Otological Features of Patients with Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Pathogenic Variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.; Byers, P.; Belmont, J.; Berglund, B.; Black, J.; Bloom, L.; Bowen, J.M.; Brady, A.F.; Burrows, N.P.; et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfait, F.; Castori, M.; Francomano, C.A.; Giunta, C.; Kosho, T.; Byers, P.H. The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, A.F.; Demirdas, S.; Fournel-Gigleux, S.; Ghali, N.; Giunta, C.; Kapferer-Seebacher, I.; Kosho, T.; Mendoza-Londono, R.; Pope, M.F.; Rohrbach, M.; et al. The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, rare types. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 70–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dündar, M.; Müller, T.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Steinmann, B.; Vodopiutz, J.; Gruber, R.; Sonoda, T.; Krabichler, B.; Utermann, G.; et al. Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 function results in adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, N.; Kosho, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Furuichi, T.; Hatamochi, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Arai, E.; Takahashi, K.; Kawamura, R.; Wakui, K.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations of CHST14 in a new type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfait, F.; Syx, D.; Vlummens, P.; Symoens, S.; Nampoothiri, S.; Hermanns-Lê, T.; Van Laer, L.; De Paepe, A. Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (former EDS type VIB) and adducted thumb clubfoot syndrome (ATCS) represent a single clinical entity caused by mutations in the dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 encoding CHST14 gene. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Suresh, I.; Komatsu, Y.; Vodopiutz, J.; Dundar, M.; Straub, V.; Lingenhel, A.; Melmer, A.; Lechner, S.; et al. Loss of dermatan sulfate epimerase (DSE) function results in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosho, T. CHST14/D4ST1 deficiency: New form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosho, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshizawa, T.; Miyake, N.; Yamada, S. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Genes 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatogawa, M.; Unzaki, A.; Morisaki, H.; Syx, D.; Sonoda, T.; Janecke, A.R.; Slavotinek, A.; Voermans, N.C.; Lacassie, Y.; Mendoza-Londono, R.; et al. Clinical and molecular features of 66 patients with musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by pathogenic variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14). J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Takahashi, N.; Tangkawattana, P.; Minaguchi, J.; Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Miyake, N.; Hayashi, S.; Hatamochi, A.; Nakayama, J.; et al. Structural alteration of glycosaminoglycan side chains and spatial disorganization of collagen networks in the skin of patients with mcEDS-CHST14. