PKD1 Nonsense Variant in a Lagotto Romagnolo Family with Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Examination and Investigations
2.2. Animals and DNA Extraction
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.4. Variant Calling
2.5. Gene Analysis
2.6. Allele-Specific PCR and Sanger Sequencing
3. Results
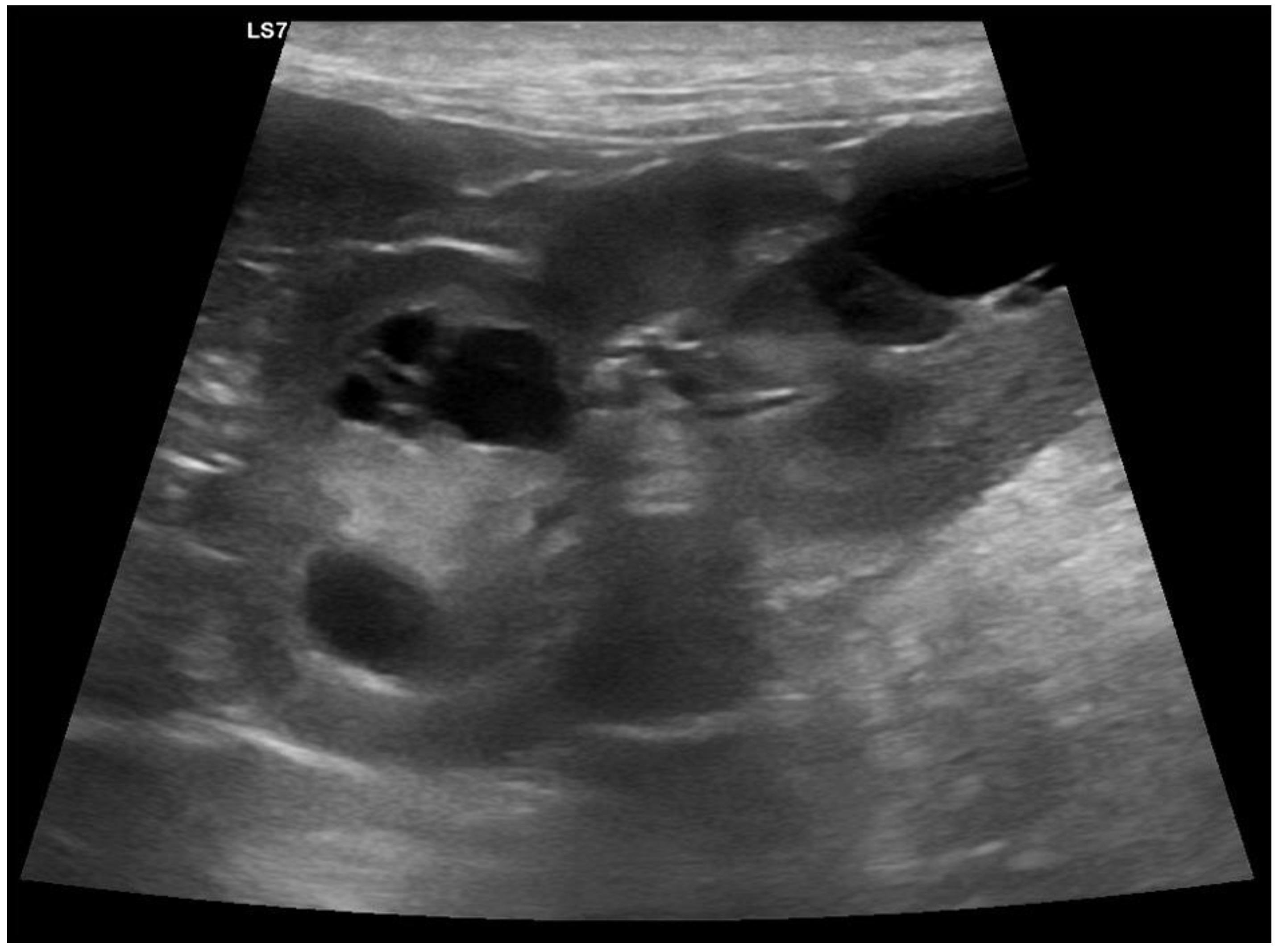
3.1. Clinical Phenotype
3.2. Pedigree Analysis and Mode of Inheritance
3.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.A.; Gissen, P.; Sergi, C. Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Roy, S.; Li, L.; Ma, M. Polycystic kidney disease: Novel insights into polycystin function. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, F.; Otto, E. Cilia and centrosomes: A unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Audrézet, M.-P.; Chen, J.-M.; Hourmant, M.; Morin, M.-P.; Perrichot, R.; Charasse, C.; Whebe, B.; Renaudineau, E.; Jousset, P.; et al. Type of PKD1 mutation influences renal outcome in ADPKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Review of the use of animal models of human polycystic kidney disease for the evaluation of experimental therapeutic modalities. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Umeyama, K.; Nakano, K.; Matsunari, H.; Fukuda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Tajiri, S.; Yamanaka, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Generation of heterozygous PKD1 mutant pigs exhibiting early-onset renal cyst formation. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiyama, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakaya, M.; Iwatani, C.; Seita, Y.; Tsuchiya, H.; Matsushita, J.; Kitajima, K.; Kawamoto, I.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Monkeys mutant for PKD1 recapitulate human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.A.; Biller, D.S.; Erdman, C.A.; Lipinski, M.J.; Young, A.E.; Roe, B.A.; Qin, B.; Grahn, R.A. Feline polycystic kidney disease mutation identified in PKD1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharahkhani, P.; O’Leary, C.A.; Kyaw-Tanner, M.; Sturm, R.A.; Duffy, D.L. A non-synonymous mutation in the canine Pkd1 gene is associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Bull Terriers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodney, A.R.; Buckley, R.M.; Fulton, R.S.; Fronick, C.; Richmond, T.; Helps, C.R.; Pantke, P.; Trent, D.J.; Vernau, K.M.; Munday, J.S.; et al. A domestic cat whole exome sequencing resource for trait discovery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, S.C.; Carpenter, J.L. Polycystic disease of the kidney and liver in the Cairn Terrier. Vet. Pathol. 1980, 17, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAloose, D.; Casal, M.; Patterson, D.F.; Dambach, D.M. Polycystic kidney and liver disease in two related West Highland White Terrier litters. Vet. Pathol. 1998, 35, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, K.J.; Hytönen, M.K.; Fischer, D.; Tanhuanpää, K.; Lehti, M.S.; Vainio-Siukola, K.; Sironen, A.; Anttila, M. A splice site variant in INPP5E causes diffuse cystic renal dysplasia and hepatic fibrosis in dogs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, V.; Drögemüller, C.; Leeb, T. Dog Biomedical Variant Database Consortium (DBVDC) A comprehensive biomedical variant catalogue based on whole genome sequences of 582 dogs and eight wolves. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, A.; Zdora, I.; Hitzler, V.; Jagannathan, V.; Beineke, A.; Möhrke, C.; Drögemüller, C. A de novo in-frame duplication in the COL1A2 gene in a Lagotto Romagnolo dog with osteogenesis imperfecta. