions. Microbiome 2022, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zou, W.; Wang, J.; Pang, L. Minimum training sample size requirements for achieving high prediction accuracy with the BN model: A case study regarding seismic liquefaction. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 115702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Feeding Scenarios | FM | FO | Tissue | Additive/Substitute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSAQUA | ||||
| Scenario 1 | 10 < FM ≤ 20 | 4 < FO < 12 | AI | NO_ADDS |
| Scenario 2 | ≤10 | 4 < FO < 12 | AI | LSAQUA |
| Scenario 3 | ≤10 | 4 < FO < 12 | AI | LSAQUA |
| EGGHYDRO | ||||
| Scenario 1 | >20 | 4 < FO < 12 | AI | NO_ADDS |
| Scenario 2 | 10 < FM ≤ 20 | ≤4 | AI | NO_ADDS |
| Scenario 3 | ≤10 | ≤4 | AI | EWH |
| GAIN_PRE | ||||
| Scenario 1 | 10 < FM ≤ 20 | ≤4 | PI | NO_ADDS |
| Scenario 2 | ≤10 | 4 < FO < 12 | PI | SANA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soriano, B.; Hafez, A.I.; Naya-Català, F.; Moroni, F.; Moldovan, R.A.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Piazzon, M.C.; Arnau, V.; Llorens, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. SAMBA: Structure-Learning of Aquaculture Microbiomes Using a Bayesian Approach. Genes 2023, 14, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081650
Soriano B, Hafez AI, Naya-Català F, Moroni F, Moldovan RA, Toxqui-Rodríguez S, Piazzon MC, Arnau V, Llorens C, Pérez-Sánchez J. SAMBA: Structure-Learning of Aquaculture Microbiomes Using a Bayesian Approach. Genes. 2023; 14(8):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoriano, Beatriz, Ahmed Ibrahem Hafez, Fernando Naya-Català, Federico Moroni, Roxana Andreea Moldovan, Socorro Toxqui-Rodríguez, María Carla Piazzon, Vicente Arnau, Carlos Llorens, and Jaume Pérez-Sánchez. 2023. "SAMBA: Structure-Learning of Aquaculture Microbiomes Using a Bayesian Approach" Genes 14, no. 8: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081650
APA StyleSoriano, B., Hafez, A. I., Naya-Català, F., Moroni, F., Moldovan, R. A., Toxqui-Rodríguez, S., Piazzon, M. C., Arnau, V., Llorens, C., & Pérez-Sánchez, J. (2023). SAMBA: Structure-Learning of Aquaculture Microbiomes Using a Bayesian Approach. Genes, 14(8), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081650