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, F.W.; Hatch, J.L.; Muus, J.S.; Wallace, S.A.; Meyer, T.A. Audiologic outcomes in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.; Ng, M. Otoacoustic emissions. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stenfeldt, K.; Johansson, C.; Hellström, S. The collagen structure of the tympanic membrane: Collagen types I, II, and III in the healthy tympanic membrane, during healing of a perforation, and during infection. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Nitahara-Kasahara, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Nakayama, J.; Takehana, K.; Okada, T.; et al. Systematic investigation of the skin in Chst14-/- mice: A model for skin fragility in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by CHST14 variants (mcEDS-CHST14). Glycobiology 2021, 31, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalmann, I.; Thallinger, G.; Comegys, T.H.; Thalmann, R. Collagen—The predominant protein of the tectorial membrane. ORL 1986, 48, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient | Sex | Variant (NM_130468.4) | Protein Alteration (NP_569735.1) | Major Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | c.[842C>T];[878A>G] | p.[Pro281Leu];[Tyr293Cys] | Dislocation, kyphoscoliosis, large subcutaneous hematoma, fistula, massive skin necrosis, gastric ulcer |
| 2 | F | c.[842C>T];[878A>G] | p.[Pro281Leu];[Tyr293Cys] | Dislocation, large subcutaneous hematoma |
| 3 | M | c.[2_10del];[2_10del] | p.[?];[?] | Kyphoscoliosis, large subcutaneous hematoma, retinal detachment |
| 4 | F | c.[842C>T];[842C>T] | p.[Pro281Leu];[Pro281Leu] | Dislocation, kyphoscoliosis, foot deformity, ureteral stone, large subcutaneous hematoma |
| 5 | F | c.[2_10del];[676_682delinsGCTATGGGGCT] | p.[?];[Lys226Alafs*16] | Dislocation, meniscus tear, large subcutaneous hematoma |
| 6 | M | c.[842C>T];[878A>G] | p.[Pro281Leu];[Tyr293Cys] | Foot deformity |
| 7 | M | c.[626T>C];[842C>T] | p.[Phe209Ser];[Pro281Leu] | Skin laceration, large subcutaneous hematoma |
| 8 | F | c.[626T>C];[842C>T] | p.[Phe209Ser];[Pro281Leu] | Dislocation, kyphoscoliosis, large subcutaneous hematoma |
| 9 | M | c.[842C>T];[842C>T] | p.[Pro281Leu];[Pro281Leu] | Dislocation, skin laceration, large subcutaneous hematoma, colon diverticulitis |
| Patient | Age at the Time of Otological Evaluation (Years) | Awareness of Hearing Loss | Tinnitus | Dizziness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | No | No | No |
| 2 | 13 | No | N/A | No |