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 786–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Di Giovanni, V.; He, N.; Wang, K.; Ingram, A.; Rosenblum, N.D.; Pei, Y. Systems biology of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): Computational identification of gene expression pathways and integrated regulatory networks. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2328–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, A.E.; Rossetti, S.; Bresin, E.; Corra, S.; Gammaro, L.; Maschio, G.; Pignatti, P.F. A novel nonsense mutation in the PKD1 gene (C3817T) is associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in a large three-generation Italian family. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Ward, C.J.; Peral, B.; Aspinwall, R.; Clark, K.; San Millán, J.L.; Gamble, V.; Harris, P.C. The polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) gene encodes a novel protein with multiple cell recognition domains. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, J.H. Genetic Mechanisms of ADPKD. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 933, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Segal, Y.; Pavlova, A.; Barros, E.J.; Löhning, C.; Lu, W.; Nigam, S.K.; Frischauf, A.M.; Reeders, S.T.; Zhou, J. Distribution and developmentally regulated expression of murine polycystin. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, F451–F459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvet, V.; Qian, F.; Boute, N.; Cai, Y.; Phakdeekitacharoen, B.; Onuchic, L.F.; Attié-Bitach, T.; Guicharnaud, L.; Devuyst, O.; Germino, G.G.; et al. Expression of PKD1 and PKD2 transcripts and proteins in human embryo and during normal kidney development. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Zhang, C.; Tian, X.; Coman, D.; Hyder, F.; Ma, M.; Somlo, S. Renal plasticity revealed through reversal of polycystic kidney disease in mice. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Filtering Step | Heterozygous Variants | Homozygous Variants |
|---|---|---|
| Variants in the whole genome | 3,608,700 | 2,610,423 |
| Private protein-changing variants | 2 | 2 a |
| GG | GT | TT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PKD-affected index female | - | 1 | - |
| Unaffected parents of the PKD-affected index female | 2 | - | - |
| PKD-affected offspring of the index female | - | 6 | - |
| Unaffected related dogs (offspring and littermates of the index female) | 13 | - | - |
| Other Lagotto Romagnolo dogs a | 103 | - | - |
| Sequenced Lagotto Romagnolo genomes a | 26 | - | - |
| Sequenced dog genomes from various other breeds a | 931 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drögemüller, M.; Klein, N.; Steffensen, R.L.; Keiner, M.; Jagannathan, V.; Leeb, T. PKD1 Nonsense Variant in a Lagotto Romagnolo Family with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Genes 2023, 14, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061210
Drögemüller M, Klein N, Steffensen RL, Keiner M, Jagannathan V, Leeb T. PKD1 Nonsense Variant in a Lagotto Romagnolo Family with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Genes. 2023; 14(6):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061210
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrögemüller, Michaela, Nadine Klein, Rikke Lill Steffensen, Miriam Keiner, Vidhya Jagannathan, and Tosso Leeb. 2023. "PKD1 Nonsense Variant in a Lagotto Romagnolo Family with Polycystic Kidney Disease" Genes 14, no. 6: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061210
APA StyleDrögemüller, M., Klein, N., Steffensen, R. L., Keiner, M., Jagannathan, V., & Leeb, T. (2023). PKD1 Nonsense Variant in a Lagotto Romagnolo Family with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Genes, 14(6), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061210