| 3 | 18 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 4 | 18 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 5 | 17 | No | No | N/A |
| 6 | 10 | No | No | N/A |
| 7 | 14 | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| 8 | 28 | No | No | N/A |
| 9 | 19 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
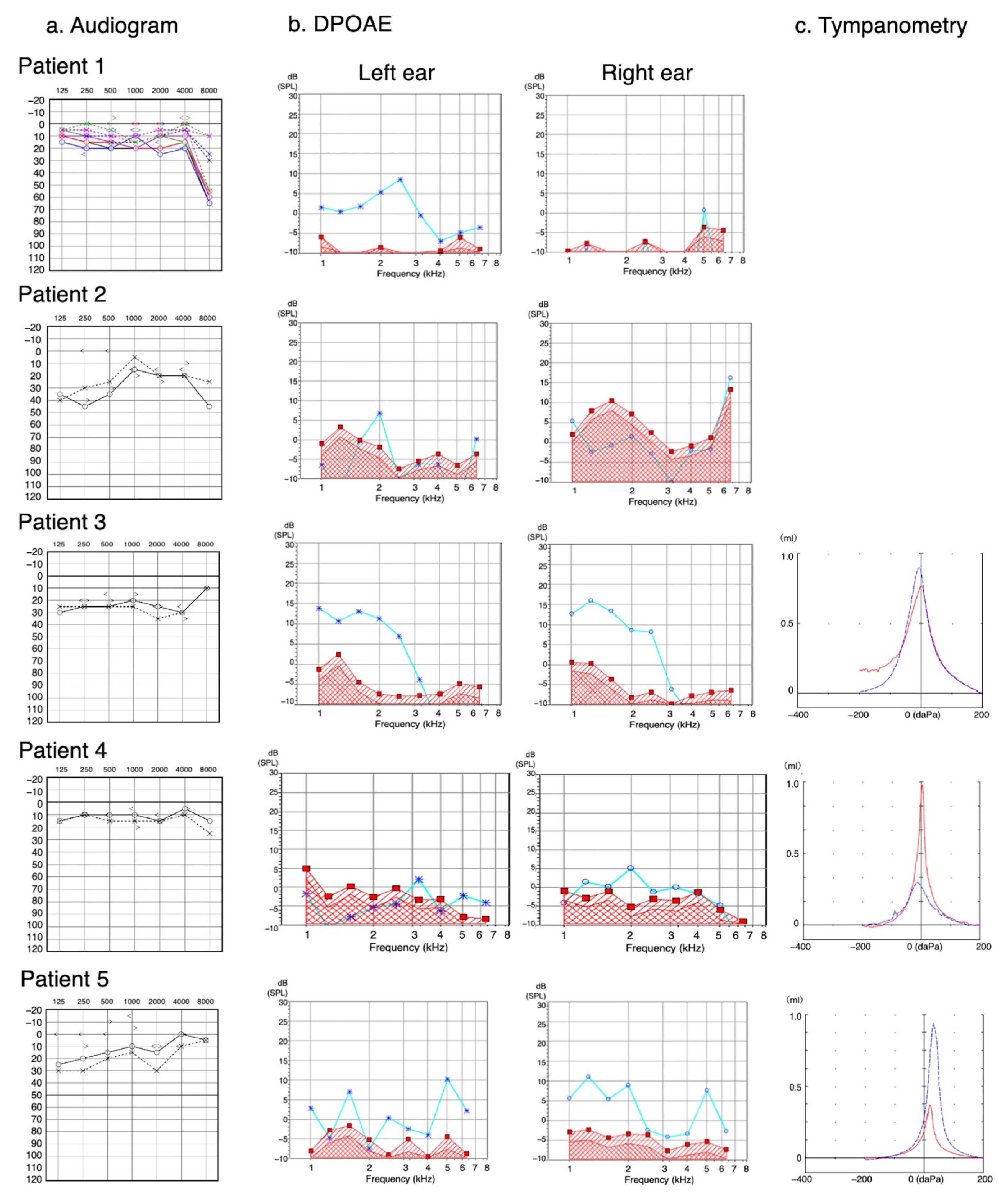
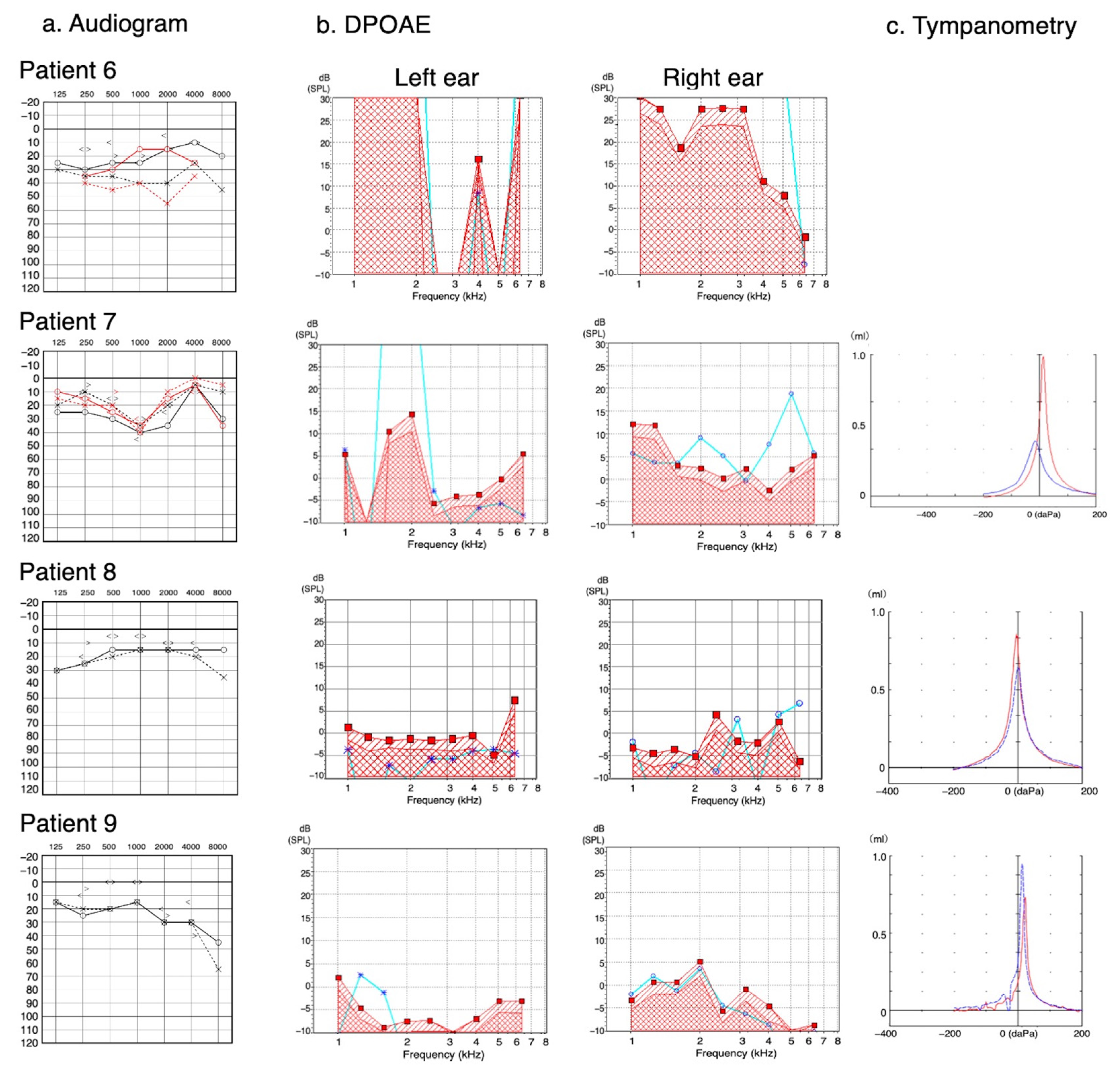
| Patient/Ear | Audiogram | AB Gap | DPOAE | Tympanogram |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/R | Moderate (high) | Negative | Absence | N/A |
| 1/L | Normal | Negative | Presence | N/A |
| 2/R | Moderate (low) | Positive (L) | N/A # | N/A |
| 2/L | Moderate (low) | Negative | Absence | N/A |
| 3/R | Mild (high) | Negative | Presence | Ad |
| 3/L | Mild (high) | Negative | Presence | A |
| 4/R | Normal | Negative | Absence | Ad |
| 4/L | Normal | Negative | Absence | As |
| 5/R | Mild (low) | Negative | Presence | Ad |
| 5/L | Mild (low) | Negative | Presence | Ad |
| 6/R | Mild (low) | Negative | N/A # | N/A |
| 6/L | Moderate (all) | Negative | N/A # | N/A |
| 7/R | Mild (moderate, high) | Negative | N/A # | Ad |
| 7/L | Mild (moderate) | Negative | N/A # | A |
| 8/R | Normal | Negative | Absence | Ad |
| 8/L | Mild (low, high) | Negative | Absence | Ad |
| 9/R | Moderate (high) | Negative | Absence | Ad |
| 9/L | Moderate (high) | Negative | Absence | Ad |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawakita, M.; Iwasaki, S.; Moteki, H.; Nishio, S.-y.; Kosho, T.; Usami, S.-i. Otological Features of Patients with Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Pathogenic Variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14). Genes 2023, 14, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071350
Kawakita M, Iwasaki S, Moteki H, Nishio S-y, Kosho T, Usami S-i. Otological Features of Patients with Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Pathogenic Variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14). Genes. 2023; 14(7):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071350
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawakita, Masayuki, Satoshi Iwasaki, Hideaki Moteki, Shin-ya Nishio, Tomoki Kosho, and Shin-ichi Usami. 2023. "Otological Features of Patients with Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Pathogenic Variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14)" Genes 14, no. 7: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071350
APA StyleKawakita, M., Iwasaki, S., Moteki, H., Nishio, S.-y., Kosho, T., & Usami, S.-i. (2023). Otological Features of Patients with Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome Caused by Pathogenic Variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14). Genes, 14(7), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071350








